Изучение ридостина Про и Poly(I:C) в качестве адъювантов, усиливающих иммуногенность противоопухолевой вакцины
Автор: Пономарев А.В., Царапаев П.В., Барышникова М.А., Соколова З.А., Рудакова А.А., Миронова М.В., Гусев Д.В., Левагина Г.М., Даниленко Е.Д., Косоруков В.С.
Журнал: Сибирский онкологический журнал @siboncoj
Рубрика: Лабораторные и экспериментальные исследования
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.23, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Цель исследования - сравнить противоопухолевую эффективность и иммуногенность вакцин с одинаковыми антигенами, но разными адъювантами: Ридостин Про или Poly(I:C); оценить влияние Ридостина Про и Poly(I:C) на цитокиновый профиль сыворотки и иммунофенотип клеток селезенки мышей. материал и методы. Для оценки противоопухолевой эффективности вакцин с различающимися адъювантами применяли две перевиваемые линии опухолей: меланома В16-F10 и лимфома EG7-OVA (экспрессирующая овальбумин) для мышей C57BL/6. Против меланомы В16-F10 проводили вакцинацию пептидом TRP2 180-188 с исследуемыми адъювантами в смешанном (профилактический/терапевтический) и терапевтическом режимах. Против лимфомы EG7 проводили вакцинацию овальбумином с адъювантами в терапевтическом режиме. Иммуногенность вакцин с различающимися адъювантами на мышах без опухолей оценивали методом ELISPOТ. Антигенами в данном случае также служили пептид TRP2 180-188 и белок овальбумин. С помощью проточной цитометрии исследовали цитокиновый профиль сыворотки крови и изменения иммунофенотипа клеток селезенки мышей после введения Ридостина Про или Poly(I:C).
Противоопухолевые вакцины, адъюванты, антигены, ридостин, poly(i:c), пептиды, доклинические исследования
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140305929
IDR: 140305929 | УДК: 616-006:615.371:616-097]-092.9 | DOI: 10.21294/1814-4861-2024-23-3-86-99
Текст научной статьи Изучение ридостина Про и Poly(I:C) в качестве адъювантов, усиливающих иммуногенность противоопухолевой вакцины
Вакцины на основе неоантигенов – новое направление в иммунотерапии рака [1, 2]. В последнее десятилетие значительно продвинулось вперед понимание функций иммунных клеток и взаимодействия их с растущими опухолями. При этом для неоангиогенных пептидных противоопухолевых вакцин существует значительная потребность в адъювантах, усиливающих иммунный ответ, и весьма перспективными кажутся лиганды толл-подобных рецепторов (TLR). При развитии иммунного ответа на вирусные или микробные антигены происходит связывание патоген-ассоциированных молекулярных паттернов (PAMP) на их поверхности с рецепторами распознавания паттернов (PRR) в иммунных клетках. В число данных рецепторов входят TLR. В результате активируются системы врожденного иммунитета, что способствует развитию адаптивного иммунитета. Адъюванту, применяемому для усиления эффективности противоопухолевой вакцины, необходимо иметь схожесть с РАМР по способности активировать иммунитет, а также важны такие его свойства, как безопасность и доступность [3].
Вирусное заражение ассоциировано с появлением в клетке двухцепочечных РНК (дцРНК), которые либо представляют собой собственно геном вируса, либо возникают в ходе вирусного репродуктивного цикла [4]. ДцРНК может распознаваться набором рецепторов врожденной иммунной системы, что запускает противовирусные и воспалительные иммунные ответы [5]. Полиинозиновая: полицитидиловая кислота (Poly(I:C)) представляет собой синтетический аналог вирусной дцРНК, является иммуностимулятором, способным вызывать секрецию интерферонов I типа [6]. Большое количество исследований посвящено изучению Poly(I:C) и его производных в иммунотерапии рака. На мышиных моделях отчетливо показано, что Poly(I:C) обладает свойствами адъюванта для пептидных вакцин [7–9]. Например, H. Sultan et al. сравнивали вакцины с одинаковым антигеном, но несколькими разными адъювантами, являющимися агонистами TLR. В результате вакцины, включающие в качестве адъюванта Poly(I:C), индуцировали образование наибольшего количества антигенспе-цифичных CD8+ Т-клеток [9]. На мышиных моделях Poly(I:C) вызывает замедление роста опухоли [10, 11]. Но когда Poly(I:C) оценивался в клиническом исследовании, R.A. Robinson et al. не обнаружили объективного противоопухолевого ответа, вероятно, из-за короткого периода полураспада полинуклеотида [12]. Создана стабилизированная поли-L-лизином и карбоксиметилцеллюлозой форма Poly(I:C), названная Poly-ICLC. Полученный препарат был более устойчив к гидролизу в сыворотке приматов [13]. Но оказалось, что Poly-ICLC имеет более высокую токсичность. В дальнейших исследованиях авторам удалось снизить токсичность Poly-ICLC за счет снижения дозы препарата и изменения способа введения [14, 15]. На данное время уже имеется ряд публикаций, где Poly-ICLC (Хилтонол) применяется в качестве адъюванта для противоопухолевых пептидных вакцин в рамках клинических испытаний [16, 17].
Тем не менее в настоящее время количество одобренных для клинического применения в составе вакцин адъювантов невелико, и потребность в адъювантах, усиливающих эффективность противоопухолевых вакцин, остается острой. В ИМБТ ФБУН ГНЦ ВБ «Вектор» Роспотребнадзора разработан препарат Ридостин Про, который представляет собой комплекс двухцепочечных и одноцепочечных рибонуклеиновых кислот из кил-лерного штамма пекарских дрожжей Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Ранее на модели опухоли В16-F10 нами показано, что Ридостин Про в качестве адъюванта пептидной неоантигенной вакцины имеет эффективность, сравнимую с Poly(I:C) [18]. Кроме того, Ридостин способствует формированию специфического гуморального иммунитета [19]. В данной работе мы продолжили исследование Ридостина Про в качестве адъюванта противоопухолевой вакцины, сравнивая его с Poly(I:C), но для иммунизации применяли пептид TRP2 [20] или овальбумин. Также мы сравнили влияние Ридостина Про и Poly(I:C) на цитокиновый профиль сыворотки крови и иммунофенотип спленоцитов мышей для лучшего понимания иммунологических эффектов, вызываемых данными препаратами.
