Иммунологические эффекты стереотаксической лучевой терапии при злокачественных новообразованиях различных локализаций: обзор литературы
Автор: Зозуля Антон Юрьевич, Балдуева Ирина Александровна, Новиков Сергей Николаевич
Журнал: Сибирский онкологический журнал @siboncoj
Рубрика: Обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 5 т.19, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Цель исследования - провести систематический анализ данных, имеющихся в современной литературе, о системных (абскопальных) эффектах лучевой терапии, которые опосредованы иммунологическими феноменами. Материал и методы. Произведен структурированный поиск рецензируемых статей в системе MEDLINE за период с января 2000 г по февраль 2019 г В обзор включены данные зарегистрированных клинических испытаний на Clinicaltrials.gov, представляющие итоги совместного применения иммунотерапии и лучевой терапии. Результаты. На данный момент, согласно литературным данным, существует мнение, что системное действие радиотерапии опосредовано иммунологическими феноменами. В связи с последними успехами иммунотерапии растет интерес к ее совместному применению с лучевой терапией с целью увеличения частоты системных эффектов. Однако частота возникновения абскопальных эффектов после применения стандартного лучевого лечения остается невысокой. В этой связи стереотаксическая лучевая терапия, учитывая ее выраженные иммуногенные свойства, возможность обеспечения высокого уровня локального контроля опухоли в полях облучения, низкий уровень токсичности и короткие сроки лечения, вероятно, является идеальным партнером для иммунотерапии у пациентов с метастатическим опухолевым процессом. Анализ данных показал, что сочетание стереотаксической лучевой терапии и иммунотерапии видится одним из наиболее прогрессивных подходов в лечении онкологических пациентов с точки зрения достижения абскопального эффекта и иммунологического контроля над метастатическим опухолевым процессом. Заключение. Учитывая вышесказанное и многогранность иммунологических эффектов радиотерапии, необходимы дальнейшие исследования влияния лучевой терапии на иммунную систему онкологических больных, продолжение совместного применения различных комбинаций иммунотерапии и лучевой терапии. Всё это в конечном итоге будет способствовать улучшению показателей выживаемости онкологических пациентов.
Абскопальный эффект, радиотерапия, иммунотерапия, стереотаксическая лучевая терапия, стлт, метастатический опухолевый процесс
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140254373
IDR: 140254373 | УДК: 616-006.04-08:615.849.1 | DOI: 10.21294/1814-4861-2020-19-5-108-113
Текст обзорной статьи Иммунологические эффекты стереотаксической лучевой терапии при злокачественных новообразованиях различных локализаций: обзор литературы
Лучевая терапия (ЛТ) является одним из основных методов лечения злокачественных новообразований, который обеспечивает достоверное увеличение локального и регионального контроля над опухолью, тем самым способствуя росту показателей общей и безрецидивной выживаемости. Накопленный опыт показывает, что около 70 % онкологических больных получают радиотерапию в качестве компонента комплексного противоопухолевого лечения [1]. При этом комбинация эффективного локального и системного лечения является необходимым условием успешной терапии больных с распространенным опухолевым процессом. В этой связи сочетание лучевой и лекарственной терапии представляется интересным и перспективным подходом.
Особого внимания заслуживают указания на то, что локально применяемая лучевая терапия может индуцировать системный противоопухолевый эффект, что подтверждается регрессом вторичных метастатических очагов, расположенных на расстоянии от облучаемого объема [2]. Системный эффект лучевой терапии, получивший название абскопального эффекта, впервые был описан R.H. Mole в 1953 г. [3]. Однако частота возникновения абскопальных эффектов после применения стандартного лучевого лечения очень невелика [4].
