Government, business and the population in the Northern regions of Russia: problems and prospects of cooperation
Автор: Kondral Dmitry P., Morozov Nikolay A.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Economics of the Northern communities. Politology
Статья в выпуске: 20, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Political strategy of the North and Arctic Russia determines the prospects of the interaction between government, business and the public, creating conditions for a long-term development of the northern territories of the country. Today, the quality of accounting and promoting the interests are extremely important and determine the need to assess and improve the mechanisms of articulation and aggregation of the interests of government, business and the population in the North of Russia.
North of Russia, government, business, civil society, political management, strategic development, the balance of interests
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148318708
IDR: 148318708 | УДК: [321,02+316,42+327,82] (470.13) (045). К64
Текст научной статьи Government, business and the population in the Northern regions of Russia: problems and prospects of cooperation
The relevance of the study : the success of the implementation of political development strategy of the North and the Arctic regions of Russia depends on the quality of the mechanisms of a balanced consideration of the interests of key actors (government, business and the public) in the process of preparing and implementing of long-term programs aimed at establishment and use of innovative potential of the territories.
Modern social and economic crisis in the country increases the imbalance of interests of key actors in the North of Russia; it leads to the intensification of contradictions and problems of strategic development of the northern territories. Today it is important to improve decision making processes and implementation of political decisions on the strategic development of the northern territories of the country through the establishment of the conditions and promotion of the interests of government, business and the public.
Method of research — analysis of key problems and prospects of interaction between the main actors in the North of Russia on the basis of methods of analysis, synthesis, comparison and classification.
Problems and prospects of cooperation between the authorities, business and the population in Northern Russia
Qualitative development of the northern territories of Russia involves the formation of control mechanisms, built on the basis of the balanced account and promotion of the parties, interested in the successful future development of the northern regions. The main actors are the state, population, business (Pic. 1) [1].
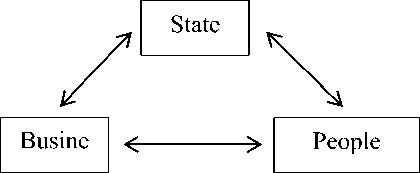
Picture 1. The model of balanced interaction of the main actors in the Russian North
An important feature of the formation of modern management mechanisms in countries and regions is the transitional nature of the political system, changing under the influence of various external1 and internal factors. External factors (political, economic, social, and cultural) largely determine internal contradictions and the need for innovative changes in the socio-political system of relations, stimulating it to modernize in order to reduce the development of the contradictions that arise.
It seems to be important to indicate some of the key issues of interaction between government, business and the population in the North of Russia: increased interests disunity among the key actors in the context of social and economic instability; the continuing weakness of the civil society institutions; the need to develop mechanisms of democratic governance; growing economic problems of small and medium-sized business; the need to modernize the mechanisms of articulation and aggregation of interests; the need to enhance synergies and the degree of mutual interests and taking into account the problems related to the decisions on the strategic development of the territories; need for enhancing the mutual responsibilities of the parties in strategic projects of the northern regions.
The transition (from authoritarian to liberal-democratic governance models) political system determines the continued sluggishness of Russians’ political culture of. For example, in the mass consciousness of citizens the affective sphere still dominates over rational one, and a certain degree of catastrophism is observed, as a reaction to the financial and economic crisis and the sanctions of the West and NATO against Russia. In society there is a low level of basic consensus and tolerance and permanent fragmentation and extreme heterogeneity are observed [2]. In conditions of the gradual development of liberal-democratic values these negative aspects of political culture have an inhibiting effect on the development of institutions of civil society and their preservation is a threat to the development of democratic governance in the country, including the northern regions. Along with this, it should be noted the increasing threat today is desocialization of personality [3] in the context of social and economic instable society, which is particularly dangerous for the remote areas of the country.
