Innovative approaches to funding startups in the transportation industry
Автор: Mussin Zh.
Журнал: Международный журнал гуманитарных и естественных наук @intjournal
Рубрика: Экономические науки
Статья в выпуске: 3-2 (90), 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This article explores innovative approaches to funding startups in the transportation industry. This crucial to the global economy sector currently experience transformative changes. Article discusses the challenges and opportunities faced by startups in securing funding, emphasizing the importance of selecting appropriate financial strategies. The article examines a variety of funding methods, from traditional to more recent innovations, and includes case studies to illustrate these approaches in practice.
Transportation industry, startup funding, innovative financing, venture capital, crowdfunding, public-private partnerships
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170203455
IDR: 170203455 | DOI: 10.24412/2500-1000-2024-3-2-106-111
Текст научной статьи Innovative approaches to funding startups in the transportation industry
The transportation industry is currently undergoing a phase of transformation, driven by technological advancement and shifts in market demands. In 2023, the electric vehicle (EV) market, valued at 162 billion dollars, indicates a shift towards more environmentally friendly forms of transportation, opening vast opportunities for startups.
The aim of this study is to explore innovative approaches to funding startups in the transportation industry. This will not only assess the current challenges and opportunities but also offer practical solutions to overcome financial barriers, thereby facilitating the advancement of innovations and progress in this crucial sector [1].
The significance of financing startups in the transportation industry lies in its direct impact on advancing technology, environmental sustainability and responding to evolving consumer demands. This industry, integral to global economic growth, is at a crucial juncture marked by rapid technological changes and an increasing focus on sustainable solutions.
The adaptability of the transportation sector, especially during global challenges like the COVID-19 pandemic, underscores the importance of ongoing innovation. Startups played a crucial role in adapting to the new normal, developing contactless delivery methods and enhancing supply chain efficiency through digital platforms.
The data presented in fig. 1 [2] vividly illustrates the fluctuating trends in investments into transportation industry startups, encompassing sectors such as EV, autonomous transportation, IoT (Internet of Things), and mobility as a service, over the period from 2018 to 2023. These fluctuations highlight the variability of market interest and investment activity across different areas of technological advancement in the transportation sector.
Fig. 1. Global investments in transportation startups by key segments, 2018-2023
Traditional methods of funding startups in the transportation industry primarily include venture capital, bank loans, and government grants. Each of these avenues has significantly supported early-stage companies but comes with inherent limitations.
Venture Capital (VC) . VC is a form of private equity investment provided by investors to startups and small companies that demonstrate potential for significant growth. VC is particularly relevant for innovative projects and tech startups, where traditional financing methods may be inefficient or unavailable.
Leading venture market analyst Kyle Stanford points to the deteriorating positions of venture investing: in 2023, the volume of VC investments amounted to 345,7 billion dollars, which is 35% lower than in 2022. In 2024, the expert predicts a further decline in venture financing. In the transport industry in 2022, financing fell by 49% to 13 billion dollars. The share of logistics startups in the total volume of venture investments decreased from 3,5% in 2021 to 2,6% in 2022 (fig. 2) [3].
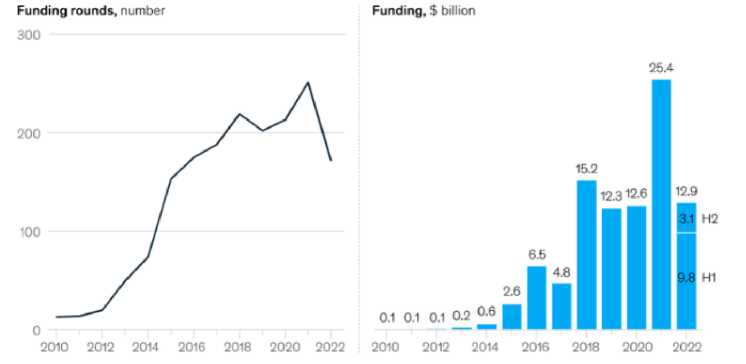
Fig. 2. VC investment in the transport industry, 2010-2022
However, the decline did not affect logistics brokers and forwarders: in 2022 their financing increased by 206% compared to
2021. This was achieved through several large funding rounds of individual startups, particularly Flexport (USA) (fig. 3).
