Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review
Автор: Vafaeva Khristina Maksudovna, Vatin Nikolai Ivanovich, Karpov Denis Fedorovich, Voronov Alexander Sergeyevich
Журнал: Строительство уникальных зданий и сооружений @unistroy
Статья в выпуске: 5 (119), 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The object of research is prefabricated building structures and the potential application of hybrid glass-basalt fiber-reinforced polymer (HGBFRP) composite pipes as an alternative material for prefabricated structural elements in temperate and Arctic environments. The study focuses on the mechanical performance, durability, behavior under extreme temperatures and suitability of HGBFRP pipes for integration into prefabrication technologies. Method. A comprehensive review and analysis of existing research on HGBFRP pipes was conducted, emphasizing their mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, strength-to-weight ratio, and performance across diverse climatic conditions. The review also examined how HGBFRP pipes work with prefabrication methods and looked at advances in manufacturing technologies to assess their potential for cost-effective production and widespread adoption. Results show that HGBFRP pipes have high mechanical performance, excellent durability, and reliable behavior under extreme temperatures, making them a promising material for precast construction. Their compatibility with prefabrication methods suggests potential for more efficient and sustainable construction practices. The combination of strength, durability, and performance in harsh conditions highlights their suitability for Arctic and temperate climates. Future research will focus on evaluating long-term performance in natural conditions and exploring innovative applications in the construction industry.
Prefabricated construction, HGBFRP pipes, Hybrid composites, Mechanical properties, Durability, Arctic environments, Corrosion resistance, Sustainability, Extreme temperatures, Material compatibility
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143185211
IDR: 143185211 | DOI: 10.4123/CUBS.119.5
Текст научной статьи Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review
Prefabricated construction has become increasingly prevalent in the modern building industry, offering notable benefits such as accelerated construction timelines, cost-efficiency and enhanced quality control [1,2]. However, traditional materials used in prefabrication face significant limitations, particularly in harsh environments like the Arctic [3,4]. For instance, concrete may crack due to permafrost melt, while steel can become brittle in extreme cold. This review explores the potential of Hybrid Glass-Basalt Fiber Reinforced Polymer (HGBFRP) pipes as an alternative for prefabricated elements in both temperate and Arctic regions.
The construction industry is experiencing a major shift as prefabrication techniques become more common. However, making sure materials are suitable for extreme conditions remains an urgent issue.
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
Environments like the Arctic pose unique challenges, where traditional materials often can't handle the harsh climate, leading to weakened structural integrity [5]. Innovative materials, like HGBFRP pipes, provide promising solutions to tackle these challenges and allow construction in such demanding environments.
Several recent review papers have explored various aspects of prefabrication and its role in sustainable construction. Studies on prefabricated volumetric modular construction (PVMC) [6] analyze its advantages, limitations and areas for further exploration. Research by [7] investigates the mental health challenges faced by construction workers and explores how prefabrication could improve their well-being. Additionally, several studies [8], [9], [10] highlight various gaps and opportunities within the field of prefabrication, ranging from its Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) attributes and applications in underground projects.
Despite this progress, a gap remains in suitable materials for prefabricated elements in harsh environments. While some reviews touch upon specific building techniques for challenging environments [11], a comprehensive exploration of novel materials for prefabrication in these conditions needs to be improved. This review aims to address this gap by investigating the potential of Hybrid Glass-Basalt Fiber Reinforced Polymer (HGBFRP) pipes as a viable alternative for prefabricated elements in both temperate and Arctic regions.
As the construction sector increasingly embraces prefabrication, the importance of sustainable building practices becomes more pronounced [12], [13]. This review aims to contribute to ongoing discussions on sustainability by examining the potential applications of HGBFRP pipes in diverse environmental contexts. The integration of such innovative materials highlights the industry's commitment to adaptability, sustainability, and environmental responsibility, aiming to create structures that are not only functional but also sustainable for the future generations.
To enrich the discourse, this review also incorporates insights from related research endeavors. Beyond material innovation, research efforts are crucial for advancing sustainable development in prefabricated construction. For instance, a study on Modular Construction (MC) [14] explores its potential to mitigate climate change within the construction industry. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting resource efficiency and encouraging sustainable land use practices, MC presents a viable pathway towards sustainability in construction.
The field of prefabricated construction continues to evolve, with significant advancements observed across various domains. Research focusing on challenges within the prefabricated construction supply chain (PCSC) [15], as well as studies exploring emerging trends like prefabricated mechanical, electrical and plumbing (MEP) systems [16], underscore the industry's commitment to innovation and efficiency. Furthermore, research in prefabricated and modular timber construction [17] and large panel buildings [18] highlights opportunities for developing sustainable approaches to design and construction.
Despite the progress made, challenges remain, particularly the gap in the level of automation of construction processes between academia and industry [19], as well as the applicability of materials in harsh climates, such as Canada's northern regions [11]. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts and ongoing research to guide the development of precast construction toward greater sustainability and efficiency. In conclusion, exploring alternative materials like HGBFRP pipes offers significant potential to overcome the limitations of traditional construction materials, especially in harsh environmental and climate conditions. Using such innovative solutions, along with promoting interdisciplinary teamwork, can help the construction industry build structures that are not only sustainable and durable but also efficient, meeting the needs of modern building practices.
-
2 Materials and Methods
This section outlines the methodology used to thoroughly assess the potential of hybrid glassbasalt fiber-reinforced polymer (HGBFRP) pipes for precast construction in temperate and Arctic climates. A detailed schematic of the methodology is provided in Figure 1.
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;

Python-Based Data Analysis
Data analysis in
VOS view er
Fig. 1 - The schematic representation of the methodology Image by the author of the article
Establishing the Goals and Objectives of the
-
2.1 Literature Search and Data Acquisition
-
2.2 Data Analysis
A systematic literature review was carried out to identify and evaluate existing research on HGBFRP pipes. Scopus was selected as the primary database due to its comprehensive coverage of engineering and materials science publications.
The search strategy combined keywords related to HGBFRP pipes, precast construction, and relevant natural and climatic conditions. Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) were applied to refine the search and ensure retrieval of the most relevant studies.
The literature search on Scopus was conducted using the query: (arctic AND (glass OR basalt) AND fiber AND reinforced AND polymer) OR (prefab AND arctic) OR (prefab AND (glass OR basalt) AND fiber AND reinforced AND polymer) OR (hybrid AND glass-basalt AND fiber AND reinforced AND polymer). This search yielded 1.916 results, with no restrictions on publication date or other criteria.
The retrieved articles were screened based on their title, abstract, and keywords to ensure they aligned with the research focus on HGBFRP pipes and their application in prefabricated construction. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were established to maintain the quality and relevance of the analyzed content data.
Data extraction was performed using a standardized format to capture critical information from the selected articles. The data obtained included:
-
- composition and material properties of HGBFRP pipes (e.g., fiber content, matrix type, mechanical properties);
-
- performance characteristics of HGBFRP pipes under various conditions (e.g., strength, durability, corrosion resistance);
-
- applications of HGBFRP pipes in precast construction projects (e.g., building components, loadbearing elements).