Классическая радиационная биология сосредоточена на изучении радиоиндуцированных повреждений ДНК, приводящих к торможению клеточного цикла в сочетании с гибелью клеток облученной опухоли посредством апоптоза, некроза и аутофагии [5]. В литературе имеются указания на то, что иммунологические реакции также играют важную роль в реализации эффектов лучевой терапии [6]. К сожалению, вопрос о взаимосвязи между степенью выраженности и характером индуцированных облучением иммунных реакций и особенностях проводимой лучевой терапии остается малоизученным. Несомненно, необходимо тщательное изучение вопроса о влиянии объема лучевой терапии, режима и технологии подведения дозы, величины суммарной поглощенной дозы на интенсивность противоопухолевого иммунного ответа. Использование режимов гипофракционирования с разовой очаговой дозой от 8 Гр и более ассоциируется с увеличением частоты возникновения абскопальных эффектов [6]. В частности, результаты метаанализа R. Marconi et al. указывают на достоверное повышение частоты абскопальных эффектов при увеличении суммарной очаговой дозы, поглощенной опухолью [7]. В связи с этим при обсуждении вопросов, связанных с радиоиндуцированным абскопальным эффектом, особое внимание уделяется стереотаксической лучевой терапии (СТЛТ) – методу дистанционного облучения, обеспечивающему возможность подведения высокой тумороцидной дозы к мишени с субмиллиметровой точностью за одну или несколько фракций. Достоинства СТЛТ заключаются в возможности достижения высоких показателей локального контроля, низкой токсичности, возможности лучевого лечения очагов, находящихся в непосредственной близости от критических органов, доставкой абляционной дозы за короткое время.
Существует мнение, что системное действие радиотерапии опосредовано иммунологическими феноменами. Фактически одной из основных реакций иммунной системы на опухоль является цитотоксический ответ, вызываемый иммуногенной клеточной смертью. Этот процесс зависит как от внутренних характеристик опухоли, так и от иммунного статуса пациента. При облучении опухоли возникает клеточный стресс, что приводит к усиленному высвобождению различных опухолево-ассоциированных антигенов (ОАА) в результате некротической и апоптической гибели опухолевых клеток. Вышеуказанные ОАА поглощаются антиген-презентирующими клетками и затем представляются CD8+ T-клеткам, которые распознают и атакуют как облучаемую опухоль, так и метастатические очаги [8].
Помимо этого, ЛТ запускает путь иммуногенной гибели клетки, что приводит к транслокации цитозольного белка-шаперона (CRT) на клеточную поверхность (сигнал «eat me»), а также к высвобождению белка группы 1 с высокой подвижностью HMBG-1 и молекулярных фрагментов, ассоциированных с повреждением (DAMPs), которые могут инициировать провоспалительные явления. Вышеуказанные события приводят к активации дендритных клеток и запуску цитотоксических реакций [9].
Радиоиндуцированное высвобождение цитокинов, главным образом интерферонов типа I и типа II, также играет роль в активации дендритных клеток [10]. Активированные дендритные клетки мигрируют в лимфатические узлы, чтобы представить антиген Т-лимфоцитам, что, в свою очередь, приводит к опухолеспецифической активации и пролиферации Т-лимфоцитов. Зрелые и активированные дендритные клетки могут секретировать хемокины, которые мобилизируют эффекторные CD8+ Т-лимфоциты в опухоль [11].
Помимо указанных иммунологических явлений, радиотерапия вызывает повышенную экспрессию на клеточной поверхности молекул главного комплекса гистосовместимости класса I. Эти молекулы содержат эндогенные пептиды, которые способствуют распознаванию опухолевых клеток цитотоксическими Т-лимфоцитами. При облучении ложа опухоли повышается экспрессия провоспалительных хемокинов, таких как CXCL16, и эндотелиальных факторов адгезии VCAM и ICAM-1, которые направляют иммунные клетки в опухолевые очаги, что также играет важную роль в иммунном ответе [12].
Обращает на себя внимание низкая частота абcкопальных эффектов в рутинной клинической практике, что может быть связано с тем, что даже активированные CD8+ T-клетки не способны преодолеть супрессирующий потенциал опухолевого микроокружения. Выделяемые опухолью иммуносупрессирующие цитокины, такие как трансформирующий фактор роста β (TGF β), а также поверхностные рецепторы, экспрессируемые на Т-клетках (CTLA4, PD-1), могут приводить к истощению Т-лимфоцитов. M2-макрофаги, клетки-супрессоры миелоидного происхождения (MDSCs) и незрелые дендритные клетки также приводят к супрессии Т-клеточного иммунного ответа. Элиминация опухоли может замедляться CD4+ T-клетками с регуляторной функцией (Т-регуляторные лимфоциты).
Облучение может привести к увеличению инфильтрации опухоли лимфоцитами с помощью 2 основных механизмов:
– увеличения проницаемости сосудистой сети опухоли для лимфоцитов [13] и повышения экс- прессии молекул эндотелиальной адгезии [14], что, в свою очередь, приводит к усилению экстраваза-ции иммунных клеток;
– высвобождения хемокинов для стимуляции миграции и инвазии иммунных клеток [15].
