Ферменты деградации рамногалактуронана I как факторы вирулентности фитопатогенной бактерии Pectobacterium atrosepticum
Автор: Ковтунов Е.А., Горшков В.Ю., Гоголева Н.Е., Петрова О.Е., Осипова Е.В., Нуриахметова Ч.Б., Татаркин С.В., Гоголев Ю.В.
Журнал: Сельскохозяйственная биология @agrobiology
Рубрика: Фитопатология
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.54, 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Фитопатогенные пектобактерии (род Pectobacterium ) известны как возбудители мягких (мокрых) гнилей. Симптомы мягких гнилей связаны с обширной мацерацией растительных тканей вследствие продукции микроорганизмами ферментов, разрушающих компоненты растительных клеточных стенок. Большинство ферментов, секретируемых пектобактериями, катализируют расщепление гомогалактуронана. Этот полисахарид, представляющий собой линейный гомополимер, состоит из остатков галактуроновой кислоты и является основным (по массе) пектиновым полисахаридом растительных клеточных стенок. Известно, что нокаут генов ферментов деградации гомогалактуронана приводит к снижению вирулентности пектобактерий. В то же время при инфекции, вызываемой пектобактериями, происходит модификация другого типа пектинов - рамногалактуронана I. Это разветвленный гетерополимер, остов которого построен из чередующихся остатков рамнозы и галактуроновой кислоты, а боковые цепи - из остатков галактозы или арабинозы. Однако роль пектобактериальных ферментов, разрушающих рамногалактуронан I, в развитии мягких гнилей не выявлена...
Пектиновые полисахариды, рамногалактуронан i, гликозил-гидролазы
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142220129
IDR: 142220129 | УДК: 632.3.01/.08:577.15 | DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2019.3.566rus
Текст научной статьи Ферменты деградации рамногалактуронана I как факторы вирулентности фитопатогенной бактерии Pectobacterium atrosepticum
Представители рода Pectobacterium — одни из наиболее вредоносных фитопатогенов в мире (1). Эти микроорганизмы вызывают у растений заболевания, названные мягкими, или мокрыми, гнилями (2, 3). Ключевыми детерминантами патогенности пектобактерий считаются экстраклеточ-ные ферменты, расщепляющие полисахариды клеточной стенки, из которых наиболее разнообразны ферменты, разрушающие полигалактуроновую кислоту (гомогалактуронан). Этот полимер, содержащийся в основном в срединных пластинках, — самый представленный пектиновый полисаха-
* Работа частично поддержана грантом Российского научного фонда (¹ 15-14-10022).
рид растительных клеточных стенок (4). Его деструкция при развитии инфекции приводит к мацерации тканей (2, 3, 5). В многочисленных исследованиях продемонстрировано, что мутантные формы пектобактерий, у которых секреция ферментов, разрушающих полигалактуронан, отсутствует или снижена, не способны вызывать симптомы мягких гнилей (6-8).
Наряду с генами, кодирующими ферменты деструкции гомогалак-туронана, в геноме пектобактерий присутствуют гены ферментов деградации другого пектинового полисахарида — рамногалактуронана I (РГУ I). В отличие от гомогалактуронана (линейного гомополимера, состоящего из остатков галактуроновой кислоты), РГУ I — это разветвленный гетерополимер. Его остов представляет собой чередующиеся остатки рамнозы и галактуроновой кислоты, а боковые цепи, присоединенные к рамнозе, состоят из галактозы или арабинозы (4).
В наших предыдущих исследованиях было показано, что РГУ I играет важную роль в колонизации пектобактериями сосудов первичной ксилемы, где микроорганизмы формируют особые биопленкоподобные многоклеточные структуры, которые мы назвали бактериальными эмболами (9). В отличие от биопленок, в которых внеклеточный матрикс представлен в основном бактериальными экзополисахаридами (10-12), первичный матрикс бактериальных эмболов формируется из РГУ I (13). Этот полимер высвобождается из растительных клеточных стенок в результате восприимчивого ответа растений и формирует своеобразный микрокосм для сборки бактериальных эмболов. По мере созревания бактериального эмбола РГУ I в составе внеклеточного матрикса замещается экстраклеточ-ными полисахаридами пектобактерий (14). Это свидетельствует о динамичном преобразовании РГУ I при развитии инфекции. Однако для пек-тобактерий роль ферментов деградации РГУ I в патогенезе ранее не была продемонстрирована.
