Entity Based Distinctive Secure Storage and Control Enhancement in Cloud
Автор: Divesh Kumar, Amit Sharma, Surjan Singh
Журнал: International Journal of Information Engineering and Electronic Business(IJIEEB) @ijieeb
Статья в выпуске: 1 vol.9, 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Cloud computing acts as rising evolution in Information Technology (IT), boosting the delivery of services and eye-catching returns to its tenants enrolled at low costs of per usage basis. Cloud computing means "everywhere" and provides enormous available resources via internet with ensured quality. With the numerous profits involved, it clears the viewpoint of various businesses to invest in cloud services for accomplishment of their needs in the cloud habitat. Cloud enables computing resources in a service oriented flair instead of burden with lags in traditional setup of unified architecture. With delivery of cloud services occur many obstacles in the cloud to work securely without downfall in its performance. Security has always emerged as a long handed concern with its progression which affects its virtuous implementation. We commence with aspect of security based on parameters named Confidentiality (C), Integrity (I) and Granular Access (GA) and then sent over a secure channel via Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) for secure storage with Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) encryption laid on data. Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) is used for hash value generation maintaining integrity. The authentication mechanism of secure Graphical One Time Password (GOTPass) provides high end to end security for retrieval process and boost security appliance for data. Data is divided into three security levels as per Secure Quality Index (SQI) generated and storage is isolated to have different security aspects. It provides supplemental controlled security and data protection as associated with the file. User is responsive to pass all security mechanisms to gain access.
Encryption, Security, Access Control
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15013492
IDR: 15013492
Текст научной статьи Entity Based Distinctive Secure Storage and Control Enhancement in Cloud
Published Online January 2017 in MECS
Cloud term means internet service facilities, deals with non-local storage for user data on the basis of pay per use .
Cloud evolved with other services like computing with different operating platforms, software, technology infrastructure and storage online at the remote locations. These combine to cater the demands of the users and are effectively optimized to conserve costs. Therefore, it provided more scalability and flexibility in terms of resource availability and cost effectiveness on demand basis rather than the traditionally used Information Technology (IT) infrastructure. Cloud computing plays a major role in the changed face of new technological advancements. It increases the scope of improvement in relation to nearly all fields of technology directly or indirectly.
With the emerging technologies, users can access the resources anytime, anywhere and anyplace giving high degree of availability, as these are empowered with the facilities of virtualization that can be used to store data, provided with different platforms and run several applications existing in the network only, i.e. no new physical hardware or software requirements needed at the user end and are vastly available [1]. There is an increase in the number of organizations turning to cloud to transform their business setup. A huge package of combined connected networks, which is vastly spread continuously provides remote access to vastly decentralized IT resources. The remotely accessed resources are in reach with much attained flexibility, scalability and measured with their usage and control. The user act as the main facilitator in terms of resources, cloud provider act as secondary facilitator in terms of profitability and has to manage the backbone of facilities. Cloud providers might also be a third party which in integration with the primary facility provider can balance the load of different resource pooling for widely spread users. It has a multi-tenant environment support and the user’s demands are different as per their interest and need to be catered in isolation from each other. This all involves the overhead of various security vulnerabilities which could occur as a distant gap for the entire cloud environment.
The outline of the aspects of cloud computing is described in section 1 as introduction. The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 refers as background, section 3 refers to related works and section 4 explains the proposed model. The work associated algorithm is presented in section 5. Functional analysis in relation to our work is referred in section 6. Finally conclusions for the future work are summarized in section 7 and references accompanied at last.
-
II. Background
Gradually, with the increase in different aspects required in cloud by the users for the type of services they wanted, there came a need to distinguish tenant services with security diversities. The cloud offers various advantages provided by the different types of clouds having varied properties as the cloud environment started to evolve. Types of clouds as based on their distribution are namely:
-
A. Public cloud:
The public cloud service provider provides various types of sharable resources and services available over the internet for different companies or for the general public at a small traditional cost or free of cost allowing each individual client to operate on a low-cost using pay per use approach. They are owned and worked by third parties or vendors. The services offer scalable and flexible sharing of resources that increase the choices of technologies for the user. These clouds offer the greatest level of efficiency, but are also more vulnerable to threats than private clouds [15].
-
B. Private Cloud:
Private clouds run services provided by a single primary organization only, where no resources are shared by other external users at all. The facilities and services are available to users distinctive of a particular organization only. They offer greater control and various facilities are implemented in the security of the data which usually lacks in a public cloud. The cloud infrastructure located may be existing on premise or off premise for selective multi tenants [16]. This adds many security benefits as the server is present at the company’s end mainly. It tends to provide optimum utilization of resources provided by the cloud, with the support of various applications. The enrolled tenants are considered under the circle of trusted users as represented by the organization.