Цель исследования – сравнить противоопухолевую эффективность и иммуногенность вакцин с одинаковыми антигенами, но разными адъювантами: Ридостин Про или Poly(I:C); оценить влияние Ридостина Про и Poly(I:C) на цитокино-вый профиль сыворотки и иммунофенотип клеток селезенки мышей.
Материал и методы
Мыши и опухолевые модели
Исследование проводили на мышах-самках линии C57BL/6 весом 20–22 г (мыши предоставлены экспериментально-биологической лабораторией (виварий) ФГБУ «НМИЦ онкологии им. Н.Н. Блохина» Минздрава России). Мышей содержали в конвенциональном виварии при естественном освещении, комнатной температуре воздуха и постоянном доступе к воде и корму. Эксперименты проводили в соответствии с этическими требованиями к исследованиям на биологических моделях и экспериментальных животных, утвержденными в ФГБУ «НМИЦ онкологии им. Н.Н. Блохина» Минздрава России.
Для получения моделей опухолей использовали клеточные линии меланомы мышей В16-F10 и лимфомы мышей EG7-OVA из Биоресурсной коллекции ФГБУ «НМИЦ онкологии им. Н.Н. Блохина» Минздрава России. Клеточные линии культивировали в среде RPMI-1640, содержащей 10 % телячьей эмбриональной сыворотки, 2мМ L-глутамина (ПанЭко), антибиотики пенициллин – стрептомицин (ПанЭко), при 37 ºС в атмосфере 5 % СО2. Для открепления B16-F10 с пластика использовали раствор Версена. Перед введением животным клетки отмывали, подсчитывали и разводили до нужной концентрации в бессыво-роточной среде. Клетки меланомы B16-F10 инокулировали подкожно по 75 тыс. клеток на мышь. Клетки лимфомы EG7-OVA вводили подкожно по 2 млн клеток на мышь.
Адъюванты, пептиды
Ридостин Про – рибонуклеинат натрия, индуктор интерферона пролонгированного действия, иммуномодулятор – предоставлен Институтом медицинской биотехнологии ФБУН ГНЦ ВБ «Вектор» Роспотребнадзора. Состав препарата Ридостин Про: комплекс двухцепочечных и одноцепочечных РНК из киллерного штамма пекарских дрожжей Saccharomyces cerevisiae с содержанием нуклеотидного материала от 70 до 90 %, двуспиральной РНК от 10 до 22 % (субстанция для изготовления лекарственных форм, ФСП № 002021/01 – 070420090769-08); поливинилпирролидон (стабилизатор, обеспечивающий пролонгацию биологических эффектов РНК). Лекарственная форма: лиофилизат для приготовления раствора для внутримышечного и подкожного введения.
Poly(I:C) (polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid sodium salt, P1530-100MG, Sigma) является синтетическим аналогом дцРНК.
Пептиды TRP2 180–188 (SVYDFFVWL) и OVA 257-264 (SIINFEKL) были предоставлены лабораторией химического синтеза ФГБУ «НМИЦ онкологии им. Н.Н. Блохина» Минздрава России.
Схемы противоопухолевой вакцинации
Для вакцинации против меланомы B16-F10 самкам мышей C57BL/6 соответствующего возраста вводили подкожно пептид TRP2 (100 мкг/мышь) с одним из адъювантов – Poly(I:C) (50 мкг/мышь)
или Ридостином Про (100 мкг/ мышь), или отдельно адъюванты. Для вакцинации против лимфомы EG7-OVA самкам мышей C57BL/6 соответствующего возраста вводили подкожно рядом с опухолью Овальбумин (Sigma) в дозе 100 мкг/мышь с одним из исследуемых адъювантов – Poly(I:C) (50 мкг/ мышь) или Ридостином Про (100 мкг /мышь), или отдельно адъюванты.
На модели опухоли B16-F10 исследовали вакцинацию TRP2 и/или адъювантами в смешанном (профилактическом/терапевтическом) и терапевтическом режимах. При смешанном режиме мышам четырехкратно подкожно вводили Ридостин Про (n=5), Рoly(I:C) (n=4), Ридостин Про+TRP2 (n=5), Рoly(I:C)+TRP2 (n=5), в 0, 7, 14 и 21-й дни эксперимента, на 10-й день от начала введения пептида и адъювантов мышам перевивали подкожно опухоль B16-F10. Мыши контрольной группы (n=8) не получали препараты.
Терапевтическую вакцинацию пептидом TRP2 и/или адъювантами проводили после введения опухоли. Мышам подкожно вводили клетки меланомы B16-F10, а на 4-е и 10-е сут после перевивки опухоли вводили пептид Trp2, Ридостин Про, Рoly(I:C), Ридостин Про+Trp2, Рoly(I:C)+Trp2, мыши контрольной группы не получали препаратов. В каждой группе было по 5 мышей.
На модели опухоли EG7-OVA исследовали вакцинацию только в терапевтическом режиме. Мышам на 7-е и 14-е сут после перевивки опухоли вводили Овальбумин и/или исследуемые адъюванты подкожно рядом с опухолью. В каждой группе было по 6 мышей. Мыши контрольной группы не получали препараты. Размеры опухолей измеряли 2–3 раза в нед и рассчитывали объемы опухолевых узлов по формуле
V = π/6×L×W×H, где L, W, H – линейные размеры опухоли.
ELISpot
Иммуногенность вакцин оценивали методом ELISpot с помощью набора для определения мышиного IFN-γ (3321-2AW-Plus, Mabtech). Мышам-самкам C57BL/6 вводили подкожно TRP2 c Poly(I:C) (n=3), TRP2 c Ридостином Про (n=3), овальбумин с Poly(I:C) (n=3) и овальбумин с Ри-достином Про (n=3) в 0-й и 7-й дни эксперимента. На 12-й день у мышей в каждой группе удаляли селезенки и выделяли спленоциты для определения количества IFN-γ-продуцирующих клеток. Выделенные спленоциты инкубировали 48 ч с пептидами TRP2 180–188 (SVYDFFVWL) или OVA 257-264 (SIINFEKL) (100 мкг/мл), конканавалин А (ПанЭко) использовали как положительный контроль. Через 48 ч подсчитывали количество IFN-γ-продуцирующих клеток.
