Evaluation of some upland cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.) varieties for salinity tolerance screening
Автор: Saleh Basel
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.9, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This investigation aimed to evaluate five upland cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.) (Aleppo118, Aleppo33/1, Aleppo90, Raqqa5, and Deir-Ezzor22) varieties based on physiological indices and genetic variation using AFLP marker. These varieties were evaluated under control and saline conditions (50, 100 & 200 mM NaCl) for 56 days. Various physiological indices were detected in this investigation. In this respect, Deir-Ezzor22 variety differed by showing high salt tolerance relative to the other tested varieties. Otherwise, PCR amplification with 7 AFLP PCs primer combinations revealed that Deir-Ezzor22 variety characterized by 15 unique positive markers compared to the other tested varieties. Based on physiological study and AFLP technique, it can be concluded that genetic variation detected by AFLP marker supported the physiological indices among the tested cotton varieties. These varieties present considerable interest for genetic studies and plant improvement.
Aflp marker, cotton, physiological parameters, salt stress
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323785
IDR: 14323785
Текст научной статьи Evaluation of some upland cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.) varieties for salinity tolerance screening
Cotton is an economically important plant grown world-wide as a principal source of staple fiber and vegetable oil. A great deal of effort has been made to improve cotton cultivation and characteristics by breeders. Cotton is one of the major fiber crops in Syria, with a cultivated area amount to 125,000 hectares, and a production of 470,000 tons of seed cotton and lint production is estimated at 160,000 tons. Yarn spinning capacity is estimated at 180,000 tons (USDA 2011). Salinity tolerance is a complex trait that involves physiological, biochemical, cellular and genetic strategies. At present, out of 1.5 billion hectares of cultivated land around the world, about
The determination of variability at molecular level by using molecular markers techniques is of a great importance for the continuation of germplasm and plant breeding. The genetic alterations produced by NaCl application was detected by AFLP marker. Due to the physiological damages caused by NaCl treatment, polymorphism observed between plants treated with NaCl compared to their control respective.
Many PCR-based markers have been successfully used to monitor genetic variations in different plant crops. Among others RAPD marker has been extensively applied in plant breeding program, such as in date palm ( Phoenix dactylifera L.) (Kurup et al ., 2009), aquatic plants Hydrilla verticillata and Ceratophyllum demersum (Gupta and Sarin 2009), in Euplotes vannus (Protozoa, Ciliophora) (Zhou et al ., 2011) and in fish full-sib Nile tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus ), Blue tilapia ( Oreochromis aureus ) and their diallel interspecific hybridization (El-Zaeem 2012). Previously, RAPD technique has been successfully used to detect genetic instability in bacteria, plants, invertebrate and vertebrate animals (Savva 1998, Atienzar et al ., 2000).
Most variability/taxonomic affinity studies in cotton focused mainly on morphology, physiology and nuclear DNA diversity. While, create of genetic variation in cotton induced by NaCl stress application has received little attention. On the other hand, only few studies evaluated the biomarkers assays for cotton salinity tolerance screening. The major aim of the General Commission for Scientific Agricultural Research, Damascus, Syria (GCSAR) programs was to increase cotton yield and to develop line quality, increase protein and oil contents of seeds, select the most adapted ones under local environmental conditions which could be integrated in a hybridization and breeding program and improve biotic and abiotic stress tolerance.
Thereby, this study aimed to evaluate genetic variation induced by salt treatment (NaCl) using physiological indices and molecular markers (AFLP) for salinity tolerance screening in cotton varieties.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
Seeds of five upland cotton ( G. hirsutum . L) [Aleppo118 (A118), Aleppo33 / 1 (A33/1), Aleppo90 (A90), Raqqa5 (Raq5), and Deir-Ezzor22 (DE22)] varieties were provided by the General Commission for Scientific Agricultural Research, Damascus, Syria (GCSAR) (Table 1). Seeds were soaked in distilled H 2 O for 24 h and then planted in pots filled with a 1 / 3:2 / 3 (v / v) mixture of perlite / peat moss. Germination was carried out in a greenhouse at temperature of 18◦C, 12 h photoperiod, and relative humidity of 80%. Seedlings were grown in a greenhouse under controlled conditions (temperature of 25◦C, 12 h photoperiod, and relative humidity of 80%). Seedlings were watered for 1 week with 0.1 Hoagland’s nutrient solution (Hoagland and Arnon 1950) before the intiation of NaCl treatment. The seedlings were subjected to salt stress by adding NaCl (0, 50, 100, and 200 mM)
to the nutrient solution. The same environmental conditions were maintained during salt treatment. All solutions were changed twice a week. The experiment (five replicates by treatment) was carried out in the greenhouse for 56 days.