-
C. Hybrid cloud:
It refers to the formation of combined environment by both the private and public cloud thus named hybrid. It is a typical private cloud which essentially provides services and resources to other public cloud employed by different vendors where partial data resides between the two cloud environments. It combines the infrastructural facilities, maintaining different business applications of both the cloud (private or public) but is bounded by different standards and technology. One drawback of these services is that it is complex to manage different security platforms together, so different levels of security in cloud service is required [4]. The users of these clouds are considered as trusted and untrusted as per characteristics or their attributes defined by the service provider to identify them [16]. It tends to increase flexibility involved in computation of various resources and as well as help in managing workload and working flow.
The variations in different types of clouds are represented by their types of services which the different cloud providers offer. These types of services can be broadly classified as under:
-
A. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service):
Hardware and other physical resources which control the complete computational operations which are accessed and shared as desired, offering full infrastructural control to the users. It offers storage, network capability enhancement, computing and various infrastructural form of services for lease in terms of cost. This helps users to avoid the overhead implementation of the required infrastructure to work [17]. A virtual form of infrastructure is provided to the user, but the real physical infrastructure is held by service provider at various far-off isolated locations. Example: Google’s Compute Engine, Amazon Web Services etc.
-
B. PaaS (Platform as a Service):
It develops and manages the applications of the users. Applications can be uploaded and installed on the same platform and can be run and tested in an application oriented environment using different programming languages, libraries, services and tools as provided in compatibility by the cloud provider and these installed applications also have predefined settings to work in the application environment [18]. It provides the different supported platforms or environments to the customers for their applications and development over the Internet. Example: Google Gears, Microsoft Azure. In this, the consumer is not able to control or manage the underlying setup associated with its services [16].
-
C. SaaS (Software as a Service):
Applications and other software are made accessible in various user end devices via web browsers and no control of the operating system, network support, servers etc. needed separately. Applications are enabled for the user which are made compatible with cloud environment, supports an architecture that can run multiple instances irrespective of their locations. Software as a service has non deterministic and flexible application support provided to handle the software service for various users in the cloud. So instead of purchasing the software, the cloud provider rents the software for the user and the user pay as per usage [19]. In this, whole software is provided as a service to the user which exist in the form of various instances or copies. Example: Gmail, Google Drive, Drop Box etc. [20].
Service delivery is an inevitable part of the Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) and defined by the objectives with the quality of the service to be assured which indicates the service performance. Robust and precise values affect delivery of services as desired by the consumer essential for establishing trust factors of the consumers. Repetitive services and needful updates act as an impactful route for bringing out dynamic results [22]. Customer satisfaction through service delivery becomes the prime aim of service oriented architecture with enriched quality assurance.
Various challenges are faced by SOA in terms of testing and reviewing perspectives. Problem viewing occur while testing process and is regarded as an important part of SOA based applications. Testing requires different methods and ways to help tackle the problems with respect to cloud services [23]. SOA should have intelligence of various risk detections and vulnerable problems which could tend to occur.
Content may also not be trustworthy. Credibility searching and ranking with improved information retrieval methods are required to effectively manage content to increase the reliability [24]. The retrieval process is effectively full in the retrieval of results of communication.
Outsourcing of information reflects privacy matters. It is creditable to outsource information in encrypted form, but would raise the computational overhead including cost. Several keyword searches with encryption schemes are being proven to be non-effective. Ranked keyword search with encryption enhance privacy and ensures the fi le retrieval accuracy [32]. It also ensures decline in computation overhead.
Reverse engineering in web-related applications help validate the extracted concepts as well as modelling them to correlate with the aim of the enhancement of the indexing process making it better and more productive [25]. Reverse engineering may empower the process in the enhancement of indexing process.
Cloud computing resources are delivered in the form of web services. These services are improved by efficient utilization, reduced administration and infrastructure costs. It shares many unified factors of peer to peer, autonomic, grid, mainframe, client server, and utility computing. It is supported by open source resources which are platform independent leading towards better utilization in terms of computing [26]. The cloud computing platform is also managed by unified loading and testing tools and other software testing tools.
The development involved in cloud computing and its setup need to have resistance and should shield the entire locale with security assets. It should care towards the secrecy and privacy of data present under cloud’s liability. Security acts as a crucial and foremost part combined as a utility attached to the cloud. Security has been a critical issue of all times since the evolution of cloud. Many cloud security implementations were based on firewalls, access control lists, virtualization of networks with virtual interfaces, protocols and policy frameworks attribute based encryption etc. This paper tends to put forward the main concern of cloud computing and helps to efficiently implement the overall secure mechanism in the cloud. It uses the advance technologies like foremost Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) for data protection, leading Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) for integrity maintenance, renowned Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) for encryption and elite Graphical One Time Password (GOTPass) authentication mechanism for distinguished validation security for tenants developed in a model structure which is capable of providing fine grained end to end security and help to improve the various concerns and threats emerging in the cloud. This modular architecture helps to ensure and satisfy the authorized access and expected behavior as per norms of cloud in today’s world.
The cloud demands a combined security implementation of data protection in the cloud environment to have a better adaptability towards various threats. There comes a need to adopt a combined approach to data security implementation and different aspects empowering security in the cloud [10].
