Evolution of NFT Marketplace for Influencing Buying Behaviour in Sportswear Industry
Автор: Medha Prabhakar, Suman De.
Журнал: International Journal of Information Engineering and Electronic Business @ijieeb
Статья в выпуске: 1 vol.16, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The advent of metaverses, NFTs, blockchain, and similar growth topics influence the future of businesses, and the industry is looking at a transformation. SAP has been a pioneer in innovation and enables some of the best businesses around the World. With its own Cloud infrastructure in place and expertise in areas of Blockchain etc., it’s time to take a leap and give the existing and new customers an edge over the others. The solution proposed here is to address how the future could look for retail, for example, in sportswear. It is possible to provide an NFT Marketplace for sportswear manufacturers like Nike, where the subscribers can sell their NFTs (digital shoes, wearables, etc.) or buy the ones available in the marketplace with the help of Crypto Wallets/Payments, etc. The idea proposed in this paper helps sellers’ who design products to have a review process, where the company can evaluate if they want to introduce those products in their physical form. Or, if a digital product sells well in the NFT marketplace, the company can decide to make a physical launch of the product as well, sharing some royalty.
Non-fungible tokens, metaverse, blockchain, virtual reality, retail, artificial intelligence, analytics
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15018898
IDR: 15018898 | DOI: 10.5815/ijieeb.2024.01.02
Текст научной статьи Evolution of NFT Marketplace for Influencing Buying Behaviour in Sportswear Industry
Published Online on February 8, 2024 by MECS Press
Geppetto has 200m users, and Animal Crossing has hosted a poll in the metaverse, demonstrating how quickly it is growing. For example, Roblox has 150m active subscribers per month, among whom 2/3 are US youngsters between the ages of Nine and Twelve and thirds are younger than sixteen. Virtual Life was the subject of preliminary research for the Metaverse in 2006. The present Metaverse though, is built here on societal expectations of Gen Z, which hold that an individual's offline and online selves are identical. A new definition is thus required for said current Metaverse because it varies as of prior Virtual world due to the growing share of social activities and products.
Initial attempts by the fashion business to interact within digital environments mostly involved the introduction of digital apparel. Some number of garment businesses have shown great innovative prowess. For instance, Balenciaga released a variety of virtual accessories and clothing within Fortnite alongside a physical collection, which led to an additional 40% rise in product results in google 2 days following the release. 97 Additionally, Gucci, a competing luxury items shop, offered similar digital replica among its Dionysus bags on Roblox for the equivalent of $6. Once the item was later resold on the secondary market for further money compared to the actual release's cost, prices reached over $4,000. This presents a grey area for research in a virtualized marketplace which is simple and efficient for users.
The scenarios discussed above present a gap in extension of metaverse concepts in the sportswear industry including the use of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). In this paper, we explore various research being done before understanding different terminologies to provide an overview to the proposed workflow. Subsequently, we explore the benefits of the same to the current sportswear industry and how buying behavior is influenced using the suggested workflow. This paper forms a conceptualized view of Metaverse and how it has impacted the sportswear industry through the NFT Marketplace while proposing a novel workflow for buyer and seller scenarios involved in the process.
2. Literature Survey
The influence of research in this topic of NFT marketplace with latest technology trends of metaverse, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, etc. is significant, even though it is still relatively young and just recently beginning to get attention. Higher processing performance may be considered pointless if website faults prevent users from understanding the actual novelty of the new product that is in consideration. In this section, we explore some latest research done and then form the basis of the current paper with respect to the development done in this area.