-
2.3 Data Processing and Evaluation
Custom Python scripts were created to facilitate a rigorous quantitative assessment of the compiled data. The processing workflow included:
-
- preprocessing and standardization of the datasets to enable consistent comparisons across different studies;
-
- application of statistical methods to uncover patterns and correlations between the characteristics of HGBFRP pipes and their behavior under varying operational and environmental conditions.
-
3 Results and Discussion
-
3.1 Analysis of Bibliometric Data
-
Figure 2 illustrates the yearly distribution of publications. The histogram shows an overall upward trend in publication output over the years, with a notable exception in 2024. This anomaly is attributed to Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
-
-
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
the fact that the 2024 data were collected early in the year, capturing only a partial representation of publications for that period.
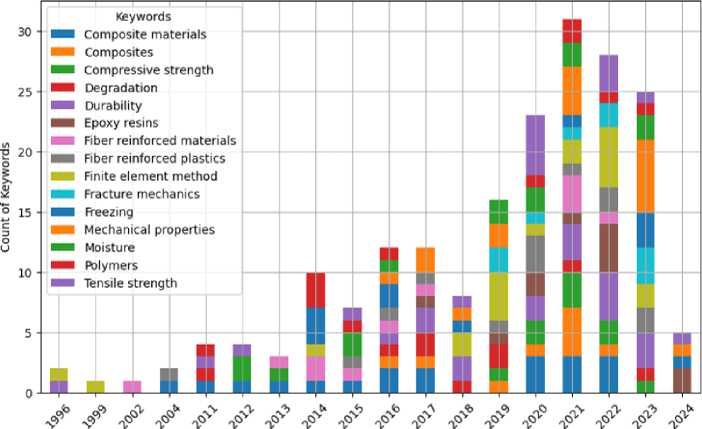
Figure 3 displays the timing of the most frequently used keywords. This analysis emphasizes the wide range of composite materials research, including materials science, mechanical properties, durability, and environmental factors. Tracking keyword trends offers valuable insights into how this field is evolving, highlighting both well-established research areas and new emerging topics interest.
"tear
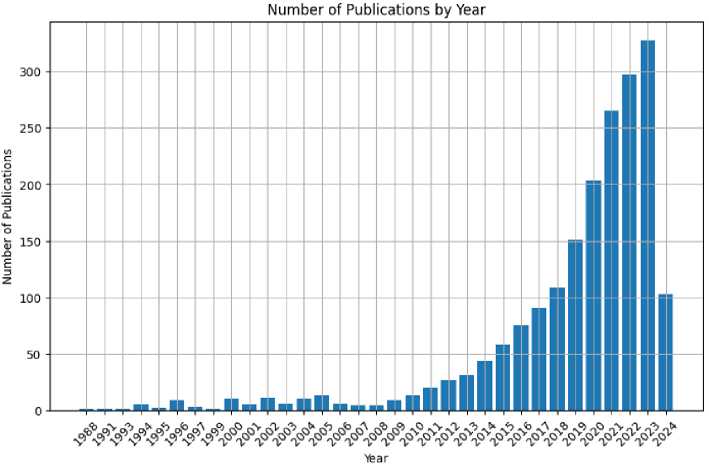
Fig. 2 - Annual distribution of publications Image by the author of the article
-
Fig. 3 - The highest frequency keywords by year
Image by the author of the article
Analysis of word clouds generated from keywords and abstracts in the field of composite materials reveals prominent research trends and focal areas (Figure 4).
Computational Modeling and Material Characterization: The frequent use of terms like “finite element method, “mechanical” and “electron microscopy” shows a strong focus on computational methods for assessing mechanical properties and conducting advanced material analysis characterization.
Development of Advanced Materials: Keywords such as “sandwich panel, “carbon fiber” and “basalt material” highlight ongoing efforts in designing new composite structures and exploring alternative reinforcements options.
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
Mechanical Performance and Durability: The frequent use of terms like “fiber reinforcement, “stiffness” and “failure” emphasizes the key role of mechanical performance in composite design. Additionally, references to “durability, “fatigue” and “dynamic” highlight increasing interest in the longterm performance of composites under different environmental and loading conditions.
Experimental Research and Broad Applicability: The abstract cloud further emphasizes experimental approaches, with phrases such as “polymer composite”, “low velocity impact” and “mechanical properties” reflecting targeted investigations of composite performance. Terms like “composite material”, “hybrid” and “fiber reinforced” additionally illustrate the versatility and wide-ranging applications of composites across multiple engineering sectors.

Fig. 4 - Word clouds by keywords and annotations Image by the author of the article
The distribution of publication types in the dataset is shown in the pie chart (Figure 5). Articles make up the largest portion at 67.5%, followed by conference papers at 12.0% and review papers at 11.5%. Other formats, such as book chapters (4.9%), books (3.8%), and miscellaneous types, each representing less than 1%, comprise the rest. This visualization provides a clear overview of the publication landscape in the field, emphasizing the dominance of articles, conference proceedings, and review papers as the main channels for sharing research findings. Additionally, the presence of other publication types highlights the diversity of scholarly communication and researchers' involvement in various forms of knowledge sharing activities.
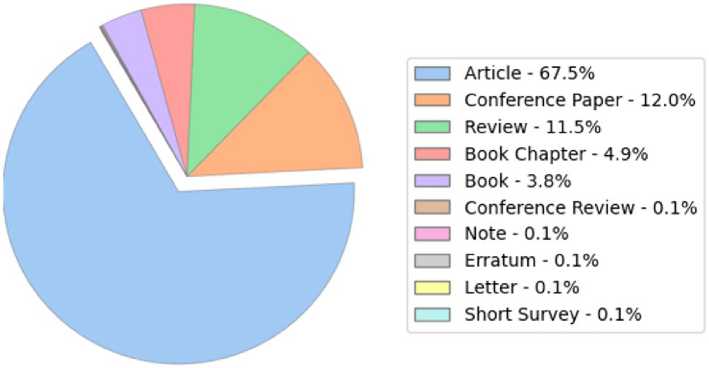
Fig. 5 - Word clouds by keywords and annotations
Image by the author of the article
The pie chart (Figure 6) illustrates the distribution of research fields within a specific dataset. The dominant fields are Engineering (1205) and Materials Science (1199), collectively accounting for over 40% of the research output.
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
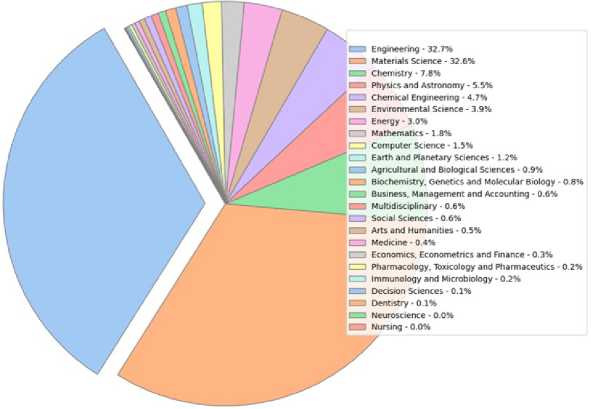
Fig. 6 - Keyword and abstract word clouds
Image by the author of the article
An analysis of the share of publications (Figure 7 and Figure 8) among the top five countries leads to the following conclusions:
-
- China leads with the highest share of publications at 35.0%, demonstrating the region's significant contribution to academic productivity and scientific research;
-
- India ranks just behind China with a 25.2% share, underscoring its expanding role in global scientific research and increasing funding for scientific initiatives;
-
- the United States commands a significant portion at 20.7%, reflecting its enduring prominence in research and innovation across multiple disciplines;
-
- Italy and the United Kingdom complete the top five with shares of 8.4% and 10.6%, respectively.