A vigorous authentic mechanism like GOTPass [21] is much more needful to account security to be laid for various tenants in the cloud. The efficient, proven authentic mechanism is widely capable of bringing a well-established combination of graphic usage embedded within password replacement as a better option than the traditional used passwords. The authentication procedure is much more powerful as yields a combination with graphics for one time password generation. It is a very good approach to attain the security in the multiuser environment of cloud.
-
III. Related Works
The term cloud is associated with a past history of the evolution of the telecommunication industry. The cloud emerged as a combination of unknown virtual environment laid and enacted with highly available resources at the door step with a service oriented design for the users. This caused the numerous facilities to be discounted and came as a face for integrated service delivery as a major advantage over traditional common service providence. Thus, with the infancy of this modern technology with benefits, it has snags that need to be addressed to make cloud computing to be more secure and keep it intact till date.
Many attacks were popular in earlier times of evolution of cloud computing, which clearly displayed the need of fine grained access security and control implemented inside the cloud to never have the probability of occurrence of any attack like Distributed Denial of Services (DDoS). The increase in resources could never let solve and overcome the DDoS attacks. It clearly defines a need of access limited approach rather than any traditional measures to reduce the effect of the DDoS attacks laid upon cloud or user [1]. Denial of service is not only an issue for the users, but also for the cloud service providers. It could produce enormous loss and the whole control over the cloud could go into the hands of intended attackers.
Virtualization provides numerous benefits of types of resources like software, network and hardware. It also improves continuity in service other than the deduction of workload, ease of services at a low price with improvement in other possessed properties. It is to be provided for all the entities involved and as far as possible. It can customize the network specification and enhance control over virtual machines [27]. With the coverage of virtualization over whole infrastructure, security remains a concern.
Cloud environment provides its users lower costs payable to the cloud service provider and involve a minimum initial cost for functionalities. Cloud architectural base needs development in terms of dynamic and versatile cloud modular approach which inhibits newly occurring solutions to any security issues pertaining in the cloud. Therefore, with these deep concerns the cloud model resources cannot be held out of any control mechanism or without any external regulatory laid upon them. Keeping aside the endless benefits of cloud environment due to its resources and computing offered to the common user, they are occupied with numerous emerging issues of security [3]. Cost enacts as a considered factor in order to migrate for services from the traditional system to the cloud environment to likely fulfil the user’s needs. Other than cost effectiveness benefit of cloud acting as a major reason for migrating the whole industrial setup onto cloud, there is security as a major consideration and a likely factor termed as the main highlight for exposed threats in the cloud environment in the minds of the general public seeking the option of cloud computing as a future for their business needs.
Despite security measures to be taken, the cloud computing process should aim to provide fluency in the process of computing carried onto the storage. Some consumers are not at all to be concerned weather from which source provider they are being facilitated. The sole purpose still lies in the demands for resources being efficiently catered within the cloud surrounded environment and faithful relation is crafted between the two major entities involved namely provider and consumer [4]. Resource utilization with security support, act as a feature which is inevitable to the user, making it clear to proficiently provide resources to the users.
With the substantial increase in the threats and gaps in security, there lies a need to integrate a newly better cryptographic scheme in the real cloud environment. Elliptic curve cryptography has been proven to be presented as a better option to implement the encryption security as well as digital signature generation effectively, which provides quality support for the encryption process where ever needed in the cloud environment. The encryption placed has the capability to involve randomness and unpredictable level of security for the intruder or any vulnerable attacker to perform any type of insider attack. Elliptic curve cryptography clearly reflects that it is highly efficient to handle the enormous number of users and in comparison to RSA 512 bit key possess equivalent encryption capabilities as 112 bit key of ECC and 256 bit key of ECC similar to 2048 bit RSA key [7]. So, surely a cloud could deal with less complex ECC keys rather than other crypto methods taken into account.
Data security analysis is a righteously need and a basic necessity of the whole cloud to survive from the undesired effects like information leaks, data variability caused leading to the formation of loopholes for the user like secrecy, availability and integrity loss and prone to other several attacks which seems to be located in the cloud. There could be chances of playing undesired brute force attempts, malicious turnaround of servers, replacements and changes occurred in identities as well as concerned data which should not be allowed to occur in cloud enforcement [10]. The working headed in the system of cloud environment is made more effective in its own terms with greater control on the parametric base within the changing environment of today’s technological cloud evolution.
There are many aspects hidden or abstracted for the users about the backend infrastructure or hardware as well as how it is being provided and being maintained to provide access to the cloud tenants in continuity without having any physical ownership over the provided types of resources by the service provider. There may occur many security threats and breaches headed by various intruders into the cloud environment that indulge to perform various types of attacks in a cloud that may vary the type of harm done to the cloud, affects the users as well as imposing threats to the cloud establishment. Attacks have much greater strength and are causing harm, even to the cloud itself.