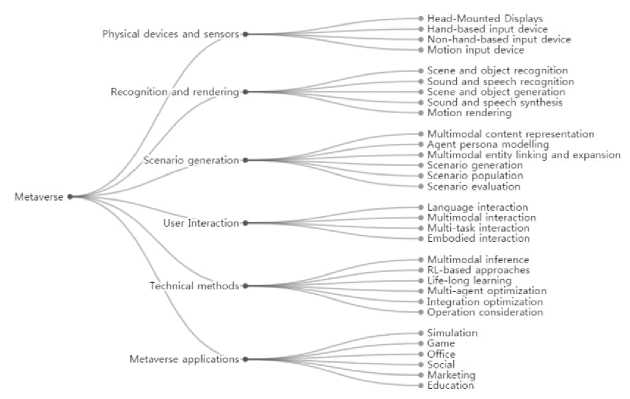
Fig.1. Generic Metaverse Taxonomy (Source: Metaverse Taxonomy paper [1])
The first work that we look at is by A. Musamih, R. Jayaraman, D. Puthal, K. Salah, S. Ellahham, and I. Yaqoob in their paper for the use of NFT in Healthcare industry. They focus on NFT and how grown as one of the most popular digital assets. They reflect ownership of one-of-a-kind assets kept on a blockchain [1, 2] that cannot be modified, reproduced, or replicated. Realization of the same are possible using open libraries as also used by the proposed paper and has been explained in detail in subsequent sections. [3] NFT-minted commodities, which can only have one official owner at a time, are sold and traded on digital markets. NFTs are penetrating many industries, from art to real estate, with healthcare being the next. Under this study, they propose the use of NFTs in healthcare. They discuss the major elements, significant characteristics, and advantages of NFTs. They evaluate the critical benefits of NFTs in domains such as supply chain management, patient-centric data management, digital twins, clinical trial management, and genomics. They explore several significant barriers to the use of NFTs in healthcare, and potential research prospects. [4]
The subsequent topic is about progress of Blockchain and how NFT has improvised there. This is the works of F. Khan, M. Patel, N. Banoth, and R. Kothari published in 2022 where they focus on the blockchain revolution that is bringing forth a plethora of innovations that the art industry potentially benefits from. One goal of research article would be for offer detailed information on the NFT, including its application, mode of operation, purchasing, producing, and sales growth, and use. Being combined with Metaverse, this NFT offers a substantial development and transformation inside the realms of virtual reality and blockchain, opening novel avenues for creators to convey their creative and valued creations. The research bridges theoretical and pragmatic information disparity through proving the utility of NFTs across areas involving significant development and revolution in new private and public blockchain applications. [5]
There are some recent works also on Digital Media and Virtual Reality for Metaverse and one of them is by the authors, M. Qu, Y. Feng, and Y. Sun where they focus on latest technologies that have impacted the space. This emergence in 5G, Virtual Reality, and XR technologies is propelling towards coming of said metaverse age. The acceptance of developing technologies is critical to the growth of the metaverse. Only software and hardware technologies can create exceptional digital environment responsiveness and engagement. The aesthetic creations used for the metaverse constitute the fundamental element. Contemporary arts are crucial in the production of NFT artwork, smart cities, cultural museum engagement, videogames, cinema, and TVs. Understanding the metaverse's artwork regulations as well as novel ways might enhance the existing digital media presentation effect and the creative quality for Virtual - reality art, attracting many creators towards the metaverse's development. [6]
Tech giants, venture capital (VC), private equity (PE), startups, and established brands are all looking to capitalize on the metaverse opportunity. According to Activision, companies, VCs, and PEs have already invested over $120 billion in the metaverse in the first five months of 2022, up from his $57 billion invested in the entirety of 2021. That's more than twice his dollar. The potential impact of the metaverse will vary by industry, but we believe it will affect all. For example, he estimates there could be a $2 trillion to $2.6 trillion market impact in e-commerce by 2030, depending on whether the base case or the upside case materializes. Similarly, the impact on the academic virtual learning market is estimated at $180-270 billion, the advertising market at $144-206 billion, and the gaming market at $108-125 billion. However, these impacts can manifest themselves in very different ways along the value chain. By 2030, more than 50% of live events could well be in the metaverse. More than 80% of commerce can be influenced by what consumers do there, from discovering brands to visiting virtual stores. Most learning and development can take place in the metaverse environment, as can most virtual or hybrid collaboration. Asset-intensive companies such as manufacturers and carriers can represent virtually all their assets and processes in a digital mirror. The same is true for simulating physical products and spaces to aid in design. By 2030, the average internet user predicts he will spend up to six hours a day on Metaverse experiences.
Building on the varied research done in this sector among others, this paper talks about creating space for sportswear industry to leverage on NFTs and create a metaverse targeting both the consumer and seller workflow which later resonates with using virtual behavior for analytical operations and bringing the right experience with the actual physical equipment produced.
