Identification and modelling of the connection between the taxonomic position and traditional medical applications of plant species in prophylaxis and treatment of virus diseases
Автор: Popov P.L., Cherkashin A.K.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.20, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
A study is made of the distribution of 674 species of flowering plants in the phylogenetic system according to the specific applications of their active materials in traditional medicine in the prophylaxis or treatment of 21 virus diseases of humans and animals. The analysis revealed statistically reliable connections between the particular applications and the taxonomic position of plant species at the level of a family or a subclass, and connections between virus diseases according to the similarity of the sets of plant species that were used in their prophylaxis or treatment. We suggest the model correlating the taxonomic position with medical applications of plant species. We identified 62 plant species holding the greatest promise as regards the detection, further investigation and antiviral activity. These virus diseases at study are divided into 7 groups such as smallpox, rabies, respiratory infection, jaundice, warts, measles and others. Class Magnoliopsida is superior to class Liliopsida in occurrence of species used in various viral infections. The proportion of these species is most large in evolutionarily later subclasses out of class Magnoliopsida . The families from division Magnoliophyta have reliably increased occurrence of species used at least against one group of diseases such as Ranunculaceae (measles, smallpox), Fumariaceae (jaundice), Euphorbiaceae (rabies, warts), Tamaricaceae (jaundice), Malvaceae (respiratory infection), Dipsacaceae (respiratory infection), Sambucacea (rabies), Viburnaceae (respiratory infection), Trapaceae (rabies), Gentianaceae (rabies, jaundice), Solanaceae (respiratory infection, jaundice, rabies), Cuscutaceae (rabies), Lamiaceae (respiratory infection), Asteraceae (jaundice), Alismataceae (rabies). Closely related families are often similar on sets of infections in which species of these families are applied. Viral diseases are reliably interconnected with similarity of sets of plant species used in the prophylaxis or treatment. Particularly strong connections are "respiratory infections-jaundice", "respiratory infections-rabies", "measles-smallpox". The 62 plant species are recognized as the most promising for discovery, further study and use of their antiviral activity accounting established relations "family - disease" and "disease - disease ". The taxonomic status of plant species is associated with their medical applications using mathematical model. The model is constructed as the equations of the theory of reliability (effectiveness). It describes the changing the frequency of the usage of plant species along the parameter of level of evolutionary development of taxons on rank of subclass. The data on the frequency of application demonstrate good correlation with calculated values (R2 = 0.91) what allows to use the equations for forecasting and valuation.
Traditional medical applications of plants, prophylaxis and treatment of virus diseases, mathematical modeling, connection of plant taxa with infections
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143182791
IDR: 143182791
Текст научной статьи Identification and modelling of the connection between the taxonomic position and traditional medical applications of plant species in prophylaxis and treatment of virus diseases
The position of the species in the phylogenetic system largely determines the chemical composition, biometric and environmental properties of plants and as a result the direction of their applications in particular in the medical practice.
The concept of many-fold connections between matter and the ways in which it is processed, and its composition, structure, properties and performance is basic to materials science (Callister, 2007). Methodologically, such a formulation is relatively common to the analysis of objects of a different nature, aimed at identifying their performance from their intrinsic properties.
There are definite correlations between the types of objects, the types of their properties and the kinds of application. For that reason, to understand the performance of different materials requires several classifications that would straighten out the different kinds of objects, their properties and the modes of application. The frequency (comparative performance, effectiveness) of appropriate materials in a particular region corresponds to a combination (relationship) of the taxonomic positions of different classifications.
The objective of this study is to establish the connections of the taxonomic position and traditional medical uses of plant species in the prophylaxis or treatment (PT) of virus infections of humans and animals, namely the interdependence of the two classifications (plants and virus diseases) where the performance criterion is represented by the proportion of the species of the taxon that were used in PT of particular diseases. A statistical analysis of initial data is made as well as developing the theory of mathematical modeling of the representation of such classification connections.
In this paper, no consideration has been given to the issue related to the nature of active substances, and to the mechanisms by which their viruses are acted upon. We solve the informational problem of establishing the “plant‒application” associative relationship in order to generate the system of knowledge and ensure the derivation on its basis. Similar problems are dealt with in data-mining procedures (Han, Kamber, 2006; Witten et al., 2011), if they are treated in some general mathematical context allowing for a broad substantive interpretation. Such an approach does not imply an a priori notion of data analyzed when detecting a useful knowledge that has hitherto been unknown, for describing the latent regularities and predicting the unknown properties in objects under investigation.
Origin of the problem.
The 1960s‒1970s saw an upsurge of chemistry research and publications in this field, specifically on the problem of the connection between the structure of organic substances and their biological activity as applied to the creation of new remedies (Nantasenamat et al., 2009). V.A. Palm’s publications (Palm, 1967; Palm, 1977) were among the first to identify a quantitative correlation between the structure of organic compounds and their reactivity. V.A. Palm generalized the familiar logarithmic relation, the Hammett equation In k = In k0+pa, combining the constants of chemical reaction rates k and equilibrium k0, in view of the index σ characterizing in an integral way the environment in which the process is taking place. This equation relates linearly the values of free energies of reaction or activization (AF ~ In k). According to V.A. Palm, such an approach leaves room for a broad (not only physicochemical) treatment where the quantitative characteristic of a complex system is regarded as a function of the set of elementary parameters f = f(x), x = {xi}, i=1 n. This function is represented as a linear or polylinear dependence of transformed, curvilinear coordinates, such as x ’=ln x. Noteworthy is the section method (Palm, 1967) for reconstructing the function f = f(x) = G xo[ f(x0), f1(x1),... fn(xn)], fi (xi) = f(x01,... xi,.. .xon) from a set of partial dependences f (xi) (sections) in the neighborhood of the point x = xo.
The fundamental character of such an approach is confirmed by a wide occurrence of the power functions f= axb, ln f= b ln x +ln a for describing the dependencies of variables in various sciences, such as allometric relationships of the attributes of organisms in biology (Calder, 1984; Mina, Klevezal, 1976) or the Cobb-Douglas equation in economics (Walsh, 2003). fx) = axi ax2е, Inf = a In x1+в In x2+ln a, where f(x) is the volume of production, x1 is the volume of capital, x2 is labor input, and α and β are the output elasticities for capital and labor inputs, respectively. This equation, expressed in terms of the sections x = x0 in the form of power functions, has a simple form of a first-order homogeneous function without coefficients f(x) = f1f2/f0.
