Improvement of tool support of the spatial approach to regional planning: problems, specifics, trends
Автор: Yushkova Nataliya Gennadievna
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Innovation development
Статья в выпуске: 6 (36) т.7, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The emerging imperatives of innovation economic development in Russia determine the content of conceptual and institutional constraints to the development of regional economic systems (RES). They consider the regional planning system as a leading priority in its inseparable unity with modern public administration tasks. However, the practice of development of long-term plans in the RF subjects proves that the innovation challenges of economic policy are not reflected properly in them or they are significantly distorted. The following reasons reduce the effectiveness of modernization processes in the RF subjects and hamper the appropriate reaction of RES on their impact: the lack of coordination between socio-economic and spatial regional plans, the imbalance of interaction between state authorities engaged in long-term planning, the lack of real prerequisites for the implementation of innovation initiatives in the regions. Systematization and analysis of long-term plans make it possible to substantiate the consistency of the spatial approach to regional planning expressed in the dominance of the transformational function that synchronizes the configuration and parameters of RES, and to establish ways to integrate spatial components in the system of regional planning through optimization of its tool support...
Public administration, regional system, transformational function, socio-economic development, regional planning, tool support, spatial approach
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223673
IDR: 147223673 | УДК: 332.145 | DOI: 10.15838/esc/2014.6.36.17
Текст научной статьи Improvement of tool support of the spatial approach to regional planning: problems, specifics, trends
The main provisions of the national policy in the sphere of innovation development are formulated and set out in concepts, legislative and normative-legal acts primarily at the federal level of government [5, 6, 7].
Public administration system at the regional level perceives the innovative orientation of public policy objectives with varying degrees of adequacy [8, 10, 14, 12].
The situation in federation subjects shows that their progressive implementation takes place in exceptional cases, while in general this process is not universal and it is uneven. In order to establish the factors that hinder its normal course, the author has conducted a study that reveals modern features of regional planning in the Russian Federation subjects.
When such causes of decreased efficiency modernization processes in the subjects of the Russian Federation are revealed, the attention is drawn, first of all, to the mismatch between the socio-economic and spatial components of regional planning, unbalanced participation of state authorities engaged in long-term planning, and to the bias of the estimates of the existing prerequisites that the regions possess for the implementation of innovation initiatives.
The author considers that the actual scientific problem and the purpose of this study lies in the justification of the ways to eliminate these contradictions in the functioning of regional economic systems (RES). The author’s hypothesis is based on the fact that, provided that the contradictions in the existing methods of regional planning are eliminated, the quality of regional plans will increase due to their greater adaptability concerning the institutional requirements and limitations for innovation development of RES. Thus, the object of the study is a meandering system of long-term regional planning that is subject to the influence of external and internal factors that determine the nature of transformational changes in RES. The subject of research is tool support corresponding to the object, reflecting the intensity of transformational changes in RES occurring due to the use of the spatial approach to regional planning.
One of the least studied aspects of the problem, according to the author, is the identification of contradictions in RES that are caused by a mismatch between the socio-economic and spatial components of regional planning [19]. In order to justify directions for elimination of these problems and improvement of existing methods of planning it was necessary to take a look at the content of regional development plans in the RF subjects with the subsequent comparative analysis of the plans. Along with this type of analysis, the methods of research also include the effect-cause analysis, comparative analysis, empirical method, and methods of spatial analysis.
The study shows that the main directions of the policy for innovation economic development in our country are expressed in a set of conceptual and institutional constraints [2] that are a starting point in the development of any management decisions, including long-term plans for regional development.
Their dissemination occurs in various forms that are mainly not regulated [14, 15]. This is what largely determines the specifics of regional plans.
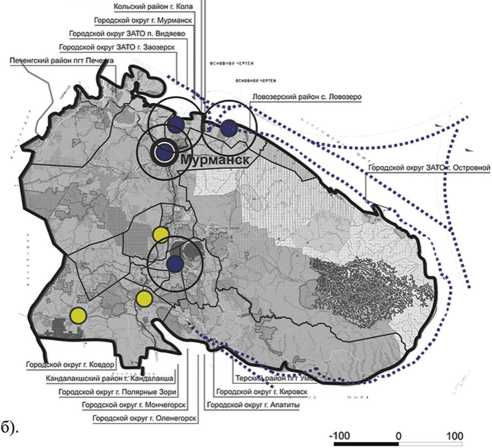
For instance, regional economic systems that experience the impact of the requirements of innovation development react through the emergence of new socioeconomic processes with further reflection of elements revealing their content. But in most cases there is no compliance with socio-economic provisions of the plans in the spatial aspect, or it is reflected to a small extent (fig. 1) .
