Ethanol induced toxicity and lipid peroxidation in pregnant mice: protective effects of butanolic extract from leaves of Chrysanthemum fontanesii, vitamin E and C
Автор: Amrani Amel, Boubekri Nassima, Benaissa Ouahiba, Zama Djamila, Benayache Fadila, Benayache Samir
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.10, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Background: The objective of the present study was to investigate the ability of butanolic extract from leaves of Chrysanthemum fontanesii, vitamin E and C to modulate ethanol-Induced toxicity and oxidation damage in maternal and fetal tissues of mice. Butanolic extract from leaves of Chrysanthemum fontanesii (200 mg/Kg per day), vitamin E (100mg/Kg per day) and C (8.3mg/Kg per day) were administered by gavage to groups of pregnant mice from the 6 th to 17 th day of gestation. A number of animals received plant extract, vitamin E and C, also treated with an oral administration of ethanol (0.02ml/g of 25% v/v absolute ethanol in water per day) in same conditions. On day 18 of gestation, pregnant mice were killed, fetus, placenta, fetal liver, liver, kidneys and brain were removed, homogenised and used for determination of lipid peroxidation (LPO) using TBARS method. Embryotoxicity was assessed by counting the number of live and dead fetus and growth retardation. Results: Severe alterations in all biomarkers were observed after injury with ETOH. ETOH produced significant decreases in fetal weight and significant increases in embryolethality and lipid peroxidation relative to control values. Treatment with Chrysanthemum fontanesii extract, vitamin C and vitamin E resulted in markedly decreased embryolethality and fetal growth retardation, while increased fetal weight were observed. Conclusion: The butanolic extract from leaves of Chrysanthemum fontanesii, vitamin E and C protected against ethanol induce fetal and maternal toxicity as revealed by the decrease in the extent of lipid peroxidation. So that butanolic extract from leaves of Chrysanthemum fontanesii posses in vivo antioxidant properties.
Ethanol, embryotoxicity, lipid peroxidation, chrysanthemum fontanesii, vitamin e, vitamin c
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323873
IDR: 14323873
Текст научной статьи Ethanol induced toxicity and lipid peroxidation in pregnant mice: protective effects of butanolic extract from leaves of Chrysanthemum fontanesii, vitamin E and C
The toxic effects of maternal ethanol (ETOH) consumption have been documented for over two decades, yet the mechanisms underlying this devastating phenomenon remain uncertain (Henderson et al ., 1999). In the recent years an increasing number of studies exposed to ETOH display biochemical signs of oxidative damage, suggesting the possible involvement of free radical in causing some of the toxic effects of ETOH (Kotch et al ., 1995). Several mechanisms including, the depletion of antioxidant, such as vitamin E and glutathione (GSH) might account for the oxidative stress associated to ETOH intoxication (Nordmann, 1993). Nonetheless, recent finding indicate that the ETOH fetotoxicity include deficiency in a type of vitamin A compound, retinoic acid (Cogswell et al ., 2003).
Flavonoids (Silymarin, Pycnogenol), Vitamin E and C supplementation has been studied by several investigators as a form of prevention and treatment of ethanol toxicity. (Yanardag et al ., .2007; Ramírez-Farías et al ., 2008; Siler-Marsiglio et al ., 2004; Martínez and Egea, 2007).
The present study was performed to investigate the protective effect of butanolic extract from leaves of Chrysanthemum fontanesii , vitamin E and vitamin C on ethanol induced developmental toxicity and oxidative damage in maternal, fetal and placental tissues.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plants
Chrysanthemum fontanesii endemic to North Africa was collected during the flowering stage in the area of bijaia, north east of Algeria and authenticated by Pr. M. Kaabeche (University of Sétif, Algeria). Leaves (1500 g) were powdered and macerated at room temp with EtOH–H 2 O (8:2 v/v)
for 48 h three times. The filtrates were combined, concentrated and successively extracted with chloroform, ethyl acetate and n -butanol. The organic layers were dried with Na 2 SO 4 . Removal of solvents under reduced pressure, CHCl 3 (5.0 g), EtOAc (28.0 g), n -butanol (42.0 g) resulted in final extracts (Amrani et al., 2012).
