Изменение экспрессии антиоксидантных генов при росте Escherichia coli на различных источниках углерода и энергии
Автор: Петерс М.А., Музыка Н.Г., Тюленев А.В., Октябрьский О.Н., Смирнова Г.В.
Журнал: Вестник Пермского университета. Серия: Биология @vestnik-psu-bio
Рубрика: Микробиология
Статья в выпуске: 4, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Стрессы бактерий нередко сопровождаются усилением продукции активных форм кислорода (АФК). Вследствие этого уровень экспрессии антиоксидантных генов может играть важную роль в адаптации бактерий к изменяющимся условиям среды. В данной работе, используя аэробно растущие культуры E. coli, мы изучили влияние источников углерода и энергии на экспрессию антиоксидантных генов katG, katE и sodA, кодирующих, соответственно, каталазы HPI, HPII и Mn-супероксиддисмутазу. При росте на сукцинате, малате, а-кетоглутарате и ацетате как единственных источниках углерода и энергии, экспрессия гена katG была, соответственно, в 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 и 2.3 раза выше, чем при росте на глюкозе. Экспрессия гена katE у бактерий, растущих на сукцинате, малате, а-кетоглутарате или ацетате, была выше, чем у растущих на глюкозе, в 1.8, 1.95, 1.5 и 2.1 раза, соответственно. При росте на глюкозе, сукцинате и малате наблюдалось снижение экспрессии гена sodA в течение периодики. На ацетате экспрессия sodA оставалась постоянной и превышала уровень, характерный для глюкозы в 1.2-1.8 раза. Скорость продукции супероксида и накопление Н2О2 в среде снижались в условиях, способствующих повышенной экспрессии антиокси-дантных генов.
Супероксид, н2о2, каталазы hpi и hpii, mn-супероксиддисмутаза, бактерии
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147204795
IDR: 147204795 | УДК: 579.22
Текст научной статьи Изменение экспрессии антиоксидантных генов при росте Escherichia coli на различных источниках углерода и энергии
Активные формы кислорода (супероксидный анион, перекись водорода, гидроксильный радикал и др,) постоянно образуются при нормальном аэробном метаболизме. и с ЭТОЙ ТОЧКИ Зрения ЯВЛЯЮТСЯ неизбежными побочными продуктами жизни в присутствии кислорода. Образование супероксида или Н2О2 происходит в результате слузганного переноса одного или двух последовательных электронов с редокс-акгивных сайтов флавиновых ферментов на кислород [Imlay, Fridovich, 1991; Gonzalez-Flecira, Demple, 1995; MessnerJmlay, 1999].
У E. colt скорость продукции эндогенного cy-
(C Петерс M. А., Музыка H. Г, Тюленев А. В., Октябрьский О. Н., Смирнова Г. В., 2016
пероксида в цитоплазме составляет порядка 5 м кМ/сек. а эндогенной Н2О2 - около 15 м кМ/сек [Imlay, 2008]. Скорость продукции активных форм кислорода (АФК) нс является постоянной. определяется количеством рсдокс-активных сайтов и зависит от условий культивирования. Резкое торможение дыхания или повышение уровня ApFT может продлевать промежуток времени, в течение которого компоненты электрон-транспортной цепи находятся в восстановленном состоянии, тем самым повышая вероятность неферментативного восстановления кислорода с образованием супероксида и Н2О2 [Skulachev, 1998]. АФК способны повреждать все виды макромолекул в клетке, включая ДНК. липиды и белки, и нарушать метаболизм клетки путем инактивации ферментов, содержащих железо [Imlay, 2008; Anjem. Imlay, 2012; Gu, Imlay, 2013].
Для борьбы с этими окислительными повреждениями клетки Е. со И используют ряд ферментативных защитных систем, включая супероксид-дисмутазы (MnSOD, FeSOD и CuZnSOD), каталазы (HPI и ПРИ) и а л кил гидропероксидредуктазу (AhpFC) [Imlay, 2008]. Активность антиоксидантных систем регулируется таким образом, чтобы снизить концентрацию АФК до безопасного уровня. Различные стрессы у бактерий часто сопровождаются торможением дыхания, что может приводить к повышению скорости образования АФК. При этом степень индукции антиоксидантных ферментов может играть важную роль для процесса адаптации к новым условиям окружающей среды.