Цитокиновый профиль сыворотки мышей
Мышам-самкам C57BL/6 подкожно вводили по 50 мкл физиологического раствора (n=3), 50 мкг Poly(I:C) (n=5) или 100 мкг Ридостина Про (n=5). Через 6 или 24 ч мышей умерщвляли и собирали кровь для получения сыворотки. Уровень цитокинов IL-12p70, TNF, IFN-γ, MCP-1, IL-10, IL-6 исследовали в сыворотке крови у каждой мыши в группе с помощью набора BD Cytometric Bead Array (CBA) Mouse Inflammation Kit (CatNo. 552364, BD).
Проточная цитофлуориметрия
Мышам-самкам C57BL/6 подкожно вводили по 50 мкл физиологического раствора (n=5), 50 мкг Poly(I:C) (n=5) или 100 мкг Ридостина Про (n=5). Через 24 ч мышей умерщвляли, забирали селезенку и готовили суспензию одиночных клеток. В полученной суспензии клеток селезенки проводили гипотонический лизис эритроцитов. Далее клетки окрашивали антителами (таблица).
Подсчет проводили на проточном цитофлуориметре FACS Canto II с использованием
Таблица /table
Антитела, применяемые в работе antibodies used in the study
|
Антитело/Name |
Краситель/Dye |
Клон/Clone |
Производитель/Manufacturer |
|
NKp46 (CD335) |
eFluor450 |
29A1.4 |
eBioscience |
|
CD62L |
eFluor450 |
MEL-14 |
eBioscience |
|
CD45 |
PerCP-Cy5.5 |
30-F11 |
Biolegend |
|
CD4 |
PE-Cy7 |
GK1.5 |
Biolegend |
|
CD44 |
APC-Cy7 |
IM7 |
Biolegend |
|
PD-1 (CD279) |
APC |
29F.1A12 |
Biolegend |
|
CD8 |
FITC |
53-6.7 |
Biolegend |
|
CD69 |
PE |
H1.2F3 |
Biolegend |
|
CD19 |
FITC |
6D5 |
Biolegend |
|
CD3 |
PE |
17A2 |
Biolegend |
|
CD3 |
APC |
17A2 |
Biolegend |
Примечание: таблица составлена авторами.
Note: created by the authors.
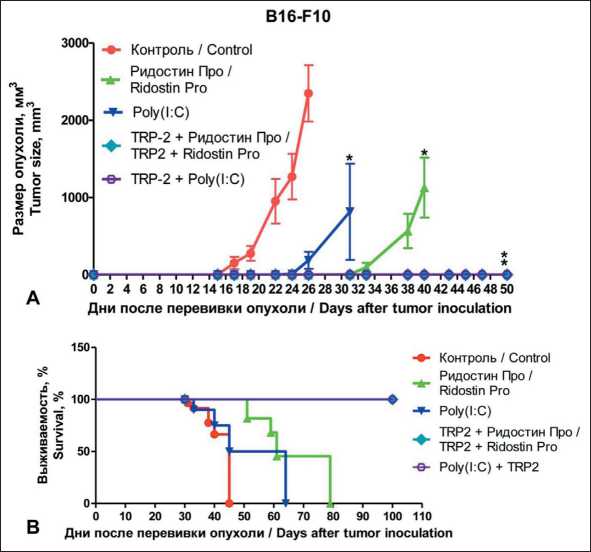
Рис. 1. Противоопухолевый эффект смешанного режима вакцинации мышей с меланомой B16-F10: размер опухоли ± SEM (А); графики выживаемости мышей (В). Примечания: * – p<0,01 по сравнению с контролем; рисунок выполнен авторами
Fig. 1. Antitumor effect of a mixed vaccination regimen in mice with B16-F10 melanoma.
Tumor size ± SEM (A); mouse survival schedules (B). Notes: * – p<0.01 compared to the control; created by the authors программного обеспечения FACSDiva™ (Beсton Dickinson). Погибшие клетки исключали из анализа по окрашиванию Fixable Viability Stain 510 (BD Biosciences). Для блокирования неспецифического связывания использовали Mouse BD Fc Block (2.4G2) (BD Biosciences). Процент исследуемых клеток высчитывали от всех живых CD45+ клеток селезенки. Стратегия гейтирования представлена в [21].
Для статистического анализа использовали критерий Манна–Уитни и применяли программу STATISTICA v.7. Различия считали достоверными при уровне значимости p<0,05.
Результаты и обсуждение Противоопухолевый эффект
При применении адъювантов с TRP2 в смешанном (профилактическом/терапевтическом) режиме против меланомы B16-F10 обнаружили торможение роста опухолей и увеличение продолжительности жизни у мышей по сравнению с контролем (рис. 1). Ридостин Про и Рoly(I:C) при введении без пептида замедляли рост опухолей статистически значимо по сравнению с контролем (р<0,01) (рис. 1А), а при введении адъювантов с TRP2 опухоли не развились ни у одной из мышей. Отмечено увеличение продолжительности жизни мышей после применения адъювантов, причем положительный эффект был более выражен для Ридостина Про (рис. 1Б). После лечения пептидом TRP2 с Ридостином Про и с Poly(I:C) отсутствие опухолей у мышей детектировали более 100 дней (рис.1Б).
Далее мы исследовали эффективность вакцинации пептидом TRP2 с адъювантами в терапев- тическом режиме, что является более вероятным вариантом применения противоопухолевых вакцин в клинических условиях. После введения мышам клеток меланомы B16-F10 на 4-е и 10-е сут производилось введение адъювантов с пептидом TRP2 или без него, и одного пептида без адъювантов.
Пептид TRP2 при применении без адъювантов не оказывал противоопухолевого эффекта (рис. 2). Введение одних адъювантов, а также адъювантов с пептидами статистически значимо вызывало торможение роста опухоли у мышей по сравнению с контрольной группой и с группой, получавшей только TRP2 (р<0,05) (рис. 2), однако при терапевтическом режиме применения не было достигнуто излечение мышей в группах, получавших TRP2 с адъювантами, как было показано при режиме, когда две вакцинации проводили до перевивки опухоли и две после.
Полученные нами результаты по противоопухолевой эффективности Poly(I:C) и TRP2 согласуются с имеющимися литературными данными. J. Castle et al. показано, что введение в терапевтическом режиме отдельно Poly(I:C) приводило к некоторому торможению роста опухоли, а введение Poly(I:C) с пептидом TRP2 вызывало более сильное торможение роста B16-F10 [22]. Исходя из имеющихся данных, вакцинация одним пептидом TRP2 с адъювантом в терапевтическом режиме хотя и давала некоторый положительный эффект, но он не был слишком значительным. В то же время H. Lam et al. показано, что добавление дополнительных иммуногенных пептидов к TRP2 при вакцинации с адъювантом в терапевтическом режиме приводило к достаточно выраженным положительным эффектам на модели меланомы B16-F10 [23].
