Impact of exogenous salicylic acid on growth and ornamental characteristics of calendula (Calendula officinalis L.) under salinity stress
Автор: Bayat H., Alirezaie M., Neamati H.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.8, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Application of salicylic acid (SA) as a phytohormone has been increased due to resistance to stresses such as salt stress. Pot experiments were conducted to determine the effect of exogenous salicylic acid application on growth and ornamental characteristics of calendula grown under salt stress and greenhouse conditions. For this purpose a factorial experiment based on completely randomized design was conducted with 3 levels of SA (0 (control), 1, 2 mM) and 3 levels of NaCl (0, 100 and 200 mM) with 4 replications. At flowering stage, SA was applied with spraying two times two week intervals. NaCl was also applied as drench (200 ml per pot) in two day intervals. The results showed that salinity decreased the growth, Chlorophyll reading values, number per plant and flower diameter. However, foliar applications of SA resulted in greater root, shoot and totaldry weight, plant height and leaf area calendula plants under saltstress. The highest chlorophyll reading values was obtained from 2.00 mM SA application in all NaCl treatments. decreased number of flower per plant and flower diameter as ornamental characteristics; however SA increased them under salinity stress. Plants treated with 1.00 mM SA had the highest diameter at 100 and 200 mM of NaCl. leakage increased by salinity, however foliar application of SA significantly reduced electrolyte leakage under salt stress. Based on the present results, foliar application of SA treatments can ameliorate the negative effects of salinity on the growth and ornamental characteristics of calendula plants.
Calendula, electrolyte leakage, foliar application, salicylic acid, salinity
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323593
IDR: 14323593
Текст научной статьи Impact of exogenous salicylic acid on growth and ornamental characteristics of calendula (Calendula officinalis L.) under salinity stress
Salinity is one of the major environmental factors limiting plant growth and productivity. It is estimated that about one-third of world’s cultivated land is affected by salinity (Kaya et al., 2003). In most arid and semiarid areas this problem is accentuated by competition for high quality water among agriculture, industry and landscape users has promoted the use of alternative water sources for irrigation. Thus marginal quality water, somewhat saline, will become important in these areas (Chartzoulakis et al., 2002) and could be used for the irrigation of ornamental plants (Carter et al., 2005). However, the use of low quality water for irrigation affects plants in different ways, depending on the degree of salt tolerance of the species (Alarc´ on et al., 1994) and even within a given species (S´ anchez-Blanco et al., 2003). Salt stress can affect plant survival, biomass, plant height and plant morphology and affect the capacity of a plant to collect water and nutrients (Parida and Das, 2005). Salinity can cause hyperionic and hyperosmotic effects on plants leading to membrane disorganization, increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and metabolic toxicity (Jaleel et al., 2007a). The great effect of salinity is the inhibition of crop growth by the reduced hormone delivery from root to leaves (Jaleel et al., 2007b).
Calendula, mostly known as the pot marigold, is planted widely in gardens and landscapes. It is popular for the lush color and aromatic scent it provides. It grows in sun or partial shade and is easy to grow requiring little cultivation (Dole and Wilkins, 2004).
Salicylic acid (SA), a naturally occurring plant hormone, acts as an important signaling molecule in plants, and has diverse effects on tolerance to abiotic stress (Bergmann et al., 1994; Van Breusegem et al., 2001). Exogenous application of SA may participate in the regulation of physiological processes in plants, such as ion uptake and transport, stomatal closure (Gunes et al., 2005), membrane permeability (Barkosky and Einhellig, 1993) and photosynthesis and growth (Khan et al., 2003). SA has been shown to play a role in mitigating the adverse deleterious effects of some environmental stresses including low temperature on banana (Kang, 2003), high temperature on (He et al., 2005), drought stress on tomato (Hayat et al., 2008) and wheat (Singh and Usha 2003), heavy metal on maize (Krantev et al., 2008). The ameliorative role of SA to deleterious effects of salinity has been examined in different crops e.g. maize (Turan and Aydin 2005), tomato (Stevens et al., 2006), barley (El-tayeb, 2005), carrot (Eraslan, 2007) and wheat (Hamada and Al-Hakimi, 2001).