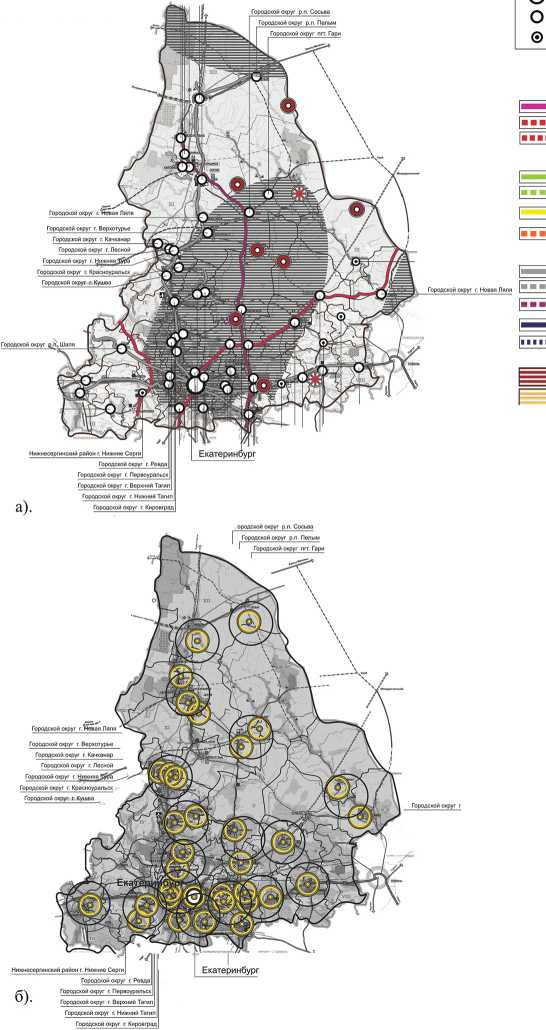
At present, transformation processes in RES that express the action of innovation factors are characterized mainly by infrastructural socio-economic change connected with the hierarchical levels of the region’s administrative-territorial division. This trend of detecting infrastructural relations in the structure of socio-economic processes is reflected in regional plans even less. The exception is found in long-term plans of certain RF subjects, in which infrastructure models are calculated both in terms of socio-economic development of regions and territorial plans (fig. 2).
Improvement of the spatial approach, taking into account new conditions, allows us to represent the development of RES as a process of their controlled transformation synchronized with the modernization trends within which the development goals of RES adapt to actual opportunities of their implementation through the interaction of socio-economic and spatial forms.
The very fact that the essence of economic processes is conditioned by their territorial affiliation focuses the attention of public authorities and leading representatives of modern scientific community on the comprehensive assessment of factors in the development of RES by highlighting the spatial factors [4, 6, 10, 11, 15].
As a consequence, the regional planning system is changed through the identification of its transformational function that is implemented through the development of integrated spatial and strategic decisions, that align the configuration and parameters of RES development. The feasibility of this function that is revealed in the system of spatial and strategic planning, in turn, is inseparable from the modernized system of tool support reflecting the change in the target-setting in the development of RES [3, 13, 17].
In the context of the spatial approach, the transformational function manifests itself with varying degrees of activity in such a way that leads to the improvement of planning: initially – through the cohesion of socio-economic spatial components and then – through their integration. The specifics of interaction between the components, already in the spatial
Figure 1. Identification of socio-economic processes in the development of regional economic systems on the basis of comparative analysis of long-term plans in the spatial aspect on the example of the RF subject characterized by a low threshold of perception of institutional constraints
MURMANSK OBLAST
Городской округ ЗАТО Александровск
Кольский район г. Кола
Area -144,902 km2
Length from south to north - 400 km, from east to west - 550 km
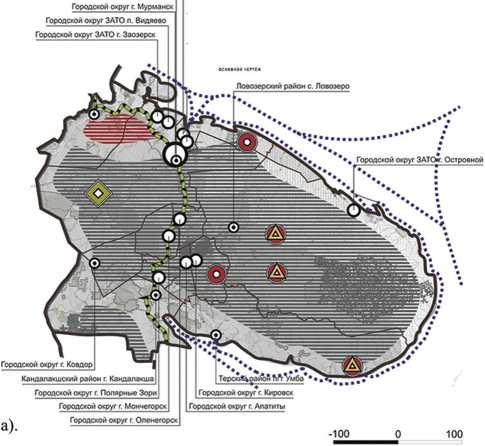
Городской округ ЗАТО г. Североморск
Городской округ ЗАТО Александровск

border of the subject of federation border of the municipal district city – center of the subject of federation name of the municipal district administrative center of the municipal district transport corridors international Eurasian transport corridor Transsib:
current state branch prospect international Eurasian transport corridor
North-South:
current state branch
Pan-European transport corridor international Eurasian transport corridor Primorye-1
railway lines:
current state construction and reconstruction construction and reconstruction of motor roads inland waterways sea routes zones of socio-economic development:
of agglomerations and innovation technology of agro-industrial complexes of tourism and recreation development of natural resources and/or manufacturing objects (centers) of socio-economic development:
centers for innovation development and high technology industrial and agro-industrial centers port and other transport and logistics hubs tourism, recreation and cultural centers natural resources development sites
-
a) scheme of socio-economic development planning,
-
b) scheme of territorial development planning

border of the subject of federation border of the municipal district zones of socio-economic development:
zones of priority town-planning and economic development, zones of economic and investment activity multifunctional zones zones of inter-regional activity innovation, research-and-industrial and gambling zones centers for planned location of capital construction objects objects (centers) of socio-economic development:
areal types of innovation objects
point types of innovation objects poles and growth points, centers for attraction of investments, industrial centers and objects of innovation activity nodes and centers of technological development centers for advanced economic activity centers for economic development, concentration of urban construction activity and active functional centers
Figure 2. Identification of infrastructure specifics of socio-economic development of regional economic systems in the spatial aspect on the example of the RF subject characterized by a high threshold of perception of institutional constraints of RES