Although smaller in comparison, these contributions still represent notable scientific productivity and sustained involvement in scholarly activities.
Collectively, these figures illustrate the wide geographic spread of research efforts and emphasize the importance of international collaboration in advancing knowledge and tackling complex global challenges.
United Kingdom
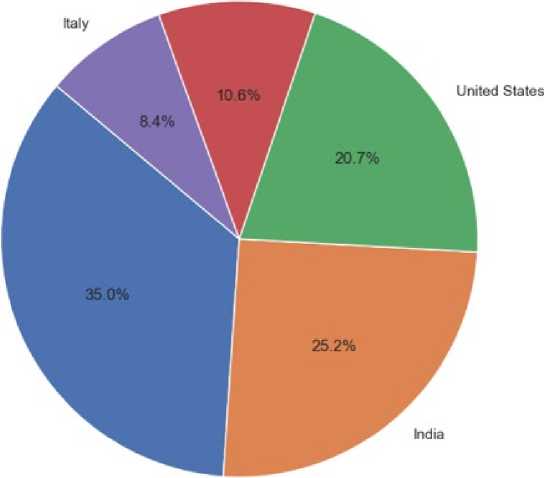
Fig. 7 - Chart of the most active countries by number of publications Image by the author of the article
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
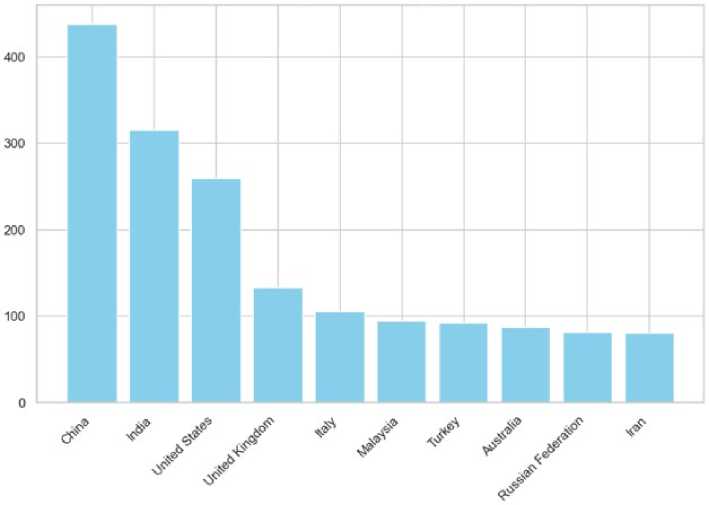
Fig. 8 - A histogram of the distribution of the most active countries by the number of publications Image by the author of the article
This visualization (Figure 9) depicts a network of interconnected research topics in materials science and engineering, highlighting fiber-reinforced polymers (FRPs) and their practical applications:
-
- Cluster 1 focuses on FRPs, emphasizing their role as a main area of research. Within this cluster, sea sand concretes are emphasized, highlighting studies on the use of FRPs combined with sea sand concretes, possibly for marine or coastal construction applications;
-
- Cluster 2 seems less connected to the main research network, implying that its specific focus needs further exploration;
-
- Cluster 3 highlights glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP), emphasizing its widespread use in FRP research. It also includes steel fibers and bars, showing comparative studies between FRPs and traditional metal reinforcements. The analysis covers bond behavior and material strength, focusing on adhesion mechanisms and the structural performance of FRP composites. Offshore structures are part of this cluster, indicating FRP applications in marine environments, likely due to their resistance to corrosion resistance;
-
- Cluster 4 focuses on structural loads and forces, especially in offshore applications identified in Cluster 3. It highlights offshore oil well operations and emphasizes the importance of FRPs in oil and gas production structures. Additionally, it considers reinforced concrete and traditional concrete, showcasing studies that compare or integrate FRP composites with conventional concrete materials;
-
- Cluster 5 focuses on structural analysis and deformation, highlighting the use of analytical methods to examine material behavior and structural responses under load. Corrosion resistance is once again emphasized, underscoring a key benefit of FRP composites in tough environmental conditions;
-
- Cluster 6 focuses on advanced mechanical behavior and performance analysis of materials. Crushing and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) demonstrate the use of simulation techniques to predict and examine material crushing behavior. Failure modes in Arctic engineering reflect research into how materials respond and fail under extreme cold conditions typical of polar environments. Fatigue, stressstrain curves, and cryogenics highlight investigations into material performance under repeated loading and exposure to very low temperatures, offering insights into long-term durability and structural reliability in harsh environments conditions.
Additional Insights:
-
- the visualization highlights a broad spectrum of material properties under investigation, including stiffness, durability, energy absorption and thermal insulation;
-
- sustainability is considered through studies on recycled and eco-friendly materials;
-
- fabrication techniques such as 3D printing and lamination are explored;
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
-
- testing methods including tensile tests, impact tests and non-destructive evaluation are employed for thorough material characterization;
-
- microscopic and chemical analyses like SEM, FTIR and DSC offer detailed understanding of material microstructure and composition.
Overall, the visualization provides a comprehensive view of research trends in materials science and engineering, emphasizing fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites and their applications in areas such as marine construction, arctic engineering, and sustainable materials development. The analysis depends on the selected keywords and may only reflect a portion of the broader research field.
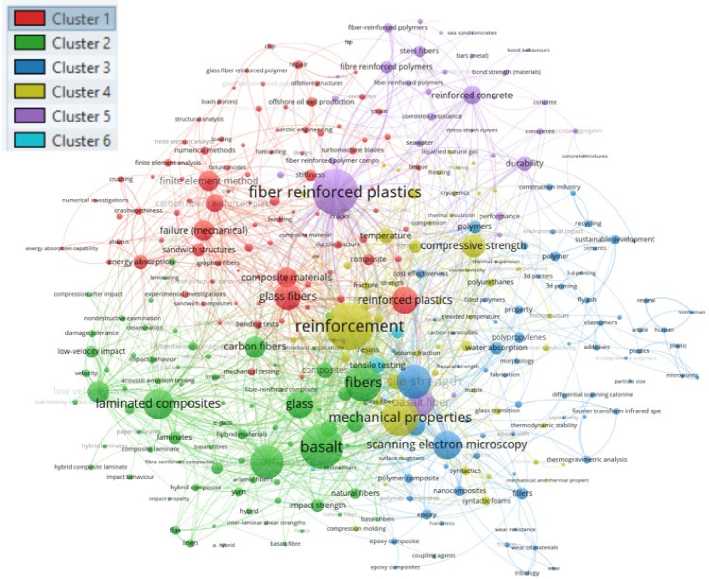
Fig. 9 - General view of relationships in VOSviewer
Image by the author of the article
The heat map (figure 10) illustrates the distribution of research topics in materials science and engineering, emphasizing fiber-reinforced polymers (FRPs) and their applications; color intensity indicates the prominence of each topic. Overall, the heat map offers insights into current research trends, with FRPs as a key focus, especially in applications that require high strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Attention to sustainability and alternative materials also reflects the shifting priorities and developments within the field.