Investigated Parameters
The parameters investigated for this work were seedling height (HT), leaf number (LN), leaf area (LA), chlorophyll SPAD, leaf Chl a and b , and osmotic potential under control and saline conditions. Plant height and leaf number were measured and counted at the end of the experiment. The experiment was terminated 56 days after salt application. Leaf area of detached leaves from all five varieties under control and saline conditions were measured using an area meter AM100 (ADC, Bioscientific) instrument and expressed as cm2 per plant. The osmotic potential was measured using a micro-osmometer (Osmometter) apparatus. Chlorophyll SPAD reading were determined using Minolta Chlorophyll Meter-SPAD 502 (Spectrum Technologies Inc., Ill.). Chlorophyll a and b content were calculated according to Arnon (1949).
Plants were uprooted carefully and washed properly with tap water. Then, they were separated into roots and leaves for mineral analysis. Fresh weight of leaves and roots was recorded for each variety under control and stress conditions. Leaves and roots fractions were oven-dried at 70◦C for 48 h, weighed, crushed in a hammer-mill and stored at room temperature. Nutrient analyses were carried out on dried leaves and roots. Samples were ground and 0.5 g of a fine powder was burnt at 400◦C for 4 h. The resulting ashes were dissolved in 100 ml of 0.5 N concentrated nitric acid. Determination of Na+ and K+ was carried out using flame photometer procedure, while that for Ca2+ and Mg2+ cations using calibration by EDTA methods. While, chloride concentration was determined using an Ion Selective Crystal Membrane Electrode Cl- (ISE 6.0502.120 Metrohm- Switzerland). For all cations and ions, their content was expressed in mg/g of dry material.
Total DNA isolation
Plant genomic DNA was extracted from (bulk of 5 plants/ variety) young leaves including the control (unstressed plants) for the five cotton varieties tested by a CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) protocol as described by Doyle and Doyle (1987) with minor modifications. DNA concentration was quantified by DNA Fluorimeter at 260/280 nm and adjusted to final concentration of 10 ng/ μl. DNA was stored at -80 °C until needed.
AFLP assay
AFLP analyses were performed according to Vos et al ., (1985) with a minor modification. Template DNA preparation of 130 ng were restricted with 0.1 U/μl Mse I/ Tru 91 and 0.1 U/μl Pst I/ EcoR 1 (Promega) (a rare 6-base cutter) and ligated to Mse I/ Tru 91 adaptor (0.25 pmol/μl) and Pst I/ Eco R1 adaptor (0.25 pmol/μl), 0.2 mM rATp and 0.065 U/μl T4 DNA over night at 37°C, in a total volume of 20 μl.
An inactivation of restriction endonuclease has been done by incubating the mixture at 70°C for 15 min. After checking for complete digestion, the digested DNA was stored at 4°C until required. Preamplification of DNA fragments was performed using non selective primer combination in a total volume of 50 μl. Pre-amplification reaction was carried out as following: 5 μl of ligated DNA, 0.3 μmol of each primers PstI/EcoR1 and MseI/Tru91 (MWV, Germany), 1.25 mM MgCl2, 0.3 mM dNTP (Promega) and 0.05 U of Taq DNA polymerase (Promega). Samples were run in a thermal cycler programmed for the first 12 cycles, the thermal profile was 94°C for 30 s, 65°C (-0,7°C/cycle) for 30 s, and 72°C for 60 s. For the last 23 cycles, the annealing temperature (aT°) was set to 56°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 1 min. Pre-amplification products were then diluted 50-folds in double-distilled H2O, and used as templates for selective amplification.
