Heavy metal accumulation potential and medicinal property of Bacopa monnieri- a paradox
Автор: Hussain K, Abdussalam Ak, Ratheesh Chandra P, Salim Nabeesa
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.7, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Bioaccumulation of Mercury and Cadmium in Bacopa monnieri (L.) Pennell, cultivated in Hoagland medium artificially contaminated with micro quantities of HgCl2 and CdCl2 is investigated. Bioaccumulation potential of B. monnieri is more towards Cd than Hg. Absorption and translocation of Hg and Cd are proportional to the availability of the metal in the growth media and period of growth. Effect of acidic pH showed enhanced accumulation while basic pH resulted in significant reduction in the accumulation of Hg and exorbitant reduction of Cd. As a result of combined treatment of HgCl2 and CdCl2, accumulation was very low in both acidic and basic pH. In addition to pH, antagonistic effect of Ca2+ present in lime water which was added to raise the pH of the growth medium also controls the accumulation and absorption of Hg and Cd ions. Bioaccumulation of Hg and Cd in B. monnieri reveals the phytoremediation potential while the bioaccumulation is hazards to health since the plant is highly medicinal and one important ingredient of many Ayurvedic preparations.
Bioaccumulation, bacopa monnieri, phytotoremediation
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323567
IDR: 14323567
Текст научной статьи Heavy metal accumulation potential and medicinal property of Bacopa monnieri- a paradox
Bacopa monnieri (L.) Pennell is a fast growing wetland species and is well adapted to thrive in polluted areas which receive regular flushing of sewage waste and industrial effluents. Lenka et . al., (1992) reported that B. monnieri accumulate mercury in the roots and shoots of plants growing in the wetlands in the vicininty of Chloralkali industry.
This plant has been recommended as an agent for phytoremediation (Sinha and Chandra, 1990, Sinha et. al., 1996, Sinha, 1999, Yadav et. al. 2005). Potential of B. monnieri to accumulate As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn has been reported by analyzing the quantities of these elements in the naturally growing plants collected from different polluted areas of Kerala (Hussain et. al. 2010).
Mercury is a global pollutant that cycle through bacteria, air, soil and water as a result of natural and anthropogenic activities and hence plants are directly exposed to this toxic heavy metal. Even though angiosperms have not yet been reported as tolerant to mercury (Lepp, 1981, Orcutt and Nilson, 2000; Cseh, 2002) and no plant has been identified as mercury hyper-accumulator (Henry, 2000, Raskin and Ensely, 2000), considerable absorption and accumulation of mercury have been reported in B. monnerie (Sinha and Chandra, 1990, Sinha et. al . 1996), Brassica jencea (Moreno et. al. 2005a, b, 2008). Chromolaena odorata is an accumulator of Hg and has been recommended as a phytoremediant (Velasco-Alinsug et al ., 2005).
Cadmium is a wide spread toxic heavy metal of geogenic and anthropogenic pollutant (Prasad, 1997; Salt et. al. 1998; Orcutt and Nilson, 2000. Perfus-Barbeoch et. al. 2002) Phytoremediation of cadmium has been effectively performed by Silene vulgaris (Joop et. al . 1994), Brassica juncea (David et.al. 1995, Ishikawa et.al . 2006, Polygonum thumberhii (Shinmachi et. al. , 2003) Potomegoton pectinatus (Rai et. al . 2003) Salia viminalies (Mleezek et. al ., 2009).
Bacopa monneri has been used as important incredient of Ayurvedic system of medicine for centuries. Traditionally the entire plant is used as a brain tonic to enhance memory, development, learning ability, concentration etc. and the compounds responsible for pharmacological effect include alkaloids, saponins and sterols (Nair, 1987, Wohlmuth, 2001, Anonymous, 2004).
