Increase of efficiency of symbiotic systems in agrocenoses of north ecotype soya varieties
Автор: Parahin N.V., Kuzmicheva Y.V., Petrova S.N., Botuz N.I., Tychinskaya I.L.
Журнал: Вестник аграрной науки @vestnikogau
Статья в выпуске: 2 (47), 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The investigations on studying the ACC-utilizing bacteria influence on the efficiency of symbiotic systems of different soya varieties are carried out. The stimulatory effect of introduced microorganisms on the formation of nitrogen-fixing symbiosis of plants and local populations of nodule bacteria is proved. Thereby the yield capacity increment reached 2,4…6,3 dt/ha. Thereat the efficiency of the used biopreparations mainly depends on the variety.
Soya, variety, plant-microbial systems, acc-utilizing bacteria, symbiotic nitrogen-fixing
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147124534
IDR: 147124534 | УДК: 633.34:631.559.2:631.461.52:631.461.74
Текст научной статьи Increase of efficiency of symbiotic systems in agrocenoses of north ecotype soya varieties
The cropping capacity growth is impossible without soil microflora, which intensive life activity mainly determines soil fertility. More than that forming the associations and symbioses with cultivated plants, microorganisms provide their water and mineral nutrition, adaptation to abiotic stresses and also pathogens and phytophages protection allowing maximum realization of biological potential at resource expenditures decrease [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]. The most important for agriculture integrated plant-microbial systems (PMS) are the legume-rhisobia, endomycorrhiza and growth stimulating symbioses [6] that being taken separately or in complex are typical only for leguminous crops in connection with their enhanced symbiotrophicity and habitat forming function. At the same time the formation of the effective symbioses is provided by the complex of abiotic and biotic factors including plant varietal individuality and it is possible only at creating favorable conditions for microbiological soil activity that are not often observed in intensive agro technologies.
In this connection the search of methods and ways of increase of symbiotic systems efficiency in agrocenoses of leguminous crops is significantly vital; at this the application of microbiological approaches in connection with intensification negative effects is of special interest.
That is why the goal of our research was to study the influence of microbial drugs on the base of associative ACC-utilizing bacteria on the soya PMS efficiency in the Orel region conditions.
MATERIALS AND RESEARCH METHODS
Laboratory test were done in the Common Use Center (CUC) «Ecological and agrochemical monitoring of agricultural production and environment» of Orel State Agrarian University, and field tests were carried out in Scientific Educational Production Center «Integration» in 2012-2013.
Plants were grown in crop rotation on plots with area of10 m2 in fourfold replication. The method of experimental plots distribution is randomized.
The experimental plot soil is grey forest and slightly acid (рН - 5,4) with average humus content (4,63%), labile phosphorus (12,7 mg/100g of soil) and exchange potassium (8,9 mg/100g of soil).
The research object is two early-ripening soya varieties: Sv a p a (selection of AllRussian Research Institute of Legumes and Groat Crops) and Bara (selection of LLC Company «Soya Complex», Krasnodar).
Mic r o bia l drug s u se d in tes ts a r e s tr a in s of a sso ci a tiv e b a cte r ia h a v in g A C C d e a m in a se activity Pseudomonas oryzihabitans EP4 and Variovorax paradoxus 3P-4, produced in AllRussia Research Institute of Agricultural Microbiology (St. Petersburg). A C C-utilizing bacteria in liquid form were introduced in rows in the sprouting phase (10% sol.). I n th e te st w e u se d general background of fertilizers – 70% the NPK doze, ca lcu la ted f o r p la n n e d y ield ca p a city , in t he f orm of fertiliz e r m ix tu r e w ith p e r ce n tag e cont en t of m ine r a l e le m e nt s 10:26:26.
The tests were carried out according to the following scheme:
-
1. Control (background – NPK 70%);
-
2. Background + Pseudomonas oryzihabitans, st . EP4 ( in t r o d u ctio n i n the sp r o u ting phase);
-
3. Background + Variovorax paradoxus, st . 3P-4 ( in t r o d uct io n in the sprouting p h a se).
RESULTS AND DISCISSION
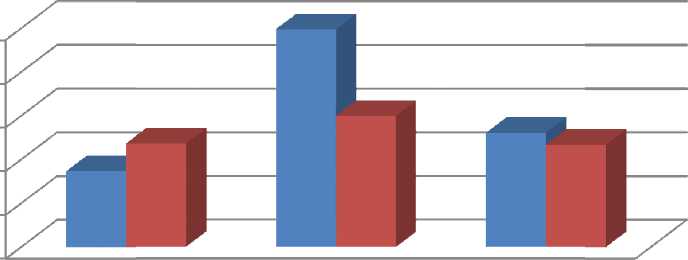
T h e r esu lts of our r e se a rch e s d e m o n s tr ate d r e spo n se of th e in v e stigate d so y a v a r ie tie s to usage of strains of ACC-utilizing bacteria th at p r o d uce d p ositive bio l o gic al e f fec t o n th e plants. It was mainly ob se r v e d in a ctiv a tio n o f th eir in te r actio n wi th ab o r iginal strains of nodule bacteria. At t h is t h e r e a ctio n of th e v a r ie tie s to th e bio lo gic al ag r ic u ltu r a l methods was not similar (Fig. 1).
