Glycosylated hemoglobin: the importance in management of type 2 diabetes
Автор: Yavari Abbas
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.7, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Type 2 diabetes is a major public health problem with high and increasing prevalence, morbidity and mortality. The association between diabetes and microvascular and macrovascular complications is well known besides, tight glycemic control is a necessity. HbA1Chas clinically been used since 1980s as a gold standard for monitoring glycemic control and predicting of diabetic complications. The present review article was prepared by computerized sources of literature searches 2000 - 2009. The history of Hemoglobin A1C, its assay techniques, optimal A1C targets, its reliability in control of diabetic complications, limitations of test results and its importance in control of diabetes patients and their complications are discussed.
Glycemic control, hba1c, type 2 diabetes
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323544
IDR: 14323544
Текст обзорной статьи Glycosylated hemoglobin: the importance in management of type 2 diabetes
Diabetes is a major health concern at worldwide and despite increasing diagnostic techniques, knowledge about its effects on public health and complex complications in current life of diabetic patients, only modest progression has been achieved in glycemic control. On the other hand, hemoglobin A 1C (HbA 1C ) is an important index of glycemic management (Brownlee & Hirsch, 2006). High levels of A 1C is associated with high risk of peripheral arterial diseases even among individuals without diabetes (with A 1C levels 5.3% - 6%).
Therefore, efforts to reduce the levels of A1C may reduce the risk of these complications (Day & Bailey, 2007; Munter et al., 2005; Selvin et al., 2006). A trial on 2412 diabetic and nondiabetic patients with symptomatic chronic heart failure showed that the A1C level is an independent progressive risk factor for cardiovascular death, hospitalization for heart failure, and total mortality (Gerstein et al., 2008; Qaseem et al., 2007). Another large study on 47904 persons confirms that A1C levels are strongly associated with subsequent mortality in both men and women without prior diabetes diagnosis (Brewer et al., 2008).
Glycosylated hemoglobin
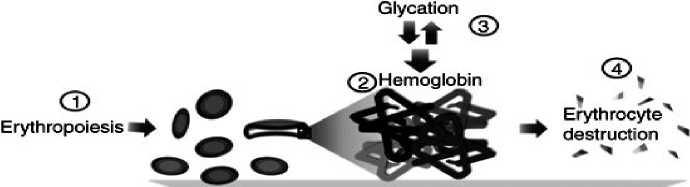
Hemoglobin (Hb) is made up two globin dimmers each with a heme moiety. HbA comprises 97% of the total Hb and hemoglobin A 1C is an irreversible complex that forms when glucose binds to hemoglobin (Gallagher et al., 2009). HbA 1C constitutes about 60-80% of total glycated hemoglobin (Tran et al., 2004).
First 60 years ago it was shown by Allen that HbA contains three minor components; HbA 1c , HbA 1b, and HbA 1c (or A 1C ). A 1C is nonenzymatic glycated product of the hemoglobin beta-chain at the valine terminal residue. The number 1C represents the order of Hb detection on chromatography (Kahn & Fonseca, 2008; Tran et al., 2004). HbA 1C was first separated by Huisman and Meyring in 1958 and was identified as a glycoprotein by Bokchin and Gallop in 1968, but it was characterized as an unusual hemoglobin" in diabetic patients by Iranian scientist "Samuel Rahbar" in 1969 who noted that diabetes is clearly associated with an elevation in glycated hemoglobin.
The use of HbA 1C for control of blood sugar in diabetic patients was proposed by Cerami and Koenig in 1976 (Kahn & Fonseca, 2008; Tran et al., 2004). After clinical works in 1980s, it was introduced as a better index of diabetic control trials (Gallagher et al., 2009; Kahn & Fonseca., 2008).
An important change in diabetes care occurred in the 1970s and 1980s as two methods became available: self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and HbA1C testing (A1C). Regular SMBG has positive effect on improving glycemia particularly in testing the individuals treated with insulin. SMBG reflects the immediate plasma glucose levels, while HbA1C measures long-term glycemic control (Saudek et al., 2006).