The medicinal use and heavy metal bioaccumulation potential of B. monnieri are found to be paradoxical because consumption of
Ayurvedic medicines containing this species which accumulates considerable quantities of toxic metals may lead to serious health hazards. So the present study was undertaken to assess the potential of Bacopa monneri to absorb and accumulate mercury and cadmium by growing the plant in Hoagland nutrient solution artificially contaminated with different concentration of HgCl 2 and CdCl 2 . Since pH of the nutrient solution is found to change the toxic effect of Mercury and Cadmium in B. monnieri (Hussain, 2007) effect of different ranges of pH on bioaccumulation potential was another important objective of this study.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Bacopa monnieri (L.) Pennell cuttings of 7-8 cms consisting of 5-6 nodes were collected from the medicinal plant collection of Calicut University Botanical garden. Rooted propagules were planted in Hoagland solution prepared following the modified method of Epstein (1972) as described by Taiz and Zeiger (1991). Three sets of experiments were conducted to assess the bioaccumulation pattern and potential of B. monneiri towards mercury and cadmium.
Dose response studies by mercuric chloride and cadmium chloride
For the treatments with HgCl 2 nutrient solution was contaminated with three concentrations of HgCl 2 (2, 5 and 10 µM) and based on dose- response studies conducted, about 50% growth retardation and reproducible responses were observed in 10 µM HgCl 2 . Similarly, three concentrations (10, 20 and 30 µM) solutions of CdCl 2 proved similar responses in 30 µM concentration. So, 10 and 30 µM concentrations of HgCl 2 and CdCl 2 respectively were selected for the experiments. Plants cultivated in the Hoagland nutrient medium served as the control.
Good quality plastic containers of 12x8.5x3 cm were used for nutrient culture. Plastic wire of 1mm diameter was tied on the mouth of the container interweaving length-wise and breadth-wise forming a mesh to provide mechanical support to the propagules. Hoagland medium with known quantities of HgCl2 and CdCl2 were within repaired contaminating rooted propagules were planted in the nutrient medium by inserting through the mesh without disturbing the root system. The gap provided underneath facilitated room for growth of root system. All experimental containers were kept under green house condition.
Random sampling was followed to collect plants from ten replicate containers of each treatment and control at an interval of 2 days up to 12 days. Propagules collected were cut in to root, stem and leaf and were used for bioaccumulation studies of Hg and Cd.
Effect of additional supply of HgCl2 and CdCl2:
To study the effect of additional Hg and Cd content on growth for prolonged period, the schedule of treatments is given below (Table 1):
Table 1. Quantitative schedule of Hg and Cd treatments
|
Treatment |
Concentratio n |
Interval - Days |
|||
|
HgCl 2 |
10 µM |
20 |
30 |
40 |
50 |
|
Quantity of Hg/Cd µg per container |
|||||
|
500 |
600 |
700 |
800 |
||
|
CdCl 2 |
30 µM |
840 |
1008 |
1176 |
1344 |
Effect of pH on the accumulation of Mercury and Cadmium
Acidic pH
Distilled water was used as the growth medium because change in pH resulted in the precipitation of nutrients in the Hoagland solution pH was adjusted to 5.5 by adding known quantities of 1M NH 4 Cl solution, to distilled water and solutions of HgCl 2 and CdCl 2 , were added to the containers to obtain the concentrations 20 and 30 µM respectively.
Alkaline pH
To distilled water, known quantity of calcium hydroxide solution was added to obtain alkaline pH (7.5). HgCl 2 /CdCl 2 solution was added to get 10 and 30µM respectively. Concentrations of Hg Hg2+ and
Cd2+ added to growth medium under different pH are given below (Table 2).
Estimation of Mercury and Cadmium
Plant parts-root, stem and leaf tissues of B. monnieri were sampled for analyzing Mercury and Cadmium contents. Samples were prepared according to the method of Allan (1969). Known weight of the samples were wet digested by refluxing in 10 ml of nitric acid, and perchloric acid in the ratio of 10: 4 until the solution became colorless by using Kjeldhahls flasks heated in a sand bath and digest was analyzed to estimate mercury and cadmium by using Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (Perkin Elmer model Analyst 300). All experiments were repeated a minimum of five times.
Table 2. Quantitative treatments at different pH
|
Medium |
pH |
Treatments and quantity given |
||
|
Distilled water |
6.8 |
HgCl 2 (400µgHg) |
CdCl 2 (224µgCd) |
HgCl 2 +CdCl 2 , (400µgHg+224µgCd) |
|
Acidic medium |
5.5 |
do |
do |
do |
|
Basic medium |
7.5 |
do |
do |
do |
|
Hoagland |
6.2 |
do |
do |
do |
RESULTS
During growth for 12 days, accumulation of mercury was maximum in roots followed by stem and leaves during all intervals (Fig. 1) Mercury accumulated in the root tissue remained unchanged during growth compared to the stem and leaf tissue which showed enhanced rate of accumulation.
