Estimation of economic crisis influence on the basic branches and prospective projects in the Murmansk region
Автор: Leus Sergey Maksimovich, Istomin Anatoly Vasilevich
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Development strategy
Статья в выпуске: 2 (6) т.2, 2009 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The global financial crisis influenced national economic systems to a variable extent. The same trends can be observed at the regional level in the Russian Federation. In this article there has been made an attempt of the analysis of the basic system-forming branches in the real sector of the Murmansk area economy in the phase of the increase of the crisis phenomena, the ways of their overcoming are also considered.
Global crisis, economic instability, national and regional systems, analysis, branch regulation, enterprises, regional administration, business and authority
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223130
IDR: 147223130 | УДК: 338.124.4(470.21)
Текст научной статьи Estimation of economic crisis influence on the basic branches and prospective projects in the Murmansk region
Sergey M.
LEUS
Minister of the Department of Industry and Transport
The Murmansk area government
Anatoly V.
ISTOMIN
Senior Researcher of the Institute of Economic Matters
Kola Scientific Centre of the Russian Academy of Science
Originally the object of this article was defined narrowly enough; the purpose was to view the crisis phenomena in the economic system of a separate region. However while analyzing the facts it became clear, that this could be practically impossible without taking into account the national tendencies which were caused by the mega economic processes. That’s why a brief introduction with the initial preconditions is objectively necessary; and it should contain not only the separate figures, but the general information of crises’ theory and practice.
Economic crises are sure to be the integral part of any social and economic formation. We shouldn’t be afraid of loss. It is inevitable. At the crisis period the main economic target for a country, a company, or a person should be the increase of their efficiency. The problem is that the efficiency is not so much connected with the economy of the resources used in the completed cycle, but with the choice of the new goal. It is the goal that is more often forgotten at the crisis time, and the panic perception of the crisis is connected with this point.
This clear conclusion can be very painful from the conceptual point of view when we face to it in practice. The time instability is not so terrible; for the last decades the term “creative destruction” has been understood better; as it determines the inevitable positive influence, for instance the renewal of the reproduction systems.
The crisis’ influence on separate groups and layers of the population, on a family, as the basic cell of a society, and on each person is dangerous. It is possible to assert, that for the last 80 years the set of the measures smoothing crisis’ consequences in the society both at the national and at the international levels has been performed. The more successfully the real sector of the economy stabilizes, the faster this smoothing occurs.
The up-to-date global financial crisis is a part of the crises chain which was de-scribed in the economic literature. Only in 1990th there were some economic crises, which captured the whole groups of countries. In 1992 and 1993 some countries of the European Union (Great Britain, Italy, Sweden, and Norway) suffered from the current crises. In 1994 and 1995 the strong crisis which began in Mexico, spread to the other countries of the Latin America. In 1997 and 1998 the global financial crisis began in the countries of the Southeast Asia (Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines), and then it spread to the East Europe (Russia and some countries of the former USSR).
It is possible to recall a well-known Japanese recession at the end of the previ-ous century which in scales of a separate country was almost completely identical to the up-to-date global crisis.
In 1980th the cost course of the Japanese corporations’ shares increased to 20 – 30% a year. At the last, exponential stage of growth in 1986 – 1989 the national actives’ cost grew three times. Japan outstripped the USA and won the first place in the world in the absolute sizes of capitalization, having drawn off to itself the two fifth of the world capitalization [1]. At the end of December, 1989 no one of the Japanese and international investors could assume, that the stock Klondike would turn into a real hell and would involve the second largest economy in the world into a long one and a half ten years painful period of the hardest recession. At the very beginning of January, 1990 Japanese shares “fell down”. Ten months later this process was followed by the rise in prices for the land and the premises. During the first year of the market falling the share capital lost 38% of its cost, ruining investors and putting hundreds of the financial institutions, having given credits provisioned by the stock assets, on the verge of bankruptcy. In spring of 2003 “Nikkei” index fell to the level of the begin-ning of the 80th and was approximately five times below the maximal marks achieved in the apogee of “Heicei boom” in December, 1989. After that Nikkei actives’ index never rose above 60% of the precritical maximum, and nowadays, 19 years later, it has failed to the one fifth of its brilliant mark. During the considered period more than half of purchases of the Japanese shares were done by foreign investors, without their support the local share market “would fail” more strongly [1].
