Inter-municipal cooperation as an institution of strategic development of territories
Автор: Kozlova Olga A., Makarova Maria N.
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Development of municipal formations
Статья в выпуске: 3 (57) т.11, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The purpose for the article is to substantiate the ways of developing the institution of inter-municipal cooperation in the context of strategic planning at the local level. Most municipal units do not have the necessary resources to develop and implement plans and programs for social and economic development aimed at the integrated solution of all local issues. At the same time, the analysis of projects on strategic socio-economic development of some municipal units in the Sverdlovsk Oblast demonstrates the territories’ disinterest in resource integration for implementing development projects to solve common problems on mutually beneficial terms. The present study is the result of the need to seek mechanisms to increase the efficiency of socio-economic development of municipal units amid limited resources. The authors propose a methodical basis of the multicomponent analysis of strategic development factors based on sectoral and territorial cooperation of municipal units...
Inter-municipal cooperation, territorial development, strategic planning, quality of life
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147224051
IDR: 147224051 | УДК: 332.1 | DOI: 10.15838/esc.2018.3.57.9
Текст научной статьи Inter-municipal cooperation as an institution of strategic development of territories
Relatively low rates and negative trends in the socio-economic development of certain municipal units are often associated with limited resources of various kinds absent in these territories and present in others. One of the solutions to this problem may be joint use of resources by several municipal units on a contractual basis and consideration of this type of interaction when elaborating the strategy of socio-economic development of the territory.
Despite much literature devoted to cooperation between municipal units, the elaboration of socio-economic development strategies that would identify joint solutions to social, economic, and environmental problems of municipal development based on voluntary inter-municipal cooperation is not sufficiently implemented in Russia. Thus, the purpose of this article is to justify the ways to develop the institution of inter-municipal cooperation in the context of strategic planning at the local level.
Theory and methodology
Strategic planning applied to municipal units refers to the process through which local communities “form an image of their future and determine the stages of its achievement based on local resources” [1].
At the same time, the strategy itself does not guarantee that the goal will be achieved, unless effective mechanisms for its implementation are involved. When developing a strategy for municipal unit development it is necessary to take into account many factors, including the interests of the population and business, as well as relations, existing or still emerging: vertical – with regional, federal authorities, and horizontal – with nearby municipal units [2]. Thus, in order to avoid territorial differences it is necessary to view strategic objectives of the municipal unit development in their correlation with other municipal plans. Moreover, numerous problems of municipal units’ daily life due to the functions assigned to local authorities cannot be effectively solved in terms of resource scarcity, which objectively indicates the need for developing various types of territorial interaction. In this regard, inter-municipal cooperation as an institution of territorial cooperation involves building close relations between spatial organization and socio-economic development of municipal units. In our opinion, analysis and consideration of its two aspects (internal and external environment; Fig. 1) is an important part of elaborating the socio-economic development strategy.
Analysis of the internal environment is associated with defining factors in the strategic areas of territory’s socio-economic development, indirectly affecting the interests of the neighboring municipal units. At this stage of strategy development, an effective type of development is determined based on the territory’s own natural, capital, labor, and other resources.
Analysis of the external environment is associated with defining objective cooperation factors and finding forms of interaction with the neighboring areas, which makes it possible to jointly solve problems of mutual interest and leading to:
– to the development of all spheres of economy, increased quality of life in interacting territories;
– an opportunity to prevent the possible negative consequences associated with resource constraints of municipal units;
– an opportunity to find compensating measures to implement the socio-economic policy.
Many problems related to increasing the efficiency of the institution of inter-municipal cooperation are analyzed in terms of the development of strategic spatial planning documents. This research aspect is very relevant for domestic territorial planning since the plan content will largely depend on the involvement of municipal units in intermunicipal cooperation.
The right of local communities to cooperate is enshrined in Article 10 of the European Charter of Local Self-Government (ratified in Russia by Federal law “On ratification of the European Charter of Local Self-Government” no. 55-FZ, dated 11.04.1998).