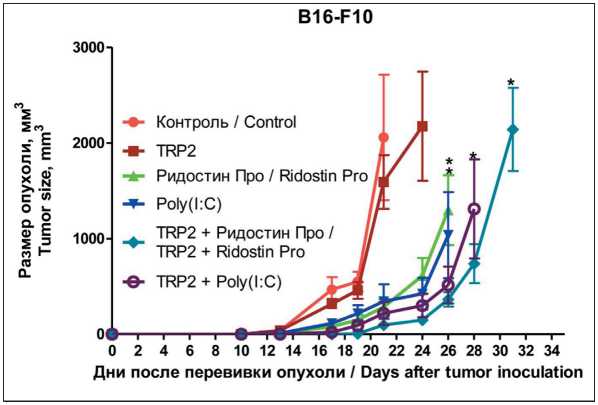
Рис. 2. Противоопухолевый эффект терапевтической вакцинации мышей с меланомой B16-F10. Размер опухоли ± SEM. Примечания: * – p<0,05 по сравнению с контролем; рисунок выполнен авторами
-
Fig. 2. Antitumor effect of mice therapeutic vaccination with B16-F10 melanoma. Tumor size ± SEM.
Notes: * – p<0.05 compared to the control; created by the authors
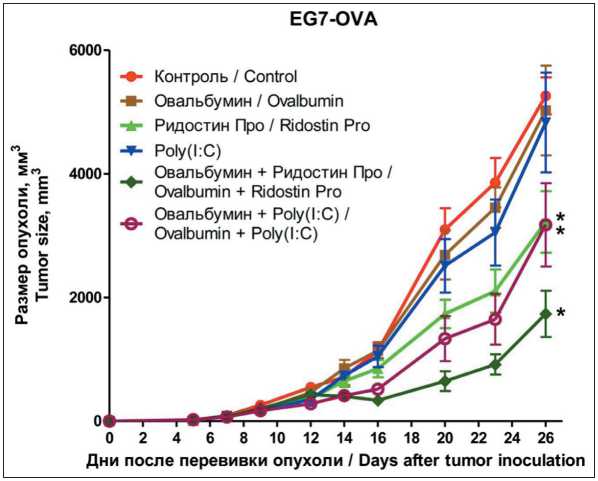
Рис. 3. Противоопухолевый эффект терапевтической вакцинации мышей с лимфомой EG7. Размер опухоли ± SEM. Примечания: * – p<0,05 по сравнению с контролем; рисунок выполнен авторами
-
Fig. 3. Antitumor effect of therapeutic mice vaccination with EG7 lymphoma. Tumor size ± SEM.
Notes: * – p<0.05 compared to the control; created by the authors
На модели опухоли EG7-OVA (клеточная линия лимфомы, экспрессирующая овальбумин) мы исследовали вакцинацию овальбумином с адъювантами также в терапевтическом режиме применения. Мышам перевивали подкожно по 2 млн клеток EG7, а на 7-е и 14-е сут после перевивки опухоли вводили исследуемые препараты. Овальбумин без адъювантов не вызывал торможения роста опухоли (рис. 3). Адъюванты без овальбумина вызывали торможение роста опухоли, причем Ридостин Про статистически значимо, по сравнению с контролем (р=0,01). Введение адъювантов совместно с овальбумином также приводило к торможению роста уже имеющейся опухоли, статистически значимому по сравнению с контрольной группой, причем Ридостин Про (р=0,004) в качестве адъюванта в данном случае был более эффективным, чем Рoly(I:C) (р=0,03) (рис. 3).
Можно отметить, что вакцины с Ридостином Про имели небольшое преимущество в противоопухолевой эффективности, по сравнению с вакци- нами с Poly(I:C). Данное явление можно частично объяснить тем, что Ридостин Про включает в себя не только двухцепочечную РНК (лиганда TLR-3), но и одноцепочечную РНК. В результате чего дополнительно вовлекаются такие рецепторы, как TLR-7 и TLR-8 [24], что может усилить иммунный ответ.