The present-day financial crisis differs from the mentioned one in its depth and scope; for the first time after the Great depression it captured the whole world. The problems in the market of the mortgage lending in the USA became the “trigger”, which started the crisis mechanism. The bases of the crisis are fundamental reasons, including macroeconomic, microeconomic and institutional ones. The leading macro-economic reason was liquidity surplus in the USA economy, which was determined by many factors, among them are the following ones [2]:
-
► the general decrease of trust to the countries with the developing market after the crisis 1997 – 1998;
-
► investment into the American securities by the countries accumulating monetary reserves (China) and oil funds (the countries of the Persian gulf);
-
► the policy of the low interest rates which was carried out in 2001 – 2003, so as to prevent the cyclic recession of the USA economy.
Under the influence of superfluous liquidity the process of the “bubbles” market formation (various deformed, overestimated kinds of actives) became more active. During the separate periods such “bubbles” were formed in the markets of fixed property, shares and raw goods;
and all that became the important component of the crisis mechanism. According to the data of the international researches covering long time periods, credit expansion is one of the typical conditions of financial crises. Thus, the risks of the crisis development as the result of easing monetary and credit policies, having taken place in 2007 – 2008, are the general rule, not the exception.
Against this background microeconomic factors such as the development of the new financial tools (first of all the structured derivative bonds) promoted the crisis approach. It was considered, that their distributing among investors allowed to lower risks, and to provide correct estimation. Actually the use of derivative tools resulted in masking the risks connected to the poor quality of the substandard mortgage lending, and to their opaque distribution among the broad audience of investors. Finally, among the institutional reasons we should note the insufficient level of the risks estimation by regulators and rating agencies.
It is possible to note an interesting detail: at the Japanese corporations, which survived their own crisis ten years ago, the decrease of capitalization less appeared, in comparison to the leading companies in the USA and Europe. It is expected, that the economy recession in this case will be “softer”.
It is typical, that the real sector of the leading countries both now and in the long term can avoid strong and sometimes catastrophic consequences, which are characteristic for the financial sphere. The analysis of the economic situation in 2008 allows predicting the global growth delay in the current year. In the November forecast of IMF the global growth delay is estimated at the level of 2,2%, and in the World bank forecast it is estimated at the level of 0,9%. Further it is possible to expect the reduction of these indices. The most advanced economies will face to serious recession this year.
Some analysts predict global recession as the result of the year 2009; such recession was not observed even at the periods of the greatest economic crises in the leading countries’ econo- mies in previous years. The most significant economic delay was observed in 1975 when the global growth made only 0,93% in comparison to the previous year; and in 1980 when its mark went down to zero (0,3%). But even in this case the re-cession was just the shares of interest.
However it is obvious, that the same real sector in different countries will have distinguished dynamics. According to analysts, to a greater extent the setback in production can mainly influence the economic systems of the raw orientation. Anyway, according to the changes brought into the Budget, the governmental bodies of the Russian Federation prepare for such variant.
On the eve of the crisis the Russian economy showed very good macroeconomic parameters: the significant proficiency of the budget, the fast growth of gold, currency reserves, and means in budgetary funds. At the same time some easing in the monetary, credit and budgetary policy has been admitted lately. In 2007 the charges of the federal budget increased for 24,9%, their growth exceeded the growth of the gross national product more than three times. The steadily low interest rates, negative in their real expression, were generated in the economy, and that resulted in rough growth of crediting. The natural result of all that was the “overheating” of economy. On the one hand, it promoted strengthening of the inflationary pressure, and on the other hand it promoted fast escalating of the external loans. For three years (2005 – 2007) the foreign debt of the private sector increased twice. By the beginning of 2005 it had made 108 billion USA dollars, and by the end of 2007 it made 417,2 billion dollars. The increase of the oil prices and of other goods of the Russian export masked the fast growth of the state expenditure and import. All the mentioned processes made the Russian economy vulnerable to the global crisis influence [2].
