Induction of somatic embryo and plantlet regeneration from mature caryopsis culture under NaCl-salt stress conditions in traditional Indian black rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Автор: Rajalakshmi P., Vikrant
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.20, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This study was conducted to establish an efficient in vitro regeneration technique for the induction of somatic embryo and plantlet regeneration under NaCl-salt stress conditions in black rice ( Oryza sativa . L., cv Co57), a traditional Indian cereal food. Embryogenic calli were obtained from mature caryopsis culture on Murashige and Skoog (1962) medium fortified with 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2.0mg/L) either alone or in combination with various concentrations of NaCl (10mM, 25mM, 50mM, and 100mM) in order to induce the salt tolerant somatic embryo differentiation. Furthermore, embryogenic calli were found to show shoot regeneration on MS-medium fortified with 2.0mg/L of 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP) in combination with 0.5mg/L of α-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) and in presence of NaCl (10mM, 25mM, 50mM, and 100mM). Significantly, the high concentration (150mM) of NaCl was proved to be lethal for both somatic embryogenesis as well as plantlets regeneration. Moreover, the low frequency (40.3%) of somatic embryogenesis and minimum number of salt tolerant somatic embryos per callus (3.2±0.1) was recorded with the caryopsis explants that were treated with the high concentration (100mM) of NaCl-salt added embryo induction medium. Significantly, low frequency of salt-tolerant plantlets regeneration (25%) and minimum number of plantlets per embryogenic callus (1.5±0.1) was recorded in the embryogenic callus that was treated with 100mM of NaCl in regeneration medium containing BAP (2.0mg/L) in combination with NAA (0.5mg/L). Further, salinity tolerant plantlets were transferred to soil and gradually acclimatized under growth chamber conditions. This study thus offers a suitable technique for production of salt tolerant black rice, an alternative approach for the traditional Indian black rice crop improvements.
Mature caryopsis, plant growth regulators, somatic embryogenesis, plant regeneration, salinity
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143182801
IDR: 143182801
Текст научной статьи Induction of somatic embryo and plantlet regeneration from mature caryopsis culture under NaCl-salt stress conditions in traditional Indian black rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Rice is the most important food crop world-wide and in Asia more than 90% of rice is being cultivated and consumed as the main food source. Black rice is known as a good source of antioxidant (Yawadio et al ., 2007) and proteins, vitamins such as (niacin, vitamin B, riboflavin) (Ichikwa et al ., 2001; Sompong et al ., 2011; Jang et al ., 2012). The black color of the rice kernel is due to containing high amount of anthocyanin pigment which is present in the aleurone layer, pericarp layer and seed coat (Bolea and Vizireanu, 2017).
Salinity in soil is one of the major abiotic stresses and it thoroughly affects the metabolic activities in plant (Zinnah et al ., 2013). Unfortunately, high salt concentration in the soil and water particularly near the coastal land restricts the production of rice. In recent past, different strategies such as traditional breeding program, tissue culture stress selection approach and genetic engineering have been in practice to produce the salt tolerant crop variety (Ahmad et al ., 2007; Khaleda et al ., 2007; Tariq et al ., 2008; Evangelista et al ., 2009; Abiri et al ., 2015; Rattana and Bunnag, 2015).
Additionally, literature reveals the production of salt tolerant crop varieties through in vitro culture technique has been reported in sugarcane (Mallikarjun et al ., 2008), wheat (Benderradji et al ., 2007), rice (Aditya and Baker, 2006; Prajuabmam et al ., 2009). Moreover, reports on callus formation and plantlet regeneration using immature embryos and mature seeds (Cai et al ., 2013; Azizi et al ., 2015; Kumar et al ., 2017; Binte Mostafiz and Wagiran, 2018), leaf base segments (Ramesh et al ., 2009), microspores (Shariatpanahi et al ., 2006), immature inflorescence (Kavas et al ., 2008), and anthers (Maharani et al ., 2020) are also available.
Plant development through in vitro culture technique depends on some of the factors such as amount and type of plant growth regulators (PGRs) treatments, culture medium components, explant type, solidifying agents, and culture condition etc. (Ge et al ., 2006; Feng et al ., 2011; Parmar et al ., 2012; Ahmad et al ., 2016; Kumar et al ., 2017; Bente Mostafiz and Wagiran, 2018; Repalli et al ., 2019).
This study deals with the induction of somatic embryos under salt stress conditions in black rice food crop followed by regeneration of salinity stress tolerant plantlets using mature caryopsis as explant. Regeneration of salt tolerant rice could be a meaningful approach to achieve production of black rice under salinity conditions of soil and water prevailing near the coastal land. Moreover, this study based on regeneration of salt tolerant black rice is of its first kind of report and thus it would be significant step in rice crop improvement program.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seed collection and Explant Sterilization
To begin with, healthy and dry seeds of black rice ( Oryza sativa L., cv. Co57) were collected from TNAU, Coimbatore (India). The seeds were dehusked and washed by sterile distilled water 2-3 times followed by further sterilization with Tween-20 for 8-10 mins. Rice seeds were washed further with distilled water repeatedly 3-4 times and treated with (70%) of ethanol (v/v) for 1 min followed by rinsing with three to four times with sterile distilled water (SDW).
Seeds were then treated with mercuric chloride (0.1%) for 8-10 mins and rinsed 3-4 times with sterile distilled water. Further, sterilized seeds were dried on autoclaved Whatman paper for 5 mins under laminar air flow cabinet to minimize the chance of water born contamination. The seeds containing embryonic axis were kept away from the medium and scutellum region which is inoculated up position in the nutrient medium.
