Financial possibilities for providing expenditure obligations of local self-government
Автор: Barasheva Tatyana Igorevna
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Regional economy problems and directions of perfection of local government
Статья в выпуске: 1 (9) т.3, 2010 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article assesses financial provision of expenditure obligations of local self-government. Problems requiring urgent solutions and including decrease of financial autonomy of municipalities and increasing their dependency on decisions and financial support from upper level budgets are revealed.
Local self-government, revenue basis of local budgets, financial provision, financial support
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223174
IDR: 147223174 | УДК: 336.025.2(470.21)
Текст научной статьи Financial possibilities for providing expenditure obligations of local self-government
Expenditure commission of municipalities forms their rights and duties set for controlling budget legal relationship, organizing and realizing budgetary process, observing direction and amount of finance expense. Complete and qualitative discharge of expenditure obligations is connected directly with financial providing local self-government, which organizational principles were transformed during realizing reform of local self-government and interbudg-etary relations.
During 2000 – 2008 amount of accrued in municipalities budgets finance in current prices has increased essentially, but in comparable conditions it has decreased. Total income volume of the municipalities in
Murmansk region accounts for 25.8 billion roubles or 1.1% from total income volume of the all Russian municipalities. Income distribution according to types of the region municipalities in 2008, as in previous years, is characterized by irregularity: urban district budgets have received 77.1%, metropolitan region budgets – 18%, settlement budgets – 4.9% (table) . It should be noted that in contrast to situation in the Russian Federation in whole income distribution according to the municipalities in Murmansk region is more irregular, the reason for this is difference in socio-economic development of cities, presence of enterprise forming a company town in the urban district's territory.
Table 1. Income ratio of local budgets in profile of main municipalities types, %
|
Type of municipality |
2007 |
2008 |
||
|
The Russian Federation |
Murmansk region |
The Russian Federation |
Murmansk region |
|
|
Urban districts |
53.2 |
75.8 |
51.7 |
77.1 |
|
Metropolitan regions |
39.9 |
19.4 |
39.8 |
18.0 |
|
Federal cities |
0.5 |
- |
0.5 |
- |
|
Urban settlements |
2.6 |
3.9 |
4.0 |
4.0 |
|
Rural settlements |
3.8 |
0.9 |
4.0 |
0.9 |
|
Total |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
Source of information: Author's calculation according to figures from collected statistical articles “Russia's regions. Socio-economic indexes” 2009.
Figure 1. The own income ratio sources of urban districts, %
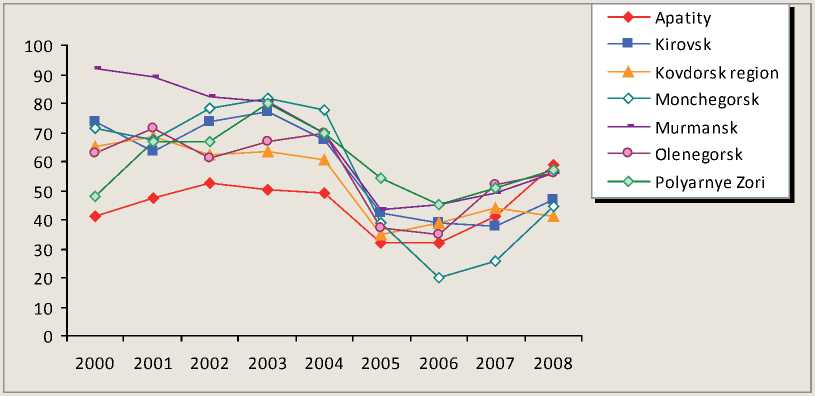
By this transforming structure components of local budget income have considerably changed. Urban districts had a high tax potential and provided up to 70 – 90% of their funds in budgets income during the pre-reform period have lost their own income by 2006 and income volume has decreased 1.5-3.5 times (fig. 1) .
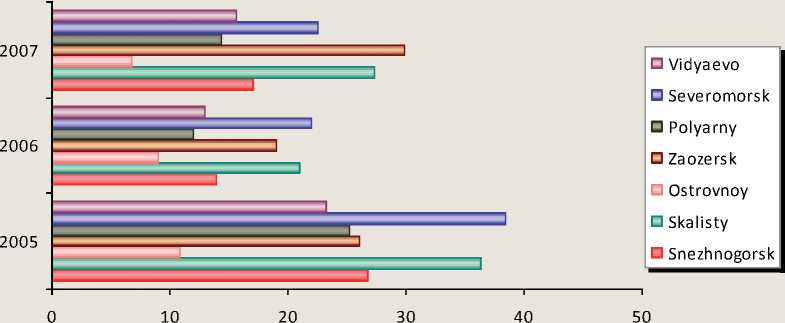
In metropolitan regions which level of economic development does not exceed mean value in the region their own sources of budget ratio has decreased 1.5-2.0 times (fig. 2) . The lowest figures are noticed in urban districts of closed administrative-territorial divisions (fig. 3) .
