Impact of pre-anthesis salt stress on biochemical and yield related traits in salt sensitive and salt tolerant genotypes of Triticum aestivum L
Автор: Singh Divya
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.19, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Salinity stress negatively affects the growth and development of wheat leading to diminished grain yield and quality. Salt stress during reproductive stage is one of the significant factors leading to the drastic reduction in grain yield. The objective of this study was to investigate the biochemical responses of pre-anthesis stage salt stress and yield related traits in KRL1-4 salt tolerant and UP2338 salt sensitive cultivar of Wheat. Three different levels of salinity stress (100, 200 and 300 mM NaCl) was induced. Untreated plants were kept as control. Samples were analyzed at pre- anthesis stage (50 DAS and 60 DAS) for various biochemical parameters viz., proline content, total reducing sugar content, total nitrogen content and total protein content. Yield related traits harvest index, tiller numbers per plant, spike height and spike weight were recorded at maturity stage. The amount of proline and reducing sugar increased with increasing salinity, the increase being more in tolerant than in sensitive cultivar. Total nitrogen and total protein content, however, decreased with increasing salt concentration and reduction being more in sensitive than in tolerant cultivar. Yield attributes were affected negatively. The effect was more pronounced in sensitive cultivar compared to tolerant.
Salinity, pre-anthesis, osmolytes, harvest index
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143179381
IDR: 143179381
Текст научной статьи Impact of pre-anthesis salt stress on biochemical and yield related traits in salt sensitive and salt tolerant genotypes of Triticum aestivum L
Soil salinity is a major threat to crop yields, especially in arid and semi-arid countries where irrigation is an essential aid to agriculture ((Liu et al. , 2020). 20% of global cultivable land is affected by salt stress. Change in climate and anthropogenic activities are increasingly affecting the arable lands (Arora, 2019). The stress created by high salt concentration in the soil is attributed to early osmotic stress and sodium and chloride ion stress that appears late significantly reducing plant growth and development (Odjegba, 2013). Osmotic stress immediately affects growth because of the salt (Singh, 2022). Plant response towards salinity stress depends upon many factors like concentration of salts, variety of plant, growth stage and environmental conditions Reproductive age of any crop is the most sensitive stage to salinity stress (Ehtaiwesh and Rashed, 2020), and cause massive reduction in yield in wheat (Kalhoro et al. , 2016).
Wheat, rice, and maize are the most important staple crops globally and contribute a significant part of daily calories and protein intake (Kizilgeci et al. , 2021). Among the cereals, Triticum aestivum is ranked at the first position due to its domestication and contribution as the primary staple food crop globally (Iqbal et al. , 2021). Wheat has been reported to provide 73% of the calorie and protein requirements of the daily diet (Arif et al. , 2010). It plays an important role in food security and poverty alleviation as a strategic crop and has an important role in economy (Khan et al. , 2011).
Unavailability of sufficient photo assimilates during pre-anthesis stage is the leading cause of loss in production in wheats. Plants develop a large number of physiological and biochemical strategies to cope with stresses (Liang et al, 2018). The response to osmotic stress primarily involves osmotic adjustments. Osmotic adjustment is crucial for cell turgor maintenance, which maintains plant metabolic activity and in turn plant growth and productivity (Yue et al. , 2012). Proline, soluble sugars, glycine, betaine, and other osmolytes synthesized by plants to promote osmotic balance can serve as sensitive markers for the selection of tolerant genotypes under salt stress (Kerepesi and Galiba, 2000).
The present study was performed to determine the salt tolerance for two wheat cultivars during preanthesis stage and to examine the changes in biochemical and yield parameters. The biochemical markers can be incorporated into high yielding salt tolerant wheat varieties.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The field experiment was conducted at the Department of Botany, D.D.U. Gorakhpur University during Wheat growing period (Nov.-Feb 2009)
Healthy grains of wheat (salt tolerant KRL 1-4 and salt sensitive UP 2338 cultivars) were surface sterilized with ethanol for 5 min followed by thorough wash with distilled water. Seeds were obtained from Narendra Dev Agriculture University, Faizabad Grains were then inoculated with 96 h grown culture of Azotobacter (culture of Azotobacter chrococcum was obtained from the Department of Agriculture and Co-operation, National Biofertilizer Development Centre Ghaziabad, U.P.)