Nutrient Medium for Embryogenic Callus Induction
Sterilized seeds or caryopses were inoculated in MS (Murashige and Skoog, 1962) medium supplemented with 3% sucrose, 0.8 % agar supplemented with various concentrations of 2,4–D (0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0mg /L). The pH of the nutrient medium was adjusted 5.5 to 5.8 with 1N (NaOH or HCl) and further nutrient medium was autoclaved at 1210C for 20 mins. The culture tubes were incubated under fluorescent light at 5000 Lux with an ambient temperature of 25 ±20 C and maintenance of 16 hours light and 8 hours dark.
Nutrient Medium for Plantlet Regeneration
Embryogenic callus was transferred to MS-medium fortified with sucrose (30g/L) + agar (0.8%) + BAP (0.5,
1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0mg/L) + 0.5mg/L of (α-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) as constant. Moreover, for shoot initiation, non-embryogenic part of callus was removed to obtain the embryogenic part of the callus. After 4-weeks of incubation time, shoot regeneration was obtained from the embryogenic callus. Interestingly, regenerated shoots were later found to show root formation in the same regeneration medium as mentioned above.
Salinity Stress Treatments
In order to induce somatic embryogenesis and identification of the salt tolerant embryogenic callus, mature seeds were inoculated in the MS-nutrient medium fortified with 2,4-D (2.0 mg /L) in combination with various concentrations of (10, 25, 50, 100, and 150 mM) NaCl (Hi – media). Somatic embryogenesis was recorded after 6-weeks period. Due to nutrient deficiency, embryogenic callus was further sub-cultured on the same MS-medium for proliferation and also to check the salt tolerance level of the embryogenic callus.
Salt tolerant embryogenic calli were later transferred to regeneration medium supplemented with various concentrations (10, 25, 50, 100, and 150mM) of NaCl along with (2.0 mg/L of BAP + 0.5 mg/L of NAA) for the selection of the salt tolerant plant regeneration.
Transplantation to Soil
Regenerants grown under control and salt-treated conditions were transferred to the cup soil containing vermiculite, vermicompost and sand (20%, 20%, and 60%) respectively and gradually acclimatized in growth chamber.
Statistical Analysis
Frequency of Somatic embryogenesis (%)=
No. of embryogenic callus
Л 1 v U
Total No. of explants
Frequency of Plantlets Regeneration (%)=
No. of embryogenic callus with plantletregeneration Total No. ofexplantwith embryogeneic callus
X 100
During callus induction, somatic embryogenesis, and plantlets regeneration, 25-30 seeds were used for each experiment and 3 replicates were conducted for each experiment to calculate the mean (%) and (SE) by applying SPSS software.
RESULTS
Induction of Callus and Somatic Embryogenesis
In the control experiment, mature caryopsis was seen to germinate and develop into the mature seedlings within 10 days of culture initiation. Moreover, callus formation was apparent from the base of the germinated seedlings in explants that were treated with various concentrations (0.5mg/L, 1.0mg/L, 2.0mg/L, and 4.0mg/L) of 2,4-D ( Fig. 1A-D ) respectively. The texture of the callus was recorded after 4-weeks of culture initiation. In case of calli obtained from the explants that were growing with 2,4-D (2.0 mg/L), the texture of the calli was appeared to be compact, nodular, and embryogenic ( Fig. 1C ) while lower concentrations (0.5mg/L and 1.0mg/L) of 2,4-D were proved to be less effective for the induction of compact and nodular callus ( Fig. 1A & B ) respectively. Moreover, the colour of the callus was creamy white after 4-weeks of culture initiation, globular structure was formed in the compact callus.
Significantly, when the 2,4-D concentration was increased up to (4.0mg/L), it gradually decreases the embryogenic potential of the callus and the texture of the calli was seen as friable and brownish in colour ( Fig. 1D ). After 4-weeks of culture initiation, embryogenic calli were sub-cultured into the same medium for the proliferation of the embryogenic callus. The highest frequency (90%) of embryogenic callus formation and maximum number of somatic embryos per callus (9.3±0.4) was recorded with the 2,4-D (2.0mg/L) whereas the low frequency (23.3%) of embryogenic callus and minimum number of somatic embryos per callus (1.1±0.1) was obtained with the 2,4-D (4.0mg/L) (Table 1 ).
Somatic embryogenesis under Salinity Stress
In this study, mature caryopsis was used as the explant for the establishment of somatic embryogenesis and the culture was initiated with the concentration of 2,4-D (2.0mg/L) in combination with various concentrations (10mM, 25mM, 50mM, 100mM, and 150mM) of NaCl and after 4-weeks of culture initiation, explants were found to show the embryogenic callus formation.
Embryogenic callus was sub-cultured into the same medium for another 2-weeks for the proliferation of the embryogenic callus and also to obtain the salt tolerant embryogenic callus. Embryogenic callus formation was recorded with the (10mM-100mM) of NaCl treatments.
Moreover, explants that were treated with the low concentration (10mM) of NaCl salt solution, callus texture was seen to be compact and the calli were apparent white in colour (Fig. 1E) . However, with the increase in NaCl concentrations, callus texture was found to be affected by salinity stress and, therefore, with 50mM of NaCl treatments, induced callus was turned out to be less embryogenic ( Fig. 1F ) in nature. Moreover, when the NaCl concentration was increased up to 100mM, it decreases the embryogenesis events (Fig. 1G) . Significantly, the explants that were treated with the very high concentration (150mM) of 2,4-D into NaCl, were emerged as poorly effective to show callus formation including embryogenesis ( Fig. 1H ).
The highest frequency (85.3%) of embryogenic callus was obtained from the concentration 10mM of NaCl and also the maximum number of somatic embryos per callus was found to be (9.2±0.3) while the minimum frequency (40.3%) of embryogenic callus along with number of somatic embryos per callus (3.2±0.1) was obtained with the high concentration (100mM) of NaCl-treatments. Moreover, when NaCl concentration was increased up to 150mM, it was proved to be lethal and the induced callus was failed to show differentiation of somatic embryos (Table 2) .