It is expected, that in 2009 and during 2010 and 2011 the external conditions of the Russian economy development will worsen in comparison with the previous three-year period. The delay of the demand growth which has begun this year in the group of the countries – leading importers of the Russian goods, the decrease of the growth rates of the consumer prices in the group of the countries – leading suppliers of the goods to Russia, and also the low prices for the raw goods will influence the Russian economy in the direction of economic growth restriction and inflation restraint.
The instability of financial systems, the aggravation of social problems and the delay of economic growth compel the governments of many countries to take various measures on stabilization of this situation and stimulation of their economies, including the measures of a fiscal policy. As the historical experience of carrying out the stimulating economic policy during crises shows, in most cases the basic role was played by means of the monetary and credit policy measures by virtue of their great efficiency. Nevertheless the discretionary fiscal policy can be used, with some restrictions, especially in the countries with the developing economy.
Let's note that the automatic stabilizers of a fiscal policy are considered to be rather effective and adequately working both in the conditions of recession and in case of economic “overheating”. In Russia they are enough sensitive to the changes of the economic conditions, and also beyond the boundaries of the country; for instance, during the world delay of economic growth the tax for the oil sector considerably decreases, as the price for energy carriers reduces.
The analysis of the international experience and of the national tendencies of the economic instability under the crisis conditions allowed the Government of the Russian Federation to develop the Program of anti-recessionary measures for 2009, which is focused on seven basic priorities. Taking into account the basic aim set by the authors at the beginning of this article, we shall only note the main principles and measures of this direction support. It is necessary that the industrial and technological potential of the future growth should be kept and strengthened. Money will not be invested in preservation of inefficient manufactures [3].
At the same time the enterprises which have lately raised their efficiency, have invested in the new production creation and the development, and have raised their labor productivity, have the right to get the state assistance in the decision of the problems caused by the crisis. The main enhancement task is the change of the developed model of economic growth. The country will have to proceed from the raw dynamics to the innovational development. The major innovational processes, including the energy effectiveness increase, will be supported.
It is clear, that both in national and in regional economic systems the crisis phenomena proceed with a various degree of intensity. The Murmansk area is a typical raw region, and in this aspect the global recession influence on the basic regional enterprises at the end of 2008 was very serious. However at the beginning of the current year in some part of them the stabilization signs could be observed. The antirecessionary measures of the Murmansk area Government were taken for two basic directions, developing from the basic strategic purpose, such as the increase of regional economic system efficiency. The first of them is stabilization, which has already been mentioned, and the second one is the strengthening of the innovational processes, and the support of the perspective strategic projects.
The Ministry of industry and transport made the detailed analysis of the tendencies in the basic regional branches and complexes. It showed that the largest enterprise Open JointStock Company “Kola mining and metallurgical company” (joins the holding “Norilsk nickel”) has kept the pre-crisis positions in producing nickel along with some reduction of the copper commodity. Mass reductions of the workers’ number at the enterprise are not planned; the actions on optimization are car-ried out. The similar situation takes place at the enterprise Open Joint-Stock Company “Apatite” with the personnel number of about 12 thousand people (Holding “FosAgro”). The enterprise capacity is 8,2 million tons of the apatite concentrate; nowadays the produc- tion volume corresponds to the pre-crisis level. Open Joint-Stock Company “Olenegorsky GOK” (Holding “Severstal”) also stabilized the release of the iron-ore concentrate; however the building rubble production was practically reduced in 2 times.