Gibrat’s law (Chesher, 1979; Santarelli et al. , 2006) relates the characteristic of production organization for a current t and subsequent t + τ periods by an identical logarithmic relation ln f ( t+τ ) = a + b ln f ( t ) . Such a recurrence relationship, reflecting the fact of selfsimilarity, is obtained, in particular, from the Gompertz equation for biological growth (Mina, Klevezal, 1976)
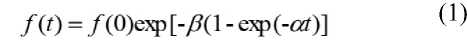
where α and β are positive constants. The Gompertz equation is usually used in approximating the reliability functions ( f (0)=1, α<0, β<0 ), specifically in survival analysis (Hosmer et al. , 2008). It results that the logarithmic similarity connections have an interdisciplinary interpretation, and their formation is based on complex dependencies of the estimating characteristics f ( x ) on the set of influencing factors x . The main problem is that of identifying these dependencies and regularities of the similarity permitting the conclusions to be drawn.
Medical treatment of virus infections is one of the most important missions of modern medicine. Inadequate effectiveness of the use of antiviral remedies is due to the existence of physiological barriers interfering with inactivation of virus in sick organism. One of the sources of substances capable of inactivating viruses is provided by the plants that have long been used in traditional medicine of various countries; over the last several decades they have been investigated actively (Vanden Berghe et al. , 1986; Jassim, Naji, 2003; Pushpa et al. , 2013).
MODEL AND METHODS
Analysis of the initial information
This study uses information from the eight-volume edition (Sokolov, 1984 – 1993; Sokolov, 1994) on medical uses of 2715 species of wild-growing flowering plants of the flora within the boundaries of the USSR’s territory, with due regard for medical traditions of other
countries where these species occur. On the basis of this information, we compiled a list of 674 species of flowering plants used in traditional medicine, for PT of 21 kinds of virus infections of humans and animals, distributed in seven groups (Popov, 2008) (Table 1).
Listed in Table 1 are only subclasses and families of plants, showing reliable concentrations (increased occurrence frequencies) of the species used for PT of at least one of the virus infections. Of the entire list (2715 species), 513 plant species were used against one disease, and 161 species against two or more (not exceeding five); therefore, the total number of uses (the sum under “virus diseases”) is larger than the number of medicinal plants (674 species against 890 uses).
As regards rabies, plants were mainly used for the prophylaxis of the disease; sometimes, however, publications do not specify the particular uses prophylaxis or treatment. In most cases, the particular application is indicated treatment or prophylaxis of this disease in humans, but sometimes also for rabies of animals. All these variants of application against rabies (treatment or prophylaxis, humans or animals) are grouped together as “rabies|”. However, the statement concerning treatment of rabies is open to question, because this disease was considered incurable, but traditional medicine was taking advantage of any possibilities.
A statistical preprocessing used data for six groups of diseases that were dominant with respect to the number of plant species used for their treatment or prophylaxis respiratory infections, jaundice, rabies, warts, measles, and smallpox. The uses of plants for PT of the other kinds of virus infections are not numerous.
First we ascertain the fact that traditional medicine used against different groups ( j ) of virus infection a particular ( k ) species of plants u ijk of a given taxon ( i ) at the level of a family and a subclass u ijk ∈ U ij ⊆ U i ⊆ U , U ij ↔ V ji ⊆ V j ⊆ V , where U , V are the sets of all medicinal plants and diseases taken into account U = ∪ i U i , V = ∪ j V j ); U ij is the set of plants of the i -th taxon used in treatment of diseases v jil of the j -th group ( v jil ∈ V ji ⊆ V j ). The arrows ( ↔ ) correspond to the relationships of association, representations of sets. The plants ( k ) of the taxon U i can belong to different subsets U ij , i.e. they can be used for different diseases ( j ) u ijk ↔ v jil ∈ V ji . Similarly, different plants can be used against the particular diseases, v jil ↔ u ijk ∈ U ij . The union V i = ∪ j V ji is a set of diseases against which the plants of the i -th taxon were used, and the union U j = ∪ i U ij is a set of plants of different taxa used in PT of diseases of the group j . Let us denote μ ij = μ ( U ij ), μ ji = μ ( V ji ) is the power of the sets U ij and V ji , i.e. the number of elements (species of plants or kinds of diseases) in these sets μ i = μ ( U i ), μ j = μ ( U j ), μ u = μ ( U ).
Taxa of plants and groups of diseases are compared with respect to the similarity of plants used in PT ( U ij ↔ V ji ). The criteria for judging the performance of a plant and appropriateness of its investigation as the source for medical remedy are the following conditions 1) the fact that a plant of a given species was used in PT of a particular virus infection ( u ijk ↔ v jil ∈ V ji ); 2) the belonging of a species to the taxon ( u ijk ∈ U i ), which showed a concentration ρ ij = μ ij / μ i of the species used for PT of the j -th virus infection, and 3) the use of a plant against different ( j =1 and j =2) infections ( u i1k ↔ V 1i , u i2k ↔ V 2i ,) similar in the set of species (the intersection U 12 = U 1 ∩ U 2 ) used for their PT ( u ik ∈ U 12 ).
Reliability of associative relations is estimated using Fisher’s multi-functional test φ* of the difference of the proportions (Bland, 2000). The procedure involves verifying the hypothesis of the difference between the appearance (in the taxon i) of the proportion ρij = μij/μi of the plants used in PT of the j-the disease, from the proportion ρ͞ ij = (μj - μij)/(μu - μi) in an additional set of medicinal plants U - Ui and the difference of the frequency ρ0ij = μij / μj of using the plants of the i-th taxon for PT of the j-th disease from the value of ρ͞ ij=(μi-μij)/(μu-μj) in an additional set of plants U ‒ Uj. Fisher's angular transformation ϕ=2arcsin√ρ is carried out, and the value of ϕ*=|ϕij–ϕj|√µij(µj-µij)/µ is calculated, which is compared with its critical values for a given reliability p≥ 0.99.