The inoculated seeds were sown in earthenware pots containing sterilized sand. These pots were treated with saline water containing 100mM, 200mM, 300mM NaCl respectively and corresponding E.C. was maintained as 9.83, 21.9 and 32.5 dS/m respectively. Plants were supplied with Hoagland’s nutrient solution weekly. Water was applied to each pot daily to keep the sand moist and hence to maintain the salt level. Untreated plants were kept as control. All the biochemical parameters were recorded at pre-anthesis stage (50 and 60 DAS) for various treatments and yield parameters were recorded post harvesting.
Biochemical parameters
Proline content was estimated by the method of Bates et al. (1973). Estimation of total reducing sugar was done by the method of Somogyi's (1952). Determination of insoluble and total nitrogen was done by the method of Doneen (1932). For measurement of protein content, the amount of insoluble nitrogen fraction as obtained by micro-Kjeldahl digestion method was multiplied by a factor 6.25. Relative water content was measured by Barr and Weatherly (1962).
Yield Parameters
Plants of different saline treatments were harvested at 110 DAS. Data on wheat harvest index, tiller numbers per plant, spike height and spike weight were recorded. Spikes were oven-dried at 70 1 °C for 72 h and their dry weights determined. Tiller numbers per plant were recorded from 5 randomly chosen plants. Spike weight per plant was recorded from 5 randomly chosen plants.
The data have been statistically analyzed. Least significance difference (LSD) has been calculated for the data where F-test was found significant.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
For better yield and growth at pre-anthesis stage leaf osmotic potential is of paramount importance. During salinity stress plants accumulate organic osmolytes for osmotic adjustments. In the current study proline increased gradually with increasing salt concentration. The increment was more in tolerant cultivar KRL1-4 than sensitive cultivar UP2338. However, proline content decreased at 60 DAS in both the cultivars at all salt concentration (Fig.1a 1b)
Our findings are in consideration with previous work of Sairam et al. (2002) in wheat genotypes. Sehrawat et al. (2013) reported that accumulation of osmolytes (proline and trehalose) increased significantly with increase in salinity in all the genotypes but the tolerant genotypes showed greater increase in these osmolytes under salinity than the susceptible genotypes of mungbean. Hasan et al. (2015) reported an increase in flag leaf proline content in salt tolerant wheat genotypes under salt stress. while a decrement was observed in sensitive genotypes as compared to control plants.
Reducing sugar followed the same trend as that of proline (Fig. 2a 2b). Zheng et al. (2009) found that sugar content increased in wheat under salt stress. High carbohydrate concentrations under salt stress prevent plants from oxidative damage and also maintain the structure of proteins (Hajihashemi et al, 2006). Confirmed with our data, there are other reports indicating that the soluble carbohydrates content increased in response to salt stress especially in tolerant varieties (Areftan et al., 2014). The decrease in reducing sugar at advanced stage is due to unavailability of sufficient photo-assimilates caused by salt stress during the pre-anthesis and grain filling stage. Alteration of sucrose 1-fructosyltransferase, sucrose: fructan6-fructosyltransferase, and fructanexohydrolase hampers the fructan accumulation, and remobilization of carbohydrate to grains (Sharbatkhari et al., 2016).
Salt in soil water affects available soil water, tissue water, cell turgidity, water potential and osmolytes. In our study relative water content declined significantly with induction and duration of salt stress. Decline in relative water content was lower in salt tolerant cultivar KRL1-4 as compared to sensitive cultivar UP2338 (Fig. 3a 3b). Our results are in agreement with those of Sairam et al. (2002) and Zheng et al. (2009) who reported greater reduction in RWC of salt sensitive wheat cultivar as compared with tolerant one under salt stress. It was proposed that retention of higher RWC was associated with higher proline accumulation in tolerant cultivar. At reproductive phase reduction in water potential reduces cell elongation, leaf area and hence productivity (Farouk et al. , 2011).
Nitrogen and Protein content decreased with increasing levels of salinity. Yousfi et al. (2013) reported that nitrogen metabolism and stomatal limitation at anthesis stage are major causes of reduction in biomass under different salinity regimes. In the current study the decrement was more in sensitive than in tolerant cultivar (Fig. 4a 4B, Fig. 5a 5b). Kaya et al. , 2009 reported salinity stress can decrease N concentration. Upadhyaya et al. (2007) reported that protein content decreased under Hydrogen peroxide oxidative stress in rice.