Determination of total flavonoids content
Total flavonoids content was estimated according to the method described by (Wang et al., 2008). Briefly, to 0.5 ml of sample, 0.5 ml of 2% AlCl 3 methanol solution was added. After 1 h incubation at room temperature, the absorbance was measured at 420 nm. Total flavonoid content was calculated as µg of quercetin equivalents (QE) per 1 mg of extract.
Animals and treatment
Female Albino Swiss mice aging from 6-8 weeks were purchased from Pasteur Institut Algiers and were maintained on 12h light/dark cycle. The animals were kept in 12h light/ dark cycles, maintained in an air-conditioned room at 22–25 °C, with free access to food and water ad libitum. The general guidelines for the use and care of living animals in scientific investigations were followed (Council of European Communities, 1986). Animals were caged over night with breeder males. In the morning, when a vaginal plug was observed, this was considered as the first day of gestation.
Pregnant mice were divided in to eight groups (Gr). All substances were given from the 6 th to 17th day of gestation.
-
1- Gr.1 served as control.
-
2- Gr.2 received an oral administration of ETOH (0.02ml/g of 25% v/v absolute ethanol in water per day)
-
3- Gr.3 received plant extract (200mg/kg by
gavage).
-
4- Gr.4 received plant extract (200mg/kg) and ETOH at the same dose mentioned earlier.
-
5- Gr.5 received an oral administration of vitamin E (100mg/kg).
-
6- Gr.6 received vitamin E (100mg/kg) and ETOH at the same dose mentioned earlier.
-
7- Gr.7 received an oral administration of vitamin C (8,3mg/kg).
-
8- Gr.8 received vitamin C (8,3mg/kg) and ETOH at the same dose mentioned earlier
Embryotoxicity estimation
Pregnant mice were sacrificed on the 18th day of gestation. Embryotoxicity was assessed by counting the number of implants, live and dead fetuses, resorptions and fetal body weight.
Malondialdehyde (MDA) measurement
Lipid peroxidation was determined by measuring the formation of thiobarbituric reactive substance (TBARS) using the colorimetric method of Uchiyama and Mihara (1978). Liver, Brain, kidneys, fetuses and placenta were removed and homogenized with cold KCl 1, 15% to make a 10% homogenate. 3ml of 1% phosphoric acid and 1ml of 0, 67% TBA aqueous solution were added to 0,5ml of 10% homogenate pipetted into 10ml centrifuge tube. The mixture was heated for 45min in a boiling water bath. The mixture was cooled to room temperature, and then 4ml of n- butanol was added and mixed vigorously. The butanol phase was separated by centrifugation and absorbance was measured at 532nm. Malonadialdehyde was employed as the standard.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as the mean±SD. The student test and a one-way analysis of variance
(ANOVA) were used for multiple comparisons (SPSS program, ver 12.0).
RESULTS
Total flavonoids content
Flavonoids as one of the most diverse and widespread group of natural compounds are probably the most important natural phenols. These compounds possess a variety of chemical and biological activities including radical scavenging properties (Khatiwora et al ., 2010) Butanolic extract from leaves of Chrysanthemum fontanesii contained higher flavonoid content (117.20µg quercetin equivalent/ mg extract)
Effect of ETOH, plant extract, vitamin E and C on fetuses toxicity
ETOH produced significant decreases in fetal weight (Fig 1) and significant increases in embryolethality relative to control values. Neither plant extract, vitamin E nor vitamin C given alone exhibited any fetotoxic effects relative to control animal. The results also show that plant extract, Vitamin E and vitamin C produced significant decreases in ETOH-induced embryolethality and fetal growth retardation.
Effect of ETOH, plant extract, vitamin E and C on LPO in fetal and maternal tissues
Significant increases in lipid peroxidation were observed in fetal, placental and maternal tissues after administration of ETOH to pregnant mice from the 6th to 17th day of gestation. When admistrated together with ETOH, plant extract; vitamin E and C resulted significant decreases in ETOH-induced lipid peroxidation in maternal, fetal and placental tissues. The data in (Fig 2 and Fig 3) show that either plant extract; vitamin E and C exhibited the same protective effect against ETOH-induced lipid peroxidation in liver, kidney, fetuses and liver of fetuses. The results also show that vitamin E provided significantly more protection than plant extract and vitamin C against ETOH-induced lipid peroxidation in brain (Fig 2). While plant extract provided more protection than vitamin E and C in placenta (Fig 3).