Selective amplification of the pre-amplified DNA was carried out using various selective primer combinations. This last amplification was performed in 25 μl reaction volume containing 5 μl of diluted DNA pre-amplified, 10X PCR buffer without MgCl 2 , 0.5 ng of Pst I/ EcoR 1 selective primer, 1.5 ng of Mse I/ Tru 91 selective primer, 1.5 mM of MgCl 2 , 0.2 mM dNTP and 0.04 U of Taq DNA polymerase. PCR reactions for selective amplification were performed in a thermal cycler programmed as following: 94°C for 30 sec, 65°C (-0,7°C/cycle) for 30 sec and 72°C for 1 min for the first 14 cycles. For the last 24 cycles, the annealing temperature (aT°) was set to 56°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 1 min. Amplification products were separated on a 6% polyacrylamide (acrylamide : bisacrylamide 19 : 1) / 8 M urea sequencing gel (SequaGel® XR, National Diagnostics, Inc.) at 120 W for 2 h in 1X TBE buffer (0.09 M Tris-borate and 0.002 M EDTA), and detected by silver staining according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Sigma). Band sizes were determined by comparison with a 1kb DNA ladder size standard.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using Statview 4.5 statistical package (Abacus 1996) at the 5% significance level (P = 0.05). Data were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the determination of differences in means between tested plants of each concentration of NaCl applied. Differences between means were tested for significance by Fisher’s least significant difference (PLSD) test.
AFLP analysis
To match more loci at the genomic level, seven AFLP PCs primer combinations were tested for detecting the polymorphism among the five cotton varieties. Data was scored manually as (1) for the presence and (0) for the absence of a DNA band for each locus in each variety tested.
RESULTS
Physiological indicators
Our investigation demonstrated genotypic variation in salt tolerance present among tested cotton varieties based upon various examined physiological indices. Analysis of variances of data for the different investigated parameters for the five cotton varieties tested in this study was summarize in table 2. Overall, salt stress application negatively affected various indicators detected in this investigation, except for Deir-Ezzor22, where there was an increase in LA with increasing salinity levels (Saleh 2012).
Analysis of variance indicated that the effect of NaCl levels on the major tested indicators in all varieties tested was highly significant ( P < 0.001), except for some other indicators such as, leaf K+ /Na+, leaf and root Ca2+ and Mg2+ content (Table 2). While, the significant effect ( P < 0.001) of variety on the major tested indicators in all varieties tested was less noticeable (Table 2). Whereas, a low significant effect was recorded for the interaction between variety and treatment (Table 2). These results were in agreement with Saleh 2011a, 2011b & 2012.
AFLP Markers
The current study based on AFLP fingerprinting permitted the discrimination among the five cotton tested varieties. The findings presented herein allowed to somewhat to distinguishes between DE22 (salt tolerant) variety and other tested ones through revealing species-specific markers.
AFLP fingerprinting revealed that some of DNA fragments may characterize gene(s) coding for specific traits such as salinity or/and drought tolerance. Our data stated that different observed fragments in DE22 (salt-tolerant( variety may provide a marker for salinity tolerance. Our findings revealed that DE22 variety characterized by 15 unique positive markers compared to the other tested varieties using 7 AFLP PCs primer combinations (Table 4).
Table 1. Descriptive of 5 certificated cotton varieties used in this study
|
Variety |
Agro-ecological zone |
Yield (kg /ha) Upon certification |
Certification year |
Origin |
|
Aleppo118 |
Aleppo - Idleb |
6252 |
2004 |
Hybrid (Syrian var. Aleppo40 x American var. BW 76-31) |
|
Aleppo1/33 |
Hama - Homs |
5166 |
1987 |
Created from selected line Acala SG-4 |
|
Aleppo90 |
Hassakeh |
5130 |
1977 |
Hybrid ( Russian var. Tashkand-3 x American var. Deltapine 70) |
|
Raqqa5 |
Raqqa |
4840 |
1988 |
Created from selected Russian var. Tashkand-3 |
|
Deir Ezzor22 |
Deir Ezzor |
5420 |
1988 |
Created from selected American var. Deltapine 41 |
Source: General Commission for Agricultural Research Damascus – Duma, Syria (GCSAR).