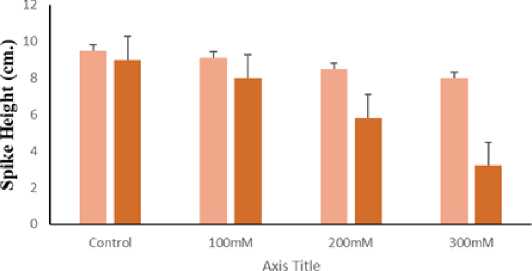
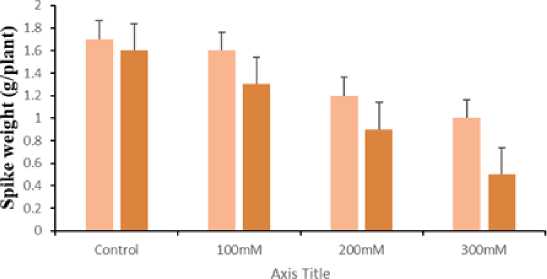
Subjecting wheat plants to salt stress had negative effect on agronomic traits like harvest index (Fig.6), spike height (Fig. 7), spike weight (Fig.8) and tiller number (Fig 9). However, the impact was more pronounced on UP2338 as compared to KRL1-4. Significant decrease was observed on 60DAS at higher concentration of salt stress. Mass and Grieve,1990 suggested salinity cause decrease in number of spikelet primordia and early anthesis. Our result is in accordance with Tareq et al. (2011) who suggested 8,3, 37, 20 and 10 % reduction in spike length, spike weight, filled spike let per plant, total spikelet per plant and weight respectively under stress condition. Eroglu et al. (2020) reported that salt stress at pre anthesis and post anthesis stage caused reduction in ear weight and biomass.
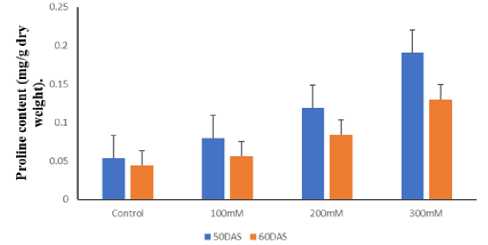
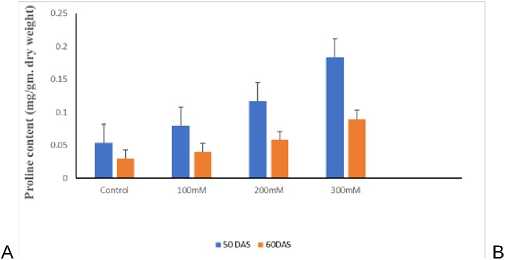
Figure 1. (A). Effect of salt on Proline content in 50 60 DAS KRL1-4 cultivar of wheat under different NaCl concentrations (B) Effect of salt on Proline content in 50 60 DAS UP2338 cultivar of wheat under different NaCl concentrations.
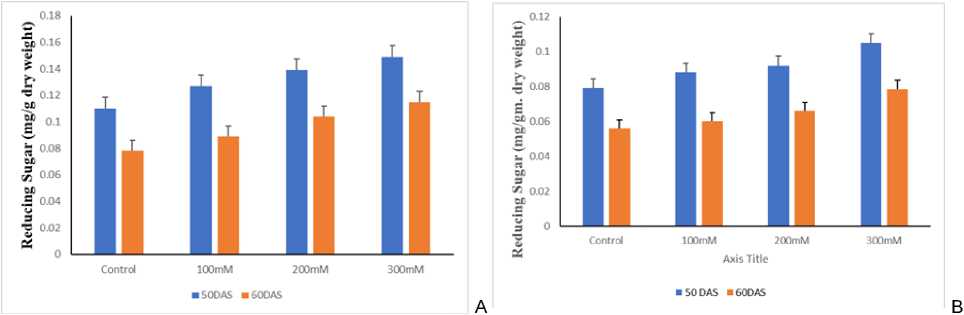
Figure 2. (A). Effect of salt on Reducing Sugar in 50 60 DAS KRL1-4 cultivar of wheat under different NaCl concentrations, (B) Effect of salt on Reducing Sugar in 50 60 DAS UP2338 cultivar of wheat under different NaCl concentrations.
