Ethical network surveillance using packet sniffing tools: a comparative study
Автор: Ibrahim Ali Ibrahim Diyeb, Anwar Saif, Nagi Ali Al-Shaibany
Журнал: International Journal of Computer Network and Information Security @ijcnis
Статья в выпуске: 7 vol.10, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Nowadays, with growing of computer's networks and Internet, the security of data, systems and applications is becoming a real challenge for network's developers and administrators. An intrusion detection system is the first and reliable technique in the network's security that is based gathering data from computer network. Further, the need for monitoring, auditing and analysis tools of data traffic is becoming an important factor to increase an overall system and network security by avoiding external attackers and monitoring abuse of the IT assets by employees in the workplace. The techniques that used for collecting and converting data to a readable format are called packet sniffing. Packet Sniffer is a tool that used to capture packets in binary format, converts that binary data into a readable data format and log of that captured data for analyzing and monitoring, displaying different used applications, clear-text user names, passwords, and other vulnerabilities. It is used by network administrator to keep the network is more secured, safe and to support better decision. There are many different sniffing tools for monitoring, analyzing, and reporting the network's traffic. In this paper we will compare between three different sniffing tools; TCPDump, Wireshark, and Colasoft according to various parameters such as their detection ability, filtering, availability, supported operating system, open source, GUI, their characteristics and features, qualitative and quantitative parameters. In addition, this paper may be considered as an insight for the new researchers to guide them to an overview, essentials, and understanding of the packet sniffing techniques and their working.
Packet Sniffing Tools, Packet Sniffer, Network Vulnerability, Network Analysis, Wireshark, TCPdump, Colasoft
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15015614
IDR: 15015614 | DOI: 10.5815/ijcnis.2018.07.02
Текст научной статьи Ethical network surveillance using packet sniffing tools: a comparative study
Published Online July 2018 in MECS
Information technology is becoming an integral part and basic of infrastructure for industries and organizations. With the huge growth and development of computer networks and Internet, the administration and auditing of the data traffic are important for increasing an overall networked system security and efficiency. The packet sniffing is the process of collection data packets from the network as binary data, converts that binary data into a readable format and analyzes them showing the protocols used, plaintext passwords, etc., this help the network administrators to monitor and control the computer network to overcome the abuse of IT assets and decrease the risk of an external attacks and computer malfunction. As well as simplify troubleshooting of network by detecting and recognizing the errors and wrong use of data by disgruntled employees and/or attackers [1].
The packet sniffer is either hardware or software piece that legitimately used by network administrator to capture the data frames transmitted between network devices. It is considered as the important surveillance tool for the computer network like camera surveillance monitoring. In some of packet sniffing tools, you can save the data as audit logs for later use and analysis. Packet sniffing tools are passive in which they only collect data and do not make any change or decision upon those data. In other words, they only work as an intrusion detection by collecting and detection of protocols and data without prevention. They help in discovering the vulnerabilities in the network or work like penetration test for the given network [2].
The most important topic that related to packet sniffing is network security which is defined as the policies, standards and procedures for monitoring and preventing denial of computer network services, misuse of IT assets and resources, unauthorized access, and so on. The important factors of network security and access control are confidentiality, integrity, availability, authorization, authentication, accountability, and integrity. As an example, authentication process which is the way of access and exchange information between two systems. The old authentication technique is used the user name and password. The network sniffer scans the packet traffic inspecting on user names, passwords, addresses and plain text data. Further, the packet sniffing tools guide the network administrator with any undesired changes on the computer network such as packet flooding and IP spoofing [3].
Furthermore, Packet sniffer prints collected data on the screen and reports the log of the captured traffic according to parameters such as destination address, source address, target port number, protocol that is used. The network administrators can make the depth analysis of traffic to overcome any weaknesses in the network and to simplify troubleshooting of errors. Also, they can save an audit logs for accountability and later use. In addition, detecting plaintext passwords, the abuse of computer resources, all of that can lead to malfunction of computer network and decrease the network performance. For all of these reasons, network analysis tools or packet sniffing tools are needed [1].
There are various objectives for enabling packet sniffing tools, some of them in the following points:
-
• They are used by network administrators in analysis monitoring and auditing of network traffic to investigate of employees' abuse of IT assets that lead to prevent violation of polices standards, and procedures of an industry or organization.
-
• Packet sniffers are used as intrusion detection and penetration test by network applications' developers, programmer, network and security engineers, especially alarm on the network malfunction or attack when the network performance is slow or down.
-
• Help the network administrators to detect the network weaknesses, threats and vulnerabilities for enhancing the overall security of networks.
-
• Understanding the different network applications that use Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP), their parameters, payload type, IP, Media Access Control (MAC) addresses, etc.
But, the main objective in this research study is to compare between three different network analysis tools; Wireshark, TCPdump, and Colasoft Capsa by using different parameters such as Graphical User Interface (GUI), operating systems supported, libpcap library, o,pen source Packet Capturing (PCAP) supporting, user interface, cost, decoding forms, determined abnormal packets, etc. [1][5].
The rest of this research paper is organized as follows. Section II defines vulnerability and attacks of a network. Section III provides an overview of network sniffing that presents the packet sniffer components, sniffing work process, and the most types of packet sniffing. Section IV explains the three packet sniffing tools: Wireshark, TCPDump, and Colasoft tool, explain their features, advantages and limitations. Section V presents the experimental analysis and filtering methods by using these packet sniffing tools. Section VI presents the comparative study between those three packet sniffing tools. Section VII shows the result and discussion. Finally, the conclusion is given in the section VIII.