Establishing and developing the institution of inter-municipal cooperation in Russia is

Figure 1. Correlation between inter-municipal cooperation and development strategies of municipal units
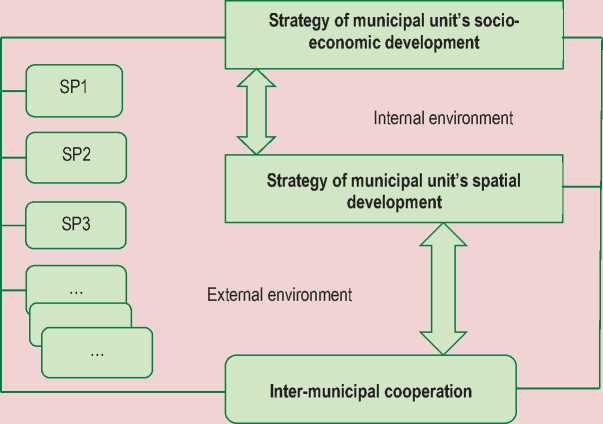
defined in Federal Law “On general principles of local self-government in the Russian Federation” no. 131-FZ, dated 06.10.2003, which establishes its basic organizational forms (unified all-Russian association of municipal units, the council of municipal units of the Russian Federation, inter-municipal organizations, non-profit organizations of municipal units); the legal status of forms of inter-municipal interaction is identifies, including agreements and contracts concluded for the purpose to combine resources to address local issues, which is becoming very important in modern conditions.
The aim of the institution of inter-municipal cooperation in Russia is to increase the sustainability of territories’ development by addressing local problems and reducing dependence on external socio-economic threats. Among the existing areas of cooperation the most effective are: transfer of experience of municipal government; advocacy of interests of local communities at the regional level; optimization of resources of local communities to address socio-economic and environmental challenges of municipal units [3].
In socio-economic terms the mechanisms of inter-municipal cooperation ensure a more pronounced effect through resource saving, which can be achieved through addressing socio-economic problems of several settlements. However, some Russian and foreign authors note that the development of inter-municipal cooperation causes certain problems: increased transaction costs, issues of competence and responsibility in solving specific problems; in some cases, it is possible to limit the freedom of action of subjects involved in cooperation [4].
In territorial terms, inter-municipal cooperation is designed to stimulate joint solution of socio-economic development objectives locally, improving the efficiency of using local resources, land resources in particular [5], and the efficiency of decisionmaking [6]. It is possible to defend the interests of the territory at the regional and national level more reasonably [7].
In terms of regional interests, intermunicipal cooperation, on the one hand, is aimed at overcoming the fragmentation of local self-government and promoting joint solutions of individual tasks on a contractual basis, as well as at the development of the middle, intermediate level of local government able to provide the necessary services to small territorial units, especially located in rural areas. On the other hand, it is an instrument of regional economic development and implementation of the local federal policy through providing appropriate organizational and financial support [8]. The key principles of inter-municipal cooperation are preserving the independence of municipal member-units of cooperation, political and socio-economic feasibility, as well as voluntary participation (although not always1).
V.L. Tambovets distinguishes between four types of municipal cooperation: (1) competition, (2) cooperation, (3) co-competition (combination of competition and cooperation), as well as a “marginal” form of interaction such as (4) merger (association) of municipal units [9]. Analyzing the possible forms of municipal cooperation, the author concludes that the most promising area of inter-municipal cooperation is co-competition, where municipal units closely cooperate to provide services to the local population on mutually beneficial terms, and compete for grants from regional and central governments.
In Russia, the organizational forms of intermunicipal cooperation are dominated by contractual (joint services to the population and a possibility of transferring powers to another municipal unit or inter-municipal association) and associative forms (primarily representative, coordination and advisory functions). The Coordination Board on Regional Councils Promotion and Unified all-Russian Association of Municipal Units established in 2005 developed model documents (memorandum and articles of association) and recommendations on methods, terms, and forms of municipal councils establishment. Thus, an institutional design of the system of inter-municipal cooperation at the state level took place [10].
At present, there are a number of intermunicipal associations in Russia, including the Association of Siberian and Far Eastern cities, the Association of municipal units “Goroda Urala” (Ural Cities), the Association of cities of the Volga Region and others. Moreover, in most of Russia’s constituent entities municipal councils are established. It would seem that the development of these institutions shows the prospects for inter-municipal cooperation in areas such as territorial and strategic planning, implementation of joint infrastructure and investment projects, territory development, etc., but in general their functioning is informative rather than practical [7].