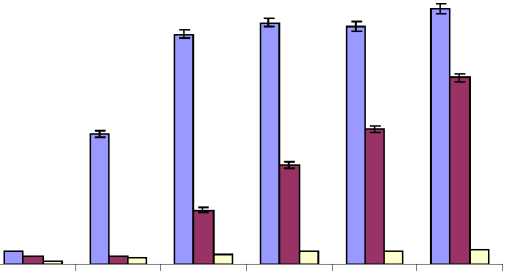
Accumulation of cadmium also was maximum in root tissue and order of accumulation was Root>Stem>Leaf. Cadmium content accumulated in the root was progressively increased during growth. Similar trend was seen in stem tissue and Cd content of leaf was very low. (Fig. 2)
When the plants were exposed to additional doses 100µg each of Hg at an interval of 10 days each during 50 days, Hg concentration per plant was increased Cd proportional to the content given (Table 4). The quantity accumulated at each interval was approximately 25% of the total given in the medium. In the case of cadmium also more or less similar pattern of accumulation was observed (Table 4). But the quantity accumulated was above 50% of the total given in the medium at each interval.
Effect of acidic (5.5) - and alkaline (7.5) pH showed remarkable differences in metal accumulation (Table 4). At acidic pH, mercury accumulation was more than the control and showed two fold increase compared to the alkaline medium. Propagules grown in acidic medium accumulated Cd content more than 8 times in comparison with the control whereas in alkaline medium, only very low quantity was accumulated (less than 1%). When mercury treatment was given in Hoagland nutrient medium (pH 6.0) accumulation was similar to that of the control and acidic pH whereas Cd content was significantly reduced compared to that of the acidic pH but was more than the control (Table 3).Combined treatment of HgCl 2 and CdCl 2 showed very low amount of Hg in all treatments and control whereas Cd content was reduced compared to their individual treatment. Similarly in alkaline and acidic media, Hg accumulation showed negligible difference whereas Cd accumulation in the acid medium remained unchanged, but in alkaline medium an exorbitant reduction was observed compared to their respective control. (Table 3).
Table 3 Bioaccumulation of Mercury and Cadmium in Bacopa monneri during 50 days of growth in different concentrations
|
Treatment |
Concentration |
Interval (days) |
Quantity given |
Accumulation mg |
|
HgCl 2 |
10µM |
20 |
500 |
121± 4.6 (24.2) |
|
30 |
600 |
164± 4.1 (27.3) |
||
|
40 |
700 |
189± 5.2 (27.3) |
||
|
50 |
800 |
204± 5.7 (25.5) |
||
|
CdCl 2 |
30 µM |
20 |
840 |
409± 12.8 (48.6) |
|
30 |
1008 |
491± 11.6 (48.7) |
||
|
40 |
1176 |
508± 12.4 (50.3) |
||
|
50 |
1344 |
565± 12.8 (49.9) |
Values in parenthesis are percentage of accumulation
Table 4 Effect of pH on mercury and cadmium uptake in B. monnieri during growth in different media (mg-1 dry tissue)
|
Treatments |
Distilled water pH 6.8 |
Acidic pH 5.0 |
Basic pH7.5 |
Hoagland pH 6.2 |
|
|
HgCl 2 400µgHg |
Hg |
54.00±1.03 |
68.88±.1.04 |
36.20±0.82 |
66.3±1.04 |
|
CdCl 2 224µgCd |
Cd |
35.46±0.90 |
266.80±2.07 |
2.39±0.03 |
72.30±1.04 |
|
HgCl 2 + CdCl 2 400µgHg+ +224µgCd) |
Hg |
0.60±0.01 |
0.47±0.01 |
0.77±0.01 |
0.60±0.01 |
|
Cd |
23.98±0.82 |
28.80±1.02 |
1.02±0.02 |
1.90±0.01 |
|
10 µM
□ Root
□ Stem
□ Leaf
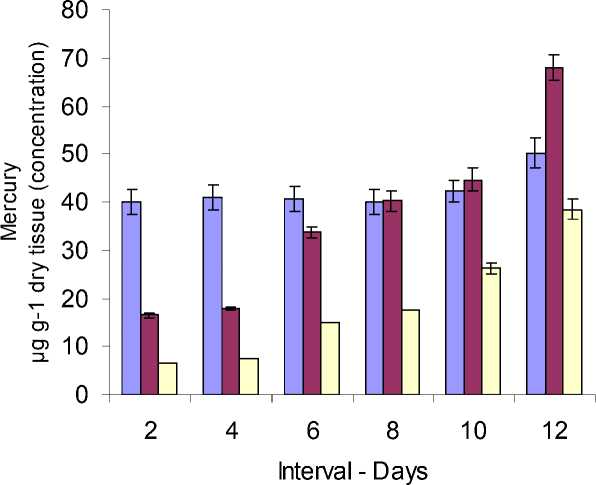
Figure 1 Accumulation of Mercury contents in different parts of Bacopa monnieri treated with HgCl 2 during growth. µg/g-1 dry tissue(concentration)
30 µ M ф = <д <д
□ Root □ Stem □ Leaf
о) Ь
О)
ф о с о о
го о
10 12
Interval - Days
Figure 2 Accumulation of Cadmium contents in different parts of Bacopa monnieri treated with CdCl 2 during growth. mg/g-1 dry tissue (concentration)
