Evaluation of seed germination and early seedling growth under heavy metals stress conditions in coastal red rice (Oryza sativa L.) crop
Автор: Girija D., Abirami K., Vikrant
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.18, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Among cereals, rice is known as the major components of our food consumption worldwide; however, recently accumulation of heavy metals in soil and water has emerged as big constraints for rice yields. This study was undertaken with analyzing the impacts of various heavy metals (Hg, Co, Ni, Cd, Zn and Cu) stress treatments on seed germination and early seedling growth in coastal red rice ( Oryza sativa L. cv. Poongar) crop. Responses in terms of germination percentage mean were recorded as partial germination and full germination after 5-days and 10-days of stress treatments respectively. Moreover, stress responses of heavy metals during early seedling growth were measured in terms of root and shoot lengths of the seedlings after 10-days of treatments. Mature seeds were initially treated with HgCl2 (0.01%, 0.1% and 1.0%) and equivalent concentrations of CoCl2, NiCl2 and CdCl2 (1.0mg/L, 5.0mg/L, 10mg/L, 25mg/L and 50mg/L) followed by ZnSO4 and CuSO4 solutions (0.5mg/L, 1.0mg/L, 2.5mg/L and 5.0mg/L). Results reveal that HgCl2 even at very low concentration (0.01%), was found to be the lethal for seed germination (5±0.0%), however, these poorly germinated seeds were further failed to grow into seedlings. Like HgCl2, CoCl2 was also found to exhibit strong toxicity but at high concentration (50mg/L) where seed germination was completely lacking. Furthermore, unlike CoCl2, NiCl2 solution was found to be less toxic where germination frequency was recorded as (12±0.0%) and suppressed root formation completely at high concentration (50mg/L). Moreover, among chloride solutions of cobalt, nickel and cadmium, CdCl2 was proved as little weak inhibitor because complete seedling development with root-shoot length was observed at high concentration (50mg/L) and root-shoot length ratio (0.28±0.19cm/0.96±0.23cm) was recorded as compared to control seedlings (3.97±0.71cm/4.52±0.45cm). Furthermore, in case of sulphate solutions of zinc and copper, ZnSO4 stress proves to be strongly lethal even at very low concentration (5.0mg/L) and seed germination was completely lacking in comparison to CuSO4 treatment (15±0.0%). However, CuSO4-treated germinated seeds were grown into incomplete seedlings without roots (0.0cm/0.05±0.02cm) after 10-days of treatments. Hence this study shows that HgCl2 proves to be the most toxic heavy metal for seed germination and early seedling growth followed by ZnSO4, CuSO4, CoCl2 and NiCl2 while CdCl2 was emerged as the least inhibitory heavy metals among all tested metals in rice crop.
Abiotic stress, heavy metal, rice, seed germination, seedling
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143179053
IDR: 143179053
Текст научной статьи Evaluation of seed germination and early seedling growth under heavy metals stress conditions in coastal red rice (Oryza sativa L.) crop
Abiotic stress has emerged recently a big challenge in cultivation of food crops and is mainly known to negatively influence the plant metabolisms such as photosynthesis, enzyme activity, mineral nutrition and respiration (Maiti and Satya, 2014) leading to reduction in crop yields. Rice ( Oryza sativa L.) is the second most widely cultivated crop in the world (Sandhu et al ., 2017).
Moreover, red rice is known to provide lipid-soluble antioxidants, including ferulated phytosterols such as γ-oryzanol, tocopherols and tocotrienols along with complex nutrients that are essential for human health (Britz et al. , 2007). Unfortunately, the size of available land for rice cultivation is under declining state rapidly because of urbanization as well as industrial establishments (Kumar, 2017; Mostafiz and Wagiran, 2018).
In general, metals in terrestrial ecosystems are known as important for their influence on development and growth of plants (Lepp, 1981; Alloway, 1995; Hall and Williams, 2003). Like other organisms, plants are very sensitive to deficiency and excess of heavy metals (El Rasafi et al ., 2016). Unfortunately, studies reveal that soil ecosystems are known to be badly contaminated with heavy metals by human-induced activities (Naidu et al ., 1996; Younas and Shahzad, 1998) and once present in the soil, the heavy metals are known to be persistent (Alloway, 1995; Mahmood et al., 2007).
In most of the countries, a major source of heavy metals intake by humans is the rice grain produced through the paddy soils contaminated with heavy metals such as As, Al, Cu, Cr, Cd, Pb, Hg, Mn, Se and Zn (Arif et al ., 2019). Like other organisms, plants are very sensitive to either deficiency or excess of heavy metals (El Rasafi et al ., 2016). Hence, accumulation of toxic concentration of heavy metals in the agricultural soils has emerged as a threat for the cultivation of cereal crops or failure of crops (Munzuroglu and Geckil, 2002; Mahmood et al , 2007).
However, some of these elements such as Cu and Zn are essential for plant growth at low concentrations and they start to be toxic at higher levels (Wintz et al., 2002; El Rasafi et al., 2016). Copper is known as one of the most important and essential micronutrients for plant growth and is an integral component of numerous enzymes. Copper is proved as actively involved in lignification (Hall and Williams, 2003).
Similarly, zinc is a non-redox micronutrient element, which plays key structural and catalytic roles in many proteins and enzymes involved in energy metabolism (Sresty and Madhava Rao, 1999; Hall and Williams, 2003). Moreover, lead is neither an essential nor a beneficial element for plant growth (Alloway, 1995).
Thus, gradual accumulation of heavy metals in rice grains and their subsequent transfer to the food chain is a major constraint to agriculture and human health (Arif et al ., 2019). Under this situation, heavy metals tolerant crop cultivars are considered as a feasible and stable alternative to sustain the productivity of the crops.
Moreover, seed germination is a crucial phase in plant life that plays important roles in seedling establishment and subsequent growth of seedlings (Bewley, 1997). Moreover, various growth hormones play major roles during seed germination and early seedling growth (Cho et al ., 2012; Miransari and Smith, 2014; Liu et al ., 2018). Hence, evaluation of seed germination and early seedling growth under heavy metals stress conditions could be a meaningful approach to grow heavy metals stress tolerant red rice crop is required for coastal region as well.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seed Collection and Sterilization
Seeds of wild coastal red rice ( Oryza sativa L. cv Poongar) a local variety were collected from Krishi Vigyan Kendra (PKKVK), Puducherry (India). Healthy, uniform seeds of rice were selected and washed thoroughly with teepol-20 and further were surface sterilized with ethanol (70%) for a minute followed by HgCl 2 (0.1%) treatments for 7-8 minutes.
Furthermore, sterilized seeds were washed 3-4 times with distilled water and were soaked in the respective stress solutions for 3hrs. The soaked seeds were further placed in sterile Petri dishes (9.0cm diameter) lined with two sterile filter papers with 5ml of distilled water or the respective test solutions as designed for heavy metals stress experiments.
Stress Treatments
During present study, chloride solutions of heavy metals (Hg, Co, Ni and Cd) and sulfate solutions of heavy metals (Zn and Cu) were applied in various concentrations to study the responses of these heavy metals in terms of rate of seed germination under stress conditions and further impacts of heavy metals solutions during early seedling growth.
To begin with, chloride solutions of HgCl 2 (0.01%, 0.1% and 1.0%) and CoCl 2 , NiCl 2 and CdCl 2 in equivalent concentrations (1.0mg/L, 5.0mg/L, 10mg/L, 25mg/L and 50mg/L), were employed to induce stresses Furthermore, during initial experiments, (10mg/L, 25mg/L, 50mg/L and 100mg/L) solutions of ZnSO 4 and CuSO 4 were employed and these concentrations of ZnSO 4 and CuSO 4 solutions were proved to be highly toxic for rice seed germination (data not given). Later, sulfate solutions (0.5mg/L, 1.0mg/L, 2.5mg/L and 5.0mg/L) of Zn and Cu in equal concentrations were considered for the present study.