Table 2. Analysis of variances (mean squares) of data for the five cotton varieties after 56 days growth at 0, 50, 100 and 200 mM NaCl
|
S.O.V |
df |
HT |
LN |
LA |
SPAD502 |
Chl a |
Chl b |
Osmotic potential |
Biomass |
|
V |
4 |
209.565* |
1.765ns |
393.091* |
382.702* |
162.622* |
33.716* |
3.52* |
3.391* |
|
T |
3 |
314.067* |
15.2* |
1266.859* |
743.988* |
407.982* |
71.454* |
5.794* |
11.428* |
|
V x T |
12 |
23.892ns |
7.358* |
369.299* |
56.463* |
21.888* |
4.179* |
0.339* |
1.189* |
|
S.O.V |
df |
FWL |
FWR |
DWL |
DWR |
Leaf K+/Na+ |
Leaf Mg2+/Na+ |
Na+ Leaf |
Na+ Root |
|
V |
4 |
5.758* |
1.047* |
0.611* |
0.138ns |
42.666* |
375.017* |
772.723* |
24.807* |
|
T |
3 |
7.793* |
5.099* |
0.667* |
0.496* |
89.958* |
289.57* |
2172.101* |
162.353* |
|
V x T |
12 |
0.653ns |
0.102ns |
0.077ns |
0.095ns |
32.271* |
267.264* |
234.631ns |
4.572ns |
|
S.O.V |
df |
K+ Leaf |
K+ Root |
Cl- Leaf |
Cl-Root |
Ca2+ Leaf |
Ca2+ Root |
Mg2+ Leaf |
Mg2+ Root |
|
V |
4 |
109.774* |
2.532ns |
845.552ns |
13.397ns |
4621.245* |
72.706* |
2080.578* |
262.644* |
|
T |
3 |
16.65ns |
0.14ns |
9783.503* |
99.62* |
247.233ns |
0.677ns |
9.462ns |
19.167ns |
|
V x T |
12 |
15.111ns |
1.264ns |
281.123ns |
6.536ns |
268.878ns |
0.388ns |
148.749ns |
9.739ns |
* : significant at 0.05 level, ns: Non-significant, V: variety, T: treatment.
Table 3. Physiological traits investigated into the five cotton varieties used in this study
|
Index |
A118 |
A33/1 |
A90 |
Raq5 |
DE22 |
|
HT |
3 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
LN |
2 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
|
LA |
3 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
SPAD502 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
Chl a |
2 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
|
Chl b |
2 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
|
Osmotic potential |
3 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
Biomass |
3 |
3 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
|
FWL |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
1 |
|
FWR |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
1 |
|
DWL |
2 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
DWR |
2 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
1 |
|
Leaf K+/Na+ |
3 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
Leaf Mg2+/Na+ |
3 |
3 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
|
Na+ Leaf |
3 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
Na+ Root |
3 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
K+ Leaf |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
K+ Root |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Cl- Leaf |
3 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
Cl- Root |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
|
Ca2+ Leaf |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
|
Ca2+ Root |
2 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
|
Mg2+ Leaf |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Mg2+ Root |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1: Tolerant 2: Moderate 3: Sensitive
Table 4. Number and marker size (bp) of unique positive markers identified into DE22 variety using 7 AFLP PCs primer combinations
|
PCs primer combinations |
Unique positive markers Number and Marker size (bp) |
|
E- ACG / T- CTG |
(2) 350 & 590 |
|
E- ACC / T- CTG |
(3) 350, 500 & 850 |
|
E- GAG / T- GTT |
(2) 420 & 490 |
|
E- GAA / T- CTT |
(1) 750 |
|
E- AGG / T- GTG |
(3) 350, 890 & 950 |
