Extracellular polysaccharides of potato ring rot pathogen
Автор: Shafikova T.N., Rymareva .V., Kopytchuk V.N., Epova E.Y., Romanenko A.S.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Рубрика: Original article
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.2, 2006 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Many bacteria, including phytopathogenic ones produce extracellular polysaccharides or exopolysaccharides which are universal molecules. Causal agent of potato ring rot, Clavibacter michiganensis subspecies sepedonicus, secretes exopolysaccharides which role in pathogenesis is poorly investigated. The aim of our research is to ascertain the composition and structure of Clavibacter michiganensis subspecies sepedonicus exopolysaccharides. Exopolysaccharides of Clavibacter michiganensis subspecies sepedonicus are determined to consist of 4-6 anionic and neutral components which have molecular weights from 700 kDa. Glucose is a major monomer of polysaccharides and arabinose, rhamnose and mannose are minor monomers. Glucose is present in α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose configurations. Calcium is determined to be a component of exopolysaccharides. Components of exopolysaccharides of potato ring rot pathogen are probably capable to associate via calcium ions and other ionic interactions that may result in a change of their physiological activity. Further studies of Clavibacter michiganensis subspecies sepedonicus exopolysaccharides composition and structure can serve a base for the synthesis of their chemical analogues with elicitor action.
Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus, exopolysaccharides, potato ring rot
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323446
IDR: 14323446
Текст обзорной статьи Extracellular polysaccharides of potato ring rot pathogen
Extracellular polysaccharides or exopolysaccharides (EPSs) produced by many bacteria, including phytopathogenic species are greatly various. This diversity is due to a monosaccharide variation, condensation bindings and non-carbohydrate substituting groups. The EPSs property mentioned above and their localization on external bacterial cell surface play an important role in the adaptation of bacteria, defence from the environment, nourishment and also display of antigenic properties of bacterial cells (Becker and Puhler, 1998). The structural variety of oligosaccharides, forming EPSs allow them to function as signal molecules in extracellular interactions (Lomovatskaya et al., 2000; Ozeretskovskaya and Romenskaya, 1996). EPSs of symbiotic and pathogenic bacteria play a significant role in the interactions with host plants, in particular, in the recognition reactions of potential partners (Romanenko et al., 1998; Romanenko et al., 2003). EPSs of many bacterial pathogens are virulence factors. For example, EPSs of bacteria Erwinia stewartii, Erwinia amylovora, Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. indiosus, Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis determine the virulence of phytopathogens mentioned (Bermpohl et al., 1996; Geier and Geider, 1992).
Bacterial pathogen Clavibacter michiganensis ssp. sepedonicus (Spieck. et Kotth.) Skaptason et Burk (Cms), causing wilt of overground potato parts and ring rot of tubers produces EPSs which role for pathogenesis remains poorly investigated. There is evidence that EPSs of Cms virulent strains participate in the rise of disease symptoms, in particular, of wilt (Benhamou N., 1991; Daly, 1981; Metzler et al., 1997; Van Alfen, 1989). At the same time it is noted that EPSs of Cms are more important for the enhancement of colonization or survival of bacteria in planta (Denny, 1995). For example, Cms is capable to cause latent infections in potato. Such plants have no clear symptoms of disease but they form tubers infected (Vidaver, 1982). As Cms EPSs structure is complex and poorly studied there is evidence to suppose multifunctionality of such molecules for potato ring rot pathogenesis. The aim of the present study is to determine the structure and composition of Cms EPSs. The data obtained may promote the elucidation of significance of these metabolites for different pathogenesis stages.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Culture of Cms virulent mucoid strain 5369 was received from the Potato Research Institute (Korenevo, Moscow Region). The bacteria were cultivated in liquid feed medium, containing 5 % yeast extract dialyzed (Sigma, USA), 1.5 % glucose, 0.5 % CaCO3 (Reachem, Russia) for three weeks at 230C in dark. The extraction and purification of Cms EPSs were carried out, using the technique described previously (Shafikova et al., 2003).