Describing the current state of Russian society, the researchers note the following [4]: the growth of governmental sentiments and strengthening the executive power; political opposition is inertia; strengthening the effectiveness of legal mechanisms and law enforcement agencies; attempt to use legal means to limit the power of the oligarchs (separating business from governance); intensification of foreign policy aimed at restoring the country's active influence on global processes; existing threat of terrorism and radicalism; and possibility of unpopular social reforms due to the weakness of civil society (the monetization of benefits, etc.).
The main threat to the development of democracy in the North of Russia is an excessive strengthening of conservative tendencies in regional governance system and the reduction of innovation component in the strategic development programs with the participation of busi-ness. All this in connection with the socio-economic instability can lead to greater imbalance in the social and political relations. Possible imbalance may also be caused by a high level of social and political inertia and alienation of Russian society. Even now, when the approval of the authorities is growing (from 10.7% in 2002 to 22.7% in 2008), the population itself assesses the development of civil society as low (4.48 points out of 10). In particular, the estimation of civil society in Russia is following (maximum score — 10): human rights organizations — 2.91 points; the rule of law — 3.02 points; democracy and freedom — 4.62 points; openness and access to information — 4.83 points; the possibility of free acquisition of property — 4.89; freedom of speech — 5.37; political and ideological diversity represented by political parties — 5.7 [5].
Significant threat to the development of democracy and balanced mechanisms of cooperation at the regional level is possible increase in the spread of radical ideas and concepts [6, 7, 8], poverty [9]
and the marginalization of the population [10, 11, 12], reduce in effectiveness of democratic management institutions and values of civil society [13] accompanied by the process of political decision making and the spread of negative samples of political behavior that prevent the development of the liberal-democratic values and practices of mana-gement. Negative meaning of specified threats increases under relatively low level of economic welfare in the majority of Russian regions [14].
In order to counter those threats it is important to suppress the spread of undemocratic tendencies and radical ideas, to create conditions for the greater importance of the individual values, and institutions of civil society in the regional political process, enhance the objectivity of the evaluation indicators and ways of socio-economic development of the northern regions to prevent threats and to reduce the overall dynamics of poverty and marginalization.
In order to improve the quality of aggregations of people’s interests in the arctic and subarctic regions of Russia, it is important to stimulate the development of civil society [15, 16]. Support for civil society is significant in today's socio-economic instability, leading to the impoverishment of the population. In these circumstances, the importance of democratic institutions in the system of regional government is high, especially when the population dec-lines, leading to a leveling of the values of pluralism, freedom of the individual and individualism. Today, therefore, it is also important to create certain conditions to improve the situation: the development of civil society; the spread of liberal democratic values (including the culture of democracy and pluralism), the humanization of the management system and the development of democratic mechanisms and management practices in the region [17].
The main issues of civil society and its institutions in the north of Russia are: increased identification of citizens’ future with the future of the state and a particular territory; faith in the ability to influence the development of social and political conditions of the region and the availability of open political channels to promote the interests of citizens; objective vision of favorable prospects of social and economic life in the country and the region; desire of the population to participate actively in the preparation and adoption of programs to improve the quality of life and socio-economic development of the northern regions of the country. In order to strengthen civil society institutions today we need to create conditions for the development of the civil initiative and small businesses in the regions of North and Arctic Russia [18].
A serious threat to the successful strategic development of the North and Arctic Russia today is the possibility of increasing divergence of interests of authorities, public and business. The imbalance between the interests of key actors can lead, in our opinion, the following negative consequences:
-
1. The discrepancy between the interests of government and business: unfavorable conditions for economic development of the northern territories, reduced innovation activities of business and reduction of promising ideas of economic development in the region, reducing of the regional profits and economic opportunities for regional authorities (including the possibility to encourage experts and make them living in the northern regions), reduction long-term strategic potential of economic development of the North and Arctic Russia and decline in investments in the regional economy and infrastructure.
-
2. Violation of the state and people’s interests: the decline in the quality of life and low participation of the state in creation of favorable conditions in northern regions, increasing discontent of the population and the level of social apathy, decomposition of democratic values and practice management, the stagnation of the liberal democratic culture, luck of interest in development programs, reduction of social guarantees.