|
E- CTG / T- CTG |
(1) 560 |
|
E- CTT / T- CTA |
(3) 390, 980 & 1000 |
E-GAG / T- GTT E-GAA / T- CTT E- AGG / T- GTG
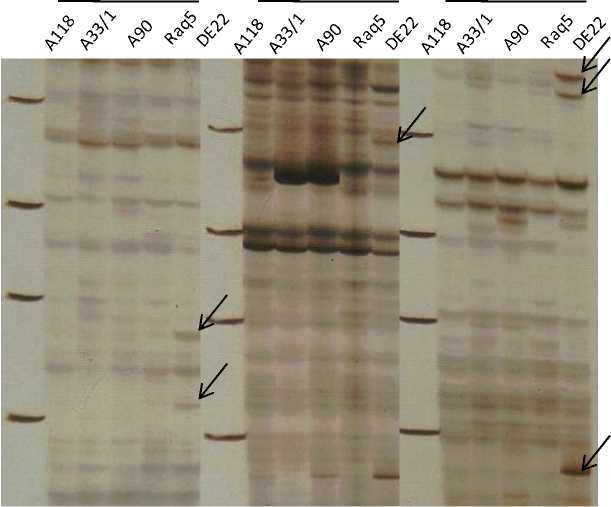
Figure 1: AFLP banding profiles generated by E-GAG/T-GTT, E-GAA/T-CTT and E-AGG/T-GTG AFLP PCs into the five tested cotton varieties. Arrows indicate new bands identified as a positive unique marker in DE22
As shown in Table 4, fragments were ranged between 1 (E- GAA/ T- CTT and E- CTG/ T- CTG AFLP PCs combinations) and 2 (E- GAG/ T- GTT and E-ACG/ T- CTG AFLP PCs combinations). While, the highest number (3) was yielded by (E- ACC/ T- CTG, E- AGG/ T- GTG and E- CTT/ T- CTA AFLP PCs combinations). These data are in accordance with physiological tested indices obtained herein.
Regarding the degree of relatedness among the varieties tested upon UPGMA clustering method, DE22 was too genetically distinct from the other tested varieties (unpublished) using AFLP markers..
Our results demonstrated that variant bands observed in amplification products for DE22 variety were revealed by different AFLP PCs combination primers compared to other tested varieties. As shown in Figure 1, DNA polymorphism yielded by using the E-GAG/T-GTT, E-GAA/T-CTT and E-AGG/T-GTG AFLP PCs combination primers in the five tested varieties.
Kurup et al ., (2009) used RAPD marker to evaluate morpho-physiological traits characterization of date palm ( Phoenix dactylifera L.) varieties for salinity tolerance. The previous investigation mentioned that DNA fragments amplified of about 1200, 1400 and 1600 bp could be used as a marker for salinity tolerance in date palm.
Gupta and Sarin (2009) stated that the DNA polymorphisms detected by RAPD analysis can be applied as a suitable biomarker assay for the detection of genotoxic effects of heavy metal contamination on aquatic plants Hydrilla verticillata and Ceratophyllum demersum. Zhou et al., (2011) also used RAPD bands for indicating DNA damage in Euplotes vannus (Protozoa, Ciliophora) induced by nitrofurazone in marine ciliates. Recently, El-Zaeem (2012) suggest also that RAPD technique can be successfully used as a rapid and easy way for identification of the different selected genotypes of salinity resistance fish full-sib Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), Blue tilapia (Oreochromis aureus) and their diallel interspecific hybridization. Banding patterns generated by AFLP fingerprinting could be used as biomarker to identify salinity tolerance gene(s). Based upon the current results, AFLP marker could be used as potential markers for early identification of cotton tolerance to salt stress.
In conclusion, the physiological evaluated indicators in the current study could be considered as useful parameters for screening salt tolerance among different cotton varieties cultivated in Syria. Thereby, cotton varieties that could be considered as salt tolerant will help boost plant production in salt-affected regions. Other wise, it is possible that the variant bands observed in amplification products for DE22 variety may be linked to salinity tolerance gene(s).
Overall, It can be concluded that physiological indices could reflect genetic variations among the tested cotton varieties.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr. I. Othman (Director General of AECS) and Dr. N. Mirali (Head of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Department in AECS) for their support, and also the Plant Biotechnology group for technical assistance.
