Features of participation of the population of cities of the European North of Russia in public and municipal administration
Автор: Sekushina I.A.
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Regional economy
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.16, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Citizens’ participation in managing the country’s development contributes to the formation of civil society and acts as a key element of democracy. In Russia, where three-quarters of the population are urban residents, it is especially important to study these issues in relation to cities, so as to understand the processes taking place in society and work out effective strategies for its development. The aim of the work is to consider ways in which residents of cities in the European North of Russia participate in state and municipal administration and to identify its features in settlements of different sizes. Based on the data of the Central Election Commission of the Russian Federation we analyze the turnout of residents of 68 cities of the European North of Russia for the presidential election of the Russian Federation (2018) and the election to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation (2021). We also assess the level of voter support provided to President Vladimir Putin and the United Russia party. It is revealed that the electoral activity of residents is determined to a greater extent by the peculiarities of the structure of the city’s economy rather than the size of the city. Based on the analysis of the results of voting for the choice of urban improvement objects, it was found that residents of sparsely populated cities are more motivated and involved in these processes. We also find out that territorial public self-government is most actively used in small, rather than large, cities. In order to assess the informal mechanisms of citizens’ participation, we analyze the availability of official profiles of local self-government bodies on VKontakte social media and the number of their subscribers, as well as data on the number of participants in informal urban communities. We have revealed that this method of communication with the authorities is mostly used by residents of small settlements. Scientific significance of the study lies in determining the features of dissemination of various mechanisms of civic participation, depending on the type of city. Practical significance lies in the possibility of using our findings by the authorities in improving the policy of involving citizens in management processes.
Cities, civic participation, political participation of the population, local self-government, election, territorial self-government, european north of Russia
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147241613
IDR: 147241613 | УДК: 332.1(470.12) | DOI: 10.15838/esc.2023.4.88.7
Текст научной статьи Features of participation of the population of cities of the European North of Russia in public and municipal administration
The research funded by Russian Science Foundation grant 23-28-01615 “Formal and informal mechanisms of people’s participation in the development of municipalities: Features and prospects of development in modern conditions”,
In December 2023, Russia will celebrate the 30th anniversary of the adoption by popular vote of the country’s highest normative legal act – the Constitution of the Russian Federation1. This document establishes the foundations of the constitutional system of the state, according to which “the people exercise their power directly, as well as through state authorities and local selfgovernment bodies”. A referendum and free elections are the highest form of expression of the power of the people. Also, Russian citizens have the right to participate in the management of state affairs both personally and through their representatives; to send individual and collective appeals to state authorities and local selfgovernment. In any democratic society, the active participation of the population contributes to the formation of civil society as the main condition of the rule of law and an important tool for building a mutual dialogue between citizens and authorities (Kudashova, Zhukova, 2021).
In Russia, the importance of involving the population in the processes of managing the development of territories is noted at the highest level. In April 2023, at a meeting of the Council for the Development of Local Self-Government, Russian President Vladimir Putin stressed the importance of direct participation of residents in decision-making2. In the Fundamentals of the State Policy of Regional Development of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2025, the involvement of citizens to participate in the governance of the country, increasing their civic responsibility in solving issues of socio-economic development of territories is indicated as one of the tools for improving the efficiency of the work of state authorities and local self-government.
The effectiveness of the work of public authorities and local self-government is also largely ensured by the presence of a developed system of social communications with citizens, focused on the mutual exchange of information on possible ways to solve urgent problems. For example, the authorities, unlike the residents themselves, do not always manage to fully assess the existing difficulties in the work of transport or housing and communal infrastructure. An equally important issue is the choice of locations for the construction of social or cultural and leisure facilities. As practice shows3, making such decisions without taking into account the opinions of citizens can lead to conflict situations and even protests.
The Russian Federation is characterized by a fairly high level of urbanization: almost three-quarters of its population lives in urban settlements. In many ways, they determine the trajectory of socio-economic development in Russian regions. This is especially true for the country’s Northern territories, a specific feature of which is the concentration of population and production mainly in cities.
In the scientific literature devoted to the study of civic participation, the problems of involving the population in solving issues of territorial development are considered mainly on the examples of large and largest cities and in much rarer cases – medium and small cities. At the same time, there are very few studies in Russian science that address the peculiarities of citizen involvement in cities of various types, depending on the number of people or the specifics of socio-economic development.
Taking into account the above, the aim of the work was to study the practice of participation of residents of the cities of the European North of Russia (ENR) in state and municipal administration and to identify its features in settlements of different sizes. In order to achieve this goal, the following tasks have been solved: a review of modern research devoted to the study of forms and instruments of public participation has been conducted; indicators of electoral activity of residents of the cities of the ENR in the RF presidential elections and elections to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation have been analyzed; the analysis of the number and proportion of the population of the cities of the ESR who took part in the voting on the choice of improvement facilities within the framework of the federal project “Formation of a comfortable urban environment” is presented; the activity of citizens in terms of using such a tool as territorial public self-government (TPSG) is considered; the number of subscribers to the official pages of local self-government of the cities of the ENR on the social media VKontakte and unofficial urban communities was analyzed.
Scientific novelty of the work consists in analyzing both formal (elections of the President of the Russian Federation and to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly, citizens voting for the choice of objects of landscaping, territorial public self-government) and informal (social media of local self-government bodies and informal urban communities) mechanisms of public participation in state and municipal government, as well as identifying features of their distribution depending on the size of the city.
Research materials and methods
The methodological basis of the research includes the works of domestic and foreign scientists in the field of regional economy, state and municipal administration, institutional foundations of the formation of civil society. In the process of work, methods of synthesis and generalization, monographic, statistical, qualitative and quantitative data processing were used. The main sources of information were the official data of Rosstat, including databases of indicators of municipalities; information contained on the official websites of local self-government bodies of the cities within the ENR.
The general logic of the study was to consider not only formal, i.e. legislatively fixed, mechanisms for the participation of citizens, but also informal or unregulated ways of showing civic activity. At the same time, a big problem is the almost complete absence of any statistical data in the context of municipalities that allow making such an assessment. Annual reports on the activities of heads of cities or local administrations do not always have a section dedicated to the participation of residents in the development of the city.
That is why, within the framework of this study, the mechanisms of civic engagement were taken as a basis, the assessment of which could be carried out in all 68 cities of the European North of Russia. Among the official forms of citizens’ participation are the elections of the President of the Russian Federation (March 18, 2018) and the elections to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the eighth convocation (September 19, 2021). Data from the Central Election Commission of the Russian Federation (CEC of the Russian Federation) served as materials for analysis about the turnout at the elections and the share of voters who voted for the current President of the Russian Federation Vladimir Putin and the United Russia party.
In addition to studying the electoral activity of the population, an analysis of the practice of citizens’ participation in voting on the choice of public spaces for landscaping was carried out within the framework of the federal project “Formation of a comfortable urban environment” of the national project “Housing and urban environment”.
The experience of using such a mechanism of civic participation as territorial local self-government (TLSG) is also considered. The main source of information in this case was the information provided on the official websites of local selfgovernment bodies of cities, as well as Associations of municipalities of constituent entities of the ENR.
To assess the informal mechanisms of participation of residents in all cities of the European Union, an analysis of the availability of official pages of local self-government bodies on the social media VKontakte and the number of their subscribers was carried out. Data on the number of participants of informal urban communities on the social media were also analyzed (if there are several of them, the largest group was taken).
Theoretical aspects of the study
Many works of both regionalist scientists and sociologists are devoted to the study of issues of population participation in the development of settlements. At the same time, there is currently no consensus in the academic community regarding the definition of the very concept of “public participation”. Mainly in domestic and foreign literature, modern authors consider social, civil, and political participation. These concepts are quite closely interrelated and are largely determined by the scale of issues in which citizens participate.
In one of the studies4, the authors identify four levels of social activity of the population: 1) neighborhood, 2) social (interpersonal) participation, 3) civic participation, 4) political participation. If in the first case people are ready to participate in solving issues of a rather domestic nature, and the ways of expressing activity are more informal, then in the latter case we are already talking about formalized participation in political life through such forms as elections or citizens’ meetings. The basic directions of social or interpersonal participation are volunteering and charity; activity in solving citywide problems; cultural, sports, professional associations of citizens; protection of the interests of individual social groups (Ukhanova, 2021).
Researchers (Nikovskaya, Skalaban, 2017) consider civic participation as “a process by which citizens directly or indirectly influence what decisions are made by authorities, affecting public interests”. At the same time, the authors identify a number of key characteristics of civic participation, including the presence of motivation, voluntariness and awareness of the actions of participants.