Water is becoming more and more rare resource in arid and semi arid regions of Iran that characterized by little rainfall, high solar radiation and high temperatures in the summer. In recent years, the normal seasonal droughts that have occurred in Iran have caused local and state government to enact water conservation ordinances. Urbanization and increases in population, however, are seriously threatening sustainable natural resources. At present, non-renewable groundwater resources are being depleted to an alarming extent. As high-quality water supply becomes limited, the use of saline water with high salt levels for landscape irrigation is being encouraged. While crop tolerance to salinity has been given considerable attention; fewer studies have dealt specifically with ornamental plants. Therefore, the aim of this paper was to report the effects of SA on growth and quality flower of calendula grown under normal and salinity stress conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant material, growth conditions and treatments
Calendula seeds ( Calendula officinalis L. cv.‘‘Nana Bon Bon Naranja’’) were selected and germinated in coco peat in plastic germination trays under greenhouse conditions of Ferdowsi University of Mashhad (36° 17' 44" N and 59° 36' 42" E), Iran. Uniform size seedlings (40-day-old) were transplanted to plastic pots (15 cm top diameter) and filled with mixture of loam soil:sand:compost (1:1:1,v:v). The plants were grown in a naturally illuminated greenhouse with night/day set temperatures of 18/24 °C. A factorial experiment based on completely randomized design was conducted with 3 levels of SA (0 (control), 1, 2
mM) and 3 levels of NaCl (0, 100 and 200 mM) with 4 replications. Salicylic acid was dissolved in absolute ethanol then added drop wise to water (ethanol/water: 1/1000, v/v). Thirty days after transplanting, SA was applied on the foliage of calendula plants with a hand sprayer. The volume of the spray was 30 mL per pot. NaCl was also applied as drench (200 ml per pot) in two day intervals. A control group of plants was grown without NaCl and sprayed with deionized water. All plants were harvested 60 d after planting (30 days after treatments) and separated into leaves, stem, and root.
Measurements and data collection
At the end of the experimental period, dry weights of separated roots and shoots were recorded on four randomly selected plants per treatment. Total leaf area was determined with a
Delta-T Image Analysis System (Delta-T, LTD, Cambridge, UK). Electrolyte leakage which is used to assess membrane permeability was determined according to Lutts et al., (1996). Leaf greenness or chlorophyll reading values (measured as the optical density, SPAD reading) was recorded at the end of the experiment on three leaves per plant at similar middle positions of shoots for all plants in each treatment using a portable SPAD chlorophyll meter (SPAD 502, Minolta, Japan). Plant height, flower diameter and number of flower per plant were also measured.
Statistical Analysis
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for all the variables was carried out using the JMP8 software. Treatment means were compared using the protected least significant difference (LSD) test at p<0.05 level.
Table 1: The dry weight of shoot, root and total plant of calendula in response to foliar SA applications under salt stress.
|
NaCl |
SA |
Shoot dry weight |
Root dry weight |
Total dry weight |
|
(mM) |
(mM) |
(g/plant) |
(g/plant) |
(g/plant) |
|
0 |
0 |
5.7 cd |
3.9 c |
9.5 c |
|
1 |
7.0 b |
5.0 a |
12 b |
|
|
2 |
10.7 a |
5.1 a |
15.7 a |
|
|
100 |
0 |
3.5 f |
2.0 e |
5.6 ef |
|
1 |
5.4 de |
3.8 c |
9.7 c |
|
|
2 |
6.8 bc |
4.2 b |
10 c |
|
|
200 |
0 |
2.2 g |
1.6 f |
3.8 f |
|
1 |
4.3 ef |
2.7 d |
7.1 de |
|
|
2 |
5.9 bcd |
2.8 d |
8.6 cd |
|
|
NaCl |
** |
** |
** |
|
|
SA |
** |
** |
** |
|
|
NACl × SA |
** |
** |
** |
Numbers with the same letters in the same column are not statistically different (P < 0.05).