SVERDLOVSK OBLAST
Area -194,307 km2
Length from south to north - 660 km, from east to west - 560 km
-100 0 100
-100 0 100
border of the subject of federation border of the municipal district city – center of the subject of federation name of the municipal district administrative center of the municipal district transport corridors international Eurasian transport corridor Transsib: current state branch prospect international Eurasian transport corridor North-South: current state branch
Pan-European transport corridor international Eurasian transport corridor Primorye-1
railway lines: current state construction and reconstruction construction and reconstruction of motor roads inland waterways sea routes zones of socio-economic development:
of agglomerations and innovation technology of agro-industrial complexes of tourism and recreation development of natural resources and/or manufacturing objects (centers) of socio-economic development:
centers for innovation development and high technology industrial and agro-industrial centers port and other transport and logistics hubs tourism, recreation and cultural centers natural resources development sites border of the subject of federation border of the municipal district zones of socio-economic development:
zones of priority town-planning and economic development, zones of economic and investment activity multifunctional zones zones of inter-regional activity innovation, research-and-industrial and gambling zones centers for planned location of capital construction objects objects (centers) of socio-economic development:
areal types of innovation objects
-
a) scheme of socio-economic development planning,
-
b) scheme of territorial development planning
point types of innovation objects poles and growth points, centers for attraction of investments, industrial centers and objects of innovation activity nodes and centers of technological development centers for advanced economic activity centers for economic development, concentration of urban construction activity and active functional centers and strategic planning system (SSPS), justify the phenomenological effects of multiplication that extend their impact on economic activity in the region. They are provided by the activity of the tool support of SSPS.
According to the research findings, the system of tool support of SSPS has three main groups of tools: organizing, regulating, and coordinating.
The group of organizing tools consists of two subgroups: the legal and resource support of SSPS.
Analysis of the current application of the tools of organizational and legal support of regional planning processes confirms the effectiveness of the use of public-private partnership (PPP).
Intensive development of PPP in the regions is often constrained by the incomparability of socio-economic and spatial estimates of the potential to fulfil the strategic objectives based on criteria such as: the need for resources, payback period, the ability to improve the socio-economic condition in the region in a given direction, the ability to replenish regional budgets and to create new jobs [4, 14].
Prospects of development of modern forms of PPP and concepts of their formation are associated with the definition and consideration of regional characteristics, as well as their consistency with the overall development strategy of the federal districts. In conditions of pronounced nonuniformity of transformational change in RES, the projects of their infrastructure development through PPP, in a general sense and in the terminology of this study, are a way to align these imbalances for achieving rapid economic growth, attracting investment and planned spatial transformations.
As a consequence, the level and status of activities under the PPP increase, as defined, on the one hand, by their socioeconomic importance for the region, the increase in the intensity of interaction between actors of the regional economy in the process of their implementation, the submission of their content to the national policy priorities of innovation development, and on the other hand, the elaboration of spatial forms adequate to the changing needs of the population.
Regional specifics influence the structure of PPP through a step-wise and component-wise implementation of activities in their framework in such a way as to fit into the format of the developed strategies and long-term regional development plans, taking into account possible changes in the conditions of their implementation, for example, through the provisions set out in regional target programs.
Consolidation of PPP projects in the provisions of the region’s long-term development plans helps to ensure continuity of government objectives of innovation economic development set out at the federal level and, at the same time, to require the mandatory unity of partnership forms of their implementation, adapted to the objectives from the level of plan to the level of project.