In the scientific literature, there are several levels of involvement of residents in management processes according to the degree of increase in the intensity of interaction between the authorities and the population: informing, consulting, involvement, delegation and partnership (Koroleva, Kournikova, 2019).
According to the level of influence of the population on management decisions, three main models can be distinguished:
– imitation or lack of participation;
– nominal participation;
– real influence of citizens (Revyakin, 2017).
For a long time in Russia, only the practices of informing and consulting, which relate to the nominal participation of the population, were mainly used. In recent years, there has been a gradual transition to more active involvement of citizens in making managerial decisions, but these processes do not always proceed smoothly.
The mechanisms of public participation in state and municipal administration can also be conditionally divided into formal, i.e. legally regulated, and informal, i.e. not fixed from a legal point of view, but playing a significant role in the management processes for the development of territories ( Fig. 1 ).
Elections to state or local government bodies are a form of direct democracy and one of the ways of political participation of the population in the management of territorial development, and issues of electoral activity of the population are considered by a large number of researchers (Larichev, 2019; Dementieva, 2020; Nikitina, 2021; Tavares, Carr, 2013; Gok^e-Kizilkaya, Onursal-Be§gul, 2017).
Among the major scientific organizations, the Global Citizenship Observatory (GLOBALCIT) can be distinguished. Scientists of this organization have published a whole set of works devoted to the study of public participation in national and local elections in the European Union (Peltoniemi, 2018; Carvalhais, Oliveira, 2019; Korzec, Pudzianowska, 2021, etc.). There are studies conducted not only in the context of a particular state, but also cross- country comparisons. For example, the work (Hutcheson, Russo, 2021) presents an analysis of voter turnout in municipal elections and elections to the European Parliament in 28 EU countries.
In Asian countries, the issue of public participation in elections to state or local authorities is also very relevant. In particular, the study of the political activity of the population in China is considered in the works (Zhang et al., 2015; Hill, 2020; Martinez-Bravo et al., 2022). Elections in China are fundamentally different from elections in Western democracies, since there is no party competition. However, at present, the Communist Party of China allows competitive elections at the lowest level of government: urban and rural residents have the right to elect their representatives to local committees (Villagers’ Committee and Residents’ Committee, respectively) (Xi, Wen, 2019). We should note that, since for a long time until the beginning of the 2010s, the rural population prevailed over the urban population in China, the attention of scientists was mainly focused on studying electoral activity in Chinese villages and villages. This was also due to the fact that elections were allowed in cities only in 2000, whereas in rural areas since the late 1980s. Research results show that one of the features of
Figure 1. Formal and informal mechanisms of public participation in state and municipal governance
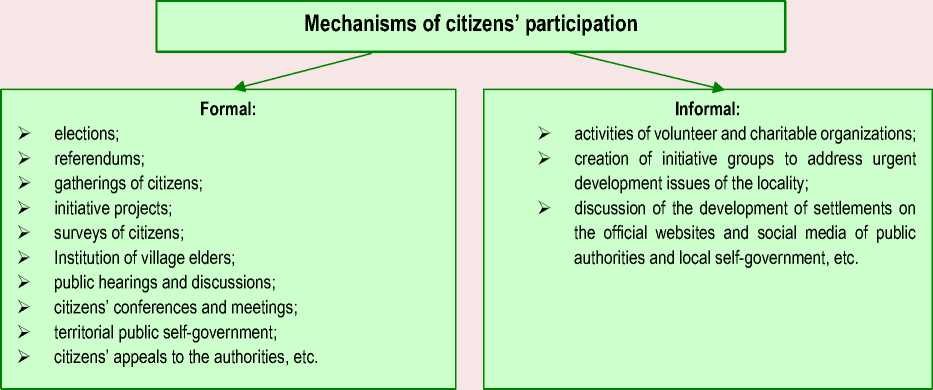
Source: own compilation.
local elections in China is the high activity of rural residents (Kennedy et al., 2018; Xi, Wen, 2019).
Among the domestic works on the study of electoral activity of citizens, it is possible to single out studies conducted on a regular basis by the Russia Public Opinion Research Center (VCIOM)5 or the Russian Public Institute of Electoral Law6.
One of the current issues is the involvement of the population in the processes of strategic management of the development of their settlements. According to Article 13 of Federal Law 172-FZ, dated June 28, 2014 “On strategic planning in the Russian Federation”, a public discussion of the documents being developed is envisaged, however, the residents themselves are not among the participants in strategic planning. Unfortunately, in Russian practice, local governments are often not interested in in-depth discussion of the developed draft strategic planning documents and receiving feedback from the local community (Charakhchyan, Bondarenko, 2017). In the vast majority of cases, the population is involved in the strategic planning process only at the stage of strategy approval through a public hearing procedure, which is often formal in nature (Dus, Vlaskina, 2018).
At the same time, it is extremely important at the earliest stages to involve residents in the development of strategies for the socio-economic development of territories, since ultimately the main mission of these documents is to create comfortable living conditions and ensure the wellbeing of citizens (Marquart, 2017).
One of the forms of attracting the population and taking into account their opinions is sociological surveys on the problems and prospects of the development of the territory of residence. Another tool can be an expert interview with representatives of professional communities whose activities are of great importance for the development of a particular locality.
A significant form of citizens’ participation in the management of territorial development is their involvement in budgetary processes at the local level. In the scientific literature of recent years, there has been an increasing number of works devoted to the study of issues of civil or popular budgeting (Bulabic, Jennie, 2021; Szczepanska et al., 2022; Smoleva, 2021) and crowdfunding (Stiver et al., 2015; Langley et al., 2020; Koniagina et al., 2021; Latysheva, 2020) as forms of public participation in urban development. In the first case, citizens are directly involved in the processes of targeted allocation of public funds. It is the society that determines the urban infrastructure facilities that are necessary to construct for citizens, and which objects should receive funding in the first place. An example of the implementation of this approach in Russia is initiative budgeting within the framework of the “People’s budget” project or voting on the choice of public spaces for improvement within the framework of the national project “Housing and urban environment”.
Civic crowdfunding is not a full-fledged substitute for conventional municipal budgeting, but rather acts as an additional financial instrument (Mayer, 2016). Crowdfunding platforms allow city residents to participate financially in the creation of infrastructure or cultural facilities that are important to them.
One of the forms of public participation in urban development is territorial public selfgovernment (TPSG), which is also reflected in many scientific papers (Bulakh et al., 2021; Gnezdilova, Oganesyan, 2021; Safarov, 2022; Mikhailov, 2023). Unlike local self-government bodies, the presence of TPSG in a municipality is not mandatory and does not have a legally established list of issues that this institution deals with. The main advantage of TPSG is that residents of even a small territory inside the city (for example, a courtyard or a street) can solve problems in a fairly short time, unlike state authorities or local selfgovernment that require much more time in this regard.
An important form of civic participation and a way of interacting with public authorities or local self-government are citizens’ appeals, which can be presented in the form of a proposal, statement or complaint. At the same time, in the era of rapid development of the Internet and social media, citizens have more opportunities to communicate with authorities and express their civic position (Frolov, Agurova, 2019). One of the key advantages of digital technologies is also an increase in the speed of reporting information about an existing problem, which means a reduction in the time it takes to solve it.
The topic of the influence of digitalization processes on the activity of the population has been reflected in the works of many modern authors. For example, the study (Ferrucci et al., 2020), based on the analysis of data from Facebook7 users, analyzes the political activity of U.S. citizens in the online format and the relationship between the frequency of use of the social media and the degree of political involvement. The study (Zagidullin et al., 2021) examines the use of social media as a tool for protest activity of the population in Turkiye.
In general, the literature review allows us to conclude that a fairly large number of works by Russian and foreign authors are devoted to the study of forms and mechanisms of public participation in the development of local territories, in particular cities. At the same time, most authors choose one or more cities as the object of research. At the same time, settlements, as a rule, are either located in the same subject of the Russian Federation, or belong to the same category in terms of population (for example, large cities or million-plus cities). However, the modern urban system is characterized by a variety of different types of cities, respectively, they may differ in the level of activity of residents. The social ties that bind the local community are much less developed in large cities than in small towns (Larichev, 2019), respectively, there may be differences between these types of cities in the use of certain forms of citizen participation in the development of a locality.
In this study, using the example of the European North of Russia as one of the Russian macroregions, an attempt is made to consider the issue of the dissemination of citizen participation practices in cities of different sizes.