DISCUSSION
During 12 days of growth under the simulated laboratory conditions, mercury content of root was almost uniform whereas stem and leaves showed significant (p<0.01) increase (Fig.1). The mercury uptake pattern of Bacopa monnieri is similar to that reported in Chromolaena odorata which has been recommended as a phytoremediant. ( Velasco - Alinsug et.al , 2005). About 40µg gram Hg g-1 dry tissue of roots appear to be the thresholed level of accumulation to which the plant is tolerant and above this level, it may cause toxicity to root system as suggested by Bauford et.al , (1977) . Notwithstanding, Additional application of HgCl 2 and prolonged growth period exhibit proportionate increase in accumulation on per plant basis (Table 4) and so this observation indicates the phytoremediation potential of B. monnieri Although no plant has yet been identified as natural hyperaccumulator of Hg (Henry, 2000: Ruskin and Ensley, 2000), transgenic plants such as Arabiidopsis thaliana, Liriodendron tulipifera and Nicotiana tabacum are reported to be capable of converting methyl mercury to Hg2+ and are having the potential of phytoremediation in alleviating Hg polluted areas (Bizily et. al. ,1997; Rugh etal. , 1996;1998).In the present study Bacopa monnieri is found to accumulate about 25% of the Hg content available in the growth medium. This is inconformity with views of (Sinha et al., (1996) and Sinha (1999 ) who recommended Bacopa monnieri as a plant for phytoremediation of metals such as Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Mn and Pb from contaminated water and wetlands. Nevertheless, this plant is not a hyper accumulator of heavy metals.
Bio accumulation potential of Bacopa monnieri towards cadmium is not similar to mercury on per plant basis. About 50% Cd present in the medium is absorbed during prolonged period of growth (Table
4). Accumulation of Cadmium is also maximal in roots and this metal reported to be easily taken up by the roots and transported to the leaves since Cd2+ ion are fast mobile in plants (Siedlecka and Krupa, 1997). According to Sersen et. al. , (2005 ), Maize plants grown in nutrient medium containing Cd is able to absorb Cd and the accumulation is proportional to the availability of the metal. The accumulation pattern of Cd in the roots of Bacopa monnieri is almost in consistent with the views of Sersen et. al. ,(2005 ) because Cd accumulation is proportional to the increase of CdCl 2 concentration in the nutrient medium. According to Sanita-di-Toppi and Gabbrielli (1999) immobilization of Cd by binding to the cell wall is one of the causes of Cd hyperaccumulation in plants. Many plants such as Potamogeton pectinatus (Rai et.al ., 2003 ) Arabidopsis thaliana (Perfus –Barbeoch et. al ., 2002. Phragmites australi s (Ederli et.al , 2004 ), Cannabis sativa (Linger et. al ., 2005) Brassica juncea (Ishikawa et. al , 2006 ) are reported as hyper accumulators of Cd. Eventhough most of the Cd accumulators are recommended for phytoremediation (Pilon-Smits, 2005), translocation of Cd2+ to rice grains causing health hazards have been reported recently by Tanaka et. al ., (2007)
