Features of GABA-transaminase functioning in Zea mays L. leaves under salinity
Автор: Shakhov Z.N., Anokhina G.B., Eprintsev A.T.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.20, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Salt stress has a significant effect on plants, causing a whole range of changes in metabolism. Unfortunately, the mechanisms that ensure the adaptive response of cells in response to salinity have not been sufficiently studied. The study examined changes in the functioning of one of the enzymes of the anaplerotic pathway of the Krebs cycle - GABA shunt - GABA transaminase (GABA-T, EC 2.6.1.19). It has been shown that salt stress caused by incubation of corn seedlings in a 150 mM sodium chloride solution causes activation of GABA transaminase (GABA-T, EC 2.6.1.19). The established increase in GABA-T enzymatic activity in the first hours of incubation in saline solution reaches a maximum at 3 hours of incubation. At the same time, differences are observed in the expression profilees of the GTA-1 and GTA-2 genes, which encode this enzyme in the maize genome. Salinity in the first three hours induces an increase in the expression of the GTA-1 GABA-T gene, while the GTA-2 gene demonstrates an increase in transcriptional activity from 6 to 12 hours of the experiment. An increase in GABA-T enzymatic activity under salinity indicates activation of the GABA shunt to maintain the energy metabolism of the plant cell under stress conditions.
Gaba transaminase, gaba-shunt, metabolism, salt stress, expression
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143182788
IDR: 143182788
Текст научной статьи Features of GABA-transaminase functioning in Zea mays L. leaves under salinity
The mechanisms of adaptation of the plant cell to salt stress conditions at the biochemical level include the regulation of ionic homeostasis, osmotic pressure, the synthesis of phytohormones, the antioxidant system, and protection by polyamines (Abd-Alla, et al. , 1992).
Due to the fact that NaCl is an osmotically active substance, its high concentrations can be detrimental to plants that maintain a constant osmotic pressure (Garcia et al. , 1997). Salinization has a negative effect on growth, photosynthetic apparatus, and nutrient transport (Popova et al. , 1995). Mechanisms for plant adaptation to salinity, implemented at the molecular level, are usually aimed at inducing the expression of genes encoding enzyme proteins, which, in turn, ensure the functioning of adaptive biochemical pathways (especially the regulation of ion homeostasis), or intermediary molecules that activate signaling pathways of the response to salt stress (Hussain et al. , 2010).
The GABA shunt is an adaptive anaplerotic pathway activated by various types of abiotic stress. As a result of the functioning of this metabolic pool, bypass of the 2-oxocethoglutarate dehydrogenase and succinyl-CoA synthase reactions of TCA-cycle occurs (EC 1.2.4.2, EC 6.2.1.4), since under salt stress this section of the Krebs cycle can be deactivated due to the instability of the 2-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex to the negative effects of sodium chloride (Araújo et al. , 2012). Under these conditions, TCA-cycle is supported by the following group of enzymes: glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH, EC 1.4.1.3), which ensures the redirection of 2-oxoglutarate from Krebs cycle to glutamate synthesis; glutamate decarboxylase (GAD, EC 4.1.1.15), which catalyzes the cleavage of the carboxyl group from glutamic acid to form γ-aminobutyric acid; GABA transaminase (GABA-T, EC 2.6.1.19), which catalyzes the amino group transfer reaction to form amber semialdehyde, which succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH, EC 1.2.1.24) converts into succinate, the end product of GABA shunt. Succinate, in turn, is routed along the classical TCA cycle pathway via succinate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.5.1). Thus, the cycle closes (Zhang et al. , 2022).
As a result of the effects of salinity on plants, there is an overgrowth of ROS in cells (Gilliham and Tyerman, 2016). The GABA shunt, along with specialized antioxidant protection enzymes, is able to inhibit the production of ROS, which have a cytotoxic effect. Yeasts knocked out by the GABA shunt enzyme genes show a reduced tolerance to the effects of hydrogen peroxide. At the same time, overexpression of the genes GAD, SSADH, and GABA-T increases resistance to ROS (Gilliham and Tyerman, 2016).
It is well known that plants can accumulate various solutes such as carbohydrates and amino acids, which are a source of energy, regulators of osmotic motion, as well as signaling molecules in saline conditions. γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is of particular interest because GABA levels are known to increase rapidly in plants under salt stress (Szalai and Janda, 2009, Omoto et al. , 2012., Wang et al. , 2017). This amino acid plays an important role in the formation of plant salt tolerance as a signaling substance or a temporary pool of nitrogen, as well as a regulator of cytoplasmic pH and antioxidant reactions (Seifikalhor et al. , 2019, Hichem and Mounir, 2009, Wang et al. , 2017).