At the same time, the real use of organizational and economic forms of cooperation can enable municipal units to implement ambitious investment and infrastructure projects aimed to implement the strategies of socio-economic development of cooperating municipal units.
As noted in a number of studies, the development of inter-municipal economic cooperation in the form of economic societies in Russia is hampered by contradictions between legislative provisions on local selfgovernment and the civil legislation standards, as well as lack of special legal regulation of forms of such cooperation [11; 12]. Moreover, one of the reasons complicating the formation and development of organizational and economic forms of inter-municipal cooperation is insufficient funds and experience of municipal employees in this area [9; 13].
In European countries, the institution of inter-municipal cooperation is actively developing in two main areas. On the one hand, horizontal ties are developing (most European countries), on the other hand, vertical cooperation between different levels of territorial administration (for example, Spain, Australia) is being built [6]. There are examples of developing network forms of inter-municipal cooperation involving both local authorities, regional and national government, as well as various social structures. A common form of cooperation is joint administration which integrates the actions of individual municipal units in a new organization which they jointly manage [14].
Public law and target agreements are relevant for Germany [15]. The main scope of their application is operation of public facilities – cultural facilities, sports, utilities. In Denmark, several small municipal units may enter agreements with one large municipal unit, which enables them to purchase the necessary services at a better price. Another type of inter-municipal cooperation is presented in the form of companies (cooperative societies, partnerships, limited liability companies, etc.). As in Germany, cooperation is particularly preferable in the sphere of public services [16].
The results of foreign studies of intermunicipal cooperation, its advantages and disadvantages show that the use of this institution in municipal administration has certain limitations, first of all due to the effect of administrative resources, reluctance of management personnel to deal with the issues of building cooperative relations, as well as incompetence in this area [9], secondly, due to the scope of its application characterized, as a rule, by significant financial investment and fall into the influence zone of several municipal units. In this regard, joint companies engaged in public and road infrastructure, projects related to tourism development, spatial planning of territories, as well as the implementation of regional projects have been mostly developed. The advantages of cooperation include the expansion of opportunities to receive funding from the region, cost savings and joint representation of municipal interests in higher administrative bodies [17]. Along with the advantages, there are also the disadvantages associated with lack of effective mechanisms for coordinating financing of joint strategic projects, which is constrained by many factors (insufficient legislative framework, financial incentives for the representatives of different levels of administration, human resources, time and ideas, etc.).
At the same time, much attention is paid to the search for ways of further development of inter-municipal cooperation. For example, some publications note that despite the existing solutions in the local environmental policy and sustainable development at the regional level, there are significant challenges in voluntary inter-municipal cooperation on environmental issues [18]. In this regard, studying the development of a conceptual framework for analyzing the factors determining territorial interactions, primarily through forming human-oriented institutions, is very relevant. Other research results in voluntary formation of inter-municipal coalitions conducted between 1995 and 2002 based on data from 1056
municipal units in the French Brittany leads to a conclusion that the decision of a municipal unit to cooperate in provision of local public goods depends on the decisions taken by its neighbors [19].
In our view, the authors conclude that cooperation with the neighboring municipal units is much more likely if the latter are already engaged in provision of any shared public goods at the local level. This fact may indicate that functional cooperation is more likely to arise because of the so-called simulation motivation and will be poorly motivated at the same time by administrative levelling of the socioeconomic situation in municipal units, i.e. this type of interaction should be initiated by the municipal units themselves, rather than by higher authorities.
Methodological tools
To substantiate the ways of inter-municipal cooperation development in the context of strategic planning at the local level, texts of strategies for socio-economic development of a number of municipal units of the Sverdlovsk Oblast have been used. Assessment of intermunicipal cooperation potential is carried out through using the methods of multicomponent analysis of factors in strategic development taking into account sectoral and territorial interaction of municipal units. For this purpose, methods of comparative analysis, content analysis of socio-economic development documents, methods of socioeconomic space localization, as well as elements of foresight are used. The case study of the city of Krasnoufimsk in the Sverdlovsk Oblast substantiates the prospects of formation of the institution of inter-municipal cooperation taking into account the strategic projects of the neighboring territories not only of internal subordination, but also of territories administratively subordinated to other Russia’s constituent entities.