-
3. Difference between the interests of business and population: business lacks orientation for potential labor resources in the region, long-term problems of socio-economic development of the northern regions of the country, lack of understanding of the socio-economic problems of the population and the lack of long-term plans of involvement of the local population in the region's economy, reducing the corporate social responsibility and consumer attitude to the northern areas by businesses community.
These negative factors will undoubtedly mutually influence each other, determining the degree of socio-economic and political empowerment of the northern territories. Preventing these negative factors today directs the authorities towards the system approach and search for balanced solutions for the problems and contradictions of the strategic development of the arctic and subarctic areas of the country, taking into account the balance of interests of government, business and the public.
The negative socio-economic processes and difficult climatic conditions lead to the desire of the population to move to more advanced and favorable regions. Today the population outflow is observed in the northern territories [19], along with the complex demographic situation in the country [20].
Low interest of the population in living in the North entails the loss of the main factor nece ssary for territorial development — population, which should be active participant in the activities of regional authority’s independent development programs.
In terms of complicated foreign policy, sanctions and reduce of the oil and gas cost a decline in investments for development programs in the North and Arctic Russia has been a significant [21, 22]; it is leading to slower implementation of programs and projects 2. It actually made the state a main sponsor of their development. Therefore, the issue of quality of territorial development programs and management practices [23] gets more and more important because of the efficiency of state control over mechanisms that determine the future of the Arctic and subarctic areas and the country as in general. An important task for the regional government today is to find the financial resources for the implementation of announced strategic goals of territorial development. For example, the analysis of the legal and regulatory plan of the RF Ministry on Development of the Far East for 2015 shows that the key issues are: to proved the areas with the bigger share of taxes, search for funding, establishment of priority development territory and land issues 3.
Today there is a reorientation in the search for strategic partners and investors for the development of the Arctic [24] from the western to the eastern countries (for eg., China). It has rather painful impact on the socio-economic system of the northern regions, and in case of negative economic trends [25], it could influence the level of subsidized regions. And it is a serious threat to the strategic development of the country. Today, it is necessary to develop mechanisms for the temporary support of socio-economic development of the northern territories and a decent standard of living using the direct involvement of the federal financial institutions.

•IMWM
Major role in shaping the mechanisms for quality policy strategy of the northern territories of Russia is played by the State [26] that has a sufficient amount of power to influence internal and external factors of the territory and population. It should be emphasized that the socio-economic and political development of the northern territories is based on the political power [27] of the center and the regions; it depends on the quality of methods of strategic up-governance and balanced distribution of powers and responsibilities of actors. Existing strategic importance of the Arctic and subarctic areas of the country creates conditions for restructuring them into an integrated “area of advanced development”.
СТРАТЕГИЯ
РАЗВИТИЯ АРКТИЧЕСКОЙ ЗОНЫ РФ И ОБЕСПЕЧЕНИЯ НАЦИОНАЛЬНОЙ БЕЗОПАСНОСТИ
НА ПЕРИОД ДО 2020 ГОДА
МОСКВА 2011
Important functions of the federal and regional authorities are: to support and maintain the programs that give new socioeconomic impulses for northern regions of the country; to identify and resolve the conflict [28] of the interests between the authorities, population and business related to strategic development of the North and Arctic Russia.
It should be noted that today the idea of the development of the northern territories through the establishment of “urban shift camps” is under threat and needs new approaches to the development of these areas.
Today, a great attention should be paid to the life of the local population, which has become a key aspect of strategic development. However, the establishment of favorable conditions of the population today is neglected [29]. This is largely due to incomplete elaboration of the issue of people’s participation in the process of strategic development of the northern areas 4.
Thus, we should point out the need to develop, a strategy, objective scientific model of balanced development and strategic development of the North and Arctic regions of Russia, taking into account the ability of territories to adapt to the changing environment, while maintaining a stable dynamics of the northern territories.