In the depressive group of enterprises it is possible to mark the branch of Open JointStock Company “SUAL” “KAZ-SUAL” (Holding “RUSAL”). In connection with the crisis sharply, almost in 2 times, the world price for aluminium has fallen; now it makes about 1350 USA dollars for a ton. At the same time the production cost price makes 1700 dollars; that has compelled the enterprise to lower the production in one and a half times, to preserve a part of electrolytic cells and to reduce about 30% of the personnel.
At the Society with Limited Liability “Lo-vozyorsky GOK” (Holding “Mineral-group”) the economic problems are not connected with the crisis and are caused by limitations of selling of the basic product (loparite concentrate, tantalum, and niobium). Nowhere in the world this type of the raw material is used, in this connection the price for its production depends on the stability of the only consumer Open Joint-Stock Company “Solikamsk Magnesium Factory”. The problems of Open Joint-Stock Company “Kovdor Mica”, which was in deep crisis for five years, became traditional. The procedure of bankruptcy towards this enterprise has been initiated. Number of the enterprise personnel now makes less than 400 people.
The problems of the ship-repair branch are connected with the obsolete equipment, with the loss of qualified personnel, with the irrational use of the fixed capital (huge empty spaces are heated), and with the low competitiveness in the sphere of repair services.
The realization of the government contractual work of the Russian Defence Ministry is restrained from year to year in connection with the late opening of financ-ing and the necessity of carrying out competitions and auctions.
The creation of the Associated Ship-Building Corporation is carried out slowly; basically the organizational actions, which do not influence the industrial and economic activities, are realized.
At the same time the tendency to the improvement of the situation in ship re-pairing can be noted; it is connected with some increase in orders. The index of production in January and February, 2009 has made 100,2% in comparison with January and February, 2008.
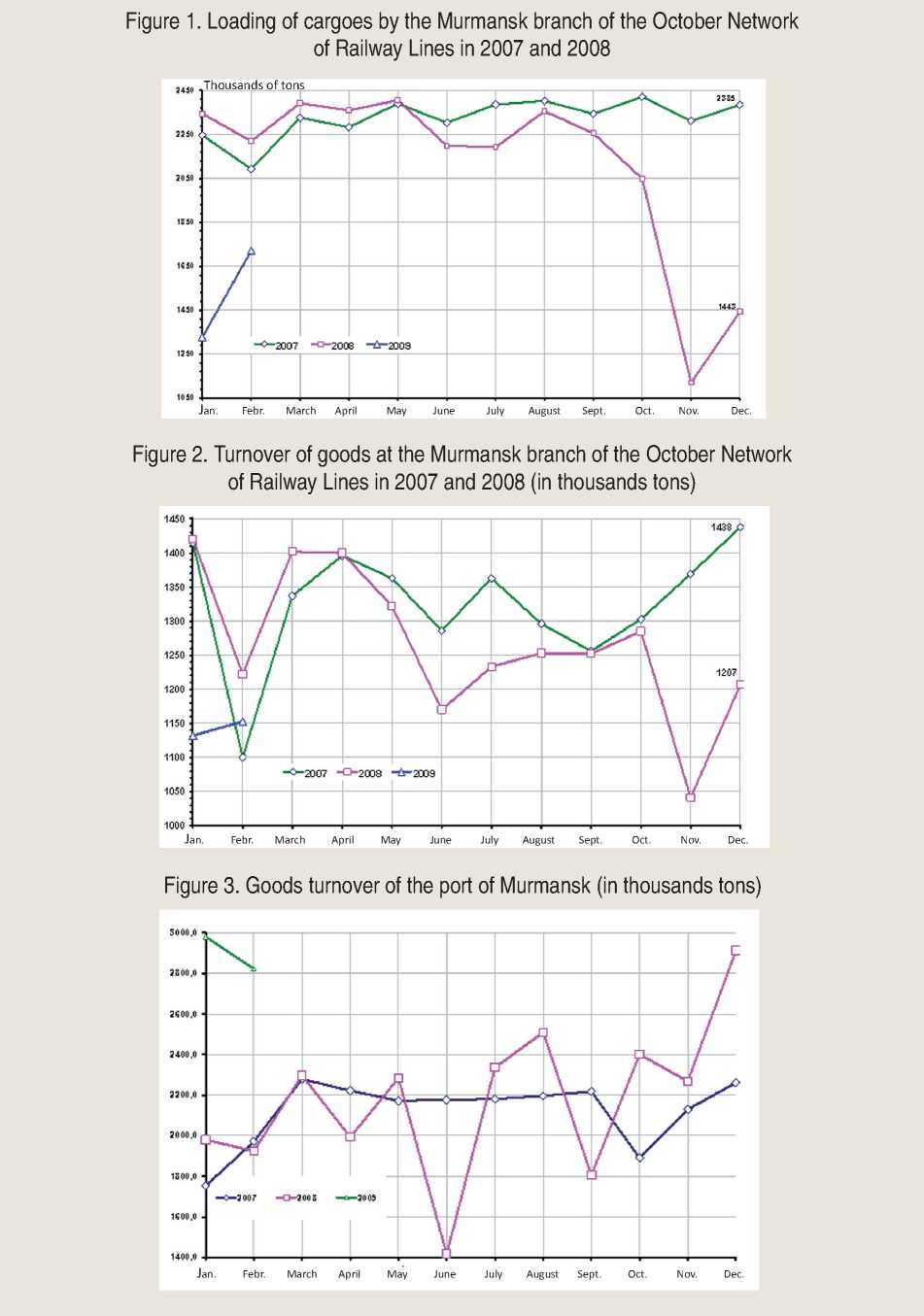
The global financial crisis has affected transits by rail freightage. In 2008 it was transported 25 336,8 thousand tons cargoes; it is 8,8% less, than in 2007 (27 786 thousand tons).