Results and discussion
In the framework of expert evaluation of draft strategies of socio-economic and spatial development of twenty municipal units in the Sverdlovsk Oblast, which involved the authors of this article in February 2018, a number of problems were identified in their development. In most cases, draft strategic documents indicate that municipal authorities have little idea of the goals and objectives of spatial development. Only two out of 20 municipal units (Krasnoufimsk and Malyshevskoye urban districts) presented their vision of development in the context of implementation of transport projects in the future, which will ensure the development of these territories. For example, in the development strategy of Krasnoufimsk takes into account the prospect of building a high–speed highway connecting Ekaterinburg and Kazan, the implementation of which will form the socio-economic space of Krasnoufimsk as a “transport and logistics gate of the Sverdlovsk Oblast”.
In many strategies the goal does not reflect the essence of spatial development and repeats the goal of socio-economic development of a municipal unit. But, most importantly, absolutely all draft strategies do not take into account the opportunities and threats related to the development prospects of the neighboring territories with a common settlement frame; there is no understanding of the need to analyze legal documents for territorial and sectoral planning with the information about territories’ development plans, potential projects at the level of neighboring municipal units and at the regional level. The mechanisms of spatial development are disclosed formally and do not reflect the characteristics of the municipal units’ development. In all the analyzed strategy projects there is no such institution of development as inter-municipal cooperation.
In order to determine the methodological framework for assessing the prospects of municipal unit development based on building relations between the neighboring municipal units, we use Krasnoufimsk urban district (UD) in the Sverdlovsk Oblast as an example: it has the most successful draft strategy of spatial development.
The city district has common administrative boundaries not only with intra-regional municipal units, but is also located in immediate vicinity to other regions (Perm Krai and the Republic of Bashkortostan).
The economic space of Krasnoufimsk UD consists of municipal units located within the limits of possible daily circular migration. Their brief description is presented in Table 1 .
Taking into account the opportunities of inter-municipal cooperation when elaborating development strategies is due to the need to level the negative effects of labor circular migration on the socio-economic condition of certain municipal units.
The degree of circular migration between territories is primarily determined by transport availability. When taking into account the time spent on moving from one point to another, three zones of transport availability are usually distinguished [20, pp. 63–68]. Based on the criterion of time spent on the trip, the economic space of Krasnoufimsk has the following zone distribution of municipal units.
The first belt (30 min or 50–55 km) includes three municipal units: Krasnoufimsky okrug MD, Achit UD in the Sverdlovsk Oblast and Oktyabrsky MD in Perm Krai. These municipal units have smaller population compared to Krasnoufimsky MD, lower income and a higher level of registered unemployment ( Fig. 2 and 3 ). The economic structure in these territories is dominated by agriculture. Analysis of investment passports of municipal units
Table 1. Economic space of Krasnoufimsk UD in the Sverdlovsk Oblast*
|
Name of municipal unit, central residential area, region |
Distance to Krasnoufimsk, km |