HbA1C assays and limitations
Standardization of A 1C measurement has been proposed in different countries to ensure accuracy in A 1C results (Gallagher et al., 2009).
Assays for A 1C use technologies based on either charge differences high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or structure (boronate affinity or immunoassay combined with general chemistry) and newly techniques based on combined immunoassay and general chemistry (Bode et al., 2007).
In past decades, the trials such as DCCT (Diabetes Control and Complications Trial) and UKPDS (UK Prospective Diabetes Study) considered A 1C as the gold standard of diabetes care (Dailey, 2009; Gallagher et al., 2009; Saudek et al., 2006). Furthermore, the programs such as NGSP (National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program) and associations such as AACC (American Association for Clinical Chemistry) (Kahn & Fonseca, 2004) have worked on standardization of A 1C values leading to present methods in measurement of A 1C. Recently, NGSP-certifies rapid HbA 1C assays have become available, allowing office and home testing (Saudek et al., 2006).
Because A1C is based on hemoglobin, quantities or qualitative variations in hemoglobin can affect the A1C value and interpreting of results (Bloomgarden, 2008). These variations include the case of reduced total Hb or turnover of red blood cells that cause reduced level of A1C even in the presence of high ambient plasma glucose (Tran et al., 2004) Generally, abnormal results of A1C test may get with sickle-cell disease, glucose-6-phospahte dehydrogenase deficiency, B12 or folate deficiency, alcoholism, chronic renal or liver disease, contain other hemoglobins such as HbA2 and fetal splenectomy or splenomegaly, chronic opiate use, hemoglobin (HbF). Figure 1 questions remain about large doses of aspirin, vitamin C and vitamin E supplements, creatin and drugs such as dapsone, ribavirine and so forth (Gallagher et al., 2009; Tran et al., 2004). Besides HbA of human erythrocytes exact mechanisms of these abnormal situations (Gallagher et al., 2009; Goldstein et al., 2004; Saudeket al., 2006).
Blood sample

|
Factor influencing |
Increased Au |
Decreased Alc |
Variable change in A. |
|
Iron deficiency, vitamin B„ deficiency, decreased erythropoiesis |
Administration of erythropoietin, iron or vitamin B„; reticulocytosis, chronic liver disease |
Fetal hemoglobin, hemoglobinopathies, methemoglobin |
|
3. Glycation |
Alcoholism, chronic renal failure, decreased erythrocyte pH |
Ingestion of aspirin, vitamin C. vitamin E; certain hemoglobinopathies, increased erythrocyte pH |
Genetic determinants |
|
4, Erythrocyte |
Increased |
Decreased |
|
|
destruction |
erythrocyte lifespan: splenectomy |
erythrocyte lifespan: hemoglobinopathies, splenomegaly, rheumatoid arthritis, drugs such as antiretrovirals, ribavirin, and dapsone |
|
|
5. Assays |
Hyperbilirubinemia, carbamylated hemoglobin. alcoholism, large doses of aspirin, chronic opiate use |
Hypertriglyceridemia |
Hemoglobinopathies |
Figure 1: Factors influencing A 1C
It seems that HbA1C has negative correlation with age (El-Kebbi et al., 2003; Gilliland et al., 2002) and shift in the onset of diabetes to younger ages is notable. This difference may be the result of differences among age groups in treatment strategies or poor control as well as visit frequency in older people (Gilliland et al., 2002).
Monitoring value and recommended ranges
A 1C is nonenzymatic glycated product of the hemoglobin beta-chain and it is normally present at low levels in circulating red cells because of the glycosylation reaction between Hb and circulating glucose, but in the presence of excess plasma glucose this glycation is increased, thus making the A 1C a useful index of glycemic control (Tran et al., 2004).
Average life span of erythrocytes is 117 days in men and 106 days in women. Because erythrocytes are freely permeable to glucose, the level of HbA 1C in a blood sample provides a glycemic history of the previous 120 days, therefore diabetic patients are recommended to be tested every 3 months (Gallagher et al., 2009; Goldstein et al., 2004; Smaldone, 2008).