-
II. Network Vulnerability and Attacks
The vulnerability is the weakness in the protocols, applications and data transferred in the computer networks. Hence, threats exploit these weaknesses to damage resources, systems and applications. The first thing that the attackers do it is the reconnaissance of the victim's network system by gathering vulnerable information by using tools such as dig, whois, traceroute and nslookup as well as packet sniffing tools. Network scanning is used to find vulnerabilities in the network system. Port scan is the process of finding the active port when a client requests the server [3].
There are two types of network attacks which are active or passive. Packet sniffing is considered as the passive attack type in which the attacker monitor and collect the network's information to obtain the vulnerabilities such as clear-text passwords, routing information, financial transactions, emails, Media Access Control (MAC) addresses, Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, critical and sensitive information that are not encrypted can be obtained via packet sniffing tools without the user knowledge. The other type of network attacks is active attacks in which the attacker compromises the network system by masquerades to the other entity in the network system. IP spoofing, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) spoofing and MAC spoofing are an examples of active attacks.
While the TCPDump, Wireshark, and Colasoft are considered as the packet sniffing methods. There are some tools used for spoofing. ETTERCAP is the tool used for ARP spoofing and poisoning which can be performing Man-in-the-Middle attack. It requires selecting the network interface to work on it. After the interface is selected, the network is scanned for hosts in the network and hosts are showed from their list in the tool. The packet sniffing tools are used for gathering information from computer network, converting the binary information to hexadecimal and human readable format for analysis, diagnostic network failures and troubleshooting. They are used for detecting errors and abnormal traffic in the network. The network administrators are using these tools also to predict the weakness and vulnerabilities in the network by showing the protocols that are insecure to replace them by strong protocols [3].
In addition, there are various systems and applications are used the user name and password which is becoming an integral part of our personal and business life. As an example of the environment of using user names and/or
Personal Identification Number (PIN) logins are banking systems, electronic mails login, All Time Money (ATM), Point of Sales (POS), server login, etc. all of these ways are considered as the sources of computer's network vulnerability if there is no strong protection of login methods. The packet sniffing tools are used efficiently and effectively to test the weakness of the user names and passwords login methods. These packet sniffing tools provide the network administrator with full details of user names and passwords that are plain text or not have strong encryption techniques to take a suitable countermeasure to solve weaknesses in the network system.
Moreover, there are many types of password attacks that make an attackers and hackers to crack passwords. From these types are the brute-force, dictionary attack, malware/key logger, SQL injection, rainbow table attack, and phishing attack. As network administrator, you can use the packet sniffing application to determine the field of the user names and passwords in the data traffic and test the complexity of the passwords and take an appropriate countermeasure to prevent attackers from stealing of the passwords, for example, when the network administrator shows the passwords contains on a combination of numbers, characters and special characters that is brute force attack type, he must advice to prevent this type of attack by make the password more complex and very long [4].
-
III. Network Sniffing
The network sniffing is the process of capturing, monitoring, and analysis of the data traffic travelling in the network both incoming and outgoing traffic. The tool that performed this process is called packet sniffer which is the program that captured traffic either in wired network via the wired or wireless network via the air. Packet sniffer has the benefits of analyzing the traffic, determining and understanding the characteristic of the network, possible malicious and attacks, peak usage of bandwidth and its availability and finding the unsecured applications, data and protocols [1].
There are two types of packet sniffing which are either monitor mode or promiscuous mode. When the Network Interface Card (NIC) is set in promiscuous mode, then the host is becoming able to sniff all packets. In the monitor mode, or sometimes called "rfmon" mode, the NIC does not care about the Cyclic Redundancy check (CRC) and the capturing process is occurred without associating or authentication, for example between access point and wireless NIC in wireless networks [5].
-
A. Components of Packet Sniffer
The packet sniffer consists of the following components.
-
• Hardware: the piece of hardware that used like a standard network adapters.
-
• Capture driver: It is critical part of packet sniffer. It has the role of capturing data from network either
wire or wireless, filters the particular traffic and protocols and then store data into the buffer.
-
• Buffer stores the captured frames that gathered from the network.
-
• Analysis and decode: in this phase the network data is displayed in descriptive text format, and analysis is figured for each part of data [4].
-
B. Packet Sniffing Types
There are some parameters of the classification of the packet sniffing, as shown in the following points.
-
• IP based sniffing: This is the fundamental and commonly used packet sniffing method. In this way the network card is set in promiscuous mode for capturing all packets that passes the network. It uses an IP based filtering, and only the packets are captured when they are matching the specified IP addresses. In general, the IP based filter is not set, so the IP sniffing can capture all packets. IP based sniffing filter works in non-switched networks.
-
• MAC Sniffing: like IP based filter, the MAC sniffing filter allows the host captures all the network's packets according to the corresponding MAC addresses.
-
• ARP Sniffing: This way is used efficiently in switched networks. It works little different and does not require putting the network card into promiscuous mode because the ARP packets will be send to us. This occurred for the reason that the ARP protocol is stateless [1][2].
-
C. Packet Sniffing Work Process
The packet sniffing is worked as in the following steps.
-
• Collection in which the packet sniffer gathering and collecting the binary raw data from the network interface either wire or wireless interface.
-
• Conversion in which the captured binary data is converted into readable data format to know the protocols used and data payload.