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
Fig. 10 - VOSviewer-generated heatmap
Image by the author of the article
In summary, the bibliometric analysis in this section provides a detailed overview of the current state of composite materials research. The increasing number of publications indicates a growing interest in this field. Keyword analysis highlights a strong focus on materials science, mechanics, durability, and environmental concerns, emphasizing the diverse scope of composite research. Word clouds display key research areas, including computational modeling, advanced materials development, mechanical testing, and studying long-term composite behavior. Examining publication types reveals that articles, conference proceedings, and reviews are most common, underscoring the importance of scholarly communication and knowledge sharing. The distribution of research areas shows that engineering and materials science are leading disciplines, while geographic analysis identifies China, India, the United States, Italy, and the United Kingdom as major contributors. Network visualizations and heat maps offer a comprehensive view of interconnected research topics, especially highlighting fiber-reinforced polymers (FRPs) and their applications across various engineering sectors.
Overall, the findings demonstrate the high level and ongoing progress of research in composite materials. The focus on sustainability and alternative materials underscores continuous efforts to develop environmentally responsible, high-performance composites capable of meeting future technological and industrial needs challenges.
-
3.2 . Composition and Properties
Hybrid glass-basalt polymer composite pipes (HGBFRP) are made from a unique blend of glass and basalt fibers embedded in a polymer matrix. This specially designed composition creates a high-performance composite with excellent mechanical properties and long-term durability, making it especially suitable for prefabricated structural elements used in extreme environments, including the Arctic. Glass fibers, valued for their high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion, significantly contribute to the structural strength of HGBFRP pipes and improve their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Beyond the specific advantages of HGBFRP, it is essential to consider the broader context of fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites. A review by [20] highlights the versatility of FRPs across multiple sectors, emphasizing their benefits as well as ongoing research directions such as long-term durability and environmental impact. Additional studies [21–24] investigate focused aspects of FRP performance, including fire resistance [25], crashworthiness [26], aging processes [27], protective interactions with other materials [28] and advanced fabrication methods for water piping systems [29]. Collectively, this body of research establishes a robust foundation for the further development and practical implementation of HGBFRP technologies.
Table 1 summarizes recent studies on composite materials, covering various aspects of their design, application, and improvement. The research includes developing new composite formulations, exploring reinforcement strategies to boost mechanical strength, and optimizing design and manufacturing processes. The insights from these studies provide valuable guidance for advancing
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
composite materials and expanding their use in different sectors, such as construction, automotive engineering, and biomedical fields applications.
Table 1. Research on composite materials
|
No. |
Research |
Brief description |
Conclusions and recommendations |
|
1 |
[30] |
Developed pseudo-ductile composites with graphene-based materials on glass and carbon fiber fabrics. |
This method shows great potential for expanding the use of composites in more applications because of its improved ductility. |
|
2 |
[31] |
Investigated the impact of recycled macro fibers in USSC to improve toughness. |
Recycled macro fibres can be a viable reinforcement option for UHPC, but must be balanced with other properties. |
|
3 |
[32] |
Used adjustable cooling rates to produce tungsten fiber-reinforced MGCs, enhancing impact toughness. |
This finding indicates a new approach to enhance the damage resistance of metallic glass composites. |
|
4 |
[33] |
Developed reinforced laminated veneer lumber that surpasses conventional LVL. |
RLVL with proper reinforcement can be effectively used in outdoor structural applications. |
|
5 |
[34] |
Developed glass fiber/polyurethane composite plates for bone fixation, offering a promising alternative to metal implants. |
This approach offers a promising alternative for metal bone fracture plates. |
|
6 |
[35] |
Produced personalized glass fiber-reinforced PLA composite plates for bone stabilization. |
This technology has the potential to improve patient recovery after bone fusion surgery |
|
7 |
[36] |
Studied customized fiber configurations to enhance GFRP composite properties. |
This finding can lead to lower cost and higher quality composite materials |
|
8 |
[37] |
Investigated the structural performance of concrete joints reinforced with hybrid GFRP and steel bars. |
The recommended reinforcement ratio is 60% to 75% GFRP to steel bars |
|
9 |
[38] |
Explored soil reinforcement using vertical fiberglass micro-piles, providing an economical solution for ground improvement. |
This technique has potential for ground improvement applications |
|
10 |
[39] |
Developed a ground improvement technique using prefabricated vertical fiberglass micropiles. |
Optimization of reinforcement geometry to achieve maximum efficiency |
|
11 |
[40] |
Studied glass fiber-reinforced composite leaf springs with selfhealing agents. |
This innovation could improve the safety and durability of automobile suspension components |
|
12 |
[41] |
Examined the durability of the bond between hybrid FRP bars and concrete in water environments. |
HFRP bars are a more durable alternative to GFRP bars for concrete reinforcement in wet environments |
|
13 |
[42] |
Evaluated machine learning for fatigue crack detection in GFRP composites using acoustic emission |
This strategy provides an effective means for assessing and tracking the structural integrity of composite materials |
|
14 |
[43] |
Investigated aging effects on the tensile strength of GFRP and hybrid composites. |
These results indicate that glass fiber-reinforced polymers (GFRP) and hybrid composites possess the durability required for extended service in structural applications |
|
15 |
[44] |
Characterized mechanical properties of natural particulates-filled and E- |
Using natural particulates as fillers in composite materials can boost their |
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
|
No. |
Research |
Brief description |
Conclusions and recommendations |
|
glass fiber-reinforced sandwich polymer composites. |
mechanical performance, and adding fiber reinforcement can further improve strength and structural integrity. |
Basalt fibers are a valuable part of HGBFRP pipes because of their exceptional thermal stability and resistance to extreme temperatures, as shown in Table 2. Compared to glass fibers, basalt fibers offer higher thermal resistance, enabling HGBFRP pipes to maintain their structural integrity over a broader temperature range conditions.