"American Diabetic Association" (ADA) recommends measuring HbA 1C at least 2 times per year for patients who have met their therapeutic goals and quarterly for patients who have not met their glycemic goals or have changed their therapies (Dailey, 2009; Gallagher et al., 2009).
The normal range of HbA1C test for nondiabetic people is between 4-6% (Goldstein et al., 2004). In diabetic patients the recommended value by "International Diabetes Federation" and "American College of Endocrinology" is below 6.5%, while acceptable level of ADA is below 7% in general but suggesting an A1C level as close to normal (<6%) as possible without causing significant hypoglycemia in individual patients (Cefalu, 2008). The suggested target hemoglobin A1C level by "American Association of Clinical Endocrinology" is ≤ 6.5%. Their guideline states that the normalization of blood glucose levels should be the goal, while the guideline of "American Academy of Family Physicians" states that due to differences in patients' life expectancies and co-morbid conditions, a uniform target A1C level for all patients with type 2 diabetes is inappropriate. The guideline of "American Geriatrics Society" suggests "individualized" A1C levels for older persons. This organization accepts ≤ 7% level for relatively healthy adults with good functional status and 8% level for others with a life expectancy of less than 5 years or the risk of intensive glycemic control outweighs the benefit. Other organizations such as "Canadian Diabetes Association" and "Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement" recommend "individualized" goals for certain populations (Cefalu, 2008; Qaseem et al, 2007). It is difficult to achieve or maintain target A1C levels and only about a third of diagnosed patients achieve that goal (Dail , K h F nseca, 2008; Tran et al, 2004). In general, level of approximately 7% is confirmed in trials on high-risk populations, specially the use of aggressive pharmacological therapy is under consideration (Cefalu, 2008).
Epidemiologic studies suggest that each 1% increase in the A 1C value is associated with a 18% increase in the relative risk of cardiovascular diseases for patients with type 2 diabetes (Buse et al., 2007) and with 15% for type I diabetes (Selvin et al., 2004). In normoglycemic range, this risk has been estimated about 20-30% (Day & Bailey, 2007).
Meta-analysis of clinical trials shows that every 1% reduction in A 1C , lowers the risk of developing eye, kidney complications, and neuropathy by 40%. This reduction for myocardial infarction (MI) is 14% (Bode, 2007; Selvin, 2004).
The meta-analysis of observational studies indicates that the relationship of A1C with cardiovascular diseases in diabetic persons is less clear than microvascular diseases, thus further randomized trials is necessary (Cefalu, 2008; Selvin, 2004).
Some authors believe that optimal diabetes management involves adjunct control of fasting (FBS); preprandial, postprandial glucose (PPG) levels. A 1C can not be used to identify whether an abnormal glycemic level is primarily due to high FBS or high PPG levels. In fact, elevated A 1C signals a need for a change in therapy (not what type changes), whereas PPG is increasingly important as A 1C decreases toward target levels (Dailey, 2009; Day & Bailey, 2007; Shiraiwa et al., 2005). Continuously, A 1C is the gold standard for monitoring glycemic control and serves as an indicator for diabetic related diseases.
Список литературы Glycosylated hemoglobin: the importance in management of type 2 diabetes
- Bloomgarden ZT. (2008). American college of endocrinology pre-diabetes consensus conference: Part three. Diabetes Care. 31, 2404-2409.
- Bode BW, Irvin BR, Pierce JA, Allen M, Clark AN. (2007). Advances in hemoglobin A1Cpoint of care technology. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 3, 319-321.
- Brewer N, Wright CS, Travier N, Cunningham CW, Hornell J, Pearce N, et al. (2008). A New Zealand linkage study examining the associations between A1Cconcentration and mortality. Diabetes Care. 31, 1144-1149.
- Brownlee M & Hirsch IB. (2006). Glycemic variability: A hemoglobin A1Cindependent risk factor for diabetic complications. JAMA. 295, 1707-1708.