Целью настоящей работы было изучение влияния различных источников углерода и энергии на продукцию активных форм кислорода и степень экспрессии антиоксидантных генов sodA, katG и katE. кодирующих Мп-супероксилднсмутазу и каталазы HPI и ПРИ, соответственно.
Материалы и методы исследования
Штаммы бактерий и условия культивирования. В качестве объекта исследований использовали штамм Е. coli BW25113 ^(craD-araB)567, &lacZ4787(: тгнВ-3), Z-, rphA, MyhaD-rhaB>5<&, hsdR5\4. полученный из Е» coll Genetic Stock Center (CGSC). Штамм NM300I, несущий слияние промотора гена sodA со структурным геном hcZ, кодирующим Р-галактозидазу, был сконструирован путем трансдукции фагом PI слияния sodA::lacZ из Е. coli QC772 (дар проф. D. Touati) в BW25113. Штамм NM3021, несущий транскрипционное генное слияние kaiG::lacZ, был получен путем трансформации клеток Е. coli BW25113 плазмидой рКТЮЗЗ [Tao et al., 1989]. Штамм NM3031 со слиянием katE::lacZ был создан путем трансформации клеток Е. coli BW25113 плазмидой pRS
KatElO (дар проф. М. Volkert). Бактерии выращивали на минимальной среде М9 (Na2HPO4 * 12Н3О - 15.13 г/л; КН2РО4 - 3 г/л; NH4C1 - 1 г/л; NaCl -0.5 г/л; MgSO4*7H2O - 0.246 г/л: СаС13 -0.011 г/л) с добавлением 10 мМ источников углерода и энергии (глюкозы и натриевых солей сукцината, а-кетоглутарата, малата или ацетата). За ростом следили путем измерения оптической плотности при длине волны 600 нм (OD6№). Клетки из выращенной в аэробных условиях ночной культуры после центрифугирования переносили в 250 мл-вые колбы с 50 мл свежей среды (начальная OD^-0.1) и культивировали на шейкере (150 об/мин) при 37°С.
Удельную скорость роста культуры (ц) рассчитывали по формуле где 006оо(/2) и ОВ^л) - оптическая плотность культуры измеренная при длине волны 600 им, во времена и .
Уровень растворенного кислорода в среде непрерывно измеряли с использованием электрода Кларка InPro 6800 (Mettler Toledo) и блока регистрации и управления ферментера BioFlo 110 (New Brunswick Scientific Co., USA).
Измерение внеклеточ кого суперокс ид кого радикала (О3) осуществлялось по методу; предложенному Korshunov, Imlay [2006], который основан на способности супероксида восстанавливать цитохром с, добавленный в клеточную суспензию. С этой целью клетки из экспоненциальной фазы ресуспендировали в двух 50 мл-вых колбах, содержащих 10 мл ростовой среды с исследуемыми субстратами и 20 мкМ цитохрома с. В одну из колб добавляли супероксиддисмутазу (30 U/мл) и обе колбы инкубировали при 37°С в течение 2.5 ч., отбирая пробы с 30 мин.-ным интервалом. Пробы (1.5 мл) из обеих колб пропускали через мембранный фильтр и в каждом образце измеряли спектр поглощения между длинами волн 570 и 530 нм. Затем к каждому' образцу7 добавляли 0.2 мМ феррицианида калия, чтобы окислить цитохром, и вновь измеряли спектр. Количество восстановленного цитохрома рассчитывали, используя индуцированное феррицианидом изменение поглощения при 550 нм. Концентрация экстра клеточного супероксида определялась в парных образцах по разнице концентраций восстановленного цитохрома с в колбах без супероксиддисмутазы и в ее присутствии.