For instance (Table 2), among the μ u =2715 species of medicinal plants, the family Gentianaceae includes μ i = 38 species ( ρ i = μ i / μ u =0.014). There are μ ij = 6 species for PT of rabies from this family ( ρ ij =0.158) among the μ j =98 species of this flora ( ρ 0 ij = 0,061, ρ ͞ 0ij = 0.036). If the intersection of the kinds of diseases and plant species were accidental, then the significance of this event ρ ij would equal the product of the proportion of the plants from the family ρ i = μ i / μ u by the proportion of useful (in this case) plants ρ j = μ j / μ u . This product corresponds to the number of species 1,4 out of the set of all medicinal plants of the family Gentianaceae used for PT of rabies. Actually, the number of such plant species is markedly larger ( μ ij = 6), and this difference must be estimated statistically.
The medicinal characteristics of the species of a taxon can be identified in two ways, namely by comparing the characteristics of a given taxon (the presence of effect) with characteristics of 1) all taxa, including a given taxon, and 2) the remaining taxa (Table 2), except for a given taxon. The former variant emphasizes the prominence of the properties inherent in the family of plants at the general background of performance of all medicinal plants, and the latter variant highlights the difference from the properties of all the other taxa. Since Fisher’s test involves comparing observational results for independent groups, the latter variant is preferable to the former, although it involves additional calculations and a complexity of interpretation; in the case of a large number of species, μ =2715, the two variants yield comparable results.
A comparison of ρij and ρ͞ ij in the former variant uses the ratios 6/38 and 98/2715; we have φ* = 2.66, and the hypothesis of an accidental difference of the proportions ρij and ρ͞ ij is discarded with the p≥0.99 significance. A comparison of the proportions in the latter variant assumes the ratios 6/38 and 92/2677; we have φ* = 2.72, and the hypothesis is also discarded. The two variants of calculations suggest that the connection of attempts at PT of rabies with the family of plants under consideration is reliable. Identification of the specialization of all medicinal plants in the case of PT of rabies compares the values of ρ0ij = 6/98 and ρ͞ 0ij = 32/2617. The results of calculations yield φ* = 2.70, and the similarity of the proportions is not confirmed. This suggests a reliable concentration (in the family under consideration) of the plants used for PT of rabies.
There are many examples where an increased concentration of species in a family used against a particular infection is statistically unreliable. Thus, in a large family, Rosaceae , 24 species (17.4%) were used against respiratory infections while, as regards the portion of the flora of medicinal plants not involved in this taxon, the proportion of the species used for such purposes makes up 14.2%. The difference of the percent proportions in this case is not reliable, i.e. a specialization of the species of this family for PT of respiratory diseases is not identified. There are several families which, according to Fisher’s test, closely approach the threshold of statistical reliability Scrophulariaceae for jaundice, respiratory infections and rabies, and Crassulaceae for jaundice. Notice that the family Scrophulariaceae belongs in the subclass of Lamiidae which includes also a number of families, showing reliable concentrations of the species used against relevant virus infections.
Use was made of μ(U23) = 27 kinds of different families both for rabies (μj=2 = 98, ρj =2 =0.036) and for respiratory infections (μj=3 = 391, ρj=3 =0.144). In the case of a random combination, the total number of species would be nearly twice as small, μuρj=2ρj=3=14.1. A comparison is made of the two relationships ρ02= μ(U23)/μj=2 = 27/98=0.276 and ρ͞ 02 = (391-27)/(2715-98) φ*=3.31, and the hypothesis of a coincidental difference of the contributions from ρ02 and ρ͞ 02 is discarded. Similarly, for the ρ03 =27/391=0.07 and ρ͞ 03 =71/2324 φ* =3.30 relationships the hypothesis of an accidental difference of the contributions from ρ03 = μ(U23)/μj=3 and ρj=2 is also not accepted. Thus the connection of these two groups of diseases according to the total number of species used in their PT is not accidental and implies some associative rule if the plants are employed for PT of respiratory infections, then, with the ρ02=0.276 significance, they can be used against rabies. Based on the validity of such conclusions, different diseases in a pair combination are not equivalent; for instance, if the plants have been used against rabies, then, according to information available, they can be used against respiratory diseases with the ρ03 =0.07 significance only.
Such associative connections between diseases are represented as a plot (Fig. 1), where the arrows of representations are oriented along the direction of conclusions, indicating the significance of a correct answer. Respiratory diseases turn out to be most informative, and measles and smallpox are more predictable. The “families – infections” relationship is clearly seen in the Table 1 data. A total of 15 such reliable relationships was identified at φ* >1.9. Of the C 62 =15 possible pair combinations, nine cases show a reliable “disease – disease” relationship.
There occur the more complex relationships of the “diseases‒plants‒diseases” type where some of the families show a concentration of the species used in PT of two infections or more. Thus, the family Solanaceae includes μ i = 19 species of medicinal plants, and among them the PT of rabies as well as respiratory infections used μ ( U 23i ) = 4 species ρ ( U 23i ) = 0.211. In the entire flora of medicinal plants, the species with such a property μ ( U 23 ) = 23 ρ ( U 23 ) = 0.0085. The ratios 4/19 and (23-4)/(2715-19) are compared. The value of φ* = 3.41, and the difference of the proportions is reliable; therefore, the representatives of this family relate, in some way, these two diseases with one another.
Statistically reliable concentrations of the species with a definite application are identified not only at the level of classes, subclasses and families but also for the general of plants (Popov, 2008; Popov, Botvinkin, 2008). However, the concentrations of useful species at the level of genera are difficult to study by statistical methods, because a genus is usually represented by several species, and only one among them is considered a medicinal plant. The families that include a reasonably large set of specific (in chemical composition) useful plants then provide an optimal taxonomic level for analysis.
Subclasses of species are clearly distinguished according to the percent proportions of the uses of plants in virus infections (Popov, 2008). There is a continuity of the families and subclasses as regards this property. The family Gentianacae , for example, shows a concentration of applications against rabies (6/38). This, along with Solanaceae, Lamiaceae, Scrophulariaceae and others, belongs in the subclass of Lamiidae in which such plants are also concentrated (28/478). In the subclass of Lamiidae , the proportion of the species used against rabies makes up 5.9%, with 3.1% (70/2237) corresponding to the remaining flora; these differences are reliable ( φ* = 2.64). On the contrary, a comparison for the species of the family Gentianacae and the subclass of Lamiidae (without taking into account the species of the family, the ratio 22/440) shows unreliability of their differences, i.e. the species of the family merely reflect the properties of the species of the subclass in terms of the concentration of the species used for this disease.
Mathematical model.
