Information support of a vehicles preventive system
Автор: Bulgakov Nikolai F., Kovalenko Vasiliy V.
Журнал: Журнал Сибирского федерального университета. Серия: Техника и технологии @technologies-sfu
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.6, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This article consider of automation in information support prevention system. Automation consist in creating of a program for quality improvement operating control prevention system of vehicles. Describes the methods of work in the program, its possibilities and prospects for the future.
Prevention system, management of technical service, operating control, information technology
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146114732
IDR: 146114732 | УДК: 656.07
Текст научной статьи Information support of a vehicles preventive system
Work of a vehicles represents continuous process. For maintenance of an efficient condition of a vehicles, at operation, the technical service of the enterprise spends planned maintenance service, according to accepted 2 step system of preventive maintenance. However, as shows the experience, it is not enough one planned works and existing system of preventive maintenance (maintenance service system (MS) and repair) demands additional researches and perfection. On Fig. 1 the diagramme relative frequency of operating repair between planned works MS for the bus of mark MAZ-103 operating in conditions of Krasnoyarsk. In addition to this did not improve the existing technologies of prevention of the bus there is not a uniform loading of production of the enterprise. As consequence there are situations when the service zone is overloaded by sudden refusals and descents of buses before an exit in a line, at operation. The overload of the manufacture is reflected in: the information support system of the enterprise, the shortage of staff, the additional costs of current repairs (CR), increase in the intensity of work, lack of needed spare parts. Therefore the existing system of preventive maintenance of a vehicles demands studying and perfection.
The problem decision
To change the current situation has been proposed algorithm design of technical regulation for a vihicles [2]. In the basis, which is a theory of information, regulatory, institutional and mathematical software. With the consideration of the proposed algorithm has been proposed a model of management of the system of prevention as a system of mass service, see Fig. 2. In the given model the entering
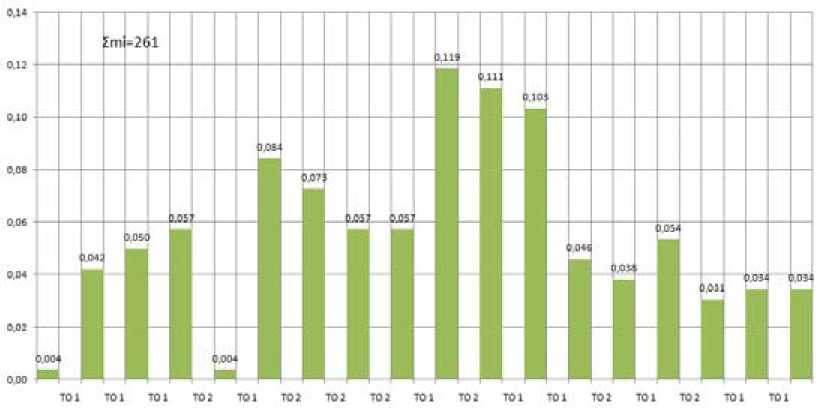
Fig. 1. Diagram of particular current (alarm) between planned repair works for MS bus MAZ-103
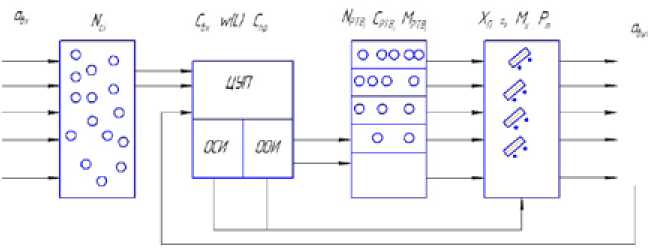
Fig. 2. Model of management of the system of prevention as a system of mass service stream is represented not as the chaotic process occurring during the casual moments of time, but as a stream of planned versions of technical influences (TI).
At work of the this model receipt of sudden refusals arrives in control centre of manufacture (CCM) which consists of department of gathering the information (DGI) and department of processing the information (DPI). The accumulated information of refusals and descents of a vehicles will allow to improve existing preventive maintenance system through the development of new steps of a variety of technical impact (VTI-1, VTI-2, VTI-3, etc.) basis on the received indicators of reliability, durability and maintainability. After CCM the entering stream is represented as a stream of demands for planned maintenance service. Therefore the information on a leaving stream, on existing channels of service and efficiency of service as arrive in CCM for the purpose to estimation the efficiency of the accepted maintenance service system of a vehicle. For today of function CCM carry out enterprise divisions: technological department (TD), operation department, a warehouse, accounts department. For minimization of expenses for management of preventive maintenance system it is necessary to allocate the elements participating in decision-making on perfection of preventive maintenance system, and – 204 – departments requiring the given information to form ready reports and inquiries. It will be possible at the developed system of a information supply of the enterprise.