Мы впервые установили, что разрушение РГУ I в процессе инфекции вносит значительный вклад в развитие симптомов мягких гнилей, вызываемых Pectobacterium atrosepticum .
Цель настоящего исследования — проверка необходимости присутствия ферментов, разрушающих РГУ I, для развития мягких гнилей в растениях, инфицированных пектобактериями.
Методика . Штамм Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 (ранее Erwinia carotovora ssp. atroseptica SCRI1043) (15) (коллекция Белорусского государственного университета; любезно предоставлен Е.А. Николайчиком), Escherichia coli и штаммы, мутантные по локусам eca0852 ( ∆ eca0852) и eca3749 ( A eca3749), выращивали при 28 °C в среде Luria-Bertani (LB) (16), содержащей 10 г/л пептона, 5 г/л дрожжевого экстракта, 10 г/л NaCl, рН 7,5. При необходимости добавляли антибиотики канамицин (30 мкг/мл), стрептомицин (100 мкг/мл), тетрациклин (12,5 мкг/мл).
Поиск последовательностей целевых ферментов осуществляли с помощью алгоритма BLASTp в банках данных PDB (Protein Data Bank Europe, и UniProt . Филогенетическое древо строили методом ближайшего соседа; бутстрэп-поддержка указана у ветвей дерева. Молекулярно-филогенетический анализ выполняли в программе MEGA 6.0 . Биохимическое описание ферментов заимствовали из базы данных CAZy (CarbohydrateActive enZyme, .
Мутантный локус для нокаута генов eca0852 и eca3749 конструировали с помощью ПЦР по методу перекрывающегося сплайсинг-расши-рения. Большую часть кодирующей области гена удаляли, а на ее место в качестве маркера для селекции мутантных клеток встраивали кассету устойчивости к канамицину. Полученную конструкцию лигировали в суицидный мобилизуемый вектор pKNG101 (любезно предоставлен профессором L.N. Moleleki, университет Претории, ЮАР), и сконструированную таким образом плазмиду переносили в клетки донорного штамма E. coli СС118 при помощи электропорации. Рекомбинантный мутантный локус в составе полученной плазмиды вводили в клетки P. atrosepticum SCRI1043, используя трехродительское скрещивание. Клетки, получившие рекомбинантную плазмиду, отбирали на среде со стрептомицином и канамицином. Затем клетки, в которых прошел второй акт рекомбинации, сопряженный с заменой целевого гена и элиминацией донорной плазмиды, селектировали на среде с сахарозой. После этого отбирали клоны, устойчивые к канамицину и чувствительные к стрептомицину. Мутацию верифицировали с помощью ПЦР и определяли нуклеотидную последовательность мутантного локуса, как описано ранее (8).
Анализ мутантных форм пектобактерий на вирулентность проводили, оценивая массу пораженных (мацерированных) тканей листьев пекинской капусты (Brassica rapa spp. Pekinensis) сорта Cha Cha, инокулированных микроорганизмами. Клетки пектобактерий выращивали в среде LB до поздней логарифмической фазы роста, после чего собирали центрифугированием и ресуспендировали в 10 мМ растворе сульфата магния, менее стрессогенном для растений, чем хлорид натрия (17). Плотность инокулята доводили до 1½107-3½107 КОЕ/мл серийными разведениями. Поверхность листьев стерилизовали отбеливателем «Белизна» (содержание активного хлора 0,8 %) и 70 % раствором этанола. Затем листья промывали стерильной водой и делали небольшие надрезы, в которые вносили 10 мкл бактериальных суспензий (1½105-3½105 КОЕ/мл) или стерильного раствора сульфата магния. Инфицированные таким образом листья помещали в чашку Петри и инкубировали при 28 °C в течение 48 ч. Мацерированные ткани растения извлекали скальпелем и взвешивали. Результаты, полученные как минимум в 10 биологических повторностях, визуализировали в виде бокс-плотов, простроенных с помощью графического пакета ggplot2 . Для измерения пектатлиазной активности бактериальные клетки выращивали в синтетической среде D5 следующего состава, содержащей пектин в качестве единственного источника углерода: 13,6 г/л KH2PO4, 1,0 г/л NH4Cl, 0,3 г/л MgSO4 (добавляли в виде 100½ стокового раствора после стерилизации), 1,4 г/л NaOH, 2 г/л пектина, pH 7,5.