Strengthening the divergence of interests of authorities, public and businesses [30], in terms of socio-economic instability, can lead to a decrease in the quality of strategic development of the northern areas. So, today it is necessary to take measures to increase the efficiency of regional management system [31]. In the North of Russia, it is important to develop and implement specific programs to:
-
a) develop the civil society;
-
b) enhance the democratic culture of the population;
-
c) increase the positive activity and believe in the future development of the northern territories;
-
d) reduce social apathy of the population [32].
Modernization of articulation and aggregation mechanisms of interests in the North Russia can be based on:
-
I. An effective discussion platform within the executive and legislative authorities of the northern regions, involving government, business and public, and a balanced consideration of their interests in the regional development strategy.
-
II. Improvement of importance of regional research institutions in the formation of mechanisms for analyzing the interests of regional actors.
-
III. Creation of quality assessment mechanisms and promotion of the governmental, business and the public interests to develop effective programs of territorial development.
An important aspect of an effective regional development system is support of balanced relations between the government, business and public. Therefore, the processes of development of the northern territories should be determined by the nature of the system and focused on improving mutual assistance and responsibility of the key actors. In this regard, today we need to focus on the methodological postulates of the arctic and subarctic areas of the country on the basis of responsible regional social and economic policy that involves a long-term mutually beneficial goals and responsible relationships based on trust, support and cooperation.
Due to the importance of the economic component, northern development today involves attracting the support for favorable taxation for business and social security. This is especially important for independent businessmen and small enterprises [33], whose contribution to the development of specific areas is great. But they are not always able to compete with the larger companies.
The system of taxation and social benefits should be in favor of dynamic development and wider activities of business in the arctic and subarctic regions of the country due to importance of business for creating a stable framework and infrastructure for the development of the Arctic.
Thus, the success of socio-economic development of the northern regions is largely dependent on a combination of balanced interests, political concepts and strategic development programs of the northern territories. Strategic development programs are determined by dichotomy of the pulse development processes and are aimed both at preventing negative trends and opening the way for innovative development prospects.
Accordingly, the steps to promote an integrated area of advanced development may be listed in the first case:
-
a. identifying a negative process;
-
b. develop specific programs to overcome it;
-
c. implementation of the program that prevents the development of crisis tendencies.
In the second case, the following steps are possible:
-
a. identification of innovative potential of the Arctic and subarctic areas;
-
b. the development of a specific innovation development program of the areas;
-
c. implementation of the program to give a new impetus to the strategic development of the northern territories of the country.
Successful strategic development [34] of arctic and subarctic areas in Russia is impossible without high-quality accounting mechanisms and promotion of the interests of key regional actors. It is, therefore, necessary to improve the system of support of the main actors and their attempts to develop democratic mechanisms of regional management and political communi-cation; to create a responsible attitude, which should facilitate the integration of governmental, business and the public efforts to create favorable conditions for “territory of priority development”. Strategic programs based on quality accounting and balanced interests are needed to minimize the risks of inefficient financing of individual socio-economic development projects. This is important, because in terms of inefficient investments, stable strategic perspectives for self-development of the areas won’t be established. On the contrary, such projects will give the northern regions dependency on investors and form a consumer approach to their development. From this point of view, the territory will be considered a temporary resource base, the use of which can only be successful in the short term perspective. That situation becomes a threat for stable of strategic development of the areas.
Today it is necessary to focus on the development of the northern regions, mechanisms to establish mutual responsible relations between the key actors and improvement of living standards of the population and its activity; search for modern efficient mechanisms and ways of strategic development through liberal-democratic practices of the regional administration; an attractive economic environment for business and improvement of socio-economic conditions for the population.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it must be noted that a significant threat to the successful development of the North and Arctic Russia today, in terms of socio-economic crisis, is a high degree of dissociation of governmental, business and the public interests. This tendency can strengthen the socio-economic problems in the country.
The management system in the North of Russia should be aimed at preventing the negative social and economic processes and the formation of innovative prospects for the development of territories. This requires the presence of a strategic management system highly structured and balanced with its political and administrative mechanisms.