A new public-private partnership model built on the structural independence of consistently interacting socio-economic and spatial components of regional planning and, at the same time, on their purposeful association, is intended to ensure the implementation of regional development plans in coordination with the overall strategic direction of public policies for regional development.
The substantiation of the tools for resource supply of SSPS is based on two schemes of assessing the factors in the region’s development – social factors and market factors, which are reflected in the complex and in accordance with which two analytical blocks – social analysis and market analysis – are formed. Within these blocks specific research operations are carried out simultaneously (in parallel), gradually and consistently; they reveal different features of the regional system functioning. This analysis reveals the complex characteristics that diagnose the status of RES with regard to their potential changes in the most optimal forms.
Based on the systematization of data on the structure of public service, characteristics of the housing stock and classification of consumers, as well as a comprehensive assessment of this information identifies the prospects for changes in the condition of RES described by quantitative and qualitative indicators. To do this the following activities are carried out: the “problematic” elements of RES with defective and inefficient service are revealed; the consequences of placing the service sectors in space that lead to socioeconomic imbalances are identified; market niches are identified (that are not occupied or that are poorly developed, but that have prospects of further development); the percentage ratios of elements of social and commercial services are established. Depending on the combination of the detected signs of change in the status of RES, the motivated degree of intervention of authorized management authorities in the socio-economic and spatial aspects is determined.
The group of regulatory tools can include the subgroups of instruments of regulatory zoning and investment regulation of SSPS [1, 18].
The content of regulatory zoning (RZ) is disclosed within the procedures of endowing the zones with the differentiated status of development and the establishment of appropriate boundaries. Its practical result is the development of regulatory activities that reflect planned changes in the development indicators with different amplitude and the frequency of repeatability of processes by their graphical fixation in special schemes of the region’s zoning.
This ensures the regulated order of socio-economic and spatial intervention through both the increase and the intentional decrease of the attractiveness of the use of separate fragments of RES and identification of the objects of regional development planning necessary to implement public interests.
In order to do this, the work proposes to consider a set of requirements to the regulation of RES development through synchronization of its socio-economic and spatial components, which affects the process of identifying and securing the regulatory zones (so far, similar developments are implemented in practice on the initiative basis; this fact proves that they are only the subject of discussion rather than the regulations enshrined in law).
Among the possible requirements it is necessary to identify the most anticipated ones, such as:
-
• continuity of ways to implement the state policy of spatial development from the level of strategic planning through their integration into regulatory zoning by specifying the directions of transformation of RES with the relevant fixing in the provisions of RZ;
-
• coordination of management decisions on the settlement of the state, social and private interests, which aims to eliminate and prevent conflict situations; the coordination is expressed in the differentiated schemes of management decisions that differ by the lists of regulating measures;
-
• forecast of the indicators of RES utilization with maximum consideration of the set of factors that determine its functioning, preventing the destruction of the spatial integrity of RES, contradiction between the chosen strategy of regional development and the principles of rational resource usage.
These requirements create prerequisites for the transition from direct administrative control to more efficient indirect forms of economic management of the processes of RES development. This transition is most expedient to be made by using regulatory characteristics of RZ, through which the non-segmented territorial mass of RES is differentiated. On the basis of enlarged differentiation the most promising zonal objects from the viewpoint of socio- economic and spatial development are distinguished, which forms the economic basis of zoning.
The establishment and consolidation of forecast economic indicators of RES development in RZ plays a leading role in the context of improving the regulatory principles of regional planning: the allocation of zones of a particular usage type means highlighting and supporting the socio-economic and spatial priorities that collectively determine the way to disclose the strategic vector of RES development.
The prospects of regulatory zoning are determined by the proposed methodological provisions formed on the basis of the combination of the following principles:
– consistency of the proposed typological methods with the spatial organization of RES elements, including the determination of the variability of their functional purpose, defined on the basis of the results of a comprehensive analysis of existing conditions and characteristics of the development of a particular region so that they were as close to the actual existing spatial structure of socio-economic processes with the appropriate types of zones;
– interconnection between the forms of spatial organization of RES elements and their socio-economic content, defined by the specifics of location of regulatory zones, the purpose of the types of their economic use, achieved through a gradual and consistent logic of the process of transformation of zones and objects that does not violate and preserves the existing structural order on the basis of a set of objective factors and prerequisites;
– ranking of the types of economic activity, carried out by taking into account the set of political, historical, cultural, social, demographic, natural landscape, and territorial factors, including the specifics of location, existing types of usage, historically developed combination of functional processes, the potential for possible spatial transformations within the established regulatory zones;
– structuring of RES elements within the regulatory zones in the socio-economic and spatial aspects simultaneously using hierarchical sequential transition from the elements of the upper levels to the lower levels on the basis of the existing organization of RES and future trends of polyfunctional or monofunctional development.