Main results of the study
The European North of Russia includes the republics of Komi and Karelia, the Vologda, Murmansk and Arkhangelsk oblasts, including Nenets Autonomous Okrug. The territories under consideration fully meet the criteria for the allocation of regional space, since they are characterized by the presence of well-established economic, infrastructural, socio-cultural intraregional ties, and also differ from other territories by common natural, geographical and climatic conditions, the predominance of the raw materials sector in the economy, the unity of transport and energy infrastructure, low level of population spread, high rates of urbanization (79.8%), exceeding the national average (74.8%).
On the territory of the RF constituent entities under consideration there is a large variety of cities of various types: large (Arkhangelsk, Murmansk, Vologda, Cherepovets), big (Petrozavodsk, Syktyvkar, Severodvinsk), medium (Kotlas, Ukhta, etc.) and small, in a quarter of which the population is less than 10 thousand people ( Tab. 1 ).
The choice of the object of research was also due to the fact that cities vary by economic specialization or features of the structure of the economy. In particular, there are cities with a predominance of mining (Vorkuta, Ukhta, Kostomuksha, Olenegorsk, etc.) and manufacturing (Cherepovets, Segezha, Monchegorsk, etc.) industries, tourist cities (Veliky Ustyug, Kirillov, etc.), etc. Many localities are single-industry towns (Novodvinsk, Yemva, Koryazhma, Sokol, etc.) or belong to the category of closed administrative-territorial entities (Zaozersk, Mirny, etc.).
Table 1. Number of cities in the regions of the European North of Russia / share of the population living in them, in the total population of the RF constituent entity*, %
|
Region |
Population |
Total |
||||
|
250 thousand – 1 million people |
100–250 thousand people |
50–100 thousand people |
10–50 thousand people |
less than 10 thousand people |
||
|
Republic of Karelia |
- |
1 / 44.7 |
- |
5 / 19.1 |
7 / 10.0 |
13 / 73.8 |
|
Komi Republic |
- |
1 / 30.3 |
2 / 18.5 |
5 / 16.3 |
2 / 2.4 |
10 / 67.5 |
|
Arkhangelsk Oblast (including NAO) |
1 / 31 |
1 / 16.2 |
1 / 5.8 |
7 / 18.0 |
4 / 1.9 |
14 / 72.9 |
|
Vologda Oblast |
2 / 54.3 |
- |
- |
5 / 8.8 |
8 / 5.0 |
15 / 68.1 |
|
Murmansk Oblast |
1 / 40.6 |
- |
- |
11 / 41.2 |
4 / 4.1 |
16 / 85.9 |
|
Total for ENR entities |
4 / 29.4 |
3 / 15.3 |
3 / 4.8 |
33 / 19.0 |
25 / 4.3 |
68 / 72.8 |
* As of January 1, 2023.
Source: own compilation on the basis of Rosstat data: The population of the Russian Federation by municipality. Available at:
At the first stage of our research, we analyzed the political activity of residents of the cities of the ENR on the basis of data from the RF Central Election
Commission on the results of the presidential election held in 2018 and the election to the State Duma of the Federal Assembly held in 2021 ( Tab. 2 ).
Table 2. Results of the RF presidential election (2018) and the election to the State Duma of the RF Federal Assembly (2021), %
|
City |
Population, people (2023) |
RF presidential election (2018) |
election to the State Duma of the RF Federal Assembly (2021)* |
||
|
Turnout |
Proportion of those who voted for Vladimir Putin |
Turnout |
Proportion of those who voted for the United Russia party |
||
|
Petrozavodsk |
235793 |
60.2 |
71.4 |
40.5 |
30.6 |
|
Kostomuksha |
25928 |
61.3 |
77.8 |
38.8 |
34.1 |
|
Kondopoga |
25295 |
61.8 |
69.0 |
44.1 |
26.7 |
|
Segezha |
23074 |
57.3 |
74.7 |
35.3 |
34.6 |
|
Sortavala |
14787 |
59.9 |
75.1 |
39.9 |
30.4 |
|
Medvezhyegorsk |
11737 |
53.9 |
69.4 |
40.3 |
29.3 |
|
Kem |
9712 |
57.4 |
75.1 |
43.2 |
26.1 |
|
Pitkyaranta |
8094 |
54.4 |
71.7 |
33.3 |
33.0 |
|
Olonets |
7631 |
56.0 |
73.7 |
39.5 |
35.1 |
|
Belomorsk |
7407 |
50.5 |
72.0 |
36.3 |
36.1 |
|
Pudozh |
7207 |
52.4 |
72.0 |
41.1 |
24.8 |
|
Suoyarvi |
6819 |
53.7 |
68.7 |
41.0 |
32.5 |
|
Lahdenpohya |
5855 |
55.9 |
75.2 |
38.9 |
30.2 |
|
Republic of Karelia |
527880 |
57.1 |
73.0 |
39.6 |
31.7 |
|
Syktyvkar |
220042 |
61.3 |
68.9 |
40.3 |
27.2 |
|
Ukhta |
78081 |
61.8 |
71.1 |
41.0 |
28.1 |
|
Vorkuta |
56389 |
50.3 |
74.1 |
26.6 |
27.6 |
|
Pechora |
34383 |
57.8 |
72.6 |
35.8 |
27.3 |
|
Usinsk |
31358 |
62.4 |
74.2 |
35.7 |
28.7 |
|
Sosnogorsk |
22032 |
62.1 |
68.0 |
41.1 |
26.8 |
|
Inta |
19529 |
50.4 |
68.5 |
30.9 |
31.2 |
|
Yemva |
10779 |
59.6 |
64.8 |
43.1 |
28.7 |
|
Vuktyl |
9198 |
62.8 |
70.1 |
41.7 |
26.4 |
|
Mikun |
8401 |
63.5 |
69.6 |
42.2 |
29.3 |
|
Komi Republic |
726434 |
60.4 |
71.4 |
39.5 |
29.4 |
|
Arkhangelsk |
298617 |
57.0 |
73.7 |
38.6 |
31.5 |
|
Severodvinsk |
156056 |
64.9 |
78.3 |
45.0 |
27.7 |
|
Kotlas |
56122 |
64.4 |
72.2 |
41.4 |
23.6 |
|
Novodvinsk |
32826 |
61.6 |
74.7 |
38.4 |
33.2 |
End of Table 2
|
City |
Population, people (2023) |
RF presidential election (2018) |
election to the State Duma of the RF Federal Assembly (2021)* |
||
|
Turnout |
Proportion of those who voted for Vladimir Putin |
Turnout |
Proportion of those who voted for the United Russia party |
||
|
Koryazhma |
34002 |
61.8 |
70.9 |
41.0 |
27.6 |
|
Mirny |
27174 |
76.4 |
82.0 |
62.0 |
53.5 |
|
Velsk |
21406 |
59.8 |
69.4 |
39.2 |
26.4 |
|
Nyandoma |
18146 |
57.3 |
74.0 |
39.8 |
29.2 |
|
Onega |
16449 |
54.2 |
72.8 |
35.3 |
31.8 |
|
Kargopol |
8737 |
59.4 |
71.5 |
40.7 |
31.1 |
|
Shenkursk |
4524 |
54.3 |
72.6 |
32.4 |
33.9 |
|
Mezen |
2832 |
62.5 |
71.1 |
41.7 |
31.2 |
|
Solvychegodsk |
1858 |
61.5 |
67.5 |
46.3 |
28.5 |
|
Arkhangelsk Oblast |
964304 |
59.2 |
75.3 |
41.6 |
32.2 |
|
Naryan-Mar |
23579 |
60.0 |
71.3 |
40.4 |
25.4 |
|
Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
41383 |
63.6 |
71.6 |
42.6 |
29.1 |
|
Vologda |
311628 |
66.3 |
69.7 |
42.9 |
30.9 |
|
Cherepovets |
301040 |
69.2 |
73.4 |
42.0 |
33.4 |
|
Sokol |
34298 |
58.7 |
73.1 |
40.3 |
34.3 |
|
Veliky Ustyug |
28266 |
64.6 |
73.6 |
45.7 |
25.7 |
|
Gryazovets |
14424 |
64.3 |
72.5 |
46.7 |
33.2 |
|
Babaevo |
11646 |
63.6 |
74.1 |
43.0 |
35.4 |
|
Vytegra |
10292 |
56.2 |
71.9 |
45.2 |
33.2 |
|
Totma |
8647 |
63.3 |
68.7 |
48.2 |
36.2 |
|
Kharovsk |
8361 |
59.3 |
72.0 |
45.6 |
36.6 |
|
Belozersk |
8183 |
56.8 |
69.8 |
43.3 |
32.2 |
|
Ustyuzhna |
62.9 |
71.3 |
44.8 |
37.2 |
|
|
Nikolsk |
7607 |
60.3 |
70.1 |
44.3 |
32.4 |
|
Kirillov |
7069 |
64.1 |
70.3 |
47.0 |
33.3 |
|
Krasavino |
63.8 |
76.5 |
46.0 |
37.3 |
|
|
Kadnikov |
4022 |
59.4 |
74.5 |
47.0 |
33.7 |
|
Vologda Oblast |
1128782 |
66.1 |
72.4 |
45.5 |
34.3 |
|
Murmansk |
267422 |
64.8 |
76.9 |
34.9 |
28.8 |
|
Apatity |
48748 |
68.8 |
71.2 |
38.5 |
30.8 |
|
Severomorsk |
43394 |
70.8 |
79.4 |
49.1 |
49.7 |
|
Monchegorsk |
39477 |
64.6 |
76.2 |
36.7 |
30.8 |
|
Kandalaksha |
28438 |
61.2 |
74.1 |
36.9 |
31.4 |
|
Kirovsk |
24271 |
72.1 |
71.1 |
38.2 |
28.4 |
|
Olenegorsk |
20875 |
62.6 |
79.1 |
39.4 |
34.4 |
|
Polyarny |
12154 |
70.5 |
77.8 |
50.5 |
29.6 |
|
Kovdor |
15423 |
62.6 |
76.3 |
36.3 |
29.2 |
|
Polyarnye Zori |
14078 |
74.4 |
72.2 |
40.3 |
35.7 |
|
Zapolyarny |
14231 |
62.4 |
75.4 |
37.5 |
32.4 |
|
Snezhnogorsk |
10023 |
65.5 |
76.8 |
34.5 |
27.7 |
|
Gadzhievo |
77.8 |
80.1 |
53.6 |
39.8 |
|
|
Kola |
8933 |
60.7 |
77.0 |
34.2 |
32.0 |
|
Zaozersk |
7760 |
69.0 |
80.6 |
47.2 |
40.8 |
|
Ostrovnoy |
63.0 |
82.7 |
41.7 |
34.5 |
|
|
Murmansk Oblast |
658698 |
66.3 |
76.4 |
43.7 |
35.8 |
|