Il IIIIII I1 III I
Control
lOOmM
200mM
300mM
Control
lOOmM
200mM
300mM
Axis Title
■ SODAS «600AS
A
■ SODAS 1600AS
B
Figure 3. (A). Effect of salt on Relative Water Content in 50 60 DAS KRL1-4 cultivar of wheat under different NaCl concentrations (B) Effect of salt on Relative Water Content in 50 60 DAS UP2338 cultivar of wheat under different NaCl concentrations
в 2850
£ 2800
■5 2750
~ 2700 a Ы 2650
= 2600
^ 2550
Il II II II ! Il II II h
Control
lOOmM
200mM
300mM
Control
lOOmM
200mM
ЗООтМ
SODAS 1600AS
A
SODAS ■ SODAS
B
Figure 4. (A) Effect of salt on Nitrogen Content in 50 60 DAS KRL1-4 cultivar of wheat under different NaCl concentrations, (B) Effect of salt on Nitrogen Content in 50 60 DAS UP2238 cultivar of wheat under different NaCl concentrations.
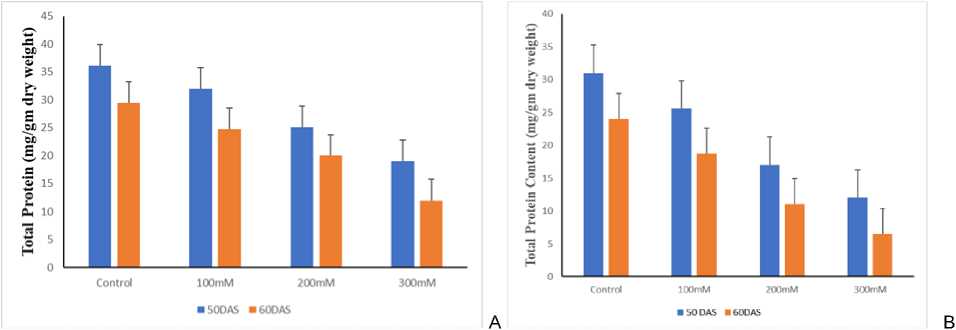
Figure 5. (A) Effect of salt on Total Protein Content in 50 60 DAS KRL1-4 cultivar of wheat under different NaCl concentrations, (B) Effect of salt on Total Protein Content in 50 60 DAS UP2338 cultivar of wheat under different NaCl concentrations
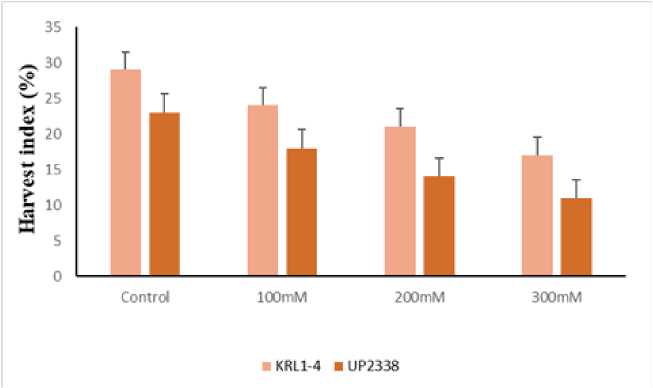
Figure 6. Effect of salt on Harvest Index (%) in KRL1-4 and UP2338 wheat plants under different NaCl concentrations
■ KRll-4 1UP2338
Figure 7. Effect of salt on Spike height in KRL1-4 and UP2338 wheat plants under different NaCl concentrations
KRL1-4 eUP2338
Figure 8. Effect of salt on Spike weight in KRL1-4 and UP2338 wheat plants under different NaCl concentrations
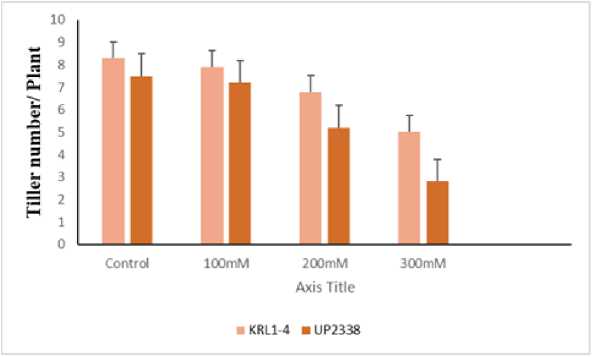
Figure 9. Effect of salt on Tiller number in KRL1-4 and UP2338 wheat plants under different NaCl concentrations
CONCLUSION
Anthesis and grain filling period are crucial stages under environmental stresses including salinity and have been identified as major constraints to wheat production worldwide (Ghosh et al., 2016). Salinity tolerance is an outcome of various features that depend on different physiological interactions, which are difficult to determine. According to our study better growth and yield of KRL1-4 tolerant cultivar compared to UP2338 sensitive cultivar when exposed to stress may be due to increased osmolyte production, higher water content and total nitrogen and proteins in leaves.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
I am thankful to Prof. Malvika Srivastava for providing lab facility and her able guidance.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Impact of pre-anthesis salt stress on biochemical and yield related traits in salt sensitive and salt tolerant genotypes of Triticum aestivum L
- Arefian, M., Vessal, S. and Bagheri, A. (2014). Biochemical changes and SDS-PAGE analyses of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genotypes in response to salinity during the early stages of seedling growth. J. Biol. Environ. Sci. 8 : 99-109.
