Hardware implementation of the unit of the GNSS consumer
Автор: Sokolovskiy A.V., Veisov E.A., Ratushniak V.N., Rizhkov D.N., Vysotsky S.V.
Журнал: Сибирский аэрокосмический журнал @vestnik-sibsau
Рубрика: Авиационная и ракетно-космическая техника
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.18, 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Navigational equipment is currently used to solve a variety of tasks, such as providing civil and special aviation, navigating, surveying and mapping, Internet devices and unmanned vehicles perfomance. The level of technological development of digital signal processing devices at first glance removes the need for deep study of computational algorithms, but this is only at first glance. As a result of expanding the scope of navigation tools, there is a need to increase the working channels, increase the dynamic range of the processed signals, and also improve the reconfiguration capabilities of signal processing devices. Any synthesized computational algorithm that can be described in hardware description languages, such as VHDL and Verilog, consists of summation operations and a shift operation of the register. There are several basic architectures of adders, each of which has the advantage of either speed of operation or simplicity of implementation. The development of computational architectures working at frequencies of 100 - 200 MHz requires pipeline calculations. Despite the fact that the pipeline architecture has large overheads for equalizing the delays of the computational blocks, its use is justified when processing and converting signals while solving the navigation task. The architecture of hardware computational blocks for constructing navigation equipment for the GLONASS / GPS consumer is considered in the article. The possible ways of increasing the efficiency of some architectures when implementing them on the basis of programmable gate arrays (FPGA) are given.
Cordic, pipeline, hardware adder, hardware multiplier
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148177740
IDR: 148177740 | УДК: 621.396.62
Текст научной статьи Hardware implementation of the unit of the GNSS consumer
Introduction. The development of the hardware architecture of the digital processing of GLONASS/GPS signals is one of the priority directions of development of consumer navigation equipment. The computational costs of the implementation of algorithms for processing navigation signals as a result affect the cost of the device and also determine the future path of hardware development.
The processing of navigation signals at the intermediate frequency requires increased hardware costs due to the fact that computing units operating at frequencies above 100 MHz requires pipelining calculations, and the combined use of computational algorithms. After dropping the navigation signal processing frequency it is possible to reduce hardware costs through the use of a suitable architecture.
Adders architectures overview. Any synthesized computational algorithm, which can be described in hardware description languages such as VHDL and Verilog, consists of the sum and shift register operations. There are several major architectures of adders, each of which has the benefit of either the speed or ease of implementation [1–5].
The simplest architecture is the architecture of the adder, based on sequential bitmap summation of binary numbers and carry bit propagation from the least significant bit (LSB) to the most significant bit (MSB). The basic computational element of this architecture is called a full adder (FA). Despite its simplicity, the main drawback of this architecture is a linear dependence of the delay calculation on the amount of bit terms, as at each iteration of addition it is necessary to consider the carry bit propagation [6–8].
Another, the most demanded, architecture differs in that the propagation of carry bit is pre-calculated according to the so-called scheme of Manchester [9; 10]. The concepts of carry generation and carry transition are introduced in this architecture. Preliminary calculation (1) is carried out once for a group of bits. It reduces the amount of calculations for the following group of bits proportionally:
g . = X y , Pi = XY + XY. ,
Q + i = g . + pC n , . ,
C. + 2 = g . + + P . + 1 g . + P . + 1 PC n , . ,
C . + n = g . + n - 1 + ... + P + n - 1 ... P + 1 g . + P + n - 1 ... PC n , . .
In this architecture the speed of calculations depends on the length and composition of the terms of the bit sequence and depends on the length of the carry bit pre-calculation unit. For this architecture it has a value of a parameter logic circuits like fan-in. It is the number of inputs that can be connected to a circuit.
Another effective adder architecture is based on the simultaneous preliminary carry bit calculation to MSB bits for the group at C n = 0 and C n = 1, and then selecting the active unit based on the calculated value of С n. In contrast to the architecture of a preliminary carry bit calculation to MSB, in this architecture, the calculation of transfer is possible to perform consistently in the elements of full adders. In this case, the sum bit sequences are possible in areas to which the input value of the carry bit has not reached yet. Thus it is possible to reduce the bit sequences calculation time in multiplies of the length of the selected transfer to MSB calculation interval.
There are combinations of bits in the bit string of terms that lead to the propagation of carry bit just for a group of bits. In this case, the calculation of carry bit transfer to MSB bit may be skipped [10; 11]. Then the sum of bit sequences in a limited range is calculated according to (2).