Regeneration of Plantlets
In order to achieve the plantlets regeneration, embryogenic calli were transferred after 6- weeks of culture initiation into the regeneration medium supplemented with various concentrations (0.5mg/L, 1.0mg/L, 2.0mg/L, and 3.0mg/L) of BAP with constant NAA (0.5mg/L). After 2-weeks of transfer, shoot initiation was visible from the embryogenic callus. The lowest concentration of BAP (0.5mg/L) with NAA (0.5mg/L) gives the minimum number of shoot initiation (merely in form of green spots) from the embryogenic callus (Fig. 2A), while with the further increased concentration of BAP (1.0mg/L) along with NAA (0.5mg/L), green spots were found to be converted into young elongated emerging shoots (Fig. 2B).
However, the maximum number of shoot initiation per callus and the length of the regenerated shoots were obtained with the calli which were growing with BAP (2.0mg/L) and NAA (0.5mg/L) concentration (Fig. 2C) . Significantly, when the concentration of BAP was further increased (3.0mg/L) with NAA (0.5mg/L), callus was found to show inhibitions in the shoot initiation (Fig. 2D) .The highest frequency (80.3%) of plantlet formation was recorded with the BAP (2.0 mg/L) with NAA (0.5 mg/L) and the maximum number of shoot initiation per embryogenic callus (7.7±0.3) was obtained while the lowest frequency (40%) of plantlet regeneration was seen with the BAP (3.0mg/L) in combination with NAA (0.5mg/L) and also the minimum number (1.2±0.1) of shoot initiation was recorded (Table 3). Interestingly , same nutrient medium was proved to be effective for root initiation as well.
Plantlets regeneration under salinity stress
In present study, seeds that were growing with basal medium were found to grow into complete seedlings ( Fig. 3A ) after 2-weeks of culture initiation while the embryogenic calli that were growing in regeneration medium (2.0mg/L of BAP + 0.5mg/L of NAA) were seen to exhibit plantlet regeneration ( FIG. 3B ) after 4-5 weeks of culture initiation.
Moreover, embryogenic calli that were grown under salinity stress conditions and further were transferred to regeneration medium (2.0mg/L of BAP + 0.5mg/L of NAA) added with respective concentrations (10mM, 25mM, 50mM, and 100mM) of NaCl salt solutions, also could show the regeneration of plantlets. Embryogenic callus was sub-cultured once in every 2-weeks in order to obtain multiple-shoot and root formation on the same regeneration medium (2.0mg/L of BAP + 0.5mg/L of NAA) added with respective concentrations of NaCl.
The lowest concentration (10mM) of NaCl was proved to be the least inhibitory for plantlets regeneration and therefore, maximum number of green plantlets formation was observed ( Fig. 3C) . However, highest concentration (100mM) of NaCl in regeneration medium proved to be significantly inhibitory for both shoot and root regeneration (Fig. 3D) .
The highest frequency (79.2%) of embryogenic calli exhibited plantlet regeneration in the nutrient medium containing (10mM) of NaCl and the also the maximum number of plantlets regeneration per embryogenic callus (7.3±0.2) was recorded. Moreover, in contrast, the lowest frequency (25%) of plantlet regeneration was obtained with the calli growing in presence of high concentration (100mM) of NaCl and thus the minimum number (1.5±0.1) of plantlet regeneration per embryogenic callus (Table 4) was recorded.
Transplantation of Regenerants
Regenerated plantlets were washed with sterile distilled water until the agar removed from the rooting part and the plantlets were transferred to the sterile cup containing vermiculite, vermi-compost and sand (20%:20%:60%) and plantlets growing under control and salt-treated conditions were gradually acclimatized under growth chamber conditions (Fig. 3E & 3F) respectively.
Table 1. Effect of various concentrations of 2,4-D on the frequency of somatic embryogenesis from mature caryopsis culture in black rice (Oryza sativa L.).
|
Concentration of 2,4-D (mg/L) |
Mean frequency of somatic embryogenesis (%) |
No. of Somatic Embryos/Callus (Mean ± SE) |
|
0.5 |
30.0 |
2.0 ±0.2 |
|
1.0 |
56.6 |
3.5±0.3 |
|
2.0 |
90.0 |
9.3±0.4 |
|
3.0 |
80.0 |
5.7±0.3 |
|
4.0 |
23.3 |
1.1±0.1 |
Table 2. Effect of various concentrations of NaCl with 2,4-D (2.0mg/L) on the frequency of somatic embryogenesis from mature caryopsis culture in black rice ( Oryza sativa L.).
|
Concentration of NaCl (mM) with 2,4-D (2.0 mg/L) |
Mean frequency of somatic embryogenesis (%) |
No. of Somatic Embryos/Callus (Mean ± SE) |
|
Control |
90.0 |
9.3±0.4 |
|
10 |
85.3 |
9.2±0.3 |
|
25 |
77.2 |
7.8 ±0.2 |
|
50 |
63.3 |
6.1±0.2 |
|
100 |
40.3 |
3.2±0.1 |
|
150 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
Table 3. Effect of various concentrations of BAP in combination with NAA (0.5mg/L) on the frequency of plantlets regeneration from the embryogenic callus induced during mature caryopsis culture in black rice ( Oryza sativa L.).
|
Concentration of BAP (mg/L) with NAA (0.5 mg/L) |
Mean frequency of somatic embryogenesis (%) |
No. of Regenerated Plantlets/Embryogenic Callus (Mean ± SE) |
|
0.5 |
51.7 |
3.1±0.1 |
|
1.0 |
70.0 |
5.6 ±0.2 |
|
2.0 |
80.3 |
7.7±0.3 |
|
3.0 |
40.0 |
1.2±0.1 |
|
4.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
Table 4. Effect of various concentrations of NaCl in combination with BAP (2.0 mg/L) and NAA (0.5 mg/L) on plantlet regeneration from the embryogenic callus induced during mature caryopsis culture in black rice ( Oryza sativa L.)