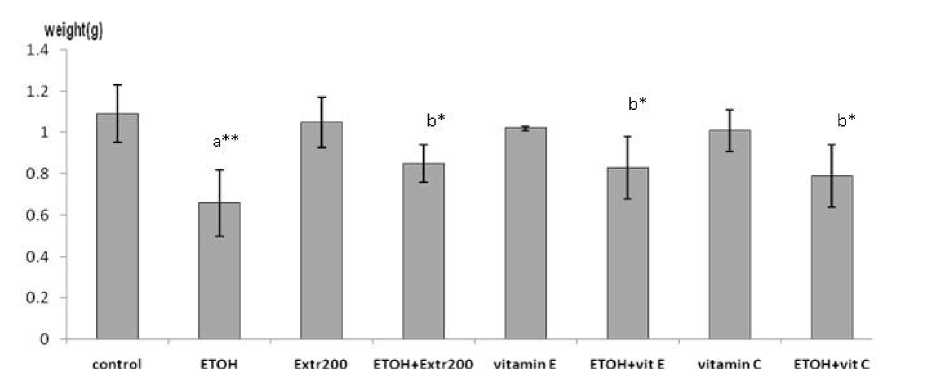
Figure 1. Effects of Vitamin E, Vitamin C and Plant extract on fetal growth retardation induced by Ethanol.
Control; ETOH, treated with ETOH (0.02ml/g of 25% v/v absolute ethanol in water per day); ETOH + Ext200, treated with 0.02ml/g of 25% ETOH and plant extract200 mg/kg; ETOH +VitE, treated with 0.02ml/g of 25% ETOH and 100mg/kg vitamin E; ETOH +Vit C, treated with 0.02ml/g of 25% ETOH and 8.3 mg/kg Vitamin C. All substances were given by gavages from the 6th to 17th day of gestation. The fetal weight was significantly decreased by 1.60-fold from that control (p<0.01) but it increased significantly in the ETOH +VitE (p<0.05), ETOH +VitC (p<0.05) and ETOH +Ext200 (p<0.05) groups. Data are mean ± SD a : Compared to control ; b : Compared to animals given ETOH alone
*: Significant p<0.05 **: Highly significant p<0.01 ***: Very highly significant p<0.001
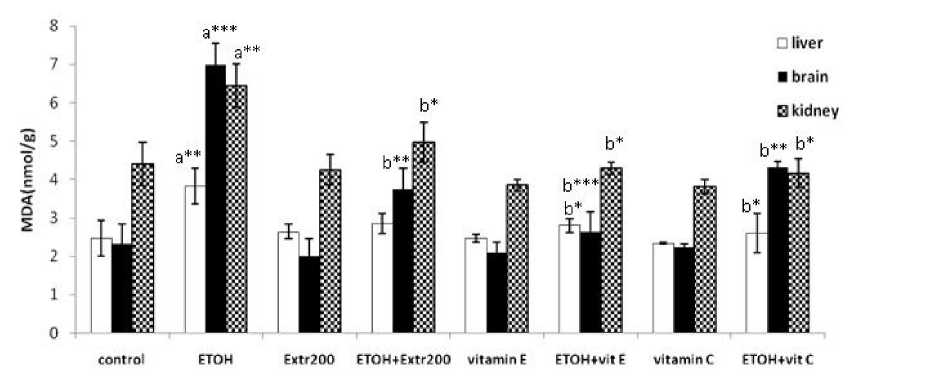
Figure 2. Effects of Vitamin E, Vitamin C and Plant extract on lipid peroxydation, induced by Ethanol in pregnant mice.
Lipid peroxidation was estimated by the measurement of MDA.data are mean±SD. The level of MDA in group given ETOH alone(0.02ml/g of 25% v/v absolute ethanol in water per day) was significantly increased by by 2.9-, 1.54-, 1.60-fold respectively, in maternal brain, liver and kidney over that in control group (p<0.01), but it decreased significantly in groups received vitamin E (100 mg/kg)+ ETOH, vitamin C(8.3 mg/kg)+ ETOH, and plant extract(200 mg/kg) + ETOH.