■ Svapa ■ Bara
Control
Pseudomonas
Variovorax
Figure 1 – Nitrogenase activity of soya depending on application of m icrob i a l d rug s , nM С 2 Н 4 /sol./hour (flowering phase), average 2012 – 2013
According to the two years experimental data of S vap a v a r ie ty the strains of associative bacteria being introduced into rhizosphere provided to geth er with the increase of root nodulation ability the sufficient increase of n it ro ge na se co m p le x a ctiv it y , w hich e x ce e d ed the control value in 1,5…2,9 times. A t th is m a x im u m p osi tiv e e ffe c t w as p rovide d by b a cte r ia Pseudomonas.
S ym bi otic sy ste m o f B ar a v a r ie ty w a s le ss r e sp o n siv e to ch a n ge o f pla n t n ut r itio n conditions but in general it wa s c ha r a cte r i z e d wi th h igh er f unct ion a l a cti vit y in co m p a r iso n with Svapa variety. Thus, nitrogen- f ix in g a ctiv ity of p la n ts o f th e g iv e n var ie ty in cr e a se d o n l y in the variant of introduction into soil bacteria Pseudomonas . It e x ce e de d the control level in 1,3 times. Probably, this variety reaction is co n ne cte d w ith in te n sity a n d co m p o sitio n of p la nt r o ot e x u d a te s th at m a in ly d e te r m in e lif e a ctiv ity an d sy m b io tic a ctiv it y o f s o il microorganisms [7].
Functioning of symbiotic system is closely co n ne cte d w ith p la n t p h o to sy n t h e tic a ctiv ity , which is an energy source for nodule bacteria [8], a nd wh ich is p r ov ed b y th e o b ta in e d results.
Intensification of the symbiotic activity of soya agrocenoses b y m e a ns of r egu la tio n of plant-microbial interactions (PMI) provided increase of both linear and f u nctio n al p a r a m e ters of photosynthetic apparatus. A t th e s am e time so y a v a r ie tie s r e a ctio n to th e ch ang es of nutrition conditions was different (Table 1).
Table 1 – Main indicators of soya photosynthetic activity d ep e ndi ng on co ndi t io ns of plant s nut ritio n (flowering phase), average 2012-2013
|
Variants |
Leaf area, sm2/plant |
Quant um y i el d (Yield), units. |
|
Svapa |
||
|
1. Control (background) |
454,26 |
0,648 |
|
2. Background + Ps.oryzihabitans |
585,22 |
0,702 |
|
3. Background + V. paradoxus |
570,67 |
0,668 |
|
Bara |
||
|
1. Control |
612,98 |
0,652 |
|
2. Background + Ps.oryzihabitans |
944,15 |
0,672 |
|
3. Background + V. paradoxus |
703,44 |
0,674 |
Thus, for example, m a x im u m le a f area su rfa ce e x ce e d in g th e co n t r o l le v e l by 5 4 %, wa s f o r m e d b y B a r a v a r ie ty a s a r e a ctio n to th e in tr o d uc tio n of st r a in of p se ud o m o n a d es Pseudomonas oryzihabitans E P 4 in to the so il. It wa s c on n e cte d with a ctiv a tio n o f p la n t symbiotic activity. Thereto, the efficiency inc r e a s e of primary p r o ce sse s of p h o tosynthesis was detected in the given variant. I t is co n n e c ted wit h th e f act th a t n o dule s b e in g p o w e rf u l attr a ctiv e ce n te r s n e ed in gr e a t n u m b er of p la stic su b sta n ce s to p ro v id e th e ir e n e r gy demands [8, 9].
At the same time the usage of strain Variovorax p ar a do x us 3P -4 also allowed con s ide r a b le in cr e a se o f b iom e t r ica l a n d f u n c ti o n a l p a r a m e ter s of a ssi m ila tin g surf a ce of lea v e s o f th e given v a r ie ty in co m pa riso n w ith con trol w h ich w a s pr o v id e d by gro wth stimulating effect of introduced microorganisms on plants.
I n th e m e a n tim e th e fo r m atio n o f s tr o ng a n d a ctiv e s y m b io tic a p p a r a t u s o f S v a p a variety under the influence of bacteria Pseudomonas in itiat ed c on sid e r a b le in cr e a se o f leaves functional activity at quantum yield increase by 8,3% in co mp a r is on w ith control. At this the leaf area of plants in the given variant was also maximal.