Gel-filtration separation of Cms EPSs was carried out on a 2,2×44 cm Toyopearl HW-55-fine column (Toyo Soda Meg, Ltd., Japan) with elution rate 30 ml per hour. 1 ml of 6 % Cms EPSs solution in 0.1 M sodium-phosphate buffer pH 7.2, containing 0.1 M NaCl was placed on the column and eluted by the same buffer. The optical density of eluate was fixed at 206 nm on chromatographic device Uvicord (LKB, Sweden). The calcium quantity in EPSs of Cms was determined according to the standard technique on AAS-1 atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Carl Zeiss Jena, Germany), using LaCl3. The Cms EPSs dissociation was conducted, using 0.05 % Na-EDTA and 0.1 % SDS for 1 hour in 0.1 M Na-phosphate buffer pH 7.2. The EPSs dissociated were eluted at the same conditions as native ones.
Carbohydrates forming EPSs were fixed by anthron method (Philippovich et al., 1975), proteins by Bradford method (Bradford, 1976). 20 mg of EPSs dry preparation were hydrolyzed by 6N HCl at 1100C for 24 hours in vacuum to determine amino saccharides and amino acids. The analysis was carried out on AAA 881 amino acid analyzer (Microtechna, Czech Republic) in sodium cycle. To determine monosaccharide composition EPSs and their hydrolysates in the form of acetates of polyols were analyzed by gas liquid chromatography method on device CROM-5 (Czech Republic) at 2200C, using 0.3×30 cm 5 % XE-60 column on N-AW chromatone, gas-bearer N2. The identification of monosaccharides was carried out, using standard samples. Quantitative measuring was conducted, defining the areas of corresponding peaks on chromatograms. 13C-NMR-spectra were fixed on Bruker DRX-400 spectrometer (Germany) at 600C, using D2O as solvent and (CD3)2CO as internal standard. Infrared spectra were fixed on Specord IR-20 device (Germany) in KBr tablets.
RESULTS
EPSs of Cms have shown to be a pool of polysaccharides, consisting of 4-6 components. High-molecular-weight compounds >700 kDa compose a significant part of EPSs. Fractions 2, 3 and 4 contain compounds with weights of 120, 71 and 11 kDa respectively. Low-molecular-weight compounds of 2.1 kDa and <1 kDa form fractions 5 and 6. On the base of data obtained by measuring pH of different EPSs fractions eluted by bidistilled water we may conclude that Cms strain 5369 EPSs contain anionic and neutral EPSs. Compounds of 11 and 2.1 kDa have the most anionic properties.
EPSs of Cms strain 5369 was determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry method to contain 0.04 mg of calcium per g dry weight.
Processing EPSs of Cms by solution Na-EDTA in superfluous concentration (0.05 %) leads to dissociation of high-molecular-weight compounds. The quantity of Cms EPSs with weights >700 kDa decreases and compounds with weights of 58, 13.8, 6.3 and <1 kDa appear.
The EPSs dissociation accomplishes more effectively at presence of anionic detergent sodium dodecylsulphate (SDS). The quantity of high-molecular-weight fraction decreases significantly, 22.4 kDa fraction appears and the share of low-molecular compounds with weights from 2.1 to <1 kDa increases.
EPSs complex of Cms strain 5369 was determined to contain carbohydrates (up to 80 %) as well as nitrogen-containing compounds amino saccharide N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (6 %) and 14 amino acids (2.3 % ser, 2.2 % glu, 2.1 % ala, 1.5 % gly, 1.4 % thre, 1.0 asp, 0.8 % val, 0.7 % leu, 0.6 % phe, 0.5 % ile, 0.4 % lys, 0.3 % tyr, 0.1 % arg and 0.1 % his).