Список литературы Evaluation of some upland cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.) varieties for salinity tolerance screening
- Abacus Concept (1996) Statview 4.5 Statistical Program Abacus Concepts Corporation, Berkeley, CA, USA.
- Arnon, D. I. (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant. Physiol., 24: 1-15.
- Atienzar, F.A., Conradi, M., Evenden, A.J., Jha, A.N. and Depledge, M.H. (1999) Qualitative assessment of genotoxicity using random amplified polymorphic DNA: comparison of genomic template stability with key fitness parameters in Daphnia magna expose to benzo [a] pyrene. Environ. Toxicol. & Chem., 18: 2275-2282.
- Badigannavar, A., Myers, G., Agcenter, L.S.U. and Baton-Rouge, L.A. (2010) Genetic analysis of AFLP markers associated with seed quality traits in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). 2010 Beltwide Cotton Conferences, New Orleans, Louisiana, January 4-7. Nat. Cotton Counc. Am., Memphis, TN.
- Chaudhary, L., Sindhu, A., Kumar, R. and Saini, M. (2010) Estimation of genetic divergence among some cotton varieties by RAPD analysis. J. Plant. Breed. Crop. Sci., 2(3): 39-43.
- Doyle, J.J. and Doyle J.L. 1987. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytoch. Bull., 19: 11-15.
- El-Zaeem, S.Y. (2012) Identification of different selected genotypes of salinity resistance of each of full-sib Nile tilapia, Blue tilapia and their diallel interspecific hybridization using random amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprinting. Afr. J. Biotech., 11(35): 8645-8652.
- Gupta, M. and Sarin, N.B. (2009) Heavy metal induced DNA changes in aquatic macrophytes: Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis and identification of sequence characterized amplified region marker. J. Environ. Sci., 21: 686-690.
- Hoagland, D.R. and Arnon, D.I. (1950). The water culture method for growing plants without soil. Circular 347, College of Agriculture, University of California, Berkeley; College Agriculture circular No. 347.
- Hussein, E.H.A., Marwa, H.A., Hussein, O.M.H. and Adawy, S.S. (2007) Molecular characterization of cotton genotypes using PCR-based markers. J. Appl. Sci. Res., 3(10): 1156-1169.
- Kurup, S.S., Hedar, Y.S., Al Dhaheri, M.A., El-Heawiety, A.Y., Aly, M.A.M. and Alhadrami, G. (2009) Morpho-physiological evaluation and RAPD markers-assisted characterization of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) varieties for salinity tolerance. J. Food. Agric. & Environ., 7 (3&4): 303-507.
- Moradi, A., Tahmourespour, A., Hoodaji, M. and Khorsandi, F. (2011). Effect of salinity on free living -diazotroph and total bacterial populations of two saline soils. Afr. J. Microb. Res., 5 (2): 144-148.
- Saleh, B. (2011a) Effect of salt stress (NaCl) on biomass and K+/Na+ ratio in cotton. J. Stress. Physiol. & Biochem., 7 (4): 05-14.
- Saleh, B. (2011b) Ion partitioning and Mg2+/Na+ ratio under salt stress application in cotton. J. Stress. Physiol. & Biochem., 7 (4): 292-300.
- Saleh, B. (2012) Effect of salt stress on growth and chlorophyll content of some cultivated cotton varieties grown in Syria. Comm. Soil. Sci. Plant. Anal., 43 (15): 1976 -1983.
- Savva, D. (1998) Use of DNA fingerprinting to detect genotoxic effects. Ecotoxic. Environ. Saf., 41:103-106.
- Vos, P., Hogers, R., Bleeker, M., Reijans, M., van de Lee, T., Hornes, M., Frijters, A., Pot, J., Peleman, J., Kulper, M. and Jabeau, M. (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl. Acid Res., 23: 4407-4414.
- Zhou, L., Li, J., Lin, X. and Al-Rasheid, K.A.S. (2011) Use of RAPD to detect DNA damage induced by nitrofurazone in marine ciliate Euplotes vannus (Protozoa, Ciliophora). Aquat. Toxicol., 103: 225-232.