As a result of the combined action of the identified principles the regulatory zoning schemes are prepared, in which the zones are defined that are formed in accordance with the classifier of dominant and auxiliary types of economic use of RES with their quantitative and qualitative characteristics.
Formation of investment tools for regulating the relations of the subjects of the regional economy provides for active involvement of private investment in the processes of regional development, since they implement the potential of the few competitive, cost-effective urban spatial elements of RES [1].
The research into the modern experience of implementing project management solutions conducted by the author shows that the declarative and initiatory investment tools are the most prevalent among investment regulation tools. The logic of using regulatory investment tools is defined by the relationship between the forms of participation of state management authorities and the processes of RES development. Public authorities regulate the process of implementation of territorial projects mainly by direct participation in them, but it does not exclude the creation of special organizational and managerial structures [16].
Due to the targeted impact on the development of RES (stimulating or constraining) it is possible to implement state control in the regions. It is expressed both in the form of increasing the effectiveness of practical implementation of projects in general and also in the continuing emergence of the objects of regional development planning that become a catalyst for the transformation of regional systems.
The process of territorial projects implementation, with the reduction of the degree of participation of authorities, is characterized by the transition of initiatives to private investors, which also expands the investment opportunities of the subjects of regional economy.
The results of research into the world regional practice management prove that under certain conditions (such as economic crisis that causes the limitation of resources of all kinds) it becomes advisable for state authorities to use flexible (compromise) schemes for the implementation of regional development projects. Such schemes based on the principles of combined regulation of the use of public (municipal) and private investment help, depending on the changes in the socio-economic situation, to use them (schemes) in different ways, adapting to changes and thereby achieving performance efficiency.
Since the very fact of fixing the compromise schemes of regulation of RES development processes in relevant planning decisions does not guarantee that they will be implemented, and also the fact that the scheme will not change, it is necessary to provide systematic and comprehensive monitoring of this process, also in the form of aligning of the interests of all the interested parties.
The group of coordinating tools is concentrated in the system of regional monitoring of SSP. Directions of improvement of regional monitoring in the framework of the spatial approach are determined primarily by the fact that the definition of its characteristic stages (operations) such as analysis, evaluation, control, and subsequent determination of their internal content takes into account the specifics of interaction between socioeconomic and spatial components of regional planning.
Depending on how this interaction is carried out, the specifics of SSP tasks and the peculiarities of the technological chain of information circulation are determined. The main emphasis in this modernized monitoring system is placed on the integration of special tools used in the planning of the region’s socio-economic development and in territorial planning. New opportunities are opened for integrated solution of RES management tasks due to the introduction of the system of information description of changes in the state of RES caused by the effects of the implementation of the infrastructure model of its development.
The analysis of theoretical works, as well as direct acquaintance of the author with practical solutions to this problem in some regions of Russia (Moscow, Saint Petersburg, the republics of Tatarstan and Chuvashia, the Samara, Saratov, Rostov and Leningrad oblasts) on examples of existing monitoring services in the regional management system help to find out the following. The existing developments that optimize the monitoring and reveal the specifics of dynamically changing tasks in the regional management system are focused mainly on the improvement of information support as a whole.
If applied to the object and subject of the research, this is connected, first, with defining the content of the basic concept of information [1, 9, 19]. Although this urgent question is rather well studied, experts have not yet reached a consensus yet. This is confirmed by the systematization and analysis of the works on the prospects of information support to regional management processes, taking into account the specifics of the federation subjects and characteristics of the spheres of information usage.
At the same time, many researchers, in particular those who study Volgograd region (A. Kalinin, 2005; D. Dontsov, 2006; Oleinik, 2007; Petrova G., 2008; Sokolov A., 2013), are unanimous in their assessments of current standards of formation of regional monitoring schemes and finding the opportunities for their improvement. They point out the need to supplement the existing regional planning techniques with block schemes of information organization [1, 12, 18].
This means that when state and municipal authorities solve certain management tasks, there emerges the necessity to use special information along with some general information constantly involved in this process. If these informational interaction processes are not structured, and the ways in which state authorities address this information are not designed properly, there can be the cases of inefficient use of resources.
The proposals to improve the regional monitoring system aim to address an important economic problem of resource savings. The block scheme of the organization of information in this regard will help to create a rational system of accumulation, processing and analysis of information, to prevent crossing its flows and a possible imbalance from multiple references of users [12, 19].
The adoption of the block scheme of information arrangement entails the reconsideration of existing attitude toward spatial information – one of its constituent blocks. So far, it is believed that it is necessary to use the information from this block as a support in handling a variety of situational tasks in the regional management system.