Today, the need for modernization of the management system is increasing [35], the strategic development of the North and Arctic regions of Russia on the basis of the high-quality accounting and balanced implementation of the governmental, business and the public interests in the planning and implementation of strategic socio-economic development programs.
The result of the study, according to the authors, is in the fact that it is possible to formulate some constructive proposals, aimed at the development of the northern territories:
-
a) the need to create a balanced accounting of the governmental, business and the population interests in the North of Russia, based on mutual responsibility approach;
-
b) overcoming the “consumer” approach to the development of the Arctic and subarctic areas of the country;
-
c) the need for temporary state investment in specific strategic development programs to balance the development of the northern territories;
-
d) creating attractive conditions for business in Northern regions of the country in order to establish “integrated priority development territory”;
-
e) support of development of the civil society on federal and regional levels by preserving the liberal democratic values and their use for management practices in the region, based on enhancing the role of identification based on humanism and individualism;
-
f) in the context of social and economic instability, modernization of mechanisms of the balanced accounting and implementation of governmental, business and public interests within the social and economic development programs of the Arctic and North of Russia.
Modernization of the strategic management and development of the northern territories should take into account the modern all-Russian and specific regional threats and tendencies in the political and administrative and socio-economic development.
Список литературы Government, business and the population in the Northern regions of Russia: problems and prospects of cooperation
- Kondral D.P., Morozov N.A. Upravlenie processami modernizatsii politicheskoi sistemi sovremennoi Rosiii (regionalnii aspekt) [Management of processes of modernization of political system of modern Russia (regional aspect)]. Syktyvkar, GAOU VPO CRAGSiU, 2012. 165 pp.
- Lapshin O.Yu. Spetsifika politicheskoi kulturi sovremennoi Rossii [The specifics of the political culture of modern Russia]. Bulletin of the Nizhehorodskogo universiteta im. N.I. Lobacheva, 2004, no.1, pp. 266—271.
- Andreev A.L. Rossiiskaya model modernizatsii: “obshestvo obrazovaniya” [Russian model of modernization, “society of education”]. Monitoring obshestvennogo mneniya: ekonomi-cheskie I socialnie peremeni, 2010, no.6 (100), pp. 111—126.
- Agranat D.L. Grazhdanskoe obshestvo v Rossii [Civil society in Russia: problems of establishment]. Nauchnie trudi Moskovskogo gumanitarnogo universiteta [Scientific publications of the Moscow Humanitarian University]. Vol. 101.M: MHU University Press, 2009, pp. 3—12.
- Ryabev V.V. Grazhdanskoe obshestvo v sovremennoi Rossii: problemi I perespektivi stanovleniya [Civil society in modern Russia: problems and prospects of establish-ment]. Vestnik MSTU, 2010. Vol. 13, no 2, pp. 439—445.
- Sovremenii rossiiskiij natsionalism kak socialno-politicheskiij faktor [Modern Russian nationalism as a socio-political factor]. Russkiij obozrevatel. Available at: http://www. rusobr.ru/ru-web/15356 (Accessed: 14 February 2015).
- Sharov V.L. Ideologia radikalnogo natsionalizma v sovremennoi Rossii. Diss. Dokt. polit. nauk [The ideology of radical nationalism in modern Russia. Doct. Diss.]. Mos-cow, 2008. 26 pp.
- Novikov I.A. Radikalizm v sovremennoi Rossii I ego vliyanie na socio-kulturnie vzglyadi molodezhi [The radicalism of modern Russia and its impact on the socio-cultural attitudes of youth]. Vestnik Adygeiskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta, 2008, no. 8, pp. 178 —184.
- Korczak E.A. Blagosostoyanie naseleniya Severnih i arkticheskih regionov Rossii [The well-being of the population of Northern and Arctic regions of Russia]. Sovermennije problem nauki I obrazovaniya, 2013, no. 3. Available at: www.science-educa-tion.ru/109-9380 (Ac-cessed: 27 March 2015).