|
Concentration of NaCl (mM) with BAP (2.0 mg/L) and NAA (0.5 mg/L) |
Mean frequency of somatic embryogenesis (%) |
No. of Regenerated Plantlets/Embryogenic Callus (Mean ± SE) |
|
Control |
80.3 |
7.7± 0.3 |
|
10 |
79.2 |
7.3 ±.0.2 |
|
25 |
70.4 |
5.7± 0.2 |
|
50 |
50 |
3.0± 0.1 |
|
100 |
25 |
1.5±0.1 |
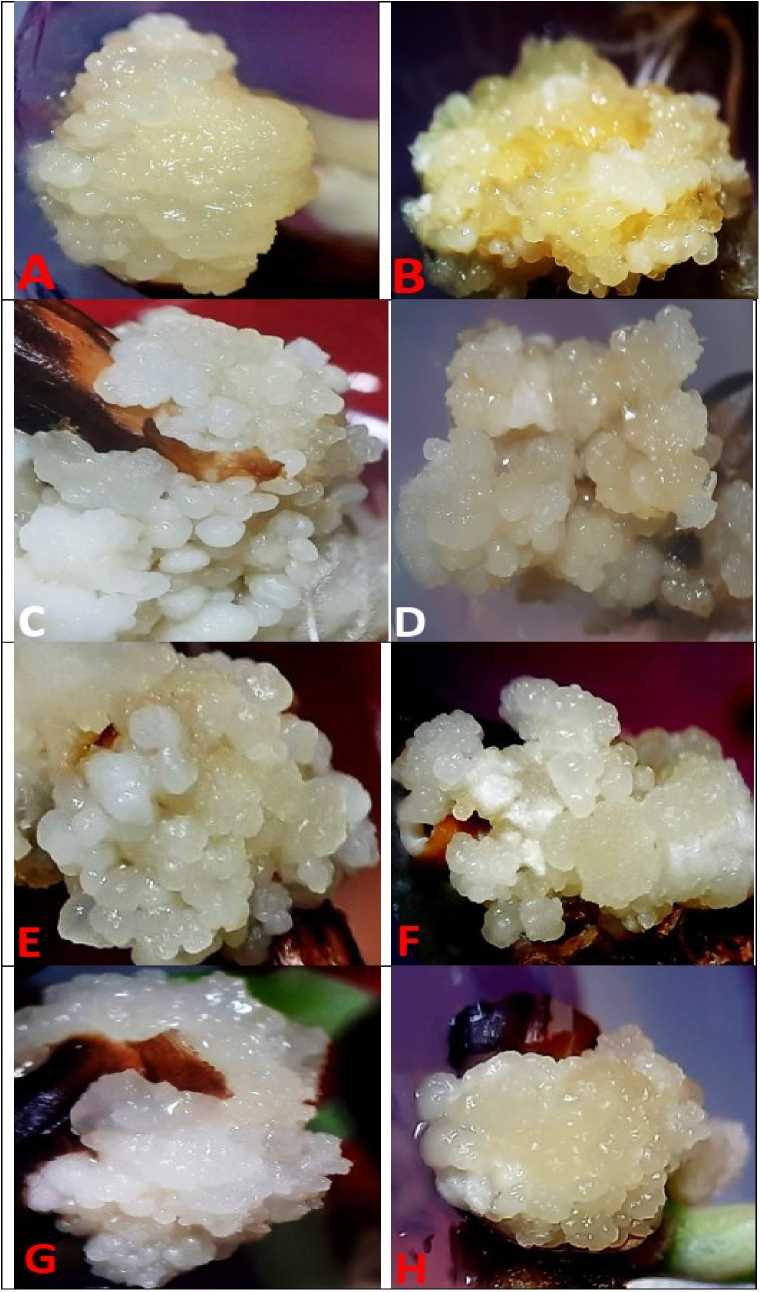
Figure 1. Black rice ( Oryza sativa L.) ; Mature caryopsis culture showing effects of salinity stress on somatic embryogenesis; (A) 2,4-D (0.5 mg/L) (B) 2,4-D (1.0 mg/L) (C) 2,4-D (2.0 mg/L) (D ) 2,4-D (4.0 mg/L) (E ) 2,4-D (2.0 mg/L) + 10mM of NaCl (F ) 2,4-D (2.0 mg/L) + 50mM of NaCl (G) 2,4-D (2.0 mg/L) +100mM of NaCl (H) 2,4-D (2.0 mg/L) +150mM of NaCl salt treatments (after 6-weeks of culture initiation).