This means that the block can be referred to for any kind of visualization of socio-economic processes in the region, as a service. Accordingly, the successful realization of the potential of information is out of the question. A similar spread of this somewhat negative attitude toward this block of information when solving problems of regional monitoring leads in most cases to the fact that its importance is downgraded and, therefore, it is not involved actively in addressing the issues of region’s management.
At present, its functioning is also considered in a fairly narrow, purely special, framework, limited by solving the issues of development and utilization of individual elements of RES, its territories in the implementation of procedures related to the realization of investment intentions of the developers. There have been the ongoing discussions concerning the fact which option of functioning of spatial information block better reflects the fullness of its opportunities in the regional planning system and which is most preferable for its improvement. Given the fact that supplementing information resources of the monitoring with this block is a relatively new requirement to its structural organization, it can be assumed that this conceptual design will be developed further.
The set of modern requirements for information flows in information systems highlights the advantages of market-based relations of the subjects of the regional economy that actively use different kinds of information [9]. Taking into account this requirement, as well as the feasibility of construction of the block scheme of information, it is proposed to integrate the spatial component in socio-economic information. This approach will expand the possibilities of information classification: in addition to existing unification methods it will make it possible to apply the methods of its ranking depending on the objectives of the monitoring: analysis, evaluation, control, acquisition, from the source of information request – the subject of regional economy that defines the volume, content, form and timing of information provision. The proposals relate primarily to the implementation of diversified types of information, which allow it to be used multifunctionally and repeatedly, depending on the areas of its designation, specific functional correspondence, and consumers.
In general, the proposals aimed to improve the regional monitoring system discussed in this work are reduced to the justification of the conceptual scheme of the information monitoring system (IMS). The main feature of designing the principal scheme of IMS functioning is to synchronize information flows – socioeconomic and spatial information and their intersection in the “zones” of managerial decision-making requiring concentration and synthesis of the original data.
Accordingly, IMS has other features. In particular, the process of moving from the initial (incoming) to the final (outgoing) information is optimized in such a way that it is not only limited in time, but it is also not associated with a large and unnecessary amount of labor-intensive and unproductive auxiliary technological operations. Due to the modernization of the structure of IMS, with the allocation in the monitoring scheme of subsystems, corresponding to the stages of the analysis, assessment and control, the content of operations such as collection, documentation, updating, processing, systematization, recording and storage of information is defined strictly, depending on the characteristics of information processes.
The functioning of the IMS is carried out in two main directions corresponding to the stage of fulfillment of characteristic successive operations through their proposed grouping.
The first direction groups the operations of collection, processing, recording, storage, and updating of information; and the second direction deals with the provision of information.
The separation of information in the framework of the second direction is critical, since the category of information request can drastically change the form and content of the output material. It means that their targeting and affiliation with different consumers generates the schemes of information organization, which differ in the number of internal operations, their content, the order of sequence, ways of interaction, etc.
Among such schemes of organizing information it is necessary to distinguish those used for the preparation of legal documents, long-term plans and programs for regions’ development. These cases are characterized by the fact that the information schemes should take into account the dual nature of requirements that proceed from socio-economic and spatial components dictating informational structure of developed materials. Thus, state and municipal authorities involved in this process of development of information schemes can not be completely isolated and independent from each other, as it is currently practiced.
The way of organizing IMS is subject to the requirement of its smooth functioning in terms of diversification of regional development processes, involving different groups of consumers, professional actors of the regional economy and management authorities.
The results of IMS functioning can be manifested in two ways: through the final documents, the use of which by different consumer groups (governments, professional participants of the regional market and average consumers) determines their content; and by providing authorized direct access to information resources to a limited list of users approved by the information system manager.
The fact that authorities comply with the duality of requirements theoretically leads to the fact that of all potentially existing (or possible) operations within the developed information schemes, depending on the specifics of the tasks at hand, one can and should reasonably define the elements of schemes that are really relevant, and, at the same time, exclude the elements that are irrelevant and that complicate their functioning.
The main result of the implementation of this approach to the organization of regional monitoring is expected, in particular, to be the elimination of duplicate functional processes in the regional management system and the emergence of the sets of information blocks adapted to specific model changes of RES.
The use of IMS in the future will help to create the tools for monitoring based on adaptive principles that will ensure the adequacy and efficiency of the planned regional development activities that correspond to the objectives of public administration, and implementation of the mutual interests of the state and population. Such problems can be solved through the development and adoption of the law of the Russian Federation or the law of the subject of the Russian Federation on the improvement of the procedure of formation and provision of information on the development planning of the region.
The combination of the proposed organizing, regulating and coordinating tools forms a system of tool support in the context of a spatial approach to regional planning that implements the strategic direction of the state policy for sustainable innovation development of the regions.
