Интеллектуальный анализ цифрового следа при оценке контрольно-измерительных материалов для поддержки принятия решений в образовательном процессе
Автор: Углев В.А., Сычев О.А., Аникин А.В.
Журнал: Журнал Сибирского федерального университета. Серия: Техника и технологии @technologies-sfu
Рубрика: Информационно-коммуникационные технологии
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.15, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В работе рассматриваются проблемы моделирования предметной области, генерации контрольно-измерительных материалов, а также оценки и интерпретации ответов на них методами интеллектуального анализа. Для решения этих проблем предложено ответы обучаемого, рассматриваемые как образовательный цифровой след, дополнить информацией, позволяющей делать выводы как об уровне развития компетентностей, так и о затруднениях учащегося и их причинах. Оценку уровня развития индивидуальных и групповых компетентностей предложено осуществлять через экспертные оценки и автоматическую проверку гипотез. Для генерации заданий и выявления причин затруднений учащихся предлагается использовать онтологические модели предметных областей на уровне«понимания» таксономии Блума. Рассмотрены свойства таких моделей. Приведены примеры применения этих подходов к принятию решений в образовательном процессе различных дисциплин. В результате были сформулированы требования к перспективному модельному обеспечению интеллектуальных обучающих систем.
Интеллектуальный анализ данных, электронное обучение, принятие решений, автоматизированная обучающая система, контрольно-измерительный материал, образовательный цифровой след, таксономия блума, уровень развития компетентности, онтология, генерация заданий, адаптивное обучение
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146282416
IDR: 146282416 | УДК: 004.832.3:004.891.3:37.013.41
Текст научной статьи Интеллектуальный анализ цифрового следа при оценке контрольно-измерительных материалов для поддержки принятия решений в образовательном процессе
Современное образование неразрывно ассоциируется с понятием информатизации, когда учитель и обучаемый непосредственное взаимодействие заменяют на опосредованное, опирающееся на высокотехнологичные устройства и глобальные вычислительные сети. Рассинхронизация контактов приводит к переходу сначала на дистанционные, а затем и на электронные формы обучения, что позволяет детально фиксировать и анализировать события и их результаты (цифровые образовательные следы), которые произошли в процессе взаимодействия обучаемого с обучающей системой. Целью анализа следа является оценка учебной ситуации и выработка управляющего воздействия, что может происходить на различных уровнях от учебных – 122 – планов до непосредственной коррекции поведения обучаемого в процессе работы с электронным курсом. Чем «разумнее» действует подсистема анализа и принятия решений в автоматизированной обучающей системе, тем выше результативность обучения. Важный компонент следа – результаты проверки знаний, полученных в процессе решения контрольно-измерительных материалов (КИМ).
КИМ могут выполняться и оцениваться в ручном, автоматизированном и автоматическом вариантах. При ручном процессе оценивания задач педагог, являющийся опытным экспертом предметной области, может обеспечить качественное оценивание и обратную связь обучаемому при решении задач любой сложности, включая творческие. Однако этот процесс трудоемок, что резко ограничивает количество заданий, по результату выполнения которых студент может получить обратную связь, в то время как многократное выполнение однотипных задач с получением качественной обратной связи повышает усвоение материала.
Типовым решением этой проблемы выступает автоматизация составления и проверки КИМов, как правило, в виде тестов или тренажеров. Автоматически выполняемый и оцениваемый КИМ обладает рядом важных преимуществ:
-
– обучаемые могут выполнять их в удобное для себя время;
-
– обучаемые могут выполнять необходимое им количество заданий без дополнительных трудозатрат педагога на каждого обучаемого;
-
– небольшое время цикла обратной связи обучаемому, что способствует активному усвоению знаний [1, 2];
-
– процесс выполнения заданий оставляет детальный цифровой след, который легко поддается последующему анализу.
Все это сдерживается рядом недостатков большинства методов автоматической проверки КИМов, включающих, как правило, сравнительно простой уровень решаемых задач, низкое качество обратной связи (если студент не понял, почему его ответ неправильный и как его исправить, он вынужден дождаться консультации с преподавателем), а также значительной ролью угадывания правильного ответа при выполнении заданий в тестовой форме.
Другой важный ограничивающий фактор – трудозатраты педагога на составление КИМов, что даже в условиях их автоматической проверки ограничивает количество задач, которые доступны для решения обучаемым, что приводит к увеличению вероятности списывания при повторении заданий и ограничивает возможности самостоятельной тренировки. Эти проблемы вызвали к жизни такое научное направление, как автоматизированная генерация вопросов. Однако в настоящее время генерируемые вопросы остаются очень простыми, работы по представлению обратной связи почти отсутствуют; кроме того, встают проблемы надежной оценки сложности сгенерированных вопросов [3].
Обрабатывая ответы обучаемого, недостаточно просто оценить уровень корректности ответов, важно оценить глубину освоения учебного материала и выявить уровень развития компетентностей. Поэтому все чаще ставится задача применения методов искусственного интеллекта, расширяющих возможности анализа и, как следствие, адекватности реакций обучающей системы при взаимодействии с обучаемым.
Успешность анализа наборов КИМов и результатов их прохождения в большинстве случаев опирается на статистические модели Г. Раша [4], что позволяет оценить качество заданий – 123 –
(обычно в форме тестов) и выявить наиболее проблемные моменты на этапе контроля. Но как выявить проблемы обучаемых и их причины, особенно для когнитивных задач высоких уровней сложности согласно таксономии образовательных целей Б. Блума [5]? Проверка гипотез такого уровня сложности осуществляется интеллектуальными алгоритмами, базирующимися на знаниях экспертов. Очевидно, что в таком случае потребуется как модель описания знаний предметной области для КИМов, так и ряд методических решений. Исследуем этот вопрос подробнее.