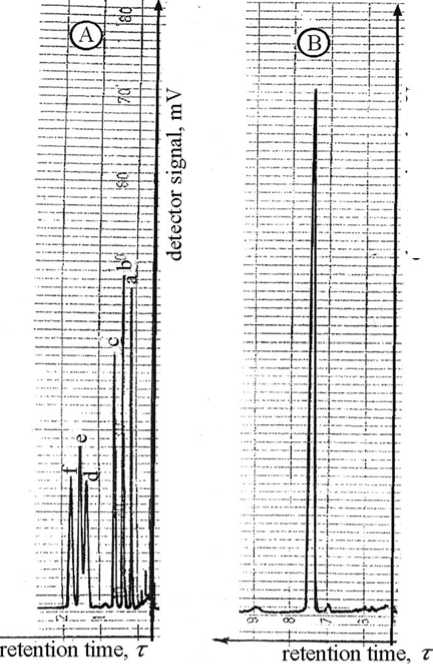
detector signal, mV
Figure 1. Gas liquid chromatograms.
А - standard mixture: a) rhamnose, b) arabinose, c) xylose, d) mannose, e) galactose, f) glucose.
B - intensive peak corresponds to glucose in EPSs hydrolysate.
The monosaccharide composition of Cms EPSs was detected by gas liquid chromatography method. The data obtained confirm the presence of one intensive peak, corresponding to glucose in EPSs hydrolysate, which occupies 97.5 % of square of all peaks. The rest 2.5 % are distributed in the field of mannose, rhamnose and arabinose (Fig. 1). Thus, the monosaccharide composition of EPSs of Cms strain 5369 includes glucose as major monosaccharide and mannose, rhamnose and arabinose as minor monomers. According to the data obtained by 13C-NMR spectroscopy method glucose is present at α-and β-D-glucopyranose space configurations in correlation 2:3 (Tab. 1). The positions of C-6 (60.97 m.p.) and C*-6 (61.12 m.p.), characterizing pyranose form of glucose confirm this fact. The configurations of anomer atoms of glucose residues are confirmed by position of the first carbon atom: C*-1 (96.26 m.p.) signal indicates β-configuration and C-1 (92.41 m.p.) signal indicates α-configuration of anomers. The data obtained were confirmed by results of infrared spectroscopy. Stereochemical peculiarity of monosaccharides determines absorption bands in the region from 700 to 1000 cm-1. Absorption band 845±15 cm-1 is typical of α-D-glucopyranose while absorption band 890±15 cm-1 is characteristic of β-D-glucopyranose. Absorption bands in the region of 3200-3500 cm-1 indicate the presence of NH-containing groups. This fact coordinates with results obtained on amino acid analyzer that amino saccharide N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and amino acids present in EPSs.
Table 1. Position and interpretation of 13С-NMR-spectrum signals of Cms EPSs.
|
Monosaccharide residue of polymer chain |
Chemical changes of signals, millionth parts, (m.p.) |
|||||
|
С - 1 |
С - 2 |
С - 3 |
С - 4 |
С - 5 |
С - 6 |
|
|
α-D-glucopyranose |
92,41 |
71,87 |
73,13 |
70,03 |
71,75 |
60,97 |
|
β-D-glucopyranose |
С* - 1 |
С* - 2 |
С* - 3 |
С* - 4 |
С* - 5 |
С* - 6 |
|
96,26 |
74,52 |
76,14 |
69,97 |
76,26 |
61,12 |
|
DISCUSSION
We investigated the structure and composition of Cms EPSs. EPSs consist of 4-6 components with molecular weights from <1 kDa to >700 kDa. We must note that 120 kDa and 71 kDa fractions occur in EPSs irregularly according to the preparation series eliminated from cultural liquid in different time. Our data show that conditions of bacteria cultivation influence the quantity of fractions and molar correlation of EPSs, forming the EPSs complex. It correlates with conclusion given in the work by Westra and Slack (Westra and Slack, 1992). Cms in culture was shown to synthesize EPSs of two types. EPSs with molecular weights from 2 kDa to >1 MDa (type A) have anionic properties and EPSs with molecular weights from 1 kDa to 10 kDa (type B) are neutral (Denny, 1995). The data on pH of different EPSs fractions confirm this fact, indicating the presence of both type A and type B EPSs.