Accumulation of Hg and Cd by Bacopa monnieri is dependent on the presence of other ions as well as the pH of the growth medium. The plants cultivated in distilled water containing HgCl2 and CdCl2 having the pH 5.5 showed a slight increase in accumulation of Hg (Table 4.). The accumulation of Cd was 8 times higher. The behavior of Bacopa monneri towards pH changes in the absorption mode of Cd is in accordance with the findings of Hattori et. al., (2006) in Helianthus and Hibiscus where a doubling of Cd uptake was occurred by the application of Cl- to reduce soil pH. Accumulation of Cd is reduced exorbitantly in basic pH in comparison with the pH 5.5 (Table 4). This may not be due to the effect of pH alone. The control of influx and /or antagonistic effect of Ca2+ due to the addition of Calcium hydroxide to the medium cannot be ruled out in accordance with the view of Hough et al., (2003) in wheat where liming to reduce soil pH resulted in reduced Cd uptake. According to Kim et al., (2002) Ca2+ inhibits Cd accumulation in rice roots by substituting Ca2+ to Cd2+ ions. Perfus-Barbeoch et. al., (2002) suggested that in Arabidopsis thaliana, CdCl2 induced stomata closure by controlling Ca2+ channels of plasma membrane of guard cells and Cd2+ mimics Ca2+ channels and enter guard cell through calcium channels. According to Ried et. al. (2003) Cd accumulation in plants is due to many physical similarities between Ca2+ and Cd2+ in such a way that the ionic radius of Ca2+ (9PM) and that of Cd2+ (7PM) causes sharing of Ca2+ channels with Cd2+ for the absorption and translocation in potato tuber.
Bacopa monneri plants grow wildly in wetland which naturally get contaminated with sewage and other waste water and considerable accumulation of Hg, Cd, Cr, Cm, Mu and Pb in naturally growing of Bacopa monneri plants have been reported (Hussain-Koorimannil et.al. 2010) . This stimulated experimental study confirms the accumulation potential of this plant. Collection of B. monneri plants from contaminated wetlands is a common practice of manufacturers of Ayurvedic medicines and food supplements and consumption of these products by human beings will lead to serious health hazards.
The effect of changing pH on the combination of HgCl2 and CdCl2 treatment reveals significant inhibition of Hg uptake and partial control over CdCl2. The antagonistic effect Hg and Cd on one hand and that of Ca2+ and NH4+ on the other may be the plausible reason. In Bacopa monneri increased pH due to the addition of calcium hydroxide to nutrient medium control the entry of Cd2+ through Ca2+ channels and the overwhelming flux of the latter may be due to the similar ionic radius of Cd2+ and Ca2+ as suggested by ( Raid et. al., 2003). In this context, liming can be recommended as a measure against Cd2+ and Hg2+ absorption and translocation. On the contrary, reduced pH of the growth medium (5.5) by adding NH4Cl (chlorination) results in signified increase of Hg and Cd uptake (Table 4).
CONCLUSION
The medicinal property and wide use of Bacopa monnieri as an ingredient of many Ayurvedic medicines and food supplements on one hand and the bioaccumulation potential and phytoremedeiation efficacy on the other are paradoxical . The absorption and accumulation of Hg and Cd is maximum at acidic pH and very low at alkaline pH by B. monneri convey that, for medicinal and phytoremediation purposes, cultivation in alkaline soil/water and acidic soil/water respectively is recommended.