Проблематика
Первые алгоритмы искусственного интеллекта для анализа результатов решения КИМов начали применять на заре программированного обучения, а теперь в этой области работают ученые, ассоциирующие свою деятельность с такими научными направлениями, как Learning Analytics и Intelligent Tutoring Systems (например, [6–8]). При этом до сих пор остается нерешенным вопрос по оценке результатов сформированности у учащегося элементов мышления высокого порядка (в пределе – компетентностей) [9]. Но, несмотря на многолетние исследования, качество работы интеллектуальных обучающих систем на сегодняшний момент недостаточно интеллектуально (см., например, критику [10]).
Решением указанных затруднений служит расширение модели описания КИМа (опираясь на экспертные оценки и онтологии) и применение алгоритмов интеллектуального анализа учебной ситуации во всех случаях, где уровень сложности оценки не вынуждает прибегнуть к мнению педагога-предметника.
Выделим основные направления анализа, которые должны обеспечивать адекватную реакцию обучающей системы на действия учащегося:
-
1. Выявление индивидуальных целей и предпочтений обучаемого.
-
2. Формирование индивидуального состава учебного курса и норм контроля.
-
3. Формирование исходной индивидуальной траектории обучения.
-
4. Оценка степени освоения учебного материала (как в знаниевом, так и в компетент-ностном представлении).
-
5. Формирование развернутых рекомендаций обучаемому на текущем этапе обучения.
-
6. Синтез ситуационного диалога при обращении обучающегося за помощью (подсказки с возможным использованием наводящих вопросов) или разъяснениями (обоснования решений системы).
-
7. Автоматическая генерация контрольно-измерительных материалов согласно целям обучения.
-
8. Автоматическая адаптация генерируемых КИМ к обучаемому по сложности заданий и охватываемым темам.
-
9. Оценка поведения обучающегося и прогнозирование его результатов обучения.
Рассмотрим два подхода к организации процесса анализа образовательного цифрового следа при принятии решений в интеллектуальных обучающих системах: назовем их условно нисходящим и восходящим. Нисходящий подход предполагает, что анализ решений КИМов будет нацелен на наиболее абстрактную форму проявления результатов обучения (компетентности и индивидуальные целевые установки) и его использования для принятия методических – 124 – решений по управлению процессом обучения. Восходящий подход предполагает описание КИМов с позиции предметных знаний и целей, которые важны при изучении конкретной дисциплины и служат решению текущих задач обучения за счет выявления проблемных моментов и попытке помочь их разрешить. Поэтому рассмотрим каждый подход на предмет описания КИМов, извлечения знаний из результатов их решения и последующего использования этих знаний при формировании обратной связи с обучаемым.
Нисходящий подход к анализу образовательного следа
Нисходящий подход (от общего к частному) предполагает, что результаты освоения учебной программы должны проецироваться на конкретные учебные дисциплины, а те, в свою очередь, на дидактические единицы, для которых и составляются проверочные задания. При таком подходе результаты обучения становятся надпредметными и должны выражаться достаточно абстрактно. Для этой цели хорошо подходит компетентностное представление, которое задает набор компетенций на уровне образовательного стандарта, а проверяет их проявление (развитую компетентность) непосредственно во время обучения (при прохождении учебных дисциплин). Поэтому наравне с оценкой уровня овладения предметным учебным материалом нам понадобится и уровень развития (владения) компетентности (УРК) как индивидуальной латентной характеристики личности (по [11]), отражающей степень овладения человеком той или иной компетенцией в конкретный момент времени. Если УРК оценивает человек-эксперт, то он сначала формулирует гипотезу, а потом ее проверяет через систему прямых и косвенных вопросов, постепенно утверждаясь в суждении об уровне развития компетентности. При такой стратегии каждый вопрос, а точнее, вариант ответа на вопрос, будет свидетельствовать в пользу или против выдвинутой гипотезы, изменяя уверенность эксперта. В случае, когда одновременно проверяется ряд независимых гипотез, каждый эксперт стремится минимизировать время оценки за счет подбора таких вопросов и вариантов ответов, которые помогут работать сразу с несколькими гипотезами, т. е. в нашем случае компетенциями. Базируясь на этой идее, введем модель описания КИМов и ответов на них, опираясь на механизм экспертных оценок.
Пусть имеется множество заданий Ti, каждое из которых имеет несколько вариантов решений. Каждое из заданий должно иметь как знаниевую оценку (меру правильности), так и ком-петентностную, ориентированную на проверку гипотезы об УРК одной или нескольких компетенций из множества A. Тогда часть цифрового следа, касающегося результата ответа, можно представить в виде вектора Xt в момент времени t Абстрагируемся сейчас от определения меры правильности (это прерогатива восходящего подхода) и сконцентрируемся на измерении УРК. Если задание Ti имеет демонстрируемый обучающемуся набор вариантов ответов (закрытая форма), то для каждого из этих вариантов можно поставить в соответствие априорную экспертную оценку qujk из области определения [0,1], относящуюся к компетенции ak (здесь u - порядковый номер задания; j - порядковый номер варианта ответа). Ряд заданий, включаемых в КИМ, составляются таким образом, чтобы все варианты ответов оценивались не столько по степени корректности (желательно, но не обязательно), сколько по предпочтительности для обучающегося (с априорной ассоциацией с теми или иными компетенциями из А). Тогда задача оценки УРК сводится к задаче проверки гипотезы по совокупности свидетельств (ответов из образовательного цифрового следа) [12]. При этом значения экспертных оценок можно – 125 – хранить в матрице, отражающей связь между вариантами ответов и компетенций, являющейся своеобразной базой знаний.