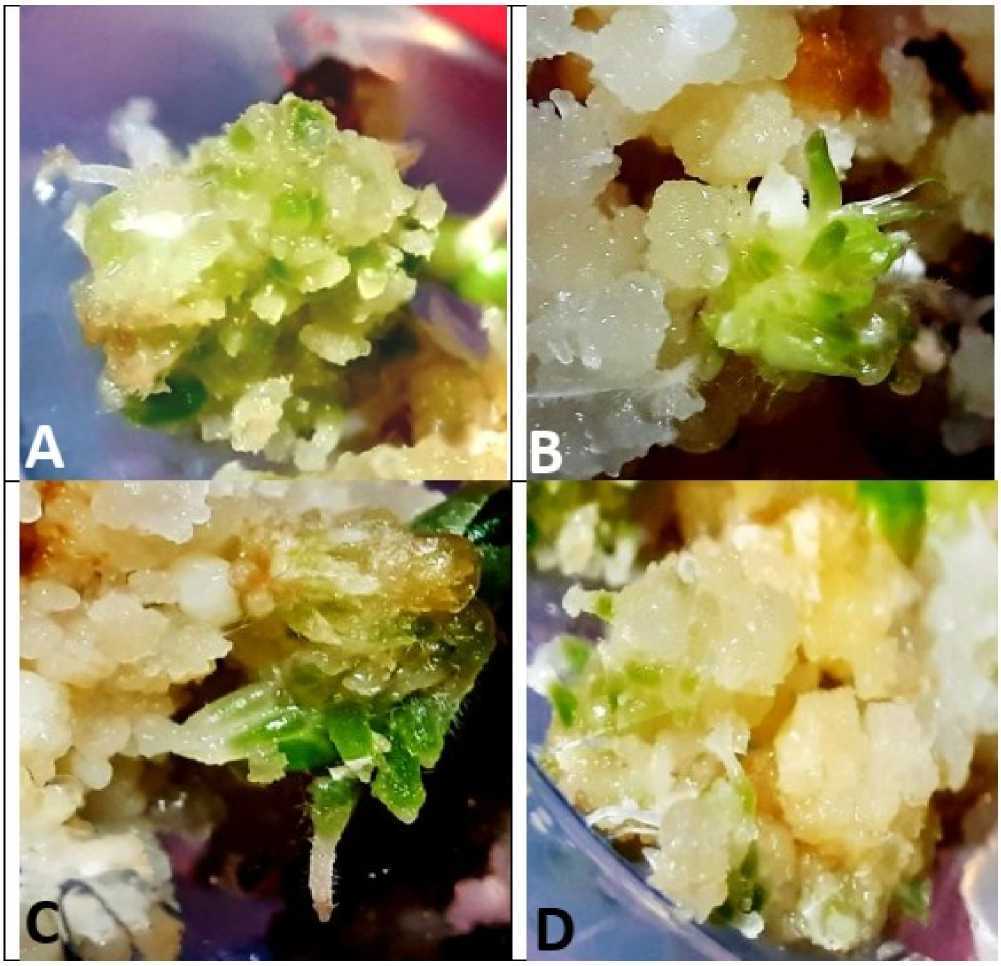
Figure 2. Black rice ( Oryza sativa L.)- Mature caryopsis culture showing effects of various concentrations of BAP in combination with NAA (0.5mg/L) on plantlets regeneration; (A) 0.5mg/L (B) 1.0mg/L (C) 2.0mg/L (D) 3.0mg/L (after 2-weeks on transfer of embryogenic callus to regeneration medium).
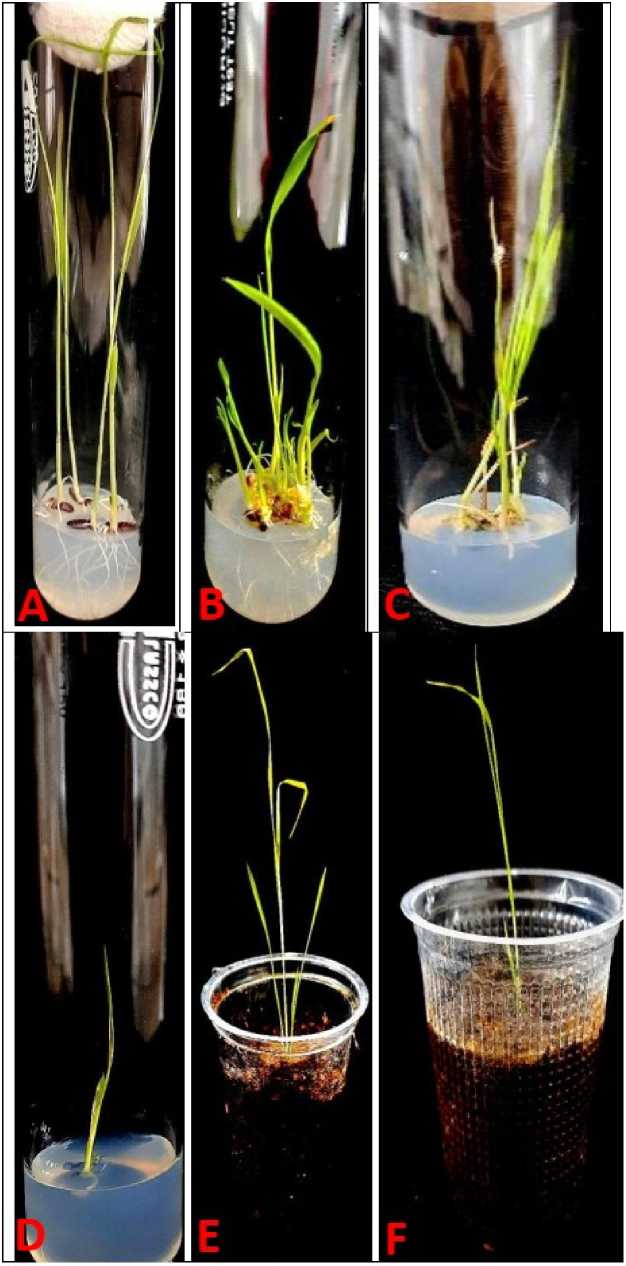

Figure 3. Black rice ( Oryza sativa L.)- Mature caryopsis culture showing effects of various concentrations of NaCl in combination with BAP (2.0mg/L) and NAA (0.5mg/L) on plantlets regeneration; (A) Normal seedling development from mature caryopsis culture on basal medium (B) 2.0mg/L of BAP + 0.5mg/L of NAA (C) 10mM of NaCl (D) 100mM of NaCl (E) Hardening of normal regenerated plantlet (F) Hardening of salt tolerant regenerated plantlet (After 4-weeks of plantlets regeneration).
DISCUSSION
It is expected that world population would to reach about 9.1 billion by the year 2050, so the production of food is required to be increased by 70% to meet the requirements and therefore, food production worldwide needs to be increased by 60-110% (Tilman et al ., 2011; FAO, 2009; 2012).