The effectiveness, or the medical performance of plant species of the taxon i for treatment of diseases of the group j is empirically estimated by Pij = μij / μi. . The suggested model describes a change in the performance distribution Pij(t) along a certain route x(t), determined by the parameter t, and, in the simplest case, by the time and position in space; in the general case, by some homotopic attribute t. Its transformation t→t1 leads to a transformation of independent characteristics of the system x(t) ={xi(t)}→ x(t1) and of the performance index P(t,x) → P(t1,x). In this manner the scheme for derivation of a new knowledge is realized, if the law of transformation of P(t,x) from the parameter t is known and if the connection of the indices of the taxa i and diseases j with the characteristics from the set x(t)={xi(t)} i → x1, j → x2 is established. In general, there can be many such characteristics, because for each notion its own classification scheme is constructed; for instance, in addition to virus diseases, there exist other types of diseases (nervous, cardiac, etc.), the PT of which uses appropriate medicinal plants. The plants can also be related with their geographical location, and with the types of landscapes. Information regarding the uses of plants for PT of particular infections can be correlated with chemosystematic data on the occurrence frequency of different chemical substances in plants of different families. This evidence must all be ranked in terms of a unified model for assessment of the performance as a function of the numerous partial characteristics.
Such a problem can be solved by relating P ( t,x ) to a loss of effectiveness (performance) P* ( t,x ) of the system under consideration, along the route x ( t ) with a loss intensity (hazard) p ( t,x )
dP\t,x) .
P(t, x) =--= p(t, x)P (t, x) (2)
dt
It is a basic relation from reliability theory (Høyland, Rausand, 2009), and is convenient for investigating different flows of elements with losses (failures). The positive effectiveness value of P* ( t,x ) increases or decreases with an increase of the value of t . The value of P ( t,x ) is a function of effectiveness density, the derivative with respect to the parameter t (with a minus) and corresponds to the price (value) of the elements with the set of characteristics ( t,x ).
The connection law (2) can be developed by using the total derivative (the Lagrangian derivative, the case of two characteristics x 1 , x 2 )
dP _dP dP dP _ . _dx, _dx2 (3)
Let us apply the similar mathematical transformations for the hazard rate function
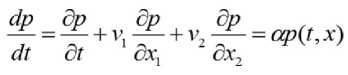
where α is an individual constant coefficient. A solution to the partial differential equation (4), in view of the characteristics of the system x, is found from the first integrals q = p!exp(at), c2 = —-—,c3 = f-“ (5)
' V1 V2 1 2
in the form c 1 = G ( c 2 , c 3 ), where c 1 , c 2 , c 3 are the individual constants characterizing the system of particular connections. The function G is fitted experimentally and, in this case, it corresponds to the requirements of the Cox proportional hazards model (Andersen, Gill, 1982), i.e. to an exponential dependence
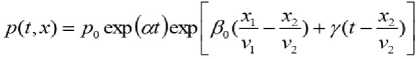
where β 0 , γ , p 0 are the species-specific constants. If, for simplicity, it is assumed that γ = 0 and if the resulting expression (6) is substituted into equation (3), we can evaluate the first integrals of this equation and use them to construct the relation
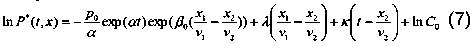
which ensures a logarithmic connection of the functions ln P* ( t,x ) in view of the shift of the variables ( A , B being constants dependent on the shifts Δ t , Δ x )
In P" (7 + АЛ x+Ar) = ^ In P* (t, x) +В (8)
Formula (8), under certain conditions, corresponds to the aforementioned “deductive” regularities, i.e. the Hammett equation, and the Gibrat law. The quantity E ( t,x )=- ln P* ( t,x ) has the meaning of a generalized energy.
Let us simplify the expression (7) y assuming that λ
= 0, κ = 0, - ν 1 =ν 2 =ν , and by fixing the parameter t
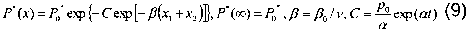
This relation is similar to equation (1), which is widely used in survival analysis. In this case, however, the performance function (9) increases with an increase of x1 and x2. A positive function of variation density in the variables x1 and x2 corresponds to it
P(x) = P^Cp exp [- jB^ + -v, )]exp {- C exp [— /5^ + x2 )]} (10)
It is a bell-shaped curve peaking at the point x m1 =- x 2 + ln C / β and x m2 =- x 1 + ln C / β , with the maximum value of P m = P 0 * β /e , whence it follows that β = eP m /P 0 * , which makes it possible to simply calculate the coefficient β and the function (10).
In view of this notation, we have
P(x) = P0 /3 exp [j3(xnl, — x, )] exp {— exp [В(хт2 — x2 )]}. (11)
This equation describes the performance P ( x ) as a function of one variable x 2 and is a section from a fixes value of the other variable, x 1 , the value of which governs the position x m2 of the maximum of P ( x m2 ) = P m . This means that a change in the values or a complement of the number of factors transforms the form of the relation (11), and this transformation can be estimated numerically. The value of is determined as the sum of the values of P ( x ) for all x 2 ; therefore, it depends on the value of x m2 and, hence, on x 1 .
A remarkable property of equation (11) is the existence of its invariant form
l(z) = P(x)!p‘ =eze^-z), z(x) = p(x)I/} = exp\p{xm2 -x,)](12)
which appears due to a change of the variables x 2 → z . The similarity of the theoretical λ ( z )= ez exp ( -z ) and the empirical λ ( z )= P ( x )/ P 0 * ( x 1 ) values provides insight into the quality of approximation across the whole data set.
RESULTS
Results of modeling
A practical implementation of the model presented herein requires solving the problem of transforming the indices of classification taxa i and diseases j to the variables i → x 1 , and j → x 2 , for which purpose it is necessary to establish a correspondence of the linear sequence of numbers. With this in mind, the categorical codes of the classification position are converted to an ordinal integer-valued scale and, then, to relative fractional values specifying the positions of the taxa in the linear sequence.
The subclasses (from A to H) of flowering plants within Magnoliopsida are identified according to A.L.
Takhtadzhyan (Takhtadzhyan, 1987) and numbered ( i = 1,2,…8) in accordance with the level of their evolutionary perfection. The diseases are arbitrarily arranged in an orderly fashion into a sequence, in accordance with the degree of hazard (risk) of a particular disease and the lethal outcome for the formation period of traditional medicine. Based on this criterion, the diseases are ordered form natural smallpox and rabies to measles ( j = 1,2,…7). These ordinal values are used as a first approximation of the variables x 1 and x 2 . Under the assumptions made, the value of p from (6) decreases with an increase of these variables.