Currently, there is evidence to support the key role of GABA as a plant phytomediator under changing environmental conditions (Seifikalhor et al. , 2019). As a non-proteinogenic amino acid, this molecule is involved in stress signal transduction due to the presence of specific receptors on the mitochondrial membrane – a family of aluminum-activated malate transporter proteins (ALMTs) (Ramesh et al. , 2017, Seifikalhor et al. , 2019). However, there is very little information on the functioning of GABA catabolism under salt stress. Moreover, the mechanism of regulation of the functioning of GABA-metabolizing enzymes has not yet been established. The level of GABA depends not only on the level of its synthesis, but also on the rate of its catabolism. One of the critical stages of GABA catabolism is the reaction catalyzed by GABA transaminase (GABA-T, EC 2.6.1.19), an enzyme of the transferase class that provides reversible transamination of GABA to succinic acid semi-aldehyde.
Only one GABA-T (AT3G22200) has currently been annotated in the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana, while two genes encoding this enzyme have been found in the genome of maize. Unfortunately, the functional role of having two copies of the genes of this enzyme in Zea mays L. has not yet been established.
In this regard, the aim of the study was to study the functioning of GABA-T in the leaves of Zea mays L. corn during salinization in the first 24 hours of salt exposure.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The object of the study was the leaves of 12-day-old corn sprouts (Zea mays L.) of the Voronezhskaya-76 variety, grown hydroponically at a temperature of +25 °C. To induce salt stress in seedlings, the root system was removed, after which a 150 mM NaCl saline solution was placed for 1, 3, 6 and 24 hours. The seedlings of the control group were not exposed to salt stress and were in water throughout the experiment.
To isolate the enzyme, the corn leaf weight was homogenized with the isolation medium in a ratio of 1:10. The release medium contained 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5), 0.1 μM pyridoxal-5-phosphate, 0.05% Triton X100, 20 μM β-mercaptoethanol. The resulting drug was used to determine the activity of GABA-T.
The activity of GABA-T was determined by the change in the optical density of the reduced NAD at 340 nm in the auxiliary reaction (Awad et al. , 2007). The spectrophotometry medium contained 0.1 μM pyridoxal-5-phosphate, 5 mM 2-oxoglutarate, 200 μL mitochondrial fraction from maize, 4 mM NAD+, Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5). After adding the drug to the spectrophotometry medium, the solution was incubated for 10 minutes at 25 °C, followed by the addition of 16 mM GABA and the optical density values of the solution at 340 nm were recorded (Awad et al. , 2007).
Mitochondrial isolation was carried out by homogenization of plant samples with an isolation medium (0.15 M potassium-phosphate buffer (pH 7.4); 0.4 M sucrose; 2.5 mM EDTA; 1 mM potassium chloride; 4 mM magnesium chloride) in a ratio of 1:10. The homogenate was filtered and centrifuged for 3 minutes at 3000 rpm on an Еppendorf Centrifuge 5804 R centrifuge at a temperature of +4 °C. The supernatant was centrifuged for 10 minutes at 20,000 rpm (t = +4 °C). The supernatant was removed and the precipitate was dissolved in 0.15 M potassium-phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) with dissolved sucrose (0.25 M), MgCl2, and TDF. The resulting mitochondrial suspension was used to determine GABA-T activity by spectrophotometric method.
Total RNA was isolated by phenol-chloroform extraction. Sodium dodecyl sulfate was used as the main component of the lysis buffer in the homogenization step of plant material. To analyze the transcriptional activity of the genes, quantitative realtime PCR was performed, using as a template the cDNA obtained during the reverse transcription PCR with the MMLV RT kit ("Evrogen", Russia) according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer.
Amplified cDNA was used for real-time PCR with specific primers (Table 1) using the LightCycler96 device (Roche, Sweden) using Taq polymerase ("Evrogen", Russia) according to the manufacturer's recommendations. SYBR Green I was used as an intercalating dye. Amplification was carried out according to the following parameters: preliminary denaturation – 95 °C, 5 min; 35 cycles, including the following stages: 95 °C – 10 sec; 58 °С – 10 sec; 72 °С – 10 sec. At the end, a 10-minute final elongation was carried out at 72°C. Quantitative control of the matrix was carried out using gene-specific primers for household genes (Ef-1α elongation factors). Total RNA was used as a negative control, without the RT-PCR step. The values of the relative level of transcripts of the studied genes were calculated using 2-∆∆Ct (Eprintsev et al. , 2008).