Пектатлиазную активность определяли по ранее описанной методике (18). Бесклеточный супернатант культур (50 мкл), выращенных в среде D5 в течение 24 ч при 28 °C в термостатируемом шейкере-инкубаторе (Orbi Safe, «Sanyo», Япония) при 160 об/мин смешивали с 450 мкл реакционной смеси (pH 8,5), содержащей 50 мМ Трис-HCl, 0,1 мМ CaCl2 и 0,05 % полигалактуроновой кислоты, инкубировали при 37 °С в течение 5 мин и оценивали возрастание поглощения при X = 235 нм на спектрофотометре Solar PB2201B (ЗАО «СОЛАР», Беларусь). За единицу активности принимали количество фермента, катализирующего превращение 1 мкМ субстрата за 1 мин. Удельную активность выражали в ед/мг белка.
Способность к роению оценивали при выращивании пектобакте-рий в полужидкой среде D5, содержащей 0,4 % микробиологического агара Pronadisa («Laboratorios CONDA, S.A.», Испания) и 2 г/л сахарозы или пектина. В полужидкий агар вносили 3 мкл культуры бактерий на ранней стационарной фазе роста, инкубировали при 28 °С и через 24 ч измеряли диаметр макроколоний.
Статистический анализ проводили с помощью стандартных математических методов (расчет средней M и среднеквадратического отклонения ±σ, сравнение средних по t -критерию Стьюдента) в программе Microsoft Excel 2000. Для визуализации значений массы мацерированных тканей использовали пакет ggplot2, уровень достоверности различий (p-значение) рассчитывали с помощью непараметрического теста Вилкоксона. Различия считали статистически значимыми при p < 0,05.
Результаты. Использованные штаммы бактерий, плазмиды и праймеры охарактеризованы в таблице 1.
1. Штаммы, плазмиды и праймеры, использованные для создания мутантных штаммов Pectobacterium atrosepticum (Pba), дефектных по генам, кодирующим рамногалактуронил гидролазу и галактаназу
Название I Описание
Штаммы
Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 Дикий тип (15)
SCRI1043 ∆ 3749 Мутант штамма SCRI1043 со вставкой кассеты устойчивости к Km в
Согласно аннотации, представленной в базах данных CAZy и UniProt, в геноме P. atrosepticum SCRI1043 присутствует 8 генов, кодирующих ферменты, которые разрушают РГУ I. Экспрессия этих генов повышается при колонизации пектобактериями растений-хозяев (23). Для нокаута генов, кодирующих ферменты деградации РГУ I, были выбраны геномные локусы eca3749 и eca0852 P. atrosepticum, один из которых кодирует фермент, расщепляющий остов РГУ I, а второй — боковые цепи. Последовательность первого локуса аннотирована как кодирующая рамногалактуро- нил-гидролазу — фермент, разрушающий остов РГУ I. Согласно аннотации, eca0852 кодирует галактаназу, расщепляющую боковые цепи РГУ I. С помощью филогенетического анализа подтверждено, что целевые ферменты ECA3749 и ECA0852 были близки к группам белков соответственно с рамногалактуронил-гидролазной и галактаназной активностью (рис. 1).
