Holistic marketing toolkit
Автор: Xajikulov Bektash Eshmamatovich
Журнал: Экономика и социум @ekonomika-socium
Рубрика: Основной раздел
Статья в выпуске: 9 (88), 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This article is devoted to the justification of the need for a holistic management of enterprise marketing and management at the regional level. The author identified and described in detail the main components of a holistic marketing management tools at the enterprise and regional holistic marketing.
Marketing, holistic marketing, market, management, tools, integrated, socially responsible model
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140254924
IDR: 140254924 | УДК: 339
Текст научной статьи Holistic marketing toolkit
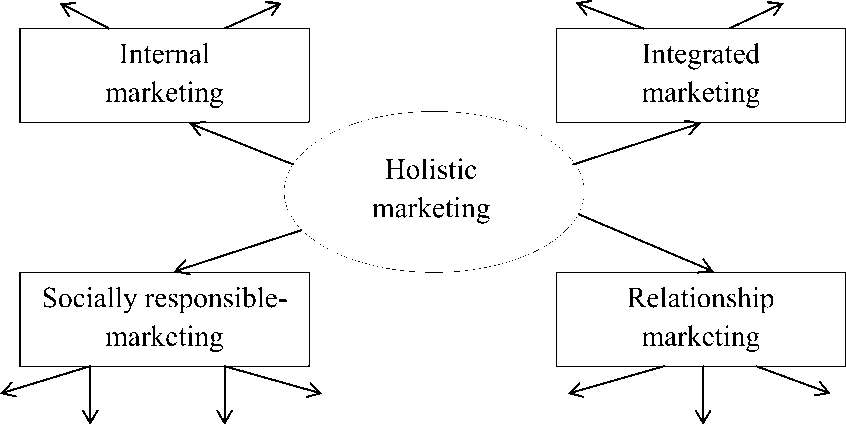
Holistic marketing is a relatively new direction in the development of management concepts, in which all attention is focused on the integrated elements of a firm's business interactions with customers, suppliers and intermediaries. This concept does not consider a collection of individual elements, but all components as a whole. Holistic marketing is an attempt to balance the individual components and put them together.
Holistic marketing can be viewed from two perspectives: enterprise holistic marketing and regional holistic marketing.
Each of these approaches has its own characteristics and its own set of tools.
The concept of holistic marketing at an enterprise involves increasing production volumes and attracting customers and partners through holistic marketing programs and taking into account the interests of consumers, partners, society and company employees as much as possible.
The components of holistic marketing [6] are shown in Figure 1.
Marketing department Top-management Communications Goods and services
Society
Buyers
Ethics
Partners
Ecology
Right
Channel
-
Figure 1 - Components of holistic marketing.
Each of the elements of this approach has its own tools to improve the efficiency of the company.
The task of integrated marketing is to develop activities and draw up a complete integrated marketing program for creating, promoting and delivering value to consumers. [2] These activities can be very diverse and traditionally they are usually described as a marketing mix or a "4P" system. J. McCarthy proposed to classify marketing tools in four areas: Product, Price, Place and Promotion.
The components of the marketing mix, from the point of view of the seller, are the marketing tools with which he can influence the buyers. From the point of view of the buyer, the purpose of each marketing tool is to increase the value of the consumer.
In addition to the well-known traditional and extended models of integrated marketing, there are other models based on them. These models are presented in Table 1.
Table 1
Marketing mix models
|
Model |
The constituents |
Authors |
|
5P |
4P + Packaging |
J.T. Russell, W.R. Lane |
|
5P |
4P + Perception |
N. Hart |
|
6P |
4P + Public opinion + Politics |
F.Kotler |
|
7P |
6P+ Policy |
F. Popcorn |
|
8P |
Traditional 7P + Pace |
L. Tweed |
|
12P |
8P + Permission + Paradigm + Pass + Practice |
S. Godin |
|
12P + 4A |
12P + Adressability + Accountability + Affordability + Accessibility |
S.Rapp, C.Martin |
The development and implementation of any marketing activity is carried out with an eye to all other marketing activities of the company. The company must integrate demand management, resource management and partner network management systems.
Internal marketing is the provision of proper marketing principles to the enterprise by all employees of the organization. This element of holistic marketing is aimed at promoting and understanding ideas both within the enterprise as a whole and at the level of individual departments.
By analogy with traditional marketing and the 4P model, the internal marketing mix includes the following tools:
-
1. The job offered by the organization to the employee is an internal product. The satisfaction of the staff with the internal product (work) depends on how the consumer properties of this product meet the expectations of the staff.
-
2. Payment - the price of the domestic product. Domestic product pricing is based on the assumption that employee benefits from work must be greater than this opportunity cost. In other words, the price of an internal product is determined by the degree of employee motivation.