**: significant at 1% probalility .
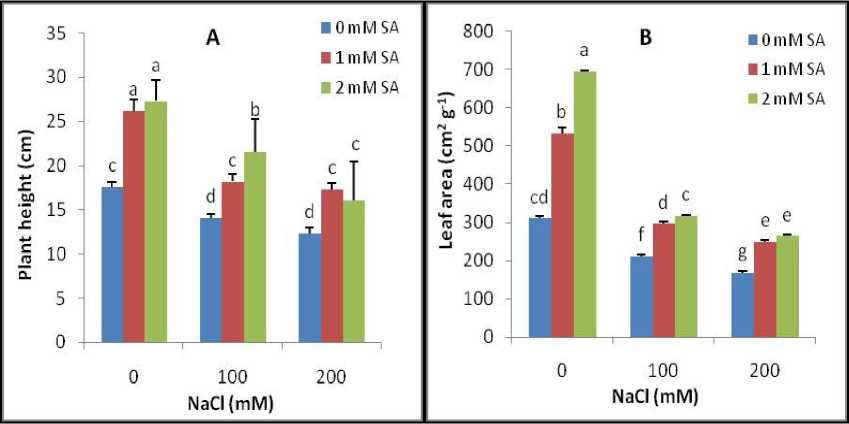
Figure 1. Plant height (A) and leaf area (B) of calendula plant in response to foliar SA applications under salt stress. Different letters on top of bars indicate significantly differences according to LSD test (p < 0.05) at each salt level. Vertical bars indicate the mean ± SE.
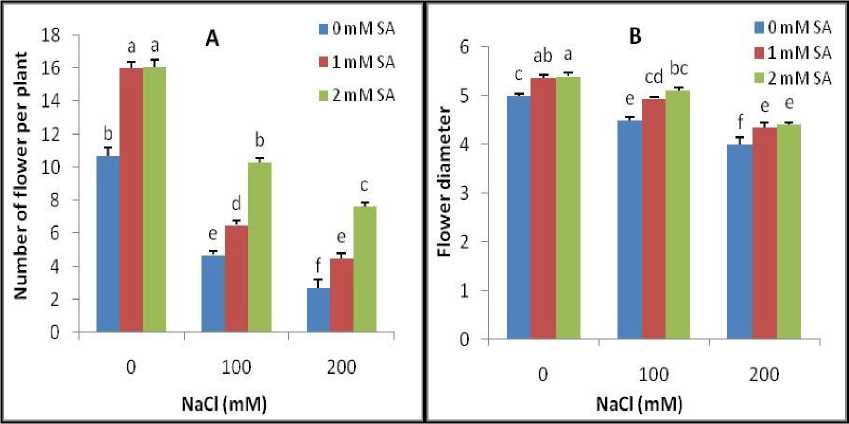
Figure 2. Flower number per plant (A) and flower diameter (A) of calendula plant in response to foliar SA applications under salt stress. Different letters on top of bars indicate significantly differences according to LSD test (p < 0.05) at each salt level. Vertical bars indicate the mean ± SE.