A
100 1001----------
Bacteria
---------4XUV Glycoside hydrolase family protein Thielavia terrestns*
C 3QWT Glycoside hydrolase family protein Salmonella entenca * . 3PMM Glycoside hydrolase family protein Klebsiella pneumoniae*
Gammaproteocacrena
fP011095250 probable unsaturated rhamnogalacluronyl hydrolase! Pectobactenum atrosepticum J

Firmicutes
■031521 unsaturated rhamnogalacluronyl hydrolase Bacillus subtilis-^
—034559 unsaturated rhamnogalacluronyl hydrolase Bacillus subMs * +
Bacteroidetes
3K11 Putative glycoside hydrolase Bacteroides thehatotaomicron*
Fungi
Aspergillus lw
CHa^omiaceae ‘
Б
IQQi -------P48842 endo-p-1.4-galactanase 1 Aspergillus aculeatus * +
-
74] I—Q9Y7F8 endo-p-1.4-gaiactanase Aspergillus tubingensis +
' । Q5B153 endo-p-1 4-galactanase Aspergillus niduians * *4
-
—У I Q2UN61 probable arabinogalactan endo-p-1,4-galactanase Aspergillus oryzae
1-----Q0CTQ7 probable arabinogalactan endo-p-1.4-galaclanase Aspergillus terreus
_____г A1D3T4 probable arabinogalactan endo-p-1,4-galactanase Neosartorya fischeri 100LBOXPR3 probable arabinogalactan endo-p-1,4-galactanase Neosartorya fumigate
I P83691 endo-|$-1.4-galactanase Humicola insolens * +
1001-----P83692 endo-p-1.4-galactanase Thielavia heterothallica *
bactena--- Rammaproteohaclwa ^™'092456 Probableendo-n,4-galacianase Pectob.ctenumатгомресит"^
m---------—-----------------------------P48841 endo-p-1,4-galactanase Ceilvibno japomcus +
Bacillus
10O1
—007013 gaiactanase Bacillus subtiiis +
-Q65CX5 endo-p-1 4-galactanase Bacillus hcheniformis* +
■P48843 Uncharactenzed protein Bacillus circuians
Рис. 1. Кладограммы аминокислотных последовательностей, наиболее схожих с рамногалакту-ронил-гидролазой Pectobacterium atrosepticum (ЕСА3749, WP011095250) (А) и β -1,4-эндогалак-таназой P. atrosepticum (ЕСА0852, WP011092456) (Б): «+» — белки с известными биохимическими характеристиками, « * » — белки, для которых в литературе имеются данные рентгеноструктурного анализа.
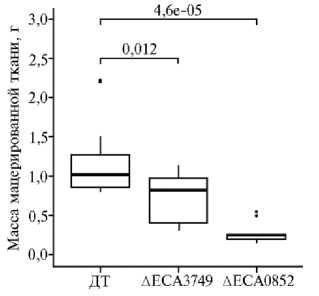
Рис. 2. Бокс-плоты, отображающие распределение значений массы мацерированных тканей в листьях пекинской капусты ( Brassica rapa spp. Pekinensis ) сорта Cha Cha, инокулированных диким штаммом Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 (ДТ) и его формами, мутантными по геномным локусам eca3749 и eca0852 , которые кодируют соответственно рамногалактуронил-гидролазу и галактаназу. Темной горизонтальной линией внутри бокс-плота обозначено медианное значение массы мацерированной ткани, верхняя и нижняя граница отображают 1-й и 3-й квартили распределения проанализированных значений варианта, вертикальные линии — крайние значения, лежащие в пределах полутора межквартильных размахов; черные точки — значения, которые выходят за пределы полутора межквартильных размахов. Над скобками, объединяющими
бокс-плоты, приведены достоверности различий, рассчитанные с помощью непараметриче-
ского теста Вилкоксона.