3. Research Methodology
This study's research approach begins with a thorough literature analysis aiming at completely comprehending the present environment of metaverses, NFTs, blockchain technology, and their impact on different industries, notably retail and sportswear manufacturing. This research contributes to the identification of current ideas, concepts, and best practices related to NFT markets, blockchain integration, and their applications in the retail industry.
Following the analysis of the literature, the study collects data from numerous sources to get insights into the current condition of the sportswear market, including market size, important industry participants, and consumer preferences. Furthermore, data on the use of blockchain technology and NFTs across many industries, particularly fashion and retail, is gathered to offer a thorough basis for the research. Surveys and interviews are undertaken to acquire a better understanding of the planned NFT marketplace and its prospective user base. Sportswear producers, retailers, and future market participants are surveyed to learn more about their individual needs, preferences, and expectations. These interactions also aid in the identification of obstacles and possibilities related with the deployment of such a marketplace.
The study approach includes an examination of pertinent case studies, which look at successful examples of organizations that have successfully integrated blockchain technology and NFTs into their business strategies. The purpose of this research is to comprehend the influence of such technology adoption on important variables like as sales, customer engagement, and brand loyalty. In the meantime, a full technological evaluation is being carried out to determine the technical viability of establishing an NFT marketplace. The underlying blockchain architecture, smart contract creation, and seamless connection with cryptocurrency wallets and payment systems are all factors to consider. Potential technological obstacles are recognized, and solutions are investigated.
Market study is critical in this research since it involves an evaluation of the proposed NFT marketplace's target market. This study considers factors such as the size of the possible user population, demographics, and spending habits. It also contains an analysis of the competitive environment and possible rivals in the field. Following that, a business model for the NFT marketplace is created, describing revenue generating techniques, pricing models, and cost estimations. Special consideration is given to how the corporation may make it easier for developers of digital items displayed on the platform to share royalties. A prototype or proof of concept for the NFT marketplace is created as part of the research phase to demonstrate its functionality and user experience. This prototype is tested with a small number of users to get useful feedback and insights, allowing for iterative changes. Throughout the study, ethical and legal problems are addressed, with an emphasis on NFT-related issues such as copyright, intellectual property rights, and data privacy. Compliance with appropriate rules and industry standards is critical.
The research concludes with the development of an implementation strategy that outlines the actions, resources, and deadlines necessary for the effective implementation of the NFT marketplace. Post-implementation monitoring and assessment allow for modifications depending on user input and changing market circumstances.
4. Proposed Workflow
The advancements in virtual reality and the use of concepts from Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning has made large impacts on how we perceive our environment. This paper helps explore the consumer space which has evolved, and the final end-user is willing to explore the possibility of virtually testing different equipments before the physical mode of verification. The proposed idea talks about virtual absorption of NFTs and creation of a new space for metaverse to provide a neutral view of the application even before the actual physical version is presented to the user. Building on the Ledger based approach with a combination of intelligent algorithms makes the virtual space much for affordable and reduces a significant amount of cost for the consumer as well as the producer. In case of NFTs in sportswear industry, the larger growth of feel it before you use it shapes the producer to focus on a virtual experience even in case of production of the physical entity getting delayed.
The addition of Analytics and Data visualization for such instances plays a crisp role in understanding the customer needs for these NFTs. In a world where Industry 4.0 has evolved leaps and bounds paves the way for a Digital Twin of the physical entity to be realized for being used not just for a virtual experience but for analytical perceptions. Usage of Heat maps and sentiment analysis makes it a major play with respect to how the product is perceived and hence paving the way for the manufacturer to delve into the creation of the physical product for the customer. [7-9] The presence of entity data through Digital Twin in one way provides a better clarity to the customer but also provides insights by using techniques like Conjoint or Multi-Dimensional Analysis. [10] Adding the power of Constraint Satisfaction and Machine learning measures of Random Forest classifiers makes it easier to selectively focus on techniques that are catchful for the end-user. Here is a general outline of the steps required to create a metaverse with a Non-Fungible Tokens Marketplace.
-
• Choose a blockchain platform: There are various blockchain platforms available for creating NFTs, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polygon. Choose a platform that suits your needs and preferences.