Due to drought, salinity, and submergence tolerance stress in rice field is a primary challenge for the production of rice yield therefore stress tolerant rice production is major priority for the world population (Grover et al ., 2000). Amongst various ionic species (Na, Ca, Cl, SO 4 , and HCO 3 ), NaCl is the most dominant ion present in the saline soil condition (Akbar and Ponnam-peruma, 1982). Moreover, the salt added to water or soil gives the secondary osmotic stress to the plant (kirst, 1977).
Moreover, when the soil contains very high concentration of NaCl, it leads to the hyperosmotic stress to the plant and it consequently leads to reduction in nutrient absorption by the plant (Wani et al ., 2010).
Effect of Plant Growth Regulators on Embryogenic Callus Induction
In previous study, callus formation could be observed with 2mg/L of 2,4-D in combination of 1mg/L of NAA supplemented nutrient medium and moreover, the callus was induced after 21 days of culture initiation (Evangelista et al ., 2009). Significantly, the high percentage (75%) of callus induction during mature embryo culture was obtained with 2,4-D (3.0mg/L) for Chini kanai (local variety) of rice while in other cultivar of rice (BRRI Dhan38) same frequency of callus induction was obtained with high 2,4-D (5.0mg/L) (Zinnah et al ., 2013).
As per only solitary report available in black rice , embryogenic callus was obtained from the anther in the combination of the hormone (2.0mg/L of NAA + 0.5 mg/L of kinetin + 20µM of putrescine) in Indonesian black rice and the callus was kept in the dark condition for 4-6 weeks culture induction period (Maharani et al ., 2019).
Significantly, results reveal in present study indicate that 2.0mg/L of 2,4-D alone was good enough to induce very high frequency (90%) of embryogenic callus formation and also the maximum number of somatic embryos per callus (9.3±0.4) in Indian black rice (cv. Co57). Moreover, high concentration (4.0mg/L) and low concentration (0.5mg/L) of 2,4-D in present study were turned out to be strongly inhibitory and therefore, 23.3% and 30% respectively of mature caryopses could show callus formation with differentiation of somatic embryos.
Somatic embryogenesis under salinity stress
Previous study in rice, callus formation was obtained in presence of 2,4-D (2.5 mg/L) + KIN (0.5 mg/L) and after 4-weeks of culture, induced callus was subcultured into the different concentrations of NaCl to identify the weight of the callus and after another 4-weeks, callus was transferred into the regeneration medium. Once the NaCl concentration present in the medium increases it sharply decreases the fresh weight of the callus (Wani et al ., 2010).
Moreover, earlier study on mature embryo culture, callus was induced after 3 weeks with 2,4-D (2.0mg/L) in the dark conditions and after 3-weeks, the callus was sub-cultured into the different concentrations of NaCl for 4-weeks in order to check the proline content (Shankhdhar et al ., 2000).
In case of mature seed culture in rice cultivars (BRRI dhan32, BR10, and BRRI dhan47) for the formation of the salt tolerant somatic embryo formation and the embryos were formed with the concentrations (2.5 mg/L of 2, 4-D and 1.0 mg/L of KIN) and 4 to 5 weeks old embryogenic callus were transferred into different concentrations of the NaCl (2.9, 5.9, 8.8, 11.7g/L) (Siddique et al ., 2014).
However, present study involves the application of NaCl (10mM-100mM) with the beginning of the callus initiation in callus induction medium containing (2mg/L) of 2,4-D. Moreover, somatic embryogenesis was recorded maximum (85.3%) in presence of 10mM of NaCl. Significantly, 100mM of NaCl resulted the induction of salt tolerant embryogenic callus (40.3%) while further increase in NaCl (150mM) concentration was proved to be lethal for both induction of callus and somatic embryos. Interestingly, report on induction of somatic embryos under NaCl-salinity stress conditions in black rice is completely lacking.
In another study, salt tolerant callus formation 2, 4-D (2.0 mg/L) was possible keeping in the dark for 30 days and the callus was sub-cultured into the same medium with different concentration of the NaCl. Moreover, salt tolerant callus was again sub-cultured into the same NaCl concentrations in order to check the salt tolerant line and the callus was sub-cultured into the regeneration medium (Kalhori et al ., 2017). Of late, mature seed of black rice (cv. CHAK HAO-AMUBI) was used for in vitro mutagenesis by using EMS (0.00.015%) in regeneration medium (Tripathy et al ., 2022)
Plantlet Regeneration from Embryogenic callus under Salinity Stress
In previous study, after 4-weeks shoot induction formed from the concentration 2.0mg/L (KIN) + 1.0 mg/L (BAP) and the percentage of shoot induction in control (82%) was found to be higher than 50mM (44%) and it was followed by 100 mM NaCl (15%) and after 4-weeks root induction formed from the concentration (0.5mg/L of BAP, 1.0mg/L of KIN, 1.0 mg/L of IBA, and 0.5mg/L of NAA) (Kalhori et al ., 2017).
To obtain plant regeneration, in earlier study, 4-week-old salt tolerant callus was transferred into the regeneration medium with the different concentrations of kinetin with 1.0mg/L NAA+2.0mg/L BAP added with different concentrations of NaCl. After 4-weeks, BRRI 38 cultivar was found to support regeneration (20%) with 50mM of NaCl and (0%) in 150mM NaCl concentration and similarly, Chini kanai cultivar gives (20%) regeneration with 100mM while with 200mM of NaCl, there was no plantlet regeneration (Zinnah et al ., 2013).