Концентрацию перекиси водорода (ЩО?) определяли флуоресцентным методом [Seaver, Imlay. 2001]. Метод основан на окислении реагента Amplex red в присутствии перекиси водорода и пе- роксидазы до флуоресцирующего продукта резору фина (максимумы облучения и эмиссии - 563 и 587 им)* Исследуемые образцы (2 мл) пропускали через мембранный фильтр, и перекись водорода в фильтрате измеряли согласно методу [Seaven Imlay, 2001]. Флуоресценцию конвертировали в концентрацию Н2О2. используя калибровку со стандартными растворами перекиси водорода.
Активность р-галактозмдазы определяли по методу Миллера [Miller, 1972] в штаммах Е, сой NM300L NM3021 и NM3031 несущих генные слияния sodAJacZ, katGwlacZ и katEwlacZ, соответственно.
Статистическую обработку экспериментальных данных осуществляли с помощью пакета программ Microsoft Excel и Statistica 6.0, вычисляя среднее значение, стандартную ошибку и доверительный интервал. Каждый результат показан как среднее значение из не менее трех независимых экспериментов ± стандартная ошибка среднего.
Результаты и их обсуждение
В наших экспериментальных условиях удельная скорость роста бактерий (ц) варьировала от 0.65 ± 0.01 час"1 до 0.18 ± 0.01 час"1 в зависимости от вида используемого источника углерода и энергии (рисунок). Максимальный уровень р достигался на глюкозе, минимальный - на ацетате. При росте на малате, сукцинате и а-кетоглутарате скорость роста бактерий снижалась по отношению к значению этого параметра на глюкозе на 24, 32 и
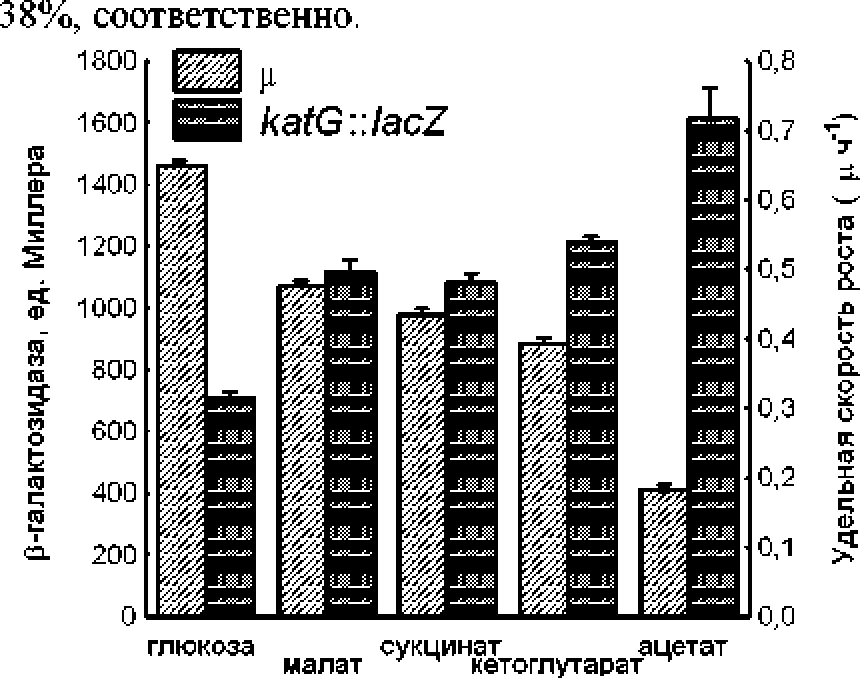
Изменение скорости роста и экспрессии гена katG при культивировании штамма Е. сой NM3021 на разных источниках углерода и энергии
Урожай биомассы через 2.5 ч. при культивировании на глюкозе был почти в 2 раза выше, чем на сукцинате, малате и а-кетоглукарате, и более чем в 3 раза превышал уровень, достигаемый на ацетате (не показано).