Table 2. Essential Properties of Basalt Fibers and Their Impact on HGBFRP Pipes
|
No. |
Property |
Influence on HGBFRP pipes |
|
1 |
High thermal stability [45–49] |
Enables pipes to withstand high temperatures and maintain structural integrity in extreme thermal environments |
|
2 |
Good chemical resistance [45,50–52] |
Provides resistance to aggressive environments, extending the service life of the pipes |
|
3 |
High impact strength [53–56] |
Improves resistance to mechanical stress and impact, contributing to overall durability |
|
4 |
Low thermal conductivity [57–60] |
Reduces heat loss in hot water applications and minimizes heat gain in cold environments |
|
5 |
Good adhesion to polymers [45,61–64] |
Ensures a strong interfacial bond with the polymer matrix, leading to improved mechanical performance of the composite |
Although thermal stability is a major benefit, basalt fibers offer other valuable features that are increasingly gaining attention across various applications:
-
- durability in marine environments: limited studies [65] indicate that basalt fibers experience an initial reduction in strength when exposed to seawater due to alterations in their surface layer, followed by stabilization as a protective layer forms. The use of epoxy resin matrices further enhances their longterm performance in such conditions [65];
-
- high-performance composites: Melamine-hexamethylenediamine (MH) resin demonstrates excellent compatibility with basalt fibers, enabling BFRMH composites to achieve high flexural strength, heat deflection temperature and flame retardancy, making them suitable for demanding electrical/electronic applications [66];
-
- reinforcing organic coatings: Basalt fibers and scales can improve the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of organic coatings. However, surface modification techniques are crucial to enhance the compatibility between basalt and organic resins [67];
-
- biodegradable alternatives: Basalt fibers offer a promising eco-friendly replacement for carbon fibers due to their excellent properties and lower cost. Research is ongoing to optimize their performance for green composites [68];
-
- geopolymer reinforcement: Basalt fiber composites (e.g., MiniBars™) significantly enhance the mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymers, presenting a sustainable alternative to traditional Portland cement concrete [69];
-
- multi-scale composites: Combining basalt fibers with carbonaceous nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes (CNT) and graphene creates novel eco-friendly composites with improved functionalities [70]. Research focuses on efficient fiber treatment methods to achieve optimal load transfer between fiber and matrix [71].
The glass and basalt fibers in HGBFRP pipes are encased in a polymer matrix, usually based on resins like polyester or epoxy. This matrix functions as a binding agent, uniting the fibers and providing structural cohesion to the composite [72,73]. It also offers a protective barrier, guarding the fibers against moisture, chemical exposure and other environmental factors that could lead to degradation [74–76]. By reinforcing the structural integrity and resistance of the composite, the polymer matrix significantly contributes to the long-term durability and reliable performance of HGBFRP pipes in prefabricated construction applications.
Table 3 (Figure 11) presents the typical mechanical characteristics of polymer matrices commonly used in HGBFRP pipes, including polyester and epoxy. These matrices display tensile strengths ranging from 60 to 120 MPa, elongation at break between 1 and 6%, elastic moduli of 1–4 GPa and thermal
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
stability within the 80-200 °C range. The specific values can vary depending on the exact polymer type and testing methods employed

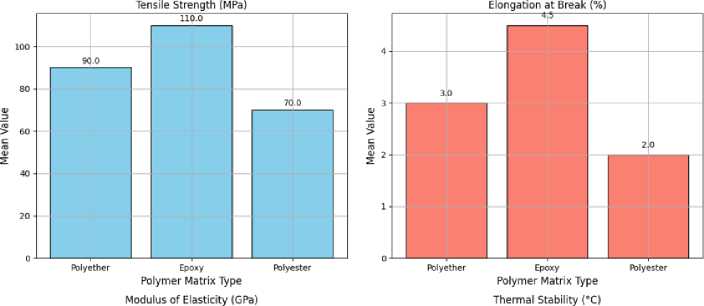
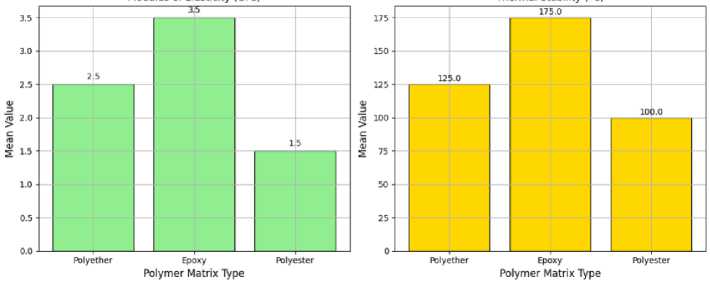
Fig. 11 - Mechanical properties comparison of different polymer matrices
Image by the author of the article
Table 3. Mechanical properties comparison of different polymer matrices
|
No. |
Polymer matrix type |
Tensile strength (MPa) |
Elongation at break (%) |
Modulus of elasticity (GPa) |
Thermal stability (°C) |
|
1 |
Polyether [77–79] |
80-100 |
2-4 |
2-3 |
100-150 |
|
2 |
Epoxy [80–83] |
100-120 |
3-6 |
3-4 |
150-200 |
|
3 |
Polyester [84–87] |
60-80 |
1-3 |
1-2 |
80-120 |
Table 4 (Figure 12) provides a comparative analysis of the chemical resistance of the three polymer matrix types most commonly used in HGBFRP pipes: polyester, epoxy and polyester resin. It is important to consider several key points:
-
- chemical resistance can vary: the specific resistance of a polymer matrix to various chemicals depends on several factors, including the type of polyester, the specific acid or alkali and the properties of the solvent;
-
- as shown in Table 4, the terms “good”, “fair” and “poor” are used for general comparison.
Qualitative terms: these terms are qualitative in nature and may not reflect the exact level of resistance in all situations. For specific applications, consulting technical data sheets or conducting compatibility tests is recommended.
Table 4. Comparison of chemical resistance of various polymer matrices
|
No. |
Polymer matrix type |
Water resistance |
Acid resistance |
Alkali resistance |
Solvent resistance |
|
1 |
Polyether |
Good |
Moderate |
Poor |
Moderate |
|
2 |
Epoxy |
Very Good |
Very Good |
Very Good |
Good |
|
3 |
Polyester |
Good |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Poor |
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
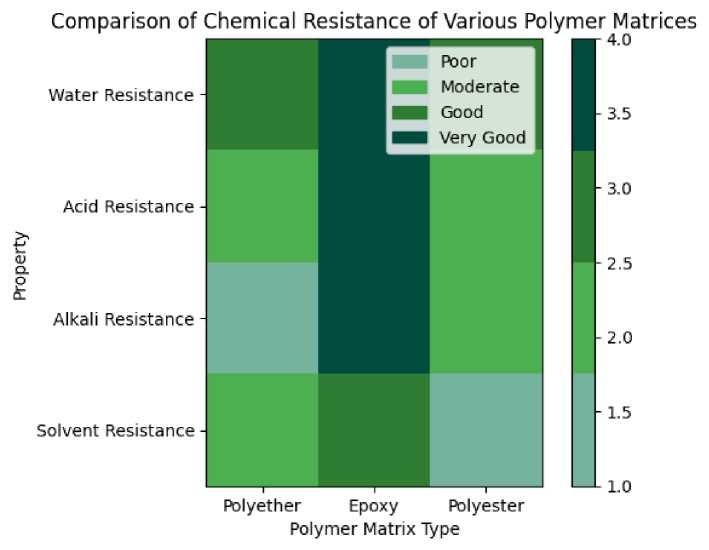
Fig. 12 - Comparison of chemical resistance of various polymer matrices
Image by the author of the article
Table 5 (Figure 13) summarizes the thermal conductivity of different polymer matrices commonly used in HGBFRP pipes. As can be observed, polyether exhibits the lowest thermal conductivity, followed by epoxy resin and polyester.