In whole Russia's economic growth in 2000-s stimulated receipt of tax proceeds to Russia's budget, but virtually it did not invest to the municipality budgets. Share of tax proceeds declined steady and only since 2007 we can notice some changes for the better.
First of all tax funds decline in local budgets is caused by removal of some local taxes from Russia's tax system. In the year of tax code (TC) enacting the number of local taxes has been decreased from 26 to 5, after enacting changes to the TC (since 2005) there are only 2 taxes being in force in metropolitan regions. Their tax income ratio varies from 1.5% to 12%.
For tax independence expansion of municipal officials’ new standard of assessments from federal taxes to municipal budgets was assigned by the Budget Code (BC) on continuing basis.
At the same time the BC authorized a region of the federation to give a share of incoming to regional budget taxes to the municipal level. Two regional taxes (transport tax and gambling business tax) and about 10% of income tax (IT) in excess of the standard was assigned to local budgets by the regional law. This fulfilled steps raised slightly the tax part in income of Murmansk municipalities, but amount of accrued finance did not allow to make up losses of local budgets from omitted local taxes in full and as the result their own income level has decreased.
Choice of such mechanism as transmission of assessment norms from federal and regional taxes to the local level is reasonable so far as federal subjects of the Russian Federation form tax superstructure taking into account the regional differentiation features of tax potential according to the types of municipalities and real opportunity of local self-government to influence on the assessment basis and tax collection. But the reason of this mechanism insufficient application in the federal subjects is a low tax component in the regional budgets, and it forces the federal subjects to be guided by financial aid transmission to the local budgets.
Establishment of basic taxes (income tax, single imputed earnings tax, agriculture tax) as the main local budget making source is appreciated positively because this allows the local self-government to forecast the amount
Figure 2. The own income ratio sources of municipalities, %
Kandalaksha
Kola region Lovozyorsk region Pechegensk region Tersk region
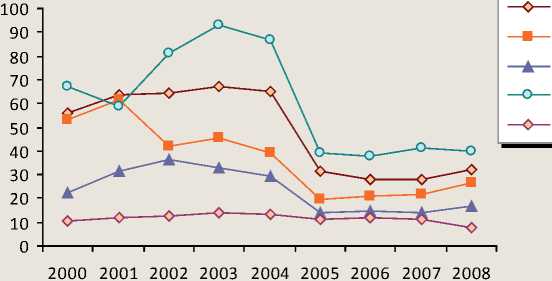
Figure 3. The own income ratio sources of closed administrative-territorial divisions, %
of finance and plan without assistance the expense of accrued finance. And with this the differentiation tax norms approval according to the types of municipalities is one of the main courses of tax income irregular allocation to the budgets of urban districts, metropolitan regions and settlements, and also of difference in their tax income structure.
Settlement budgets are presented by a short list of taxes which assessment norms are minimum. As a result settlement budgets risk to be stable by considerable share of free payment transfers and little tax proceeds amount formed mainly by income tax (IT), land tax, assessed tax and income from property use and sale.
The bases of metropolitan region budgets are income tax (IT) – 70.8%, total revenue tax – 6.2%, transport tax – 5.9%. Budget concentration of easy predictable taxes – income tax (IT) and single imputed earnings tax (SIET) providing in aggregate up to 77% tax income – make metropolitan region budgets more stable than settlement budgets are.
Income structure of urban districts can be identified as most diversified and presented the following main budget taxes: income tax (IT) – 61%, land tax – 4.2%, total revenue tax – 5%, transport tax – about 6%, gambling business tax – about 5%. By the Budget Code (BC) enacted main taxes ratio as a sum of settlement and district norms provided the most budget stability of urban districts among the groups of municipalities. With this the developed tax basis according to the income tax (IT) provided by functioning in the large, medium-sized and small enterprises of urban districts provided rather a lot of receipt of funds to their budgets according to this tax.
Beginning and functioning history of closed administrative-territorial municipalities having status of urban districts predetermined problems of their budget income basis. Limited tax basis provides small degree of budget stability in closed administrative-territorial municipalities having status of urban districts.
With this a low level of tax income in oblast and local budgets and also under effectiveness of tax collection are directly connected with the special approach to forming of Russian's tax system and with choice of correlation between direct and indirect taxation.