-
• Develop smart contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that contain rules and regulations for transactions on the blockchain. You will need to develop smart contracts for creating, managing, and trading NFTs.
-
• Create NFTs: Use your smart contract to create NFTs, which are unique digital assets that can represent anything from art to virtual real estate.
-
• Build a metaverse: Choose a platform to build your metaverse, such as Decentraland or Somnium Space. Create the virtual world by designing and building objects, buildings, and landscapes. [11]
-
• Integrate the NFT marketplace: Integrate the NFT marketplace with your metaverse platform. This can be done by building a custom marketplace or integrating with existing NFT marketplaces.
-
• Launch the metaverse: Once the metaverse is complete, launch it for users to explore and interact with. Users can buy, sell, and trade NFTs within the metaverse marketplace.
-
• Maintain and update the metaverse: Regularly maintain and update the metaverse to ensure it runs smoothly and provides an optimal user experience.
Such implementations are possible using various functional programming libraries, eg., for Node JS, metaversejs [3] provides a developer to create and implement a metaverse blockchain. [12] A typical Wallet generation algorithm as per the library is as follows:
let Metaverse = require('metaversejs')
let number_of_addresses = 10
.then((wallet) => { let addresses = []
} return {
"mnemonic": mnemonic,
"addresses": addresses, "wallet": wallet
}
}))
-
4.1. Buyer Workflow
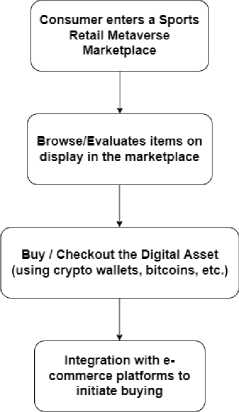
Fig.2. Buyer Workflow
The first phase is how we look at the consumer and the following workflow steps would suffice the same needs for their persona:
-
1. Consumer enters a Nike Metaverse Showroom/Marketplace
-
2. Tries objects on display in the Marketplace (3D format helps make the choice easier & more realistic)
-
3. Optionally invites a family/friend to decide to buy/checkout the digital asset (using crypto wallets etc)
-
4. Some real-world integration to be provided so the user can do an online shopping for the selected product (a checkout workflow which complements the e-commerce shopping experience).
-
4.2. Seller Workflow
The next phase is how we look at the seller and the following workflow steps let the seller achieve a virtual space for the initial experience sharing of the products:
-
1. Creators of assets can propose their digital designs and creations (sportswear) in the Seller’s space in the metaverse
-
2. The buyers can buy them again using crypto wallets etc.
-
3. The company can shortlist best Selling designs to see potential physical production of those assets and share Royalty with the designers, and/or it can have a shortlisting process right at the beginning before letting the seller place his/her asset in the marketplace.
-
4.3. Usage of Analytics
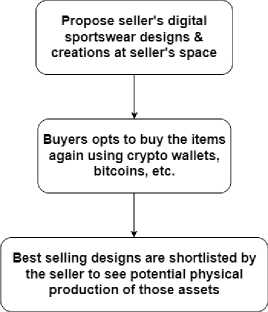
Fig.3. Seller Workflow
The generation of such large amount of data with the virtual experience enables the workflows to provide insights on consumer behavior at one hand and on the other side enables the seller to adjust the product even before the release of the items at certain times. It is an essential part for any sustainable business to know beforehand how a commodity might perform in the actual market.
The evolution of Business Analytics and Artificial Intelligence enhances the possibility of performing various analytical operations like feature selections, conjoint analysis, multi-dimensional analysis, among others. [13-14] This provides the baseline for garnering a clarity on feasibility, experience and in certain scalability of a future product. In case of sportswear, the industry even dives further into the seamless integration with specific sporting activities and how it helps the end-user to perform better. This segment on top of the Buyer and Seller workflow creates a channel for any implementation project to run in the right direction. An early feedback mechanism in this case makes it even more convenient to delve into metrices and report on issues, bugs, extended feature requirements, and trends.