The ultimate (additional) performance (effectiveness P ( x 1 , x 2 ) ↔ P ( i , j ) = μ ij / μ i of the plants of subclass i is determined by the number of species μ ij used in PT of the j -th infectious disease, referred to the number μ i of the known medicinal plants of the flora of Russia and neighboring countries from a given subclass (Table 3). The sum P ( x 1 , x 2 ) from all subclasses P 0 * ( x 2 ) is largest for respiratory infections, while the maximum sum for infectious diseases P 0 * ( x 1 ) corresponds to subclass H, Asteridae .
It is evident from the data listed in Table 3 that the performance of plants for PT of respiratory infections increases almost linearly (R 2 = 0.78) with an increase of x 1 . The variation of P ( x 1 , x 2 ) for subclasses x 1 for rabies and other virus infections (R 2 > 0.75) as well as for the sums of P 0 * ( x 1 ) correlates quite well with this tendency. The sum P 0 * ( x 2 ) for subclasses of plants represents the general tendency for change in their performance. Variations in x 2 of all subclasses (except for A) are correlated with it (R 2 > 0.73). A good correlation (R 2 > 0.96) is shown by cumulative data P i * ( x 2 ) and their logarithms P i *(x 2 ) according to formula (7) as well as by the intensity relations p i ( x 2 )= P i ( x 2 )/ P i * ( x 2 ), corresponding to formula (6) it is a decreasing exponential dependence of the form p i ( x 2 )=exp(‒0.41 x 2 + 0.52), i.e. the hazard of diseases p i ( x 2 ), as expected, must decrease with an increase in the index x 2 .
In approximating the Table 3 data, for each subclass i we determined the modal values of x m2 , P m and P 0 * , and calculated the value of the coefficient β = eP m /P 0 * and the value of P ( x ) by formula (11). A slight variation of the variables x 2 and P 0i * is used to attain the best similarity
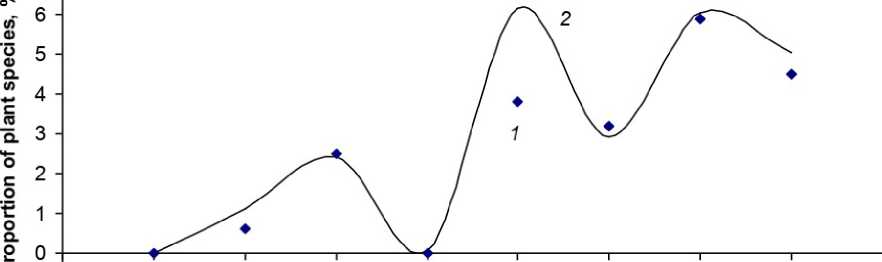
(R 2 > 0.9) of the calculated curves and data (Fig. 2). The accuracy of approximation in the context of subclasses depends strongly on the total number P 0 * ( x 1 ) of medicinal plants in subclasses x 1 (Fig. 3). By varying the value of x 2 , we attain the best similarity of the theoretical and empirical data. Such an approach is useful for refining the classification position; for instance, it is best to assume that j =1.5, rather than j =1, etc.
Fig. 4 compares the theoretical and empirical values of the function λ ( z ) (12). Most of the points show a good similarity at the R 2 =0.91 level. The equations introduced above and our calculations provide a possibility of assessing the anomalies in the distribution of the kinds of diseases in subclasses and groups of medical application, and using them in assessing the potential performance of the species of different taxa, with due regard for the identified associative connections.
Prospects for medical application of the species of families.
When families and separate species are used in equation (11), the values of x m2 , P m and P 0 * are changed, in which case P 0 * =1 is assumed for a separate plant species, and the function P ( x ) becomes a probability function. It can be treated as a fraction of the cases of performance of a given plant. For the subclass of Rosidae , the transition to the level of a family does not involve any change in the modal value of x m2 =3 (respiratory diseases), with the exception of the family Trapaceae , two representatives of which were only used in the case of rabies, x m2 =2 (see Table 1). In the subclass of Dillenidae , x m2 =3, x m2 =4 and x m2 =5 correspond to the families Malvaceae , Tamaricaceae and Euphorbiaceae . This means that the introduction of an update knowledge alters the value of x m2 for the level of a subclass, i.e. implies using an additional factor variable x m2 =- x 1 - x 3 + ln C / β , causing a shift Δ x 1 = x 3 of the base index x 1 of the taxon of the subclass level. For that reason, the introduction of an additional factor can always be interpreted as the shift of the base index. For the cumulative curve of effectiveness (9) the old P* ( t,x ) and the new P* ( t,x + Δ x ) values will be linearly related by formula (7). Consequently, prediction of the properties is determined by a substantiated variation of the system’s parameters.
Most of the families (68%) show a good similarity of the theoretical and empirical values of λ ( z ) at the R 2 > 0.7 level. The sum of the positive у and the negative y 1 differences between the theoretical and empirical values was calculated separately. They showed a high correlation for all taxa у = ‒0.83 y 1 + 6.38 (R 2 = 0.96), and the sum approached zero (x + у = ‒0.54 ± 4.11%). The identified correlation shows that the positive and negative deviations carry similar information and can be used interchangeably.
To interpret the meaning of the deviation of empirical data from calculated theoretical values uses results of statistical analysis of associative connections derived from identifying the individual plant species that hold promise for discovery, research and application of antiviral activity of materials. The following types of connection are taken into consideration 1) the fact of application of a species in two or more virus infections; 2) the presence of a statistically reliable connection between at least two virus infections in which case a given species was used, and 3) the presence of a statistically reliable connection of the family in which a given species belongs, with at least one infection in which case the species of the family were used. In accordance with these conditions, the list of the especially useful plants incorporates only the species, each of which is involved in ensuring reliable connections of the “disease‒disease” and “taxon‒ disease” type. Rank I of performance of a species is determined by the number of reliable connections of these two types in which a plant species is involved. In the case where the ranks are identical, preference is given to the species that was used in treatment of a larger number of infections.