Since beginning of current Russian tax system tax income of Russian’s subject and local budgets formed by receipting of direct and indirect tax funds. On the one hand combination of two tax types in territory budgets provided achievement of fiscal taxation objectives by introduction of direct taxes, and on the other hand it allowed realizing controlling functions of direct taxes.
Since the last years the basis of subordinate budgets are only direct taxes: profit tax, total revenue tax, income tax and assessed tax. In spite of the tax control process is handed over to federal authorities, the degree of collected taxes is rather low. Tax collection depends on the income level of natural persons – taxpayers and results of keep house subjects reacting to changes in microeconomic situation and depending on conjuncture of world prices for raw materials because most enterprises of the region are export-oriented. So most of all from the financial-economic crisis suffered both regional budget by under receipt of income tax because of decline in prices for raw materials and local budgets through growth of unemployment entailing decrease in receipt from income tax. In whole direct taxes can be characterized as laborious because of process of their collection and their correct computation control.
On the contrary in the structure of federal budget prevail indirect taxes which as a fiscal instrument provide national treasury with finance. The process of these taxes collection is less laborious and more easily controlled.
Difficulties in direct taxes consolidation of regional and local authorities become more complex through establishment and expansion of federal and regional tax benefit by federal legislative bodies.
Particularly social and property tax deductions from income tax are being revised permanently, federal allowances of firm property tax are continuing to be effective, use of amortization bonus is increasing and it leads to falling out of tax income in regional and federal budgets.
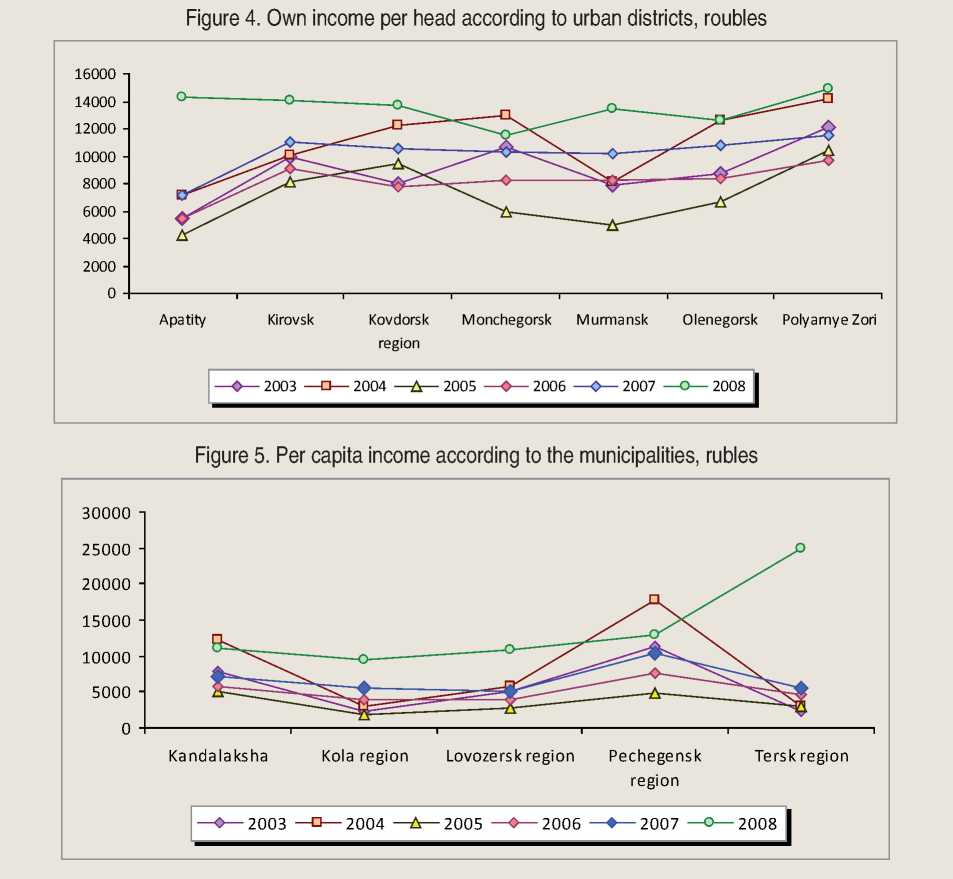
Amount of own income assessment per head in Murmansk municipalities shows that in 2005 this index was reduced in comparison with the pre-reform period and was increased in the next years (fig. 4 and 5) .
Choice of special tax put to local budgets caused some decreasing of own income differentiation within the municipalities of the same group.
With it the creation of various municipalities non registering their difference in economic potential and the establishment of unequal tax norms according to each municipality type led to preservation of own income differentiation between the cities.