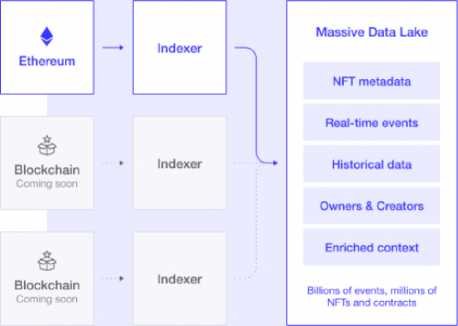
Fig.4. API and Collection Analytics by Mnemonic

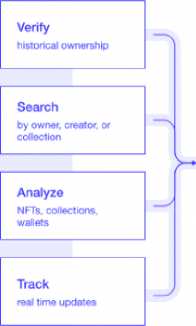

There has been an evolution of analytical tools for NFT like BitDegree, CryptoSlam, Nansen, Compass Art, and so on. [15-17] they have the capability to generate visualization of data, target KPIs for aspects like decentralized finance, sales analytics, wallet tracking, real-time analytics, notification alerting, portfolio management, historical data analysis, discovery, and basic predictive analytics. A generic table comparing some of the key performance metrics that can be used to evaluate the efficiency of a metaverse. [18] These metrics include:
-
• Response Time: The time taken to respond to a user's request or input.
-
• Throughput: The rate at which the metaverse can process requests or transactions.
-
• Scalability: The ability of the metaverse to handle increasing user loads without degrading performance.
-
• Latency: The time delay between a user's input and the corresponding response from the metaverse.
-
• Reliability: The ability of the metaverse to provide consistent and error-free performance over time.
Table 1. Sample table comparing two hypothetical metaverse implementations based on these performance metrics
|
Performance Metric |
Metaverse A |
Metaverse B |
|
Response Time |
200ms |
300ms |
|
Throughput |
1000 requests/sec |
500 requests/sec |
|
Scalability |
Scalable up to 10,000 concurrent users |
Scalable up to 5,000 concurrent users |
|
Latency |
50ms |
75ms |
|
Reliability |
99.9% uptime |
99.8% uptime |
It's important to note that the specific implementation details and design choices of each metaverse will heavily influence these performance metrics. Therefore, this table should be considered only as a general guideline and not an exhaustive comparison of all possible metaverse implementations. Actual performance metrics for any specific implementation will need to be measured and compared through real-world testing.
NFT Marketplace for sportswear forms an extended channel of growth for metaverse and its related technologies. It has evolved over time to provide several benefits to the consumer space and this paper highlighted a workflow that targets the sportswear industry and influences the consumer mindset as well as the seller space. [19-20] There are major benefits of this, and the benefits are as follows:
-
• Provides a gamified version of releasing a product in the digital marketplace to gauge the consumer perception towards the product.
-
• The possibility to collaborate at a lower expense with digital avatars of acquaintances makes it appealing for consumers and enhances the possibility for the seller to widen the target market and the market segment.
-
• This also helps the customer to identify the likeability of the product and experiment with various items.
-
• The seller space receives maximum benefits as it creates a channel for getting early feedback and also control feature decisions based on real-time feedback.
-
• Adding analytics to this huge data that is gathered in the workflows makes it comparatively a definite means to identify feasible and cost-effective solution.
-
• Low cost and better experience for both personas of buyer and seller.
Table 2. Growth of NFT market over the years
|
Year |
Number of NFTs sold (in millions) |
Total sales volume (in billions) |
Sportswear industry impact |
|
2017 |
0.05 |
0.02 |
Negligible |
|
2018 |
0.1 |
0.05 |
Negligible |
|
2019 |
0.3 |
0.1 |
Negligible |
|
2020 |
4.9 |
0.25 |
Emergence of NFTs |
|
2021 |
19.4 |
2.5 |
Significant impact |
|
2022 |
50 |
10 |
Growing trend |
As shown in the table, the non-fungible token (NFT) market has experienced a significant evolution in recent years, especially in the sports industry. In 2017-2019, the sales volume was negligible, but in 2020, the market began to emerge, with 4.9 million NFTs sold and a total sales volume of 0.25 billion dollars. In 2021, the market exploded with 19.4 million NFTs sold and a total sales volume of 2.5 billion dollars, leading to a significant impact on the sportswear industry.