-
• Analysis of the captured and converted data to extract the protocols that used and analyze their parameters.
Each device in network has NIC's physical address that uniquely identified. When the device is sending the packet, it passes on all of the network machines. With the principle of shared Ethernet, all machines on network can see the traffic but not response to that traffic if it does not belong to that machine.
When the NIC sets on promiscuous mode, the machine can see all traffic on the segment. However, when the NIC puts in promiscuous mode for one machine, the NIC takes and gathers all frames and packets on the network even if that frames and packets do not destined for that machine, which in this situation called sniffer. The sniffer begins the reading all information entered into the machine via NIC [1].
As we know, the data travelling as packets or frames, group of compound bits formatted to some specified protocols. For this reason, packet sniffer does not peel the encapsulation layers and decode the traffic according to destination computer, source computer, payload, targeted port number or piece of information exchanged between two computers. The following points are definition for both shared Ethernet and switched Ethernet.
-
• Shared Ethernet: As we know the shared Ethernet environment, all machines on the network share same cable and alternate using of bandwidth. In this type, each machine receives the traffic that travelling via network. In this situation, the network environment placed in promiscuous mode, and each one of the machines can listen to that traffic.
-
• Switched Ethernet: in this case, the network used a switch instead of the hub which named switched Ethernet. The switch is more intelligent and has the filters table that forward the traffic at the next time only to the intended machine without broadcasting that traffic to all other machines in the network. In this case, the sniffer is not suitable. The switched Ethernet provides better performance, but the NIC putting in promiscuous mode does not work. The network administrators assume that the sniffers do not work in this environment [1].
There are many packet sniffing applications and tools available in the market. Some of them are graphical interface and the other are command line interface. We will explain and compare between three popular packet sniffing tools; TCPDUMP, Wireshark and Colasoft.
of libpcap library. The developers designed libpcap library as an independent-platform API to work on a variety of applications and to eliminating the system dependency for data capturing modules in each application. TCPDump is considered as parsing tool.
By default, it intercepted and prints out the summary that captured from the network; the other features like storage are performed by specified commands. TCPDump works as: 1) Read/Write the captured file from network in the Packet CAPture (PCAP) by using CLI commands. 2) It filters packets according to some given parameters. 3) It prints on the screen the captured data according to the specified parameters [4]. It is more easy and portable packet sniffer tool, because it is depends only on CLI and the network administrators use it to access to the network devices from remote location [5][6].
Fig. 1 shows the TCP/IP traffic and its analysis of TCPDump packet sniffing tool, displaying the addresses and contents of data traffic.
rootQyoshiki # tcpdump -i lo -к
server
[/homeAoakira] 11:17
tcpdump: listeni ng
11:17:49.511973
Uncal host .338871Я localhost.87651
P 1502698231:1502609255(102^ k 1504308678 win ЗУь/
X 4500 0434 5ai6 4000 4006 ^ь 7f00 0001
- - ^ 7f00 0001 845a 223d 5991 5af7 59a9 edc6
cl lent
8018 7fff^*W*w*itiL.°80a 0166 20fcL 0166 13( ^6865 6c6c 6fQa>j4U УОЬб 1440 0100 OOOOW^^^^^COOOO 44f7 ffbf
Io
11:17:49.5162271 localhost^fs Mlocalhost.338821 P 1:1025(1024) ack 1024 min
7
4500 0434 e524 4000 4006 539d 7f00 0001
7f00 0001 223d 845a 59a9 edc6 5991 5ef7 , ~
8018 7fff Ш^^^Д^1 080а 0166.209®- H I ( )
0166 209 CS45 4c4c 4fp£> 4erg06F144O 1 1 V 0100 00007Й1Л1 UWW UWUTOOOO 44f7 ffbf
11:17:49.516271 localhost.33882 > localhost.8765: . ack 1025 win 32767 <пор,пс mestamp 23470238 23470238> (DF)
4500 0034 5al7 4000 4006 e2aa 7f00 0001
7f00 0001 845a 223d 5991 5ef7 59a9 flc6
8010 7fff 0a23 0000 0101 080a 0166 209e
0166 209e
3 packets received by filter 0 packets dropped by kernel
Fig.1. TCPDump Overview shows the TCP/IP Characteristics flow [7].
-
IV. Packet Sniffing Tools
There are many tools for decoding and analysis of the data transmitted in the network, usually these tools work under mode of promiscuous enabling the computer capturing full traffic based on IP packets and ports that used for variety of applications. The important attention here, the sniffing tools are passive and designed for both wired and wireless networks measurement. In this research paper, we take three packet sniffing tools as showed in the following points.
-
A. TCPDUMP
It is popular Command Line Interface (CLI), and an open source packet sniffer tool compatible on Unix and Linux platforms. It was invented in the 1987 at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and after that published after few years.
It has the libpcap library developed by C programming language that worked to gather network's information. The libpcap provides the interface to all common Unix based platforms including FreeBSD and Linux. The libpcap interface in Windows platform called WinDump. Windump is used the WinPcap which is the windows port
The major limitation of TCPDump, it does not provide the network administrator visually GUI of the captured data for more analyzing, there is only CLI. Since, it is a text based and easy for the user to use it remotely through Telnet connection. There are other few disadvantages with TCPDump. These include:
-
• Limitations on the analysis of traffic, there is a TCP based protocols only may be used.
-
• It reports only what it finds in packets, if the IP address is forged in the traffic, it has no ability to report anything else [10].