A higher index level is provided in urban districts which economy is presented by enterprise forming a company town (excepting Apatity) and rather high-capacity tax basis according to income tax. In municipalities the level of own income per head is lower than in urban districts, but deviation of own income peak value from minimum value is higher in municipalities. The reason is admission of municipalities with unequal economic potential to the group of metropolitan regions.
Thereby differences in tax potential, consolidation of most collected taxes into federal budget and transmission of the least collected and profitable taxes become another reason of financial problems in local budgets.
Own incomes concentrated in local budgets for financing of discharge obligations and consideration of their sufficiency shows that in the pre-reform period the level of cost reimbursement through own incomes was rather higher than at present. Taxes paid by enterprise forming a company town provided financing from 60 till 80% of all expenditure budget items. In 2006 – 2008 the level of cost reimbursement through own incomes decreased up to 40 – 45% in local budgets, and it does not exceed 10 – 15% in municipalities not having any enterprises forming a company town. After local budgets lost income and firm property tax principal taxpayers take part in forming of budget income indirectly, mainly through income tax deducted from payment to employees, and incomes of local budgets are formed mainly through the subjects of entrepreneurship.
Local self-government should have necessary hand levers to stimulate economic activity of small management subjects for expansion of tax basis. Right measure for regulation of smallscale business paid tax elements is excepted from their authority by federal legislator. So according to single imputed earnings tax went into local budget from small management subjects authority of local administration applies to establishment of entrepreneurship types and concretization of basis income corrective factor – F2 reflecting characteristics of entrepreneurship.
With regard to simplified tax system all the numeration of taxation elements (tax basis, tax rates, tax remissions etc) is formed by federal legislative bodies without participation of local authorities. The region has a right to impose the simplified conditions on its territory and regulate some elements of patent system. Financial crisis called for transmission of additional rights to the regions to support small and mediumsized enterprises in federal subjects. Governmental bodies have such authority as regulation of single tax rate though it will be more logical to give this right to local self-governments because assistance to development of small and mediumsized enterprises is of importance on local level. So estimate of legislative norms indicates the restrictions of municipality body possibilities in taxation depriving them stimuli to form a full-grown tax basis and own finance source.
Low tax collecting into local budgets forces the authorities of federal subject to assign means as transfers for their support. At the average the amount of gratuitous transfers in urban districts is 56%, in metropolitan regions – 75%, in settlements – more than 80% of budget income. Target funds prevail in finance support structure. A large part of subsidies (more than 30%) indicates increase in influence of region authorities on choice of priority during municipal charge financing. Growth of subvention ratio in incomes of municipal budgets (40 – 60%) indicates decrease of the fiscal autonomy level of municipalities according to charges and realization of state budget policy through municipalities.
Summing up we should notice that finance problems of municipalities were not solved finally during in the country realized reforms and these problems became aggravated with finance-economic crisis. Active governmental participation in regulating of tax-budget relations lead to decrease of tax component in local budget and degree of tax income structure diversity in local budgets, growth of local self-government dependence on decisions and finance resources of higher levels of federal budget system.
It is necessary on federal level to create arrangements for strengthening of income basis in local budgets and developing stimuli for effective financial management for providing of finance situation stability on the level of municipalities in order to discharge of obligations by local self-government.
Particularly it is also necessary to fix local taxation system. It is suggested considering the matter of giving status “local” to some taxes, for example transport tax and single tax, functioning according to simplified diagram. In addition particularly all specialists uphold the idea of local real estate tax introduction for urban districts and settlements, this tax will come in local budgets entirely and become their main income source. Putting a tax into effect needs form a benefit system for low-income groups. It is rationally to transfer additional instruments for regulation of local taxes to local self-governments. Particularly in simplified taxation system regulation possibility of single tax rates should be assign just to local self-governments on long-term basis not only during financial-economic crisis, this allows to consider local features and support small-scale entrepreneur activity in for town privileged branches.
Effective measures for strengthening of finance basis in municipalities should become realization of important budget policy by regional and local self-governments.
Список литературы Financial possibilities for providing expenditure obligations of local self-government
- Russia’s regions. Socio-economic indexes. 2009 : stat. coll. -Access mode: http://www.gks.ru/wps/PA_1_0_S5/Documents/jsp/Detail_default.jsp?category=1112178611292&element Id=1138623506156
- Budget performance reports of the Murmansk municipalities 2000 -2007.
- Performance data base of municipalities . -Access mode: http://www.gks.ru/dbscripts/munst/munst.htm
- Tax Code of the RF . -М., 2005. -Chapters 1-2.