A EPSs polymerization degree has known to determine their role in pathogenesis which may be quite opposite (elicitor or supressor) (Ozeretskovskaya and Romenskaya, 1996). Taking into account the ability of EPSs for association the presence of Ca2+ ions as well as their dissociation under detergent (Westra and Slack, 1992), there was an important reason to determine whether structural changes occur under the dissociation agents or not.
The presence of calcium and data on dissociation of EPSs under detergents prove a significant role of
Ca2+ in phytoimmunity for the "plant-pathogen" system. It is possibly that dissociation or association of EPSs occur not only under the lytic enzymes of pathogen and/or host plant but under calcium ions. Polymerization degree of EPSs may determine their elicitor or supressor properties and induction or supression of defence responses of plants relatively (Ozeretskovskaya and Romenskaya, 1996).
An efficient dissociative action of sodium dodecylsulphate on EPSs allows a conclusion to be made that association of EPSs subunits results from not only Ca2+ influence but from other ionic interactions. Sodium dodecylsulphate is known to bind with components of exometabolite complex via hydrophobic interactions and disrupt -S-S-linkages. Whereas dissociation under SDS modifies structure of exometabolite complex greatly we can suppose that protein compounds are in the complex.
The presence of positive charged (lys, his, arg) and neutral (glu, thre, ser, gly, tyr) amino acids confirms structural changes of complex under an ionic detergent. The considerable content of amino acids (14 %) in EPS complex permits to suppose the availability of peptides in it. According to the data published exometabolites of Cms carry protein factor, inducing hypersensitive reaction (HR) of plant at incompatible interactions of organisms (Nissinen et al., 1995). Also there are data that some Cms strains secrete extracellular cellulase and amylase (Metzler et al., 1997). However proteins were not determined among compounds of exometabolites, which may be on account of their breakdown at extraction. Consequently it will be advisable to search extracellular proteins and enzymes assumed in mucoid layer of Cms cells or in the medium where they were cultured.
The monosaccharides, composing EPSs include glucose as major compound and mannose, rhamnose and arabinose as minor compounds. Bacterial EPSs content is known to diversify greatly according to strain and conditions of its cultivation. Some Cms strains synthesize EPSs in which fucose, galactose, rhamnose and ribose present together with glucose and mannose (Westra and Slack, 1992). The minor monomers of EPSs may determine their functional role. So, on the one hand substitution of minor xylose monomer in exooligosaccharide of Phytophthora infestans by another monosaccharide changed its activity on the quite opposite one, on the other hand free from fucose molecules became inactive physiologically (Ozeretskovskaya, 2002). Most possible that mannose, rhamnose and arabinose present in trace quantities are structural components of EPSs, for example, terminal monomers, which can determine the affinity of Cms EPSs molecules to conformable receptors of potato cells.
The results of our search have allowed the following conclusions to be drawn:
-
1. Exometabolites secreted by bacterium Cms strain 5369 in culture are pool of anionic and neutral polymers with weights from <1 kDa to >700 kDa, which associate via Ca2+ ions and other ionic interactions.
-
2. Carbohydrates compose the major part of exometabolite complex (up to 80 %).
-
3. Glucose is a major monosaccharide; arabinose, mannose and rhamnose are minor monosaccharides.
-
4. Glucose is present in two space configurations: α- and β-D-glucopyranose in correlation 2:3.
-
5. Nitrogen-containing compounds were determined in the exometabolite complex among of which amino acids (14 %) and amino saccharide N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (6 %).
Further study of structure and composition of Cms EPSs as well as investigation of the mechanism of their action in potato ring rot pathogenesis can serve the base for the synthesis of their chemical analogues, having elicitor activity.
Acknowledgements
We thank Scherbuhin V.D. and Smirnova N.I. (Bach Institute of Biocemistry, RSA, Moscow) for scientific advice and having done GLC analysis. We thank Gavrilova G.A. (Favorsky Institute of Organic Chemistry, SB, RAS, Irkutsk) for having done IRS and Fedorov S.V. (Favorsky Institute of Organic Chemistry, SB, RAS, Irkutsk) for carrying out 13C-NMR-spectra survey.