- Arif, M., Bangash, J. A., Khan, F. and Abid, H. (2010). Quality assessment of different iron fortified wheat flours. Pak. J. Biochem. Mole. Biol. 43 : 192-94.
- Arora, N. K. (2019). Impact of climate change on agriculture production and its sustainable solutions. Environ. Sustain. 2, 95–96. doi: 10.1007/s42398-019-00078-w
- Barr, H.D. and Weatherley, P.E. 1962. A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating water deficit in leaves. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 15:413-428.
- Bates, L. S., Walden, R. P. and Teare, J. D. (1973). Rapid determination of free proline of water stress studies. Plant Soil 39 : 205-07
- C. Kaya, M. Ashraf, O. Sonmez, S. Aydemir, A. Levent Tuna, M.A. Cullu. (2009).The influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal colonisation on key growth parameters and fruit yield of pepper plants grown at high salinity.Sci. Hort., 121 (2009), pp. 1-6
- Divya Singh. (2022). Juggling with reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense system – A coping mechanism under salt stress, Plant Stress, Volume 5, 100093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2022.100093.
- Doneen, L. D. (1932). A micromethod for nitrogen estimation in plant materials. Plant Biochem. 14 : 74-82
- Ehtaiwesh, F. A., and Rashed, H. F. (2020). Growth and yield responses of libyan hard wheat (Triticum durum Desf) genotypes to salinity stress. Zawia Univ. Bull. 22, 33–58.
- EL Sabagh Ayman, Islam Mohammad Sohidul, Skalicky Milan, Ali Raza Muhammad, Singh Kulvir, Anwar Hossain Mohammad, Hossain Akbar, Mahboob Wajid, Iqbal Muhammad Aamir, Ratnasekera Disna, Singhal Rajesh Kumar, Ahmed Sharif, Kumari Arpna, Wasaya Allah, Sytar Oksana, Brestic Marian, ÇIG Fatih, Erman Murat, Habib Ur Rahman Muhammad, Ullah Najeeb, Arshad Adnan. (2021). Salinity Stress in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the Changing Climate: Adaptation and Management Strategies. Frontiers in Agronomy, 3. 661932.
- Eroglu, Ç., Cabral, C., Ravnskov, S., Topbjerg, H., and Wollenweber, B. (2020). Arbuscular mycorrhiza influences carbon-use efficiency and grain yield of wheat grown under pre- and post-anthesis salinity stress. Plant Biol. 22, 863–871. doi: 10.1111/plb.13123
- Farouk, S. (2011). Ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol minimize salt-induced wheat leaf senescence. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 7, 58–79.
- Ghosh, B., Md, N. A., and Gantait, S. (2016). Response of rice under salinity stress: a review update. Rice Res. 4:167. doi: 10.4172/2375-4338.1000167
- Hajihashemi, S., Kiarostami, K., Enteshari, S. and Saboora, A. (2006). The effects of salt stress and paclobutrazol on some physiological parameters of two salt tolerant and salt sensitive cultivars of wheat. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 9 : 1370-74.
- Hasan, A., Hafiz1, H. R., Siddiqui, N., Khatun, M., Islam, R. and Al-Mamun, A. (2015). Evaluation of wheat genotypes for salt tolerance based on some physiological traits. J. Crop Sci. Biotech. 18 : 333-40. DOI No. 10.1007/s12892-015-0064-2.
- Iqbal, M. A., Junaid, R., Wajid, N., Sabry, H., Yassir, K., and Ayman, S. (2021). Rainfed winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars respond differently to integrated fertilization in Pakistan. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 30, 3115–3121.