- Buse JB, Ginsberg HN, Bakris GL, Clark NG, Fonseca V. (2007). Primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases in people with diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 115, 114-126.
- Cefalu WT. (2008). Glycemic targets and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 358, 2633-2635.
- Dailey G. (2009). Assessing glycemic control with self-monitoring of blood glucose and hemoglobin A1C measurements. Available at: http://www.mayoclinicproceedings.com/content/82/2/229.full.4/27/2009>.
- Day C & Bailey CJ. (2007). control is important. J Diabetes Vasc Dis. 7, 197-198.
- El-Kebbi JM, Cook CB, Ziemer DC, Miller CD, Gallina DL, Phpllips LS. (2003). Association of younger age with poor glycemic control and obesty in urban African American with type 2 diabetes. Arch Intern Med. 163, 69-75.
- Gallagher EJ, LE Roith D, Bloomgarden Z. (2009). of hemoglobin A1Cin the management of diabetes. Diabetes. 1, 9-17.
- Gerstein HC, Swedberg K, Carlsson J, McMurray JJV, Michelson EL, Olofsson B. et al, (2008). The hemoglobin A1Clevel as a progressive risk factor for cardiovascular death, hospitalization for heart failure or death in patients with chronic heart failure. Arch Inter Med. 168, 1699-1704.
- Gilliland SS, Carter JS, Skipper BS, Action KI. (2002). HbA1C levels among American Indian/Alaska native adults. Diabetes Care. 25, 2178-2183.
- Goldhaber JD, Goldhaber SN, Tristan ML, Nathan DM. (2003). Controlled community-based nutrition and exercise intervention improves glycemia and cardiovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetic patients in rural Costa Rica. Care. 26, 24-29.
- Goldstein DE, Little RR, Lorenz RA, Malone JI, Nathan D, Peterson CM, et al. (2004). Tests of glycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 27, 1761-1773.
- Kahn R, Fonseca V. (2008). Translating the A1Cassay. Diabetes Care. 31, 1-4.
- Khaw KT, Wareham N, Bingham S, Luben R, Welch A, Day A. (2004). Association of hemoglobin A1C cardiovascular disease and mortality in adults: the European prospective investigation into cancer in Norfolk. Ann Intern Med. 141, 413-420
- Munter P, Wildman RP, Reynolds K, Desalvo KB, Chen J, Fonseca V. (2005). Relationship between HbA1C and peripheral arterial disease. Diabetes Care. 28, 1981-1897
- Qaseem A, Vijan S, Snow V, Cross JT, Weiss KB; Owens DK. (2007). Glycemic control and type 2 diabetes mellitus: The optimal hemoglobin A1Ctargets. A guidance statement from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 147, 417-422.
- Saudek CD, Deer RL, Kaylani RR. (2006). Assessing glycemia in diabetes using self-monitoring blood glucose and hemoglobin A1C. JAMA. 295, 1688-1697.
- Selvin E, Marinopoulos S, Berkenbit G, Rami T, Brancati FL, Powe NR, et al. (2004). Intensive glucose control and cardiovascular outcomes. Ann Intern Med. 141, 421-431.
- Selvin E, Wattanakit K, Steffes MW, Coresh J, Sharrett AR. (2006). HbA1Cand peripheral arterial disease in diabetes. Care. 29, 877-882
- Shiraiwa T, Kaneto H, Miyatsuka T, Kato K, Yamamoto K, Kawashima A. (2005). hyperglycemia is a better of the progression of diabetic retinopathy than HbA1C in Japenes type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 28, 2806-2809
- Smaldone A. (2008). Glycemic control and hemoglobinopathy: When A1C may not be reliable. Diabetes Spectrum. 21, 46-49.
- Tran HA, Sivla D, Petrovsky N. (2004). Case study: Potential pitfalls of using hemoglobin A1Cas the sole measure of glycemic control. Clin Diabetes. 22: 141-143