В отличие от удельной скорости роста, экспрессия гена katG при культивировании на сукцинате, малате, а-кетоглутарате или ацетате повышалась, соответственно, в 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 и 2.3 раза по сравнению с уровнем экспрессии этого гена при культивировании на глюкозе (рисунок) Статистический анализ выявил наличие обратной зависимости экспрессии гена katG от скорости роста с г = -0,99 <р < 0,05). Ген kaiG кодирует каталазу HPI и находится под контролем транскрипционного регулятора OxyR, который индуцирует экспрессию большого числа генов в ответ на повышение концентрации перекиси водорода [Slorz el al„ 1990], Кроме OxyR. ген kaiG регулируется транскрипционным фактором RpoS (os) являющимся глобальным регулятором общего стрессового ответа и перехода в стационарную фазу роста [Ivanova el al., 1994]. Уровень RpoS в клетке контролируется на уровне транскрипции, трансляции и стабильности белка [Hengge-Arronis, 2002], Было показано, что независимо от факторов, ограничивающих рост, экспрессия RpoS изменяется обратно пропорционально удельной скорости роста [Ihssen, Egli, 2004], В периодической культуре внутриклеточная концентрация RpoS возрастает при снижении скорости роста вследствие перехода из экспоненциальной в стационарную фазу. При росте на разных источниках углерода и энергии скорость роста бактерий в экспоненциальной фазе определяется энергетической эффективностью используемого источника. Следует ожидать, что снижение скорости роста Е. сой при культивировании на малате, сукцинате, а-кетоглутарате и ацетате, относительно роста на глюкозе, сопровождается пропорциональным повышением уровня RpoS в клетках. Такое повышение RpoS должно приводить к возрастанию экспрессии гена katG RpoS-зависимым образом, что и наблюдалось в наших экспериментах.
Ген katE, кодирующий каталазу НРП, также находится под контролем RpoS, Мониторинг активности р-галакгозидазы в штамме NM3O31, несущем слияние katEJacZ, показал, что экспрессия гена kaiE у бактерий, растущих на сукцинате, малате, а-кетоглутарате и ацетате, была выше, чем у растущих на глюкозе, в 1.8, 1,95, 1.5 и 2.1 раза, соответственно (не показано). Таким образом, как и б случае с katG, максимальный уровень экспрессии гена katE наблюдался при культивировании на ацетате, когда удельная скорость роста имела минимальное значение. Высокий уровень корреляции (г = 0,83:р<0,05) между уровнями экспрессии генов katG и katE может свидетельствовать, что экспрессия обоих генов контролируется одним и тем же фактором.
Ген 50^4, кодирующий Мп-супероксиддисму-тазу, находится под контролем нескольких глобальных транскрипционных регуляторов, вклад каждого из которых определяется условиями окружающей среды [Compan, TouatL 1993]. К числу этих регуляторов относятся Arc АВ, Fnr, SoxRS, Mar A* Fur и IHF. В анаэробных условиях ген st>ci4 репрессируется регуляторными белками Fnr и Аг-сАВ. Эта репрессия снимается при переходе к аэробным условиям* Дальнейшая активация экспрессии sodA в аэробных условиях происходит под действием окислительного стресса, вызванного добавлением редокс-ииклических генераторов супероксида, и регулируется системой SoxRS* Измерение активности р-галактозидазы в штамме NM3001, несущем слияние ^odA JucZ. показало, что при росте на глюкозе, сукцинате и малате наблюдается снижение экспрессии гена sodA в течение культивирования (не показано). На ацетате экспрессия sodA оставалась относительно постоянной и превышала уровень* характерный для роста на глюкозе в 1*2-1.8 раза* Снижение экспрессии sodA в ходе периодики определяется, по-видимому, постепенным падением рО2 в культуре по мере увеличения плотности биомассы и происходит под контролем регулятора АгсАВ. Из-за низкой скорости роста и медленного потребления кислорода при культивировании бактерий на ацетате значение рО2 в среде поддерживалось на высоком уровне в течение всей периодики, что, по-видимому, объясняет постоянный повышенный уровень экспрессии sodA*
Для того. чтобы определить, каким образом степень экспрессии антиоксидантных генов соотносится с уровнем активных форм кислорода, измеряли скорость продукции супероксидного радикала и концентрацию Н2О2 в среде (таблица). Не наблюдалось достоверной разницы между' скоростями продукции внеклеточного супероксида при росте Е. coli на глюкозе, малате, сукцинате и а-кетоглутарате* Скорость продукции супероксида при культивировании на ацетате была в 1.55 раз ниже* чем на глюкозе.