Иммуногенность
Способность адъювантов усиливать Т-клеточ-ный иммунный ответ исследовали при вакцинации мышей совместно с пептидом TRP2 или с овальбумином. Ридостин Про и Poly(I:C) повышали иммуногенность пептида TRP2 и овальбумина. Важно отметить, что адъюванты повышали иммуногенность только тех пептидов, которые входили в состав вакцины. Например, если мышей вакцинировали пептидом TRP-2 c адъювантами, то при культивировании спленоцитов in vitro добавление пептида OVA не повышало количество IFN-γ-продуцирующих клеток относительно кон-
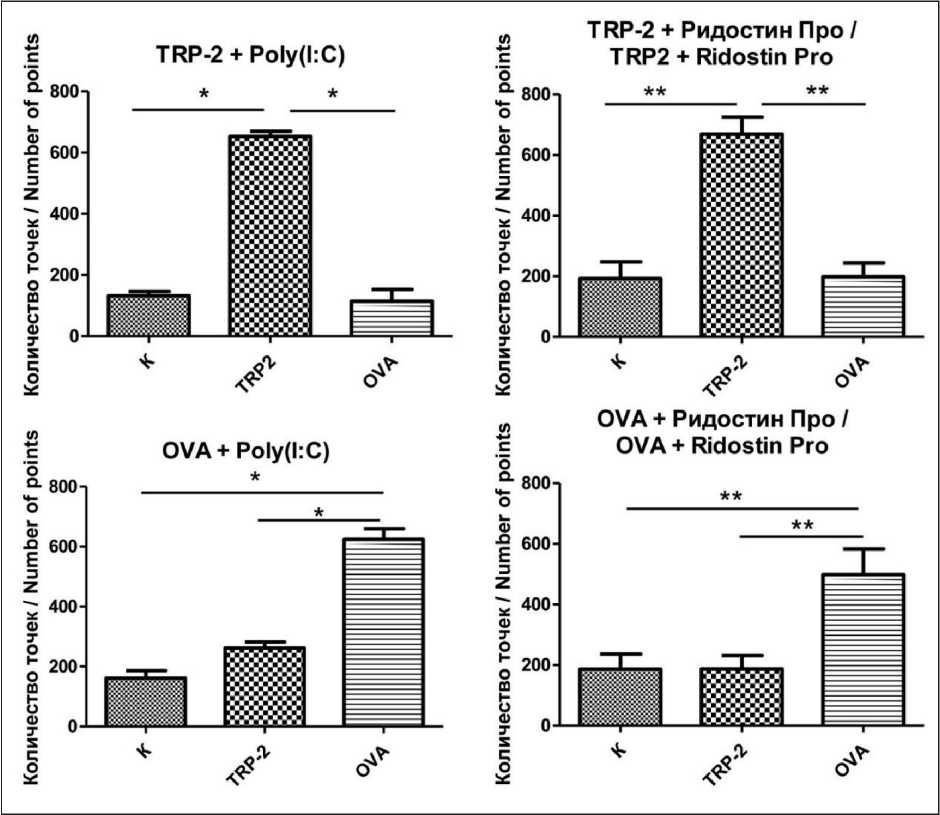
Рис. 5. Влияние стимуляции пептидами OVA или TRP2 на продукцию спленоцитами IFN-γ в каждой группе вакцинированных мышей. Примечания: * – р<0,05; ** – p<0,01; рисунок выполнен авторами Fig. 5. Impact of stimulation with OVA or TRP2 peptides on IFN-γ production by splenocytes in each group of vaccinated mice. Notes: * – p<0.05; ** – p<0.01; created by the authors
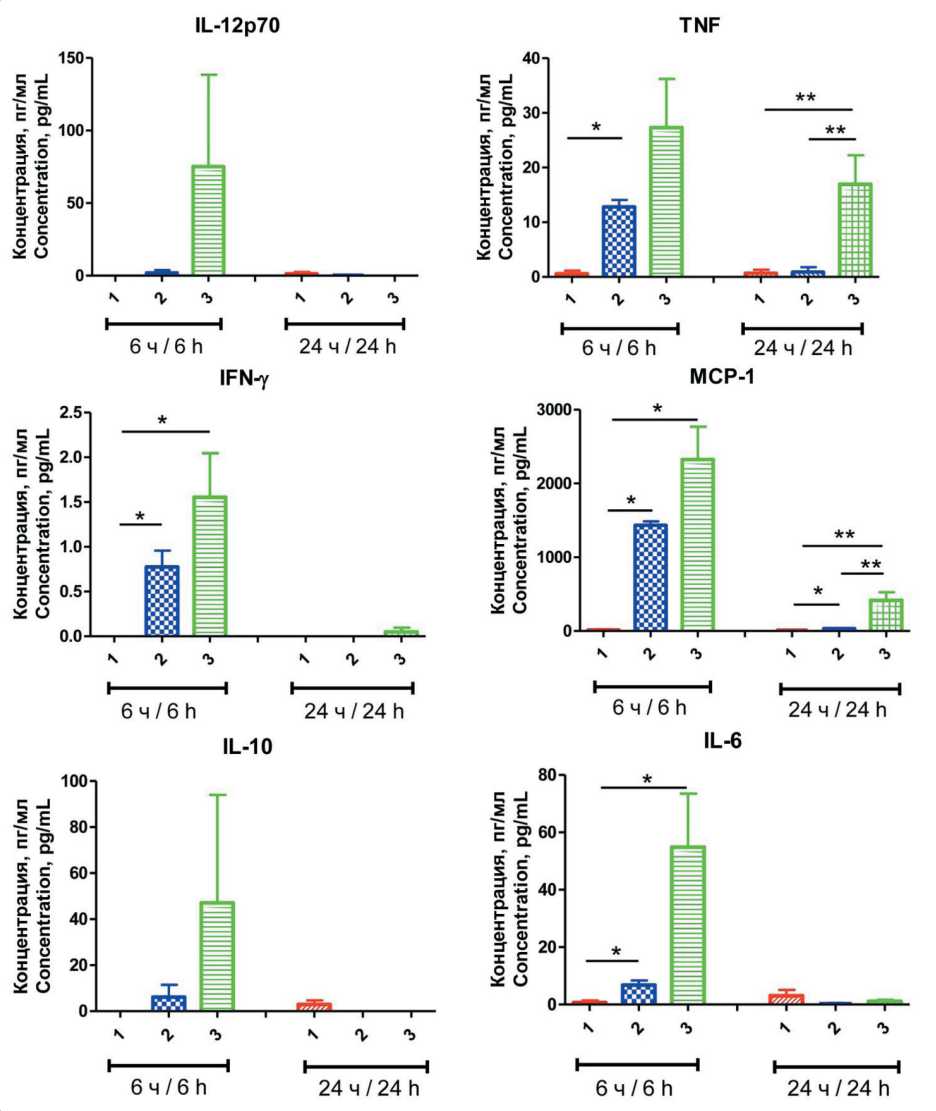
Рис. 6. Влияние адъювантов на уровень цитокинов в сыворотке крови мышей: 1 – физраствор; 2 – Poly(I:C); 3 – Ридостин Про. Примечания: * – р<0,05; **p<0,01; рисунок выполнен авторами Fig. 6. Impact of adjuvants on cytokine levels in mouse serum: 1 – saline;
-
2 – Poly(I:C); 3 – Ridostin Pro. Notes: * – p<0.05; **p<0.01; created by the authors
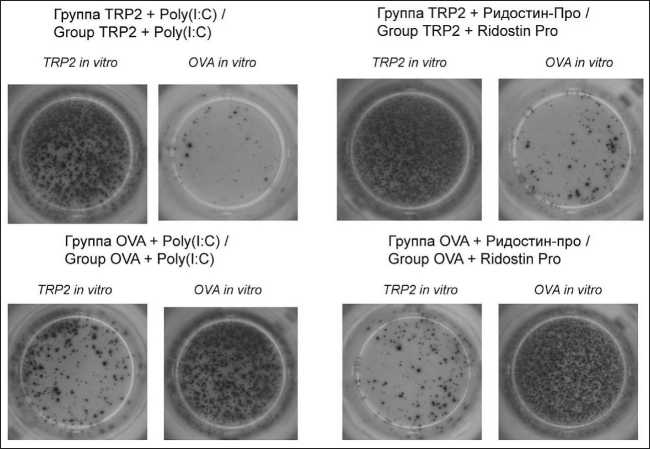
Рис. 4. Примеры изменения количества IFN-γ-продуцирующих спленоцитов мышей из разных групп после in vitro стимуляции TRP2 или OVA. Примечание: микрофото выполнено авторами
Fig. 4. Examples of changes in the number of IFN-γ-producing mouse splenocytes from different groups after in vitro stimulation with TRP2 or OVA. Note: created by the authors
троля. Если вакцина состояла из овальбумина и адъювантов, добавление пептида TRP-2 также не вызывало увеличения продукции IFN-γ (рис. 4, 5). Таким образом, Ридостин Про и Poly(I:C) одинаково повышали иммуногенность и TRP2, и овальбумина.