The cloud should be modelled to provide supportive and trusted data sharing upon which a common user could rely upon and become secure in dynamically ever changing environs. The threats in categorized forms presented to be more identifiable namely Inner-Outer, Active-Passive and Collusion threats out of which Inner threats may be caused by any identity associated with the cloud and would be unauthorized other than the owner himself and outer threats prevail from outside into the cloud led by some external malicious intruding entities or any forced adversaries far from the system reach or not being a part of the system. Active attacks refer to those in which harm is done actively and intentionally ejected malicious files onto the cloud and passive ones being rolled by intruding and performing snooping as a spy and reveal parts of the secret conversation or any communication currently being held between two entities in the cloud. Collusion threats take place between the cloud service providers (CSP) and the users from getting access to collect data of others for their self-concerns. [2].
In the dynamically changing environment around the data, threats are more likely to embrace the malicious working and unexpected changes in the cloud habitat.
DDoS attacks are impactful over application layer and appropriately determination of DDoS attacks is a very challenging task [28]. DDoS attacks appear as much weighted concern in the cloud.
Other attacks too began to change the scenarios demanding the lookout needs in security and began to state security as a hand in hand concern with increasing technological advancements in the cloud. Some of the attacks commonly concerned with networks are Man in Middle attacks, cookie poisoning, xml signature element wrapping, sniffing attacks, cross site scripting attacks etc. The threats could probably lead to failure [11]. Several attacks intentionally put the whole working scenario of the cloud into a face of the larger threat that needs immediate catering in order to avoid any situation of loss to occur with any such type of attacks emerged as a possibility in the cloud.
Seemingly each resource, computing and infrastructure in cloud turn out to be a service in every aspect of the cloud functionality available in modern computing. Dynamically levels must be defined for the computing assets present with the cloud. Virtualization technologies should be provable defined to bring efficiency and better flexibility in scaling. Resource allocation must effectively utilize all the physical as well as virtual resources. There must be a balance maintained, which clearly defines the allocation limits for each entity usage of assets. This could probably lead to increase in resource management and performance of the cloud [6]. There comes a need of security with the data to be layered and allocated to different availed facilities as data is precious as to be kept securely when any facility modification is done in the cloud.
Elliptic curve cryptography easily scores over RSA and could be integrated effectively to provide protected remote access to storage, data in possession to the owner and is applicable to varied fields. It is capable of providing strong form of encryption for the data protection in terms of its comparison to other popular encryption adopted in today’s world [8]. There is need of new capable cryptographic enriched new methods and better data protection to be embedded with systems to bring the data into involvement and its utilization in various fields of cloud.
The threats to be identified in a large scale is efficient only when we carry out reports and results of their still occurrences from time to time. The large number of threats require to be catered efficiently and the information which is to be gathered from analysis and reports must also be frequently updated with new threats. Attacks not only evolve by technological improvements and network infrastructure but also from many physical factors and other natural calamities which may cause loss of control over the infrastructure. Thus, there is a large number of factors under consideration which puts the cloud computing environment in multiple risks in one way or the other. The number of threats and their amount of risk incurred, both are an important part of type of threats and their risk assessment [12]. In case of large scale build of number of resources in a cloud, many attacks can be left unseen and which could be without any intended purpose that just let break the norms in the large spread working environment of the cloud. These can be better analyzed with the reports and analysis of the overall measure of behavior of cloud working involving its expected change of states.
The Quick Response (QR) code is in popular demands to perform small information related encoding and is useful in the cloud environment. These began to establish as new trend with mobile access user verification and compatible device support to enhance security with cloud involved technology. These are easily deployable, robust, decode abilities of the form 2-dimensional matrix barcodes used to encode vital material and are inexpensively empowered with characteristics of high information density. There are 40 types of QR code.
It’s widely used in organizations like Pay-Pal payment oriented companies, and also for mobile one click payments. Combining these non-readable codes by humans with one time passwords makes them much more secure. Different security features can be embedded and can behave as a digital signature verification utility as like Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). These codes opt to enhance and increase the security features enriched within cloud [9]. Quick Response (QR) codes could turn out to be malicious, replicated and modified. There arise many concerns before putting these codes into practice.
Data can be existing of various types and in different forms too. Data is closely remarked as a critical, precious asset to any individual or an organization concerned with its ownership. There also comes the need of setting up many unique security parameters and barriers to treat the importance and sensitivity concerned with this asset as security in modern cloud computing is an everlasting concern with its pertaining privacy issues and needs to work with the approach of giving restricted access and authorization. Basically the whole security view is revolved broadly around the three important classified factors, namely confidentiality, integrity and availability of data to protect and formation of a categorized, defined approach in giving levels to the data to handle the sensitivity range to cater the incoming resources and efficiently secure them in this vulnerable environment [5]. Data is the only asset for the upholding of the cloud service provider and data has to be treated without any chance of its loss and should be kept in guard from the all threats which could occur in any scenario after its possession.
DDoS attacks seem to be much more prevalent in the cloud even in secure environments. They are needed to be prevented and solved with acute mechanisms like Anti-DDoS with help of effective advanced protocols [29]. This would also help to undo the effect caused by the DDoS attacks abstracted within networks.