S ,+ n
p = X iYi + X . Y , pi+ n p .' + n - 1 ... pi = 1, 0, C n ,= 0, 1, C n ,= 1.
For this architecture such factors as the probability of the emergence of groups of bits, that create transportation of the carry bit, are of great importance (fig. 1).
Usually, the best result is obtained by sharing multiple architectures. At the same time, organizing a pipelined calculation [10; 11], for such an option another important element of computing is introduced as a carry-save adder (CSA). This adder is based on the fact that the transfer to MSB is passed to the next iteration of the pipeline, that allows avoiding the transference computation in the current iteration, and allows you to work in parallel adder.
High throughput hardware design. There are several ways to improve the effectiveness of the described architectures (fig. 1). For the carry-lookahead adder one must use logic with a large fan-in. For the carry-select adder, ripple-carry adder and carry-skip adder one may iteratively use one and the same group of adders for different groups of bit sequences included in the terms [10; 11].
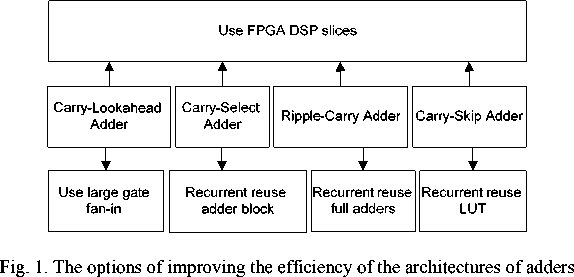
Рис. 1. Варианты повышения эффективности архитектур сумматоров
Hardware processing units operating at frequencies below 10 MHz are greatly simplified due to the choice of architecture adders, using the capabilities of FPGA chip more effectively.
In the development of computer architectures, operating at frequencies 100–200 MHz, pipelining calculations are necessary (fig. 2). Despite the fact that the pipelined architecture has a large overhead for alignment of delay of computing unit, its use is justified in such tasks as:
-
1) the encoding / decoding signals in real time;
-
2) decrease / increase in operating frequency of the signal;
-
3) the processing of wideband signals.
To build consumer navigation equipment GLONASS / GPS the following building blocks of digital processing are needed:
-
1) the scheme of frequency conversion;
-
2) the correlator of pseudo-random sequence;
-
3) the signal tracking scheme.
Frequency conversion scheme is realized based on the pipelined adder and pipelined multiplier (fig. 3). Pipelined multiplier is capable of operating at a frequency of
-
> 100 MHz and perform calculations for 1 clock cycle. Also in the GLONASS / GPS navigation consumer device the multiplier is used for the correlation processing of a navigation signal at the intermediate frequency. After down-frequency conversion the navigation signal may use frequency multipliers operating at frequencies less than 10 MHz (fig. 4). For such processing frequency extra hardware optimization and the use of asynchronous adders to construct a pipelined multipliers are possible (fig. 4). In addition, modern FPGA chips have a large number of DSP layers that can also be used to implement computational units. For example, the implementation of complex pipelined multiplier operating at a frequency of 100 MHz takes 25–30 thousands triggers. At the same time in current FPGA chips it will take only 3 DSP hardware layers.To build consumer navigation equipment GLONASS / GPS the following building blocks of digital processing are needed:
-
1) the scheme of frequency conversion;
-
2) the correlator of pseudo-random sequence;
-
3) the signal tracking scheme.