For maintenance the efficiency to work of the offered model at the enterprise the information supply system should function in the enterprise. The information supply consists in gathering and processing of the information necessary for acceptance of proved administrative decisions.
The transfer of information on the situation and the activities of production to the highest level of management and mutual exchange of information between all interrelated units of the company are made on the basis modern computing technology and other technical means of communication. The various information and technical innovations should be seen as a means of reducing and reduction of price of the government apparatus of production.
Much of the information on the enterprise shall be subject to processing, storage, transfer, collection, bringing to users, the rest of the information comes from external sources or generated in production. Thus we can speak about the processes of circulation and processing of the information (information processes).
Information technology is based and depends on the technical, software, information, methodological and organizational support. Technical support – the personal computer, office equipment, communication lines, equipment networks. The software, which is in direct dependence on the technical and information support, implements the functions of collection, processing, analysis, storage, interface with the computer. Information support – the totality of the data, presented in the form specified for computer processing. Organizational and methodological support represent a complex of measures aimed at the functioning of the computer and the software to get the required result.
For functioning maintenance at the enterprise of information supply system it is necessary to execute a number of a spadework:
-
– to make algorithm of gathering the information;
-
– to develop databases: the carried out works, used spare parts, refusals and descents of the vehicle, executors, etc.;
-
– to create the automated workplaces (AWP) where there is a gathering, accumulation, storage and processing of the received information.
Taking into account the done work the algorithm of gathering information at the motor transportation enterprise has been developed Fig. 3 see.
According to the developed algorithm information gathering consists of 4 stages of its formation.
The first stage assumes record creation. Record of the primary information thus is supposed. And it: route number, garage number, time of arrival for service, the arrival reason, character of display of arrival (sudden, planned), a technical resource (indications of a speedometer or norm of a business hour), the driver, and in the developed program occurs not filling of this information, and its choice from available databases on each requirement that promotes fast filling of a leaf and reception of the exact information.
At the second stage the information on the reason of arrival of vehicle is brought.
The third stage is filling of the information on the executed works: the maintenance of works, a kind of works, executors, labour input, the beginning and the termination of performance of works.
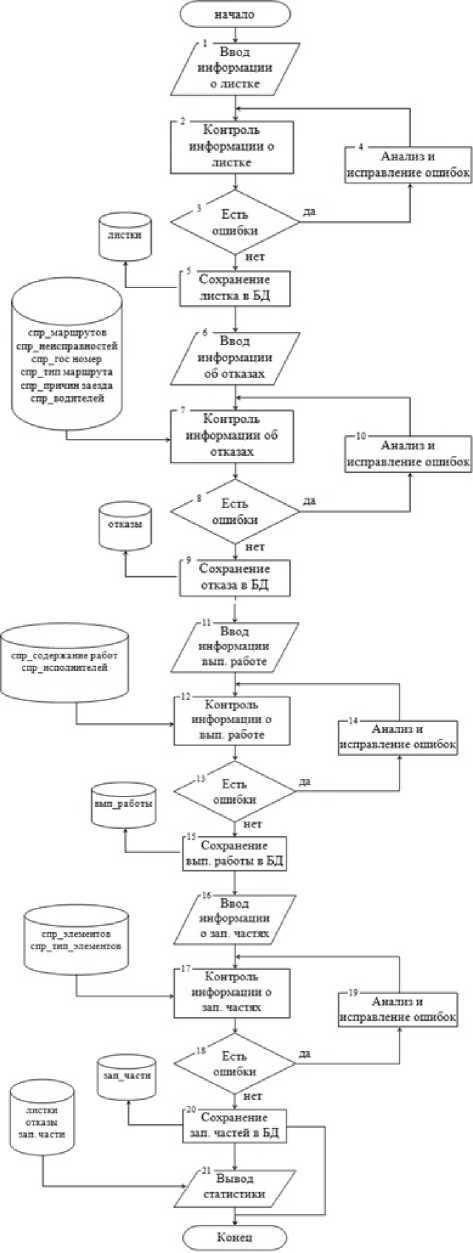
Fig. 3. The algorithm of the collection of information on road transport enterprise
At the fourth stage the information on use of spare parts or materials is brought at demand performance if those have been applied. The information includes: an account element, quantity, element type.
After filling all information remains in the created databases. Creation of a database in the collected information is very important stage for development of preventive maintenance system. Use of algorithms and models at processing and the analysis collected (storing) information simplifies this process. It is possible to carry to such functions:
-
– creation of statistics to demands for vehicle service for a year, month, thus it is possible to specify the reasons of arrivals, to choose the vehicle;
-
– information selection for the concrete reason, the executor, a kind of the carried out works, used spare parts, etc.
-
– drawing up of reports;
-
– the creation of the statistics of the consumption of spare parts for servicing the vehicle for a year, month;
-
– creation of statistics of demands on vehicle systems;
-
– working out of plans of carrying out of preventive works (MS-1, MS-2, etc.);
-
– formation of variation numbers for works and vehicle elements.