Population in municipal unit in 2016, thousand people |
Economic specialization field of municipal unit |
|
Krasnoufimsk UD, City of Krasnoufimsk, Sverdlovsk Oblast |
0 |
39.3 |
Social sphere, food processing, transport, manufacturing |
|
Krasnoufimsk okrug, Natal’insk, Sverdlovsk Oblast |
20 |
26.0 |
Agriculture |
|
Achit UD, Achit, Sverdlovsk Oblast |
26 |
16.0 |
Agriculture, manufacturing, trade |
|
Oktyabrsky MD, Oktyabrsky, Perm Krai |
54 |
28.1 |
Constructions, agriculture |
|
Arti UD, Arti, Sverdlovsk Oblast |
59 |
27.9 |
Agriculture, manufacturing |
|
Suksun MD, Suksun, Perm Krai |
78 |
19.6 |
Manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture |
|
Mechetlinsky MD, Bolsheustyikinskoye, Republic of Bashkortostan |
91 |
23.0 |
Agriculture, food processing, energy |
|
Bisert UD, Bisert, Sverdlovsk Oblast |
103 |
10.0 |
Agriculture, manufacturing |
|
Kungur MD, Perm Krai |
127 |
42.1 |
Agriculture, mineral extraction, tourism |
|
UD City of Kungur, Perm Krai |
127 |
66.2 |
Food processing, plasterwork manufacture, constructions, transport and communication |
|
Duvansky MD, Mesyagutovo, Republic of Bashkortostan |
140 |
30.9 |
Food processing, agriculture, energy, crude oil production, forestry |
|
Askino MD, Askino, Republic of Bashkortostan |
149 |
18.9 |
Energy, food processing, constructions, agriculture |
|
Nizhniye Sergi MD, Nizhniye Sergi, Sverdlovsk Oblast |
149 |
40.5 |
Steelmaking, manufacture of machine and equipment |
|
MD City of Ekaterinburg, Sverdlovsk Oblast |
202 |
1455.9 |
Industry; social sphere; management and administration; finance; real estate; trade, constructions, energy |
|
City of Perm, Perm Krai |
208 |
1048.0 |
Manufacturing, energy, transport and communication, real estate, constructions, trade, IT, social sphere |
|
City of Ufa, Republic of Bashkortostan |
369 |
1126.1 |
Manufacturing, energy, transport, constructions |
|
* UD – urban district, MD – municipal district. |
|||
indicates that in the near future in these areas none of major investment projects involving the creation of new jobs (see Table 2) is planned. Thus, municipal units in the first zone serve as suppliers of labor resources for Krasnoufimsk, and are active consumers of social services provided by the city organizations.
The second zone (1 hour or 100–110 km) includes four municipal units: Arti and Bisertsk UDs in the Sverdlovsk Oblast, Suksun UD in Perm Krai, and Mechetlinsky MD in the Republic of Bashkortostan. These territories have lower population, lower income levels and higher (Arti and Suksun MDs) or comparable (Mechetlinskiy MD, Biserts UD) unemployment rates (see Figure 2 and 3). The economy of these territories is prevailed not only by agriculture, but also by manufacturing, resort and sanatorium services (Suksun MD) and energy (Mechetlinsky MD) spheres.
Thus, municipal units in the second zone are suppliers of labor resources for Krasnoufimsk. At the same time, a wide range of investment projects is expected to be implemented in these municipal units, which will give an opportunity to create new jobs
Figure 2. Characteristics of labor markets of municipal units included in the economic space of Krasnoufimsk UD
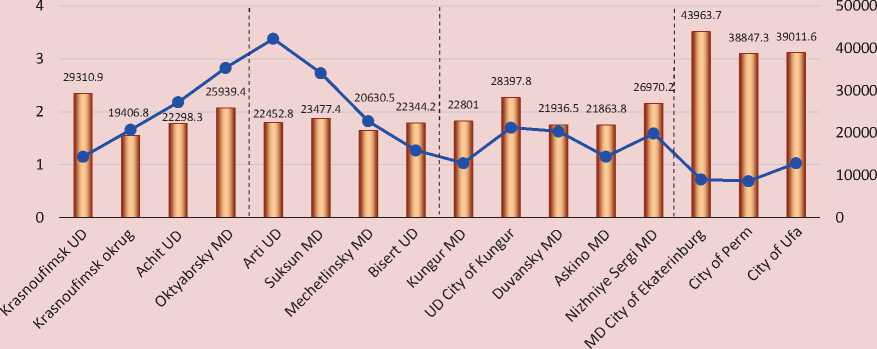
■ ■ Average wage paid in 2016, RUB
• Registered unemployment rate in 2016, %
Figure 3. Characteristics of economic development of municipal units included in economic space of Krasnoufimsk UD
798.6
682.5
619.7
594.0
208.2
106.1
27.6
76.8
24.0 20.5
13.4 90.1 29.8
900.0
800.0
700.0
600.0
500.0
400.0
300.0
200.0
100.0
0.0
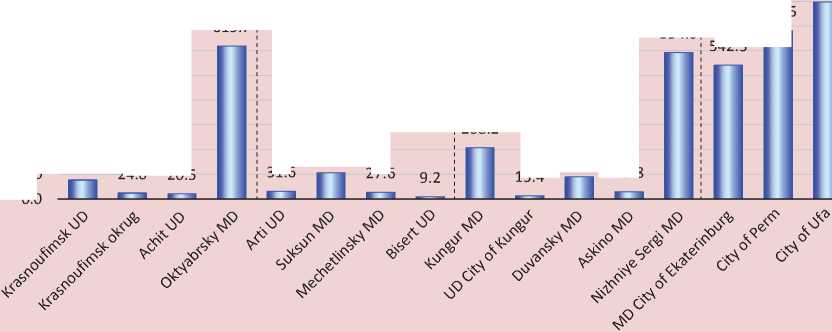
542.3
31.6
□ Shipped domestic goods and services per capita in 2016, thousand RUB/person
in these territories ( Tab. 2 ), which is very likely to pose a threat of labor outflow from Krasnoufimsk to actively developing territories.