Intrusions are harmful against security parameters for delivering cloud services. Firewall not itself is sufficient for handling all network threats. Intrusion detection and avoidance are to be positioned for effectiveness and securement [31]. The adoption of soft computing techniques can improve the security aspects and uphold service protection in the form of trusted platform for the Internet of Things (IoT) environment of cloud.
Furthermost imperative security threats displayed recognized via Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) are focused on various attacks from network, breaches caused for data loss and also done via other users or the other cloud environment entities. Hence security methods must be adopted and there is an urgent need for solving problems caused by security mistreatments [13]. The recommendations may help in cloud to better understand present scenario and to have a clear view of emerging problems faced in today’s cloud establishments.
Networking has a major role to play along with concerns for migration onto the cloud. Issues crucial like network breaches are accompanied by resource distribution in the virtual environs [30]. There comes a need for robust infrastructure and services for cloud empowerment.
Most kind of passwords cannot be grasped in mind and are vulnerable to hacking. Passwords as credentials used of the type GOTPass is a new form of single time numerical code in combination to usually small graphical image type used to secure the login and clearly is very secure to be used with low cost and is easily deployable. It seems to be much better than the multiple device password systems as not only saves hardware costs, but also the load of availing access. The login part is very secure in its terms. Images are distractions and being random decoys. There is a generation of an eight digit random one time code and has to be submitted in order to avail login access. It has the advantages of the secure password setup of graphical representation and one time code is to be used for access. It is used as initial and advanced security as per way of producing one time password, additionally producing more security in terms of passwords [21].
Fine grained supply of access grants exposed data to the attackers may fail system functional working, performance loss and loss of data resources. Changes in the data and services within security mechanisms with breaches manually manage the whole complex control rules, thus producing error prone configuration states eventually interrupting workflow. Flexible but complex infrastructure defines the difficulty in trusting the administrators to appraise and validate security mechanisms occasionally. Unsafe medium involves integrity and confidentiality attacks further denying service and unreliable authentication. Attackers may control the underlying network infrastructure. Easy catchable traffic can be further treated to be modified by running cryptanalytic measures. The functional accuracy and security is to be more polished and adopted mutually in infrastructure developmental setup. It creates a clear observation to involve the security integrated solutions to save the cloud environment from various attacks still into picture in today’s world [14]. Access control should be established to a very fine level and with the support of other utilities and protocols in order to have security. Attackers may take the unwanted advantage and cause breaches easily in weak security implementation and could disrupt the whole cloud working.
-
IV. Proposed Model
The architectural working of our model is based on several proportions and strict procedures for the cloud environment. This scheme lets the end to end security laid above entire entities including the cloud. Consequently empowered with the varied purpose specific mechanisms by the support of legalized advanced protocols, the security is being provided for the cloud computing environment and aims to accomplish precarious data to be secured with fine grained functionality. First proportion displays the secure storage of the owner’s files to the cloud. It is clearly subdivided into activities, namely registration of the owner himself, index allocated for the file to be uploaded containing the keyword, in-transit secure encryption, computed hash value of the file and lastly followed by the security quality index desired logically to be set by owner on the basis of Confidentiality, Integrity and Granular Access as desired. Second proportion deals with the activities of retrieval of data from the cloud, following certain secured procedural communications of requests for data access. This activity further consists of user registration with GOTPass authentication mechanism [21], resource request via authentication, retrieval process and thereby providing authorization decryption code for the file via owner himself on passing all security mechanisms referenced with protocols support for file retrieval.
-
A. Secure Storage of File:
It deals with several steps as below:
-
1) Owner’s Registration: This proportion relates to the initial step concerned with the owner’s identity to be created with the collaboration of cloud. It includes owner’s registration with credentials and then the cloud updates the owner’s record and sends a grant notification when validates a valid owner and authorizes the owner to
use cloud services.
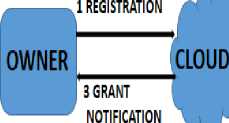
Fig.1. Owner Registration
2 UPDATE |
D ™Y OWNER DIRECTORY
The owner now uploads file to the cloud after several steps, namely Indexing, Standard Encryption, Computing Hash Value and Security Quality Index Setup. Thereafter, the file undergoes all these protection mechanisms, and sent over the cloud in an isolated, secure medium having in-transit security.
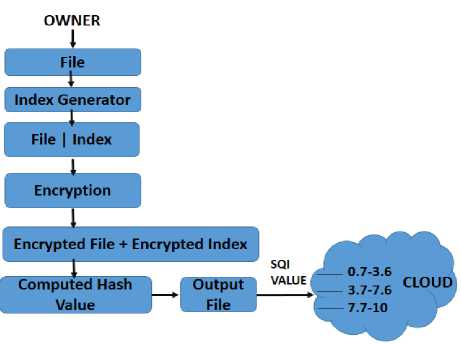
Fig.2. File to Secure Storage
-
2) Indexing: Indexing of file generally refers to a reference made to the file for its easy searching and retrieval. In our model, indexing refers as a process where our file contains some important arbitrary keyword which is to be stored with file in the cloud storage. The information about the file needed or requested can only be accessed through indexing as made searchable and users are catered with encrypted files if matched as per our model.