However application of biopreparations on the base of ACC-u tiliz in g b a cte r ia a s th e ma in a g r o tech n o lo gy e le m e n t of th e in v e stigate d v a r ie tie s p r o d u ce d p o sitiv e e ff ect o n th e ir seed productivity (Fig. 2).
The varieties under investigation were responsive to all b iolo giz a tio n m eth o d s, at the same time maximum economic effect was provided by bacteria P se u do m on a s .
Thus, y ie ld ca pa cit y in cr e m e n t o f v a r ie tie s S v a p a an d B a r a a s th e r esu lt of u sing pseudomonades on the average for two years was 6,3 and 2,4 dt/ha, correspondingly exceeding the control level by 26,6 and10,1%.
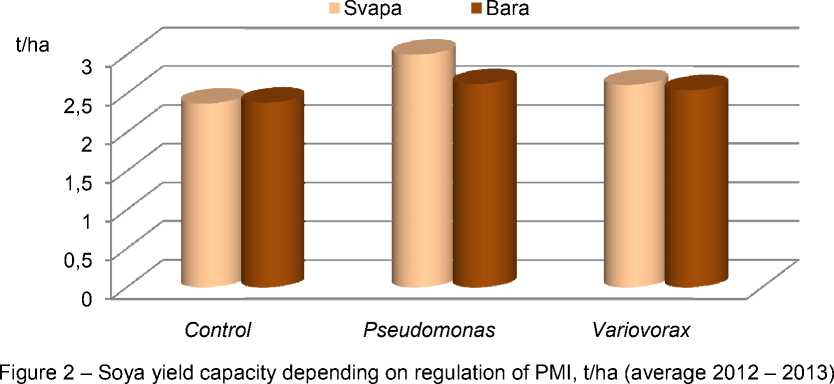
In our opinion this positive economic effect is provided by improvement of metabolic important functions of plants at forming associations with ACC-utilizing bacteria Pseudomonas oryzihabitans, st. EP4.
CONCLUSION
Thus, introduction of ACC-utilizing bacteria into agrocenoses of modern soya varieties of north ecotype in the Orel region conditions allowed efficiency increase of their symbiotic systems on the base of nodule bacteria and maximum realization of productivity potential at the account of symbiotically fixed nitrogen. In this case, the efficiency of the introduced strains of microsymbionts mainly depended on the variety.
Список литературы Increase of efficiency of symbiotic systems in agrocenoses of north ecotype soya varieties
- Tikhonovich I.А. Symbioses of plants and microorganisms: molecular genetics of agrosystems of the future/I.А. Tikhonovich, N.А. Provorov//St. Pb.: Publishers St.-Petersburg of Univ., 2009. -210p.
- Shaposhnikov А.I. Interaction of rhizosphere bacteria with plants: mechanisms of formation and factors of associative symbioses efficiency (survey)/А.I. Shaposhnikov, А.А. Belimov, L.V. Kravchenko, D.М. Vivanko//Agricultural biology. -№3. -2011. -P. 16-22.
- Kuiper I. Rhizoremediation: a beneficial plant microbe interaction/I. Kuiper, E.L. Lagendijk G.V. Bloemberg e.a. -MPMI, №17(1). -2004. P. 6-15.
- Petrova S.N. Resource saving role of plant microbial interactions in plant science: Abstract of a thesis for Doctoral degree in agricultural sciences. -Orel, 2011. -41p.
- Kuzmicheva Y.V. Energy saving methods of increasing productivity of pea varieties (Pisum sativum L.) on the base of plant microbial interactions. Abstract of a thesis for Candidate degree in agricultural sciences.-Orel, 2011. -22p.
- Borisov, А.Y. Plant microbial interactions and their practical importance/А.Y. Borisov, О.Y. Shtark, Т.S. Naumkina and others//The ways to increase agricultural production stability in modern conditions/Materials of All Russian Research-to Practice Conference 13-15 July 2005. -Orel. -2005. -P. 325-348.
- Kravchenko L.V. Role of root exometabolites in integration of microorganisms with plants: Abstract of a thesis for Doctoral degree in biological sciences, М., 2000.
- Sytnikov D.М. Photosynthesis intensity and lectin activity of soya leaves at inoculation by rhizobias together with homological lectin/D.М. Sytnikov, S.J. Kots, S.М. Malichenko, D.А. Kiriziy//Plant physiology. -2006. -Vol. 53. -№2. -P. 189-195.
- Mokronosov А.Т. Photosynthesis. Physiologic-and-ecologic and biologic aspects: Textbook for students of higher educational establishments/А.Т, Mokronosov, V.F. Gavrilenko, Т.V. Zhigalova; edited by I.P. Ermakov. -2nd edition, corrected and added -М.: Publishers Center «Academy», 2006. -448 p.