Table 5. Comparison of thermal conductivity of various polymer matrices
|
No. |
Polymer matrix type |
Thermal conductivity (W/m*K) |
|
1 |
Polyether [88–91] |
0.15-0.25 |
|
2 |
Epoxy [92,93] |
0.20-0.30 |
|
3 |
Polyester [94–96] |
0.25-0.35 |
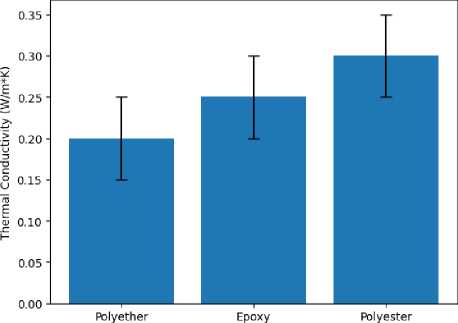
Polymer Matrix Type
Fig. 13 - Comparison of thermal conductivity of various polymer matrices
Image by the author of the article
The data in Tables 3-5 are averaged and may vary depending on the manufacturer, material type, production method and other factors.
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
Studies explore the capability of fiber-reinforced composites for gradual failure [97], nanoparticle effects on damage tolerance [98], mitigation of seawater-induced degradation [99] and enhancement of crushing properties under hydrothermal aging [100]. Another article discusses the increasing use of Basalt Fibers (BF) in composite production, emphasizing sustainability benefits and potential research areas [101].
A recent study also investigates the fracture behavior and energy absorption capacity of selfcompacting concrete reinforced with asphalt emulsion and fibers [102] . In summary, Hybrid Glass-Basalt Fiber Reinforced Polymer (HGBFRP) pipes combine the unique benefits of glass and basalt fibers within a polymer matrix, resulting in a material that is high-strength, corrosion-resistant, and thermally stable.
-
3.3 Mechanical Performance
The mechanical properties of HGBFRP pipes highlight their exceptional performance, making them suitable for precast components in both temperate and Arctic regions. Features such as a high strength-to-weight ratio, increased stiffness, and dimensional stability demonstrate the material’s mechanical efficiency, supporting its potential as an innovative solution in modern construction. HGBFRP pipes exhibit an outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, combining structural strength with low mass. The combination of glass and basalt fibers within the polymer matrix offers excellent load-bearing capacity, enabling the pipes to withstand significant stresses without adding much weight. This feature is especially beneficial for precast construction, as it allows the production of components that are both durable and lightweight, making transportation, assembly, and handling easier installation.
Although this section emphasizes HGBFRP pipes, broader research on fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites provides valuable context about their structural capabilities. Studies on glass fiber-reinforced polymer (GFRP) and basalt fiber-reinforced polymer (BFRP) in concrete components offer relevant insights [103] , [104] , [105] .
Although existing studies provide valuable insights, targeted research on HGBFRP pipes is essential to thoroughly assess their suitability for precast construction. Examining their performance across various environmental conditions, especially those common in Arctic regions, would be particularly beneficial. Comparative studies evaluating HGBFRP pipes against traditional materials used in precast elements would also help determine their effectiveness and cost-efficiency.
Stiffness and Flexural Strength. The structural rigidity of HGBFRP pipes is a key property that ensures dimensional stability and resistance to deformation. By combining the inherent stiffness of glass and basalt fibers with a polymer matrix, HGBFRP pipes achieve high flexural strength and stiffness, making them suitable for structural applications. This combination enables the pipes to retain their shape and integrity under various load conditions, supporting long-term durability and reliability in construction projects.
For comparison, study [106] investigates the seismic behavior of reinforced concrete (RC) columns strengthened with advanced composites such as FRP, PET FRP and ECC. Unlike previous research focused on failures within strengthened zones, this study examines failure occurring outside the retrofitted area. It demonstrates that the failure mode and location depend on the type and extent of strengthening. Weaker retrofits, such as ECC alone, result in failures within the original zone, while stronger combinations (CFRP-ECC, PET-ECC) shift failure to unstrengthened regions. Nevertheless, strengthening consistently improves ductility, energy dissipation and stiffness. The study also highlights how variations in the ACF ratio influence failure patterns, emphasizing the need to consider ductilitybased effects in shear strength models.
In [107] , the effects of steel, basalt and recycled PET fibers on high-performance concrete with calcium oxide-activated slag (HPC-CAS) are examined, focusing on mechanical performance, environmental impact and microstructure via SEM analysis. Incorporating 3% recycled PET or basalt fibers significantly boosts tensile and flexural strengths. Basalt fibers offer superior mechanical performance and strong bonding with the geopolymer matrix, although their environmental footprint is larger compared to recycled PET fibers, which have the lowest social and environmental impact. This evidence highlights the potential of hybrid fiber composites, like HGBFRP, to improve stiffness, flexural performance, and durability for precast construction elements while also considering environmental and material factors optimization.
Finally, [108] investigates the effectiveness of unidirectional BFRP sheets for strengthening slender square RC columns under axial concentric and eccentric compression loading. Results indicate that although the effectiveness of BFRP wrapping diminishes under eccentric loading, both partial and full wrapping improve column performance by increasing load-bearing and moment capacity. Columns
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
reinforced with BFRP also show reduced lateral displacement under varying eccentricities, with complete wrapping providing the greatest stability.
Dimensional Stability. HGBFRP pipes demonstrate outstanding dimensional stability, a critical feature for prefabricated construction elements. Research [109] investigated BFRP-confined ceramsite concrete columns reinforced with bamboo strips, revealing improvements in load-bearing and deformation capacity. Study [110] explored the application of composite materials to strengthen structures against seismic forces. In [111], the tensile behavior of Fiber-Reinforced Cementitious Matrix (FRCM) composites was analyzed, focusing on glass FRCM. Additionally, [112] addressed weight reduction in automotive bumpers using hybrid fiber-reinforced polymer composites, with higher carbon fiber content correlating with greater tensile strength.
Table 6 (Figure 14) compares the mechanical properties of glass and basalt fibers. Glass fibers have tensile strengths of 2500-4500 MPa, while basalt fibers are slightly stronger at 3000-4800 MPa. Both types of fibers resist corrosion, with basalt fibers offering marginally better resistance. Additionally, basalt fibers have a higher modulus of elasticity (80-90 GPa) compared to glass fibers (70-80 GPa) and demonstrate superior thermal resistance, rated as “very high” versus “moderate” for glass fibers.
The values reported in Tables 6–8 represent the average mechanical properties of glass and basalt fibers. It should be noted that these properties can vary due to several factors including:
-
- fiber type and composition. The particular type and chemical composition of glass or basalt fibers can influence their performance. For instance, S-glass fibers typically exhibit higher tensile strength compared to E-glass fibers;
-
- manufacturing process. The manufacturing process can also affect fiber properties. For example, changes in temperature or cooling rate can affect tensile strength and heat resistance;
-
- testing conditions. Testing conditions, such as temperature and humidity, can also affect the measured properties.