The population of municipal units in the second zone is a potential consumer of social services presented in Krasnoufimsk. However,
Table 2. Promising investment projects in the economic space of Krasnoufimsk UD*
|
Name of municipal unit, region |
Distance from City of Krasnoufimsk, km |
Promising investment projects |
|
Suksun MD, Perm Krai |
78 |
Therapeutic tourism (Kacha sanatorium) |
|
Bisert UD, Sverdlovsk Oblast |
103 |
Building fitness and health complexes, transport and logistics center; brickworks; woodworks; agricultural products refinery; gas well |
|
UD City of Kungur, Perm Krai |
127 |
Nebesnaya Derevnya theme park , tea-packing factory; tourist cluster |
|
Askino MD, Republic of Bashkortostan |
149 |
A full wood processing production cycle; construction of a ski complex in Kubiyazovskii rural council |
|
Nizhniye Sergi MD, Sverdlovsk Oblast |
149 |
Cement plant construction; launch of a gas engine power plant; construction of Triumph fitness and health complex |
|
MD City of Ekaterinburg, Sverdlovsk Oblast |
202 |
Construction of a zoo, water sports palace, Hermitage-Ural cultural and educational center, casting and heat treatment center; establishment of a multi-profile tourist and recreational complex Yekaterinburg-Europe-Asia |
|
City of Perm, Perm Krai |
208 |
“Development of innovative territorial cluster of rocket engine-building project “”New Star” Technopolis”; Photonics cluster (development and production of individual devices based on photonic integrated circuits) |
|
City of Ufa, Republic of Bashkortostan |
369 |
Serial production of helicopter engines such as VK-2500; Belaya Reka sports complex, three swimming complexes, several shopping and business centers; cable production plant; hemodialysis center; scientific and technological park at Institute of Petrochemical Processing of the Republic of Bashkortostan, etc. |
|
* SO – Sverdlovsk Oblast, PK – Perm Krai, RB – Republic of Bashkortostan, UD – urban district, MD – municipal district. |
||
regional centers (Yekaterinburg and Perm) located at the same distance from these municipal units are in a much more favorable position than Krasnoufimsk in terms of attractiveness for consumers for various types of services.
The third zone (1.5 hours or 150 km) includes 5 municipal units: Kungur MD, Kungur UD, Askino MD (Perm Krai), Duvansky MD (Republic of Bashkortostan), and Nizhniye Sergi MD (Sverdlovsk Oblast). Three of them have comparable population, the population in one of them is much smaller, the population in the other is much higher than that of Krasnoufimsk UD (see Table 1). In all territories, income levels are comparable or slightly lower than in Krasnoufimsk UD, the registered unemployment rate is approximately at the same level (see Figure 2). It is also worth noting that three out of five municipal units in the third zone have significantly higher economic development results (see Figure 3).
The economy in these territories is represented by agriculture, various industries, manufacturing, mining, energy, transport, constructions, and tourism (see Table 1). In the future, several major investment projects are planned: they are aimed to create new jobs; they are related to creation of a tourist cluster, construction of a ski resort, a cement plant, etc. (see Table 2) Thus, the third zone of the economic space in the City of Krasnoufimsk has a significant potential of attracting labor resources from the city.