Продукция внеклеточных АФК при росте Е* coli BW25113 (wt) на различных ист очниках углерода и энергии
|
Источник углерода и энергии |
Скорость продукции супероксида, пмоль/0. lOD^oo мин |
Концентрация Н2О2, мкМ |
|
Глюкоза |
4*59 ±0*36 |
0.21 ±0.01 |
|
Малат |
4.40 ± 0*43 |
0.09 ±0.01 |
|
Сукцинат |
4*30 ±0*34 |
0.22 ± 0.02 |
|
а-кетоглутарат |
4*48 ± 0*46 |
0.08 ±0.01 |
|
Ацетат |
2*95 ± 0*44 |
0.10 ±0.01 |
Следует отметить, что в наших экспериментах измерялся супероксид. который образуется переносчиками дыхательной цепи (главным образом, мена хиноном) с наружной стороны цитоплазматической мембраны [Korshunov, Imlay. 2006]. По скольку в нормальных физиологических условиях анион супероксида не может пересекать цитоплазматическую мембрану* для защиты периплазмы от внеклеточного супероксида Е. coli имеют специальную псриплазматичсскую супсроксиддисмутазу CuZnSOD, кодируемую геном sodC. Экспрессия гена sodC находится под контролем RpoS и активируется при переходе в стационарную фазу [Gort, Ferber* Imlay. 1999], В связи с этим, наблюдаемое снижение продукции супероксида при росте Е. coli на ацетате может быть следствием его повышенной деструкции с участием CuZnSOD в медленно растущей культуре с высоким уровнем RpoS.
Поскольку Н2О2 легко проникает через цитоплазматическую мембрану; ее концентрация в среде является результатом динамического равновесия между продукцией и деструкцией с участием цитоплазматических каталаз и алкилгидроперок-сидредуктазы. В течение всего периода наблюдений концентрация Н2О2 в культуре Е, coli поддерживалась вблизи постоянного уровня, который был характерен для данного источника углерода и энергии (таблица). Максимальные уровни перекиси водорода накапливались в культурах, растущих на глюкозе и сукцинате. Бактерии, растущие на малате, а-кетоглу тарате и ацетате, поддерживали в 2.33, 2.63 и 2.1 раза более низкую концентрацию Н2О2 в среде, чем при росте на глюкозе* В целом наблюдалась тенденция к снижению уровня Н2О2 с повышением экспрессии гена katG. кодирующего каталазу HPI, в более медленно растущих культурах (г = -0*65), Исключение составлял сукцинат, который, по-видимому, способствует увеличению скорости продукции АФК. В частности, показано, что сукцинатдегидрогеназа может быть одним из источников АФК в клетках Е. coli [Imlay, Fridovich, 1991].
Заключение
Результаты наших исследований показали, что при выращивании Е. со И на разных источниках углерода и энергии, степень экспрессии генов katG и katE, кодирующих каталазы HPI и ПРИ, находится в обратной зависимости от удельной скорости роста соответствующих культур. Это связано с тем, что удельная скорость роста определяет концентрацию белка RpoS, который контролирует экспрессию обоих генов, индуцируя ее при замедлении роста. Степень экспрессии гена sodA, кодирующего MnSOD, в наших экспериментальных условиях контролируется регуляторной системой АгсАВ и зависит в основном от содержания кислорода в среде. Поскольку в медленно растущих культурах поддерживается более высокая концентрация кислорода, они демонстрируют повышенный уровень экспрессии гена sodA* Снижение скорости продукции внеклеточного супероксида при росте бактерий на ацетате также может быть связано со значительным замедлением роста, поскольку под контролем RpoS индуцируется периплазматическая CuZnSODk осуществляющая дисмутацию внеклеточного супероксида. И, наконец, концентрация Н2О2 в среде определяется, прежде всего, активностью каталаз, которая повышается в медленно растущих культурах. Таким образом, различная энергетическая эффективность источников углерода и энергии приводит к изменению скорости роста бактериальных культур и влияет на степень экспрессии антиоксидантных генов и уровень активных форм кислорода. Это может способствовать повышению устойчивости культур, растущих на субстратах с меньшей энергетической эффективностью к различным стрессам, сопровождающимся усилением продукции АФК.