-
• Packets that blocked by the firewall do not be shown.
-
B. Wireshark
It is invented by the scientist Gerald Combs at the late of 1997 for trucking and recognizing the network's problems and monitoring the data traffic. He named it Ethereal until in May, 2006 and after that its name changed to Wireshark. It is an open source software, free and GUI packet analyzer tool that has written in C programming language and released under GNU General
Public License (GPL). It runs on a variety of Unix-like operating systems including Mac OS X, Linux, Solaris platform, as well as the Microsoft Windows operating system. Command Line Interface (CLI) of Wireshark is called TShark to enable the user deal with it via commands. It is like TCPDump with additional GUI, supporting a variety of protocols and ability of filtering and sorting options. It is used in Network Forensic Analysis Tool (NFAT) in an organizations.
Wireshark is designed for capturing packets from live networks and also browsing previously saved captured data file. The supported format of packet capture is "PCAP" file format. It displays the captured data in a byte and hexadecimal formats showing different types of used packets and protocols. It is also allows the user to assemble the packets data into a TCP stream.
It has the interface with three panes; the summary pane or packet list panel which shows different captured packet analysis like frame number, date, time, destination and source IP addresses, upper layer protocols, length of packet and information of the traffic content with color for each captured packet type. The second pane is captured packet details. When the packet is determined at the packet list pane, the details appear in the following two panels; the details and the byte or hexadecimal panes. The details panel is appeared as the tree-like structure of the protocols that are captured for a variety of applications such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), User Datagram Protocol (UDP), Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP), etc.,. The third panel is named data or byte pane which shows raw of captured data displaying the packet byte in the hexadecimal, ASCII encoding and text formats [8][9][10].
The important note here, to run the Wireshark tool, it sets the NIC to promiscuous mode for enabling the sniffer to see all traffic on that interface, not just the traffic that addressed to one of the configured interfaces. Beside the promiscuous mode, it may be enable the port mirroring to any points of the network when the promiscuous mode does not coverage all network [5][6].
Fig. 2 shows Wireshark interface displaying the three windows; the summary, details and byte panel, with different characteristics of network's traffic in readable manner. The section of details shows that the frame number is 60 bytes, the network type which is Ethernet II, the protocol type is IPv4 and payload content is ARP. The frame size is measured with the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) and this unit is determined according to the used network type. For example, the MTU for the Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is 53 bytes [17], the MTU in the Ethernet and IPv4 network is 1500 bytes and there is other network types use of jumbo frames that reach to 9000 bytes [18]. Hence, the frame size changes according to MTU in a given network type.
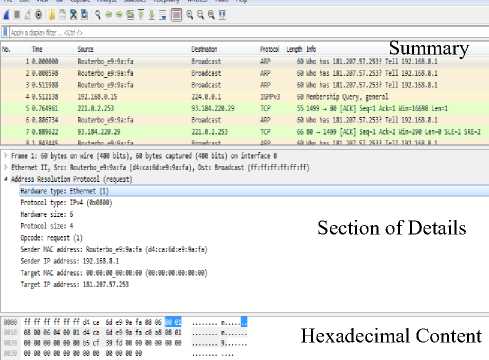
Fig.2. Wireshark Packet Sniffing Tool Interface.
Furthermore, the frame size also determine according to the used application in the network. In this case study, it is 60 bytes in which the ARP is used to find the physical link-layer address of a router interface or host when its logical IP address is given. Another example, the author [19] used the frame data size of 500 bytes by applied Quality of service (QoS) on some UDP-based healthcare applications and concluded that is suitable for both delay and jitter, as well as used some of other QoS that led to get upon frame size 1500 bytes. Then, the frame is appeared in the packet sniffing tool according to application or protocol that used in the network.
The Wireshark limitations, it needs the best understanding of the protocol formats, HTTP and Cascade Style Sheet CSS language knowledge of the byte format. It uses the PCAP file format for capturing the traffic, so it can only capture the packets on the network types that support PCAP file format. Another disadvantage is that, because the Wireshark is not automated tool, it is not support for working of long time monitoring.
-
C. Colasoft
It is closed source network protocol analyzer tool designed to work on business and personal use operated Windows operating system platform that used by network administrator to troubleshoot, monitor, and diagnose the traffic on computer network. Capsa produces free editions of Colasoft tool that is ease of use, real-time packet analysis, and reliable forensic, in-depth protocol analysis and it is worked continuously 24/7 network monitoring. It has a feature of opening multiple interfaces at single instance, providing the user with graphical interfaces and matrix representations [5].
It has in-depth analysis of packets showing different characteristics with ability of generating reports, logs and alerting with only voice and electronic mails for the licensed versions. It has a variety of GUI features, displaying the captured information in graphs, matrix and according to each characteristic of the network's traffic showing each protocol used in the network. Fig. 3 shows the Colasoft tool and its enhanced GUI features.
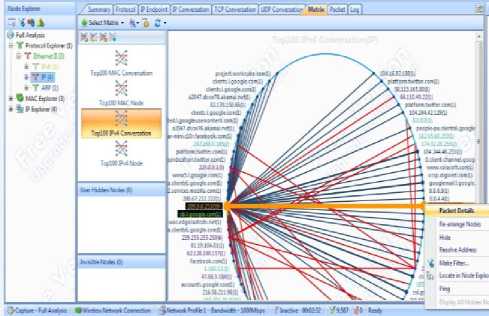
Fig.3. Colasoft Packet Sniffing Tool Interface.