Russian Federation |
146447424 |
67.5 |
76.7 |
51.6 |
49.8 |
Turnout exceeds average values for the RF constituent entity Proportion of voters exceeds average values for the RF constituent entity * Results of voting in the federal electoral district (according to party lists). Source: own compilation on the basis of data from the official website of the Central Election Commission of the Russian Federation. Available at:
In the RF presidential election, residents of ENR cities showed more activity than in the election of State Duma deputies, which corresponds to the situation on average in the regions and the country as a whole. To a certain extent, this is due to the fact that in order to recognize the presidential election as valid, a voter turnout of at least 50% is required, whereas there is no turnout threshold in parliamentary elections.
The analysis of the electoral behavior of citizens in the context of cities within the framework of individual RF constituent entities allowed us to identify the following features. In the Republic of Karelia, a high turnout for the presidential election was recorded in the administrative center – Petrozavodsk (60.2%) and in small towns with a population of 10 to 30 thousand people (with the exception of Medvezhyegorsk). In localities with a population of less than 10 thousand people, the turnout was below the regional average. High level of support for the current President of the Russian Federation Vladimir Putin was observed in the cities of Kostomuksha (77.8%), Kem (75.1%), Sortavala (75.1%), Segezha (74.7%), as well as in sparsely populated Lakhdenpokhya (75.2%) and Olonets (73.7%).
In the election to the State Duma of the Russian Federation, the highest voter turnout was typical for the monotown of Kondopoga (44.1%), as well as the small towns of Kem (43.2%), Pudozh (41.1%), Suoyarvi (41%). A higher level of support for the United Russia party was observed mainly in cities with a population of up to 10 thousand people – Belomorsk (36.1%), Olonets (35.1%), as well as the industrial cities of Segezha (34.6%) and Kostomuksha (34.1%).
In the Komi Republic, the highest turnout in the RF presidential election was recorded in the most sparsely populated cities of the region: Mikun – 63.5%, Vuktyl – 62.8%. In the cities of Usinsk, Sosnogorsk, Ukhta and Syktyvkar, it also exceeded the regional average (60.4%). However, only in three mining cities – Usinsk (74.2%), Vorkuta (74.1%), Pechora (72.6%) – the level of support for Vladimir Putin was higher than the average for the republic (71.4%).
In the Arkhangelsk Oblast, in 9 out of 13 cities, the turnout for the RF presidential election exceeded the regional average (59.2%). Among all the settlements under consideration, the city of Mirny stands out, having the status of a closed city: turnout in it was 76.4%, and the level of support for Vladimir Putin was 82%. Only in one more city in the region – Severodvinsk – the share of those who voted for the current President of the Russian Federation exceeded the average values for the region (78.3%). The turnout for the State Duma election in Mirny was also the highest (62%). More than a third of voters voted for the United Russia party in only two cities: closed city of Mirny (53.5%) and Novodvinsk (33.2%). The lowest level of support was observed in Kotlas (23.6%) and Velsk (26.4%).
In the only city of Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Naryan-Mar, the turnout rates for the RF presidential election (60%) and the State Duma election (40.4%) were lower than the national average (67.5 and 51.6%, respectively) and for the region (63.6 and 42.6%, respectively). At the same time, the level of support for Vladimir Putin by the population of the city is quite high (71.3%), while the United Russia party is supported by only a quarter of voters.
At the presidential election in the Vologda Oblast, the highest voter activity was observed in two major cities of the region: in Vologda – 66.3%, and in Cherepovets – 69.2%. In the remaining cities (all of them belong to the category of small, the turnout was below the regional average (66.1%). The lowest activity is typical for Belozersk (56.8%) and Vytegra (56.2%).
The highest level of support for Vladimir Putin was observed in the two most sparsely populated cities of the Vologda Oblast – Krasavino (76.5%) and Kadnikov (74.5%). In Cherepovets (73.4%), the indicator also exceeded the regional average. On the contrary, in Vologda, the share of those who voted for the current President of the Russian Federation (69.7%) was one of the lowest in the region; the figure is lower only in Totma (68.7%).
A somewhat opposite situation has developed with the turnout for the election to the State Duma of the Russian Federation. The greatest activity of the population was observed in sparsely populated cities: in Totma, the turnout was 48.2%, in Kadnikov and Kirillov – 47% each. In Vologda and Cherepovets, on the contrary, the turnout was very low: 42.9 and 42.0%, respectively. The United Russia Party enjoys greater support in cities with small population: Krasavino (37.3%), Ustyuzhna (37.2%) and Kharovsk (36.6%).
Among all the regions considered, the Murmansk Oblast has the highest voter turnout for the presidential election: an average of 66.3% in the region, which can be explained by the presence of a large number of closed cities. It is the cities of this category that are the leaders in terms of the share of the population participating in the elections. In 2018, the turnout for the elections in the closed city of Polyarnye Zori, closed city of Severomorsk, Gadzhievo and Polyarny (they are part of the closed city of Aleksandrovsk) exceeded 70%. High activity of residents was also observed in Kirovsk (72.1%) and Apatity (68.8%). The level of support for Vladimir Putin is also the highest in closed administrative-territorial entities: Ostrovnoy (82.7%), Zaozersk (80.6%), Gadzhievo (80.1%). The situation with the turnout for the State Duma election and the share of those who voted for United Russia is generally similar.
Conducting population surveys regarding the development of the social, transport or housing and communal services of the city is one of the ways to involve citizens in management processes. Thus, with the beginning of the implementation of the federal project “Formation of a comfortable urban environment” of the national project “Housing and urban environment”, city residents have the opportunity to directly participate in the selection of objects of improvement in their locality via online voting. Currently, as part of the implementation of the national project, more than 55 thousand objects have already been improved, including public spaces and courtyards8.
In 2023, residents of ENR cities also had the opportunity to vote for improvement objects or for specific design projects of public territories. In the context of the RF constituent entities under consideration, the Republic of Karelia and the Arkhangelsk Oblast should be singled out, because voting in these entities was held in almost every city (with the exception of Belomorsk and Solvychegodsk, respectively). For comparison, in the Vologda Oblast, only 8 out of 15 cities applied for participation in the project for the formation of a comfortable urban environment.