Список литературы Extracellular polysaccharides of potato ring rot pathogen
- Becker, A. and Puhler, A. (1998) Synthesis of exopoly saccharides. In Spaink, H.P., Kondorosi, A. and Hooykaas, P.J.J, (eds.) The Rhizobiaceae: Molecular Biology of Model Plant-Associated Bacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers Press, Dordrecht/Boston/London, pp. 119-141.
- Benhamou, N. (1991) Cell Surface Interactions between Tomato and Clavibacter michiganensissubsp.michiganensis Localization Some Tissue. Physiol. Plant Pathol., 38, 15-38.
- Bermpohl, A., Dreier, I., Bahro, R. and Eichenlaub, R (1996) Exopolysaccharide in the Pathogenic Interaction of Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis with Tomato Plants. Microbiol. Res., 151, 1-9.
- Bradford, M.M. (1976) A Rapid and Sensitive Method of the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-dye Binding. Anal. Biochem., 72, 248-254.
- Daly, J.M. (1981) Mechanisms of action. In: Durbin RD (ed), Toxins in plant disease. Academic Press, N. Y, USA, pp 331-394.
- Denny, T.P. (1995) Involvement of Bacterial Polysaccharide in Plant Pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 33, 173-197.
- Geier, G. and Geider, K. (1992) Die Levansucrase als Virulenzfactor bei der Feuerbrandentstehung. Mitt. Biol. Bundesanst. Land-und Forstwirt Press, Berlin, Germany. Lomovatskaya, L.A., Romanenko, A.S., Graskova, LA. and Salyaev, R.K. (2000) High infection loading potato ring rot pathogen causes extraordinary symptoms in host plant. Doklady Biol. Sci., 374, 712-714 (in Russian).
- Metzler, M.C., Laine, M.J. and Boer, S.H. (1997) The Status of Molecular Biological Research on the Plant Pathogenic Genus Clavibacter. FEBS Microbiology Lett, 150, 1-8.
- Nissinen, R., Laine, M.J., De Boer, S.H., Bauer, P., Ishimara, С. and Metzler, M.C. (1995) Virulence and Hypersensitivity of Clavibacter michiganensissubsp.sepedonicus. Phytopathol, 5, 1187-1188.
- Ozeretskovskaya, O.L. (2002) Problems of Specific phytoimmunity. Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 49, 148-154 (in Russian).
- Ozeretskovskaya, O.L. and Romenskaya, M.G. (1996) Oligosaccharins asregulatory molecules of plants. Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 43, 743-752 (in Russian).
- Philippovich, Y.B., Egorova, T.A. and Sevastyanova, G.A. (1975) Practical work on common biochemistry. Prosveschenie Press, Moscow, Russia. Romanenko, A.S., Lomovatskaya, L.A., Shafikova, T.N., Borovskii, G.B. and Krivolapova, N.V. (2003) Potato Cell Plasma Membrane Receptors to Ring Rot Pathogen Extracellular Polysaccharides. J. Phytopathol., 151, 1-6.
- Romanenko, A.S., Rymareva E.V., Shafikova, T.N. and Salyaev R.K. (1998) Components of potato cell walls having the affinity to the toxin of potato ring rot pathogen. Doklady Biol. Sci., 358, 277-279 (in Russian).
- Shafikova, T.N., Romanenko, A.S. and Borovskii, G.B. (2003) Potato Cell Plasma Membrane Receptors to Ring Rot Pathogen Extracellular Polysaccharides. Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2, 246-250 (in Russian).
- Strobel G.A.(1970) Purification and Properties of Phytotoxic Polysaccharide Produced by Corynebacterium sepedonicum. J. Biol. Chem., 245, 33-38.
- Van Alfen N.K.(1989) Reassessment of Plant Wilt Toxins. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 27, 533-550.
- Vidaver A.K. (1982) The Plant Pathogenic corynebacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 36, 495-517.
- Westra A.A., Slack S.A. (1992) Isolation and CharacterizationofExtracellular Polysaccharide of Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus. Physiology and Biochem., 82, 1193-1199.