Хромосомные мутанты P. atrosepticum , дефектные по генам eca0852 и eca3749 , были сконструированы посредством аллельного обмена с использованием суицидного вектора pKNG101 по ранее описанному протоколу (8). Чтобы оценить влияние целевых мутаций на способность P. atrosep-ticum вызывать мацерацию растительных тканей, листья пекинской капусты инокулировали дикой и мутантными формами пектобактерий. Масса мягкой гнили, производимой этими штаммами в течение 48 ч, различалась (рис. 2). Оба мутанта мацерировали растительную ткань значительно менее интенсивно, чем бактерии дикого типа. При этом мутация в гене, кодирующем галактаназу ЕСА0852, оказывала значительно больший эффект (см.
рис. 2). По всей вероятности, причина в том, что гидролиз боковых цепей РГУ I вносит больший вклад в процесс мацерации тканей, чем разрушение остова полимера. На листьях, инокулированных стерильным 10 мМ раствором хлорида магния, симптомов мацерации тканей не отмечали.
Возможное влияние мутаций в локусах eca3749 и eca0852 на активность ключевых факторов вирулентности — пектатлиаз (24), а также подвижность микроорганизмов, служащую критерием их вирулентности (2528), было проанализировано с применением соответствующих тестовых систем. В культурах in vitro при использовании пектина в качестве един- ственного источника углерода экстраклеточная пектатлиазная активность у обеих мутантных форм не отличалась от таковой у дикого типа (рис. 3).
При анализе роения микроорганизмов, которое обеспечивает системное
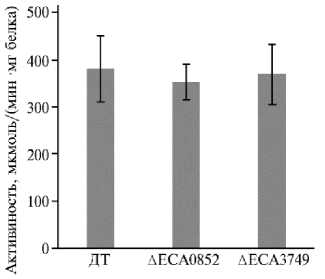
Рис. 3. Пектатлиазная активность в супернатантах культур Pectobacterium atro-septicum SCRI1043 дикого типа (ДТ) и мутантных форм с инактивированными геномными локусами eca0852 (инактивирован фермент ECA0852) и eca3749 (инактивирован фермент ECA3749) , которые кодируют соответственно галакта-назу и рамногалактуронил-гидролазу.
распространение пектобактерий по растительным тканям, способствуя расширению зоны мягкой гнили (25), мы также не обнаружили различий между дикой и мутантными формами P. atrosepticum . В полужидких синтетических средах, содержащих либо сахарозу, либо полигалакту-роновую кислоту, оба мутантных штамма и дикая форма распространялись с одинаковой скоростью (табл. 2). Все это означает, что снижение вирулентности штаммов, мутантных по геномным локусам eca3749 и eca0852 , не связано со снижением подвижности микроорганизмов и способности к разрушению гомогалактуронана.
Хотя РГУ I — менее представленный полимер во фракции пектинов по сравнению с полигалактуроновой кислотой (4), наши эксперименты указывают на важность его разрушения для развития мягких гнилей, вызываемых P. atrosepticum. Во-первых, это может быть связано с тем, что благодаря преобразованию РГУ I обеспечивается формирование своеобразного экстраклеточного матрикса для пектобактерий
2. Подвижность дикого штамма Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 и штаммов, мутантных по геномным локусам eca3749 и eca0852 (0,4 % агар)
|
Штамм |
Диаметр колоний на средах, мм ( М ± σ ) |
|
|
сахароза |
полигалактуроновая кислота |
|
|
SCRI1043 |
22±0,5 |
22±0,2 |
|
∆ eca3749 |
22±0,5 |
24±0,6 |
|
∆ eca0852 |
23±0,3 |
23±0,4 |
(13). Во-вторых, несмотря на то, что инактивация целевых локусов не приводила in vitro к снижению спо-
собности микроорганизмов разрушать гомогалактуро-нан (рис. 2), в системе in planta, где разные типы пектиновых веществ могут пред-
ставлять собой домены одной молекулы (29), неспособность разрушать РГУ I может сделать определенные участки гомогалактуронана недоступ- ными для пектобактериальных ферментов.