The presented model and algorithm has been realized in practice in the form of the computer program in language Delphi on which the program copyright certificate on the computer is received. The generated algorithm in computer see at Fig. 4, the fragment of a program code see Fig. 5.
The offered model of management has been realized by preventive maintenance system in ME a city of Krasnoyarsk «KEATE №5» and passed in some stages:
The first – creation of the automated workplaces (AWP) from which access to the program will be provided. Points of input of the information at the enterprise are: a check-point (demand registration), a maintenance service and repair zone (structure of works), a warehouse (necessary resources) also it is industrial technical department (storage and the subsequent analysis of the information).
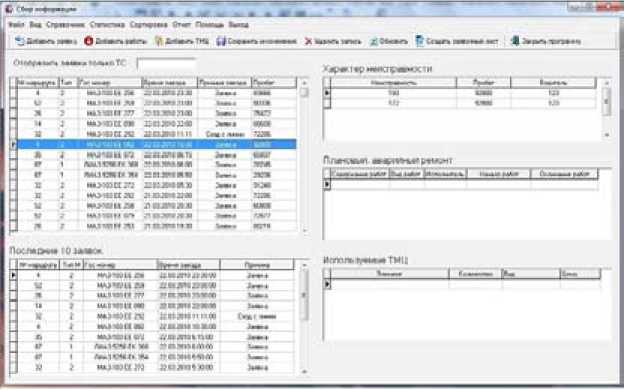
Fig. 4. The program of information-gathering on the moto transport enterprise pror*duni TFOrel-NIC!lek(Sender: TOC^ecO ,- to tel к. an л wn d a 1;
foral. qw. SetFocMf fora2.shawncdal:
procedure TFooU-MSClickf Sender? Inject H
It aesraaeDlql’Удалить техузу» залить?’. atCenfiraatisn,[ебуез, айво)* Oi-aryer then ADOQuesyl.Delete;
procedure TForel .H5C1 lek (Sender: TObjecO ;
eloee;
procedure ТГег*1-ЯЮСИс*(Sender: Tcejeet) ;
ADOQueryl.IndexFreldSanes :•’Номер хервруте';
procedure TFor»l.M15Clie)c(Sender? TC»3eet):
Fig.5. A piece of software programme for the collection of information on moto transport enterprise
The second stage – creation in the program of the accounting documentation and methods of the primary analysis хранимой information.
The third – perfection of algorithm in the course of program work.
It is necessary to notice, that at program introduction on manufacture the safety issue storing data, and also responsibility of persons bringing the information also was considered. For protection of data and the program the input system in the program with use of passwords is provided. And at each division at the enterprise the passwords limiting functionality in the program and at work with a database are developed.
Perfection (creation) of information supply system with on manufacture is only the first stage in perfection of preventive maintenance system of the vehicle. A following stage is formation of variation numbers through working model on elements and vehicle works, reception of quantity indicators of reliability, non-failure operation and durability.
Obtained data from the program are used as in educational process by preparation of experts of the higher school, and also on manufacture for an estimation the efficiency of existing preventive maintenance system and its perfection.
Conclusion
Maintenance of a technical condition of automatic telephone exchange at high level a main objective and problems of operating system of preventive maintenance. However often there are the questions connected about accuracy of statement of automatic telephone exchange for planned works, names and the amount of works, to be exact what level of reliability will provide the offered amount of
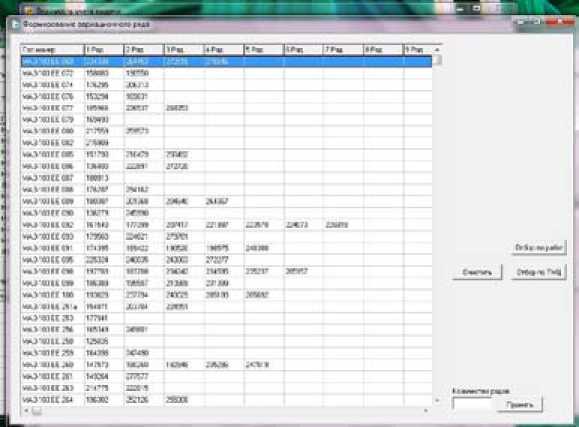
Fig. 6. Fragment of the program on formation of variational series on the separate element (or system) of f vehicles works. For perfection of system of preventive maintenance of automatic telephone exchange operating at the enterprises it is offered to introduce the developed algorithm and software product of system of a supply with information of preventive maintenance. Thus TD will have possibility to define level of reliability and to develop additional steps of preventive maintenance of automatic telephone exchange being based on the counted law of distribution of refusals (descents) of automatic telephone exchange and quantity indicators of reliability, durability and maintainability.