Overall, the increasing popularity and impact of NFTs in the sports industry are changing the buying behavior of consumers, as they seek to own a piece of exclusive and limited-edition merchandise. This trend is likely to continue to grow, making it essential for sportswear companies to incorporate NFTs into their marketing strategies to attract and retain customers.
This is a major advantage on the traditional mindset but also puts forward challenges. Some of the key limitations that require to be addressed are as follows:
Hence, considering the above aspects, it can be clearly stated that the future of sportswear and retail is going to be very different from the traditional means, but it needs to consider multiple challenges before a perfect digital marketplace is created.
He proposed workflow also forms the basis of predictions and extend the analytical capabilities where the seller can make predictive improvements on a product with a generation of large usage information in the digital marketplace. The basic need for the same will be to install maximum users but once this is there, the given system provides immense possibilities of predicting user behavior at an earlier timeframe. This creates a larger scope for business usages and how it will heavily change the existing traditional marketplace.
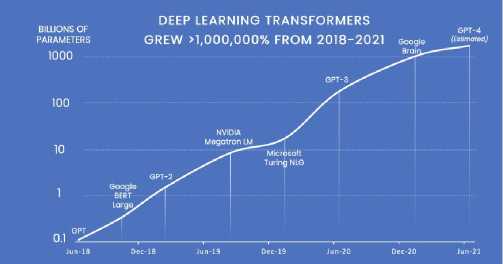
Fig.5. Google Brain Transformer growth [13]
Predictability concepts using a decision tree or for clustering and classification using supervised and unsupervised learning also paves the way for making intelligent spend decisions for the stakeholders of buyer and seller. Learning techniques add a new dimension for providing a better analysis of the consumer buying and attractability pattern that gets enhanced. Further extending the hypothesis with the use of Random Forest Classifiers only increase the rate with which we can put the proposed model to good use. Also, from a visualization standpoint of the analysis done with the collected data, real-time representations will make it further appealing for the end-users to have a better experience with the metaverse system.
This paper looks at a niche area of the NFT Marketplace utilizing the technological advancements in the metaverse. It proposes a workflow that acts beneficial for creating a digital marketplace that is inclusive of advantages for both buyer and seller personas. It also explores the data generated in such a marketplace to be used for analytics and, in the long run, for data-driven decision-making. This paper also provides an outlook on the advantage of such a workflow and the business implications associated with the same. The last section also opened possibilities of using Machine Learning to predict and improve consumer perception of the products. These workflows create a major revenue channel for the future of the sportswear industry and will impact the way business is done with a focus on a digital marketplace. This is already observed in some specific industries, and sports retail is an untapped area that can highly gain from this. The evolution of the metaverse with AR/VR and blockchain will only improve the experience over time. Optimizing algorithms for realizing such systems will only make it more affordable to be integrated as a major business model for the future. In conclusion, this research methodology combines elements of market research, technology assessment, and business strategy development to explore the feasibility and potential impact of introducing an NFT marketplace for sportswear manufacturers, leveraging SAP's expertise in blockchain and innovation. Recommendations and future research directions are provided to guide businesses considering the integration of NFTs and blockchain technology into their operations.
Future Works
The next step for this conceptual paper is to realize a digital marketplace for the sportswear industry. The realization requires multiple technical considerations and adaptations for the metaverse concept. It is possible to look at creative APIs that handle specific aspects of such a marketplace and bring a true microservice capability ensuring that the digital marketplace has relatively higher uptime as well as can scale up during a peak time of consumption.
Acknowledgment
This paper was possible thanks to the support of our parent organization, SAP Labs India. We would like to thank techNxt for creating a research community for budding authors and our managers and colleagues for extending their support in our research journeys.
Список литературы Evolution of NFT Marketplace for Influencing Buying Behaviour in Sportswear Industry
- S. M. Park and Y. -G. Kim, "A Metaverse: Taxonomy, Components, Applications, and Open Challenges," in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 4209-4251, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3140175.
- Suman De, "Addressing General Data Protection Regulations for Enterprise Applications Using Blockchain Technology", International Journal of Applied Research on Information Technology and Computing, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 67-75, 2015.