For instance, Solanum duclamara L. was used in the case of respiratory infections and jaundices. It belongs in the family Solanaceae, showing a reliable concentration of the species for PT of jaundices and respiratory infections, and these infections are reliably interconnected via the sets of the plant species used. As a result, three reliable connections were revealed one of the “disease‒disease” type, and the other two of the “family‒disease” type. The other species, Tanacetum boreale Fisch. ex DC. of the family Asteraceae was also used in the case of respiratory infections and jaundices, but there was no reliable concentration of the species for treatment of respiratory infections. This family showed a reliable concentration of the species used in the case of jaundices for treatment of respiratory infections. Hence the rank of T. boreale corresponds to two connections one of the “family‒disease” type, and the other of the “disease‒disease” type. Marrubium vulgare L. Of the family Lamiidae was also employed in treatment of these diseases. This family showed a reliable concentration of the species used in treatment of respiratory infections, but there was no reliable concentration of the species used in the case of jaundices. This species is also characterized by two reliable connections. The aforementioned three species satisfy the conditions for the inclusion of promising medicinal plants on the list, but S. duclamara has a higher rank.
As a result of our statistical analysis, 62 species were identified among the 674 promising species used in PT of virus infections of humans, which are distributed in families, indicating the number of representatives and the sum of their rank estimates. The species corresponding to the criteria formulated are unevenly distributed in taxa of the philogenetic system. In the class of Magnoliopsida , the species used in virus infections are more common than in the class of Liliopsida . In the evolutionary earlier (and, especially, in the later) subclasses of the class of Magnoliopsida , the occurrence frequency of such species is much higher than in the intermediate positions (see Table 3). The nonuniformity increases abruptly when the aforementioned selection criterion is used. The class of Liliopsida and some subclasses of the class of Magnoliopsida are not represented by promising species altogether.
The number of promising species n and their rank of potential performance I are related linearly I = 2.54 n + 2.75, R 2 = 0.95. A general regularity is observed, i.e. the better is the model approximation of data, the larger is the number of promising species identified in a taxon. In particular, this is clearly seen for PT of respiratory diseases.
Approximating curves of the form (11) are reconstructed from the position of modal values of the plots of the performance frequency of plants from different families versus the group number of virus diseases. The rank I is also determined from the previous applications; therefore, their increased values provide insight into the accuracy of data approximation.
Theoretical values were obtained by extrapolating the modal parameters of the curves. The positive bias of the values suggests that there exist potential plants species useful for PT, while the negative bias point to a need for an in-depth study of the known medicinal properties of the plants within a family.
Table 1 Distribution of medicinal plant species in classes, subclasses and families of flowering plants and in the number of their uses in the prophylaxis or treatment of different groups of virus infections
Group of viral diseases*
|
Taxon |
No. of Species |
No. of Promising Species |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
Phylum Magnoliophyta |
2715 |
62 |
29 |
98 |
391 |
228 |
65 |
50 |
29 |
|
Class Magnoliopsidae |
2383 |
62 |
28 |
88 |
357 |
209 |
63 |
42 |
26 |
|
Subclass Ranunculidae |
181 |
4 |
9 |
1 |
19 |
24 |
7 |
2 |
5 |
|
Family Ranunculaceae |
123 |
4 |
6 |
1 |
14 |
14 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
|
Family Fumariaceae |
12 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
Subclass Dillenidae |
393 |
6 |
4 |
15 |
56 |
27 |
31 |
4 |
6 |
|
Family Euphorbiaceae |
61 |
6 |
0 |
9 |
2 |
2 |
24 |
0 |
0 |
|
Family Tamaricaceae |
15 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Family Malvaceae |
30 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
12 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Subclass Rosidae |
685 |
5 |
4 |
22 |
106 |
43 |
8 |
13 |
7 |
|
Family Dipsacaceae |
16 |
3 |
0 |
2 |
6 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
Family Sambucacea |
7 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Family Viburnaceae |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
Family Trapaceae |
4 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Subclass Lamiidae |
478 |
25 |
6 |
28 |
92 |
54 |
10 |
10 |
4 |
|
Family Gentianaceae |
38 |
6 |
0 |
6 |
7 |
11 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
|
Family Solanaceae |
19 |
6 |
2 |
5 |
7 |
8 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
Family Cuscutaceae |
7 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Family Lamiaceae |
164 |
12 |
0 |
3 |
43 |
13 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
Subclass Asteridae |
378 |
22 |
4 |
17 |
67 |
48 |
3 |
13 |
4 |
|
Family Asteraceae |
352 |
22 |
4 |
15 |
66 |
48 |
2 |
11 |
4 |
|
Class Liliopsidae |
332 |
0 |
1 |
10 |
34 |
19 |
2 |
8 |
3 |
|
Subclass Alismatidae |
19 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Family Alismataceae |
5 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
* Groups of virus infections 1 – smallpox; 2 – rabies; 3 – respiratory diseases; 4 – jaundices; 5 – warts; 7 – measles; 6 – others.
Other diseases include tick-borne encephalitis, type B encephalitis, waterpox, German measles, parotitis, virus pneumonia, herpes, foot-and-mouth disease, hog cholera, canine distemper, jaundice of cattle, etc. A total of 15 diseases, and PT of each of them used one to eight plant species.
The number of species with a reliable increased occurrence frequency in the taxon is italicized.
Table 2 Fisher’s test-based comparison of the use of the species from the family Gentianaceae in the prophylaxis of rabies when the other medicinal plants are employed
|
Group of data |
Effect |
No effect |
Total |
|
Taxon |
6 |
32 |
38 |
|
Other taxa |
92 |
2585 |
2677 |
|
All taxa |
98 |
2617 |
2715 |
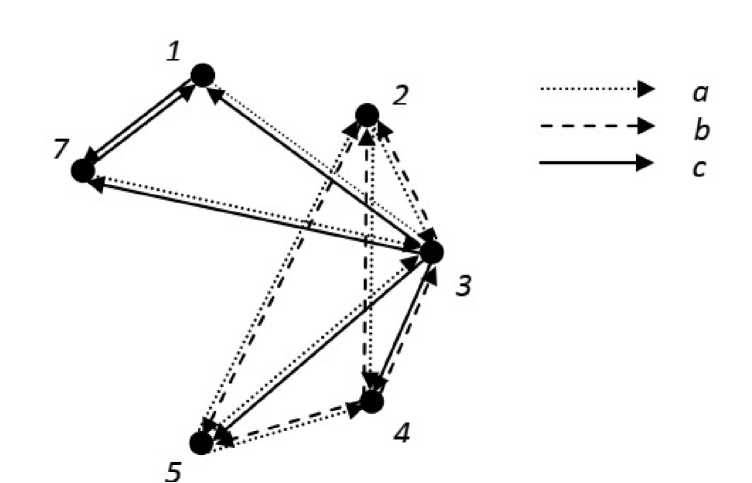
Figure 1. Reliable connections of groups of viral diseases according to the similarity of the sets of plant species as used in the prophylaxis and treatment of these diseases. The arrows indicate a different validity (significance) of correct conclusions a – 0.00 – 0.10; b -0.11 – 0.30; с – 0.31 – 0.60.