- Bednost i neravenstva soveremennoi Rossii: 10 let spustya. Analiticheskii doklad Instituta Sociologii RAN [Poverty and inequality in modern Russia: 10 years later. Analytical report of the Institute of Sociology], 2013. Available at: http://www.isras.ru/files/File/Doklad/ Analit_doc_Bednost/full.pdf (Accessed: 26 February 2015).
- Pilipenko O.S., Petrovskaya O.A. Sociologicheskiij portret rossiskoi bednosti [The socio-logical portrait of poverty in Russia]. Trudy 7 Mezhdunatodnoi studencheskoi konferencii “Studencheskiij nauchniij forum” [Proc. 7th Int. Stud. Conf. “Student scientific forum”]. Available at: http://www.scienceforum.ru/2015/1052/10910 (Accessed 26 February 2015).
- Tikhonova N.E. Phenomen bednosti v sovremennoij Rossii [The phenomenon of po-verty in modern Russia] Sociologicheskie issledovaniya, 2014, no.1, pp. 7—19.
- Kruchinin V.N. Grazhdanskoe obshestvo v sovremennoi Rossii, problem formirovaniya I funkcionirovaniya [Civil society in modern Russia, problems of establishment and functioning]. Voprosy upravleniya, 2013, no. 4 (25), pp. 7—15.
- Sokolov A., Terentyev I. Volkova O. Issledovanie RBK: sanye bogatie i samye bednye goroda Rossii [RBC study: the richest and the poorest cities in Russia]. Available at: http:// daily.rbc.ru/special/society/13/04/2015/552a6a419a79471fcb568dc8 (Accessed: 17 April 2015).
- Abdulaev S.K. Socialno-piliticheskaya modernizatsiya — osnova razvitiya grazhdan-skogo obshestva (na primere Respubliki Kazakhstan) [The social and political modernization — the foundation of civil society (example of Republic of Kazakhstan)]. Vest-nik Univesiteta (Gosudarstvennii universitet upravleniya), 2014, no.8, pp. 5—7.
- Magomedov M.A. Osobennosti formorovaniya grazhdanskogo obshestva v mnogonatsionalnom regione: na primere Respubliki Dagestan. Diss Dokt. Phil. nauk. [Features of formation of civil society in a multicultural region on the example of the Republic of Dagestan. Doct. Dis.]. Makhachkala, 2005. 199 p.
- Kondral D.P. Mekhanizmi artikulyatsii I aggregatsii interesov obshestva v arkticheskih I priarkticheskih regionah Rossii [Mechanisms of articulation and aggregation of interests of the society in the Arctic and subarctic regions of Russia]. Vorposy politologii I sociologii, 2014, no. 4 (9), pp. 40—46.
- Dzhantueva F.R. Problemi formirovaniya grazhdanskogo obshestva v Rossii [Problems of establishment of civil society in Russia]. Vestnik Adygeiskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta, 2010, no. 3. Available at: http://cyberleninka.RU/article/n/Problemy-formirovaniyagrazhdanskogo- obschestva-v-rossii (Accessed: 27 March 2015).
- Mkrtchyan N.V. Iz Rossii v Rossiu: otkuda i kuda edut vnutrennie migranti [From Russia to Russia: from where and where internal migrants go]. Mir Rossii [World of Rus-sia] Vol. XII Sotsiologiya, ethnologiay, 2003, no.2, pp. 151—164.
- Kravchenko L.I. Demographicheskaya situatsiya v Rossii. Materiali Centra nauchnoi politicheskoi misli I ideologii [The demographic situation in Russia. Materials of the Center of scientific political thought and ideology]. Available at: http://rusrand. RU/forecast/demograficheskaja-situatsija-v-rossii (Accessed: 27 March 2015).
- Krasikov N.V. Inostrannie investitsii na severe evropeiskoi chasti Rossii [Foreign investments in the north of European Russia] Rossiiskoe predprinimatelstvo, 2013, no. 1 (223), pp. 140—144.
- Rybakovsky L. H., Arkhangelskin. N., Ivanova A. E. Demographicheskie konturi regionov Rossii [The demographic contours of regions in Russia]. Moscow, Eco-Inform, 2009. 176 pp.