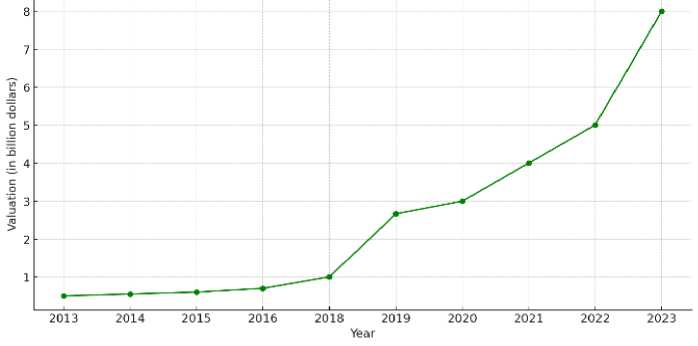
Fig. 3. Growth in the value of Flexport due to investments, 2013-2023
The company offered customers a convenient database and a free program for ordering and tracking the movement of containers by land, air and water. In 2022, the startup topped the CNBC Disruptor 50 list, and in December 2022, it raised 935 million dollars in a Series E funding round. In February 2023, the company was valued at 8 billion dollars, almost three times its last stated valuation in 2019. In February 2022, it raised 935 million dollars [4].
Bank Loans. Traditional bank loans are another avenue but less common for startups due to their high-risk nature. Banks usually require collateral and a proven revenue track record, which many early-stage transportation startups lack.
Bank loans and lines of credit: The European Investment Bank (EIB) is a long-term lending institution of the EU owned by its member states. Between 2019 and 2022, the EIB Group provided 45 billion euro in financing for transport projects in Italy. Italian carmaker Iveco Group has secured a 450 million euros loan, the first segment of a larger 500 million euros fund sanctioned by the EIB. The EIB's capital injection will support the Iveco Group's electric propulsion initiatives, marking a significant step forward in the company's technological progress [5].
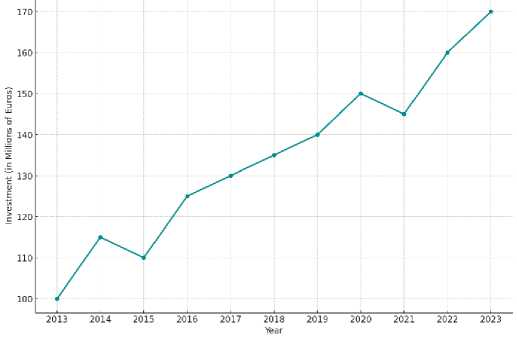
Fig. 4. EIB investments in transport startups, 2013-2023
The investment boom, which is scheduled to be completed by 2025, will allow the Iveco Group to direct funds mainly to Italy, as well as expand its financial reach in various European countries such as Germany, France, Spain, the Czech Republic and Switzerland. This comprehensive investment plan underlines the Iveco Group's commitment to inno- vation in sustainable and advanced automotive technology.
Government Grants and Subsidies. Government grants are crucial for research and development in the transportation sector. These traditional funding methods, while beneficial, have limitations that can hinder the growth and innovation of startups. The pro- longed approval processes, collateral requirements, and focus on short-term returns often do not align with the needs and potential of emerging transportation technologies.
In March 2023, Federal Highway Administration US announced it had opened applications for the first round of the CFI Discretionary Grant Program with up to 700 million dollars available from FY22 and FY23 to strategically deploy EV charging in communities and neighborhoods nationwide [6].
The Biden-Harris Administration in August 2023 opened applications for the Electric Vehicle Charger Reliability and Accessibility Accelerator. Funding for this project amounted to up to 100 million dollars in federal funding to repair and replace existing, but defunct EV charging infrastructure (chart 5).
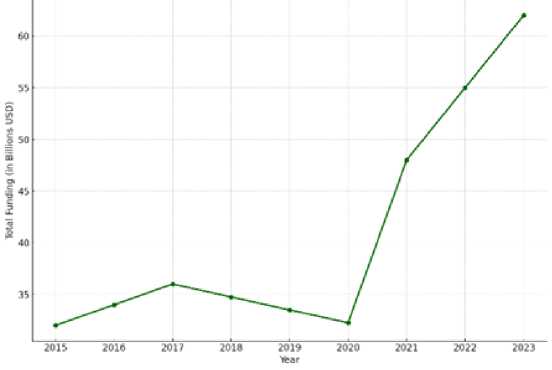
Fig. 5. US Government's investments in transportation startups, 2015-2023
In September 2023, the 5 billion dollars National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Formula Program was adopted. The program is regulated by the bipartisan infrastructure law and the Federal Highway Administration to help states build EV charging stations. Its implementation includes a 10% countdown for grants to states and localities that need additional assistance to strategically deploy EV charging infrastructure [7].
Equity Crowdfunding . This method allows a wide array of investors to fund startups in exchange for equity. In April 2023, the bike brand Cowboy (Belgium) organized a fundraiser on a crowdfunding platform Crowdcube. At least 1074 investors from 41 countries took part in the public round, and the total amount was 1,3 million euros. The volume of e-bikes shipped doubled to 19000, which the firm says gives it an active user base of 50000 people (fig. 6).