Groups of virus infections 1 – smallpox; 2 – rabies; 3 – respiratory diseases; 4 – jaundices; 5 – warts; 7 – measles.
Table 3 Proportion (%) of the plant species as used in the prophylaxis and treatment of viral diseases, of the number of species of medicinal plants of different subclasses
Infectious diseases
|
i,x 1 |
j,x 2 Subclass |
1 Smallpox |
2 Rabies |
3 Respiratory |
4 Jaundice |
5 Warts |
6 Others |
7 Measles |
Total |
|
1 |
A |
0 |
0 |
4.8 |
19.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
23.8 |
|
2 |
B |
5 |
0.6 |
10.5 |
13.0 |
3.9 |
1.1 |
2.8 |
36.9 |
|
3 |
C |
0.5 |
2.5 |
6.6 |
4.0 |
2.0 |
0 |
0 |
15.6 |
|
4 |
D |
0 |
0 |
6.5 |
2.2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
8.7 |
|
5 |
E |
1 |
3.8 |
14.4 |
6.9 |
7.9 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
36.5 |
|
6 |
F |
0.6 |
3.2 |
15.5 |
6.3 |
1.2 |
1.9 |
1 |
29.7 |
|
7 |
G |
1.3 |
5.9 |
19.2 |
11.3 |
2.1 |
2.1 |
0.8 |
42.7 |
|
8 |
H |
1.1 |
4.5 |
17.7 |
12.7 |
0.8 |
3.4 |
1.1 |
41.3 |
|
Total |
9.5 |
20.5 |
95.2 |
75.4 |
17.9 |
9.5 |
7.2 |
235.1 |
Subclasses А - Magnoliidae , B – Ranunculidae, C - Caryophyllidae , D – Hamamelidae , E – Dillenidae , F – Rosidae , G – Lamiidae , H – Asteridae.
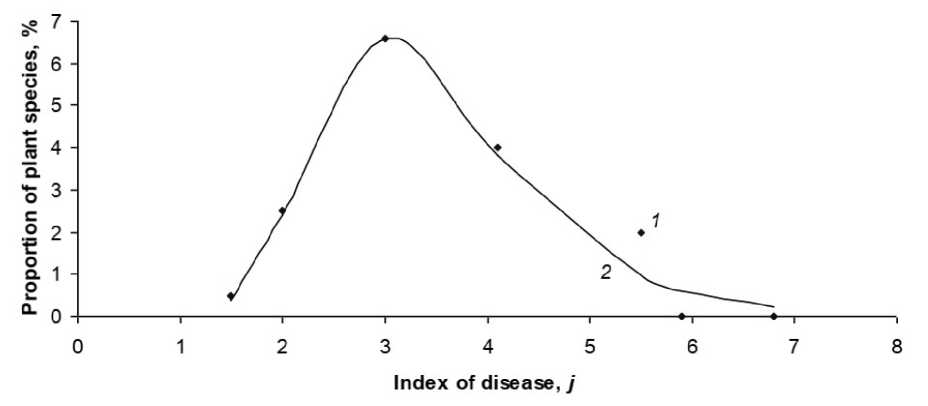
Figure 2. Approximation of tabular data (1) with curve (2) of function (10) for subclass С – Caryophyllidae .
7 о
Index of subclass, i
Figure 3. Approximation of tabular data (1) with curve (2) of the dependence of additional performance on the subclass number as calculated from function (10) for rabies.
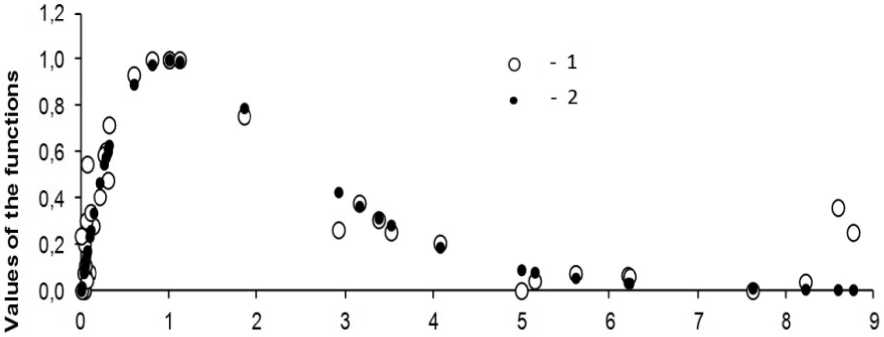
Values of z
Figure 4. Comparison of empirical (1) and theoretical (2) values of the function λ ( z )
According to these attributes, the following hold promise for PT of group 1 infections the family Cuscutaceae of subclass G, group 2 – Ranunculaceae and Asteraceae , group 4 – almost all families of subclass F Rosidae , group 5 – the families of subclasses B Ranunculidae , G Lamiidae and H Asteridae and the family Tamaricaceae , group 6 – the families Euphorbiaceae , Gentianaceae and Solanaceae , and group 7 – Solanaceae and Ranunculaceae .
The negative difference identifies the known medicinal plants, with currently available experience of uses, for PT of different groups of diseases 1 – Solanaceae , Ranunculaceae ; 2 – Euphorbiaceae , Gentianaceae , Solanaceae ; 3 – Ranunculaceae , Fumariaceae , Tamaricaceae , Gentianaceae , Solanaceae ; 4 - Cuscutaceae , Alismataceae ; 5 – no specially identified plants; 6 – Sambucacea , 7 - Fumariaceae , Dipsacaceae , Sambucacea , Viburnaceae , Gentianaceae and Asteraceae . The plant species that are not yet available for medicinal application are dominated by the families of the subclass Lamiidae , and by Solanaceae and Gentianaceae in particular. Of course, these families are also dominant as regards the number of the known (recommended for further study) plants.