The following steps are applying the Wireshark and Colasoft packet sniffing tools on HTTP protocol which is uses the TCP protocol at the transport layer [20]. To extract and analysis of HTTP protocol, do the following points.
-
• Open the browser, run the Wireshark and Colasoft in capturing state, and browsing any web site, here in this case study, we are choosing the web site " http://www.sababank.com/signin.php ", and try to type the user name and password login. After that close the web site and stop the capturing of the network traffic.
-
• Use the filter toolbar for filtering the specified packet, showing the protocols and data content.
There are some limitations of Colasoft; it is expensive application, whereas a free version is available, but with restricted features, for example the free version does not notify to the user though E-mail and voice channels. Another two disadvantages of Colasoft tool is that, it works on the Microsoft Windows operating system platform only, and it supports only 300 protocols which is considered less compared with some other packet sniffing tools such as Wireshark tool [6][8].
-
V. Experimental Analysis and Filtering
The general packet sniffing process is occurred via three steps; first, the sniffer is gathered or captured the network's information, second conversion of the captured binary data into a readable format, and finally applying analysis and filtering of the converted data. There are various ways and methods for filtering and choosing the specified protocol or some part of data traffic. The NIC interface of the machine that the sniffing tools are installed on it must be in promiscuous mode to capture all packets and frames on all segments of network. This machine is called sniffer [11]
The filtering process of the currently real time captured packets or saved captured packets is considered an important for analysis and diagnosis of various data traffic, protocols and applications that are used in the computer's network system. From that protocols like HTTP, ICMP, Domain Name System (DNS), TCP/IP, UDP, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), etc., all of the volume information and losses of packets are shown in that captured information [12].
In addition, these packet sniffing tools; TCPDump, Wireshark, and Colasoft are used for monitoring, analysis, and auditing of the data traffic on the computer networks either wired or wireless networks. Further, they are used in penetration test and intrusion detection by observing strange packets in the network. The network's security threats are shown by sniffer in which has the ability of capturing all incoming and outgoing data traffic, including the clear-text user names and passwords, and other critical information [13]. The packet sniffers include engines for discovering intrusion detection and for searching on specific types of network's attacks such as packet flooding and IP spoofing attacks [14].
Fig. 4 is an example of extracting user name and password in a Wireshark tool by filtering the HTTP protocol which shows the clear text user name and password as shown in the rectangle box which shows the user name is "Ibrahim_Diyeb" and password is "yemen_123". The filtering command is" http.request.method=="POST"". This filtering is guide the network administrator to make the remediation for this vulnerability in specified application by using the secure protocol such as Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) or encrypt the content.
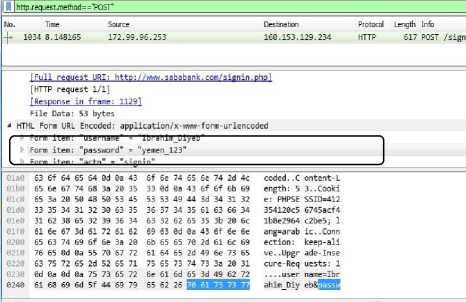
Fig.4. Wireshark Filtering Showing Clear Text of user Name and Password.
Furthermore, to extract all of TCP connection stream in a file, select the packet that you want, and then right click on the “Follow TCP Stream” by mouse, the file with all content of that packet is appeared.
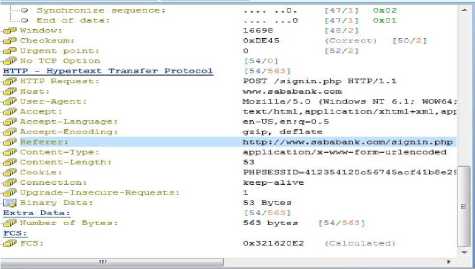
Fig.5. Colasoft Analysis and Filtering Showing Web Site.
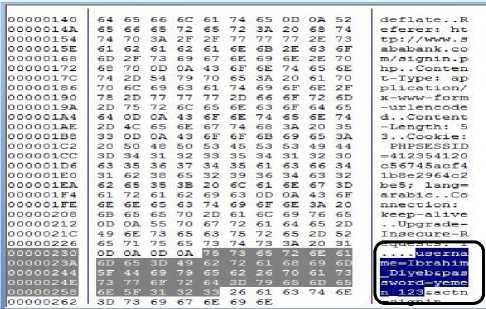
Fig.6. Colasoft Analysis and Filtering Showing the Clear Text Information.
Both Fig. 5 and 6, show that the filtering of HTTP protocol by using Colasoft Capsa tool of the same previous web site. Fig. 5 shows the HTTP protocol and web site that is used here in our case study and fig. 6, shows the user name and password in a clear text without an encryption as shown in the square box.
-
VI. Comparison Between the Three Packet Sniffig Tools
To compare between the above three network sniffing techniques, need to depend on the parameters such as open source code, number of protocols supported, operating system supported, supporting PCAP, user interface, cost, decoding forms, determined abnormal packets, reconstruct TCP stream, etc. [4][5].
Table. 1 shows the comparison between the Wireshark, TCPDump, and Colasoft tools. From the comparison table, there is no one packet sniffing tool is leading all parameters. But the comparison with advantages and disadvantages will help the developers to improve the packet sniffing tool to overcome its limitation. Here, we will compare between packet sniffing tools by using the qualitative and quantitative parameters [5].