Simultaneously, the system approach to the development of tool support for the SSP is the essence of innovation in the integrated and complex formation of socio-economic and spatial solutions, that determine the content of long-term development plans of the regions, and regulations that ensure their elaboration.
Thus, the system of tool support of SSP depends on the results of assessment of the resources required for RES transformation: intention to implement certain types of transformations initiated by the state authorities, the substantiation of the set of socio-economic and spatial conditions, appropriate forms of disclosure and retention in regional development scenarios.
The practice of modern regional management based on updated planning methodology shows that individual elements of the system of tool support are used in the development and implementation of longterm regional development plans in the RF subjects.
However, the absence of the generally accepted classification of existing diversity of tools, of the unity of the rules of their application, as well as significant differences in socio-economic development in the regions lead to the fact that when determining the set of tools universal schemes show low efficiency. And, as a result, in each case the planning procedures themselves are actually violated, since the subjects of regional economy, in fact, “design” the management tools required for the solution of urgent issues of regional development, and make their ultimate choice not on the basis of criterion assessments, but through random sampling of the most appropriate option as judged by the developers.
It seems impossible to change such practice until the accumulation of considerable experience in the usage of different options for making management decisions on the basis of various tool support planning. And not enough just to increase the amount of such examples, since of no less importance are the qualitative assessment of tools implementation in different federal districts, within which one expects the emergence of a certain trend in choosing their standardized list, which is explained by the comparability of the conditions and factors of RES development.
The research findings presented in this article refer mostly to 2008–2012, when the prospects described were only beginning to emerge and it was possible to speak only about “pioneer” forms of choosing such tools. Trying to solving the problems of combinatorics of the tools out of potential options of their combinations, the author proceeded from actual conditions limited by her practical participation in the development process of respective socioeconomic and territorial development plans for the Volgograd Oblast that was going on in this very period. No less important was the fact that the elaboration of the content of development plans of the Russian Federation subject can not be reduced to the procedures carried out only at the regional level, since this process is directly linked to the planning of development of federal districts and municipal districts.
The author’s involvement in the implementation of municipal contracts for the elaboration of plans for development of municipal districts of the Volgograd Oblast is further confirmation of the viability of the proposed model of tool support to regional planning.
Because the long-term development plans were worked out for the municipal districts comprising the single RF subject, it was decided that the content of the tools used would be relatively uniform, but allowing for variation. The plans that were prepared and approved are currently actively used in the practice of regional management in the Volgograd Oblast. And despite the fact that, in general, their provisions are relatively stable, they possess certain dynamics caused by the changing socio-economic conditions and requirements for regions’ development. This leads to the fact that development plans are adjusted and supplemented.
The composition of management tools will change in accordance with amendments introduced in the plans. Today it can not be argued that the experimental variant of tool support proposed in this work is stable and finished in its original development.
On the contrary, the author connects the prospects for its use with intensification of the practice of design and combination of tools of various compositions, and then, through critical analysis, it will be possible to select standard forms.
The differentiation of elements of the tool support system, as well as their combination, is determined depending on the choice of the type of spatial-strategic initiatives (SSI) – a basic element of spatial strategic planning responsible for the degree of compliance of planned developments with institutional constraints. Tool support is formed in such a way that allows the regional planning system to adapt to the specifics of SSI. For these purposes the author proposes its typological classification in accordance with the groups of management functions: organization – for optimization of legal interaction between the subjects of the regional economy in the format of public-private partnership, supported by actual resource potential; regulation – for appropriate and rapid response of RES to the impact of internal and external factors through investment regulators and regulatory zoning in various forms; monitoring – for accurate and timely reproduction of information about the regional development processes, focusing its performance indicators more on forecasting of potential options than on the statement of accomplished facts, through active involvement of its users in this process, seeking feedback effect.
Список литературы Improvement of tool support of the spatial approach to regional planning: problems, specifics, trends
- Dontsov D.G., Yushkova N.G. Regulirovanie funktsional'no-prostranstvennykh preobrazovanii territorii na osnove informatsionno-upravlyayushchikh system . Nedvizhimost': ekonomika, upravlenie , 2005, no. 11-12, pp. 37-44.
- Douglas N. Instituty, institutsional'nye izmeneniya i funktsionirovanie ekonomiki . Translated from English by A.N. Nesterenko; foreword and scientific editing by B.Z. Mil'ner. Moscow: Fond ekonomicheskoi knigi “Nachala”, 1997. 180 p.
- Evropeiskaya khartiya regional'nogo/prostranstvennogo planirovaniya . Available at: http://docs.cntd.ru/document/902018818 (accessed July 17, 2014).
- Ilyin V.A. Problemy sotsial'no-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya territorii Rossii v post-krizisnyi period . Ekonomicheskie i sotsial'nye peremeny: fakty, tendentsii, prognoz , 2011, no. 5, pp. 9-23.