-
3. Place (distribution) - a way of bringing an internal product to its consumer (employee). On the one hand, this component is considered from the point of view of the effectiveness of the organizational structure [7]. On the other hand, it is the correct distribution of employees within the organization. It also considers the convenience of the territorial location of the workplace for individual employees.
-
4. Promotion of an internal product is the formation of a corporate culture that contributes to meeting the needs of internal customers, the creation of a
system of effective relationships between internal customers and internal suppliers, between internal customers and external customers, the development of internal communications and other elements of internal PR. Thus, the internal marketing toolkit is:
-
• Product - A job offered by an organization to an employee;
-
• Price - Labor remuneration;
-
• Place - Organizational structure;
-
• Promotion - Internal PR.
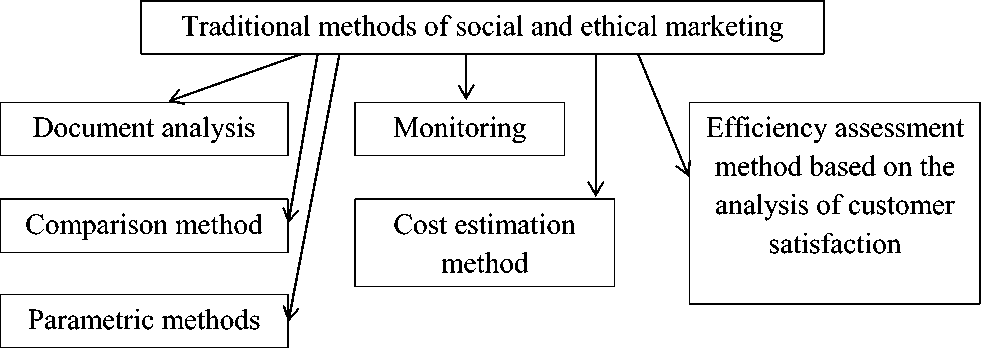
Analytical methods of social and ethical marketing [3] are presented in Figure 2.
|
Figure 2 - Traditional analytical methods Table 4 |
Multivariate analysis methods and their characteristics
|
Name |
Characteristic |
|
SPACE - analysis (Strategic Position and Action Evaluation) |
Strategic assessment of positions and actions. This method is based on the analysis of the position of the organization and the conditions of its functioning according to four groups of factors: competitive advantage, financial position, attractiveness of the industry and the stability of the economic environment. |
|
PEST - analysis |
Designed to identify and assess political (Policy), economic (Economy), social (Society) and technological (Technology) groups of environmental factors that can affect the activities of the organization |
|
ETOM - analysis (Environmental Treats and |
Matrix of external threats and opportunities. Experts, independently or from the proposed list, single out the most significant environmental factors for the |
|
Opportunities Matrix) |
organization in terms of possible threats or opportunities. Further, experts determine the most significant for the organization, which are weighed, evaluated and taken into account in operational management and in developing a strategy. |
|
SWOT - analysis |
The method of strategic planning, which consists in identifying the factors of the internal and external environment of the organization and dividing them into four categories: Strengths (strengths), Weaknesses (weaknesses), Opportunities (opportunities) and Threats (threats) |
|
QUEST - analysis |
It is considered a method of online scanning of the external environment. Thanks to it, it becomes possible to apply a balanced approach to the development of quick action programs in response to the impact of the macro environment on the company's activities. |
|
SNW - analysis |
Analysis of the strengths, neutrals and weaknesses of the organization. With the help of special scorecards, it allows you to identify satisfied, not fully satisfied and not satisfied customer needs |
|
KPI - analysis (Key Performance Indicator) |
An indicator of success in a specific activity or in achieving specific goals. Research is carried out on a specific issue to obtain information that allows you to identify and establish certain patterns (trends) |
To ensure stable relations between the client and the company, relationship marketing tools are directed: general product development with the consumer, special types of services, quality assurance, individual and technical requirements, price differentiation, discount systems, bonuses for regular customers, direct deliveries, catalogs, personal contacts, special promotions, special offers, hotline, event marketing, customer clubs, new media and communications.
We looked at the tools of holistic marketing at the firm level, which includes four components: relationship marketing, integrated marketing, inhouse marketing and socially responsible marketing. When projecting to the region, it is necessary to revise the key elements of holistic marketing.
Elements of holistic regional marketing [4] are shown in Figure 5.
Territory marketing
Socially-responsible marketing
Holistic regional marketing
Infrastructure Marketing
Marketing innovation
Figure 3 - The structure of holistic marketing in regional management
Territory marketing is the most important volumetric component of holistic regional marketing. In its composition, one can distinguish elements within that are aimed at increasing the attractiveness of the regional market: image marketing and attractiveness marketing.
Territory marketing tools: SWOT analysis, analysis and selection of target markets and positioning (determination of current and desired positions) of territories.
SWOT analysis assumes, as a result of its application, the creation of a matrix for analyzing the living conditions of the system. On its basis, a comprehensive assessment of the current state of the territory, its competitiveness is given.