Работа поддержана грантами РФФИ №16-04-00762 и №14-04-96031 и грантом по программе Уральского отделения Российской академии наук № 15-4-4-16.
Список литературы Изменение экспрессии антиоксидантных генов при росте Escherichia coli на различных источниках углерода и энергии
- Anjem A., Imlay J.A. Mononuclear iron enzymes are primary targets of hydrogen peroxide stress//J. Biol. Chem. 2012. Vol. 287. P. 15544-15556
- Compan I., Touati D. Interaction of six global transcriptional regulators in expression of manganese superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli K12//J. Bacteriol. 1993. Vol. 175. P. 1687-1696
- Gonzalez-Flecha B., Demple B. Metabolic sources of hydrogen peroxide in aerobically growing Escherichia coli//J. Biol. Chem. 1995. Vol. 270. P. 13681-13687
- Gort A.S., Ferber D.M., Imlay J.A. The regulation and role of the periplasmic copper, zinc superoxide dismutase of Escherichia coli//Mol. Microbiol. 1999. Vol. 32. P. 179-191
- Gu M., Imlay J.A. Superoxide poisons mononuclear iron enzymes by causing mismetallation//Mol. Microbiol. 2013. Vol. 89. P. 123-134
- Hengge-Arronis R. Signal transduction and regulatory mechanisms involved in control of the oS (RpoS) subunit of RNA polymerase//Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002. Vol. 66. P. 373-395
- Ihssen J., Egli T. Specific growth rate and not cell density controls the general stress response in Escherichia coli//Microbiology. 2004. Vol. 150. P. 1637-1648
- Imlay J.A. Cellular defenses against superoxide and hydrogen peroxide//Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008. Vol. 77. P. 755-776
- Imlay J.A., Fridovich I. Assay of metabolic superox-ide production in Escherichia coli//J. Biol. Chem. 1991. Vol. 266. P. 6957-6965
- Ivanava A. et al. Role of rpoS (katF) in oxyR-independent regulation of hydroperoxidase I in Escherichia coli//Mol. Microbiol. 1994. Vol. 12. P. 571-578
- Korshunov S., Imlay J.A. Detection and quantification of superoxide formed within the periplasm of Escherichia coli//J. Bacteriol. 2006. Vol. 188. P. 6326-6334
- Messner K.R., Imlay J.A. The identification of primary sites of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide formation in the aerobic respiratory chain and sulfite reductase complex of Escherichia coli//J. Biol. Chem. 1999. Vol. 274. P. 10119-10128
- Miller J.H. Experiments in molecular genetics. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. 1972
- Seaver L.C., Imlay J.A. Alkyl hydroperoxide reduc-tase is the primary scavenger of endogenous hydrogen peroxide in Escherichia coli//J. Bacteriol. 2001. Vol. 183. P. 7173-7181
- Skulachev V. Uncoupling: new approaches to an old problem of bioenergetics//Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998. Vol. 1363. P. 100-124
- Storz G., Taraglia L.A., Ames B.N. Transcriptional regulator of oxidative stress-inducible genes: direct activation by oxidation//Science. 1990. Vol. 248. P. 194-198
- Tao K. et al. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of oxyR, the positive regulatory gene of a regulon for an adaptive response to oxidative stress in Escherichia coli: homologies between OxyR protein and a family of bacterial activator proteins//Mol. Gen. Genet. 1989. Vol. 218. P. 371-376