Statistical data processing. The experiments were carried out in 3-fold biological repetition, analytical determinations for each sample were carried out in three repetitions. Statistical analysis of the obtained data was carried out using the STATISTICA 12.0 program. Quantitative measures were assessed for compliance with the normal distribution using the Shapiro-Wilk test. The results on the graphs were expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The differences were analysed for statistical significance using the Student's test. In addition, the ANOVA univariate analysis of variance was used. The differences presented in the paper are statistically significant
(p≤0.05).
RESULTS
During the study on the effect of salinity on the enzymatic activity of GABA-T in green corn leaves, it was found that from the first hour of the experiment, the total enzymatic activity of GABA-T increased relative to control samples (Fig. 1). By the third hour, there was a temporary decrease in the values of total enzymatic activity, however, starting from the 6th hour, the values of catalytic activity gradually increased, reaching their maximum by the 24th hour of the experiment (Fig. 1).
Analysis of the international NCBI database showed that two GABA-T genes are currently annotated for the genome of maize (Zea mays L.). The GTA1 (LOC103632117) gene is located on chromosome 7 and consists of 5 exons. The GTA2 gene (LOC103645944) is located on chromosome 2 and contains 19 exons (Popova et al., 1995). Unfortunately, the role of both genes in regulating the functioning of GABA-T under the influence of salt stress has not yet been established.
Measurement of the relative level of transcripts of the GTA1 GABA transaminase gene under salt stress showed that a significant increase in mRNA levels was observed from the first hour. By the 3rd hour of the experiment, the relative level of transcripts decreases by 2 times and by the 6th hour it becomes comparable to the values noted in the control group of plants. After a day (24 hours) of the experiment, there was a significant decrease in the relative level of transcripts – the GTA1 gene was almost completely inactivated (Fig. 2).
Analysis of the transcriptional activity of the GTA2 gene in the first hours of salt exposure demonstrated low values of the relative level of transcripts of this gene. However, after 3 hours, there was a significant increase in mRNA levels (Fig. 3).
Table 1 : Nucleotide sequences of primers to GABA transaminase genes
|
Gene |
Primer |
Nucleotide sequence |
Temperature, °С |
|
GTA1 |
Forward |
TGGTGCACAGCTTTAGGTGG |
62 |
|
Reverse |
GTGGTTGTGGTGGATTGCTC |
||
|
GTA2 |
Forward |
TCTACGGGGAAGCCCTCAAG |
57 |
|
Reverse |
TTGAGCCACCATTTGCTTGG |
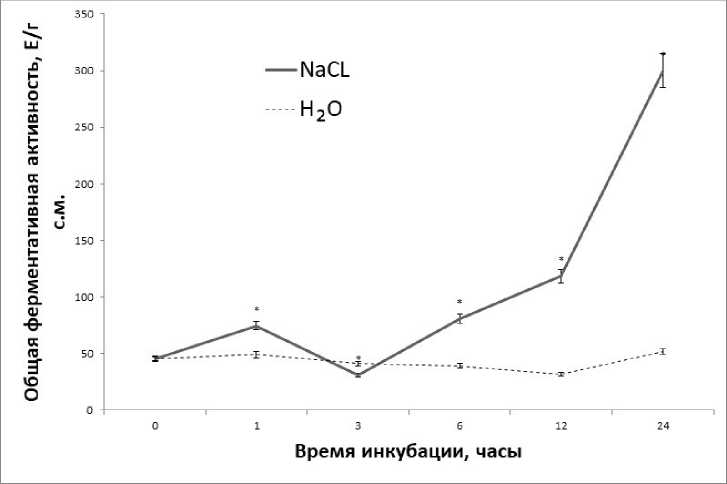
values of the control and experimental groups were statistically significant (p≤0.05).
Figure 1. Changes in the total enzymatic activity of GABA-T during salinization (n=3). The differences between the
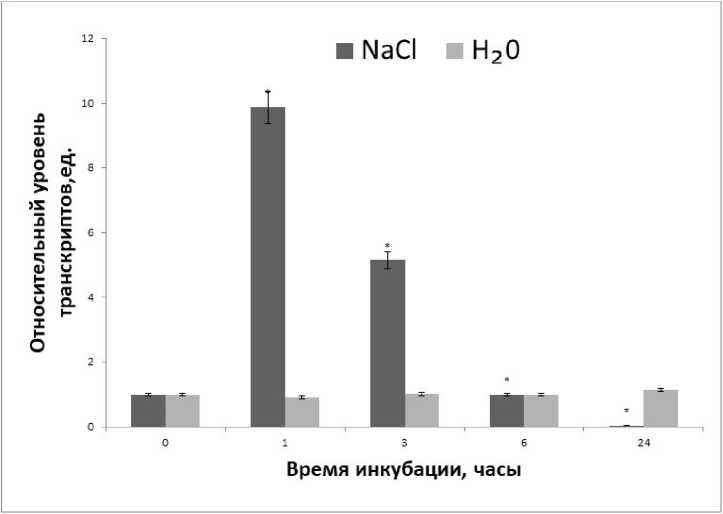
Figure 2. Dynamics of GTA1 gene expression from corn leaves incubated in a medium with 150 mM NaCl. The differences between the values of the control and experimental groups were statistically significant (p≤0.05).