- Severo-zapadnoe agenstvo razvitiya i privlecheniya investitsii [North West Development Agency and Investment]. Available at: http://Investa.spb.ru/rus/s/4/missiya.html (Accessed: 29 March 2015).
- Kondral D.P., Morozov N.A. Uchet riskov pri formorovanii strategicheskih alyansov razvitiya Arktiki Rossii: metodologicheskii i upravlencheskii uchet [Accounting risks of strategic development alliances establishment of the Arctic Russia: methodological and managerial aspects]. Voprosy upravleniya, 2014, no. (12), pp. 133—138.
- Koltynyuk B.A., Fedorov D.M. Ekonomicheskie problem regionov i otraslevyh kompleksov [The economic problems of the regions and industrial complexes] Problemy sovremennoi ekonomiki, 2009, no. №2 (30). Available at: http://www.m-economy.ru/art.php?NArtId =2551 (Accessed: 27 March 2015).
- Ageev G.V. Osobennosti sovremennogo etapa transformatsii politicheskoij sistemy Rossii [Features of the present transformation of the political system of Russia]. Vlast, 2007, no. 4, pp. 90—92.
- Borisenkov A.A. Politicheskaya vlast- politicheskaya substanciya [Political power — political substance]. Problemy politki i obshsestva, 2013, no. 6, pp. 193—217. Available at: http://enotabene.ru/pr/article_806.html (Accessed: 05 February 2015).
- Farukshin M.H. Politicheskaya sistema obshestva [The political system of the society]. Socialno-politicheskie natsii, 1991, no. 5, pp. 66—75.
- Dmitrakova T. Ne derzhat pod suknom [Do not keep under wraps]. Russiiskaya gazeta, 26 June 2014, no. 6412. Available at: http://www.rg.ru/2014/06/26 /reg-dfo/programma.html (Accessed: 17 April 2015).
- Fyodorov V., Diskin I. Responsivnost sovremennoi rossiiskoi polititcheskoi sistemi, deformatsii i disbalansi v sisteme obshestvenno-gosudarstvennih svyazei [Exercising responsive modern Russian political system, deformations and imbalances in the system of public and government relations]. Monitoring: socialnye and economiche-skie peremeny, 2010, no. 6, pp. 4—11.
- Baranov N.A. Politicheskiy rezhim v sovremennoi Rossii [The political regime of modern Russia]. Izvestiya RGPU, 2007, no. 8 (35) pp 54—64.
- Kryvau A.S., Krupnov U.V. Dom v Rossii. Natsionalnaya idea [House in Russia. The national idea]. Moscow, Olma-Press, 2004. 416p.
- Bobrovskaya I.S. Mestnye nalogi: deistvuushaya sistema o perespektivy razvitiya v Rossiskoi Federatsii [Local taxes: the current system and the prospects for develop-ment in the Russian Federation] Trudy nauchno-prakticheskoi konferencii “Problemi sovershenstvovaniya sistemi nalogooblozheniya v Rossiiskoi Federatsii” [Proc. Conf. “Issues of the tax system development in the Russian Fedration”]. Moscow, MESI publ., 2013. pp 50—55.
- Gorodetsky A.E., Ivanov V.V., Filin B.N. Pravovie i metodologicheskie problemy strategicheskogo planirovaniya razvitiya arkticheskih regionov Rossii [Legal and methodological problems of strategic planning of the Arctic regions of Russia]. Arktika: ekologiya I economika, 2014, no. 4 (16), pp. 4—13.
- Lukin Y.F. Nazrela potrebnost ne tolko sozdaniya “ministerstva Arktiki’, no i modernizatsii vsey sistemy upravleniya Rossiskoi Arktikoi [There is a need not only to create a “ministry of the Arctic”, but also the modernization of the management of the Russian Arctic]. Arctic and North, 2014. Available at: http://narfu.ru/aan/news.php?ELEMENT_ID=180947 (Accessed: 09 December 2014).