Colasoft has analysis features more visual explanation with statistics for the captured packets, displaying more information about protocols and user applications with graphs and matrix view for all connected endpoints. Additional features that the Colasoft includes reports, audit logs, and diagnostics. All of these features help the network administrator to diagnose the network problems. Also, Colasoft has a powerful analysis and interpretation of TCP flow; it has a versatile bandwidth, network traffic, and utilization analysis. It has a matrix representation and in-depth decoding features of traffic with multiple behavior of network monitoring. Further, it has eclipse visualization of computer networks [1].
In addition, Colasoft has more powerful visibility and Windows 7 style with simple graphical screens, dashboards and network analyzer. This make using this tool is easy and simple for user in which any task you want is performed by clicking the mouse. Hence, the Colasoft is becoming more user friendly packet sniffing tool, it provides easy-to-read way and it has multiple interfaces at single instance. The graphs show more visualization for various network statistics and properties. The Wireshark is limited with these capabilities of GUI and it does not opening multiple interfaces in a single instance.
Table 1. Comparison Characteristics between Wireshark, TCPDump and Colasoft Packet Sniffing Tools
|
Parameter |
Sniffing Tool |
||
|
TCPDump |
Wireshark |
Colasoft |
|
|
Open Source |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
O.S Supported |
Linux (WinDum for Windows) |
Linux and Windows |
Windows |
|
No. of Protocols supported |
TCP/IP |
More than 1000 |
300 |
|
User Interface |
CLI |
GUI and CLI |
GUI |
|
Cost |
Free |
Free |
$999 |
|
Libpcap Based |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Detemining forged data |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Disk usage |
484 KB |
449 MB (Unix), 81 MB (Windows) |
32 MB |
|
Display application layer protocols |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Decode protocol |
Only Hex and ASCII |
Only Hex and ASCII |
Hex, ASCII, EBDIC |
|
Reconstructe TCP stream |
No |
Yes(but not formatted) |
Yes |
|
Identify the abnormal protocol |
No |
No (only creates a warning) |
Yes |
|
Multiple Interfaces |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
Detection Alarm |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
Reconstruct HTTP web pages |
No |
No, Show actual traffic content individually |
No, Show Links for traffic content individually |
|
Network communication matrix map |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
Evaluation of critical business and non-critical business traffic |
No |
Yes (by ceating filters and research) |
Yes (inbuilt) |
|
Ability of development and customization by universal developers |
Yes (need potential efforts) |
Yes |
No (only the Capsa team) |
|
UDP traffic |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Compared with Wireshark, Colasoft provides more network security by alert notifications via audio and electronic mails. The disadvantage of the Colasoft, it covers only 300 protocols, which is very less compared to
Wireshark that supports 1100 protocols [1].
TCPDump is very portable and economical packet sniffing tool in terms of memory usage, since it occupies only 484 Killo Byte (KB) of installation space. While Wireshark installation file size at the beginning of installation is 18 Mega Byte (MB), but after completing of installation, it consumes 81 MB in Windows and 449 MB of disk space in Linux operating system. Colasoft installation space is 32 MB. Hence, in term of memory usage, Wireshark is very expensive [15].
Because Wireshark is an open source code, anyone can download its code and improving it. There are many universal developers in the world having the capability of customization and enhancement this tool, while Colasoft is restricted only on development's team of the Capsa company. Hence, Wireshark is considered good packet sniffing tools for understanding the programming works and it fulfills the requirements of network's users by making customization with no cost. In Colasoft tool, if the user needs some customization for some problem of network's monitoring, he requests that from the provided company with payment cost for that customization. With Wireshark packet sniffing tool, you can accept more experience of TCP/IP configuration, understanding the structure of network, and also it runs on various platforms including Linux, Solaris, OS X and Windows.
Furthermore, some of authors make researches in this field to enhance the Wireshark tool, in Ref. [16], the author improves the Wireshark packet sniffing tool for detection intrusion of the Denial of Service (DoS) attacks type especially in which to overcome the ping flooding attack that sends large number of ping commands to the victim device.
-
VII. Result and Discussion
Each one of packet sniffing tools has its own advantages and disadvantages. All of those packet sniffing tools have general characteristics for network properties, but each tool has its own competitive feature. There are a variety of qualitative and quantitative parameters are discussed and compared on the packet sniffing tools; Wireshark, TCPDump, and Colasoft. From these parameters are number of protocols supported, open source code, platform supported, libpcap library, PCAP supporting, user interface, cost, decoding forms, determined abnormal packets, network communication in matrix map, reconstruct TCP stream, etc.
Hence, each tool of network analyzer does not lead all of the network parameters. Whereas the Colasoft tool is better than the Wireshark in matrix and graphical reports, the Wireshark is an open source code, easy for developers in the world to develop and customize code according to their needs, and it is compatible to different platforms such as Linux and MS Windows operating systems while Colasoft works only on the MS operating systems. In the other hand, TCPDump tool is a lite tool that has small size of disk space as competitive feature, so it is best option for using it remotely to monitor the computer networks by using the command line interface.
The other important parameter factor is the number of protocols supported by packet sniffing tool. The Wireshark supports a huge number of protocols more than 1000 protocol, which is a superior tool for network monitoring and controlling to used on a heterogeneous networks that have diverse protocols including video and audio applications, while the other network monitoring tools only support few protocols such as Colasoft tool supports about 300 protocols only and the TCPDump only supports TCP/IP protocol and doesn't support User Datagram Protocol (UDP) transport layer protocol.