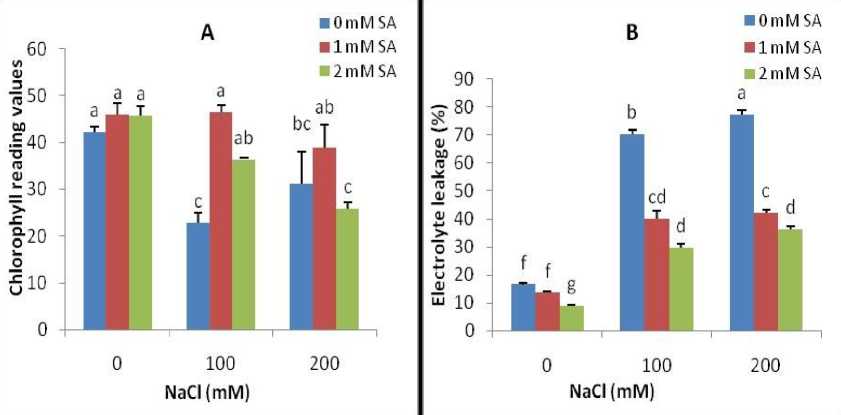
Figure 3. Chlorophyll reading values (A) and electrolyte leakage (B) of calendula plant in response to foliar SA applications under salt stress. Different letters on top of bars indicate significantly differences according to LSD test (p < 0.05) at each salt level. Vertical bars indicate the mean ± SE.
RESULTS
Plant growth
Shoot, root and total dry weight was recorded as influenced by different levels of SA and NaCl. As shown in table 1, Shoot, root and total dry weight of calendula plants were lower at salt stress treatment as compared to non-saline conditions. However, foliar application of SA increased dry matter accumulation in all parts of calendula plants under salt stress. Application of SA (2.00 mM) under salt stress (100 mM NaCl) gave the higher values for these parameters than the other treatments. It indicated that foliar application of SA alleviated the growth inhibition induced by added NaCl. Exogenous application of SA also enhanced shoot, root and total plant dry weight under no salt stress (Table 1).
Salt stress decreased leaf area as compared to the non-saline conditions. NaCl (200 mM) decreased leaf area by 45%, but the reduction was only 14% when 2 mM SA treatment was applied to NaCl-treated plants, as compared to control. Under nonsaline conditions, foliar application of SA (2mM)
significantly increased leaf area (1.2 fold) as compared to control (Fig. 1A).
Salt stress significantly decreased plant height; however, foliar application of SA improved plant height under salt stress (Fig. 1B). Treatment 2 mM SA + 100 mM NaCl had the highest plant height as compared to the other treatment under salt stress. Foliar application of SA increased plant height by 55% as compared to control (Fig. 1B).
Flower number and flower diameter
Salt treatment (100 mM) significantly decreased number of flower per plant by 74% as compared to control, but the reduction was only 30% when SA (2mM) was applied to NaCl-treated plants. Under non-salt stress condition, SA increased flower number by 50% as compared to control (Fig. 2A).
Flower diameter of calendula plants decreased dramatically with the increasing NaCl concentration. All SA treatments increased the flower diameter compared to non-treated plants both in absence and presence of salinity. Plants treated with 1.00 mM SA had the highest flower diameter at 100 and 200 mM of NaCl (Fig. 2B).
Chlorophyll reading values
Chlorophyll reading values were significantly decreased with the increasing salinity stress. However, foliar SA applications used in the study caused to the elevated reading values. The highest reading values were obtained from 2.00 mM SA application in all NaCl treatments (Fig. 3A).
Electrolyte leakage
Based on the present results, electrolyte leakage was intensively increased by salt treatment; however, SA significantly decreased electrolyte leakage under salt stress. The lowest electrolyte leakage was obtained by 1.00 mM SA in 100 mM NaCl concentration under salt stress condition. Under no salt stress, foliar application of SA only slightly decreased electrolyte leakage compared to control (Fig. 3B).