Furthermore, plant regeneration from salt tolerant callus was obtained at the concentration BAP (0.5 mg/L) with different concentrations of NaCl (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0%) after 3-4 weeks (Shankhdhar et al., 2000). After mention as 3-months, plantlet regeneration formed from the embryogenic calli that were transferred into the Linsmaier and Skoog (LS) medium added with 2.0 mg/L BA and 10mg/L NAA and the embryogenic calli were further sub-cultured into the fresh medium to obtain regenerated plantlets (Evangelista et al., 2009)
An earlier study, PAU201 and PR116 cultivars were used for shoot initiation formed with the concentrations (2.0mg/L of BAP + 0.5 mg/L of KIN + 0.5 mg/L of NAA) after 4-weeks of incubation period and the rooting was initiated from the basal medium. When the NaCl concentration in the medium was increased then the fresh weight of the callus in the medium was found to be decreased (Wani et al ., 2010).
Moreover, present study reveals plantlet regeneration were formed from the concentration (2.0mg/L of BAP + 0.5 mg/L of NAA) with different concentrations of NaCl (10mM-100mM). However, plantlet regeneration was recorded maximum (79.2%) in the presence of 10mM of NaCl. Significantly, minimum frequency of plantlet regeneration was recorded (25%) in the presence of 100mM of NaCl. During present study, regenerated plantlets under control and salt-treated conditions were gradually acclimatized in growth chamber.
CONCLUSION
In vitro tissue culture technique could be proved effective to produce the salt tolerant black rice crop (Co57) variety. In this study, salt tolerant callus induction, somatic embryogenic formation, and plantlet regeneration were achieved in order to grow salt tolerant black rice crop for the coastal land. Additionally, developed protocols of somatic embryogenesis and plantlets regeneration under salinity stress conditions in present study could be significant for the selection of salt-tolerant transgenic black rice.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are thankful to the Tamil Nadu Agriculture University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu (India) for generous supply of black rice seed (cv. Co57) for the present research study.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Induction of somatic embryo and plantlet regeneration from mature caryopsis culture under NaCl-salt stress conditions in traditional Indian black rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- Abiri, R., Alireza, V., Mahmood, M., Noor Azmi, S., Mahbod, S., ZY, Y., Narges, A., and Daryush, T. (2015). A critical review of the concept of transgenic plants: insights into pharmaceutical biotechnology and molecular farming. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol, 18, 21-42.
- Aditya, T.L. and Baker, D.A. (2006). Selection of salty tolerant somaclones from indica rice through continues in vitro and ex vitro sodium chloride stress. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 11, 349357.
- Ahmad, F.I., Wagiran, A., Abd Samad, A., Rahmat, Z., and Sarmidi, M.R. (2016). Improvement of efficient in vitro regeneration potential of mature callus induced from Malaysian upland rice seed (Oryza sativa cv. Panderas). Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 23, 69-77.
- Ahmad, M.S.A., Javed, F., and Ashraf, M. (2007). Iso-osmotic effect of NaCl and PEG on growth, cations and free proline accumulation in callus tissue of two Indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Plant Growth Regul., 53, 53-63.
- Akbar, M. and Ponnamperuma, F.N. (1982). Saline soil of south and Southeast Asia - potential rice cultivars. In: Proceedings of the 3 rd. International Symposium on Genetic Aspects of Plant Mineral Nutrition, Braunschweig., Germany, 37.
- Azizi, P., Rafii, M.Y., Mahmood, M., Hanafi, M.M., Abdullah, S.N.A., Abiri, R., and Sahebi, M. (2015). Highly efficient protocol for callogenesis, somagenesis and regeneration of Indica rice plants. Com. Ren. Boil., 338,463-470.
- Benderradji, L., Bouzerzou, H., Djekoun, A., Yekhlef, N., and Benmahammed, A. (2007). Effects of NaCl stress on callus proliferation and plant regeneration from mature embryos of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars Mahon Demias and Hidhab. Plant Tissue Culture and Biotechnology., 17, 1927.
- Binte Mostafiz, S. and Wagiran, A. (2018). Efficient callus induction and regeneration in selected indica rice. Malaysia. Agron.,8, 77.
- Bolea, C. A. and Vizireanu, C. (2017). Polyphenolic content and antioxidant properties of black rice flour. Annals of the University Dunarea de Jos of Galati, Fascicle VI: Food Technology, 41(2), 75-85.
- Cai, X., Wang, G., and Cao, W. (2013). In vitro induction and proliferation of callus from immature cotyledons and embryos of Juglans regia cv.'Xiangling'. Notulae Botanicae, Horti Agrobotanici, Cluj-Napoca.,41, 378-384.
- Evangelista, F.C., Aldemita, R.R., and Ungson, L.B. (2009). Callusing and regeneration potential of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes towards the development for salt tolerance. J Sci., 138(2), 169176.
- Feng, X., Zhao, P., Hao, J., Hu, J., Kang, D., and Wang, H. (2011). Effects of sorbitol on expression of genes involved in regeneration of upland rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell, Tissue Org. Cult.,106, 455-463.
- Ge, X., Chu, Z., Lin,Y., and Wang, S. (2006). A tissue culture system for different germplasms of indica rice. Plant Cell Reports, 25, 392-402.
- Grover, A. and Minhas, D. (2000). Towards production of abiotic stress tolerant transgenic rice plants: Issues, progress and future research needs. Proc Indian Natn Sci Acad (PINSA) B66., 13-32.
- Ichikawa, H., Ichiyanagi, T., Xu, B., Yoshii, Y., Nakajima, M., and Konishi, T. (2001). Antioxidant Activity of Anthocyanin Extract from Purple Black Rice. Journal of Medicinal Food., 4(4), 211-218.
- Jang, H.H., Park, M.Y., Kim, H.W., Lee, Y.M., Hwang, K.A., Park, J. H..... Kwon, O. (2012). Black rice (Oryza sativa L.) extract attenuates hepatic steatosis in C57BL/6 J mice fed a high-fat diet via fatty acid oxidation. Nutrition and Metabolism, 9(1), 27.