In our opinion, to understand the whole image of the socio-economic space formation of the City of Krasnoufimsk it is advisable to distinguish the fourth zone (over 200 km) which is represented by millionaire cities – regional centers on the border of which the district is located (Sverdlovsk Oblast, Perm Krai, Republic of Bashkortostan). Due to significantly higher wages and a more capacious labor market these cities are significant attraction points in the economic space of Krasnoufimsk for its labor resources and for consumers in the sphere of social services, shopping and entertainment. In the future, this trend will remain due to the implementation of a large number of investment projects which ensure active economic and social development of millionaire cities in the fourth zone of Krasnoufimsk economic space.
The analysis has indicated the need for developing municipal strategies to take into account many factors affecting the processes of formation and development of Krasnoufimsk economic space. Its boundaries depend both on time and transport costs of traveling to the nearby municipal units, and on the possible shift of the functional role of Krasnoufimsk towards a recipient , a competitor or a donor of labor, investment, social or trade services ( Figure 4 ).
Taking into account the role functions of a municipal unit highlighted in the case study Krasnoufimsk in the Sverdlovsk Oblast will, in our opinion, develop a better strategic document of territorial planning based on the institution of inter-municipal cooperation which is beneficial to all subjects of the socioeconomic space.
Today the draft strategy of socio-economic development of the City of Krasnoufimsk claims to implement two spatial development projects. Firstly, as mentioned above, it is the participation in construction of Ekaterinburg– Kazan high–speed highway, which will solve the infrastructure problems of the territory and form another industry specialization – transport and logistics services. Secondly – the formation of the Krasnoufimsk agglomeration which would provide the synergistic effect from joint solution of socio-economic problems of a group of municipal units. However, the implementation of these projects requires careful study of inter-municipal cooperation models, as well as conclusion of relevant contracts and agreements currently absent.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we emphasize that the proposed methodological approach to factor analysis of prospects for municipal units’ development based on strategic projects
Figure 4. Classification of Krasnoufimsk UD interactions with municipal units included in its economic space
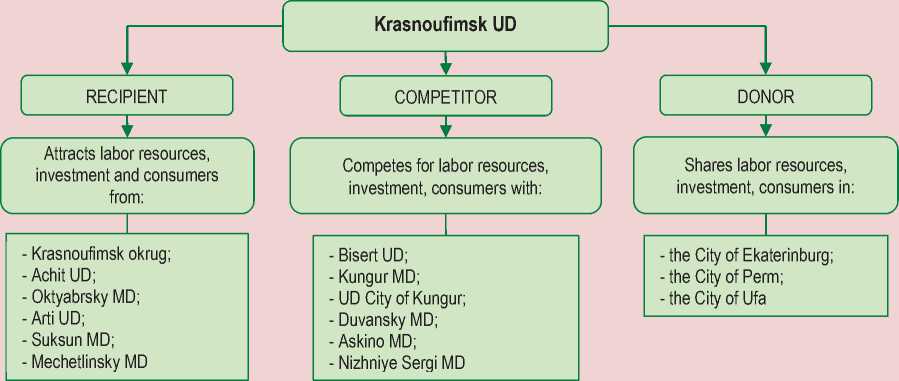
of the neighboring territories expands the opportunities of their socio-economic development, increasing the coherence of socio-economic and territorial spaces, provides an objective assessment of intermunicipal cooperation potential. Further research into building effective integrative schemes of interaction between municipal units in the context of socio-economic and spatial development needs to become a significant part on the agenda for formulating the methodology of an integrated system of strategic planning of municipal and regional development.
Список литературы Inter-municipal cooperation as an institution of strategic development of territories
- Shamarova G.M. A strategic plan for developing a municipal unit: tools, methods, practice. Praktika munitsipal’nogo upravleniya=Municipal administration practice, 2014. no. 2. Pp. 15-25..
- Antipin I.A., Kazakova N.V. Conceptual framework for the development of a spatial development strategy in a municipal unit. Rossiiskoe predprinimatel’stvo=The Russian journal of entrepreneurship, 2016, vol. 17, no. 8, pp. 1011-1026. DOI: 10.18334/rp.17.8.35119
- Petrogradskaya A.A. Vidy i formy mezhmunitsipal’nogo sotrudnichestva v Rossiiskoi Federatsii. Vestnik Samarskogo universiteta. Seriya: Istoriya. Pedagogika. Filologiya=Vestnik of Samara State University. Series: History. Pedagogics. Philology, 2010, no. 5 (79), pp. 256-262..