Механизм радиоиндуцированного иммунного ответа представлен на рис. 1.
Как показывает клиническая практика, самостоятельно ЛТ в большинстве случаев не способна индуцировать иммунный ответ, достаточный для эрадикации опухоли. Предполагается, что основным препятствием на этом пути являются ингибирующие иммунологические эффекты, которые замедляют элиминацию опухолевых клеток. В связи с этим ингибиторы контрольных точек (PD-1, CTLA-4), которые нивелируют эти тормозные сигналы, могут существенно увеличить возможности иммуноопосредованного уничтожения опухоли. Следует отметить, что в начале XXI в. достигнуты значительные успехи в иммунотерапии (ИТ) опухолей. В настоящее время ИТ рассматривается как один из наиболее перспективных методов лечения распространенных злокачественных новообразований (ЗНО). Однако использование ингибиторов контрольных точек (ИКК) иммунного ответа в качестве монотерапии показало свою эффективность только при лечении ЗНО, имеющих высокий уровень экспрессии CTLA4 и/или PD-1рецепторов, а также опухолей с богатой инфильтрацией дендритными клетками и CD8+ Т-лимфоцитами. Подобное состояние описывается как Т-клеточный «воспалительный фенотип» или «горячая» опухоль [16]. К сожалению, так называемые холодные опухоли (ЗНО со скудной инфильтрацией Т-лимфоцитами) представляют собой наиболее частый фенотип среди солидных опухолей, что является одной из причин невысокой эффективности ИКК в режиме монотерапии.
В литературе имеются указания на то, что лучевая терапия может превратить «холодную» опухоль в «горячую» [2]. Учитывая вышесказанное, сочетание ЛТ и ИТ видится одним из наиболее прогрессивных подходов в лечении онкологических пациентов с точки зрения достижения абско-пального эффекта и иммунологического контроля над опухолевым процессом. Одними из первых исследователей, представивших клиническую эффективность вышеуказанной комбинации, стали M.A. Postow et al. [17], которые в 2012 г. описали оригинальный случай устойчивого полного ответа у пациента с метастатической меланомой, который получал комбинацию стереотаксической лучевой терапии на паравертебральный очаг и иммунотерапию ипилимумабом. Накоплен обширный клинический опыт возникновения абскопальных эффектов у больных, которые получали комбинированную ЛТ и ИТ по поводу немелкоклеточного рака легкого [18], меланомы [19, 20], колоректального рака [21], почечно-клеточного рака [22], рака молочной железы [23], рака шейки матки [24].
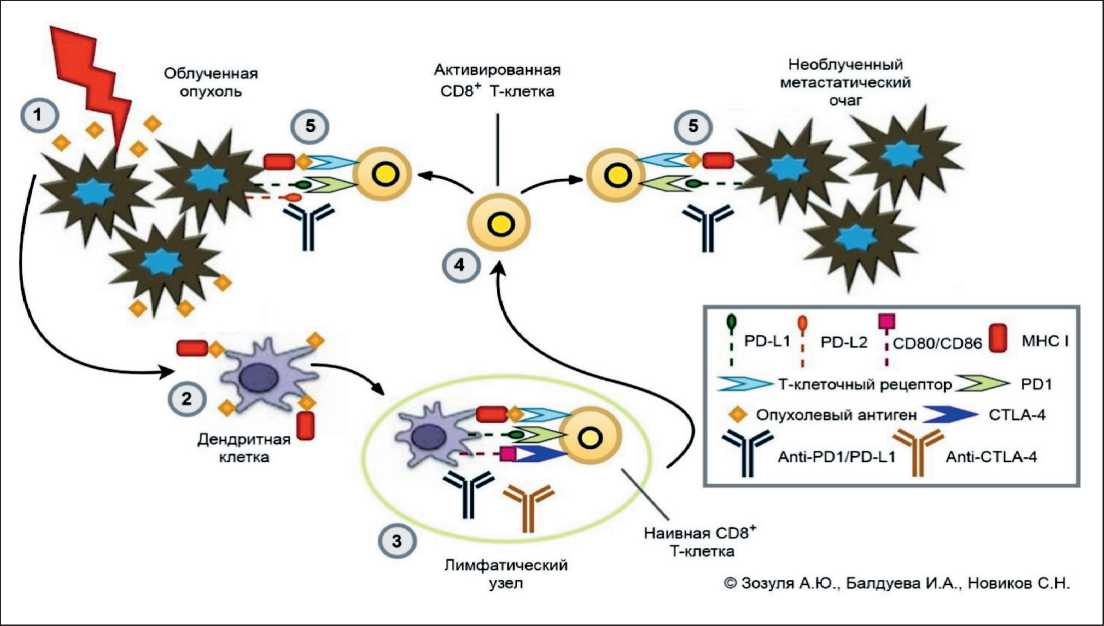
Рис. 1. Механизм радиоиндуцированного иммунного ответа:
1. Клетки опухоли высвобождают опухолевые антигены после облучения.