Индукция цитокинов in vivoвведением Poly(I:C) или Ридостина Про
Далее оценили воздействие Ридостина Про и Poly(I:C) на уровни сывороточных цитокинов IL-12p70, TNF, INF-γ, MCP-1, IL-10, IL-6. Для этого мышей иммунизировали однократно и через 6 и 24 ч оценивали цитокиновый профиль в сыворотке (рис. 6). Оказалось, что в целом через 6 ч Ридо-стин Про более выраженно, чем Poly(I:C), повышал концентрацию всех 6 цитокинов. Через 24 ч концентрация цитокинов в сыворотке снижалась, хотя в случае Ридостина Про концентрация TNF и MCP-1 не достигала контрольных значений.
С одной стороны, если учесть, что Poly(I:C) и Ри-достин Про показали незначительно отличающуюся противоопухолевую эффективность на мышиных моделях, более низкая концентрация цитокинов в сыворотке для Poly(I:C) может считаться некоторым преимуществом, так как может свидетельствовать о более низкой токсичности. С другой стороны, когда Poly(I:C) оценивался в клиническом исследовании, не было обнаружено объективного противоопухолевого ответа, вероятно, из-за короткого периода полураспада полинуклеотида [12]. В то же время его более токсичный аналог Poly-ICLC [13, 25], который, как и Ридостин Про, обладает пролонгированным действием, применяется в клинических испытаниях как адъювант противоопухолевых пептидных вакцин [16, 17]. В исследовании на приматах показано, что Poly-ICLC вызывал существенное повышение уровня интерферона в сыворотке крови, по сравнению с Poly(I:C) [13].
Поэтому на данном этапе нельзя точно сказать, что более низкие значения провоспалительных цитокинов указывают на преимущество Poly(I:C) над Ридостином Про. Можно отметить, что при сравнении с литературными данными уровень цитокинов при воздействии Ридостина Про был ниже, чем при использовании других агонистов TLR-3 [26]. Однако полученные результаты требуют внимательно отнестись к дальнейшему изучению воздействия препарата Ридостин Про на иммунную систему, подбору дозы и способа введения.
Влияние Ридостина Про и Poly(I:C) на иммунофенотип спленоцитов
Для лучшего понимания иммунологических процессов, происходящих после применения Poly(I:C) и Ридостина Про, оценивали иммунофенотип клеток селезенки мыши через 24 ч после однократного введения препаратов. Двумя молекулами адгезии, которые связаны с дифференцировкой CD4+- и CD8+- Т-клеток, являются CD44 и CD62L. Иммунофенотип CD44– CD62L+ характерен для наивных CD8+- Т-клеток (Tn). В результате инфицирования или иммунизации на антиген-активированных CD8+- Т-клетках повышается экспрессия CD44 и теряется CD62L, такие клетки становятся эффекторными Т-клетками (Teff). После разрешения инфекции популяция клеток CD8+- Teff сокращается, и происходит формирование клеток памяти. Среди CD8+- T-клеток выделяют Т-клетки центральной памяти (Tcm) CD44+ CD62L+ и Т-клетки эффекторной памяти (Tem) CD44+ CD62L–. Схожая стратегия применяется и для оценки дифференцировки CD4+- Т-клеток. Но метод проточной цитофлуориметрии позволяет отчетливо определить только две популяции: Tn и Tem [27].
Для CD4+- и CD8+- Т-клеток после введения Poly(I:C) обнаружено статистически значимое
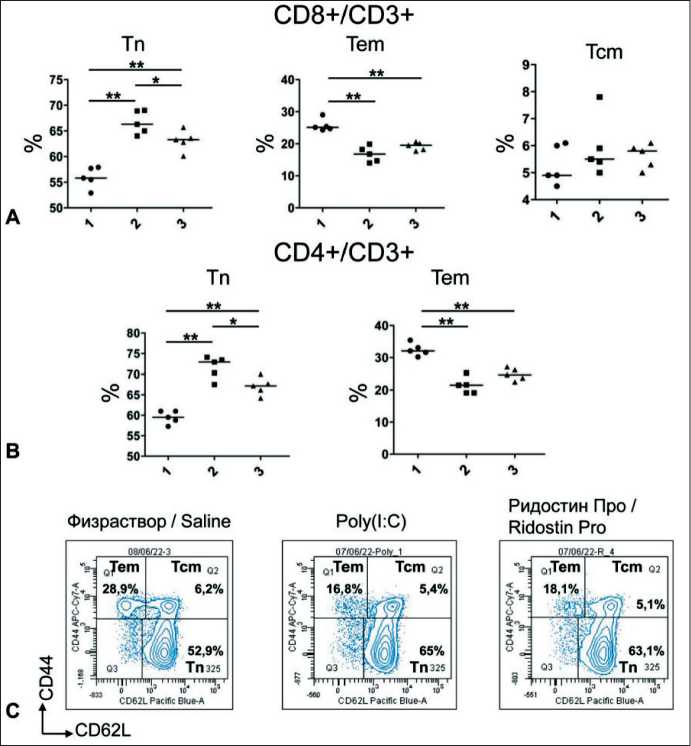
Рис. 7. Влияние Ридостина Про и Poly(I:C) на популяции Т-клеток памяти в селезенке мышей: 1 – физраствор; 2 – Poly(I:C);
-
3 – Ридостин Про;
А – количество клеток, выраженное в процентах для Tn, Tem, Tcm от всех CD8+/CD3+/CD45+ клеток селезенки; В – количество клеток, выраженное в процентах для Tn и Tem от всех CD4+/CD3+/CD45+ клеток селезенки; С – количество CD8+ Т-клеток памяти в селезенке мышей через 24 ч после введения препаратов (примеры точечных графиков).