DISCUSSION
Salinity decreased calendula plant growth significantly. Growth reduction under saline conditions has been well documented in various plants by many authors (Kaya et al., 2003; Alpaslan and Gunes, 2001; Senaratna et al., 2000; Turan and Aydın, 2005; Sivritepe et al., 2003). As stated by Munns (2003), suppression of plant growth under saline conditions may either be due to decreased availability of water or to the toxicity of sodium chloride. SA treatments alleviated the deleterious effects of salinity on plant growth. Similar results were reported by Shakirova et al. (2003) in wheat, El-Tayeb (2005) for barley, Steven et al. (2006) and Szepesi et al. (2005) for tomato, Yildirim et al. (2008) for cucumber and Khodary (2004) for maize who observed exogenous SA treatments ameliorated the negative effects of salt stress plant growth. Gutiérrez-Coronado et al. (1998) reported that foliar application of SA significantly increased the growth of shoots and roots of soybean in either greenhouse or field conditions. In ornamental plants, such as Gloxinia and violet, SA increased the number of leaves formed, and leaf area as compared to the control (Hayat and Ahmad, 2007; Martin- mex, R., 2005). This positive effect of SA could be related to an increased CO2 assimilation and photosynthetic rate and increased mineral uptake by the stressed plant under SA treatment (Karlidage et al., 2009; Khan et al., 2003; Szepsi et al., 2005). Moreover the induction of antioxidant response and protective role of membranes by SA caused increase the tolerance of plant to damage (Turan and Aydin, 2005).
Salt stress decreased chlorophyll reading values as compared to the non-saline conditions. These results are similar with those of Downton et al . (1985), Stepien and Klobus (2006) and Yildirim et al . (2008) who indicated that chlorophyll content significantly decreased in the leaves of spinach and cucumber plants with increasing NaCl concentration. In the present study, SA treated plants showed greater chlorophyll reading values than nontreated plants. These results support those of El-Tayeb (2005) and Yildirim et al . (2008) that reported SA treatments caused to the increased chlorophyll content of leaves of barley and cucumber under salt stress.
Salinity impaired membrane permeability increasing electrolyte leakage. However, application of salicylic acid (SA) partly maintained membrane permeability (Table 3B). Present study showed that SA reduced the amount of ion leakage in salt stressed calendula plants indicating that SA treatment has facilitated the maintenance of membrane functions under stress conditions. Supporting evidence was shown when SA reduced electrolyte leakage salt stressed tomato (Stevens et al ., 2006) and maize (Turan and Aydin, 2005) leaves.
Salt stress decreased flower number per plant and flower diameter as compared to the non-saline conditions. In this experiment plants treated with different concentration of SA, flowered early and their floral buds per plants were increased. SA has been shown to induce flowering in species of Lemnaccae like oncidium , an ornamental orchid species, Impatiens balsamina , Arabiaopsis thaliana and in Pistia stratiotes (Raskin, 1992) that are in agreement with the results of the present study. Moreover, salicylic acid also hastens flower initiation in Saintpaulia ionantha Wendl. (Martin-mex, 2005) and increased flower size in Campanula (Serek, 1992). Kumar & Nanda (1981a, 1981b) reported that the higher number of floral buds induced by salicylic acid was accompanied by increase in protein synthesis and appearance of new isozym bands.
Based on the present results, SA alleviates the negative effect of salt stress on growth, chlorophyll reading values, electrolyte leakage and flower quality depending on the concentration of SA used. Maximum alleviation of salt stress was found with 2 mM SA application.
Список литературы Impact of exogenous salicylic acid on growth and ornamental characteristics of calendula (Calendula officinalis L.) under salinity stress
- Alarcon, J.J., Sanchez-Blanco, M.J., Bolar?n, M.C. and Torrecillas, A. (1994) Growth and osmotic adjustment of two tomato cultivars during and after saline stress. Plant Soil, 166, 75-82.
- Alpaslan, M. and Gunes, A. (2001) Interactive effects of boron and salinity stress on the growth, membrane permeability and mineral composition of tomato and cucumber plants. Plant Soil, 236, 123-128.
- Barkosky, R.R. and Einhellig, F.A. (1993) Effects of salicylic acid on plant water relationship. J. Chem. Ecol. 19, 237-247.
- Bergmann, H.L., Maachelett, V. and Gerbel, B. (1994) Increase of stress resistance in crop plants by using phenolic compounds. Acta Hort. 381, 390-395.