Список литературы Heavy metal accumulation potential and medicinal property of Bacopa monnieri- a paradox
- Allan, J.E. (1969), The preparation of agricultural samples for analysis by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry.S.I.S. Edition; Varian TechtronBulletin.12-69
- Anonymous. (2004), Bacopa monniera-monograph. Altern. Med. Rev. 9, 79-85
- Beauford, W., Barber, J. and Barringer, A.R. (1977), Uptake and distribution of mercury within higher plants. Physiol. Plant. 39, 261-265
- Bizily, S., Rugh, C., Summers, A.O. and Meagher, R.B. (1997), Phytoremediation of methyl mercury pollution: Mer B expression in Arabidopsis thalianaconfers resistance to organo mercurials. Proc. Nalt. Acad. Sci. USA.96, 6808-6813
- Cseh, E. (2002), Metal permeability, transport and efflux in plants. In: M.N.V. Prasad and K. Strzalka (Eds.). Physiology and Biochemistry of Metal Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants. 1-36
- David, E.S., Rogfer, C.P., Ingrid, J.P. and Ilya, R. (1995), Mechanisms of cadmium mobility and accumulation in Indian mustard. Plant Physiol. 109, 1427-1433
- Ederli, L., Reale, L., Ferrauti, F. and Pasqualini, S. (2004), Responses induced by high concentration of cadmium in Phragmites australis roots. Physiol. Plant.121, 66-74
- Epstein, E. (1972), Mineral Nutrition of Plants, Principles and Perspectives. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
- Hattori, H., Kuniyasu, K., Chiba, K. and Chino, M. (2006), Effect of chloride application and low soil pH on cadmium uptake from soil by plants. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 52, 89-94
- Henry, J.R. (2000), Phytoremediation of mercury. In: An Overview of the Phytoremediation of Lead and Mercury: A Report for the U.S. Environ. Protec. Agency, D.C. USA. 44-46.
- Hoagland, D.R. and Arnon, D.I. (1950), The water culture method of growing plants without soil. Colif. Agric. Expal. Stn. Circ. 347, 461-465
- Hough, R.L., Hough, R.L., Young, E.D. and Crout, N.M.J. (2003), Modelling of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn uptake by winter wheat and forage maize, from a sewage disposal farm. Soil Use Manage. 19, 19-27
- Hussain, K. (2007), Ecophysiological aspects of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Pennell. Thesis submitted to the University of Calicut, Kerala.
- Hussain-Koorimannil., Abdussalam, A.K., Ratheesh-Chandra, P. and Nabeesa Salim. (2010), Bio accumulation of heavy metals in Bacopa monnieri (L.) Pennell growing under different habitat. Int. J. Ecol. & Devlop. 15, 66-73.
- Ishikawa, S., Ae, N., Murakami, M. and Wagatsuma, T. (2006), Is Brassica junceaa suitable plant for phytoremediation of cadmium in soils with moderately low cadmium contamination? -Possibility of using other plant species for Cd-phytoextraction. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 52, 32-42.
- Joop, A.K., Marjolein, D., Paul, L.M.K., Henk, S., Jos, A.C.V. and Wilfried, H.O.E. (1994), Phytochelatin in cadmium sensitive and cadmium tolerant Silene vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 104, 255-261.
- Kim, Y.Y., Yang, Y.Y. and Lee, Y. (2002), Pb and Cd uptake in rice roots. Physiol. Plant. 116, 368-372.
- Lenka, M., Panda, K.K. and Panda, B.B. (1992), Monitoring and assessment of mercury pollution in the vicinity of a chloralkali plant, IV: Bioconcentration of mercury in situaquatic and terrestrial plants at Ganjam, India. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 22,195-202.
- Lepp, N.W. (1981), Effect of Heavy Metal Pollution on Plants. 2. Applied Science Publishers, London.
- Linger, P., Ostwald, A. and Haensler, J. (2005), Cannabis sativa L., growing on heavy metal contaminated soil: Growth, cadmium uptake and photosynthesis. Biol. Plant. 49, 567-576
- Mleezek, M., Kasyewski, L.M., Kaezmarekm, Z.M., Rissmann, I. and Gabinski, P. (2009), Efficiency of selected heavy metals accumulation by Saliva roots Environ. Exp. Bot. 65, 48-53
- Moreno, F.N., Anderson, C.W.N., Stewart, R.B. and Robinson, B.H. (2008), Phytofiltration of mercury -contaminated water: Volatilisation and plant -accumulation aspects. Environ. Exp. Bot. 62, 78-85.
- Moreno, F.N., Anderson, C.W.N. Stewart, R.B., Robinosn, B.H., Nomura, R., Ghomshei, M. and Meech, J.A. (2005b), Effect of thioglands on plant -Hg accumulation and volatilisation from mercury contaminated mine tailings. Plant soil, 275, 233-246.
- Nair, K.K.N. (1987), Medhya Rasayana Drug 'Brahmi' -Its Botany, Chemistry and Uses. J. Econ. Tax. Bot. 11, 359-365.