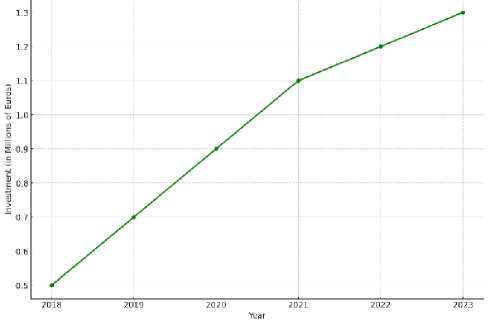
Fig. 6. Dynamics of attracting investments from crundfunding platforms, 2018-2023
By promoting its idea, Cowboy has drawn attention to the fact that it has become a certified B Corp, which is used by brands to signify genuine and measurable environmental credentials. Measuring its environmental impact, the company says its customers have saved 8,2 million kg of CO2 since 2017, on average per 0,8 million monthly trips [8].
Corporate partnerships . Strategic partnerships with established corporations have provided startups with necessary funding and expertise [9].
Strategic partnerships between startups and corporations can be very beneficial for both parties. Corporations can gain access to new technologies, innovations, and opportunities for expanding their business. Company Zipline is raising 330 million dollars in a new funding round, according to two sources and a filing obtained by Forbes in April 2023. The funding values Zipline at about 4,2 billion dollars, a 55% increase from its 2,7 billion dollars valuation reached two years ago (fig. 7).
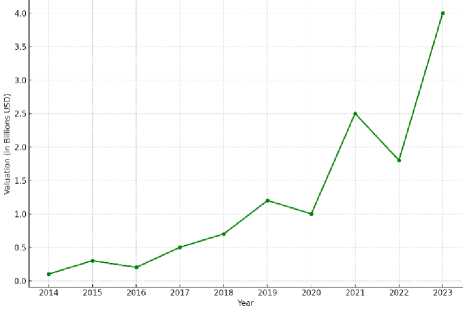
Fig. 7. Zipline’s market value growth, 2014-2023
The cash infusion comes as Zipline announced a new autonomous drone, the Platform 2, that it said could carry eight pounds of cargo at a range of 16 kilometers. Most ecommerce packages weigh 1,5 kilo or less. The aircraft, also known as a P2 Zip, is capable of charging on a docking station that resembles a lamppost. The company announced fast-casual food chain Sweetgreen, Michigan Medicine and several other health systems as partners.
Conclusion
The funding landscape in the transportation industry is a dynamic arena where tradi- tional and innovative approaches converge, each offering distinct benefits and facing unique challenges. The shift from established methods like venture capital and government grants highlights the sector's flexibility. This change reflects the industry's adaptive nature in response to evolving technological and market conditions. Through the lens of case studies from Cowboy, Iveco Group and Flexport, it's evident that strategic financial planning is pivotal for technological advancement and market growth.
Список литературы Innovative approaches to funding startups in the transportation industry
- Kudrenko I. The new era of American manufacturing: evaluating the risks and rewards of reshoring // E3S Web of Conferences. - EDP Sciences, 2024. - Т. 471. - С. 05020. EDN: OPKNCH
- Andrusiv, U., Kinash, I., Cherchata, A., Polyanska, A., Dzoba, O., Tarasova, T., & Lysak, H. (2020). Experience and prospects of innovation development venture capital financing. Management Science Letters, 10(4), 781-788. EDN: CDCICG
- Tsakalidis, A., Gkoumas, K., & Pekár, F. (2020). Digital transformation supporting transport decarbonisation: Technological developments in EU-funded research and innovation. Sustainability, 12(9), 3762.
- Кенджаев Д.А. Оптимизация операционной эффективности через AR в условиях быстро меняющегося рынка труда // Международный журнал прикладных наук и технологий Integral. - 2024. - № 1. EDN: WHDFPD
- Козлова М.Д. Стратегии успешного входа медтех продуктов на новые рынки - универсальные подходы и кейс-стади // Вестник науки. - 2024. - №1 (70) Том 4. - С. 22-29.
- Umar, M., Ji, X., Kirikkaleli, D., & Xu, Q. (2020). COP21 Roadmap: Do innovation, financial development, and transportation infrastructure matter for environmental sustainability in China? // Journal of environmental management, 271, 111026. EDN: PXXGQT
- Martynushkin, A.B., & Konkina, V.S. (2020, August). Quality improvement of public service of automobile transport: economic evaluation method. In Russian Conference on Digital Economy and Knowledge Management (RuDEcK 2020) (pp. 449-455). Atlantis Press. EDN: LXNJJE
- Ryan, M. (2020). The future of transportation: ethical, legal, social and economic impacts of self-driving vehicles in the year 2025. Science and engineering ethics, 26(3), 1185-1208. EDN: OIZFTY
- Кенджаев Д.А. Разработка AR-решений для повышения квалификации в быстро развивающихся отраслях экономики // Конкурентоспособность в глобальном мире: экономика, наука, технологии. - 2024. - № 1 (3). EDN: HSMXBD