There were 15-20 seeds per petridish and three replicates in each treatment. Germination tests were conducted under dark condition at normal room temperature (25-300c). A seed was considered germinated when radicle was 2mm long. The germination percentage was determined counting the number of germinated seeds on the 5th and 10th day of the treatments.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical data were performed after first count (5th day after treatments) and final count (10th day after treatments). Moreover, germination percentage (GP) and germination rate (GR) was calculated by the following formulae (Ruan et al., 2002).
GP = Number of total germinated seeds/ Total number of seeds tested × 100
Number of Number of
Germinated seeds Germinated Seeds
GR= ––––––––––––––––– + –––––––––––––––– 5th Day of Count 10th Day of Count
RESULTS
Observations based on stress treatments for seed germination were recorded at the end of 5thday of the treatments as the partial or incomplete seed germination and 10th day of the treatments as the full and complete seed germination. Moreover, seedlings lengths as rootshoot length ratio were recorded at the end of 14th day of treatments.
Effect of Heavy Metals Stress on Seed Germination
Moreover, results reveal that germination and early seedlings growth of rice seeds were significantly influenced by stresses caused by types of heavy metals (Hg, Co, Ni, Cd, Zn and Cu) and concentration and durations of heavy metals treatments.
Effect of Mercury Stress
In general, HgCl 2 was found to show the consistent adverse effects on the seed germination with all the treated concentrations and even after 10-days of the HgCl 2 -treatments, seed germination was found to be completely lacking. In contrast, rice seeds were found to exhibit full germination and seedling growth after 10-days of treatments in control experiment ( FIG. 1A ).
Significantly, with very low concentration (0.01%) of HgCl 2 treatments, a seed could show the poor germination ( FIG. 1B ), however, poorly germinated seed was failed to grow further even after two weeks of treatments. Moreover, seeds that were treated with HgCl 2 concentrations (0.1% and 1.0%) were failed completely to show indication of germination ( FIG. 1C ).
After 10-days of treatments, the control experiment was found to exhibit the full seed germination (100±0.0%), while during stress treatments, the maximum percentage of rice seed germination was recorded as (5±0.0%) with very low concentration (0.01%) of HgCl 2 - solution treatments. Moreover, with further higher concentrations (0.1% and 1.0%) of HgCl 2 -solution treatments, seed germination was seen as completely inhibited and germination frequency was recorded as zero ( Table-1) .
Effect of Cobalt Stress
During cobalt stress experiments, seeds that were treated with lower concentrations (1.0mg/L and 5.0mg/L) of CoCl2 solutions were found to exhibit the similar response to control experiment and failed to show significant cobalt-stress inhibitions. However, further increase in concentration (10mg/L) of CoCl2 was proved to be slightly inhibitory for seed germination and after 10-days of treatments, treated seeds were germinated and grown into little suppressed seedlings (FIG. 1D) while 25mg/L of CoCl2 concentration was recorded as very strong and lethal concentration and hence seed germination and seedling growth both were observed as strongly suppressed state (FIG. E). Moreover, very high concentration of CoCl2 (50mg/L) solution was found to be strongly toxic and seed germination was completely lacking even after 10-days of treatments (FIG. 1F).
The rate of germination was observed to decrease with the increase in cobalt concentration in the treatment solution. In control experiment, the highest germination rate was recorded as (95% and 100%) after 5th day and 10th day of treatments respectively (Table-2). The rate of seed germination was not observed to be significantly inhibited with lower concentrations (1.0mg/L and 5.0mg/L) of CoCl 2 treatments and, therefore, it was recorded as (97±1.0% and 90±0.0%) respectively at the end of 10th day of treatments.
However, further increase in CoCl 2 concentrations (10mg/L and 25mg/L) shows significant inhibitions in frequency of seed germination and obtained as (60±0.0% and 40±0.0%) respectively at the end of 10th day of treatments. However, seeds that were treated with (50mg/L) of CoCl 2 , there was no symptoms of rice seed germination. Results thus indicate that CoCl 2 treatment at very high concentration (50mg/L) proves to be fully toxic for rice seed germination ( Table-2 ).
Effect of Nickel Stress
On treatments of seeds with NiCl 2 , in comparison to cobalt, nickel was proved to be relatively less inhibitory for seed germination and early seedling growth Moreover, seeds that were treated with lower concentrations of NiCl 2 (1.0mg/L and 5.0mg/L) solutions, seed germination was found like the control treatments and hence, these concentrations were failed to show suppression of seed germination significantly.
However, further higher concentrations of NiCl2 (10mg/L and 25mg/L) were proved to be little inhibitory for seed germination (FIG. 1G and H) respectively Moreover, with very high concentration (50mg/L) of NiCl2 solution treatments, seeds were not found to germinate whereas control experiment exhibited healthy seed germination (FIG. 1I).
The rate of germination was observed to decrease with the increase in heavy metal stressor Ni concentration in the treatment solution. In comparison to control experiment where the maximum germination rate was recorded as (100±0.0%), the rate of germination with lower concentrations (1.0mg/L and 5.0mg/L) of NiCl 2 was not found to be inhibitory and rate of germination was recorded as (97±0.0% and 92±1.0%) at the end of 10th day of treatments (Table- 3) .
However, further increase in concentrations of Ni (10mg/L and 25mg/L) show significant inhibitions in seed germination and therefore, at the end of 10th day of treatments, the rate of germination was recorded as (63±1.0% and 50±0.0%) respectively. Moreover, unlike complete toxicity of CoCl 2 response, even with very high concentration (50mg/L) of NiCl 2 solution, seed germination was recorded as (10±0.0%).
Effect of Cadmium Stress
CdCl 2 treatments were given to the rice seeds and in comparison, to cobalt and nickel, heavy metal-Cd was proved to be relatively less inhibitory for seed germination even at very high concentration (50mg/L) However, after 5-days of treatments, CdCl 2 treated seeds were found to exhibit the germination at all the concentrations of CdCl 2 and further complete seedlings development could be observed within 10th day of CdCl 2 treatments.
Moreover, with lower concentrations of CdCl 2 (1.0mg/L and 5.0mg/L) solutions, seed germination was seen like the control treatments ( FIG. 2A) and these concentrations were failed to inhibit seed germination significantly. Further, with higher concentrations of CdCl 2 (10mg/L and 25mg/L) were proved to be partially inhibitory for seed germination and exhibited growth of healthy seedlings ( FIG. 2B and C ). In contrast of Co and Ni, heavy metal-Cd even at very high concentration (50mg/L) was failed to inhibit seed germination completely ( FIG. 2D ).
The rate of germination was observed to decrease with the increase in heavy metal stressor cadmium concentrations in the treatment solutions. In control experiment, the highest germination rate was recorded as (95±0.0% and 100±0.0%) after 5th day and 10th day of treatments respectively (Table-4). Moreover, inhibition in the rate of seed germination was observed to be insignificant in seeds that were treated with lower concentrations (1.0mg/L and 5.0mg/L) of CdCl2 solutions and was recorded as (98±1.0% and 95±0.0%) respectively at the end of 10th day of treatment.
Furthermore, on increase in cadmium concentrations (10mg/L, 25mg/L and 50mg/L) shows little inhibition at the end of 5th day (63±0.0%, 42±2.0% and 17±1.0%) respectively. However, percentage of complete seed germination was highly affected due to continuous stress treatment and the rate of germination was recorded as (71±1.0%, 57±2.0% and 24±0.0%) at the end of 10th day (Table- 4).