In November, 2008 there was the reduction of the volume of freight traffic more than in 2 times (fig. 1) .
Now within the frameworks of the Federal Principal Projects “Modernization of the transport system of Russia (2002 – 2010)”, “Development of the transport system of Russia (2010 – 2015)” the complex of actions on the throughput increase of the Murmansk railway transport unit is being realized. In 2008 the October Network of Railway Lines (ONRL) assimilated 55 billion rubles of investments. However, because of the crisis, in 2009 the ONRL plans to reduce the investment program to 57% (to 35 billion rubles).
In January and February 2009 the turnover of goods lowered for 35% in com-parison with the parameters of January and February 2008. Basically the transportation volume of building cargoes, iron-ore concentrate, and mineral fertiliz-ers went down. According to the data for March, 24, the turnover of goods by ONRL was reduced to 24% in comparison with the parameters for the same date of the last year (fig. 2) .
Nowadays the structural reorganization of the Murmansk branch, as well as of the Open Joint-Stock Company “RNRL”, has been started.
The crisis didn’t considerably influence the goods turnover at ports. The parameters of the port of Murmansk and the ports of Kandalaksha
bay (the specialized port of Vitino and the trading port of Kandalaksha) made 30,3 million tons in 2008, it’s 3,3% more, than in 2007 (29,3 million tons).
At the beginning of 2009 the goods turnover at the port of Murmansk consid-erably exceeded the parameters of the same period of the previous year. It is connected with the oil products volumes’ increase by the enterprise “Beloka-menka”, which increased the transshipment volumes in 4 times in January and in 2 times in February, 2009, in comparison with the same period of 2008. The transshipment volumes of coal remained at the former level (fig. 3) .
The cargo transportation volume by motor transport has decreased for 30%.
The crisis didn’t influence the passengers’ conveyance by sea and by motor transport; however the amount of the conveyance of passengers by air transport has decreased for 20%, it was influenced by the cost increase for air tickets and by the decrease of the flights’ quantity.