Для того чтобы получить численную оценку УРК с номером k, необходимо произвести следующую последовательность действий:
-
1. Выбираем ответы из следа на те задания, которые имели априорные оценки qujk.
-
2. Проверяем гипотезу о развитости компетенции ak, вычисляя меру доверия MB по формуле (1).
-
3. Вычисляем по аналогии меру недоверия MD по формуле (2).
-
4. Значение результирующего коэффициента уверенности Cf можно рассчитать по формуле (3), предложенной Шортлиффом в [13] специально для параллельной проверки нескольких сложных гипотез.
Л*.^=М^>,(1)
где x – количественная мера одного из факторов (тестовых заданий) для каждой компетенции из A.
^jw^.(2)
CfVak, qo л q-o) = МВ(ак, qo) - Mfak ^,(3)
где qa и qa - свидетельства в пользу (qujk>0.5) и не в пользу (qujk<0.5) гипотезы об УРК относительно образовательного следа Xt.
Вектор значений Cf показывает уверенность обучающей системы в развитии компетентности у учащегося. Если теперь свести оценки по (3) в единую структуру (компетентностный профиль) и визуализировать, то получится текущая характеристика каждого учащегося (например, рис. 1 а, б для двух учащихся и семи компетентностей), а обобщив эти оценки, получить усредненный профиль по учебной группе (рис. 1 в , с отражением минимального, среднего и максимального значений для каждого УРК).
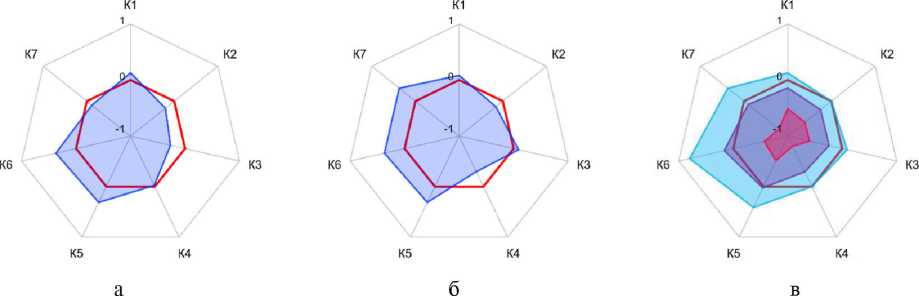
Рис. 1. Компетентностные профили двух обучающихся и группы (дисциплина «Имитационное моделирование» магистратуры специальности ИиВТ в СФУ, 2021)
Fig. 1. Competence profiles of two learners (a, b) and a group of learners (c). Data from master's degree course «Simulation» in Siberian Federal University in 2021
В результате анализа ответов учащихся по множеству КИМов не только определяется значение оценки УРК, но фиксируются дополнительные элементы цифрового следа, на которые можно опираться при синтезе подсказок и разъяснений в естественно-языковой форме. Для этого необходимо имеющийся цифровой след отобразить через специальный механизм обобщения – когнитивную карту диагностики знаний [14]. На ее основании можно не только выявлять «узкие» места процесса обучения, но и автоматически формировать фразы-разъяснения. Приведем пример синтезированного диалогового окна, предъявляемого обучающемуся после того, как он попросил показать рекомендации по результатам решения КИМов (промежуточный контроль) (рис. 2). В окне представлена область оценки текущей учебной ситуации (блок сверху) и рекомендаций обучающемуся, которые следует предпринять в первую очередь (блок по центру). Благодаря возможности наложить образовательный цифровой след на когнитивную карту диагностики знаний, были сгенерированы рекомендации как по работе с дидактическим материалом, так и по оценке целевых показателей. Задействуя в процессе интеллектуального анализа модель ученика (включая анкетные данные), модель учителя и модель предметного тьютора, имеем возможность реализовать механизмы рефлексивного управления
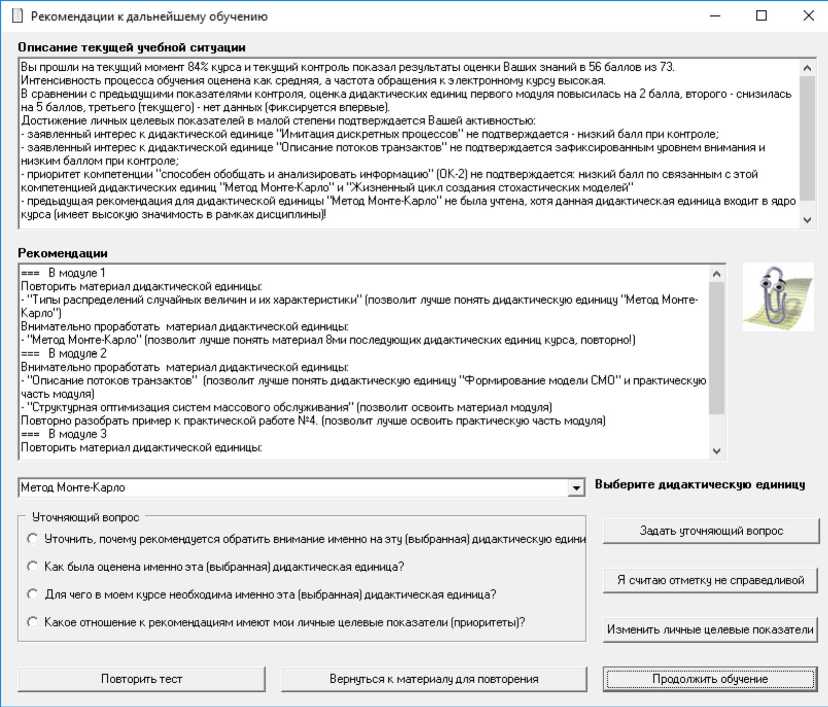
Рис. 2. Пример автоматически синтезированного диалогового окна с рекомендациями для обучающегося (дисциплина «Имитационное моделирование»)
Fig. 2. An example of automatically produced dialog box with advice for learner («Simulation» course)
[15, 16]. Для продолжения диалога упомянутые в верхнем и среднем блоке дидактические единицы загружаются на форме в раскрывающийся список и могут стать объектом обсуждения (нижний блок). Очевидно, что подобный тип обратной связи дает хорошие результаты на стратегическом уровне, где объектами являются дидактические единицы и целые учебные модули.