Effect of Zinc Stress
During initial experiments in present study, higher concentrations of ZnSO 4 (10mg/L, 25mg/L, 50mg/L and 100mg/L-data not given) were proved to be lethal and toxic for rice seed germination and suppressed seed germination completely while in control experiment, seed germination was quite visible in high frequency (FIG. 2A) .
During further experiments, lower concentrations of ZnSO 4 (0.5mg/L, 1.0mg/L, 2.5mg/L and 5.0mg/L) were employed to evaluate the influence of Zn-stress during the rice seed germination. Significantly, at the end of 5th day of treatments, seed germination was found to be little suppressed at all the concentrations of Zn tested in comparison to the control. Moreover, it was completely lacking with the seeds that were treated with ZnSO 4 (5.0mg/L) ( FIG. 2G ).
After 10th day of ZnSO 4 treatments, seeds that were treated with lower concentrations of ZnSO 4 (0.5mg/L and 1.0mg/L) were found to exhibit full germination ( FIG. 2E and F ). However, on increasing the further Zn concentration (2.5mg/L) significantly inhibited the percentage of seed germination and growth of the seedlings. However, strong inhibitory effect of Zn on seed germination was apparent on higher concentration (5.0mg/L).
The rate of germination was found to decrease with the increase in heavy metal stress caused by ZnSO4 treatments. In control experiment, the highest germination rate was recorded as (95±0.0% and 100±0.0%) after 5th day and 10th day of treatments respectively. However, in ZnSO4 treated experiments, all the concentrations were proved to be effective for germination inhibition till the 5th day of treatments.
Significantly, after 10th day of ZnSO 4 (0.5mg/L and 1.0mg/L) treatments, development of complete seedlings could be recorded as (55±1.0% and 38±2.0%) respectively ( FIG. 2E and F). Furthermore, even further high concentration of ZnSO 4 (2.5mg/L) was failed to suppress rice seed germination significantly and thus, frequency was recorded as (29±0.0%) (Table- 5).
Effect of Copper Stress
Like ZnSO 4 , CuSO 4 treatments were also initially given to the rice seeds and it was also proved completely inhibitory of rice seed germination when seeds were treated with high concentrations of CuSO 4 (10mg/L, 25mg/L, 50mg/L and 100mg/L-data not given).
During further studies, lower concentration of CuSO 4 (0.5mg/L, 1.0mg/L and 2.5mg/L) were employed during the present study and like zinc stress response, seed germination was found to be initiated at all the concentrations (0.5mg/L, 1.0mg/L and 2.5mg/L) at the end of 5th day of treatments, in comparison to the control ( FIG. 2A ). After 5-days of treatments, CuSO 4 treated seeds were found to exhibit the germination and further complete seedlings development ( FIG. 2H and I ) could be observed within 10th day of CuSO 4 treatments.
The rate of germination was observed to decrease with the increase in heavy metal stressor Cu concentration in the treatment solution. In CuSO 4 treated experiments, all the concentrations were proved to be little suppressive for germination and after 10th day of CuSO 4 (0.5mg/L, 1.0mg/L and 2.5mg/L) treatments, complete seedlings developments could be recorded as (75±1.0%, 60±0.0% and 50±0.0%) respectively ( FIG. 2H and I ). Moreover, in comparison to ZnSO 4 where 5.0mg/L was found to be completely toxic for seed germination, (5.0mg/L) of CuSO 4 concentration was proved to be little effective to cause toxicity for seed germination and after 10th day of treatment, seed germination frequency (15±0.0%) was recorded (Table-
Effects of Heavy Metals Stress on Early Seedling Growth
Effect of Cobalt Stress
Length of rice seedlings treated with various concentrations of CoCl 2 was significantly affected by continuous exposure of seeds with cobalt chloride solution. For the survival tendency and growth of the seedlings, the maximum length of the seedlings was observed in the control seedling ( FIG. 3A ) and rootshoot length ratio was recorded as (3.97±0.71cm and 4.52±0.45cm) than the CoCl 2 -stress (5.0mg/L, 10mg/L and 25mg/L) treated seedlings at ( FIG. 3B, C and D ) respectively.
Moreover, seedling length was in general found to gradually decrease with increase in concentrations of CoCl 2 solutions . Significantly, the seedlings with rootshoot lengths ratio (0.08±0.05cm and 1.39±0.45cm) were appeared to be strongly inhibited with high concentration (25mg/L) of CoCl 2 (FIG. 3D ) than the control seedlings ( FIG. 3A ). Furthermore, with very high concentration (50mg/L) of CoCl 2 solution, rice seeds were failed to germinate completely (Table- 2) .
Effect of Nickel Stress
Like CoCl 2 stress response during early seedling growth, rice seedlings which were treated with various concentrations of NiCl 2 were significantly affected by continuous treatments of NiCl 2 solution. Maximum length of the seedlings as root-shoot length ratio (3.97±0.71cm and 4.52±0.45cm) was observed in the control seedling ( FIG. 3A ) than the Ni-stress treated seedlings.
Moreover, seedling growth was in general found to decrease with increase in NiCl 2 concentrations in the solutions. The root and shoot lengths (0.05±0.05cm and 1.63±0.97cm) were appeared to be significantly inhibited in seedlings that were growing with increased higher concentrations (10mg/L and 25mg/L) of NiCl 2 solutions (FIG. 3E and F). However, with very high concentration (50mg/L) of NiCl 2 solution, partially germinated seeds were developed poor shoot without root development (0.5±0.0cm) (FIG. 3G, Table- 3).
Effect of Cadmium Stress
Among chloride solutions of Hg, Co, Ni and Cd,
CdCl 2 was found to cause minimum stress inhibitions during rice seed germination and early seedling growth However, seedling growth was in general found to decrease with the increase in concentrations (10mg/L, 25mg/L and 50mg/L of CdCl 2 ( FIG. 3 H, I and J ) solutions respectively . The root and shoot lengths were appeared to be relatively inhibited (0.91±0.39cm and 2.12±0.55cm) in seedlings (FIG. 3I) that were growing with high concentration (25mg/L) of CdCl 2 solution than the control (3.97±0.71cm and 4.52±0.45cm) seedlings .
Significantly, unlike CoCl 2 and NiCl 2 , even very high concentration (50mg/L) of CdCl 2 solution failed to suppress complete germination and therefore, poor root and shoot development (0.28±0.09cm and 0.96±0.03cm) could be observed after 10-days of treatment (FIG. 3J, Table- 4) .
Effect of Zinc Stress
Rice seedlings that were growing with various concentration of ZnSO 4 were found to be significantly affected by continuous stress of heavy metal Zn Moreover, seedling growth was in general found to decrease with the increase in concentrations of ZnSO 4 in the solutions. The maximum length of seedlings ( FIG. 3K ) was obtained in seeds that were growing with the lowest concentration of ZnSO 4 (0.5mg/L), followed by the seedlings (0.98±0.31cm/2.99±0.56cm) that were growing with (1.0mg/L) of ZnSO 4 solution ( FIG. 3L) .
Moreover, the shoots and roots length appeared to be strongly inhibited in further higher concentration (2.5mg/L) of ZnSO 4 treated seedlings and root-shoot lengths were recorded as (0.04±0.02cm/1.53±0.24cm) (FIG. 3M). However, very high concentration (5.0mg/L) of Zn was proved to be strongly lethal and toxic even for seed germination (Table- 5).
Effect of Copper Stress
Unlike ZnSO4, during this study, CuSO4 was proved to be relatively less inhibitory for seedling growth Therefore, lengths of rice seedlings which were treated with various concentration of CuSO4 were significantly affected by continuous stress of heavy metal Cu. The maximum length of the seedlings was observed in the control seedling (4.52±0.45cm and 3.97±0.71cm) than the Cu-stress treated seedlings. The shoot and root lengths were appeared to be relatively inhibited in seedlings (0.62±0.36cm /0.79±0.28cm) that were treated with high concentration of CuSO4 (2.5mg/L) than the control seedlings (FIG. 3O).