The indicator of the share of citizens who took part in the voting, from the total number of inhabitants of settlements, allows us to conclude that the population of small cities, especially those with a population of up to 10 thousand people, is much more involved in these processes. The absolute leader is the city of Kargopol, where over 40% of the population took part in the voting ( Tab. 3 ). In Ustyuzhna and Belozersk, every fourth resident made their choice in favor of the
Table 3. Participation of residents of ENR cities in voting on the choice of public spaces for improvement
|
City |
Number of public spaces put forward for voting, units* |
Number of voters, people |
Population of the city, people |
Number of voters to the population of the city, % |
|
Kargopol |
3 |
3567 |
8737 |
40.8 |
|
Kotlas |
9 |
17492 |
56122 |
31.2 |
|
Ustyuzhna |
3 |
1984 |
7653 |
25.9 |
|
Belozersk |
3 |
2121 |
8183 |
25.9 |
|
Mezen |
2 |
706 |
2832 |
24.9 |
|
Pudozh |
4 |
1734 |
7207 |
24.1 |
|
Veliky Ustyug |
9 |
6508 |
28266 |
23.0 |
8 The all-Russian vote to choose improvement objects has started. National projects of Russia. Available at:
End of Table 3
City Number of public spaces put forward for voting, units* Number of voters, people Population of the city, people Number of voters to the population of the city, % Velsk 3 4698 21406 21.9 Nyandoma 7 3979 18146 21.9 Kirillov 3 1529 7069 21.6 Koryazhma 4 7344 34002 21.6 Naryan-Mar 6 5022 23579 21.3 Kem 3 2066 9712 21.3 Shenkursk 3 962 4524 21.3 Sortavala 6 2797 14787 18.9 Polyarny 3 2167 12154 17.8 Olonets 4 1329 7631 17.4 Totma 3 1505 8647 17.4 Pitkyaranta 3 1384 8094 17.1 Olenegorsk 4 3543 20875 17.0 Suoyarvi 2 1123 6819 16.5 Severomorsk 7 7055 43394 16.3 Mirny 4 4380 27174 16.1 Vytegra 3 1603 10292 15.6 Yemva 1 1670 10779 15.5 Polyarnye Zori 4 2146 14078 15.2 Kandalaksha 4 4331 28438 15.2 Kovdor 2 2347 15423 15.2 Kola 2 1353 8933 15.1 Medvezhyegorsk 4 1770 11737 15.1 Vologda 8 46739 311628 15.0 Severodvinsk 3 23275 156056 14.9 Lakhdenpokhya 3 872 5855 14.9 Segezha 3 3401 23074 14.7 Kondopoga 4 3656 25295 14.5 Ukhta 2 11163 78081 14.3 Cherepovets 6 42893 301040 14.2 Monchegorsk 3 5557 39477 14.1 Apatity 1 6793 48748 13.9 Arkhangelsk 20 40943 298617 13.7 Onega 2 2249 16449 13.7 Petrozavodsk 25 32237 235793 13.7 Inta 3 2644 19529 13.5 Sosnogorsk 4 2978 22032 13.5 Gadzhievo 2 1189 9088 13.1 Kostomuksha 6 3203 25928 12.4 Kirovsk 1 2941 24271 12.1 Syktyvkar 18 26207 220042 11.9 Zaozersk 3 909 7760 11.7 Snezhnogorsk 1 1131 10023 11.3 Usinsk 2 3455 31358 11.0 Murmansk 9 28069 267422 10.5 Pechora 1 3596 34383 10.5 Vorkuta 3 5865 56389 10.4 Novodvinsk 3 2878 32826 8.8 * In the case where one public space is indicated, the vote was held for the choice of a design project for its improvement. Source: information on the number of voting participants was obtained on the basis of materials from websites on the implementation of the federal project “Formation of a comfortable urban environment” in the Republic of Karelia. Available at: https://10.gorodsreda. ru/; in the Komi Republic. Available at: ; in the Arkhangelsk Oblast. Available at: ; in the Vologda Oblast. Available at: ; in the Murmansk Oblast. Available at: ; in Nenets Autonomous Okrug. Available at: landscaping project they liked. Kotlas stands out among medium cities, since almost a third of the population has been active there.
Vologda has the highest rates in the group of large and big cities: about 15% of the population participated in the voting. Residents of Murmansk are less active: only one in ten citizens took part in a survey on the choice of objects for improvement.
Territorial public self-government (TPSG) established by Federal Law 131-FZ, dated October 6, 2003 is also one of the forms of participation of the population in solving issues of local importance. This mechanism is based on the interaction of the residents themselves, who independently determine the list of the most pressing problems and organize themselves on a voluntary basis to solve them. Local self-government bodies, in turn, can provide advisory assistance to TPSGs, as well as provide support in terms of material support for their activities.
The institution of territorial public selfgovernment has a significant potential for the development of small-sized territories. At the same time, at present, in our opinion, the lack of a clear system of accounting for the work of TPSG is a rather serious problem. In particular, among the ENR regions under consideration, the most complete information on the number of TPSG is available only for the Republic of Karelia.
As of July 1, 2023, 572 TPSGs have been created in the region, but only 172 of them (30%) are in cities ( Fig. 2 ). It should be emphasized that the largest number of TPSGs operates in small cities rather than the administrative center of Petrozavodsk. Thus, in the city of Kondopoga with a population of less than 30 thousand people, there are 59 TPSGs, or a third of their total number in the cities. In Belomorsk and Pudozh, where the population is less than 9 thousand people, 24 and 20 TPSGs were created, respectively. This form of civic activity is least common in the following cities: Sortavala (1 TPSG), Lakhdenpokhya (2 TPSGs) and Segezha (3 TPSGs).
In the Arkhangelsk Oblast, as of February 1, 2023, 1,204 TPSGs were registered. At the same
Figure 2. Number of functioning TPSGs in the cities of the Republic of Karelia in 2023; their share in the total number in the cities
3; 2%
4; 2%
5; 3%
5; 3%
6; 4% ----
2; 1%
1; 1%
59; 34%
9; 5%
16; 9%
18; 10%
Kondopoga Belomorsk Pudozh Petrozavodsk Olonets Suoyarvi Pitkyaranta Medveshyegorsk Kostomuksha Kem
Segezha Lakhdenpokhya Sortavala
20; 12% 24; 14%
Source: Register of territorial public self-governments in the Republic of Karelia as of July 1, 2023. Available at: time, the information is presented only in the context of municipal districts, urban or municipal okrugs. Thus, it is difficult to say how many TPSGs there are in cities that do not have this status. At the same time, according to available information, it can be concluded that the leader in the number of functioning TPSGs is Kotlas (33 TPSGs), which belongs to the category of medium cities rather than the largest cities of the oblast, Arkhangelsk (18 TPSGs) and Severodvinsk (2 TPSGs)9.
Based on the materials of the Association of Municipalities of the Komi Republic10, we can conclude that the practice of applying territorial public self-government in cities is used extremely poorly. So, out of all 87 TPSGs of the republic, only one is located in Syktyvkar and two in Inta. Unfortunately, for the Vologda and Murmansk oblasts, up-to-date information on the number of TPSGs is not presented in a systematic form, so it is difficult to draw any definite conclusions for these regions.
In general, in our opinion, TPSGs carry out a very important mission to unite and consolidate people to solve common problems, since not every citizen is ready to show their civic activity individually.
Further, as part of the study, we analyzed the availability of official accounts of local selfgovernment bodies of cities and the number of their subscribers on VKontakte. According to the data obtained during the study, currently in 33 out of 66 municipal formations11, local authorities have an account on VKontakte ( Tab. 4 ). At the same time, the analysis of the share of subscribers from the total population allows us to conclude that residents of large cities are much less active in this type of communication with the authorities.
For example, in Cherepovets, only 1.6% of residents are subscribed to the Cherepovets City Hall community, in Vologda 2.8% of the population is subscribed to the Vologda City Administration group.
Table 4. Number of subscribers to t he official accoun ts of local selfgovernment bodies of the cities of the ENR on VKontakte*
|
No. |
Municipal formation |
Population, people |
Name of the community on VKontakte |
Number of subscribers to the community, units |
Number of participants to the number of population of the municipality, % |
|
1 |
Closed City of Mirny |
27174 |
Official Mirny |
17407 |
64.1 |
|
2 |
ME Polyarnye Zori |
15726 |
Polyarnye Zori |
9570 |
60.9 |
|
3 |
Closed City of Zaozersk |
7760 |
Administration of the Closed City of Zaozersk |
4273 |
55.1 |
|
4 |
UO Naryan-Mar |
23579 |
City of Naryan-Mar |
10368 |
44.0 |
|
5 |
Closed City of Aleksandrovsk |
32232 |
Closed City of Aleksandrovsk |
13699 |
42.5 |
|
6 |
ME Kirovsk |
26253 |
Your Kirovsk |
10754 |
41.0 |
|
7 |
ME Kovdorsky District |
16763 |
Single-industry city of Kovdor |
6827 |
40.7 |
|
8 |
UO Vuktyl |
10365 |
Administration of Urban Okrug “Vuktyl” |
4157 |
40.1 |
|
9 |
Closed City of Ostrovnoy |
1432 |
Administration of the Closed City of Ostrovnoy |
565 |
39.5 |
9 Internet portal of the territorial public self-government of the Arkhangelsk Oblast. Available at: geografiya/
10 Official Internet portal of the Association “Council of Municipalities of the Komi Republic”. Available at: http://atosrk. ru/page/tos_komi
11 We consider 66 municipal entities and not 68, since three cities (Gadzhievo, Snezhnogorsk and Polyarny) are part of one municipality – the closed city of Aleksandrovsk.