-
3) In-transit Secure and Encryption: Encryption is a process of converting data or information in terms of unreadable code to protect it from unauthorized access and can be reverted back to the original form only by trusty authorized personnel. Our model uses SSH File Transfer Protocol or Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) protocol compliant encryption for data storage and transmission, which has rich file transfer capability and is highly secure to provide a high level of protection to encrypt any data transferred to the cloud. We are using Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) as our encryption process with integration of the File Transfer Protocol over Secure Shell (SSH). ECC is a public or an asymmetric key cryptography method and tends to provide security and with the help of a protocol. The public key of the owner is sent when owner interacts with the cloud for authentication. There is no risk of revealing owner’s identity with the public key as has no information contained in it and data is securely sent over network with the support of SFTP. The data is securely present in encrypted form everywhere in the cloud premises and is also protected during the transmission process with in-transit security.
-
4) Computing Hash Value: A hash value, also called a message digest, is a string of digits generated from a string of text. We are using SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256 bits) which provides security of 128 bits against collision attacks. It works very efficiently and is impactful for maintaining the file integrity and hash value computed for the file, is sent with the file to the cloud in our model.
-
5) Secure Quality Index (SQI) Setup: It is essential for securely implementing our model, which is used for categorizing data into varied security levels as desired on the level of the security for the file of the owner. The
owner has to assign this security value based on the security parameters, namely Confidentiality (C), Integrity (I), Granular Access Control (GA) to determine the exact and precise values for the security level tagged Security Quality Index (SQI) for his file. The value of confidentiality as well as integrity varies either 0 or 1, meaning as either no or full parametric entity involved and the value of granular access varies either 0 or 1 or 2, meaning as either no or half or full parametric entity involved SQI is a time-varying function for the owner to set for multiple files to be uploaded and the level of security could be availed by the owner as desired.
SQI = F ( C , I , GA ) (1)
The values of these parameters of security are involved in the calculation outcome of the function:
SQI = 0.7 + 3* C + 2.4 1 + 1.95* GA (2)
SQI is clearly used in the allocation for the types of storage of data. SQI value ranges from 0.7-10 based upon which the security is enhanced as well as quality of service support being provided in our model. As there is an increase in the SQI value, there is increase in security as well. SQI value from 0.7-3.6 represents low, 3.7-7.6 represents moderate, 7.7-10 represents a high bonding with security to the file. Hence the storage is secured by the means and type of Secure Quality Index (SQI) in relation associated with the corresponding file.
Based on the security classified value for each file, the storage is allocated and the storage is divided into three broad levels with the help of SQI. Hence the classified and isolated storage level classification of data at the storage end acts as a security enhancement to our model.
-
V. Algorithm
The storage is designated accordingly as the parameters for the specific file are setup before the uploading of user file occurs. Input is received in terms of the distinct values based on parameters to classify the file and then assigned to the file as per security achieved based on input. Further the whole procedure helps to allot the storage as for the classified files concerned.
-
1) Input: C [ ] array of n integer size, where n is the number of files as input to the cloud, consists of Confidentiality (C) value of each nth file either 0 or 1, I [ ] array of n integer size, where n is the number of files as input to the cloud, consists of Integrity (I) value of each nth file either 0 or 1, GA [ ] array of n integer size, where n is the number of files as input to the cloud, consists of Granular Access (GA) value of each nth file either 0, 1 or 2.
-
2) Output: SQI [ ] array of n integer size, where n is the number of files as input to the cloud, consists of the security level value of each nth file computed from other arrays as per formula.
-
3) for i = 1 to n
C [ i ] = Value of Confidentiality (C) for ith file.
I [ i ] = Value of Integrity (I) for ith file.
GA [ i ] = Value of Granular Access (GA) for ith file.
-
4) Calculate SQI = 0.7 + 3* C + 2.4 1 + 1.95* GA
-
5) for k = 1 to n
if SQI [ k ] = 0.7-3.6, Security is Low, else SQI [ k ] = 3.7-7.6, Security is Medium, else SQI [ k ] = 7.7-10, Security is High.
-
A. Securely Retrieval of data:
This proportion has to retrieve data securely from the cloud by the user. It would consist of user registration with GOTPass authentication mechanism [21], file request with the identity name to the cloud and decryption process followed at last for successful file retrieval for catering the requests of that authentic user.
-
1) User Registration: The user sends a registration request to the owner, in response, will prompt a screen with choice of a unique username with a shape to draw in a grid of four by four dots displayed on the screen. The user sends back the username and pattern to the owner. Then the owner assigns him four random themes as set of thirty images, out of which user has to choose one in each theme. After user decides to confirm those four images in sequences which he has to remember with his username and pattern drawn. The owner then receives the whole identities and one time password generated with respect to those images [21]. The user identities are saved in his repository. Thereafter, the owner sends only the same username to the cloud for his repository of users as an information.