But mostly the crisis phenomena showed up in the electric power industry. In 2008 the demand for the electric power in the region made 12,946 billion kilowatt-hours. The power consumption forecast, which became the basis for the “Program of the development of the electric power industry system in Murmansk area in 2008 – 2010” (further – the Program), cannot be carried out because of slowing down the economic growth rates. Quite the contrary, from the fourth quarter of 2008 the de-crease of the power consumption volumes, caused by the crisis phenomena, is observed; and the achievement of the predicted earlier level in 2009 is not obviously possible. Carrying over the beginning terms of realization of many power-intensive projects on the industrial capacities development caused the absence of the necessary applications for the technological connection to the electric networks. Therefore the planned actions have not been realized. In view of the necessity of their performance in 2009 the subsequent realization of the projects on new electro network facilities construction and reconstruction is possible in later terms.
Nowadays a number of problems have emerged while realizing the Program and the actions concerning the territorial network organization (the branch of the Open Joint-Stock Company “Northwest MRSK” “KolEnergo”).
The basic financing sources of the Program are the credit proceeds provided with a payment for the technological connection, the profit in the tariff for the electric energy transfer and depreciation charges. The tariff decisions for the branch of the Open Joint-Stock Company “Northwest MRSK” are the profit in the tariff for electric energy transfer at the rate of 194 million rubles and the depreciation charges at the rate of 204 million rubles. Taking into account the fact, that in Murmansk area the de-crease of the power consumption level, caused by the reduction of the industrial enterprises production volumes, is observed, it can be noted that, under the forecast based on the actual consumption for January and February 2009, the delivery decrease in 2009, in comparison with the balance of the federal tariffs service, can make 12,5%. As a result, in 2009 the branch of the Open Joint-Stock Company “Northwest MRSK” “KolEnergo” predicts the loss at the rate of 295,2 million rubles, and the opportunity of net profit use for financing the Program is completely expelled.
According to the decision of the tariff regulation committee of Murmansk area from 20.03.2009 № 10/2, in 2009 for the branch of the Open Joint-Stock Company “Northwest MRSK” the financial assets are stipulated at the rate of 1 063 million rubles; their source should be the payment for the technological connection to the company electric networks. The guaranteeing for the application should be the advance payment at the rate from 5 to 30% of the contract sum of the technological connection; but in most cases consumers, for various reasons, do not do that. Therefore, under the existing economic conditions, the growth of the quantity of new large electric energy consumers can turn out improbable and the means stipulated by the tariff decisions will not be accumulated.
It is also necessary to take into account a real financial position of the company which by the present moment has practically exhausted the potential of the costs de-crease and the attraction of credits characterized by short terms of repayment and high interest rates. The situation is also aggravated with a sharp growth of consumers’ non-payments. For instance, the Open Joint-Stock Company’s “KolEn-ergoSbyt” debts to the branch of the Open Joint-Stock Company “Northwest MRSK” “KolEnergo” made about 440 million rubles for March 19, 2009.
The Open Joint-Stock Company “FSK NPG” (power circuit 330 kV) doesn’t show any activity in the realization of the major civil-engineering design of a new substation 330 kV “Murmashinskaya”, and the project “Reconstruction HVL-330 kV Monchegorsk – Olenegorsk”. According to the available information, the company on the national power grid control plans significant reduction of the investment programs. The Open Joint-Stock Company “TGK-1” also reconsiders the investment planning towards the capital investments’ reductions or the significant carryings over of the projects’ realization terms, including the civil-engineering design of “Murmansk Thermal Power Station-2”.
As to the receivable accounts growth in the electro power sphere, there was a critical situation with the debt of the Open Joint-Stock Company “KolEnergoSbyt” on the payments to the wholesale market of the electric power for March 10, 2009, which exceeded 1,7 billion rubles that can cause the enterprise’s bankruptcy. The principal cause of this debts’ formation is a sharp receivable accounts growth for the electric power consumed in the retail market. So, for March 1, 2009 it reached 2 billion rubles.
It is necessary to note, that the mentioned company carries out the electric power purchase at the wholesale market of the electric energy/capacity with the subsequent sale in the region (the retail market) to the other guaranteeing suppliers, to the energy distributing organizations and to the consumers.