Недостатком указанного подхода признана его отстраненность от детальной семантической структуры знаний конкретного курса: универсальность метода дает основание для методических выводов и решений, но ответить на вопрос, что именно учащийся не понял, в автоматическом режиме не представляется возможным. Для реализации подобной возможности цифровой след должен содержать информацию о классах и причинах каждой ошибки. Также метод оценки УРК предполагает достаточно трудоемкий процесс подготовки КИМов (особенно матрицы экспертных оценок) для заданий с закрытой формой ответа. В случае когда применяются КИМы с открытой формой ответа, трудоемкость проявляется в дополнительной необходимости разработки критериев их оценки. Одним из способов решить проблему трудоемкости создания и проверки заданий, а также обеспечить подробную информацию о совершенных ошибках и их причинах служит семантический анализ ответов за счет рассуждений на онтологических моделях. Но это уже задача восходящего подхода к интеллектуальному анализу цифрового следа.
Восходящий подход к анализу образовательного следа
Как было показано ранее, успешность образовательного процесса в значительной мере зависит от возможности обучаемого познавать материал в действии, при выполнении контрольно-измерительных материалов в необходимом данному обучаемому объеме. При этом важно выполнение двух условий. Во-первых, обучаемый должен получать новые задания на заданную тему до тех пор, пока он ее не поймет и желает продолжать упражнения, что невозможно при ограниченном числе заданий, т. к. ответы на них запоминаются в ходе выполнения. Большое количество заданий также исключает повторение заданий у разных обучаемых и, соответственно, списывание ответов. Практически это возможно только при автоматической генерации заданий. Во-вторых, обучаемый должен быть обеспечен достаточным количеством обратной связи (объясняющей, подсказывающей и приводящей к правильному ответу), чтобы у него не возникали «тупики» обучения, в которых он не знает, что сделать дальше, чтобы приблизиться к правильному (или лучшему) решению задачи. При этом высокая точность обратной связи (идентификация ошибок обучаемого и их причин) позволяет накапливать значительно более точный цифровой след. Соблюдение этих двух условий позволяет замкнуть цикл быстрой обратной связи в обучении, при котором обучаемый может вести диалог с системой на заданную тему, состоящий из выполнения заданий, получения подсказок и объяснений, и ответов на наводящие вопросы до тех пор, пока необходимая степень освоения материала не будет достигнута и подтверждена цифровым следом. Таким образом, анализ будет идти непосредственно от дидактического материала к причинам ошибок, что реализует сущность восходящего подхода.
Классические системы тестирования с автоматической проверкой основаны на задании известного правильного ответа и сравнении ответа студента с правильным с помощью различных метрик. При наличии множества правильных ответов они могут быть описаны с помощью – 128 – шаблонов, в роли которых нередко выступают регулярные выражения [17, 18]; для вопросов с полнотекстовым ответом (эссе) может задаваться исходное множество правильных ответов, из которых система строит модель [19, 20].
Очевидным недостатком такого подхода является ограниченный характер анализа ответов, лимитирующий как корректирующую обратную связь, которая оказывается направленной не на объяснение причин ошибки, сделанной обучаемым, а на приведение его ответа к правильному, так и цифрового следа, который не будет содержать ни причины ошибки, ни, нередко, оценки ее серьезности с точки зрения изучаемого материала. Используемые метрики, как правило, вычисляют расстояние между строками (открытый ответ текстом) или числами (открытый ответ числом с погрешностью), которые напрямую не связаны со степенью сделанной смысловой ошибки. Эти проблемы могут быть частично преодолены лишь в простейших вопросах типа «выбор одного варианта из многих» за счет разметки каждого варианта ответа педагогом-экспертом, что, как было показано выше, значительно увеличивает трудоемкость создания набора КИМов, а также угадывания правильного ответа.