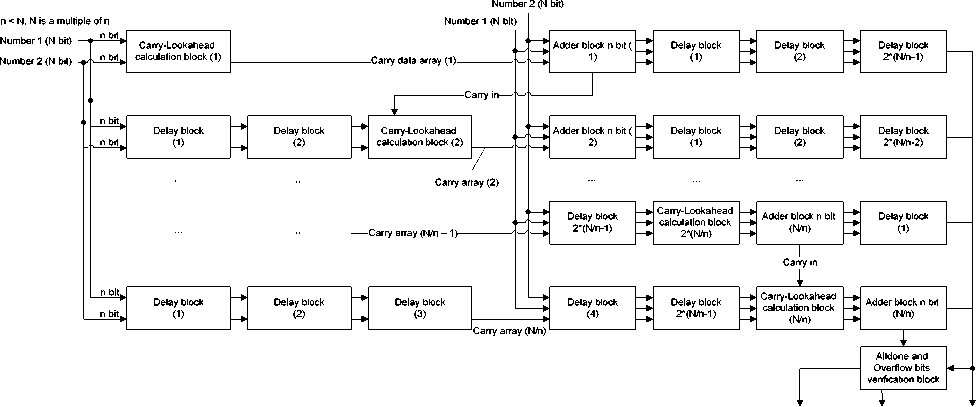
Alldone bit - - . Sum (N bit)
Overflow bit
Fig. 2. Conveyor adder with preliminary transfer calculation
Рис. 2. Конвейерный сумматор с предварительным расчётом переноса
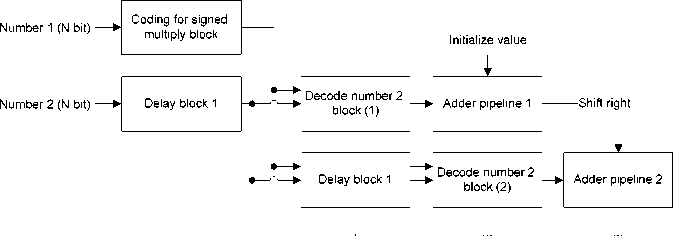
"Shift right
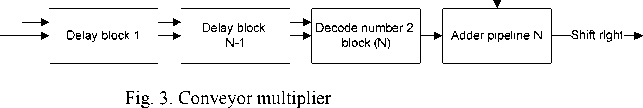
Product
Рис. 3. Конвейерный умножитель
Another important element of the GLONASS / GPS navigation consumer equipment is a digital generator of lettered frequencies (LFG). This oscillator is used to down-convert the carrier frequency of the navigation signal [12; 13].
The LFG can be implemented in two ways. In the first method LFG can be made based on parallel Flashmemory. This method is simple to implement and requires preservation of samples prior workers lettered frequencies. Among the shortcomings of this method one can distinguish that one frequency channel with a sampling frequency of 100–200 MHz requires one external chip Flash-memory. Also, with such a realization it is possible only operate at fixed frequencies with samples previously saved to Flash-memory.
Another method is based on the CORDIC processor operating in rotation mode (fig. 5). Pipelined CORDIC processor is identical to pipelined multiplier by hardware resources, at the same time it allows you to get just two harmonic components of SIN and COS signal [14; 15]. CORDIC processor operates according to the expressions:
x (- + 1) = x (-) - d i y ( i^ — i,
y(1+1) = y(i) + dix (i )2-i, (3) z(i+1) = z(-) — di tan-12-i, where x = cos (z), y = sin (z), z - target angle, de {-1, 1}.
To accelerate the computation intermediate values tan–12– i are calculated beforehand and stored in registers. At each iteration, the intermediate value of angle is checked, then angle increment is selected in the next iteration of the pipeline.
Because this algorithm implements the pseudo-rotation, the length of the vector after the rotation is increased by a factor of K = 1.64676. To compensate for this effect, the initial length of the vector is chosen to be 1 / K = 0.60725. Pipelined implementation allows to calculate the value of sin ( z ) and cos ( z ) in a single cycle, and it is capable of operating at a frequency of more than 100 MHz. The advantages of implementing LFG on CORDIC processor may include the possibility of dynamic reconfiguration of the operating frequency of the measuring path, providing performance for GLONASS / GPS signals in L1 or L2 bands. Also there is the ability to configure the LFG initial phase for hardware alignment signals paths. The disadvantage of this method is the high cost of hardware implementation, since there is a need to perform pipelining calculations at the block operating frequencies of 100–200 MHz. To implement this block not more than 10 DSP layer in FPGA are used, which can significantly reduce hardware costs.