As well, considering the other parameters such as cost, the Wireshark and TCPDump are free tools, while Colasoft is costly and more expensive than other tools. But the Colasoft is more strong tool in detecting the abnormal protocols which is a competitive feature compared to other tools such as Wireshark that only make a warning. Colasoft packet sniffing tool is developed by Capsa team that led to become good graphical interface and has more security features. The filtering interface also is considered as competitive feature in Colasoft tool which is more GUI and user friendly that facilitate on the user to filter and analyze the protocols and data traffic in easily manner.
Furthermore, some other authors have tested some of the network parameters for comparing between packet sniffing tools; the result is shown in the following points [1].
-
A. Response Time
It is defined as the length of time periods (measured in time units) for a particular specific event. The authors conclude that the response time of Wireshark is less than the Colasoft response time.
-
B. Packets per Seconds (PPS)
It is the number of transmitted packets in one second. It is seen clearly, the Wireshark has lesser packets loss than Colasoft. Hence, the Wireshark is preferred compared to Colasoft for retransmission of less packets.
-
C. Distribution of Packet Size
Less size of packets can be led to less stress on the network, while the long packet size increases the load on the network. After applied experiment scenario, they concluded that the length packet size in the Wireshark is 558.76 Byte (B), while in Colasoft is 434 B. Hence, the Colasoft is sending medium sized packet's length; it is better than Wireshark tool for the computer network load. The Colasoft Capsa does not stress the system and network.
-
D. Throughputs (bits per second)
It is the data amount processed by the system measured in second. After applying the experiment, it is show that the throughput in Colasoft Capsa is large range and it is changing swiftly. These random changes are bad for the network's system, because it hinders the performance of the system and computer network. Whereas, Wireshark has a constant behavior and good pattern range of the computer's network. The average bits per seconds (bps) in Wireshark are 115.398 kbps and in Colasoft is 6.34 kbps. Hence, Wireshark has higher throughput more than Colasoft Capsa, then Wireshark has more performance with a constant variation and also, with seeing no high cut-offs of the bps.
Table. 2 shows the best uses of packet sniffing tool for each network property. The best use of Colasoft in alarm of abnormal and forged packets and it provides more security and GUI interfaces. While the Wireshark is suitable for learning by programmers and developers by downloading the source code and customize it according to needs of network monitoring. The TCPDump tool is more suitable in remote logical access control to monitor network by using CLI.
Table 2. Best uses of the Packet Sniffing Tools; Colasoft, Wireshark and TCPDump tools.
|
Network Parameter |
Sniffing Tool |
|
Security of computer networks |
Colasoft |
|
GUI |
|
|
Identify the abnormal and forged packet |
|
|
Network alarms |
|
|
Packet size |
|
|
Network communication |
|
|
Multiple interfaces per single interface |
|
|
Decoding protocol form (Hex, ASCII, EBDIC) |
|
|
Determining the abnormal packet |
|
|
specifying the packets with forged data |
|
|
Showing protocols of application layer in OSI 7 model |
|
|
Supported OS |
Wireshark |
|
Customization and development to all developers |
|
|
Response time |
|
|
Throughputs (bps) |
|
|
Packets Per Second |
|
|
Number of supported protocols |
|
|
Portable and easy remote access control |
TCPDump |
In my viewpoint, for large business you can use Colasoft packet sniffing tool and for the education and learning, the Wireshark is dominant. Both Wireshark and Colasoft are two familiar tools that using broadly in the world and the TCPDump is simple and portable that used remotely from anywhere for only basic troubleshooting of network's problems beside the graphical packet sniffing tools. The major advantage of Colasoft is user interface. It is user friendly and easy to read. It has more visualization features; the graphs and matrix with more readable reports and audit logs. There is multiple interfaces can be open in one instance in Colasoft.
In network analysis, both the Wireshark and Colasoft are having auto detecting of network errors. But the Colasoft provides the user with details on reason and resolving those errors.
When talking about open source, the universal developers can benefit from the open source code of Wireshark and can develop it according to their requirements of network monitoring and analysis properties with no cost. The customization in Colasoft is costly and is happened by Capsa team only.
-
VIII. Conclusion
There are several tools for capturing, monitoring, auditing and analysis data traffic of computer networks both on wired and wireless networks and called packet sniffing tools. Packet sniffing tools work in three steps; collection of data traffic from computer network in a raw binary data, then convert the binary data into human readable format and after that filtering and analysis of collected data. The purpose of packet sniffing tools helps the network administrators to examine the captured packets showing the vulnerabilities and abuse of organization's IT assets by employees.
As well as, network security engineers and developers need the packet sniffing tools for investigating network security problems and debugging implementation of communication protocols and network’s applications. Packet sniffer is not a hacker’s tool. It is used to troubleshoot, monitor, analyze and audit the network’s data traffic to make the network is safe, secure, reliable and increasing the performance.
In this study, compared between the three famous packet sniffing tools; Wireshark, TCPDump, and Colasoft according to various parameters such as intrusion detection ability, supported operating systems, number of supported protocols, open source code feature, multiple interfaces, libpcap library, PCAP supporting, user interface, decoding forms, determined abnormal packets, network communication in matrix map, etc.