Решением этой проблемы служит переход к декларативному описанию правильного ответа. Для этого условие задачи и возможные ответы должны быть формализованы, после чего определен набор логических условий, описывающих правильные и только правильные ответы для данного условия задачи. В этом случае система получает возможность сама вычислять правильный ответ для произвольно сгенерированного вопроса, однако главным преимуществом является не сам найденный ответ, а система правил его проверки, т. к. любой неправильный ответ будет вызывать нарушение одного или нескольких условий правильности, которые могут быть поставлены в соответствие конкретным фактам или законам предметной области, которые обучаемый применил неверно. Таким образом мы можем получить цифровой след, состоящий из смысловых ошибок студента (а также тех ошибок, которые он мог сделать при решении данного задания, но не сделал), и обеспечить объясняющую обратную связь по фактам и законам, знание которых он продемонстрировал неверно. Для практической реализации таких систем необходимо использовать автоматические машины вывода, например, основанные на предикатах (Prolog), языках SWRL (Pellet reasoner [21]) или RDF (Jena reasoner [22]).
В общем случае описание изучаемой части предметной области будет состоять из множества концептов С, множества правил R + , описывающих правильный ответ, которые мы назовем позитивными, и множества правил, полученных отрицанием правил получения правильного ответа, которые идентифицируют различимые в рамках данной задачи ошибки, которые мы назовем негативными R-. Количество негативных правил больше, чем позитивных, т. к. по закону де Моргана после применения отрицания позитивное правило, имеющее операции логического И, на верхнем уровне распадется на несколько правил из-за его преобразования в логическое ИЛИ, что интуитивно понятно, т. к. количество способов сделать ошибку выше количества способов решить задачу правильно.
Рассмотрим для примера задачу определения порядка вычисления операций в выражении на языке программирования. В этом случае позитивное правило, описывающее возможность выполнения бинарной операции из одной лексемы (операции типа сложения, умножения и т. д.), будет формулироваться так: бинарная операция X может быть выполнена, если непосредственно слева (отношения «непосредственно слева/справа» учитывают только неисполь-– 129 – зованные операнды и невычисленные операции) от нее ∄ невычисленной операции Y такой, что (приоритет Y выше приоритет X ⋁ приоритет Y равен приоритету X ⋀ они обладают левой ассоциативностью) ⋀ непосредственно справа от нее ∄ невычисленной операции Z такой, что (приоритет Z выше приоритет X ⋁ приоритет Z равен приоритету X ⋀ они обладают правой ассоциативностью).
Легко увидеть, что это положительное правило при применении отрицания распадается на четыре вида ошибки, которые происходят, если студент выбрал X как выполняемую раньше Y или Z: операция с большим приоритетом слева; операция с тем же приоритетом и левой ассоциативностью слева; операция с большим приоритетом справа и операция с тем же приоритетом и правой ассоциативностью справа. Учет таких правил позволяет генерировать обучаемому сообщения, содержащие объяснение причины ошибки («потому что…»). На рис. 3 представлен пример таких сообщений для ситуации, когда обучаемый выделил как первую вычисляемую операцию сложения в позиции 6. Обучаемому не просто указано, какие операции должны быть выполнены до выбранной им, но и причины этого: влияние скобок и гарантированного порядка вычисления операндов логических операций (другие возможные причины включают влияние приоритета и ассоциативности операций). Этот подход также позволяет запоминать в цифровом следе, какого рода ошибки склонен делать конкретный обучаемый, что может использоваться как для оценивания его ЗУНов, так и для корректирующей обратной связи (показать необходимые обучающие материалы), а также для адаптивной генерации следующих заданий на проблемные для данного обучаемого законы. Более детальные знания о природе ошибки обучаемого могут быть получены с помощью наводящих вопросов.
При таком подходе естественной единицей знаний обучаемого становится не позитивное правило, описывающее корректный вывод в процессе решения задачи, а негативное, описывающее один конкретный способ сделать ошибку. Это открывает возможность статистического
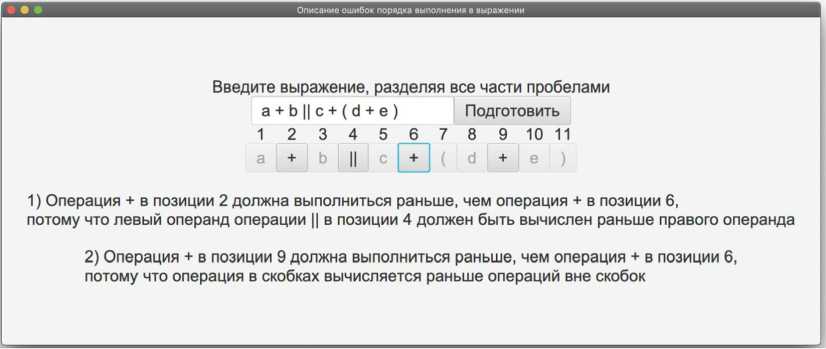
Рис 3. Пример объясняющей обратной связи обучаемому при решении задачи о порядке операций в выражении (дисциплина «Основы программирования» в ВолгГТУ)
Fig. 3. An example of explanatory feedback during «order of evaluation» assessment (course «Programming Basics», Volgograd State Technical University)
анализа, сколько возможностей сделать конкретную ошибку у обучаемого было (в зависимости от задания, какие-то знания могли не требоваться для корректного решения) и как часто он ошибался. При этом могут учитываться априорные вероятности правильного ответа (угадывание, списывание) и неправильного ответа без смысловой ошибки (невнимательность).