End of Table 4
No. Municipal formation Population, people Name of the community on VKontakte Number of subscribers to the community, units Number of participants to the number of population of the municipality, % 10 US Sortavala 17930 Administration of Sortavala Settlement 6326 35.3 11 ME Monchegorsk 41729 Administration of the city of Monchegorsk 13686 32.8 12 UO Kostomuksha 26531 Kostomukshsky Urban Okrug 8585 32.4 13 UO Inta 21092 Administration of ME UO “Inta” 5946 28.2 14 UO Severodvinsk 156731 Administration of Severodvinsk 40784 26.0 15 UO Kotlas 67023 Administration of Urban Okrug “Kotlas” 17095 25.5 16 UO Vorkuta 67702 Vorkuta City Administration 15745 23.3 17 UO Koryazhma 34002 Administration of Urban Okrug “City of Koryazhma” 7775 22.9 18 US Velsk 21815 Administration of Urban Settlement “Velskoye” 4563 20.9 19 UO Usinsk 36025 Administration of Okrug “Usinsk” 7531 20.9 20 UO Ukhta 94168 Administration of MEUO “Ukhta” 18629 19.8 21 ME Olenegorsk 27974 Olenegorsk City Administration 4348 15.5 22 ME Apatity 48763 Apatity City Administration 7205 14.8 23 UO Severomorsk 50949 Administration of the Closed City of Severomorsk 7139 14.0 24 UO Arkhangelsk 303357 Open Arkhangelsk 40796 13.4 25 UO Petrozavodsk 235793 Administration of Petrozavodsky Urban Okrug 29599 12.6 26 US Nikolsk 7607 Nikolsk City Administration 903 11.9 27 UO Novodvinsk 32826 Administration of ME “City of Novodvinsk” 3223 9.8 28 UO Syktyvkar 233105 Official Syktyvkar 21408 9.2 29 US Krasavino 5460 Territorial department in the City of Krasavino 352 6.4 30 US Mikun 8401 Administration of US “Mikun” 516 6.1 31 UO Murmansk 267422 Murmansk City Administration 14713 5.5 32 UO Vologda 318112 Vologda City Administration 8785 2.8 33 UO Cherepovets 301040 Cherepovets Mayor’s Office 4870 1.6 * The number of community members is given as of July 19, 2023. Subscribers can be residents of other municipalities, too. Source: own compilation on the basis of information from the social media VKontakte. Available at: https://
The leaders in population coverage are the closed city of Mirny in the Arkhangelsk Oblast, Municipal Okrug Polyarnye Zori and the closed city of Zaozersk in the Murmansk Oblast, where more than half of the residents are subscribed to the official accounts of local self-government bodies12. Among cities with a population of less than 10
thousand people, only three local governments have a VKontakte page, but the number of subscribers is small. In the city of Nikolsk, about 12% of the population are members of the community “Administration of the city of Nikolsk”, in the city of Krasavino – 6.2% of residents are subscribed to the “Territorial department in the city of Krasavino”, in the city of Mikun – 6.1% are subscribed to the “Administration of Mikun”. In general, greater activity in this form of interaction with local authorities is typical for cities with a population of 10 to 30 thousand people.
We should note that almost all official accounts of local self-government bodies have forms for citizens’ appeals. Any resident of the city in this way can report a problem, ask a question or express their opinion. However, modern digital technologies make it possible to track complaints or suggestions not only in official communities of local authorities. For example, the social media monitoring system
“Incident Management” helps to find and process messages that citizens leave in open sources on the Internet, for example in informal urban communities.
As part of the study, we analyzed the number of participants of such groups on VKontakte ( Tab. 5 ). According to the results, there are such communities in almost all cities of the European North of Russia,
Table 5. Unofficial urban communities on VKontakte*
|
City |
Name of urban community |
Number of participants, units |
Number of participants to the population of the city. % |
|
Ostrovnoy |
Gremikha, Murmansk-140, Ostrovnoy |
10182 |
In 7.2 times |
|
Mezen |
Podslushano Mezen |
14857 |
In 5.2 times |
|
Nikolsk |
Podslushano Nikolsk |
33973 |
In 4.5 times |
|
Shenkursk |
Podslushano Shenkursk |
16318 |
In 3.6 times |
|
Pudozh |
Podslushano v Pudozhe | Karelia |
24214 |
In 3.4 times |
|
Lakhdenpokhya |
Lakhdenpokhya - NAVSEGDA! |
19294 |
In 3.3 times |
|
Velsk |
Podslushano Velsk |
61270 |
In 2.9 times |
|
Suoyarvi |
Podslushano v Suoyarvi |
19256 |
In 2.8 times |
|
Kadnikov |
Podslushano Kadnikov |
11290 |
In 2.8 times |
|
Kargopol |
Podslushano v Kargopole |
24392 |
In 2.8 times |
|
Totma |
Podslushano Totma |
22220 |
In 2.6 times |
|
Pitkyaranta |
Podslushano v Ptk. (Pitkyaranta) |
20390 |
In 2.5 times |
|
Belozersk |
Belozersk |
20005 |
In 2.4 times |
|
Gryazovets |
Podslushano - Gryazovets |
34396 |
In 2.4 times |
|
Kem |
Podslushano | Kem |
22660 |
In 2.3 times |
|
Mikun |
PODSLUSHANO MIKUN In Culture |
18785 |
In 2.2 times |
|
Krasavino |
Podslushano v Krasavino |
12023 |
In 2.2 times |
|
Babaevo |
Podslushano Babaevo |
25152 |
In 2.1 times |
|
Solvychegodsk |
SOLVYCHEGODSK – GLUBINKA RUSI |
3960 |
In 2.1 times |
|
Vuktyl |
“Gorodok Vuktyl” |
18498 |
In 2 times |
|
Sortavala |
Podslushano v Sortavala |
28937 |
195.7 |
|
Vytegra |
Nastroenie – Moya Vytegra |
19571 |
190.2 |
|
Onega |
TIPICHNAYA ONEGA |
30423 |
185.0 |
|
Gadzhievo |
Podslushano v Gadzhievo |
16784 |
184.7 |
|
Veliky Ustyug |
Podslushano Veliky Ustyug |
50955 |
180.3 |
|
Naryan-Mar |
Podslushano | Naryan-Mar |
39670 |
168.2 |
|
Yemva |
g. Yemva (Knyazhpogostskii raion) |
18043 |
167.4 |
|
Belomorsk |
PB/ Podslushano Belomorsk |
12002 |
162.0 |
|
Polyarnye Zori |
Podslushano Polyarnye Zori |
22175 |
157.5 |
|
Snezhnogorsk |
Podslushano v Snezhnogorske |
15772 |
157.4 |
|
Pechora |
Tipichnaya Pechora |
51918 |
151.0 |
|
Kandalaksha |
KANDALAKSHA VKURSE |
41265 |
145.1 |
|
Murmansk |
Murmansk |
385775 |
144.3 |
|
Olonets |
Olonets Live | Novosti raiona |
10974 |
143.8 |
|
Sosnogorsk |
Podslushano Sosnogorsk |
30583 |
138.8 |
|
Zapolyarny** |
Nikel, Zapolyarny, Pechenga. Doska obyavlenii |
40450 |
132.2 |
|
Apatity |
Podslushano Apatity |
63735 |
130.7 |
|
Severomorsk |
Severomorsk Onlain |
56515 |
130.2 |
End of Table 5
City Name of urban community Number of participants, units Number of participants to the population of the city. % Kotlas Kotlas 71744 127.8 Olenegorsk OLENEGORSK VKURSE 25633 122.8 Kirovsk Podslushano Kirovsk Khibiny 28801 118.7 Kirillov KIRILLOV | ONLINE 8275 117.1 Kola Gorod Kola 51 (Kolskii raion) 10265 114.9 Koryazhma*** Uslyshano | Koryazhma, Kotlas 101700 112.8 Vologda Onlain Vologda 346796 111.3 Severodvinsk Severodvinsk life 171493 109.9 Zaozersk Podslushano Zaozersk 8356 107.7 Sokol Podslushano Sokol 36760 107.2 Monchegorsk Podslushano Monchegorsk – No.1 39239 99.4 Kostomuksha ANTIBESEDKA - Kostomuksha 25720 99.2 Usinsk 30139 96.1 Mirny Podslushano Mirny 25306 93.1 Inta PODSLUSHANO INTA 18113 92.7 Novodvinsk IPN † (Novodvinsk) 30419 92.7 Ustyuzhna Podslushano Ustyuzhna 6760 88.3 Vorkuta Khelou, Vorkuta! 47980 85.1 Arkhangelsk Arkhangelsk life 248635 83.3 Petrozavodsk Podslushano v PTZ | Petrozavodsk 193003 81.9 Kondopoga Podslushano Kondopoga 18617 73.6 Kharovsk Gorodok nash Kharovsk 6028 72.1 Ukhta Podslushano Ukhta 56085 71.8 Polyarny Nash Polyarny 8522 70.1 Segezha Segezha 14793 64.1 Kovdor KOVDOR VKURSE 9026 58.5 Nyandoma NYANDOMA 10538 58.1 Medvezhyegorsk Medvezhyegorsk: komanda zhitelei. Perezagruzka 5755 49.0 Syktyvkar Podslushano Syktyvkar 86851 39.5 Cherepovets Cherepovets 93714 31.1 * The number of community members is presented as of July 19, 2023. Subscribers can be not only residents of this municipality. In some cities there are several informal urban communities, the largest ones in terms of the number of participants were taken into consideration in the study. * * The share of community members is calculated from the total population of the city of Zapolyarny, urban-type settlement Nikel, urban-type settlement Pechenga. * ** The share of community members is calculated from the total population of Koryazhma and Kotlas. Source: own compilation on the basis of information from VKontakte. Available at: https://
in some cases the group unites several localities geographically located close to each other, for example, the community “Uslyshano. Koryazhma, Kotlas” unites the population of two corresponding cities, or the group “Nikel, Zapolyarny, Pechenga. Doska obyavleniy”, which includes residents of three settlements at once.