a : Compared with control ; b : Compared with animals given ETOH alone
*: Significant p<0.05 **: Highly significant p<0.01 ***: Very highly significant p<0.001
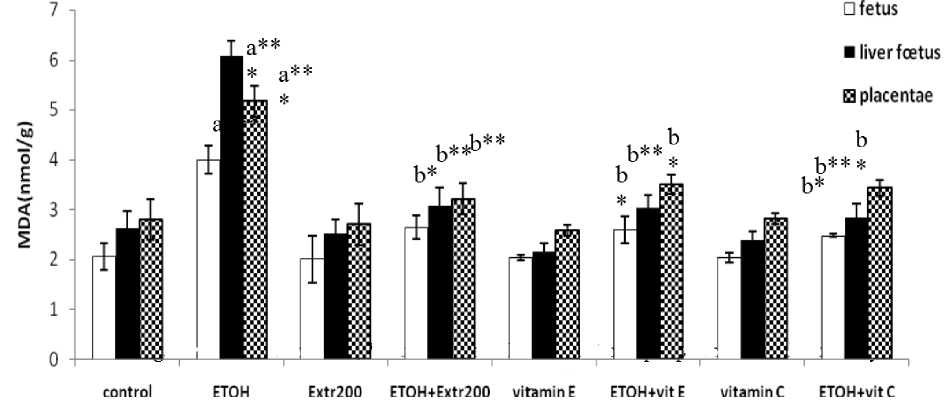
Figure 3. Effects of Vitamin E, Vitamin C and Plant extract on lipid peroxydation, induced by Ethanol in fetus, liver of fetus and placenta.
Lipid peroxidation was estimated by the measurement of MDA.data are mean±SD. The level of MDA in group given ETOH alone(0.02ml/g of 25% v/v absolute ethanol in water per day) was significantly increased by 2-, 2.2-and 1.7-fold respectively in fetus, liver of fetus and placenta over that in control group (p<0.001), but it decreased significantly in groups received vitamin E (100 mg/kg)+ ETOH, vitamin C(8.3 mg/kg)+ ETOH, and plant extract(200 mg/kg) + ETOH.
-
a : Compared with control ; b : Compared with animals given ETOH alone
-
*: Significant p<0.05 **: Highly significant p<0.01 ***: Very highly significant p<0.001
DISCUSSION
The fetotoxic effects of ETOH and their ability to produce lipid peroxidation (LPO) in mice has been previously demonstrated (Padmanbhan and Hameed, 1988; Kotch et al., 1995; Henderson et al., 1999). The current investigations confirm the previous observations. In present study, ETOH exposure in vivo was associated with LPO generation in maternal, fetal and placental tissues of pregnant Albino Swiss mice. One possible mechanism that ETOH-induced changes in liver and brain may involve an increase in lipid peroxidation and decrease in antioxidant enzyme such as GSH, vitamin E (Albano et al., 1999) and catalase (Yang et al., 2005; Schirpoor et al., 2009). Indeed, supplemental flavonoids, vitamin E and C should protect against this kinds of tissues damage. Similar observations were recorded however by Schirpoor et al., 2009 who demonstrated that vitamin E protects brain against ethanol induced oxidative stress and apoptosis and Oyinbo et al., 2006showed that vitamins C and E have hepatoprotective effect on hepatotoxicity induced by ethanol in sprague dawley rats. A recent study Lima Sanches et al., 2010 found that supplementation with lecithin and vitamin E attenuated lipid peroxidation and the hepatotoxic effects of chronic ethanol intake and contributed to a reduction of the progression of steatosis status.
This in vivo study have indicated that antioxidant (vitamin E and C) treatment can prevent or reduce growth retardation and/or the occurrence of embryolethality upon ethanol exposure during development. Similar observations were recorded Thus, Peng et al. (2005) showed that the antioxidant vitamin C could decrease microencephaly and growth retardation in embryos of Xenopus laevis that were exposed to ethanol (Peng et al., 2005; Martínez and Egea, 2007). In another study, Millar et al., 2000 found that vitamin E demonstrated a cytoprotective effect against ETOH-induced injury in embryonic chick brains.