Еще одной единицей знаний являются концепты, которые используются для описания правил, однако для них возможна проверка лишь одного вида: умение обучаемого отличать в условии задачи объекты данного концепта (принадлежащие классу или обладающие свойством) от других. Все остальные свойства концепта моделируются через правила. Неумение различить тип объекта предметной области может приводить к ошибкам, несмотря на знание законов, которые определяют ответ. При возникновении у обучающей системы сомнений в умении обучаемого идентифицировать объекты, относящиеся к различным концептам, могут быть сгенерированы специальные вопросы на их распознавание и даны соответствующие рекомендации.
Использование моделей предметной области, в том числе в виде онтологий, в настоящее время является распространенной практикой при генерации вопросов [3]. Однако большинство из этих онтологий разработаны на первом уровне (знания) по таксономии Блума: они содержат лишь простейшие отношения между изучаемыми концептами (например, таксономические); основные свойства концептов в рамках онтологий не моделируются, а содержатся в виде описаний на естественном языке. В результате генерируемые вопросы оказываются очень простыми, а обратная связь при ошибках отсутствует или слабо информативна [3].
В [23] описан пример интеллектуального облачного сервиса для отработки навыков постановки диагноза на основе онтологических моделей, включающий в себя моделирование клинической картины заболевания, при этом обучаемый в рамках выполнения задания оценивается по тому, характерны ли для этого заболевания запрошенные обучаемым дополнительные наблюдения. Разработанный сервис оперирует моделями изучаемых объектов (заболеваний) в виде клинической картины признаков, однако он не получает и не анализирует трассу гипотез и выводов обучаемого, в результате чего корректное поведение обучаемого (проверка гипотезы, оказавшейся ложной) может классифицироваться как ошибка. Это также ограничивает обратную связь от системы только сравнением действий обучаемого с правильным ответом.
Согласно оригинальной таксономии Блума [5], понимание материала определяется как то, что обучаемый знает то, что ему было передано, и может использовать изученный материал или идею, не связывая их с другими темами и без представления обо всех логических выводах из них. Проверка достижения образовательных целей на уровне понимания традиционными средствами (например, пересказ обучаемым темы своими словами) является не до конца автоматизируемой; она, как правило, решается собеседованием с педагогом, время которого нередко ограничено. На практике это приводит к тому, что студенты получают задания следующих уровней (применения, анализа и синтеза) без проверки достижения уровня понимания и нередко пытаются решить более сложные задачи, не понимая до конца используемые концепты. Решить эту проблему может автоматизация КИМов на уровне понимания.
Для реализации таких КИМов необходимо обратить внимание на вторую часть определения Блума: возможность использования изученных идей в простейших ситуациях, не связывая их с другим материалом. Таким образом, для проверки уровня понимания необходимо использовать задания, в которых изучаемые концепты раскрывают все свои свойства при решении практической задачи так, чтобы система могла идентифицировать нарушение любого свойства изучаемого концепта как отдельную ошибку и выдать необходимую поясняющую обратную связь. Для генерации и решения таких задач понадобятся формальные модели предметной области на уровне понимания.
Формальной моделью предметной области на уровне понимания назовем такую модель, в которой все изучаемые свойства понятий (концептов) описаны аксиоматически в рамках этой модели, так что при дополнении модели фактами, описывающими условие конкретной задачи, по правилам вывода возможно решение этой задачи с использованием свойств изучаемых концептов, но, возможно, без связи с другими понятиями или полного понимания последствий их применения. Такая модель может самостоятельно (при применении машины вывода) решать задачи предметной области, а при дополнении ее отрицаниями правил решения («негативными правилами») определять смысловые ошибки в ответе студента, обеспечивая объясняющую обратную связь.
Потенциальной проблемой при реализации таких моделей являются возможности современных машин вывода, поскольку модели уровня понимания с аксиоматическим определением моделируемых концептов намного сложнее моделей уровня знания. Для исследования этой проблемы в ВолгГТУ были разработаны онтологические модели уровня понимания для предметных областей «вычисление выражений» и «алгоритмические структуры».
Онтологическая модель «вычисление выражений» [24] моделирует понятия «операция», «операнд», «арность», «приоритет», «ассоциативность» на основе задачи определения порядка вычисления выражения на языке программирования. Она может определять порядок вычисления выражения в виде направленного ациклического графа (т. к. в большинстве языков программирования он не задан строго и является частичным порядком), а также ошибки обучаемого, связанные с приоритетом, ассоциативностью и нарушением гарантированного порядка вычисления операндов некоторых операций. Модель содержит 28 правил и определяет 6 типов ошибок. При определении ошибок они снабжаются всей необходимой информацией для генерации объясняющих сообщений (см. рис. 3). Модель реализована на языках OWL и SWRL с использованием машины вывода Pellet [21].
Формальная модель «алгоритмические структуры» [25] моделирует понятия алгоритмических структур «следование», «альтернатива», «выбор» и «цикл» на основе решения задачи построения трассы выполнения программы по ее алгоритму. Модель содержит 99 правил, определяя 41 тип смысловых ошибок и снабжая информацию об ошибках необходимыми данными для генерации сообщения. Пример работы модели приведен на рис. 4. Изначально модель «алгоритмические структуры» была реализована на языках OWL и SWRL с использованием машины вывода Pellet, однако она была успешно переведена на языки Prolog [26], язык правил машины вывода Jena и SPARQL-скрипты, которые показали значительно лучшую производительность и устойчивость к росту объема данных, чем Pellet.