However, seedlings that were growing with very low concentration of CuSO4 (0.5mg/L) solution appeared to be like the control seedling growth (2.63±0.49cm/2.51±0.53cm) indicated the minimum Cu- stress response (FIG. 3N) while further high concentration (1.0mg/L) of CuSO4 was seen as effective to inhibit the seedlings growth under Cu-stress (1.55±0.46cm/2.21±0.39cm). Moreover, very high concentration (5.0mg/L) of CuSO4 solution, was seen to suppress the root formation completely (0.0cm/0.05±0.02cm) and shows inhibited shoot development (FIG.3P, Table- 6).
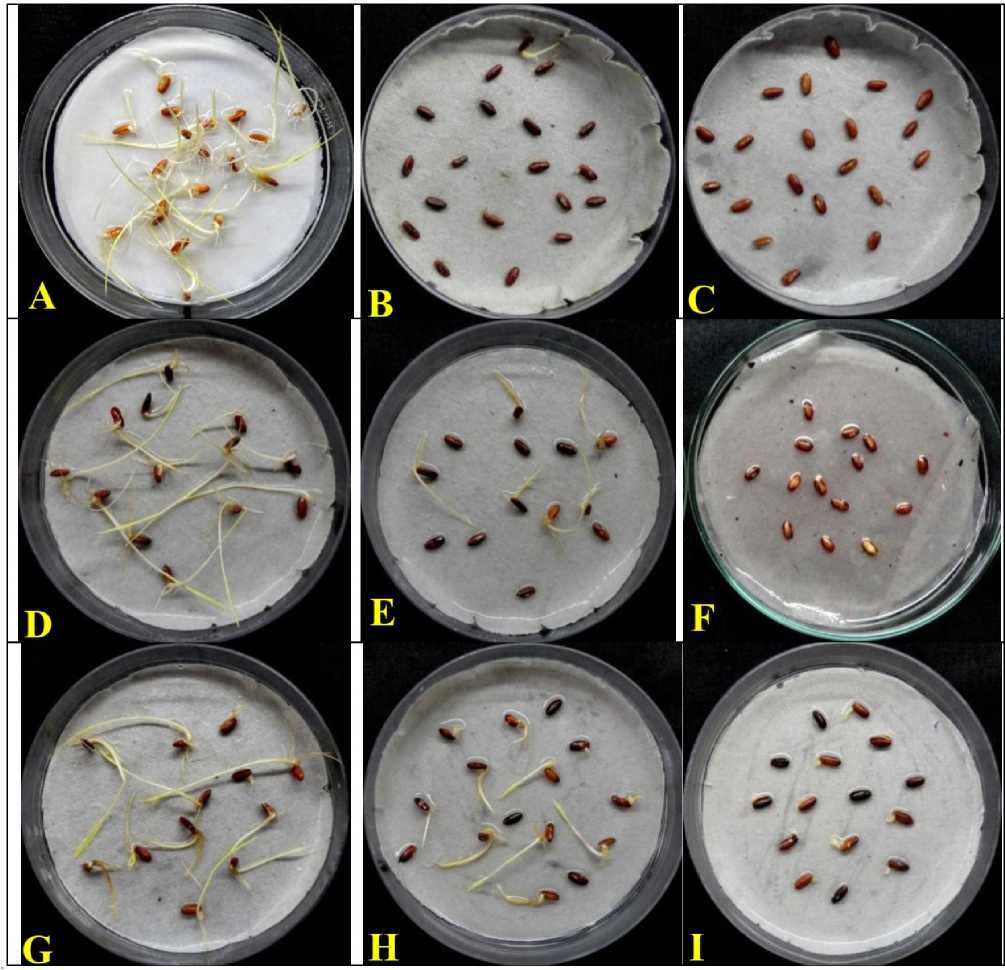
Figure 1. Oryza sativa L., response of heavy metals stress on seed germination (A) Control (B) HgCl 2 - 0.01% (C) HgCl 2 -0.1% (D) CoCl 2 - 10mg/L (E) CoCl 2 - 25mg/L (F) CoCl 2 - 50mg/L (G) NiCl 2 - 10mg/L (H) NiCl 2 - 25mg/L (I) NiCl 2 -50mg/L after 10-days of treatments.
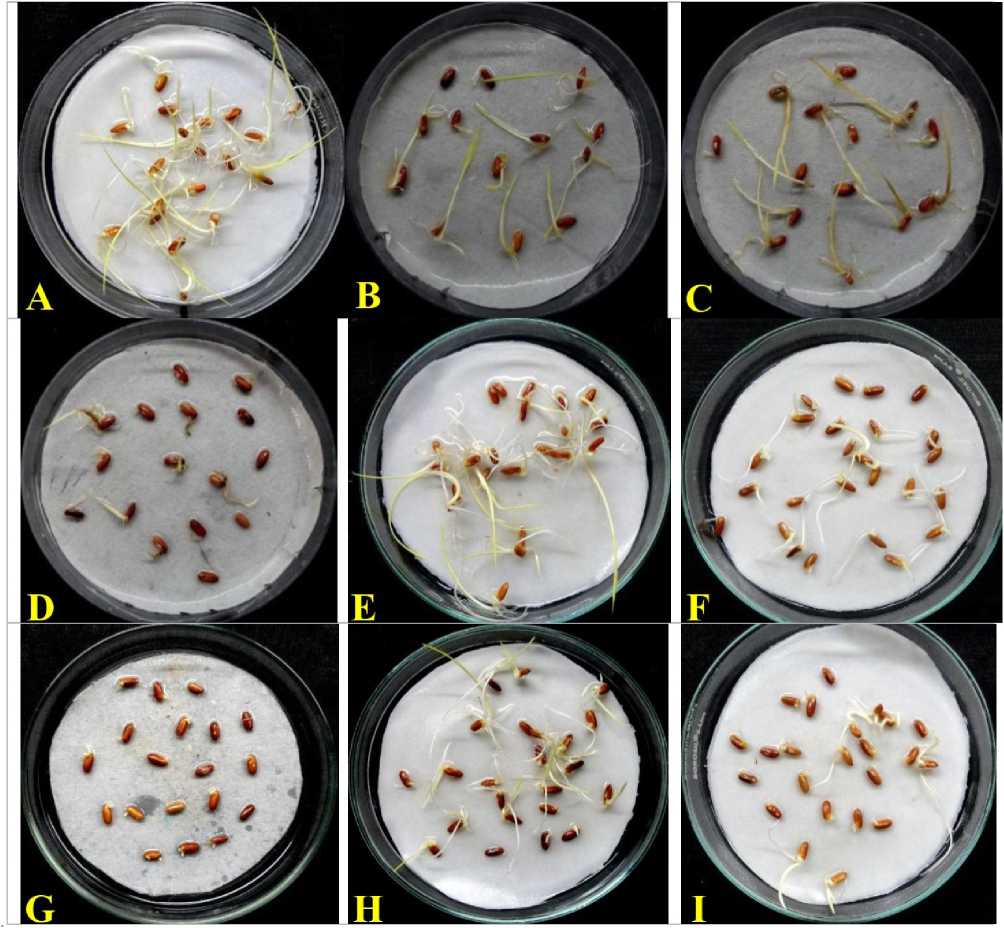
Figure 2. Oryza sativa L., response of heavy metals stress on seed germination (A) Control (B) CdCl 2 -10mg/L (C) CdCl 2 25mg/L (D) CdCl 2 - 50mg/L (E) ZnSO 4 -0.5mg/L (F) ZnSO 4 -1.0mg/L (G) ZnSO 4 -5.0mg/L (H) CuSO 4 -1.0mg/L (I) CuSO 4 - 2.5mg/ after 10-days of treatments.