The number of subscribers of groups of small cities is several times higher than the population of the city itself. For example, the community
“Gremikha, Murmansk-140, Ostrovnoy” consists of more than 10 thousand people, which is 7.2 times more than the population of the city of Ostrovnoy itself. The number of participants of the groups “Podslushano” in the small cities of Mezen, Nikolsk, Shenkursk, Pudozh, Lakhdenpokhya exceeds the population of these cities by 3.3– 5.2 times. Such activity, in our opinion, can be explained by two main factors. First, the number of participants in informal groups may include people who currently do not live in a small city, but were born in it. Second, the groups themselves are like some kind of “bulletin board”. In particular, it may publish information about the purchase/sale of goods and services, search for a traveling companion to get to a regional center or a neighboring city, available jobs in organizations and enterprises. That is, the subscribers of the community can be people for whom the published information is of interest, in particular, residents of neighboring urban and rural settlements.
In medium cities, the number of subscribers of unofficial communities is about a third higher than the population of the city itself, for example, in Apatity – 130.7% of the city’ s population, in Severomorsk – 130.2%, in Kotlas – 127.8%. With regard to big cities, we note that only the urban communities of Murmansk (“Murmansk”) and Vologda (“Onlain Vologda”) have the number of subscribers that exceeds the population of the city itself – by 44.3 and 11.3%, respectively. In Petrozavodsk, Syktyvkar and Cherepovets, the number of participants in informal groups on VKontakte is significantly less than the number of city residents.
Conclusion
Thus, according to the results of the research, several key conclusions can be drawn concerning the peculiarities of participation of residents of various types of cities in state and municipal administration.
-
1. In the context of individual constituent entities of the ENR, there are certain differences in the electoral behavior of residents of cities with different number of population. In particular, in the Republic of Karelia and the Vologda Oblast, high turnout for the RF presidential election is typical for large, rather than small, cities. However, regarding the election to the State Duma of the Russian Federation in these regions, the situation was the opposite. In general, the determining factor in the macroregion is the city’s economic specialization, rather than size. In the regions of
-
2. Residents of the most sparsely populated cities (up to 10 thousand people) are much more actively involved in voting on the improvement of the urban environment. On average, every fifth citizen is active in them, whereas in large and big cities their share ranges from 10 to 15%. The difference, in our opinion, can be explained in general by the greater willingness of residents of small cities to participate in the discussion of urban problems. Thus, according to sociological surveys, less than a quarter of residents of Vologda and Cherepovets (23.7 and 23.1%, respectively) have a desire to participate in discussions on topical issues of city development13, and, for example, the majority of residents of the small cities of Kirovsk and Kovdor (51.5 and 50.5%, respectively) are ready to discuss issues of urban improvement (Sharova, Maleus, 2022). The second important factor is that participation in federal projects for the improvement of territories in conditions of local budgets shortage
-
3. In urban settlements of the ENR, territorial public self-government, as an instrument of civic participation, is less actively used compared to rural areas. In particular, in the Republic of Karelia, less than 1/3 of 572 TPSGs are located in cities. At the same time, the analysis of the situation in the context of settlements allows us to conclude that residents of small cities, especially Kondopoga, Belomorsk and Pudozha, are the most proactive in this matter in comparison to residents of the administrative center of Petrozavodsk. This indicates a greater willingness of residents of small cities to unite and consolidate their efforts to solve common problems. In our opinion, a significant role is played by the fact that TPSGs can apply for budgetary funds or grants (Gainanov et al., 2022). Measures to support the work of TPSGs are effective due to the use of such a tool as proactive budgeting. For example, in 2022, in the territory of Belomorsky Urban Settlement, 14 TPSGs participated in the competitive selection for the implementation of projects, four of which became winners and received funding totaling more than 2.5 million rubles. The funds were allocated for repairs in the library building, improvement of parking lots and playgrounds, etc.14 Thus, territorial public self-government acts as another actually working tool for obtaining funding for the implementation of improvement measures and the formation of a comfortable urban environment.
-
4. Based on the analysis of the share of subscribers to the official accounts of local selfgovernment bodies of cities on Vkontakte, we can conclude that residents of small cities, especially with a population of 10 to 30 thousand people, are more actively using the possibilities of this method of communication with the authorities, compared
-
5. In small towns of the European Union, the level of involvement of the population in informal urban communities on the social media is significantly higher: in some, the share of participants is several times higher than the population of the city. In medium cities, the number of subscribers to informal communities exceeds the population of the city itself by about a third, and only two large cities (Murmansk and Vologda) are characterized by an excess of the number of subscribers over the population of the city itself. This feature can be explained to some extent by the fact that many members of urban communities used to live in small towns and subsequently left the locality, but they keep in touch with their “small homeland” via the social media.
the European North there is a considerable number of closed cities (Aleksandrovsk, Severomorsk, Zaozersk, Mirny), as well as cities with a singleindustry economy (Cherepovets, Severodvinsk, Apatity, Kirovsk, Polyarnye Zori). It is these two groups of settlements that are leaders in voter turnout, as well as in the level of support for Russian President Vladimir Putin. In our opinion, this can largely be due to the power of the influence of the administrative resource, since in closed cities a significant proportion of the population is employed in the public sector, and in single-industry towns the life of most citizens is closely linked to the activities of the city-forming enterprise, which in both cases can be used as a lever to control the electoral behavior of citizens. Also, one of the reasons may be that these cities have a higher level of wages, so the population is more satisfied with the policy pursued by the current authorities and is not interested in changing its course.
is often the only opportunity for small settlements to improve the state of the urban environment. It is obvious that the local governments of small cities are maximally motivated in terms of the active involvement of residents in the voting processes.
to the population of large cities. Against the background of other settlements, we can distinguish the closed city of Mirny in the Arkhangelsk Oblast, Municipal Okrug Polyarnye Zori and the closed city of Zaozersk in the Murmansk Oblast, where more than half of the residents are subscribed to the official pages of local self-government bodies. This is largely due to the peculiarities of economic structure in these cities.
Scientific significance of the study consists in determining the features of the spread of formal and informal mechanisms of participation of urban residents in management processes, depending on the number of people living in cities.
Practical significance of the work consists in the possibility of using our findings by public authorities and local self-government in improving the implemented policy of involving citizens in the processes of state and municipal administration.
Of course, beyond the scope of the study, there are still many mechanisms of residents’ political and civic participation, in particular, issues of initiative budgeting in cities or citizens’ participation in volunteer organizations. They will be the topic of further scientific papers on the problems and prospects of the development of civic engagement.