Таким образом, мы продемонстрировали, что инактивация генов ферментов катаболизма рамногалактуронана I (РГУ I) снижает способность пектобактерий вызывать симптомы мягких гнилей у растений. При этом разрушение боковых цепей этого полимера, по всей видимости, вносит больший вклад в процесс мацерации тканей хозяина, чем гидролиз остова, поскольку мутант по гену галактаназы характеризовался меньшей вирулентностью не только по сравнению с родительским штаммом дикого типа, но и с мутантом по гену рамногалактуронил-гидролазы. Полученные нами результаты позволяют отнести ферменты деградации РГУ I к факторам вирулентности фитопатогенных пектобактерий.
Список литературы Ферменты деградации рамногалактуронана I как факторы вирулентности фитопатогенной бактерии Pectobacterium atrosepticum
- Mansfield J., Genin S., Magori S., Citovsky V., Sriariyanum M., Ronald P., Dow M., Verdier V., Beer S.V.,. Machado M.A., Toth I., Salmond G., Foster G.D. Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol., 2012, 13(6): 614-629 ( ) DOI: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2012.00804.x
- Perombelon M.C.M. Potato diseases caused by soft rot erwinias: an overview of pathogenesis. Plant Pathol., 2002, 51(1): 1-12 (doi: 10.1046/j.0032-0862.2001.Short%20title.doc.x).
- Charkowski A., Blanco C., Condemine G. et al. The role of secretion systems and small molecules in soft-rot Enterobacteriaceae pathogenicity. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2012, 50: 21.1-21.25 ( ) DOI: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-081211-173013
- Горшкова Т.А. Растительная клеточная стенка как динамичная система. М., 2007 (ISBN 978-5-02-035598-9).
- Tarasova N., Gorshkov V., Petrova O., Gogolev Y. Potato signal molecules that activate pectate lyase synthesis in Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043. World J. Microbl. Biot., 2013, 29(7): 1189-1196 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s11274-013-1281-9
- Walker D.S., Reeves P.J., Salmond G.P.C. The major secreted cellulase, CelV, of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora is an important soft rot virulence factor. Mol. Plant Microbe In., 1994, 7(3): 425-431 ( )
- DOI: 10.1094/MPMI-7-0425
- Mäe A., Heikinheimo R., Tapio Palva E. Structure and regulation of the Erwinia carotovora subspecies carotovora SCC3193 cellulase gene celV1 and the role of cellulase in phytophatogenicity. Mol. Gen. Genet., 1995, 247(1): 17-26 ( )
- DOI: 10.1007/BF00425817
- Moleleki L.N., Pretorius R.G., Tanui C.K., Mosina G., Theron J. A quorum sensing-defective mutant of Pectobacterium atrosepticum ssp. brasiliense 1692 is attenuated in virulence and unable to occlude xylem tissue of susceptible potato plant stems. Mol. Plant Pathol., 2017, 18(1): 32-44 ( )
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12372
- Gorshkov V., Daminova A., Ageeva M., Petrova O., Gogoleva N., Tarasova N., Gogolev Y. Dissociation of a population of Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 in tobacco plants: formation of bacterial emboli and dormant cells. Protoplasma, 2014, 251(3): 499-510 ( )
- DOI: 10.1007/s00709-013-0546-3
- Donlan R.M. Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces. Emerg. Infect. Dis., 2002, 8(9): 881-890 ( )
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0809.020063
- Izano E.A., Amarante M.A., Kher W.B., Kaplan J.B. Differential roles of poly-N-glucosamine surface polysaccharide and extracellular DNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microb., 2008, 74(2): 470-476 ( )
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02073-07
- Flemming H.C., Wingender J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2010, 8: 623-633 ( )
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2415
- Gorshkov V.Y., Daminova A.G., Mikshina P.V., Petrova O.E., Ageeva M.V., Salnikov V.V., Gorshkova T.A., Gogolev Y. V. Pathogen-induced conditioning of the primary xylem vessels -a prerequisite for the formation of bacterial emboli by Pectobacterium atrosepticum. Plant Biology, 2016, 18(4): 609-617 ( )
- DOI: 10.1111/plb.12448
- Gorshkov V., Islamov B., Mikshina P., Petrova O., Burygin G., Sigida E., Shashkov A., Daminova A., Ageeva M., Idiyatullin B., Salnikov V., Zuev Y., Gorshkova T., Gogolev Y. Pectobacterium atrosepticum exopolysaccharides: identification, molecular structure, formation under stress and in planta conditions. Glycobiology, 2017, 27(11): 1016-1026 ( )
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwx069
- Bell K.S., Sebaihia M., Pritchard L. et al. Genome sequence of the enterobacterial phytopathogen Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica and characterization of virulence factors. PNAS USA, 2004, 101(30): 11105-11110 ( )
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0402424101
- Sambrook J., Fritsch E.F., Maniatis T. Molecular cloning: a Laboratory Manual. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1989.