Flavonoids functions as a scavenger of oxygen radicals, thereby preventing the lipid peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (Cook and Samman, 1996). However supplemental butanolic extract of the leaves from Chrysanthemum fontanesii in mice we have shown to ameliorate the cytotoxic effect of lipid peroxidation induced by ETOH. So flavonoïd from Chrysanthemum fontanesii have antioxidant properties. This finding is in agreement with results of other reports, which demonstrated that flavonoids from green tea (catechins) protects against ethanol induced lipid peroxidation in rat organs (Ostrowska et al., 2004). In similar study, ethylacetate fraction extracted from the flowers of Chrysanthemum indicum L. (Chrysanthemi Flos) protects against ethanol induced oxidative stress in liver (Choo et al., 2004).
The protective properties flavonoids have also been corroborated by several in vitro studies (Lee et al ., 2009; Mitchell et al., 1999; Sheth et al., 2009). For example, using an in vitro whole embryo culture system, Lee et al ., 2009 demonstrated that the antioxidant black ginseng has a protective effect on ethanol-induced teratogenesis through the augmentation of the embryonic antioxidant activity. In agreement, flavonoids were shown to inhibit apoptosis in cultured fetal rhombencephalic neurons (Antonio and Druse, 2008) .
These finding suggest that ethanol exposure disturbs embryogenesis by increased maternal and embryonic lipid peroxidation, and the adverse effects can be partly ameliorated by enhanced antioxidative capacity in the intrauterine environment (supplementation with vitamin E, C and flavonoïd from Chrysanthemum fontanesii might inhibit ETOH-related toxicity).
CONCLUSION
These finding suggest that ethanol exposure disturbs embryogenesis by increased maternal and embryonic lipid peroxidation, and the adverse effects can be partly ameliorated by enhanced antioxidative capacity in the intrauterine environment (supplementation with vitamin E, C and flavonoïd from Chrysanthemum fontanesii might inhibit ETOH-related toxicity).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by Algerian National Agency for Development of Health Research.
Список литературы Ethanol induced toxicity and lipid peroxidation in pregnant mice: protective effects of butanolic extract from leaves of Chrysanthemum fontanesii, vitamin E and C
- Albano, E., French, S.W. Ingelman-Sunberg, M. (1999) Hydroxyethyl radicals in ethanol hepatotoxicity. Front Biosci, 4, d533-540
- Amrani, A., Zama, D., Boubekri, N., Benaissa, O., Meraihi, Z., Benayache, F., Benayache, S., Bettuzzi, S. (2012) The protective effect of Chrysanthemum fontanesii extract, vitamin E and C on sodium valproate-induced embryotoxicity in pregnant mice. J Med Plants Res. 6, 3535-3544
- Antonio, A.M., Druse, M.J. (2008) Antioxidants prevent ethanol-associated apoptosis in fetal rhombencephalic neurons. Brain Res. 1204, 16-23
- Brocardo, P.S., Gil-Mohapel, J., Christie B.R. (2011) The role of oxidative stress in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Brain Res Rev, 67, 209-225
- Cogswell, M.E., Weisberg, P and Spong, C. (2003) Cigarette smoking, alcohol use and adverse pregnancy. J. Nut. 133,1722s-1731s
- Council of European Communities. (1986) Council instructions about the protection of living animals used in scientific investigations. Official Journal of the European Communities (JO 86/609/CEE) L358, 1-18
- Cook, N.C and Samman, S. (1996) Flavonoids-chemistry, metabolism, cardio protective effects, and dietry sources. J Nutr Biochem.7, 66-76
- Choo, M.H., Jeong, Y., Lee M.Y. (2004) Effects of an ethylacetate fraction of Chrysanthemi Flos on the antioxidative system and lipid profile in rats with ethanol-induced liver damage. J. Food Sci. Nutr, 9, 352-360
- Henderson, G.I., Chen, J.J and Schenker, S. (1999) Ethanol, oxidative stress, reactive aldehydes, and the fetus. Front Biosci. 4, d541-550