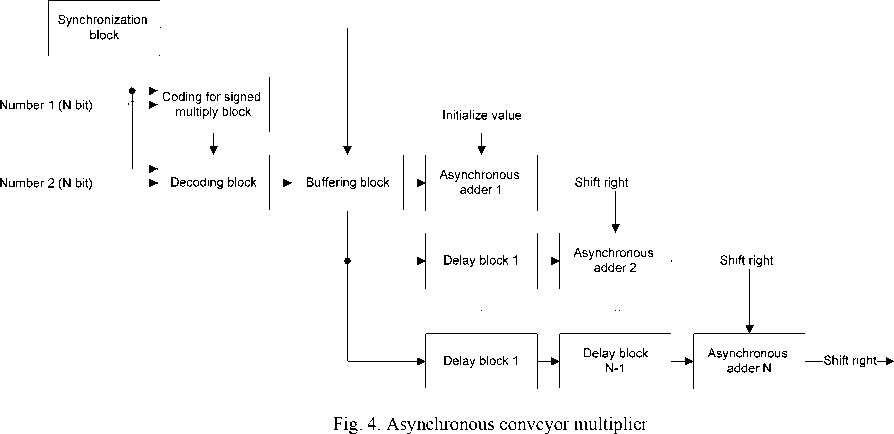
Рис. 4. Асинхронный конвейерный умножитель
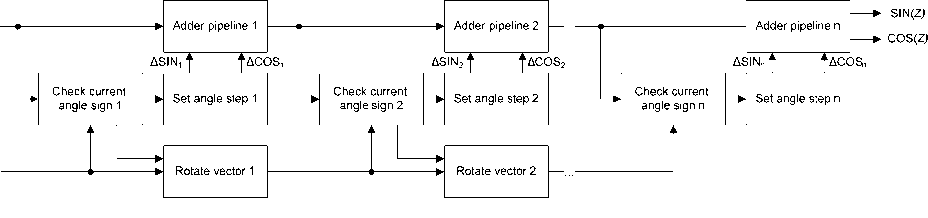
Fig. 5. Conveyor CORDIC processor
Рис. 5. Конвейерный CORDIC процессор (режим вращения)
Conclusion. The hardware architectures of computational units reviewed above have the property of determinism. This feature is of great importance in the construction of navigation consumer equipment GLONASS / GPS, because they allow taking into account the delay in the path of digital signal processing at the design stage. Despite the high price of pipelined performance of computing units, it makes possible to handle the navigation signals at a sampling frequency of 200 MHz. As the high sampling rate allows keeping the form of the navigation signal, it will eventually allow high-precision measurements of the phase of navigation signal. Collectively, the development of computing architectures will allow seeing the weaknesses of a computing device and make better use of the potential of modern FPGA devices.
Acknowledgments. This work was supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of Russian Federation № 02.G25.31.0202.
Список литературы Hardware implementation of the unit of the GNSS consumer
- Свириденко В. А. Программные навигационные приёмники: первый выход на потребительский рынок//МКА: ВКC. 2010, № 4. С. 61-64.
- Грушвицкий Р. И., Мурсаев А. X., Угрюмов Е. П. Проектирование систем на микросхемах программируемой логики. СПб.: БХВ-Петербург, 2002. 608 с.
- Проспект фирмы Falcom GmbH : официальный веб-сайт. 2015. URL: http://www.falcom.de/products.
- Проспект фирмы NTLab : официальный веб-сайт. 2015. URL: http://www.ntlab.com.
- Dr. Danny Rittman. Structured ASIC design: a new design paradigm beyond ASIC, FPGA and SoC. 2004.
- Рабаи Ж. М., Чандракасан А., Николич Б. Цифровые интегральные схемы. Методология проектирования. пер. с англ. 2-е изд. М.: Вильямс, 2007.
- Мишин Г. Универсальные аналоговые программируемые ИС: выбор элементарных функциональных узлов//ЭЛЕКТРОНИКА: Наука, Технология, Бизнес. 2004. № 4. С. 26-30.
- Бабаков В. Н. Навигационная аппаратура сегодня и завтра//Вестник ГЛОНАСС. 2011. № 6. С. 33-35.
- Руткевич А. В., Шишкин Г. В., Стешенко В. Б. Опыт разработки СФ-блоков и процессорных ядер СБИС типа СнК для навигационной аппаратуры//Проблемы разработки перспективных микро-и нано-электронных систем (МЭС). 2010. № 1. С. 237-240.
- Parhami B. Computer arithmetic: algorithms and hardware designs. 2000. P. 490.
- Israel K. Computer arithmetic algorithms. 2002. P. 281.
- Xilinx UG1046, UlatraFast embedded Design Methodology Guide. 2015. P. 231.
- Перов А. И., Харисов В. Н. ГЛОНАСС: принципы построения и функционирования. 4-е изд. перераб. и доп. М.: Радиотехника, 2010. 800 с.
- Daineko D. FPGA based CORDIC algorithm design//Components & Technologies (Russia). 2011. Vol. 12. Р. 36-46.
- 1076 IEEE Standard VHDL Langeage Reference Manual. 2002. Р. 300.