- Kalhoro, N. A., Rajpar, I., Kalhoro, S. A., Ali, A., Raza, S., Ahmed, M., et al. (2016). Effect of salts stress on the growth and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Am. J. Plant Sci. 7:2257. doi: 10.4236/ajps.2016.715199
- Kerepesi, I. and Galiba, G. (2000) Osmotic and Salt Stress-Induced Alteration in Soluble Carbohydrate Content in Wheat Seedlings. CropScience, 40, 482-487.
- Khan, S., Khan, J., Islam, N. and Islam, M. (2011). Screening and evaluation of wheat germplasm for yield, drought and disease resistance under rainfed conditions of upland Baluchistan. Pak. J. Bot. 43 : 559-63.
- Kizilgeci, F., Yildirim, M., Islam, M. S., Ratnasekera, D., Iqbal, M. A., and Sabagh, A. E. (2021). Normalized difference vegetation index and chlorophyll content for precision nitrogen management in durum wheat cultivars under semi-arid conditions. Sustainability 13:3725. doi: 10.3390/su13073725
- Liu, X., Chen, D., Yang, T., Huang, F., Fu, S., and Li, L. (2020). Changes in soil labile and recalcitrant carbon pools after land-use change in a semi-arid agro-pastoral ecotone in Central Asia. Ecol. Indic. 110:105925. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105925
- Maas, E. V., and Grieve, C. M. (1990). Spike and leaf development of sal-stressed wheat. Crop Sci. 30, 1309–1313. doi: 10.2135/cropsci1990.0011183X003000060031x
- Odjegba, V. J. (2013). Responses of Zea mays seedlings to salinity stress and exogenous nitrogen supply. Nat Sci. 11 : 63-69.
- Sairam, R. K., Rao, K. V., & Srivastava, G. C. (2002). Differential response of wheat genotypes to long term salinity stress in relation to oxidative stress, antioxidant activity and osmolyte concentration. Plant science, 163(5), 1037-1046.
- Sehrawat, N., Bhatt, K.V., Sairam, R. K., Toomoka, N., Kaga, A., Shu, Y. and Jaiwal, P. K. (2013). Diversity analysis and confirmation of intra-specific hybrids for salt tolerance in mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]. Int. J. Integrative Biol. 14 : 65.
- Sharbatkhari, M., Shobbar, Z. S., Galeshi, S., and Nakhoda, B. (2016). Wheat stem reserves and salinity tolerance: molecular dissection of fructan biosynthesis and remobilization to grains. Planta 244, 191–202. doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2497-3
- Somogyi, M. (1952). Notes on sugar determination. J. Biol. Chem. 195 : 19-23.
- Tareq, M. Z., Hossain, M. A., Mojakkir, M. A., Ahmed, R., and Fakir, M. S. A. (2011). Effect of salinity on reproductive growth of wheat. Bangladesh J. Seed Sci. Technol. 15, 111–116.
- Upadhyaya, H., Khan, M. H. and Panda, S. K. (2007) . Hydrogen peroxide induces oxidative stress in detached leaves of Oryza sativa L. Gen. Appl. Plant Physiol. 33 : 83- 95.
- Wenji Liang, Xiaoli Ma, Peng Wan, Lianyin Liu., 2018. Plant salt-tolerance mechanism: A review, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, Volume 495, Issue 1,2018,Pages 286-291,
- Yousfi, S., Serret, M. D., and Araus, J. L. (2013). Comparative response of δ13C, δ18O and δ15N in durum wheat exposed to salinity at the vegetative and reproductive stages. Plant Cell Environ. 36, 1214–1227. doi: 10.1111/pce.12055
- Yuesen Yue, Mingcai Zhang, Jiachang Zhang, Liusheng Duan, Zhaohu Li., 2012. SOS1 gene overexpression increased salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco by maintaining a higher K+/Na+ratio, Journal of Plant Physiology, Volume 169, Issue 3, 255-261.
- Yuesen Yue, Mingcai Zhang, Jiachang Zhang, Liusheng Duan, Zhaohu Li. (2012).SOS1 gene overexpression increased salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco by maintaining a higher K+/Na+ ratio,Journal of Plant Physiology,Volume 169, 255-261.
- Zheng, Y., Xu, H., Wang, M. Y., Zheng, X. H., Li, Z. J. and Jaing, G. M. (2009). Responses of salt tolerant and intolerant wheat genotypes to sodium chloride: photosynthesis, antioxidant activities and yield. Photosynthetica 47: 87-94.