Table 1. Oryza sativa L., effects of HgCl 2 on seed germination and early seedling growth in red rice crop
|
S. No. |
Concentration of HgCl 2 (%) |
5thDay |
10th Day |
||
|
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
Root length (cm) |
Shoot length (cm) |
||
|
1. |
Control |
95±0.0 |
100±0.0 |
3.97±0.71 |
4.52±0.45 |
|
2. |
0.01 |
0 |
5±0.0 |
0 |
0 |
|
3. |
0.1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
4. |
1.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
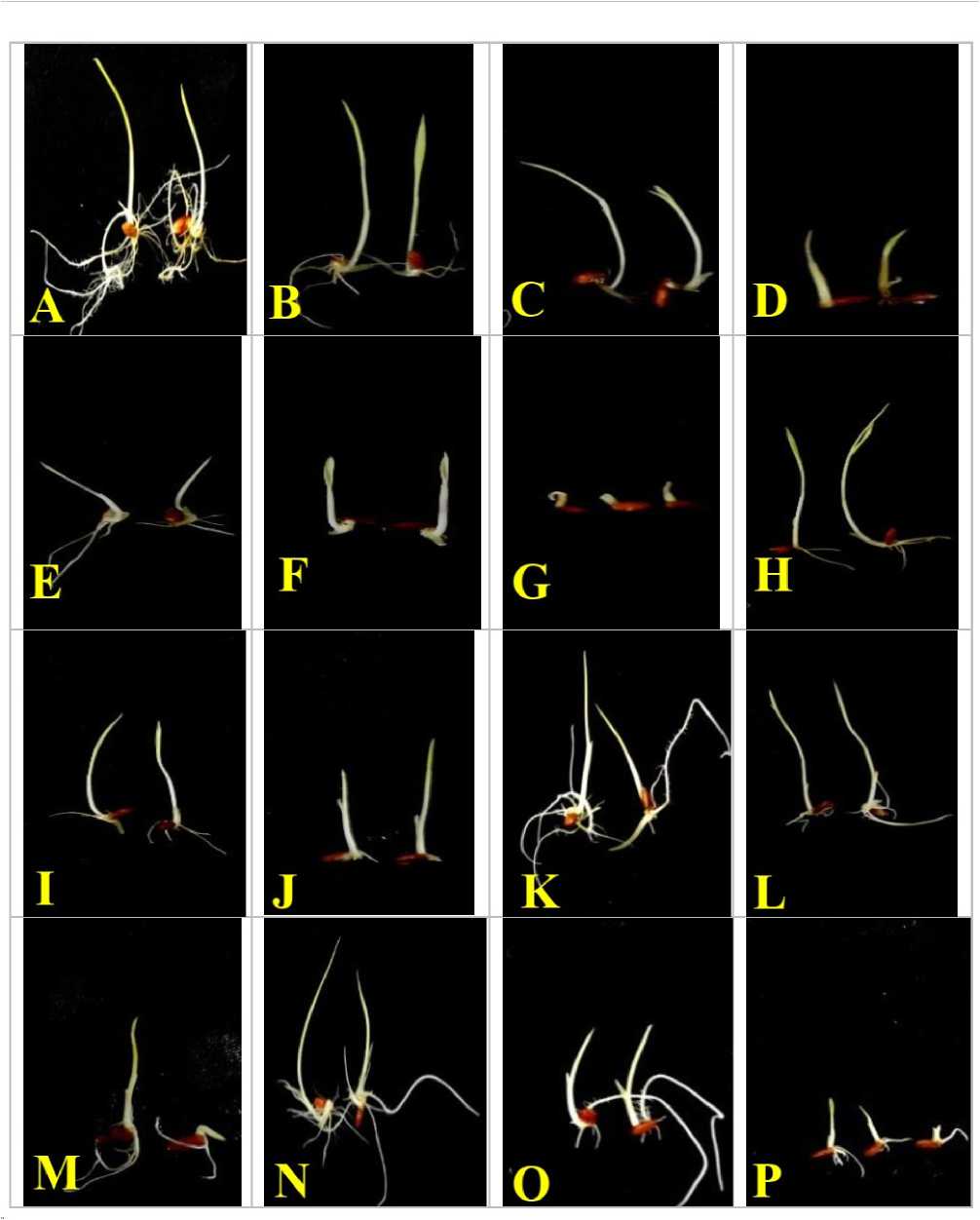
Figure 3. Oryza sativa L., response of heavy metals stress during early seedling growth (A) Control (B) 5.0mg/L of CoCl 2 (C) 10mg/L of CoCl 2 (D) 25mg/L of CoCl 2 (E) 10mg/L of NiCl 2 (F) 25mg/L of NiCl 2 (G) 50mg/L of NiCl 2 (H) 10mg/L of CdCl 2 (I) 25mg/L of CdCl 2 (J) 50mg/L of CdCl 2 (K) 0.5mg/L of ZnSO 4 (L) 1.0mg/L of ZnSO 4 (M) 2.5mg/L of ZnSO 4 (N) 0.5mg/L of CuSO 4 (O) 2.5mg/L of CuSO 4 (P) 5.0mg/L of CuSO 4 after 14-days of treatments.
Table 2. Oryza sativa L., effects of CoCl 2 on seed germination and early seedling growth in red rice crop
|
S. No. |
Concentration of CoCl 2 (mg/L) |
5th Day |
10th Day |
||
|
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
Root length (cm) |
Shoot length (cm) |
||
|
1. |
Control |
95±0.0 |
100±0.0 |
3.97±0.71 |
4.52±0.45 |
|
2. |
1.0 |
92±1.0 |
95±1.0 |
2.02±0.21 |
3.76±0.32 |
|
3. |
5.0 |
87±0.0 |
90±1.0 |
1.42±0.28 |
3.31±0.48 |
|
4. |
10 |
45±1.0 |
60±0.0 |
1.02±0.26 |
2.75±0.42 |
|
5. |
25 |
30±2.0 |
40±0.0 |
0.08±0.05 |
1.39±0.45 |
|
6. |
50 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Table 3. Oryza sativa L., effects of NiCl 2 on seed germination and early seedling growth in red rice crop
|
S. No. |
Concentration of NiCl 2 (mg/L) |
5th Day |
10th Day |
||
|
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
Root length (cm) |
Shoot length (cm) |
||
|
1. |
Control |
95±0.0 |
100±0.0 |
3.97±0.71 |
4.52±0.45 |
|
2. |
1.0 |
90±1.0 |
97±0.0 |
1.21±0.41 |
1.94±1.59 |
|
3. |
5.0 |
88±1.0 |
92±1.0 |
0.62±0.36 |
1.83±0.64 |
|
4. |
10 |
55±1.0 |
63±1.0 |
0.28±0.12 |
1.72±1.43 |
|
5. |
25 |
35±1.0 |
50±0.0 |
0.05±0.05 |
1.63±0.97 |
|
6. |
50 |
5±0.0 |
12±0.0 |
0 |
0.5±0.0 |
Table 4. Oryza sativa L., effects of CdCl 2 on seed germination and early seedling growth in red rice crop
|
S. No. |
Concentration of CdCl 2 (mg/L) |
5th Day |
10th Day |
||
|
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
Root length (cm) |
Shoot length (cm) |
||
|
1. |
Control |
95±0.0 |
100±0.0 |
3.97±0.71 |
4.52±0.45 |
|
2. |
1.0 |
90±2.0 |
98±1.0 |
1.65±0.25 |
3.52±0.31 |
|
3. |
5.0 |
90±2.0 |
95±0.0 |
1.23±0.31 |
3.17±0.18 |
|
4. |
10 |
63±0.0 |
71±1.0 |
0.97±0.24 |
2.67±0.35 |
|
5. |
25 |
42±2.0 |
57±2.0 |
0.91±0.39 |
2.12±0.55 |
|
6. |
50 |
17±1.0 |
24±0.0 |
0.28±0.09 |
0.96±0.03 |
Table 5. Oryza sativa L., effects of ZnSO 4 on seed germination and early seedling growth in red rice crop
|
S. No. |
Concentration of ZnSO 4 (mg/L) |
5th Day |
10th Day |
||
|
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
Root length (cm) |
Shoot length (cm) |
||
|
1. |
Control |
95±0.0 |
100±0.0 |
3.97±0.71 |
4.52±0.45 |
|
2. |
0.5 |
50±2.0 |
55±1.0 |
1.35±0.34 |
2.8±0.38 |
|
3. |
1.0 |
30±2.0 |
38±2.0 |
0.98±0.31 |
2.99±0.56 |
|
4. |
2.5 |
19±1.0 |
29±0.0 |
0.04±0.02 |
1.53±0.24 |
|
5. |
5.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Table 6. Oryza sativa L., effects of CuSO 4 on seed germination and early seedling growth in red rice crop
|
S. No. |
Concentration of CuSO 4 (mg/L) |
5thDay |
10th Day |
||
|
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
% Seed germination (Mean ± S.E.) |
Root length (cm) |
Shoot length (cm) |
||
|
1. |
Control |
95±0.0 |
100±0.0 |
3.97±0.71 |
4.52±0.45 |
|
2. |
0.5 |
65±1.0 |
75±1.0 |
2.63±0.49 |
2.51±0.53 |
|
3. |
1.0 |
60±1.0 |
60±0.0 |
1.55±0.46 |
2.21±0.39 |
|
4. |
2.5 |
45±0.0 |
50±1.0 |
0.62±0.36 |
0.79±0.28 |
|
5. |
5.0 |
10±0.0 |
15±0.0 |
0 |
0.05±0.02 |
DISCUSSION
Rice is one of the most important world food crops, serving as the staple food for over one-third of the world's population (Khush, 1997). It is one of the most widely grown crops in coastal areas frequently inundated with saline sea water during high tidal period (Mori and Kinoshita, 1987). With uncontrolled increase in population, there is urgent need to increase crop productivity of staple crops, but the productivity is greatly affected by various abiotic stress factors such as drought, salinity and accumulation of heavy metals in the soil (Maiti and Satya, 2014).
Heavy metals have been shown to affect different processes of plant functions and clearly have a negative impact on seed germination. They can engender damage to the root system of plants (Singh and Thakur, 2014), by causing an oxidative stress by producing free radicals (Shah et al ., 2010), or by replacing nutrient and essential metals (Henry, 2000).