- Metaverse NodeJS NPM library, Available: https://www.npmjs.com/package/metaversejs, Last Accessed: 09.08.2022
- A. Musamih, K. Salah, R. Jayaraman, I. Yaqoob, D. Puthal and S. Ellahham, "NFTs in Healthcare: Vision, Opportunities, and Challenges," in IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, 2022, doi: 10.1109/MCE.2022.3196480.
- F. Khan, R. Kothari, M. Patel and N. Banoth, "Enhancing Non-Fungible Tokens for the Evolution of Blockchain Technology," 2022 International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Data Communication Systems (ICSCDS), 2022, pp. 1148-1153, doi: 10.1109/ICSCDS53736.2022.9760849.
- M. Qu, Y. Sun and Y. Feng, "Digital Media and VR Art Creation for Metaverse," 2022 2nd Asia Conference on Information Engineering (ACIE), 2022, pp. 48-51, doi: 10.1109/ACIE55485.2022.00018.
- I. Baroi and S. De, "A Novel Application of Neuromarketing for Designing User Interface Mockups to Enhance User Experience in Software Development," 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Technology, Engineering, Management for Societal impact using Marketing, Entrepreneurship and Talent (TEMSMET), 2021, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/TEMSMET53515.2021.9768683.
- J.R. Chapman, J.C. Wang, K. Wiechert, “Into the Spine Metaverse: Reflections on a future Metaspine (Uni-)verse”, Global Spine Journal 2022, Vol. 12(4) 545–547, DOI: 10.1177/21925682221085643.
- J.H. Murray, “Virtual/reality: how to tell the difference”, Journal of Visual Culture, 2020; 19(1):11-27, DOI: doi.org/10.1177/1470412920906253.
- S. De and I. Baroi, "An Analytical Approach for Improving Workplace Environment using HRM Systems and Application Programming Interfaces," 2022 IEEE 7th International conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), 2022, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/I2CT54291.2022.9823961.
- McKinsey & Company, “Value creation in the Metaverse”, June 2022, Available: https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/value-creation-in-the-metaverse.
- R. -V. Tkachuk, D. Ilie, K. Tutschku and R. Robert, "A Survey on Blockchain-Based Telecommunication Services Marketplaces," in IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 228-255, March 2022, doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2021.3123680.
- Jon Radof, “The Metaverse and Artificial Intelligence”, Building the Metaverse, Available: https://medium.com/building-the-metaverse/the-metaverse-and-artificial-intelligence-ai-577343895411, Last Accessed: 21.08.2022.
- S. De and D. Agarwal, "A Novel Model of Supervised Clustering using Sentiment and Contextual Analysis for Fake News Detection," 2020 Third International Conference on Multimedia Processing, Communication & Information Technology (MPCIT), Shivamogga, India, 2020, pp. 112-117, doi: 10.1109/MPCIT51588.2020.9350457.
- F. Khan, R. Kothari, M. Patel and N. Banoth, "Enhancing Non-Fungible Tokens for the Evolution of Blockchain Technology," 2022 International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Data Communication Systems (ICSCDS), Erode, India, 2022, pp. 1148-1153, doi: 10.1109/ICSCDS53736.2022.9760849.
- A. Musamih, K. Salah, R. Jayaraman, I. Yaqoob, D. Puthal and S. Ellahham, "NFTs in Healthcare: Vision, Opportunities, and Challenges," in IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, 2022, doi: 10.1109/MCE.2022.3196480.
- Agrawal, Smriti & Sandhu, Mohneet & Ospanova, A.. (2022). A Comprehensive Study on the Evolution of the NFT Market & Future Prospects. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science Engineering and Technology. 11. 3485-3491. 10.15680/IJIRSET.2022.110404.
- ChatGPT. (2023). Retrieved August 15, 2023, from https://chat.openai.com/
- Bradley Baker, Anthony Pizzo, Yiran Su, “Non-Fungible Tokens- A Research Primer and Implications for Sport Management”, Sports Innovation Journal, Vol. 3, , 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.18060/25636.
- Wilson, K. B., Karg, A., & Ghaderi, H. (2021). Prospecting non-fungible tokens in the digital economy: Stakeholders and ecosystem, risk and opportunity. Business Horizons. In press.