2. Опухолевые антигены поглощаются дендритными клетками (антигенпрезентирующими клетками), которые перемещаются в регионарные лимфатические узлы.
3. Праймирование и активация наивных Т-клеток в регионарных лимфоузлах посредством взаимодействия Т-клеточных рецепторов и главного комплекса гистосовместимости класса I на Т-клетках и дендритных клетках соответственно. Параллельно с этой стимуляцией лиганды PD-L1 связываются с PD-1 Т-клеточным рецептором и посылают ингибирующий сигнал Т-клеткам, подавляя их иммунный ответ. На дендритных клетках дополнительный ингибиторный сигнал может происходить с лигандами CD80/CD86 и Т-клеточными рецепторами CTLA-4. Терапия моноклональными антителами анти-PD-1/анти-PD-L1 и анти-CTLA-4 блокирует эти ингибирующие сигналы.
4. Трафик активированных опухолеспецифических Т-клеток.
5. Инфильтрация Т-лимфоцитами опухоли как в облученном участке, так и в необлученных очагах метастазирования с последующим распознаванием опухолевых клеток Т-лимфоцитами и уничтожение опухолевых клеток
-
Fig. 1. The mechanism of the radiation-induced immune response:
-
1. Tumor cells release tumor antigens after irradiation.
-
2. Tumor antigen can be taken up by dendritic cells (i.e. antigen-presenting cells), which travel to regional lymph nodes.
-
3. Priming and activation of naive T cells in regional nodes via the interaction of T cell receptors on T cells and major histocompatibility complex class I on dendritic cells, respectively. In parallel to this stimulation, programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) ligands bind to the PD-1 T cell receptor and send an inhibitory signal to the same T cells suppressing their immune response. On the dendritic cells, an additional inhibitory signal can occur with CD80/CD86 and CTLA-4 receptors on T cells. Therapies with monoclonal antibodies
-
4. Trafficking of activated tumour-specific T cells.
-
5. Infiltration of T cells into tumor in both irradiated sites and non-irradiated metastatic sites, recognition of cancer cells by T lymphocytes and killing of cancer cells
anti-PD-1/anti-PD-L1 and anti-CTLA-4 block these inhibitory signals.
В настоящее время комбинация ЛТ и ИТ предполагает использование трех возможных последовательностей. В первом случае СТЛТ на опухолевый очаг проводится до начала иммунотерапии. Лучевой компонент в данной ситуации рассматривается как вакцинация in vivo. Предварительные результаты исследования PEMBRO-RT [25] показали значимое преимущество в выживаемости без прогрессирования у пациентов с метастатическим немелкоклеточным раком легкого, у которых наблюдалось прогрессирование опухоли после второй линии химиотерапии. Основная группа получала СТЛТ на одиночный очаг в дозе 24 Гр за 3 фракции в неделю до начала лечения пембролизумабом; контрольная группа лечения ограничивалась пембролизумабом. В этой группе больных частота объективных ответов на 12-й нед составила 41 %, тогда как в контрольной группе этот показатель равнялся 19 % [25].
Другой стратегией комбинированного лечения ЛТ и ИТ при метастатических солидных опухолях является применение лучевой терапии в качестве «терапии спасения», когда отмечается прогрессирование опухолевого процесса на фоне иммунотерапии. Так, продолжается исследование II фазы (NCT02710253) [26], а также исследование ABC-X (NCT03340129) [27], в которых изучается применение лучевой терапии у пациентов с метастатической меланомой, у которых наблюдалось прогрессирование опухолевого процесса на фоне проведения иммунотерапии.