- Khatiwora, E., Adsul, V.B., Kulkarni, M.M., Deshpande, N.R., Kashalkar, R.V. (2010) Spectroscopic determination of total phenol and flavonoid contents of Ipomoea carnea. Int J Chem Tech Res. 2, 1698-1701
- Kotch, L.E., Chen, S.Y., Sulik, K. K. (1995) Ethanol-induced teratogenesis: free radical damage as a possible mechanism. Teratology. 52, 128-136
- Lee, S.R., Kim M.R., Yon J.M., Baek, I.J., Park, C.G., Lee, B.J., Yun, Y.W., Nam, S.Y. (2009) Black ginseng inhibits ethanol-induced teratogenesis in cultured mouse embryos through its effects on antioxidant activity. Toxicol. In Vitro. 23, 47-52
- Lima-Sanches, S.C., Portari, G.V., Deminice1, R., Zucoloto, S., Chiarello, P.G., Vannucchi, H., Jordão, A.A. (2010) Effects of Lecithin and Vitamin E Supplementation on Liver Steatosis and Oxidative Stress Induced by Chronic Ethanol Consumption in Rats. Scand. J. Lab. Anim. Sci. 37, 203-210
- Martínez, S.E. and Egea, G. (2007) Novel Molecular Targets for the Prevention of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. Recent Patents on CNS. Drug Discovery. 2, 23-35
- Mitchell, J.J., Paiva, M., Heaton, M.B. (1999) The antioxidants vitamin E and beta-carotene protect against ethanol-induced neurotoxicity in embryonic rat hippocampal cultures. Alcohol. 17, 163-168
- Nordmann, R. (1994) Alcohol and antioxidant systems. Alcohol Alcohol. 29, 513-522
- Ostrowska, J., uczaj, W., Kasacka, I., Róaski, A., and El Skrzydlewska B. (2004) Green tea protects against ethanol-induced lipid peroxidation in rat organs. Alcohol. 32, 25-32
- Oyinbo, C.A., Dare W.N., Okogun, G.R.A., Anyanwu, L.C., Ibeabuch,i N.M., Noronha, C.C. and Okanlawon, O.A. (2006) The Hepatoprotective Effect of Vitamin C and E on Hepatotoxicity Induced by Ethanol in Sprague Dawley Rats. Pakistan Journal of Nutrition. 5, 507-511
- Padmanabhan, R and Hameed, M.S. (1988) Effects of acute doses of ethanol administered at pre-implantation stage on fetal development in the mouse. Drug alcohol Depend. 22, 91-100
- Peng, Y., Kwok, K.H., Yang, P.H., Ng, S.S., Liu, J., Wong, O.G., He, M.L., Kung, H.F., Lin M.C. (2005) Ascorbic acid inhibits ROS production, NF-kappa B activation and prevents ethanol-induced growth retardation and microencephaly. Neuropharmacology. 48, 426-434
- Ramírez-Farías, C., Madrigal-Santillán, E., Gutiérrez-Salinas, J., Rodríguez-Sánchez, N., Martínez-Cruz, M., Valle-Jones, I., Gramlich-Martínez, I., Hernández-Ceruelos, A., Morales-Gonzaléz, J.A. (2008) Protective effect of some vitamins against the toxic action of ethanol on liver regeneration induced by partial hepatectomy in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 14, 899-907
- Sheth, D.S., Tajuddin, N.F., Druse, M.J. (2009) Antioxidant neuroprotection against ethanol-induced apoptosis in HN2-5 cells. Brain Res. 1285, 14-21
- Shirpoor, A., Minassian, S., Salami, S., Khadem-Ansari, M.H., Ghaderi-Pakdeland, F., Yeghiazaryan, M. (2009) Vitamin E protects developing rat hippocampus and cerebellum against ethanol-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. Food Chem. 113, 115-120
- Siler-Marsiglio, K.I., Shaw, G., Heaton, M.B. (2004) Pycnogenol and vitamin E inhibit ethanol-induced apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule cells. J Neurobiol. 59, 261-71
- Uchiyama, M., Mihara, M. (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precurssor in tissues by thribarbituric acid test. Anal. Biochem. 86, 271-278
- Wang, H., Dong, G.X., Zhou, G.C., Cai, L., Yao, W.B. (2008) In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity of aqueous extract from Choerospondias axillaris fruit. Food Chem. 106, 888-895
- Yanardag, R.O., Ozsoy-Sacan, S., Ozdil., Bolkent, S. (2007) Combined effects of vitamin C, vitamin E, and sodium selenate supplementation on absolute ethanol-induced injury in various organs of rats. Int J Toxico. 26, 513-523
- Yang, S.S., Huang, C.C., Chen, J.R., Chiu, C.L., Shieh, M.J., Lin, S.J. (2005) Effects of ethanol on antioxidant capacity in isolated rat hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol. 11, 7272-7276