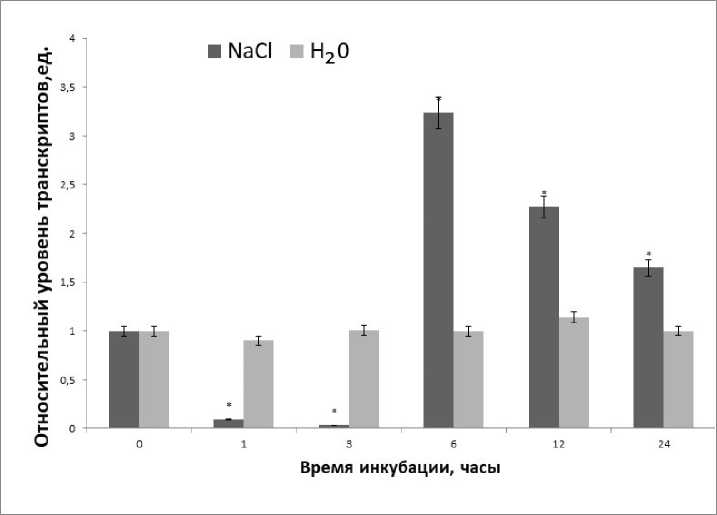
Figure 3. Dynamics of GTA2 gene expression from corn leaves incubated in a medium with 150 mM NaCl. The differences between the values of the control and experimental groups were statistically significant (p≤0.05).
DISCUSSION
transcriptional activity of the GTA1 and GTA2 genes. It
The study showed that under conditions of salinization caused by sodium chloride, the catalytic activity of GABA transaminase increases, which indicates the activation of the stress response pathway – GABA shunt. In addition, it was found that the increase in enzymatic activity values is due to the induction of is important to note that during 24 hours of salt exposure, a high level of catalytic activity of the enzyme was maintained by both genes, but in different time periods: in the first 3 hours, the GTA1 gene is actively expressed, while starting from 6 hours there is an increase in the relative level of transcripts of the GTA2 gene, while the GTA1 gene significantly decreases its transcriptional activity during this period. It is possible that the GTA2 gene plays a key role in GABA catabolism in the process of plant cell adaptation to salt stress, while the GTA1 gene ensures the backlash and accumulation of GABA in the first hours of salinity.
Moreover, the assumptions about the activation of the GABA shunt under these conditions are consistent with the results of the study of the functioning of the SSADH under salinization, obtained by us earlier, which also demonstrated an increase in the transcriptional activity of the SSADH-1 gene encoding succinyl semialdehyde dehydrogenase in the corn genome (Anokhina et al. , 2022). As previously established, in the first six hours of salinization, the TCA cycle is actively functioning, providing the cell with energy under stressful conditions, but after 6 hours, an adaptive mechanism is activated – glutamate dehydrogenase "redirects" metabolic flows from the TCA cycle to the synthesis of glutamate by aminating 2-oxoglutarate (Anokhina, 2022). Glutamate is transported to the cytoplasm where it is decarboxylated into GABA. GABA from the cytoplasm is transported back to the mitochondria, thereby signaling about salt stress conditions to the cell, activating the catabolic function of GABA-T. Subsequently, GABA is reaminated in the mitochondria to the SSA, which is supplied to the TCA cycle for some time, thereby supporting energy metabolism, providing an adaptive response of cellular metabolism to the action of salt stress.
FUNDING
The work was carried out with the financial support of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation as part of the state assignment to universities in the field of scientific activities for 20232025, project No. FZGU-2023-0009.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Features of GABA-transaminase functioning in Zea mays L. leaves under salinity
- Abd-Alla A. M., Jones R. A., Abou-Hadid A. F. (1992). Salinity stress alters the vegetative and reproductive growth of cucumber plants.