Таким образом, исследования показали, что реализация моделей уровня понимания при восходящем подходе интеллектуального анализа возможна на текущем уровне развития машин вывода. Возможность автоматической генерации большого числа КИМов для данных – 132 –
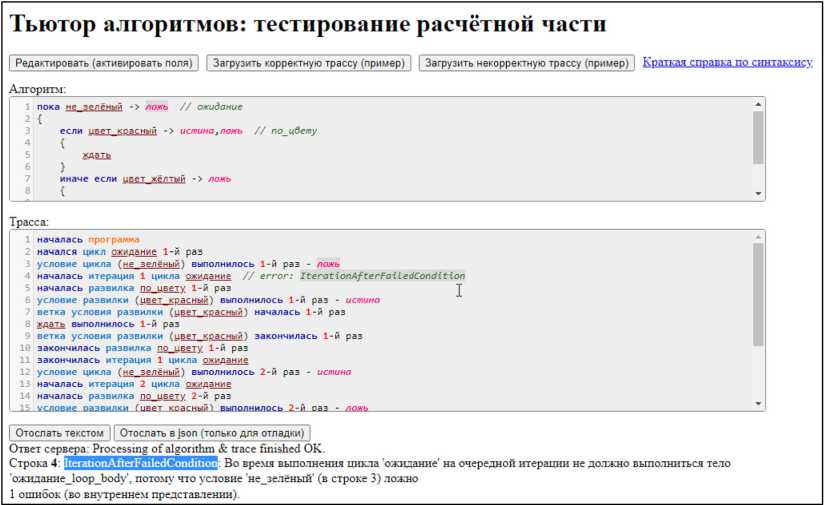
Рис. 4. Пример объясняющей обратной связи, генерируемой с помощью формальной модели «алгоритмические структуры» (дисциплина «Основы программирования» в ВолгГТУ)
Fig. 4. An example of explanatory feedback generated by the model «control flow statements» (course «Program-ming Basics», Volgograd State Technical University)
задач обеспечивается тем, что модель способна самостоятельно найти правильное решение задачи, а в качестве условий можно использовать объекты реального мира (выражения и алгоритмы функций из открытого кода программ) при условии их классификации по сложности и используемым концептам.
Заключение
Совокупность нисходящего и восходящего подходов к интеллектуальному анализу цифрового образовательного следа позволяет комплексно подойти к оценке КИМов и выработке эффективной обратной связи. На основании полученных нами результатов было выявлено, что интеллектуальные обучающие системы, оперирующие формальными моделями предметных областей, должны отвечать следующим требованиям:
-
– модель предметной области должна включать в себя модель знаний, модель условий заданий и модель обучаемого;
-
– модель знаний должна включать в себя концепты, часть из которых моделируется на уровне знаний, а другая – непосредственно изучаемые концепты – на уровне понимания, а также отношения между ними;
-
– концепты, моделируемые на уровне понимания, должны быть описаны аксиоматически в виде правил вывода, применяемых для решения заданий, в которых изучаемые концепты проявляют свои свойства, при этом должны присутствовать правила двух видов: позитивные (позволяющие найти правильный ответ) и негативные (позволяющие определить ошибки в решении студента);
-
– для сложных ошибок, определяемых негативными правилами, модель должна содержать наборы наводящих вопросов, позволяющие разобраться, незнание какого именно фрагмента информации послужило причиной ошибки;
-
– для изучаемых концептов должна существовать модель заданий, при выполнении которых эти концепты проявляют свойства, включающая в себя виды заданий, и условия заданий, категоризированные по сложности, примерному времени решения, используемым концептам и закономерностей;
-
– модель заданий должна включать в себя априорные вероятности правильных и ошибочных ответов;
-
– модель обучаемого должна включать в себя априорные распределения вероятностей знаний концептов и закономерностей предметной области, а также апостериорные оценки вероятностей знаний на основании истории выполнения упражнений;
-
– модель предметной области должна позволять решать один или несколько типов заданий, требующих применения изучаемых концептов предметной области, в том числе находить средствами машины вывода правильный ответ, находить ошибки в решениях обучаемых с указанием смыслового вида ошибки и информации, необходимой для генерирования сообщения, объясняющего ошибку и ее причину;
-
– концепты модели предметной области должны по возможности выравниваться для обеспечения связи с вышестоящими моделями, обеспечивающими планирование учебного процесса и определение формирования компетенций;
-
– модель предметной области должна быть расширяемой за счет интеграции с внешними моделями педагога (учителя) и предметного тьютора, обеспечивающих при взаимодействии с моделью ученика через механизмы работы обучающей системы процесс рефлексивного управления;
-
– модель предметной области и элементы цифрового следа должны иметь возможность визуализации, включая наложение на когнитивную карту диагностики знаний;
-
– модель обучаемого должна позволять экспортировать образовательный цифровой след, вплоть до переноса во внешние реестры, в том числе распределенные.
Таким образом, разработка интеллектуальных автоматизированных обучающих систем нового поколения должна опираться на детально проработанные модели принятия решений и предметных областей. Это позволит не только повысить качество обработки образовательного цифрового следа, но и сделает реакцию системы более адекватной потребностям текущей учебной ситуации.
Список литературы Интеллектуальный анализ цифрового следа при оценке контрольно-измерительных материалов для поддержки принятия решений в образовательном процессе
- Mendicino M., Razzaq L., Heffernan N. A Comparison of Traditional Homework to Computer-Supported Homework, Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 2009, 41(3), 331-359.