Список литературы Features of participation of the population of cities of the European North of Russia in public and municipal administration
- Bulakh E.V., Leonenko T.P., Tsoi V.G. (2021). Forms of the local community functioning in the framework of territorial self-government on the territory of municipalities of the Russian Federation. Vestnik Zabaikal'skogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta, 27(1), 34–42. DOI: 10.21209/2227-9245-2020-27-1-34-42 (in Russian).
- Carvalhais I.M.E., Oliveira C. (2019). Report on Political Participation of Mobile EU Citizens: Portugal. European University Institute. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331043203_REPORT_ON_POLITICAL_PARTICIPATION_OF_MOBILE_EU_CITIZENS_PORTUGAL_COUNTRY_REPORT_AUTHORED_BY
- Charakhchyan K.K, Bondarenko I.A. (2017). Institutions of public participation in the strategic planning of social and economic development of municipalities. Obshchestvo: politika, ekonomika, pravo=Society: Politics, Economics, Law, 37–40. DOI: 10.24158/pep.2017.3.9 (in Russian).
- Dement'eva I.N. (2020). Protest moods of residents of the region as a manifestation of destructive forms of civic activity. Society and Security Insights, 3(2), 88–103. DOI: 10.14258/ssi(2020)2-06 (in Russian).
- Đulabić V., Jerinić J. (2021). Public Participation in Local Public Action in Croatia and Serbia. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3862802
- Dus Yu.P., Vlaskina E.Ya. (2018). The inhabitant is always right, or how to involve the population in the management of territory development. Regional Economics: Theory and Practice, 16(4), 612–623 (in Russian).
- Ferrucci P., Hopp T., Vargo C.J. (2020). Civic engagement, social capital, and ideological extremity: Exploring online political engagement and political expression on Facebook. New Media & Society, 22(6), 1095–1115.
- Frolov A.A., Agurova A.A. (2019). Index analysis of active citizenship in social networks. Izvestiya Irkutskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta. Seriya Politologiya. Religiovedenie=The Bulletin of Irkutsk State University. Series “Political Science and Religion Studies”, 29. 28–43. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26516/2073-3380.2019.29.28 (in Russian).
- Gainanov D.A., Ataeva A.G., Ulyaeva A.G. (2022). Munitsipal'noe upravlenie i mestnoe samoupravlenie [Municipal Administration and Local Self-Government]. Ufa: ISEI UFITs RAN.
- Gnezdilova M.Yu., Oganesyan T.L. (2021). Interaction of territorial public self-government with the City Duma of the city of Krasnodar. Vestnik ekonomiki i menedzhmenta=Vestnik of Economics and Management, 4, 8–13 (in Russian).
- Gökçe-Kızılkaya S., Onursal-Beşgül Ö. (2017). Youth participation in local politics: City councils and youth assemblies in Turkey. Southeast European and Black Sea Studies, 17(1), 97–112. DOI: 10.1080/14683857.2016.1244239
- Hill J. (2020). Voting as a Rite: A History of Elections in Modern China (Vol. 417). BRILL.
- Hutcheson D., Russo L. (2021). The Electoral Participation of Mobile European Union Citizens in European Parliament and Municipal Elections. European University Institute. Available at: https://cadmus.eui.eu/handle/1814/71159
- Kennedy J.J., Nagao H., Liu H. (2018). Voting and values: Grassroots elections in rural and urban China. Politics and Governance, 6(2), 90–102.
- Koniagina M., Kokh L., Kirillova A. et al. (2021). Crowdsourcing and crowdfunding in the management of large cities. Theoretical and Empirical Researches in Urban Management, 16(3), 5–22. Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/27035543
- Koroleva E.N., Kurnikova M.V. (2019). Modern forms of public participation in local self-government: From theory to implementation practices. Munitsipal'naya akademiya=Municipal Academy, 4, 125–132 (in Russian).
- Korzec P., Pudzianowska D. (2021). Report on Political Participation of Mobile EU Citizens: Poland. European University Institute. Available at: https://cadmus.eui.eu/handle/1814/72561
- Kudashova I.V., Zhukova M.V. (2021). To the question of the institution of civil society in contemporary Russia: Questions of theory and practice. Pravo i gosudarstvo: teoriya i praktika, 5(197), 151–153. DOI: 10.47643/1815-1337_2021_5_151 (in Russian).
- Langley P., Lewis S., McFarlane C. et al. (2020). Crowdfunding cities: Social entrepreneurship, speculation and solidarity in Berlin. Geoforum, 115, 11–20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoforum.2020.06.014
- Larichev A. (2019). Down the stairs leading up: local communities and overcoming the municipal crisis. Sravnitel'noe konstitutsionnoe obozrenie, 3(130), 85–97 (in Russian).
- Latysheva A.N. (2020). Crowdfunding as a potential solution for social and cultural issues in rural communities in Russia. Zhurnal issledovanii sotsial'noi politiki=The Journal of Social Policy Studies, 18(1), 7–20. DOI: 10.17323/727-0634-2020-18-1-7-20 (in Russian).
- Markwart E. (2017). Participation of residents in strategic planning: An onerous duty or an untapped potential? Vestnik ekspertnogo soveta, 2(9), 26–32 (in Russian).
- Martinez-Bravo M., Padró i Miquel G., Qian N., Yao Ya. (2022). The rise and fall of local elections in China. American Economic Review, 112(9), 2921–2958.
- Mayer M. (2016). Civic Crowdfunding and Local Government: An Examination into Projects, Scope, and Implications for Local Government. Norfolk, VA: ODU.
- Mikhailov S.E. (2023). Current view on territorial public self-government. Vestnik Rossiiskogo universiteta kooperatsii, 2(52), 110–113 (in Russian).
- Nikitina A.A. (2021). Forms of direct civil participation in local administration in the Rostov region: Legal regulation and practice. Gosudarstvennoe upravlenie. Elektronnyi vestnik, 88, 119–133. DOI: 10.24412/2070-1381-2021-88-119-133 (in Russian).
- Nikovskaya L.I., Skalaban I.A. (2017). Civic participation: Features of discourse and actual trends of development. Polis. Politicheskie issledovaniya=Polis. Political Studies, 2(6), 43–60. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17976/ jpps/2017.06.04 (in Russian).
- Peltoniemi J.E.M. (2018). Report on Political Participation of Mobile EU Citizens: Finland. European University Institute. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329706638_Report_on_political_participation_of_mobile_EU_citizens_Finland
- Revyakin S.A. (2017). Mechanisms of public participation in strategic planning in Russian Federation. Vestnik Omskogo universiteta. Seriya: Ekonomika, 3(59). DOI: 10.25513/1812-3988.2017.3.62-69 (in Russian).
- Safarov S.M. (2022). Strategy for the development of territorial public self-government until 2030: On the first results of implementation. Upravlenie gorodom: teoriya i praktika, 3(45), 59–61 (in Russian).
- Sharova E.N., Maleus D.V. (2022) The small towns residents demand for the urban environment development (the case of sociological research in the Murmansk region). Vestnik universiteta, 10, 223–230 (In Russian).
- Smoleva E.O. (2021). Forming the practices of citizens’ participation in the development of the urban environment: Habitualization or institutionalization from above. Ekonomicheskie i sotsial'nye peremeny: fakty, tendentsii, prognoz=Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 14(5), 244–260. DOI: 10.15838/esc.2021.5.77.14 (in Russian).
- Stiver A., Barroca L., Petre M. et al. (2015). Civic crowdfunding: How do offline communities engage online? British HCI Conference. Association for Computing Machinery. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2783446.2783585
- Szczepańska A., Zagroba M. Pietrzyk K. (2022). Participatory budgeting as a method for improving public spaces in major Polish cities. Soc Indic Res, 162, 231–252. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-021-02831-3
- Tavares A.F., Carr J.B. (2013). So close, yet so far away? The effects of city size, density and growth on local civic participation. Journal of Urban Affairs, 35(3), 283–302. DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-9906.2012.00638.x
- Ukhanova Yu.V. (2021). Collective practices and potential for civic participation of local community (sociological research in Russian regions). Problemy razvitiya territorii=Problems of Territory’s Development, 25(1), 88–107. DOI: 10.15838/ptd.2021.1.111.5 (in Russian).
- Xi J., Wen F. (2019). Sustainable rural governance: How rural elections in China lead to long-term social stability? Sustainability, 11(22), 6196.
- Zagidullin M., Aziz N., Kozhakhmet S. (2021). Government policies and attitudes to social media use among users in Turkey: The role of awareness of policies, political involvement, online trust, and party identification. Technology in Society, 67, 101708. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101708
- Zhang T., Zhang L., Hou L. (2015). Democracy learning, election quality and voter turnout: Evidence from village elections in rural China. China Agricultural Economic Review, 7(1), 143–155.