- Symposium on Soil and Soilless Media under Protected Cultivation in Mild Winter Climates. 323, 411-422.
- Alexandrov N. N., Brover, V. V., Freidin, S., Troukhan, M. E., Tatarinova, T. V., Zhang, H., Swaller T.J., Lu Yu-Ping, Bouck J., Flavell J. B., Feldmann, K. A (2009). Insights into corn genes derived from large-scale cDNA sequencing. Plant Mol. Biol. 69, 179.
- Anokhina G.B. (2022). Analiz mekhanizmov dejstviya stressovyh faktorov na funkcionirovanie fermentov metabolizma 2-oksoglutarata v list'yah kukuruzy : dis. kand. biol. nauk: 1.5.4. ; 1.5.21. - Voronezh State University, Voronezh, 201.
- Anokhina G. B., Shakhov Z. N., Eprintsev A. T.. (2022). The role of the methyl status of the promoter ssadh1 gene in the regulation of the functioning of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase in corn leaves (Zea mays L.) under salt stress. Proceeding of Voronezh state university. Series: Chemistry. Biology. Pharmacy. 4, 44-47.
- Araujo W. L., Tohge, T., Nunes-Nesi, A., Daloso, D. M., Nimick, M., Krahnert, I., Bunik V.I., Moorhead G. B. G., Fernie, A. R. (2012). Phosphonate analogs of 2-oxoglutarate perturb metabolism and gene expression in illuminated Arabidopsis leaves. Front. Plant Sci. 3, 114.
- Awad R., Levac, D., Cybulska, P., Merali, Z., Trudeau, V. L., Arnason, J. T. (2007). Effects of traditionally used anxiolytic botanicals on enzymes of the y-aminobutyric acid (GABA) system. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 85, 933-942.
- Coleman S. T., Fang, T. K., Rovinsky, S. A., Turano, F. J., Moye-Rowley, W. S. (2001). Expression of a glutamate decarboxylase homologue is required for normal oxidative stress tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 276, 244250.
- Eprintsev A. T., V. N. Popov, D. N. Fedorin (2008). Identifikaciya i issledovanie ekspressii genov //Voronezh: Voronezh University Press, 63.
- Garcia A. B., Engler, J. D. A., Iyer, S., Gerats, T., Van Montagu, M., Caplan, A. B. (1997). Effects of osmoprotectants upon NaCl stress in rice. Plant Physiol. 115, 159-169.
- Gilliham M., Tyerman S. D. (2016). Linking metabolism to membrane signaling: the GABA-malate connection. Trends Plant Sci. 21, 301.
- Hichem H., Mounir, D. (2009). Differential responses of two maize (Zea mays L.) varieties to salt stress: changes on polyphenols composition of foliage and oxidative damages. Ind Crops Prod. 30, 144-151.
- Hussain K., Nisar, M. F., Majeed, A., Nawaz, K., Bhatti, K. H., Afghan, S., Shahazad A., Zia-ul-Hussnian, S. (2010). What molecular mechanism is adapted by plants during salt stress tolerance? AJB 9, 4.
- Omoto E., Taniguchi M., Miyake H. (2012). Adaptation responses in C4 photosynthesis of maize under salinity //J. Plant Physiol. 169, 469-477.
- Popova L. P., Stoinova Z. G., Maslenkova L. T. (1995). Involvement of abscisic acid in photosynthetic process in Hordeum vulgare L. during salinity stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 14, 211-218.
- Ramesh S. A., Tyerman, S. D., Gilliham, M., Xu, B. (2017). y-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) signalling in plants. CMLS. 74, 1577-1603.
- Seifikalhor M., Aliniaeifard, S., Hassani, B., Niknam, V., Lastochkina, O. (2019). Diverse role of y-aminobutyric acid in dynamic plant cell responses. Plant Cell Rep. 38, 847-867.
- Szalai G., Janda T. (2009). Effect of salt stress on the salicylic acid synthesis in young maize (Zea mays L.) plants. J Agron Crop Sci. 195, 165-171.
- Wang Y., Gu, W., Meng, Y., Xie, T., Li, L., Li, J., Wei, S. (2017). y-Aminobutyric acid imparts partial protection from salt stress injury to maize seedlings by improving photosynthesis and upregulating osmoprotectants and antioxidants. Sci. Rep. 7, 436.
- Zhang M., Liu, Z., Fan, Y., Liu, C., Wang, H., Li, Y., Xin.Y., Gai Y., Ji, X. (2022). Characterization of GABA-transaminase gene from mulberry (Morus multicaulis) and its role in salt stress tolerance. Genes. 13, 501.