In general, the influence of trace elements on plants depends mainly on the heavy metal kind, the concentration applied and plant species (El Rasafi et al ., 2016). Therefore, present investigation was aimed to understand the response of heavy metals stress during seed germination and early seedling growth in coastal red rice cereal crop.
Effect of Chloride Solution of Heavy Metals
Several studies have reported that plant seedlings respond quickly to a higher concentration of metals in terrestrial ecosystems by changing in their growth rates and root branching patterns compared to shoot growth (Stiborava et al ., 1986; Dinev, 1988; Breckle, 1991; Hasnian et al ., 1993).
Nickel (Ni) is reported to be toxic to most plant species affecting amylase, protease and ribonuclease enzyme activity thus retarding seed germination and growth of many crops (Ahmad and Ashraf, 2011). Ni stress has been reported to affect photosynthetic pigments, lessen yield and cause accumulation of Na+, K+ and Ca2+ in mung bean (Ahmad et al ., 2007; Sethy and Ghosh, 2014).
Moreover, cadmium is very harmful to cereals and other crops (An, 2004) and it causes many health problems in humans. For plants, cadmium (Cd) is a nonessential and toxic heavy metal element which can be actively absorbed. Elevated Cd concentration not only has adverse effects on yield and quality of crop, but also harms human being through the food chain. The capacity of Cd accumulation and tolerance varies from plant species (Grant et al ., 1998; Belimov et al ., 2003).
Cadmium (Cd) has been shown to cause delay in germination, induce membrane damage, impair food reserve mobilization by increased cotyledon/embryo ratios of total soluble sugars, glucose, fructose and amino acids (Rahoui et al., 2010) mineral leakage leading to nutrient loss (Sfaxi-Bousbih et al., 2010) accumulation in seeds and over-accumulation of lipid peroxidation products (Ahsan et al., 2007, Smiri et al., 2011) in seeds. Cd toxicity leading to up-regulated protein synthesis of the defense and detoxification, antioxidant and germination processes is reported (Ahsan et al., 2007).
In general, the tolerance to heavy metals for plants involves exclusion and accumulation mechanisms (Hall, 2002). Cobalt (Co) has been reported to induce DNA methylation in Vicia faba seeds (Rancelis et al ., 2012; Sethy and Ghosh 2014).
Cd tolerance is related to the accumulation of Cd content in plants. In general, a high level of tolerance to Cd can rely on the strategy to avoid the build-up of excess metal levels in plants and thus to prevent the onset of toxicity symptoms (Jun-Yu et al ., 2008).
During this study, a stress effect caused by Hg was very much pronounced than Co, Ni and Cd effects. At all the tested concentrations, HgCl 2 proved to be toxic and seed germination was totally inhibited even at very low concentration (0.1%). Further, with 25mg/L of CoCl 2 solutions, seedlings were found to be highly suppressed (0.08±0.05cm/1.39±0.45cm) in comparison to control seedlings (3.97±0.71cm/4.52±0.45cm). Significantly, cobalt was found to show complete toxicity at (50mg/L) and seed germination was found to be completely arrested.
However, with the same concentration of nickel (50mg/L) was found to suppress root formation in germinated seeds (0.0cm/0.5±0.0cm). Moreover, even high concentration of cadmium (50mg/L) was failed to show toxicity for complete seedling developments and root-shoot ratio (0.28±0.09cm/0.96±0.03cm) in comparison to control seedlings (3.97±0.71cm/4.52±0.45cm).
Seed germination under Cd stress could be decreased owing to accelerated breakdown of reserved food material in seed embryo. Present studies are in contrast with the previous results (Raziuddin et al., 2011; Aydinalp and Marinova, 2009; Jun-Yu et al., 2008; Titov et al., 1996) in which it was reported that Cd stress decreased seed germination, germination index and vigour index of different crops (Ahmad et al., 2012).
Present study reveals that red rice cultivar could be little tolerant for Cd because high dose of CdCl 2 (50mg/L) was not found to be significant inhibitor and seed germination and seedling growth was apparent Moreover, previous studies reveal that significant differences in seedling growth have been found among different Cd tolerance rice genotypes (Shao et al ., 2004; Liu, 2005). Moreover, in response to the heavy metal stress, plants can excrete some complex which can chelate the metal ions and reduce the content of available cadmium for detoxification (Jun-Yu et al ., 2008).
Effect of Sulfate Solutions of Heavy Metals
The most reported heavy metals in waste amended agricultural soils are Cu, Pb and Zn (Nriagu and Pacyna, 1988; Younas and Shahzad, 1998; Jamal et al ., 2002; Mahmood et al ., 2007). Copper is one of the most important micronutrients, essential for plant growth (Alloway, 1995, Hall and Williams, 2003). It is an integral component of numerous enzymes and is actively involved in lignification (Hall and Williams, 2003).