Thus, in assessing the mechanical properties of glass and basalt fibers for a given application, it is essential to take into account the fiber type, production process and testing conditions.
Table 6. Mechanical properties comparison of glass and basalt fibers
|
No. |
Property |
Glass fibers |
Basalt fibers |
|
1 |
Tensile strength [113–120] |
2500-4500 MPa |
3000-4800 MPa |
|
2 |
Corrosion resistance [67,120–125] |
High |
Very High |
|
3 |
Modulus of elasticity [126–130] |
70-80 GPa |
80-90 GPa |
|
4 |
Thermal stability [63,131–135] |
Moderate |
Very High |
□lass Fibers
Basalt Fibers
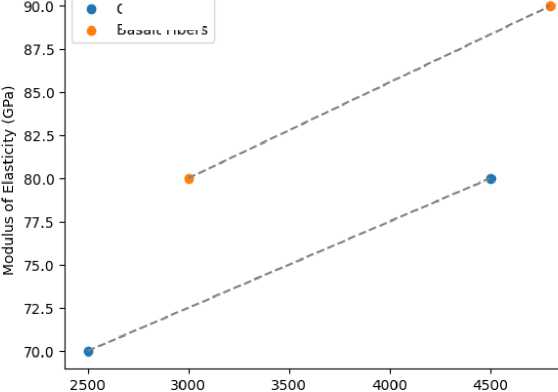
Tensile Strength (MPa)
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
Fig. 14 - Comparative analysis of the mechanical characteristics of glass and basalt fibers Image by the author of the article
Table 7 provides a comparative analysis of the effects of aging on Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastics (GRP) and Basalt Fiber Reinforced Plastics (BRP). It highlights how different types of aging influence both the mechanical properties and visual characteristics of the two materials. GRP is notably affected by oxidative aging, showing marked reductions in strength and changes in color, whereas BRP demonstrates comparatively smaller changes in these properties. Similarly, hydrothermal aging has a substantial impact on the mechanical performance of GRP, while BRP exhibits greater resilience under the same conditions. Ultraviolet aging leads to surface degradation in both materials, although the impact is less significant for BRP compared to GRP.
Table 7. Comparison of aging effects on glass reinforced plastics (GRP) and basalt reinforced plastics (BRP)
|
No. |
Aging type |
Glass reinforced plastics |
Basalt reinforced plastics |
|
1 |
Oxidative aging [136–142] |
Noticeably affects strength and color |
Less impact on strength and color |
|
2 |
Hydrothermal aging [143–149] |
Significantly affects mechanical properties |
Affects mechanical properties to a lesser extent |
|
3 |
Ultraviolet aging [150–155] |
Leads to surface degradation |
Impact is less significant |
Table 8 (Figure 15) illustrates the environmental durability of common Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) materials. It compares properties such as corrosion resistance, UV resistance, moisture absorption and biodegradability among Glass Fiber, Basalt Fiber, Carbon Fiber and Aramid Fiber (Kevlar).
Table 8. Environmental durability of common FRP materials
|
No. |
Property |
Glass fiber |
Basalt fiber |
Carbon fiber |
Aramid fiber (kevlar) |
|
1 |
Corrosion resistance [51,156–161] |
Excellent |
Excellent |
Excellent |
Good |
|
2 |
UV resistance [153,162–168] |
Moderate |
Good |
Excellent |
Moderate |
|
3 |
Moisture absorption [169–175] |
Moderate |
Low |
Low |
Moderate |
|
4 |
Biodegradability [176–181] |
No |
No |
No |
Very low |
Corrosion Resistance
Environmental Durability of Common FRP Materials
UV Resistance
Moisture Absorption
Biodegradability
|
Excellent |
Excellent Excellent |
Good |
|
Moderate |
Good Excellent |
Moderate |
|
Moderate |
Moderate |
|
|
■ |
Glass Fiber
Aramid Fiber (Kevlar)
Basalt Fiber Carbon Fiber
Materials

Fig. 15 - Environmental durability of common FRP materials Image by the author of the article
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
In summary, the exceptional mechanical properties of HGBFRP pipes, including a high strength-to-weight ratio, inherent stiffness, and dimensional stability, position them as a revolutionary material within the construction industry. These qualities not only make HGBFRP pipes ideal for prefabricated construction but also enable them to overcome the limitations of traditional building materials in extreme environmental conditions. By combining outstanding strength, durability, and adaptability, HGBFRP pipes present an attractive solution for sustainable and efficient construction in both temperate and Arctic climates, supporting the development of reliable, innovative, and resilient building practices.
-
3.4 Resistance to Corrosion
The inherent corrosion-resistant properties of hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer (HGBFRP) pipes make them highly suitable for use in tough environments, particularly in temperate and Arctic regions. This section highlights the superior corrosion resistance of HGBFRP pipes, focusing on their ability to withstand the damaging effects of aggressive elements and severe environmental conditions, making them a very promising choice for precast construction.
The notable corrosion resistance of HGBFRP pipes stems from the combined properties of glass and basalt fibers along with the polymer matrix [182], rendering them particularly effective in environments exposed to aggressive chemical or climatic conditions:
-
- traditional steel pipes suffer significant degradation in saltwater environments due to brine corrosion. In contrast, HGBFRP pipes are resistant to the corrosive effects of saltwater, ensuring longterm structural integrity and performance in coastal regions [182];
-
- HGBFRP's resistance to chemical degradation makes them suitable for applications involving various chemicals. This eliminates concerns about pipe integrity being compromised by exposure to harsh chemicals [182];
-
- environmental pollutants. HGBFRP pipes are not susceptible to degradation caused by environmental pollutants, offering an advantage over traditional materials that can become compromised over time [182].
The synergy between glass and basalt fibers within the polymer matrix contributes to HGBFRP's exceptional corrosion resistance. Studies have shown that:
-
- basalt fibers provide strong resistance to chemical degradation, while certain glass fiber variants, such as ECR-glass, exhibit even greater chemical resilience compared to conventional E-glass fibers [182]. The integration of these fibers within HGBFRP results in a composite material with exceptional chemical durability;
-
- hybrid composites featuring optimized fiber arrangements (for example, 2/2 basalt/S-glass configurations) demonstrate superior tensile performance compared to composites composed of individual fiber types across a range of temperatures [183]. This underscores the synergistic effect of combining different fibers to enhance overall material performance.