CONCLUSIONS
This case study of the associative “plant taxon – medical application” and «medical application – another medical application” illustrates the possibilities for the combined use of mathematical and statistical methods of analyzing the properties of objects with a view to revealing their performance from modal attributes. We substantiated the applicability of the equation describing change in effectiveness and additional performance in the space of attributes. The connection of these equations is demonstrated for different values of the attributes, permitting a changeover from assessments of some objects to others.
The fact that such connections do exist is verified statistically by using Fisher’s test, based on results from employing 674 species of flowering plants in traditional medicine in treatment and prophylaxis of 21 virus infections of humans and animals. The study established statistically reliable connections of the particular uses with the taxonomic position of plant species at the level of a family and a subclass, and connections between viral diseases according to the similarity of the sets of plant species used in their treatment.
The study revealed an analytical relationship of vegetation performance with their taxonomic position, and with the hazard of groups of virus infections. Such an approach is based on the hypothesis for the existence of an unambiguous connection of a classification of objects (plants) and diseases with a linear-order coordinate system. In the case of plants, such a correspondence is accounted for by a natural relationship of their classification with the phylogenetic system of evolution, with evolution stages, with evolution time, and, on the whole, with a certain homotopy parameter on which all coordinate attributes depend and which, according to the set of these attributes, is defined as some integral index. In the space of this index z , the performance curves are identical, which makes it possible to test the reliability of the model approximation and forecast (based on the deviations of calculated data from the invariant curve) the presence of promising species in taxa for treatment of virus infections.
The results of statistical analysis were used to calculate the performance index of 62 species according to its involvement in the formation of reliable connections in the “family-disease-disease” system. The rank of the families, according to the sum of the indices of its species, conforms with the estimates obtained analytically. The species of the families Sambucaceae , Ranunculaceae , Solanaceae and Gentianaceae are considered to hold promise for further investigation and medical application.
The suggested method of data analysis is based on analytical relationships from reliability and effectiveness theory which are described by using the Lagrangian derivative. The solution to the resulting equations yield complex functions of a set of variables characterizing the objects (plants) under study in the content of their performance. The approximation of the dependencies uses the section method to fix all but one variables which, in the present case, represent the position of viral diseases according to the degree of hazard. For the equations obtained we suggest a simple approximation method of curves, based on known values. Equations of such a type are widely used in applications (the Hammett, Gompertz, Gibrat and Cobb-Douglas equations), and they are developed on the basis of the general logistic principles of deployment of processes in the space of the attributes. These principles would be studied and used in solving general and particular problems of relations of useful properties of plant species with their positions in the phylogenetic system.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Identification and modelling of the connection between the taxonomic position and traditional medical applications of plant species in prophylaxis and treatment of virus diseases
- Andersen P., Gill R. (1982). Cox's regression model for counting processes: a large sample study. Annals of Statistics. 10, 1100-1120.
- Bland M. (2000). An introduction to Medical Statistics (3rd ed.). Oxford: Oxford Medical Publications. 410 P.
- Calder W.A. (1984). Size, Function and Life History. Harvard: Harvard Univ. Press, 431 P.
- Callister W.D. (2007). Materials Science and Engineering. An Introduction. New York.: John Wiley & Sons.
- Chesher A. (1979). Testing the Law of Proportionate Effect. The Journal of Industrial Economics. V. 27. 4. 403-411.
- Han J., Kamber M. (2006). Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Second Edition. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. 743 P.
- Hosmer D.W., Lemeshow S., May S. (2008). Applied Survival Analysis: Regression Modeling of Time-to-Event Data (2nd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, 392 P
- H0yland A., Rausand M. (2009). System Reliability Theory: Models and Statistical Methods. Hoboken, New Jersey:John Willey & Sons Inc.
- Jassim S.A.A., Naji M.A., (2003). Novel antiviral agents: a medicinal plant perspective. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 95, 412-427.
- Mina M.V., Klevezal G.A. (1976). Rost zhivotnyh. Moscow: Nauka,. 291 P. [in Russian].
- Nantasenamat C., Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya C., Naenna T., Prachayasittikul V. (2009). A practical overview of quantitative structure-activity relationship. EXCLI Journal, 8, 74-88.
- Palm V.A. (1967). Osnovy kolichestvennoy teorii organicheskih reaktsiy. Moscow. Himiya, 355 P. [in Russian].
- Palm V.A. (1977). Osnovy kolichestvennoy teorii organicheskih reaktsiy (2nd ed.). Moscow: Himiya, 360 P. [in Russian].
- Popov P.L. (2008). Plant Species, Using Against Virous Infections Of Man And Animals: Regularities Of The Distribution In The Phylogenetic Classification System. Journal of Stress Physiology & Biochemistry. 4(3). 17-64 [in Russian].
- Popov P.L., Botvinkin A.D. (2008). Analiz svedeniy o rasteniyah, primeniavshihsia dlia profilaktiki i lecheniya beshenstva. Sibirskii Meditsinskii Zhurnal. 3, 91-95 [in Russian].
- Pushpa R, Nishant R., Navin K., Pankaj G. (2013). Antiviral potential of medicinal plants: an overview. Int. Res. Journal of Pharmacy. 4, 8-16.
- Santarelli E., Klomp L., Thurik A.R. (2006). Gibrat's law: an overview of the empirical literature. International Studies in Entrepreneurship. 12. 41-73.
- Sokolov P.D., Ed. (1984 - 1993). Rastitelnye resursy SSSR vols. 1-7, Leningrad: Nauka. [in Russian]. 1984. -Vl.1. - 461 P. - 1986. - V.2.- 336 P.- 1987. -Vl. 3.- 328 P.- 1988. -V.4. - 359 p.- 1990.-V.5. -328 P.- 1991. -V.6 - 200 p.- 1993 -V.7.- 351 P. [in Russian]
- Sokolov P.D., Ed. (1994). Rastitelnye resursy Rossii i sopredelnyh gosudarstv. vol. 8, Sankt-Peterburg: Nauka. 272 p. [in Russian].
- Takhtadzhyan A. (1987). Sistema magnoloifitov. Leningrad: Nauka, 440 P. [in Russian].
- Vanden Berghe D.A., Vlietinck A.J.,Van Hoof L. (1986).
- Plant products as potential antiviral agents. Bulletin de l'Institut Pasteur. 84, 101-147.p
- Walsh C.E. (2003). Monetary Theory and Policy (3rd ed.). Cambridge: MIT Press, 613 P.
- Witten I.H., Frank E., Hall M.A. (2011). Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques. 3rd Edition. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 664 p