Each packet sniffing tool has its own advantages and disadvantages. The Wireshark is free of cost, open source code powerful, and supports a large number of network protocols and applications which it supports more than 1000 protocols. The network developers benefit from these features by download the source code, customize and develop it according to their needs in the network properties with free of cost. In the other hand, Colasoft is closed source by Capsa Co., but it provides more security and filtering features, it has good capabilities of GUI with tables, graphs, and matrix map. Colasoft identifies the abnormal and forged packets with detection alarm ability via electronic mail and voice notifying the network administrator with any problem occurred to the packet. The third compared tool, TCPDump is an open source code, portable and economical tool in term of memory usage. It is used remotely via Telnet by users and only supports TCP/IP protocol.
All of those packet sniffing tools need developing the applications to facilitate the visualization and supporting of more protocols analysis in which recognizing the different parts of the traffic. In future work, apply packet sniffing tools on a variety of applications such as Voice over IP (VoIP) and Video conferencing applications including analysis and filtering methods.
Список литературы Ethical network surveillance using packet sniffing tools: a comparative study
- Nedhal A. Ben-Eid, Ethical Network Monitoring Using Wireshark and Colasoft Capsa as Sniffing Tools, International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and Communication Engineering Vol. 4, Issue 3, pp 471-478, March 2015.
- Palak Girdhar and Vikas Malik, A Study on Detecting Packet Using Sniffing Method, Journal of Network Communications and Emerging Technologies (JNCET) Vol. 6, Issue 7, July, 2016.
- Nabanita Mandal and Sonali Jadhav, A Survey on Network Security Tools for Open Source, IEEE, 2016.
- Savita Kamalakarrao Kulkarn, A Survey of Password Attacks, Countermeasures and Comparative Analysis of Secure Authentication Methods, IJARCSMS, Vol. 3, Issue 11, ppt. 319-331, November 2015.
- Dr. Aruna Varanasi, P. Swathi, Comparative Study of Packet Sniffing tools for HTTP Network Monitoring and Analyzing, IJCSET(www.ijcset.net), Vol. 6, Issue 12, pp. 406-409, December 2016.
- Oludele Awodele, Otusile Oluwabukola, A.C Ogbonna, and Ajayi Adebowale, Packet Sniffer – A Comparative Characteristic Evaluation Study, Proceedings of Informing Science & IT Education Conference (InSITE), pp. 91-100, 2015.
- ANSHUL GUPTA, A Research Study on Packet Sniffing Tool TCPDUMP, International Journal of Communication and Computer Technologies, Vol. 01, No. 49 Issue 06, pp. 172-174, July, 2013.
- Dr. Charu Gandhi, Gaurav Suri, Rishi P. Golyan, Pupul Saxena and Bhavya K. Saxena, Packet Sniffer – A Comparative Study, International Journal of Computer Networks and Communications Security, Vol.2, No. 5, ppt. 179–187, May 2014.
- Dr. Mahesh Kumar and Rakhi Yadav, TCP & UDP PACKETS ANALYSIS USING WIRESHARK, IJSETR, Vol. 4, Issue 7, ppt. 2470-2474, July 2015.
- Ajay Kumar, and Jai Bhagwan Yadav, Comparison: Wireshark on different parameters, International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science, Vol. 5, Issue 3, ppt. 16041-16046, March 2016.
- Pallavi Asrodia and Hemlata Patel, Analysis of Various Packet Sniffing Tools for Network Monitoring and Analysis, International Journal of Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering, ppt. 55-58, 2012.
- Pallavi Asrodia, Mr. Vishal Sharma, Network Monitoring and Analysis by Packet Sniffing Method, International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT), Vol. 4, Issue. 5, ppt. 2133-2135, May, 2013.
- Inderjit Kaur, Harkarandeep Kaur, and Er. Gurjot Singh, Analysing Various Packet Sniffing Tools, International Journal of Electrical Electronics & Computer Science Engineering, Vol. 1, Issue. 5, ppt. 65-69, October 2014.
- Mohammed Abdul Qadeer, Mohammad Zahid, Arshad Iqbal and MisbahurRahman Siddiqui, Network Traffic Analysis and Intrusion Detection using Packet Sniffer, Second International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, ppt. 313-317, IEEE, 2010.
- Otusile Oluwabukola, Awodele Oludele, A.C Ogbonna, Ajeagbu Chigozirim, and Anyeahie Amarachi, A Packet Sniffer (PSniffer) Application for Network Security in Java, Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology, ppt. 389-400, Vol. 10, 2013.
- S.Pavithirakini, D.D.M.M.Bandara, C.N.Gunawardhana, et.al, Improve the Capabilities of Wireshark as a tool for Intrusion Detection in DOS Attacks, International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 4, pp. 378-384, April 2016.
- Ibrahim Diyeb and Dr. Sharaf A. Alhomdy, Frame Relay versus Asynchronous Transfer Mode: A Comparative Study and Simulation, I. J. Computer Network and Information Security, Volume 10, pp. 33-40, October, 2017.
- Shaneel Narayan, Paula Raymond Lutui, TCP/IP Jumbo Frames Network Performance Evaluation on A Testbed Infrastructure, I.J. Wireless and Microwave Technologies, volume 6, pp. 29-36, 2012.
- Er. Vikram Jeet Singh, Er. Vikram Kumar, Dr. Kishori Lal Bansa, Research on Application of Perceived QoS Guarantee through Infrastructure Specific Traffic Parameter Optimization, I.J. Computer Network and Information Security, volume 3, 59-65, 2014.
- Y. –J. Lee, Mean Response Time Approximation for HTTP Transactions over Transport Protocols, I.J. Computer Network and Information Security, 2015, 1, pp. 24-30.