- Vlasova N.Yu., Dzhek L.N. Theory and practice of inter-municipal cooperation amid the EU regional policy. Izvestiya UrGEU=Bulletin of Ural State University of Economics, 2010, no. 2(28), pp. 26-31..
- Serrano J., Demaziere C. The statute of suburban land in spatial planning: the influence of intermunicipal cooperation. Revue d’economie regionale et urbaine, issue 4, pp. 737-765 DOI: 10.3917/reru.164.0737
- Kurochkin A.V. Net forms of regional and local government: present day experience of Finland. Ars Administrandi, 2011, no. 1, pp. 105-112..
- Pobedin A.A. Prospects of inter-municipal cooperation in the development of urban agglomerations: the experience of foreign countries and Russia. Vestnik Omskogo universiteta. Seriya «Ekonomika»=Herald of Omsk University. Series "Economics", 2013, no. 4, pp. 43-48..
- Cherkasov A.I. Development of Intermunicipal cooperation as an alternative to enlargement of local communities in foreign countries. Gosudarstvo i parvo=State and Law, 2016, no. 2, pp. 71-78..
- Tambovtsev V.L. Inter-municipal interactions in an economic analysis framework. Terra economicus, vol.15, no. 3, pp. 19-31. DOI: 10.23683/2073-6606-2017-15-3-19-31
- Konyashkin V.V. Historical aspects of inter-municipal cooperation in Russia. Tavricheskii nauchnyi obozrevatel’=Taurida science review, 2015, no. 2 (October), pp. 47-52..
- Serebrennikova A.PP. Inter-municipal cooperation: problem of defining and legal organization form. Sibirskii yuridicheskii Vestnik=Siberian bulletin of Law, 2004, no. 2, pp. 32-34..
- Shtemenko K.PP., Maslova V.O. Problems of economic development in medium sized cities and ways to address them. Nauchnye vedomosti Belgorodskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta. Seriya: Istoriya. Politologiya. Ekonomika. Informatika=Scientific review of Belgorod State University, 2012, no. 1 (120), issue 21/1, pp. 51-55..
- Gutnikova E.A. Inter-municipal cooperation as a factor promoting the economic and social development. Ekonomicheskie i sotsial’nye peremeny: faktory, tendentsii, prognoz=Economic and social changes: facts, trends, forecast, 2012, no. 6 (24), pp. 218-230..
- Butova T.V., Pukhova M.M., Shchukin I.A. Problems and prospects for establishing the institution of inter-municipal cooperation in Russia. Upravlencheskie nauki=Management science, 2013, no. 3, pp. 4-15..
- Graf I.V. Inter-municipal economic cooperation: experience in legal management in foreign countries. Vestnik Tyumenskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta. Sotsial’no-ekonomicheskie i pravovye issledovaniya=Bulletin of Tyumen State university. Socio-economic and legal research, 2006, no. 1, pp. 150-156..
- Pindt H. A hunder years experience of cooperation in Denmark. Rossiiskaya munitsipal’naya praktika=Russian municipal practice, 2009, no. 8, pp. 17-21..
- Rus P., Nared J, Bojnec PP. Forms, areas, and spatial characteristics of intermunicipal cooperation in the Ljubljana urban region. Acta geographica slovenica-geografski zbornik, 2018, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 47-61 DOI: 10.3986/AGPP.4830
- Lintz G.A. Conceptual Framework for Analyzing Inter-municipal Cooperation on the Environment. Regional Studies, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 956-970 DOI: 10.1080/00343404.2015.1020776
- Di Porto E., Parenti A., Paty PP., Abidi Z. Local government cooperation at work: a control function approach. Journal of economic geography, vol.17, no. 2, pp. 435-463 DOI: 10.1093/jeg/lbw008
- Kozlova O.A. (Ed.). Prostranstvennaya organizatsiya sotsial’no-trudovykh sistem: genezis i problemy razvitiya: kol. monografiya . Ekaterinburg: Institut ekonomiki UrO RAN, 2010. 206 pp.