Copper (Cu) has been reported to be toxic to sunflower seedlings inducing oxidative stress via generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and by decreased catalase (CAT) activity via oxidation of protein structure (Pena et al ., 2011). Cu stress leads to reduced germination rate (Pena et al ., 2011; Sfaxi-Bousbih et al ., 2010; Singh et al ., 2007) and induces biomass mobilization by release of glucose and fructose thereby inhibiting the breakdown of starch and sucrose in reserve tissue by inhibition in the activities of alpha-amylase and invertase isoenzymes (Pena et al ., 2011; Sethy and Ghosh 2014).
Zinc, on the other hand, is a non-redox micronutrient element, which has key structural and catalytic roles in many proteins and enzymes involved in energy metabolism (Sresty and Rao, 1999; Hall and Williams, 2003; Mahmood et al ., 2007).
Previous studies reflect that the stunted and poorly developed root system (fibrous) at higher Cu, Pb and Zn concentrations are likely related to partial disorder of metabolic processes of the seedlings (Pahlsson, 1989; Obroucheva et al., 1998; Dinev, 1988; Breckle, 1991) The toxic effects of Cu often affected mitotic activity and cell division of roots with a subsequent increase in the root number of seedlings (Hall and Williams, 2003).
Additionally, a lack of consistent adverse effects exerted by Pb and Zn on seed germination is most probably related to interspecies differences in seed coat structures for regulating metal absorption. It is reported that plant seeds have inherent capability for selective absorption of metals in nature (Stefanov et al ., 1995).
During present study, stress caused by Zn was proved to be more lethal than Cu. At 2.5mg/L of Zn, frequency of seed germination was 29±0.0% whereas Cu at the same concentration proved to be less inhibitory and frequency of germination was recorded as 50±1.0%. For seedling growth also, in comparison to control seedling length as root-shoot ratio (3.97±0.71cm/4.52±0.45cm), ZnSO 4 (5.0mg/L) solution was recorded as completely toxic and inhibited complete seed germination and seedling growth (0.0cm/0.0cm) whereas on same concentration of CuSO 4 treatments (5.0mg/L), seedlings lengths were recorded as (0.0cm/0.05±0.02cm) and therefore Cu was proved to be toxic for root formation in germinated rice seeds.
Like present results, another study reveals that consistent change in the barley and wheat root: shoot ratio in response to metals especially Cu and Zn is most probably related to greater inhibition of roots by metal toxicity than shoots. Metal induced changes in the structure and morphology of the roots such as absence of root hairs, stunted and fibrous root growth and thickening or browning of roots, may be responsible to cause a decreased root: shoot ratio of the seedlings (Mehmood et al ., 2007).
Moreover, the adverse effects of heavy metals especially Cu cause structural and morphological changes of roots as well as inhibition of root hair growth of seedlings (Pahlsson, 1989; Fernandez and Henriques, 1991). Furthermore, adverse effects of Cu on roots are related to severe reduction in the elongation growth of the longest root as well as root plasma membrane permeability of the seedlings (Wainwright and Woolhouse, 1977, Nriagu and Pacyna, 1988; McBride, 2001).
CONCLUSIONS
Among heavy metals tested during present study, Hg stress response was exhibited as the most toxic heavy metals for the rice seed germination and for early seedling growth than zinc followed by copper. However, the inhibitory effect of zinc on seed germination was more pronounced than copper stress inhibition. Among cobalt, nickel and cadmium heavy metals, cobalt was proved to be the most inhibitory metal whereas cadmium was found to be least inhibitory for seed germination and early seedling growth in coastal red rice crop.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Список литературы Evaluation of seed germination and early seedling growth under heavy metals stress conditions in coastal red rice (Oryza sativa L.) crop
- Ahmad, I., Akhtar, M.J., Zahir, Z.A., and Jamil, A. (2012). Effect Of Cadmium on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Four Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Cultivars. Pak. J. Bot., 44(5), 15691574.
- Ahmad, M.S., Hussain, M., Saddiq, R., Alvi, A.K., (2007). Mungbean: A nickel indicator, accumulator or excluder? Bull Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 78, 319 24.
- Ahmad, M.S. and Ashraf, M. (2011). Essential roles and hazardous effects of nickel in plants. Rev Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 214, 125 67.
- Ahsan, N., Lee, S.H., Lee, D.G., Lee, H., Lee, S.W., Bahk, J.D. et al. (2007). Physiological and protein profiles alternation of germinating rice seedlings exposed to acute cadmium toxicity. C R Biol., 330, 735 46.
- Alloway, B.J. (1995). Heavy Metals in Soils. Blackie
- Academic and Professional, Glasgow.
- An, Y.J. (2004). Soil ecotoxicity assessment using cadmium sensitive plants. Environ. Pollut., 127, 2126.
- Arif, N., Sharma, N.C., Yadav, V., Ramawat, N., Dubey, N.K., Tripathi, D.K., Chauhan, D.K., and Sahi, S. (2019). Understanding Heavy Metal Stress in a Rice Crop: Toxicity, Tolerance Mechanisms, and Amelioration Strategies. J. Plant Biol., 62, 239-253.
- Aydinalp, C. and Marinova, S. (2009). The effects of heavy metals on seed germination and plant growth on alfalfa plant (Medicago sativa). Bulgarian J. Agri. Sci., 15, 347-350.
- Belimov, A.A., Safronova, V.l., Tsyganov, V.E., Borisov, A.Y., Kozhemyakov, A.P., Stepanok, V. V., Martenson, A. M., Gianinazzi-Pearson, V., and Tikhonovich, I.A. (2003). Genetic variability in tolerance to cadmium and accumulation of heavy metals in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Euphytica., 131, 25-35.
- Bewley, J. D. (1997). Seed germination and dormancy. Plant Cell, 9, 1055-1066. doi: 10.1105/tpc.9.7.1055.
- Breckle, S.W. (1991). Growth under Stress: Heavy Metal. In: Plant Roots: The Hidden Half. (Eds.: Waisel, Y., Eshel, A., and Kafkafi, U.), Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 351-373.
- Britz, S.J., Prasad, P.V.V., Moreau, R.A., Allen, L.H., Kremer, D.F., and Boote, K.J. (2007). Influence of growth temperature on the amounts of tocopherols, tocotrienols, and y-oryzanol in brown rice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55, 7559-7565.
- Cho, J. N., Ryu, J. Y., Jeong, Y. M., Park, J., Song, J. J., Amasino, R. M., et al. (2012). Control of seed germination by light-induced histone arginine demethylation activity. Dev. Cell, 22, 736-748.
- Dinev, N. (1988). Effects of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd) on the growth of oat plants. Soil Sci. Agrochem. Ecol., 33, 5-9.
- El Rasafi, T., Nouri, M., Bouda, S., and Haddioui, A. (2016). The Effect of Cd, Zn and Fe on Seed Germination and Early Seedling Growth of Wheat and Bean. Ekologia (Bratislava), 35 (3), 213-223.
- excess copper in plants. Botan. Rev., 57, 246-273.
- Fernandez, J.C. and Henriques, F.S. (1991). Biochemical, physiological, and structural effects of
- Toxic effects of heavy metals on early growth and tolerance of cereal crops. Pak. J. Bot., 39(2), 451462, 2007.
- Maiti, R.K. and Satya, P. (2014). Research advances in
- iНе можете найти то, что вам нужно? Попробуйте сервис подбора литературы.
- Grant, C.A., Buckley, W.T., and Bailey, L.D., (1998).
- Cadmium accumulation in crops. Can J Plant Sci, 78, 1-17.
- Hall, J.L. (2002). Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot., 53, 1-11.
- transporters in plants. J. Expt. Bot., 54, 2601- 2613.