The method of analysis, selection of target markets and positioning of the territory involves:
Segmentation
Selecting target segments
Positioning
Selection of segmentation criteria
Segment size estimation
Key needs of the segment
Search for market niche segments
Segment potential assessment
Positioning strategy
Description of segments and market niches
Setting goals by segment
Marketing plan for each segment
Figure 4 - Stages of analysis, selection and positioning
The main goal of socially responsible marketing is, first of all, to improve the quality of life of the region's population. As in the holistic marketing of an enterprise, the main tools for socially responsible marketing in the region are SWOT analysis, SNW analysis, SPACE analysis, as well as PEST analysis.
Marketing of innovations is the most relevant component of the holistic marketing of the region. The tools of this element of holistic marketing include benchmarking, internet marketing, conceptual modeling of the development of territories, ABC analysis of the resource potential of the region.
Benchmarking involves the process of comparing the performance of a territory with the best companies in the region and in the industry, followed by the implementation of changes to achieve and maintain competitiveness.
Internet marketing is currently the most ambitious tool to strengthen your own position in the market. Internet technologies allow companies to provide companies not only with general information about the socio-economic situation of the city and its infrastructural features, its geographical location and the specifics of the entire region, but also, using various information visualization tools, to clearly justify the advantages of certain business solutions.
Conceptual modeling involves assessing the level of socio-economic development at the moment in order to predict and form a development strategy for the future.
The ABC analysis of the resource potential of the region makes it possible to classify the resources of the region according to the degree of their importance.
Infrastructure marketing serves as the most important and, in the long term, the most stabilizing element of the region's marketing, since the infrastructure itself is its supporting frame and foundation at the same time. The main tools for this component of holistic marketing are SWOT, ABC, PEST -analyzes.
Thus, a modern approach to the development of management decisions, taking into account and using holistic marketing tools, creates the basis for making effective decisions and developing marketing programs both at the regional and corporate levels.
Bibliographic list:
-
1. Акулич, И.Л. Маркетинг / И.Л. Акулич. – Мн.: Высшая школа, 2008. – 447 с. – ISBN 985-06-0770-Х.
-
2. Багиев, Г.Л. Маркетинг / Г.Л. Багиев. – М.: Экономика, 2010. – 718 с. – ISBN 5-282- 02101-3.
-
3. Голубков, Е.П. Основы маркетинга / Е.П. Голубков. – М.: Финпресс, 2009. – 656 с. – ISBN 5-8001-0018-7.
-
4. Калиева, О.М. Роль концепции холистического маркетинга в формировании регионального продовольственного рынка / О.М. Калиева, А.С. Степанов, О.В. Фролова // Теория и практика общественного развития. – 2013. - № 5. – С. 62 - 69.
-
5. Калиева О.М., Михайлова О.П. Способы и методы исследования маркетингового потенциала предприятия // Вестник Оренбургского государственного университета. Оренбург, 2011. № 13 (132). С. 216-221.
-
6. Котлер, Ф. Маркетинг. Менеджмент / Ф. Котлер – СПб.: Питер, 2012. – 816 с. – ISBN 978-5-91180-361-2.
-
7. Komiljonovich B. S. Opportunities to Increase the Effectiveness of Marketing Activities in the Enterprise //Academic Journal of Digital Economics and Stability. – 2021. – Т. 6. – С. 168-175.
"Экономика и социум" №9(88) 2021
Список литературы Holistic marketing toolkit
- Акулич, И.Л. Маркетинг / И.Л. Акулич. – Мн.: Высшая школа, 2008. – 447 с. – ISBN 985-06-0770-Х.
- Багиев, Г.Л. Маркетинг / Г.Л. Багиев. – М.: Экономика, 2010. – 718 с. – ISBN 5-282- 02101-3.
- Голубков, Е.П. Основы маркетинга / Е.П. Голубков. – М.: Финпресс, 2009. – 656 с. – ISBN 5-8001-0018-7.
- Калиева, О.М. Роль концепции холистического маркетинга в формировании регионального продовольственного рынка / О.М. Калиева, А.С. Степанов, О.В. Фролова // Теория и практика общественного развития. – 2013. - № 5. – С. 62 - 69.
- Калиева О.М., Михайлова О.П. Способы и методы исследования маркетингового потенциала предприятия // Вестник Оренбургского государственного университета. Оренбург, 2011. № 13 (132). С. 216−221.
- Котлер, Ф. Маркетинг. Менеджмент / Ф. Котлер – СПб.: Питер, 2012. – 816 с. – ISBN 978-5-91180-361-2.
- Komiljonovich B. S. Opportunities to Increase the Effectiveness of Marketing Activities in the Enterprise //Academic Journal of Digital Economics and Stability. – 2021. – Т. 6. – С. 168-175.