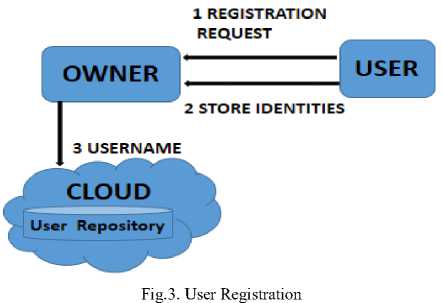
-
2) User verification and File Request: The next footstep is to request the desired file with id verification from the owner and cloud in a procedural way. In order to ask for file, user firstly needs to request the file from the cloud with his unique username registered with the owner. The cloud looks for his unique username in his user’s directory. If the username matches, then cloud passes a notification of file requested to the owner with the username attached from which the file request is arrived. Owner verifies the identity with username and according to the authentication process. After successful verification of user, owner in response supplies user with searchable
keyword of the file and the decryption key with the computed hash value to the user.
-
3) Secure Retrieval of file: User then makes a file request with keyword as a search request at cloud end with his username. After a successful request with valid and trustful identity, encrypted file is sent through the cloud to the user end with the computed hash value associated with the file previously uploaded by the owner.
-
4) Decryption Process: When the user receives the encrypted file with the hash value from the cloud and the hash computed sent separately by the owner himself, user firstly compares the two hash values and checks the modification and integrity of file. Thereafter the file is finally decoded at the user end with the help of the decryption key. This is how the user gains access to the file following all security procedures and mechanisms.
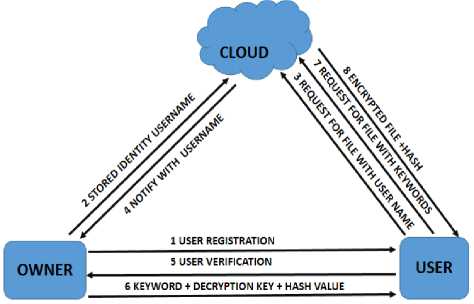
Fig.4. Secure File Retrieval
-
VI. Functional Analysis
The model securely protects data and analyze the security implementation in a cloud environment. The proposed work opts to cater to the issues concerned with data with advancement in security trends laid to achieve higher security platform in cloud environments. The model is in favor of providing reliable protection against most of the security concerns. The functional paradigms of this model with a combination of other security enhancements tend to provide security as a backbone for the cloud environment. The paradigms are based in context to the major classification which define security. The values are taken into account with today’s aspects of cloud trends essential as a need to implement security. These parameters have their values based on their requirements in order to make their importance as constitute of the security establishment in our model. They are combined in all different circumstances with different values which have a definite meaning in every scenario to depict the level of secure quality index as an outcome of security to provide secure storage and classified security of our model of data as desired by the owners.
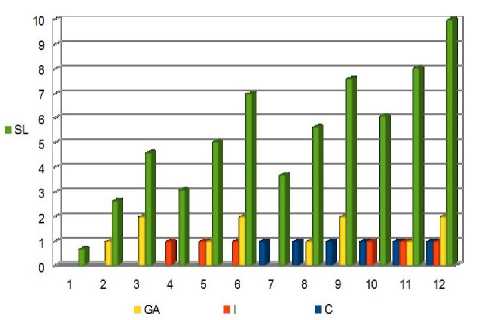
Fig.5. Secure Quality Index Variation
-
VII. Conclusion
This work would be essential to setup new paradigm in the field of security implementation in cloud computing. The proposed work opts to provide data protection with end to end security and fine grained access isolated to every particular with strong authentication mechanisms. It caters to the issues of secure access control, network breaches, privacy issues, weak cryptography, denial of service, data protection, malicious entities, controlled access and overall security enhancement in today’s world. This work acts as an advancement of other security trends laid previously and helps to combine various new technological advancements to boost up the security implementations in cloud environments.
It provides more scalability of access to various resources and also keeps the authorization applied upon various users. It totally meets the demands of the growing cloud enrollment of various traditional businesses and helps to bring more fluency in the way of facilitating the users empowered with security. It meets the solutions of the several issues still dominant in the cloud.
Список литературы Entity Based Distinctive Secure Storage and Control Enhancement in Cloud
- Sabahi F, "Cloud Computing Security Threats and Responses," in Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, Azad University, Iran, 2011, pp 245-249.
- Dong X, Yu J, Luo Y, Chen Y, Xue G, and Li M, "Achieving an effective, scalable and privacy-preserving data sharing service in cloud computing," Computers & Security, vol. 42, pp. 151-164, 2013.
- Behl A, and Behl K, "An Analysis of Cloud Computing Security Issues," in Proceedings of the World Congress on Information and Communication Technologies, Trivandrum, 2012, pp. 109– 114.
- Balasubramanian R, and Aramudhan M, "Security Issues: Public vs Private vs Hybrid Cloud Computing," International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 55, no. 13, pp. 35-41, 2012.