- Singh R., Saikhuka M., Pradhan P., Heffernan C., Heffernan N., Razzaq L., Dailey M., O'Connor C., Mulcahy C. Feedback during Web-Based Homework: The Role of Hints, Proceedings of the 15th international conference on Artificial intelligence in education, 2011, 6738, 328-336. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-21869-9_43
- Kurdi G., Leo J., Parsia B., Sattler U., Al-Emari S. A Systematic Review of Automatic Question Generation for Educational Purposes, International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 2019, 30(4), 121-204. DOI: 10.1007/s40593-019-00186-y
- Rasch G. Probabilistic models for some intelligence and attainment tests, Chicago, The University of Chicago Press, 1980, 199 p.
- Bloom B. S., Engelhart M. D., Furst E. J., Hill W. H., Krathwohl D. R. Taxonomy ofEducational Objectives: Handbook I: Cognitive Domain, New York, David McKay Company, 1956, 207 p.
- Lang C., Siemens G., Wise A., Gasevic D. (Eds.). Handbook of learning analytics, SoLAR, 2017, 356 p. DOI: 10.18608/hla17
- Beyyoudh М., Idrissi М., Bennani S. Towards a New Generation of Intelligent Tutoring Systems, International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 2019, 14:14, 105-121.
- Brusilovsky P., Rus V. Social navigation for self-improving intelligent educational systems, In Design Recommendations for Intelligent Tutoring Systems, 2019, 7, 131-145.
- Woloszynsky T., Kurzynski M. On a New Measure of Classifier Competence in the Feature Space, Advanced in Intelligent and Soft Computing, 2009, 3, 285-292. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-93905-4_34
- Baker R. S. Stupid tutoring systems, intelligent humans, International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 2016, 26(2), 600-614.
- Lazarsfeld P. F., Henry N. W. Latent Structure Analysis, Boston, Houghton Mifflin Company, 1968, 294 p.
- Uglev V. A., Ustinov V. A. The new competencies development level expertise method within Intelligent Automated Educational Systems, Trends in Practical Applications of Heterogeneous MultiAgent Systems. The PAAMS Collection. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 2014, 293, 157-164. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-07476-4_19
- Buchanan B., Shortliffe E. Rule-based Expert Systems: The MYCIN Experiments of the Stanford Heuristic Programming Project, Reading, Addison-Wesley, 1984, 748 p.
- Uglev V. A., Sychev O. A. Concentrating Competency Profile Data into Cognitive Map of Knowledge Diagnosis, Diagrammatic Representation and Inference. LNCS, 2021, 12909, 443-446. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-86062-2_46
- Лефевр В. А. Лекции по теории рефлексивных игр. Москва: Cogito-Tsentr, 2009, 218 с. [Lefebvre V. A. Lectsyypo teorii reflexivnyh igr, Moscow. Cogito-Tsentr, 2009, 218 p. (in Russian)]
- Углев В. А. Базовая модель процессов рефлексии в интеллектуальных автоматизированных обучающих системах. Математические структуры и моделирование, 2018, 1(45), 111-121. [Uglev V. A. The base model of reflexive process in the intellectual automation educational systems, In Mathematical structures and modeling, 2018, 1(45), 111-121 (in Russian)]
- Butcher P. G., Jordan S. E. A comparison of human and computer marking of short free-text student responses, Computers & Education, 2010, 55(2), 489-499
- Сычев О. А., Стрельцов В. О. Использование шаблонов в виде регулярных выражений в тренировочных и контрольных тестовых вопросах с открытым ответом. Открытое образование, 2015, 2(109), 38-45 [Sychev O. A., Streltsov V. O. Usage of regular expressions as templates in formative and summative open-answer questions. Open education, 2015, 2(109), 38-45 (in Russian)]
- Callear D. H., Jerrams-Smith J., Soh V. CAA of short non-mcq answers, Proceedings of the 5th International CAA conference, 200.
- Leacock C., Chodorow M. C-rater: Automated scoring of short-answer questions, Computers and the Humanities, 2003, 37(4), 389-405. DOI: 10.1023/A:1025779619903
- Sirin E., Parsia B., Grau B., Kalyanpur A., Katz Y. Pellet: A Practical OWL-DL Reasoner, Web Semant., 2007, 5(2), 51-53. DOI: 10.2139/ssrn.3199351
- McBride B. Jena: A Semantic Web Toolkit, IEEE Internet Computing, 2002, 6(6), 55-59. DOI: 10.1109/MIC.2002.1067737
- Грибова В. В., Островский Г Е. Интеллектуальный облачный сервис для отработки навыков постановки диагноза. Медицинская техника, 2017, 6(306), 29-32 [Gribova, V.V., Ostrovskiy G. E. Intelligent cloud service for diagnosis training, Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 6(306), 29-32 (in Russian)]
- Sychev O., Penskoy N. Ontology-Based Determining of Evaluation Order of C Expressions and the Fault Reason for Incorrect Answers, Proceedings ofthe ISWC2020 Demos and Industry Tracks: From Novel Ideas to Industrial Practice, 2020, 44-49
- Sychev O., Denisov M., Terekhov G. How it Works: Algorithms - A Tool for Developing an Understanding of Control Structures. Proceedings of the 26th {ACM} Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education, 2021, 621-622. DOI: 10.1145/3456565.3460032
- Wielemaker J., Schrijvers T., Triska M., Lager T. SWI-Prolog. Theory and Practice of Logic Programming, 2012, 12(1-2), 67-96. DOI: 10.1017/S1471068411000494