Примечания: * – р<0,5, ** – р<0,01; рисунок выполнен авторами Fig. 7. Impact of Ridostin Pro and Poly(I:C) on memory T-cell populations in mice spleen: 1 – saline; 2 – Poly(I:C); 3 – Ridostin Pro;
A – number of cells expressed as a percentage for Tn, Tem, Tcm of all CD8+/CD3+/CD45+ spleen cells;
B – number of cells expressed as a percentage for Tn and Tem from all CD4+/CD3+/CD45+ spleen cells;
C – number of CD8+ memory T cells in mouce spleen after 24 hours of drug administration (examples of dot graphs).
Notes: * – p<0.5, ** – p<0.01; created by the authors снижение количества клеток Tem и увеличение Тn, по сравнению с физраствором, и не отмечено значимых изменений для Tcm. После введения Ридостина Про получены схожие данные. Можно отметить большее увеличение Тn и снижение Tem среди CD4+- и CD8+- Т-клеток после воздействия Poly(I:C), по сравнению с Ридостином Про, но значимой разница между препаратами была только для CD4+ и CD8+ Тn (рис. 7). K. Bahl et al. показали, что через 12 ч после введения мышам Poly(I:C) происходило уменьшение количества Т-клеток памяти в селезенке за счет их апоптотической гибели [28], но через 1 сут Poly(I:C) начинает стимулировать пролиферацию CD44+- CD8+- Т-клеток памяти [29]. Вероятно, это происходит для удаления ненужных Т-клеток памяти, чтобы на их месте могли за счет пролиферации появиться Т-клетки, специфичные к нужным антигенам. Имеющихся в литературе данных недостаточно, чтобы точно определить, в какой момент времени после воздействия Poly(I:C) Т-клетки памяти перестают погибать и начинают пролиферировать. Если предположить, что этот срок примерно равен суткам, полученные нами данные могут свидетельствовать об очень схожей тенденции по снижению Т-клеток памяти для обоих препаратов, но для Ридостина Про она выражена несколько слабее, чем для Poly(I:C).
Рецептор запрограммированной гибели клеток 1 (PD-1) (англ. Programmed cell death 1; CD279) является одной из важнейших молекул иммунных контрольных точек. PD-1 экспрессируется на активированных CD4+ и CD8+- Т-клетках и некоторых других иммунных клетках. Взаимодействие PD-1 с его лигандом PD-L1 необходимо для развития иммунной толерантности, предотвращения чрезмерной активности иммунных клеток [30, 31]. После воздействия Poly(I:C) и Ридостина Про нами обнаружено небольшое, но статистически значимое повышение PD-1 на CD8+- Т-клетках, по сравнению с физраствором. Это может быть связано с повышением некоторых цитокинов в сыворотке [32]. Между препаратами не было значимой разницы, хотя Ридостин Про вызывал большее повышение PD-1 на CD8+- Т-клетках. На CD4+- Т-клетках изменения количества PD-1 положительных клеток не имели статистической значимости для обоих препаратов (рис. 8).
CD69 является маркером ранней активации лимфоцитов, его экспрессия быстро индуцируется на поверхности Т-лимфоцитов после стимуляции [33]. По поводу влияния CD69 на активацию иммунитета имеются различные данные. Более ранние исследования отмечают иммуноактивирующую роль CD69 [34]. Позднее была выявлена его иммунорегулятор-
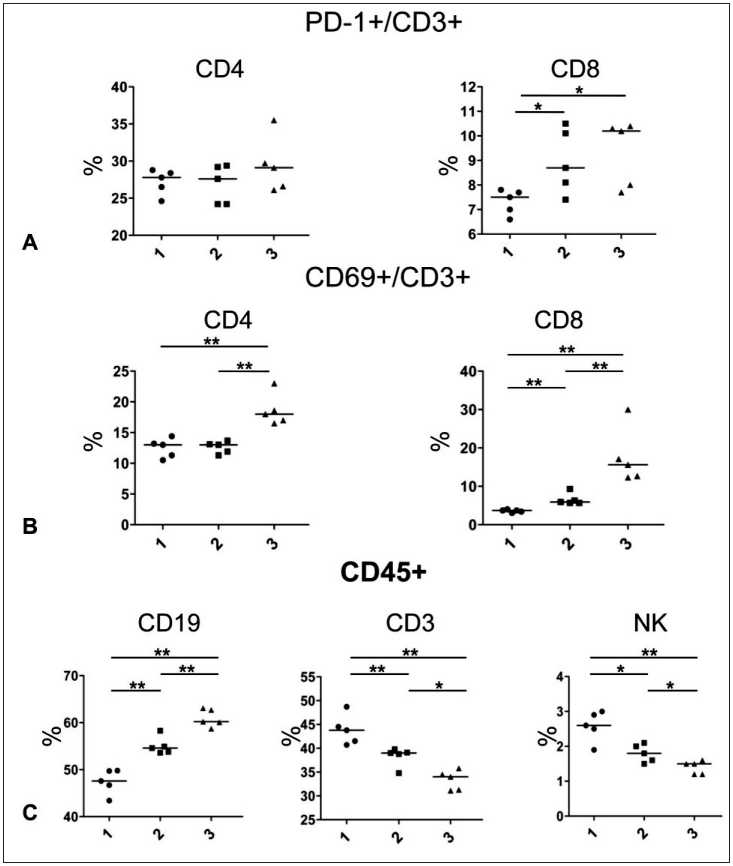
Рис. 8. Влияние Ридостина Про и Poly(I:C) на количество CD8+ и CD4+ Т-клеток, экспрессирующих PD-1 (А) и CD69 (В) от всех CD3+/CD45+ клеток селезенки мышей, а также на общее количество Т-, В-, NK-клеток от всех CD45+ клеток селезенки (С): 1 – физраствор; 2 – Poly(I:C); 3 – Ридостин Про.
Примечания: * – р<0,5, ** – р<0,01; рисунок выполнен авторами
Fig. 8. Impact of Ridostin Pro and Poly(I:C) on the number of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells expressing PD-1 (A) and CD69 (B) from all CD3+/CD45+ cells in mouse spleen, and on the total number of T, B, NK cells from all CD45+ cells in spleen (C): 1 – saline; 2 –
Poly(I:C); 3 – Ridostin Pro.