- Orcutt, D.M. and Nilsen, E.T. (2000), Physiology of Plants Under Stress: Soil and Biotic Factors.John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York.
- Perfus-Barbeoch, L., Leonhardt, N., Vavasseur, A.and Forestier, C. (2005), Heavy metal toxicity: Cadmium permeates through calcium channels and disturbs the plant water status. The Plant J.; 32, 539-548.
- Pilon-Smits, E. (2005), Phytoremediation. Annu. Rev.Plant. Biol. 56,15-39.
- Prasad, M.N.V. (1997), Trace metals In: M.N.V. Prasad (Ed.). Plant Ecophysiology. Wiley & Sons, Inc. 207-249.
- Rai, U.N., Tripathi, R.D., Vajpayee, P., Pandey, N., Ali, M.B. and Gupta, D.K. (2003), Cadmium accumulation and its phytotoxicity in Potamegeton pectinatusL. (Potamogetonaceae). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 70, 566-575.
- Raskin, I. and Ensley, B.D. (2000), Phytomediation of Toxic Metals Using Plants to Clean up the Environment.John Wiley & Sons. Inc. New York.
- Reid, R.J., Dunbar, K.R. and McLaughlin, M.J. (2003), Cadmium loading into potato tubers: the roles of the periderm, xylem and phloem. Plant Cell Environ. 26, 201-206.
- Rugh, C.L., Senecoff, J.F., Meagher, R.B. and Merkle, S.A. (1998), Development of transgenic yellow poplar for Hg phytoremediation. Natur. Bio. Technol. 16,925-928.
- Rugh, C.L., Wilde, H.D., Stack, N.M., Marin-Thompson, D., Summers, A.O. and Meagher, R.B. (1996), Mercuric ion reductase and resistance in transgenic Arabidopsis thalianaplants expressing a modified bacterial mer A gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 93,3182-3187.
- Salt, D.E., Smith, R.D. and Raskin, I. (1998), Phytoremediation. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Mol. Biol. 49, 643-668.
- Sersen, F., Clik, G., Havranek, E. and Sykorova, M. (2005), Bio-remediation by natural zeolite in plants cultivated in a heavy metal-contaminated medium. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 14,13-17.
- Shinmachi, F., Kumanda, Y., Noguchi, A. and Hasegawa, I. (2003), Translocation and accumulation of cadmium in cadmium tolerant Polygonum thunberjii. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 49, 355-361.
- Siedlecka, A.and Krupa, Z. (1997), Cd/Fe interaction in higher plants -its consequences for the photosynthetic apparatus. Photosynthetica 36, 321-331
- Sinha, S. (1999), Accumulation of Cu, Cd, Cr, Mn, and Pb from artificially contaminated soil by Bacopa monnieri. Environ. Monit. Assess. 57, 253-264.
- Sinha, S. and Chandra, P. (1990), Removal of Cu Cd from water by Bacopa monnieri (L.). Water Air Soil Pollut. 51, 271-276.
- Sinha, S., Gupta, M. and Chandra, P. (1996), Bioaccumulation and biochemical effect of mercury in the plant Bacopa monneri (L.). Environ. Toxicol. Wat. Qual. 11,105-112.
- Taiz, L. and Zeiger, E. (2002), Plant Physiology: IIIrd edition, Sinauer Associates, Inc., Publishers, Sunderland, Massachussetts.
- Tanaka, K., Fujimaki, S., Fujiwara, T., Yoneyama, T. and Hayashi, H. (2007), Quantitative estimation of the contribution of the phloem in cadmium transport to grains in rice plants (Oryza sativa.). Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 53, 72-77.
- Velasco-Alinsug, M.P., Rivero, G.C. and Quibuyen, T.A.O. (2005), Isolation of mercury-binding peptides in vegetative parts of Chromolaena odorata. Z. Naturforsch. 60c, 252-259.
- Wohlmuth, H. (2001), Brahmi update. In: Botanical Pathways, Information and Research on Botanical Medicine, 8: 1. (www.netresources.com.au/health/brahmi.pdt).
- Yadav, S., Sukla, O.P. and Rai, U.N. (2005), Chromium pollution and bioremediation. Environ. News Archiv. 11, 1-4.