Although HGBFRP pipes exhibit outstanding corrosion resistance, it is essential to evaluate how prolonged exposure to saltwater affects their mechanical performance in practical applications [184]. Research has shown that immersion in saline environments can result in:
-
- immersion in saltwater may reduce the tensile and flexural strengths of HGBFRP composites [184]. Nevertheless, the progressive failure behavior observed in hybrid composites, in contrast to nonhybrid counterparts, indicates a potential for enhanced long-term durability [184];
-
- analysis of test samples exposed to saltwater revealed delamination, explosive failure and fiber breakage as common failure modes [184]. Understanding these failure mechanisms is critical for optimizing the design of HGBFRP pipes for offshore applications. Hybridization of glass and basalt fibers can significantly improve the mechanical properties of composites [185]. Research has shown that:
-
- increased mechanical strength. Hybrid composites exhibit significant improvements in flexural, tensile and impact strength compared to non-hybrid fiberglass composites [185]. This highlights the potential of HGBFRP composites for a variety of structural applications;
-
- the mass ratios of the constituent fibers significantly affect the overall properties of the hybrid composite [185]. Determining the optimal ratios experimentally is key to maximizing performance;
-
- the type of polymer matrix used in HGBFRP composites can also influence their mechanical and morphological characteristics [186]. Research has shown that:
-
- epoxy resin exhibited superior performance compared to vinylester resin when combined with basalt/glass fiber reinforcements in terms of tensile strength [186]. Selecting the appropriate matrix material is vital for optimizing composite properties.
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
Morphological Analysis. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) analysis can confirm the mechanical test results by revealing fiber fracture and rupture modes within the HGBFRP composite [186]. This technique provides valuable insights into the failure mechanisms of the composite.
The Table 9 shows the advantages and disadvantages of corrosion resistance of various pipe materials.
Table 9. Corrosion resistance of different pipe materials
|
No. |
Material |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
1 |
HGBFRP [187–190] |
Excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, saltwater and environmental pollutants |
Lower mechanical strength compared to steel in some cases |
|
2 |
Steel [191–194] |
High strength |
Susceptible to corrosion from saltwater, deicing salts and some chemicals |
|
3 |
Concrete [195–199] |
Good durability in some environments |
Prone to corrosion from acidic environments and chloride exposure |
|
4 |
Cast iron [200–203] |
Good corrosion resistance to some chemicals and soil conditions |
Susceptible to pitting corrosion and graphitization |
|
5 |
PVC [21–24] |
Excellent resistance to most chemicals |
Lower strength and temperature limitations compared to some materials |
In conclusion, the excellent corrosion-resistant properties of HGBFRP pipes, demonstrated by their resistance to aggressive elements and durability, make them an ideal material for prefabricated construction in tough environments. Their ability to resist corrosion damage supports sustainable building practices and provides an effective solution for projects in both temperate and Arctic regions. Because of their natural corrosion resistance, HGBFRP pipes are a promising material that aligns with principles of environmental sustainability and reliability in the construction industry [21–24].
-
3.5 Challenges and Future Prospects
While hybrid glass-basalt fiber-reinforced polymer (HGBFRP) pipes offer significant advantages for precast construction, several challenges and research opportunities still need to be addressed to fully utilize their potential.
Economic Considerations. A notable limitation of HGBFRP pipes is their relatively high upfront cost compared to traditional materials like steel or concrete. Although long-term benefits such as reduced maintenance and lifecycle costs may offset the initial expense, the higher initial price can restrict their use in certain projects. Future research should focus on cost-effective manufacturing methods and alternative material formulations to lower expenses while maintaining the high performance and durability of HGBFRP pipes.
Performance in Extreme Environments. HGBFRP pipes exhibit strong mechanical and thermal performance across various climates, including temperate and Arctic regions. However, their behavior under extreme conditions, such as prolonged exposure to high temperatures or aggressive chemical environments, remains insufficiently studied. Dedicated research is necessary to assess their long-term reliability in such challenging scenarios, ensuring their suitability for diverse applications.
Material Integration. Ensuring compatibility between HGBFRP pipes and existing construction materials and methods poses another challenge. Integrating these pipes into precast elements may require modifications to standard construction practices and codes to ensure structural integrity and safety. Further research should focus on establishing guidelines, protocols, and best practices to facilitate seamless integration of HGBFRP pipes with other materials and construction technologies.
To address these challenges and further improve the application of HGBFRP pipes in prefabricated structures, several directions for future research and development can be proposed: Advanced Manufacturing Techniques. Research efforts should focus on developing advanced manufacturing methods for producing HGBFRP pipes more efficiently and cost-effectively. Innovations in manufacturing processes, such as automation, additive manufacturing, and advanced composite molding techniques, can help reduce production costs and improve the scalability of HGBFRP pipes production.
Enhanced Material Properties. Future research should aim to improve the mechanical properties and performance features of HGBFRP pipes through material optimization and engineering design. Exploring innovative fiber blends, advanced resin systems, and new reinforcement strategies can
Vafaeva, Kh.; Vatin, N.; Karpov D.; Voronov, A.
Hybrid glass-basalt fiber reinforced polymer pipes for prefabricated construction in temperate and arctic environments: A review;
produce HGBFRP pipes with greater strength, durability, and flexibility, thereby expanding their potential uses in prefabricated applications construction.
Lifecycle Assessment and Sustainability. Comprehensive lifecycle assessments (LCAs) are vital to evaluate the environmental footprint of HGBFRP pipes throughout their entire lifespan. Future research should focus on quantifying the ecological benefits of HGBFRP pipes compared to conventional materials and identifying opportunities to enhance their environmental performance and overall sustainability.
Standardization and Certification. Establishing industry-wide standards and certification procedures is essential to ensure the quality, reliability, and safety of HGBFRP pipes in precast construction. Developing standardized testing protocols, performance benchmarks, and certification criteria will require close collaboration among researchers, industry professionals, and regulatory bodies. These measures will promote wider acceptance and integration of HGBFRP pipes within the construction sector.
In conclusion, unlocking the full potential of HGBFRP pipes for precast applications relies on coordinated efforts among scientists, manufacturers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders. By addressing current limitations, advancing research and innovation, and adopting new approaches, HGBFRP pipes can become a transformative material, enabling the design and construction of sustainable, durable, and highly efficient precast structures.
-
4 Results and Discussion
In summary, the findings of this study highlight the transformative potential of hybrid glass-basalt fiber-reinforced polymer (HGBFRP) pipes in modern precast construction. HGBFRP pipes provide an exceptional combination of mechanical strength, durability, and versatility, effectively overcoming the limitations of traditional building materials and enabling innovative solutions for reliable and sustainable construction.
-
1. HGBFRP are especially well-suited for extreme environments, such as the Arctic, while also performing exceptionally well in moderate climates. Their excellent resistance to corrosion, mechanical loads, and temperature fluctuations ensures long-term structural integrity, making them an ideal choice for precast elements where performance and reliability are paramount.
-
2. Beyond their mechanical benefits, HGBFRP pipes promote environmentally responsible construction practices. By maximizing material efficiency, lowering energy consumption, and reducing the overall environmental impact, they support resource-efficient development. Their long service life, low maintenance requirements, and recyclability further increase their attractiveness to developers and builders dedicated to sustainability practices.
-
3. The development of HGBFRP technology indicates a wider application in precast construction. As innovations improve their performance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits, HGBFRP pipes are expected to play a vital role in creating resilient and durable structures. Using these materials can help build a future where efficient, sustainable, and strong construction becomes standard, providing long-lasting infrastructure while conserving ecological resources for generations to come.
5 Fundings
This research was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation No. 24-19-00691,
-
6 Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.