- Kalhori, N., Nuli, R., Rusea, G.O., Zulkifly, S., Azizi, P., and Abiri, R. (2017). Selection, characterizations and somatic embryogenesis of Malaysian salt -tolerant rice (Oryza sativa L.) cv. MR219) through callogenesis. International Journal of Agriculture & Biology., vol. 19, 157-163.
- Kavas, M., Oktem, H., and Yucel, M. (2008). Factors affecting plant regeneration from immature inflorescence of two winter wheat cultivars. Biol. Planta., 52, 621-626.
- Khaleda, L., Ahmed, A., Marzan, L., and Al-Forkan, M. (2007). Identification of callus induction and plant regeneration responsiveness in presence of NaCl in in vitro culture of some deepwater rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Asian J Plant Sci., 6, 36-41.
- Kirst, G.O. (1977). Coordination of ionic relations and mannitol concentrations in the euryhaline alga Platymonas subcordiformis after osmotic shocks. Planta, 135, 69-75.
- Kumar, R., Mamrutha, H.M., Kaur, A., Venkatesh, K., Grewal, A., Kumar Raj., and Tiwari, V. (2017). Development of an efficient and reproducible regeneration system in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants., 23, 945-954.
- Maharani, A., Fanata, W.I.D., Laeli, F.N., Kim, K.M., and Handoyo, T. (2020). Callus Induction and Regeneration from Anther Cultures of Indonesian Indica Black Rice Cultivar. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol., 23, 21-28.
- Maharani, A., Fanata, W.I.D., Laeli, F.N., Kim, K.M., and Handoyo, T. (2019). Callus Induction and Regeneration from Anther Cultures of Indonesian Indica Black Rice Cultivar. Crop science., 23(1), 21-28.
- Mallikarjun, K., Hanchinal, R.R., and Nadaf, H.L. (2008). Ethyl Methane Sulphonate (EMS) induced mutation and selection for salt tolerance in sugarcane in vitro. Indian Journal of plant physiology, 13, 44-48.
- Parmar, S.S., Sainger, M., Chaudhary, D., and Jaiwal, P.K. (2012). Plant regeneration from mature embryo of commercial Indian bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants., 18, 177-183.
- Prajuabmon, A., Theerakulpisut, P., Kijwijan, B., Muangsan, N. (2009). In vitro investigation on salt tolerant characteristics of rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L). Research Journal of Agriculture and Biological Science.,5, 423-427.
- Ramesh, M., Murugiah, V., and Gupta, A.K. (2009). Efficient in vitro plant regeneration via leaf base segments of indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Indian J. Exp. Bot, 47, 68-74.
- Rattana, K., and Bunnag, S. (2015). Differential salinity tolerance in calli and shoots of four rice cultivars. Asian J. Plant Sci., 7, 48.
- Repalli, S., Geda, C., NSN, P., and G R. (2019). Influence of Media Type and Carbon Source on Callus Induction and Regeneration Response of Different Indica Rice Genotypes. Adv. Crop Sci. Tech 7, 2. DOI: 10.4172/2329- 8863.1000425.
- Saharan, V., Ram, C., Yadav, Neelam, R., Yadav, Bishnu, P., Chapagain. (2004). High frequency plant regeneration from desiccated calli of indica rice (Oryza sativa L), India. African Journal of Biotechnology, Vol 3 (5), 256-259.
- Shankhdhar, D., Shankhdhar, S.C., Mani, S.C., and Pant, R.C. (2000). In vitro selection for salt tolerance in rice, India. Biologia Plantarum, 43(3), 477-480.
- Shariatpanahi, M.E., Belogradova, K., Hessamvaziri, L., Heberle-Bors, E., and Touraev, A. (2006). Efficient embryogenesis and regeneration in freshly isolated and cultured wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) microspores without stress pre-treatment. Plant Cell Reports, 25, 1294-1299.
- Siddique, A.B., Ara, I., Shahinul Islam, S.M., and Tuteja, T. (2014). Effect of air desiccation and salt stress factors on in vitro regeneration of rice (Oryza sativa L.), India. Plant Signaling & Behavior.Vol.9, Issue 12.
- Sompong, R., Siebenhandl-Ehn, S., Linsberger-Martin, G., and Berghofer, E. (2011). Physico-chemical and antioxidative properties of red and black rice varieties from Thailand, China and Sri Lanka. Food Chemistry, 124(1), 132-140.
- Tariq, M., Ali, G., Hadi, F., Ahmad, S., Ali, N., and Shah, A.A. (2008). Callus induction and in vitro plant regeneration of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under various conditions. J. Biol. Sci., 11, 255-259.
- Tilman, D., Balzer, C., Hill, J., and Befort, B.L. (2011). Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A., 108, 20260- 20264.
- Tripathi, S.K., Panda, S., and Kiran, K. (2022). In vitro chemical mutagenesis of Manipuri Fragrant Black Rice cv. CHAK HAO-AMUBI. Agric Res J., 59(3), 537-544.
- Wani, S.H., Lone, A.A., Da silva, T., and Gosal, S.S. (2010). Effects of NaCl stress on callus induction and plant regeneration from mature seeds of rice (Oryza sativa L.). The Asian and Australasian Journal of Plant Science and Biotechnology, 4(1), 57-61.
- Yawadio, R., Tanimori, S., and Morita, N. (2007). Identification of phenolic compounds isolated from pigmented rices and their aldose reductase inhibitory activities. Food Chemistry., 101(4), 16161625.
- Zinnah, K.M.A., Zobayer, N., Saif, U., Sikdar., Lutfun Nahar Liza, M.D., Chowdhury, A.N., and Ashrafuzzaman, M. (2013). In Vitro Regeneration and Screening for Salt Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). International Research Journal of Biological Sciences., Vol. 2(11), 29-36.