Третьим вариантом является одновременное проведение лучевой и иммунотерапии. Ретроспективный анализ совместного использования ЛТ и ИТ у больных меланомой с метастатическим поражением головного мозга показал, что конкурентное использование этих методов приводит к достоверному улучшению локального контроля и увеличению показателя выживаемости без прогрессирования [28]. Преимущество сочетанного подхода также показали S. Theurich et al. при одновременной лучевой терапии и ИТ при меланоме с
Список литературы Иммунологические эффекты стереотаксической лучевой терапии при злокачественных новообразованиях различных локализаций: обзор литературы
- O'Dell M., Stubblefield M. Cancer rehabilitation: principles and practice. Demos Medical Publishing, 2009. 1172 p.
- Xing D., Siva S., Hanna G.G. The Abscopal Effect of Stereotactic Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy: Fool's Gold or El Dorado? Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2019 Jul; 31(7): 432-443. doi: 10.1016/j. clon.2019.04.006.
- MoleR.H. Whole body irradiation; radiobiology or medicine? Br J Radiol. 1953 May; 26(305): 234-41. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-26-305-234.
- Reynders K., Illidge T., Siva S., Chang J.Y., De Ruysscher D. The abscopal effect of local radiotherapy: using immunotherapy to make a rare event clinically relevant. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015 Jun; 41(6): 503-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.03.011.
- Amaravadi R.K., Thompson C.B. The roles of therapy-induced autophagy and necrosis in cancer treatment. Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Dec 15; 13(24): 7271-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1595.
- Ngwa W., Irabor O.C., Schoenfeld J.D., Hesser J., Demaria S., Formenti S.C. Using immunotherapy to boost the abscopal effect. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018 May; 18(5): 313-322. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2018.6.
- Marconi R., Strolin S., Bossi G., Strigari L. A meta-analysis of the abscopal effect in preclinical models: Is the biologically effective dose a relevant physical trigger? PLoS One. 2017 Feb 21; 12(2): e0171559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171559.
- Grass G.D., Krishna N., Kim S. The immune mechanisms of ab-scopal effect in radiation therapy. Curr Probl Cancer. 2016 Jan-Feb; 40(1): 10-24. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2015.10.003.
- Barker H.E., Paget J.T., Khan A.A., Harrington K.J. The tumour microenvironment after radiotherapy: mechanisms of resistance and recurrence. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 Jul; 15(7): 409-25. doi: 10.1038/nrc3958.
- Gerber S.A., SedlacekA.L., CronK.R., Murphy S.P., Frelinger J.G., Lord E.M. IFN-y mediates the antitumor effects of radiation therapy in a murine colon tumor. Am J Pathol. 2013; 182(6): 2345-54. doi: 10.1016/j. ajpath.2013.02.041.
- Lee Y., Auh S.L., Wang Y., Burnette B., Wang Y., Meng Y., Bec-kettM., SharmaR., ChinR., Tu T., WeichselbaumR.R., Fu Y.X. Therapeutic effects of ablative radiation on local tumor require CD8+ T cells: changing strategies for cancer treatment. Blood. 2009; 114(3): 589-95. doi: 10.1182/ blood-2009-02-206870.
- Matsumura S., Demaria S. Up-regulation of the pro-inflammatory chemokine CXCL16 is a common response oftumor cells to ionizing radiation. Radiat Res. 2010 Apr; 173(4): 418-25. doi: 10.1667/RR1860.1.
- Ganss R., Ryschich E., Klar E., Arnold B., Hammerling G.J. Combination of T-cell therapy and trigger of inflammation induces remodeling of the vasculature and tumor eradication. Cancer Res. 2002 Mar 1; 62(5): 1462-70.
- Hallahan D., Kuchibhotla J., Wyble C. Cell adhesion molecules mediate radiation-induced leukocyte adhesion to the vascular endothelium. Cancer Res. 1996 Nov 15; 56(22): 5150-5.
- Matsumura S., WangB., KawashimaN., Braunstein S., BaduraM., Cameron T.O., Babb J.S., Schneider R.J., Formenti S.C., Dustin M.L., Demaria S. Radiation-induced CXCL16 release by breast cancer cells attracts effector T cells. J Immunol. 2008; 181(5): 3099-107. doi: 10.4049/ jimmunol.181.5.3099.
- Trujillo J.A., Sweis R.F., Bao R., Luke J.J. T Cell-Inflamed versus Non-T Cell-Inflamed Tumors: A Conceptual Framework for Cancer Immunotherapy Drug Development and Combination Therapy Selection. Cancer Immunol Res. 2018 Sep; 6(9): 990-1000. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066. CIR-18-0277.