- Kontseptsiya Strategii sotsial'no-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya regionov Rossiiskoi Federatsii (proekt Ministerstva regional'nogo razvitiya Rossiiskoi Federatsii ot 2005 goda) . Available at: http://www.gosbook.ru/node/48488.
- Kontseptsiya sovershenstvovaniya regional'noi politiki v Rossiiskoi Federatsii (proekt Ministerstva regional'nogo razvitiya Rossiiskoi Federatsii ot 2010 goda) . Available at: http://www.komfed.ru/section_42/475.htm.
- Kontseptsiya dolgosrochnogo sotsial'no-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya Rossiiskoi Federatsii na period do 2020 goda: utv. rasporyazheniem Pravitel'stva RF ot 17 noyab. 2008 g. № 1662-r . Available at: http://base.garant.ru/194365/.
- Lavrikova Yu.G. Strategicheskie prioritety prostranstvennogo razvitiya regiona v setevoi ekonomike . Vestnik UrPGU-UPI , 2008, no. 5, pp. 37-49.
- Ob informatsii, informatizatsii i zashchite informatsii: Federal'nyi zakon ot 20 fevr. 1995 g. № 24 . Rossiiskaya gazeta , 1995, no. 39, February 22.
- Prostranstvennye aspekty razvitiya regiona . Under general editorship of Doctor of Economics, Professor V.A. Ilyin. Vologda: Vologodskii nauchno-koordinatsionnyi tsentr TsEMI RAN, 2008. 298 p.
- Rossiya na puti k sovremennoi dinamichnoi i effektivnoi ekonomike . Ed. by A.D. Nekipelov, V.V. Ivanter, S.Yu. Glazyev. Moscow: RAN, 2013. 93 p.
- Sokolov A.F., Kalinina A.E., Elkhina I.A. Informatsionno-analiticheskie metody monitoringa effektivnosti sistem upravleniya regional'noi ekonomikoi . //Izvestiya Volgogradskogo gosudarstvennogo tekhnicheskogo universiteta. Seriya “Aktual'nye problemy reformirovaniya rossiiskoi ekonomiki (teoriya, praktika, perspektiva)” , 2012, vol. 13, no. 7 (94), pp. 169-179.
- Territorial'no-prostranstvennoe planirovanie: klyuchevoi instrument razvitiya i effektivnogo upravleniya s udeleniem osobogo vnimaniya stranam s perekhodnoi ekonomikoi . Economic Commission for Europe. New York and Geneva: United Nations, 2008. Available at: http://www.unece.org/hlm/documents/Publications/spatial_planning.r.pdf (accessed July 17, 2014).
- Uskova T.V. Upravlenie ustoichivym razvitiem regiona Vologda: ISERT RAN, 2009. 355 p.
- Tatarkin A.I. Programmno-proektnoe razvitie regionov kak uslovie ustoichivogo sotsial'no-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya Rossiiskoi Federatsii . Vestnik UrPGU-UPI , 2011, no. 4, pp. 46-55.
- Flyvbjerg B, Bruzelius N., Rothengatter W. Megaproekty: istoriya nedostroev, pereraskhodov i prochikh riskov stroi-tel'stva . Translated from English. Moscow: Vershina, 2005. 224 p.
- Schmidt-Kallert E. Kratkoe vvedenie v planirovanie na mikroregional'nom urovne . Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Sub-regional Office for Central and Eastern Europe. Budapest, 2005. 83 p.
- Yushkova N.G. Potentsial prostranstvennoi sistemy regiona v opredelenii innovatsionnoi strategii razvitiya territorii . Regiony Rossii: Strategii i mekhanizmy modernizatsii, innovatsionnogo i tekhnologicheskogo razvitiya: Tr. Vos'moi mezhdunar. nauchn.-prakt. konf. , 2012, part 1, pp. 400-406.
- Yushkova N.G. Problemy adaptivnosti planirovaniya razvitiya regional'nykh sotsial'no-ekonomicheskikh sistem . XII Vserossiiskoe soveshchanie po problemam upravleniya (VSPU-2014) Rossiya, Moskva, IPU RAN, 16-19 iyunya 2014 g. . Pp. 5579-5592. Available at: vspu2014.ipu.ru.
- Yushkova N.G., Dontsov D.G. Ispol'zovanie modeli informatsionno-tekhnologicheskogo obespecheniya protsessov innovatsionnogo razvitiya v dokumentakh territorial'nogo planirovaniya . “Modernizatsiya Rossii: klyuchevye problemy i resheniya” materialy XII mezhdunarodnoi nauchnoi konferentsii. 5-6 dekabrya 2012 g. . Moscow: RAN RF. Pp. 156-163.