- Carter, C.T., Grieve, C.M., Poss, J.A. and Suarez, D.L. (2005) Production and ion uptake of Celosia argentea irrigated with saline wastewaters. Sci. Hort. 106, 387-394.
- Chartzoulakis, K., Loupassaki, M., Bertaki, M. and Androulakis, I. (2002). Effects of NaCl salinity on growth, ion content and CO2 assimilation rate of six olive cultivars. Sci. Hort. 96, 235-247.
- Dole, J.M. and Wilkins, H.F. (2004). Floriculture: Principles and Species. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
- Downton, W.J.S., Grant, W.J.R. and Robinson, S.P. (1985). Photosynthetic and stomatal responses of spinach leaves to salt stress. Plant Physiol. 77, 85-88.
- El-tayeb, M.A. (2005). Response of barley grains to the interactive effect of salinity and salicylic acid. Plant Growth Regul. 45, 215-224.
- Eraslan, F., Inal, A., Gunes, A. and Alpaslan, M. 2007. Impact of exogenous salicylic acid on growth, antioxidant activity and physiology of carrot plants subjected to combined salinity and boron toxicity. Sci. Hort. 113, 120-128.
- Gunes, A., Inal, A. and Alpaslan, M. (2005) Effects of exogenously applied salicylic acid on the induction of multiple stress tolerance and mineral nutrition in maize (Zea mays L.). Arch Agron Soil Sci. 51, 687-95.
- Gutierrez-Coronado, M.A., Trejo-Lopez, C. and Larque-Saavedra, A. (1998) Effects of salicylic acid on the growth of roots and shoots in soybean. Plant Physiol Biochem. 36, 563-565.
- Hayat, S. and Ahmad, A. (2007). Salicylic Acid: a Plant Hormone. Springer, pp: 401-407.
- Hayat, S., Hasan, S.A., Fariduddin, Q. and Ahmad, A. (2008). Growth of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) in response to salicylic acid under water stress. J. Plant Int. 3, 297-304.
- He, Y.L., Liu, Y.L., Cao, W.X., Huai, M.F., Xu, B.G. and Huang, B.G. (2005). Effects of salicylic acid on heat tolerance associated with antioxidant metabolismin Kentucky bluegrass. Crop Sci. 45, 988-995.
- Jaleel, C.A., Gopi, R., Manivannan, P. and Panneerselvam, R. (2007a) Antioxidative potentials as a protective mechanism in Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. plants under salinity stress. Turkish J. Bot. 31, 245-251.
- Jaleel, C.A., Gopi, R., Manivannan, P. and Panneerselvam, R. (2007b) Responses of antioxidant defense system of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. To paclobutrazol treatment under salinity, Acta Physiol. Plant, 29, 205-209.
- Kang, G., Wang, C., Sun, G. and Wang, Z. (2003). Salicylic acid changes activities of H2O2 metabolizing enzymes and increases the chilling tolerance of banana seedlings. Environ. Exp. Bot. 50, 9-15.
- Karlidag, H., Yildirim, E. and Turan, M. (2009). Salicylic acid ameliorates the adverse effect of salt stress on strawberry. Sci. Agric. 66, 180-187.
- Kaya, C., Higgs, D., Ince, F., Amador, B.M., Cakir, A. and Sakar, E. (2003). Ameliorative effects of potassium phosphate on salt-stressed pepper and cucumber. J. Plant Nutr. 26, 807-820.
- Khan, W., Prithiviraj, B. and Smith, D.L. (2003). Photosynthetic response of corn and soybean to foliar application of salicylates. J. Plant Physiol. 160, 485-492.
- Khodary, S.E.A. 2004. Effect of salicylic acid on the growth, photosynthesis and carbohydrate metabolism in salt-stressed maize plants. J. Agric. Biol. 6: 5-8.
- Krantev, A., Yordanova, R., Janda, T., Szalai, G. and Popova, L. 2008. Treatment with salicylic acid decreases the effect of cadmium on photosynthesis in maize plants. J. Plant Physiol. 165, 920-931.