- Shaikh R, and Sasikumar M, "Data Classification for Achieving Security in Cloud Computing," in Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Computing Technologies and Applications, Mumbai, India, vol. 45, 2015, pp 493-498.
- Ramanathan R, and Latha B, "Resource Optimization Based on Demand in Cloud Computing," Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology, vol. 8, no. 15, pp. 1724-1731, 2014.
- Tripathi A, and Yadav P, "Enhancing Security of Cloud Computing using Elliptic Curve Cryptography," International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 26-30, 2012.
- Pawar P, "Public Auditability and Data Storage Security In Cloud Computing By Using RSASS And ECCSS," International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Engineering & Technology, vol. 3, no. 12, pp. 4272-4276, 2014.
- Krombholz K, Fruhwirt P, Kieseberg P, Kapsalis I, Huber M, and Weippl E, "QR Code Security: A Survey of Attacks and Challenges for Usable Security," in Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Human Aspects of Information Security, Privacy and Trust, Crete, Greece, Vol 8533, 2014, pp. 79-90.
- Sood S K, "A combined approach to ensure data security in cloud computing," Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 1831-1838, 2012.
- Kadam K, Paikrao R, and Pawar A, "Survey on Cloud Computing Security," International Journal Of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering, vol. 3, no. 12, pp. 239-249, 2013.
- Albakri S H, Shanmgam B, Samy G N, Idris N B, and Ahmed A, "A Case Study for the Cloud Computing Security Threats in a Governmental Organization," in Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer, Communication and Control Technology, Langkawi, Kedah, Malaysia, 2014, pp. 452-457.
- Kazim M, and Zhu S Y, "A Survey on top security threats in cloud computing," International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 109-113, 2015.
- Majhi S K, and Dhal S K, "A Study on Security Vulnerability on Cloud Platforms," in Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Information Security & Privacy, Nagpur, India, vol. 78, 2016, pp. 55-60.
- Bhosale P, Deshmukh P, Dimbar G, and Deshpande A, "Enhancing Data Security in Cloud Computing Using 3D Framework & Digital Signature with Encryption," International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology, vol. 1, no. 8, pp. 1-8, 2012.
- Patil V T, and Chandel G S, "Implementation of TPA and Data Integrity in Cloud Computing using RSA Algorithm," International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 85-93, 2014.
- Rumale A S, and Chaudhari D N, "Cloud Computing: Infrastructure as a Service," International Journal of Inventive Engineering and Sciences, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 1-7, 2013.
- Ojugo A A, Aghware F O, Yoro R E, Yerokun M O, Eboka A O, Anujeonye C N, and Efozia F N, "Dependable Community-Cloud Framework for Smartphones," American Journal of Networks and Communications, vol 4, no. 4, pp. 95-103, 2015.
- Subbiah S, Muthukumaran S S, and Ramkumar T, "An Approach for Enhancing Secure Cloud Storage Using Vertical Partitioning Algorithm," Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 223-230, 2015.
- Priya A, Rana Y K, and Patel B P, "Design and Implementation of an Algorithm to Enhance Cloud Security," International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 113, no. 12, pp. 41-47, 2015.
- Alsaiari H, Papadaki M, Dowland P, and Furnell S, "Secure Graphical One Time Password (GOTPass): An Empirical Study", Information Security Journal: A Global Perspective, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 207-220, 2015.
- Elabd E, "A Dynamic Reputation-Based Approach for Web Services Discovery", International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science, vol. 7, no. 8, pp. 31-36, 2015.
- Kumar A, and Singh M, "An Empirical Study on Testing of SOA based Services", International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 54-66, 2015.
- Razek M A, "Credible Mechanism for More Reliable Search Engine Results", International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 12-17, 2015.
- Dennai A, and Benslimane S M, "Semantic Indexing of Web Documents Based on Domain Ontology", International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 1-11, 2015.
- Alam M I, Pandey M, and Rautaray S S, "A Comprehensive Survey on Cloud Computing", International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 68-79, 2015.
- El-Khameesy N, and Mohamed H A R, "A Proposed Virtualization Technique to Enhance IT Services", International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science, vol. 4, no. 12, pp. 21-30, 2012.
- Aamir M, and Arif M, "Study and Performance Evaluation on Recent DDoS Trends of Attack & Defense", International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science, vol. 5, no. 8, pp. 54-65, 2013.
- Cui Y, Yan L, Li S, Xing H, Pan W, Zhu J, and Zheng X, "SD-Anti-DDoS: Fast and efficient DDoS defense in software-defined networks", Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 68, pp. 65-79, 2016.
- Moura J, and Hutchison D, "Review and analysis of networking challenges in cloud computing", Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 60, pp. 113-129, 2016.
- Modi C, Patel D, Borisaniya B, Patel H, Patel A, and Rajarajan M, "A survey of intrusion detection techniques in Cloud", Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 42-57, 2013.
- Pasupuleti S K, Ramalingam S, and Buyya R, "An efficient and secure privacy-preserving approach for outsourced data of resource constrained mobile devices in cloud computing", Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 64, pp. 12-22, 2016.