- Lee M.K., van Iersel M. W. Sodium chloride effects on growth, morphology, and physiology of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium). HortScience, 2008, 43(6): 1888-1891.
- Shevchik V.E., Robert-Baudoy J., Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat N. Pectat lyase PelI of Erwinia chrysanthemi belongs to a new family. J. Bacteriol., 1997, 179(23): 7321-7330 ( )
- DOI: 10.1128/jb.179.23.7321-7330.1997
- Herrero M., de Lorenzo V., Timmis K.N. Transposon vectors containing non-antibiotic resistance selection markers for cloning and stable chromosomal insertion of foreign genes in gram-negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol., 1990, 172(11): 6557-6567 ( )
- DOI: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6557-6567.1990
- Grinter N.J. A broad-host-range cloning vector transposable to various replicons. Gene, 1983, 21(1-2): 133-143 ( )
- DOI: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90155-5
- Datsenko K.A., Wanner B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. PNAS USA, 2000, 97(12): 6640-6645 ( )
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.120163297
- Kaniga K., Delor I., Cornelis G.R. A wide-host-range suicide vector for improving reverse Genetics in gram-negative bacteria: inactivation of the blaA Gene of Yersinia enterocolitica. Gene, 1991, 109(1): 137-141 ( )
- DOI: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90599-7
- Gorshkov V., Gubaev R., Petrova O., Daminova A., Gogoleva N., Ageeva M., Parfirova O., Prokchorchik M., Nikolaichik Y., Gogolev Y. Transcriptome profiling helps to identify potential and true molecular switches of stealth to brute force behavior in Pectobacterium atrosepticum during systemic colonization of tobacco plants. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2018, 152(4): 957-976 ( )
- DOI: 10.1007/s10658-018-1496-6
- Robert-Baudouy J., Nasser W., Condemine G., Reverchon S., Shevchik V.E., Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat N. Pectic enzymes of Erwinia chrysanthemi, regulation and role in pathogenesis. The American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, 2000.
- Matsumoto H., Umehara M., Muroi H., Yoshitake Y., Tsuyumu S. Homolog of FlhDC, a master regulator for flagellum synthesis: required for pathogenicity in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora. J. Gen. Plant Pathol., 2003, 69: 189-193 ( )
- DOI: 10.1007/s10327-002-0029-4
- Hossain M.M., Shibata S., Aizawa S.I., Tsuyumu S. Motility is an important determinant for pathogenesis of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora. Physiol. Mol. Plant P., 2005, 66(4): 134-143 ( )
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2005.06.001
- Duan Q., Zhou M., Zhu L., Zhu G. Flagella and bacterial pathogenicity. J. Basic Microb., 2013, 53(1): 1-8 ( )
- DOI: 10.1002/jobm.201100335
- Pfeilmeier S., Saur I. M, Rathjen J. P., Zipfel C., Malone J. G. High levels of cyclic-di-GMP in plant-associated Pseudomonas correlate with evasion of plant immunity. Mol. Plant Pathol., 2016, 17(4): 521-531 ( )
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12297
- Harholt J., Suttangkakul A., Vibe Scheller H. Biosynthesis of pectin. Plant Physiol., 2010, 153: 384-395 ( )
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.110.156588