- Kumar, S. and Nanda, K.K. (1981a). Gibberellic acid and salicylic acid caused formation of new proteins associated with extension growth and flowering of Impatiens balsamina. Biol. Plantarum, 23, 321-327.
- Kumar, S. and Nanda, K.K. (1981b). Effect of gibberellic acid and salicylic acid on the activity and eletrophoretic pattern of IAA-oxidase during floral induction in Impatiens balsamina. Biol. Plantarum, 23, 328-334.
- Lutts, S., Kinet, J.M. and Bouharmont, J. (1996) NaCl-induced senescence in leaves of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity resistance. Ann. Bot. 8, 389-398.
- Martinmex, R., Villaneuva-Couoh, E. Herrera-Campos, T. and Larque-Saavedra, A. (2005). Positive effect of Salicylates on the flowering of African violet. Sci. Hort. 103, 499-502.
- Munns, R. 2002. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Envir. 25, 239-250.
- Van Breusegem, F., Vraneva, E. and Dat, J.F. (2001) The role of active oxygen species in plant signal transduction. Plant Sci. 161, 405-414.
- Parida, A.K. and Das, A.B. (2005). Salt tolerance and salinity e?on plants: a review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety, 60, 324-349.
- Raskin, I. (1992) Salicylate. A new plant hormone. Plant Physiol. 99, 799-804.
- Sanchez-Blanco, M.J., Rodr?guez, P., Olmos, E., Morales, M.A. and Torrecillas, A. (2003). Contrasting physiological responses of dwarf sea-lavender and marguerite to simulated sea aerosol deposition. J. Environ.Qual. 32, 3338-3344.
- Senaratna, T., Touchell, D., Bunn, E. and Dixon, K. (2000). Acetyl salicylic acid (Aspirin) and salicylic acid induce multiple stress tolerance in bean and tomato plants. Plant Growth Regul. 30, 157-161.
- Serek, M. (1992) Does salicylic acid affect the post-harvest characteristics of Campanula carpatica? Gartenbauwissenschaft, 57, 112-114.
- Shakirova, F.M., Sakhabutdinova, A.R. Bezrukova, M.V., Fatkhutdinova, R.A. and Fatkhutdinova, D.R. (2003). Changes in the hormonal status of wheat seedlings induced by salicylic acid and salinity. Plant Sci. 164, 317-322.
- Singh, B. and Usha, K. (2003). Salicylic acid induced physiological and biochemical changes in wheat seedlings under water stress. Plant Growth Regul. 39, 137-141.
- Sivritepe, N., Sivritepe, H.O. and Eris, A. (2003). The effects of NaCl priming on salt tolerance in melon seedlings grown under saline conditions. Sci. Hortic. 97, 229-237.
- Stepien, P. and Klobus, G. (2006). Water relations and photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus L. Leaves under salt stress. Biol. Plantarum, 50, 610-616.
- Stevens, J., Senaratna, T. and Sivasithamparam, K. (2006). Salicylic acid induces salinity tolerance in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum cv. 'Roma'): associated changes in gas exchange, water relations and membrane stabilisation. Plant Growth Regul. 49, 77-83.
- Szepesi, A., Csiszar, J. Bajkan, S. Gemes, K. Horvath, F. Erdei, L. Deer, A.K. Simon, M.L. and Tari, I. (2005). Role of salicylic acid pre-treatment on the acclimation of tomato plants to salt-and osmotic stress. Act. Biol. Szeg. 49, 123-125.
- Turan, M., and Aydin, A. (2005). Effects of different salt sources on growth, inorganic ions and proline accumulation in corn (Zea Mays L). Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 70, 149-155.
- Yildrim, E., Turan, M. and Guvenc, I. (2008). Effect of foliar salicylic acid applications on growth, chlorophyll and mineral content of cucumber (Cucumis sativusL.) grown under salt stress. J. Plant Nutr. 31, 593-612.