- Postow M.A., Callahan M.K., Barker C.A., Yamada Y., Yuan J., Kitano S., Mu Z., Rasalan T., Adamow M., Ritter E., Sedrak C., Jung-bluth A.A., Chua R., Yang A.S., Roman R.A., Rosner S., Benson B., Allison J.P., Lesokhin A.M., Gnjatic S., Wolchok J.D. Immunologic correlates of the abscopal effect in a patient with melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366(10): 925-31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1112824.
- GoldenE.B., Demaria S., Schiff P.B., ChachouaA., Formenti S.C. An abscopal response to radiation and ipilimumab in a patient with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2013 Dec; 1(6): 365-72. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0115.
- Okwan-Duodu D., PollackB.P., Lawson D., Khan M.K. Role of radiation therapy as immune activator in the era of modern immunotherapy for metastatic malignant melanoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2015 Feb; 38(1): 119-25. doi: 10.1097/C0C.0b013e3182940dc3.
- Tsui J.M., Mihalcioiu C., Cury F.L. Abscopal Effect in a Stage IV Melanoma Patient who Progressed on Pembrolizumab. Cureus. 2018 Feb 27; 10(2): e2238. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2238.
- SatoH., Suzuki Y., Yoshimoto Y., NodaS.E., MurataK., Takakusagi Y., Okazaki A., Sekihara T., Nakano T. An abscopal effect in a case of concomitant treatment of locally and peritoneally recurrent gastric cancer using adoptive T-cell immunotherapy and radiotherapy. Clin Case Rep. 2017 Feb; 5(4): 380-4. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.758.
- Van de Walle M., Demol J., Staelens L., Rottey S. Abscopal effect in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Acta Clin Belg. 2017 Aug; 72(4): 245-249. doi: 10.1080/17843286.2016.1201614.
- Deipolyi A.R., Bromberg J.F., Erinjeri J.P., Solomon S.B., BrodyL.A., Riedl C.C. Abscopal Effect after Radioembolization for Metastatic Breast Cancer in the Setting of Immunotherapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018 Mar; 29(3): 432-433. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2017.10.007.
- Sharabi A., Kim S.S., Kato S., Sanders P.D., Patel S.P., Sanghvi P., WeiheE., KurzrockR. Exceptional Response to Nivolumab and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Neuroendocrine Cervical Carcinoma with High Tumor Mutational Burden: Management Considerations from the Center For Personalized Cancer Therapy at UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center. Oncologist. 2017 Jun; 22(6): 631-637. doi: 10.1634/ theoncologist.2016-0517.
- Theelen WSME, Peulen H.M.U., Lalezari F., van der Noort V, de Vries J.F., Aerts J.G.J.V., Dumoulin D.W., Bahce I., Niemeijer A.N., de Langen A.J., Monkhorst K., Baas P. Effect of Pembrolizumab After Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy vs Pembrolizumab Alone on Tumor Response in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results of the PEMBRO-RT Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Jul 11; 5(9): 1276-82. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.1478.
- Phase II trial of salvage radiation therapy to induce systemic disease regression after progression on systemic immunotherapy [Internet]. URL: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02710253 (cited 12.09.2019).
- Anti-PD 1 brain collaboration ro radiotherapy: the ABC-X Study [Internet]. URL: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03340129 (cited 12.09.2019).
- Skrepnik T., Sundararajan S., Cui H., Stea B. Improved time to disease progression in the brain in patients with melanoma brain metastases treated with concurrent delivery of radiosurgery and ip-ilimumab. Oncoimmunology. 2017 Jan 19; 6(3): e1283461. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1283461.
- Theurich S., Rothschild S.I., Hoffmann M., Fabri M., Sommer A., Garcia-MarquezM., Thelen M., Schill C., Merki R., Schmid T., Koeberle D., Zippelius A., Baues C., Mauch C., Tigges C., Kreuter A., Borggrefe J., von Bergwelt-Baildon M., SchlaakM. Local Tumor Treatment in Combination with Systemic Ipilimumab Immunotherapy Prolongs Overall Survival in Patients with Advanced Malignant Melanoma. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016; 4(9): 744-54. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0156.
- Sharabi A.B., Nirschl C.J., Kochel C.M., Nirschl T.R., Franci-ca B.J., Velarde E., Deweese T.L., Drake C.G. Stereotactic Radiation Therapy Augments Antigen-Specific PD-1-Mediated Antitumor Immune Responses via Cross-Presentation of Tumor Antigen. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015 Apr; 3(4): 345-55. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0196.