As to the strategic investment and the in-novational projects, the economic crisis influenced them differently. For instance, the project of the Closed Joint-Stock Company “Northwest Phosphoric Company” (holding “Akron”) is being realized. The new apatitenepheline ores’ deposit “Olenij Ruchej” is being exploited; there 6 million tons ores a year will be processed by means of high technologies. The infrastructure objects’ construction and the industrial projects are carried out; more than 3 billion rubles of investments should be used this year.
The development works at the platinoid deposit “Tundra Fedorova” of the Closed Joint-Stock Company “Fedorov Resources” (its founder is the Canadian firm “Barrik Gold Corporation”) are intensively carried out. The planned labor productivity, which will twice exceed the working domestic analogues, shows the innovational level at the enterprise.
The main strategic object in the Russian Arctic region for the nearest 10 years is the Shtokmanovskoye gas condensate deposit with the natural gas extraction of 90 billion m3 a year. The project has both the economic and geopolitical value determining the country’s position in the shelf development in the long term. The domestic companies of this sector remain behind the conducting operating states working in the Arctic regions (Norway, Canada, and the USA). The deposit development will allow not only to use the new technologies, but also to obtain the competitive positions, tak-ing into account the specific conditions of the project realization.
It is obvious, that the crisis will seriously amend to the terms of the project re-alization in the connection with the sharp capitalization decrease, and consequently, with the credit opportunities of the basic participants (Gazprom, Statoil-Gidro, Total). However the works on the infrastructure formation continue and the investments of the current year can reach 2 billion rubles. The company’s administration made the statements that the price-cutting for the metals and the design organizations’ services, caused by the crisis, leads to the decrease of the capital expenses and raises the object’s appeal.
As to the investment project “Development of the Murmansk transport unit”, its realization can be delayed a little; but it won’t lose its appeal considering the presence of the objective competitive advantages, such as:
-
1. The geopolitical position caused by the open exit to the Atlantic and the World Ocean, limited for the ports of the Baltic and the Black seas by the systems of the “closed” passages.
-
2. The opportunity to accept at the Kola bay moorings large-capacity water craft, including tankers with the deadweight over 100 thousand tons, and supertankers without carrying capacity restriction.
-
3. The favorable navigable conditions allowing all-the-year-round transporting cargoes to the Atlantic without icebreaking support.
-
4. A rather developed railway system, allowing to deliver cargoes to the ports in the volume of 35 million tons a year; and after the modernization and the transition to the full two-acceptable circuit of 50 million tons a year.
-
5. High industrial and personnel potential of the area that causes the investment rating among the first third of the Russian Federation subjects.
It is important to note, that the Murmansk area is a raw region with a large-scale export of concentrates and a return empty run of a rolling stock.
As a whole the anti-recessionary policy of the Murmansk area Government in the real sector is based on carrying out active conciliation procedures with the leading enterprises and the support of the small-scale business. The main purpose is work-places’ and industrial potential’s reservation. And the main principle is readiness for compromises. Not because the compliance allows getting access to the additional re-sources; but because such readiness makes the environment less intense, and in this way enables to make the way more easy for stabilization and new trends. In our opinion, readiness for compromises and for consolidation of elites and societies distinguishes those countries, regions and companies which will manage to pass the crisis successfully, from those ones which will fail.
Список литературы Estimation of economic crisis influence on the basic branches and prospective projects in the Murmansk region
- Ivanter, A. How many stones are there in Reandzi’s garden?/A. Ivanter//Expert. -2009. -№ 1 (640). -P. 80-85.
- Kudrin, A. The global financial crisis and its influence on Russia/A. Kudrin//Questions of economy. -2009. -№ 1. -P. 9-27.
- The program of the anti-recessionary measures of the Russian Federation Government for 2009//The Parliamentary Newspaper. -2009. -March, 20-26. -№ 15.