- Hasnian, S., Yasmin, S., and Yasmin, A. (1993). The effect of lead resistant Pseudomonads on the growth of Triticum aestivum seedlings under lead stress. Environ. Pollut., 81, 179-184.
- of lead and mercury. NNEMS Report (pp. 3-9). Washington, D.C. Jamal, A., Ayub, N., Usman, M., and Khan, A.G. (2002). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance Zn and Ni uptake from contaminated soil by soybean and lentil. Int. J. Phytorem., 4, 205-221. Jun-Yu, J., Yan-Fang, R., Cheng, Z., De-An, J. (2008). Effects of Cadmium Stress on Seed Germination, Seedling Growth and Seed Amylase Activities in Rice (Oryza sativa). Rice Science, 15(4), 319-325.
- Khush, G.S. (1997). Origin, dispersal, cultivation and variation of rice. Plant Mol. Biol., 35, 25-34.
- The needs of healthy life. J. Phytochem. Biochem.,
- Vol. I and II, Applied Science, London.
- Liu,
- major cereal crops for adaptation to abiotic stresses. GM Crops & Food, 5(4), 259—279.
- McBride, M.B. (2001). Cupric ion activity in peat soil as a toxicity indicator for maize. J. Environ. Qual., 30, 78-84.
- Miransari, M. and Smith, D. L. (2014). Plant hormones and seed germination. Environ. Exp. Bot., 99, 110121.
- Mori, I.K. and Kinoshita, T. (1987). Salt tolerance of rice callus clones. Rice Genet. Newsl., 4, 112-113.
- Mostafiz, S.B. and Wagiran, A. (2018). Efficient Callus Induction and Regeneration in Selected Indica Rice. Agronomy, 8, 77.
- Munzuroglu, O. and Geckil, H. (2002). Effects of metals on seed germination, root elongation, and coleoptiles and hypocotyls growth in Triticum aestivum and Cucumis sativus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 43, 203-213.
- Naidu, R., Kookuna, R.S., Oliver, D.P., Rogers, S., and McLaughlin, M.J. (1996). Contaminants and the soil environment in the Australasia-Pacific Region, Dordrecht Kluwer Acad. Publ.
- Nriagu, J.O. and Pacyna, J.M. (1988). Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water, and soil by trace-metals. Nature, 333, 134139.
- Obroucheva, N.V., Bystrova, V.B., Ivanov, O.V., Antipova, M.S., and Seregin, I.V. (1998). Root growth responses to lead in young maize seedlings. Plant Soil, 200, 55-61.
- Mahmood, T., Islam, K.R. and Muhammad, S. (2007).
- Sunflower cotyledons cope with copper stress by inducing catalase subunits less sensitive to oxidation. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol., 25, 125 9. Rahoui, S., Chaoui, A., El Ferjani, E. J. (2010).
- Hall, J.L. and Williams, L.E. (2003). Transition metal
- Henry, J.R. (2000). In an overview of phytoremediation
- Kumar, S. (2017). Phytochemistry and functional food:
- 1, 2.
- Lepp, N.W. (1981). Effects of Heavy Metals on Plants.
- L. (2005). Effects of Cd stress on biomass accumulation and active oxygen metabolism of rice seedlings and their genotype difference. Acta Agric Zhejiang,17(3), 147-150. Liu, L., Xia, W., Li, H., Zeng, H., Wei, B., Han, S., and
- Pahlsson, A.B. (1989). Toxicity of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Cd, Pb) to Vascular Plants. Water Air Soil Pollut., 47, 287-319.
- Pena, L.B., Azpilicueta, C.E., and Gallego, S.M. (2011).
- Yin, C. (2018). Salinity Inhibits Rice Seed Germination by Reducing a-Amylase Activity via Decreased Bioactive Gibberelline Content, Frontiers in Plant Science, Volume 9, 275.
- Membrane damage and solute leakage from germinating pea seed under cadmium stress. Hazard Mater. 178, 1128 31.
- different rice genotypes. Chinese J Rice Sci, 18(3), 239-244.
- Rancelis, V., Cesniene, T., Kleizaite, V., Zvingila, D.,
- and Balciuniene, L. (2012). Influence of cobalt uptake by Vicia faba seeds on chlorophyll morphosis induction, SOD polymorphism, and DNA methylation. Environ Toxicol., 27, 32 41.
- Raziuddin, F., Hassan, G., Akmal, M., Shah, S.S., Mohammad, F., Shafi, M., Bakht, J., and Zhou, W. (2011). Effects of cadmium and salinity on growth and photosynthesis parameters of brassica species. Pak. J. Bot., 43(1), 333-340.
- Ruan, S., Xue, Q., and Thlkowska, K. (2002). Effect of seed priming on germination and health of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds. Seed Sci. Technol., 30, 451-458.
- Sandhu, N. and Kumar, A. (2017). Bridging the rice yield gaps under drought: QTLs, genes, and their use in breeding programs. Agronomy, 7, 27.
- Sfaxi Bousbih, A., Chaoui, A., and El Ferjani, E. (2010). Cadmium impairs mineral and carbohydrate mobilization during the germination of bean seeds. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf., 73, 1123 9.
- Copper affects the cotyledonary carbohydrate status during the germination of bean seed. Biol Trace Elem Res., 137, 110 6.
- Shah, F.R., Nasir, A., Masood, K.R., Peralta-Videa, J.R., and Ahmad, F.D. (2010). Heavy metal toxicity in plants. In M. Ashraf, M. Ozturk and M.S.A. Ahmad (Eds.), Plant adaptation and phytoremediation (pp. 71-98). Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978-90-481-9370-7_4.
- Shao, G. S., Muhammad, J. H., Zhang, X. F., and Singh, D., Nath, K., Sharma, Y. K. (2007). Response of wheat seed germination and seedling growth under copper stress. J Environ Biol., 28, 409 14.
- Singh, K.J., and Thakur, A.K. (2014). Graviperceptional changes in the roots of cadmium treated soybean seedlings. Curr. Sci., 107(8), 1294-1298.
- Smiri, M., Chaoui, A., Rouhier, N., Gelhaye, E., Jacquot, J.P., and El Ferjani, E. (2011). Cadmium affects the glutathione/glutaredoxin system in germinating pea seeds. Biol Trace Elem Res., 142, 93 105.
- Sresty, T.V.S., and Madhava, R.K.V. (1999). Ultrastructural alterations in response to zinc and nickel stress in the root cells of pigeon pea. Environ. Exp. Bot., 41, 3-13.
- Stefanov, K., Seizova, K., Yanishlieva, N., Marinova, E., and Popov, S. (1995). Accumulation of Pb, Zn and Cd in plant seeds growing in metalliferous habitats in Bulgaria. Food Chem., 54, 311-313.
- Stiborava, M., Doubravova, M., Brezinova, A., and Friedrich, A. (1986). Effect of heavy metal ions on growth and biochemical characteristics of photosynthesis of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Photosynthetica, 20, 418-425.
- Titov, A.F., Talanova, V.V., and Boeva, N.P. (1996). Growth responses of barley and wheat seedlings to lead and cadmium. Biol. Plan., 38(3), 431-436.
- Wainwright, S.J., and Woolhouse, H.W. (1977). Some physiological aspects of copper and zinc tolerance in Agrostis tenuis Sibth: Cell elongation and membrane damage. J. Expt. Bot., 28, 1029-1036.
- Wintz, H., Fox, T., and Vulpe, C. (2002). Responses of plants to iron, zinc and copper deficiencies. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 30, 766-768. DOI: 10.1042/bst0300766
- Younas, M. and Shahzad, F. (1998). Assessment of Cd, Ni, Cu and Pb pollution in Lahore, Pakistan.
- Zhang, G. P., (2004). Effects of cadmium stress on Ernimn Intern 24 761-766