Notes: * – р<0.5, ** – р<0.01; created by the authors ная функция, например, в отсутствие CD69 у мышей проявляется более сильный противоопухолевый иммунитет [35]. Имеются данные, что Poly(I:C) может усиливать экспрессию CD69 на поверхности CD4 Т-клеток в селезенке [36], но в указанной публикации Poly(I:C) вводился мышам внутрибрюшинно. В литературе есть данные о значительном повышении количества CD69+- Т-клеток после внутривенного введения Poly(I:C) [37]. Нами ранее показано повышение CD69 на Т-клетках мышей после многократного подкожного введения Poly(I:C) [21]. После однократного подкожного введения Poly(I:C) нами не отмечено увеличения количества CD69+-клеток среди популяции CD4+- Т-клеток. Среди CD8+- Т-клеток после инъекции Poly(I:C) отмечено небольшое, но значимое повышение количества клеток CD69+. Подкожное введение Ридостина Про вызвало выраженное повышение количества CD69+-Т-клеток как в популяции CD4+, так и в популяции CD8+, что было статистически значимо. Также нами обнаружено значимо более высокое количество CD69+-клеток среди CD4+- и CD8+- Т-клеток после введения Ридостина Про по сравнению с Poly(I:C)
(рис. 8). Имеются литературные данные, что IFN-I типа индуцируют экспрессию CD69 во многих типах клеток [37]. Можно предположить, что более высокие уровни CD69 на Т-клетках могут быть связаны с более сильной выработкой некоторых цитокинов после введения Ридостина Про, по сравнению с Poly(I:C).
Также определяли CD3+- Т-клетки, NK-клетки с помощью маркера NKp46+/CD3– [38] и CD19+-В-клетки (рис. 8). Нами обнаружено, что как после введения Poly(I:C), так и после введения Ридостина Про значимо снижалось количество Т- и NK-клеток и значимо повышалось количество В-клеток по сравнению с физраствором. При этом указанные изменения проявлялись сильнее после введения Ридостина Про, где количество Т- и NK-клеток было значимо меньше, а количество В-клеток значимо выше по сравнению с Poly(I:C). Снижение общего количества Т-клеток частично можно объяснить уменьшением количества Т-клеток памяти за счет апоптоза. Возможно, одной из причин снижения количества NK-клеток и части Т-клеток в селезенке может быть их миграция.
Таким образом, сравнение иммунофенотипа клеток селезенки после введения исследуемых адъювантов показало, что оба препарата снижали количество Tem и повышали Tn. Хотя указанные эффекты были сильнее выражены после применения Poly(I:C), тем не менее можно сказать о схожих тенденциях в изменении количества Т-клеток памяти. Оба адъюванта не влияли на количество маркера PD-1 на CD4+- Т-клетках и немного повышали его количество на CD8+-клетках, статистически значимой разницы между препаратами в данном случае не обнаружено. Но Ридостин Про значительно сильнее повышал количество маркера CD69 на CD4+- и CD8+- Т-клетках, по сравнению с Poly(I:C). Это можно объяснить тем, что после введения Ридостина Про значительнее повышается уровень интерферонов в сыворотке, а известно, что IFN-I индуцируют экспрессию CD69 во многих типах клеток [37]. Нами обнаружено, что после введения адъювантов мышам в селезенке повышалось количество В-клеток и снижалось количество Т- и NK-клеток, для Ридостина Про эта тенденция была выражена сильнее.
В итоге можно отметить, что, за исключением влияния на экспрессию маркера CD69, тенденции в изменении иммунофенотипа клеток селезенки в целом схожи для обоих адъювантов.
Список литературы Изучение ридостина Про и Poly(I:C) в качестве адъювантов, усиливающих иммуногенность противоопухолевой вакцины
- Blass E., Ott P.A. Advances in the development of personalized neoantigen-based therapeutic cancer vaccines. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021; 18(4): 215-29. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-020-00460-2.
- Lybaer L., ThielemansK., FeldmanS.A, van der BurgS.H., Bogaert C., Ott P.A. Neoantigen-directed therapeutics in the clinic: where are we? Trends Cancer. 2023; 9(6): 503-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2023.02.004.
- Gouttefangeas C., Rammensee H.G. Personalized cancer vaccines: adjuvants are important, too. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018; 67(12): 1911-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-018-2158-4.
- de Faria I.J., Olmo R.P., Silva E.G., Marques J.T. dsRNA sensing during viral infection: lessons from plants, worms, insects, and mammals. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013; 33(5): 239-53. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2013.0026.
- Hur S. Double-Stranded RNA Sensors and Modulators in Innate Immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2019; 37: 349-75. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurevimmunol-042718-041356.
- Matsumoto M., Seya T. TLR3: interferon induction by doublestranded RNA including poly(I:C). Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008; 60(7): 805-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.11.005.
- Ammi R., De Waele J., Willemen Y., Yan Brussel I., Schrijvers D.M., Lion E., Smits E.L.J. Poly(I:C) as cancer vaccine adjuvant: knocking on the door of medical breakthroughs. Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 146: 120-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.09.010.
- Jasani B., Navabi H., Adams M. Ampligen: a potential toll-like 3 receptor adjuvant for immunotherapy of cancer Vaccine. 2009; 27(25-26): 3401-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.01.071.
- Sultan H., Fesenkova V.I., Addis D., Fan A.E., Kumai T., Wu J., Salazar A.M., Celis E. Designing therapeutic cancer vaccines by mimicking viral infections. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017; 66(2): 203-13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-016-1834-5.
- Akazawa T., Ebihara T., Okuno M., Okuda Y., Shingai M., Tsujimura K., Takahashi T., Ikawa M., Okabe M., Inoue N., Okamoto-Tanaka M., Ishizaki H., Miyoshi J., Matsumoto M., Seya T. Antitumor NK activation induced by the Toll-like receptor 3-TICAM-1 (TRIF) pathway in myeloid dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104(1): 252-7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605978104.
- Azuma M., Ebihara T., Oshiumi H., Matsumoto M., Seya T. Crosspriming for antitumor CTL induced by soluble Ag + polyI:C depends on the TICAM-1 pathway in mouse CD11c(+)/CD8α(+) dendritic cells. Oncoimmunology. 2012; 1(5): 581-92. https://doi.org/10.4161/onci.19893.
- Robinson R.A., DeVita V.T., Levy H.B., Baron S., Hubbard S.P., Levine A.S. A phase I-II trial of multiple-dose polyriboinosic-polyribocytidylic acid in patieonts with leukemia or solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976; 57(3): 599-602. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/57.3.599.
- Levy H.B., Baer G., Baron S., Buckler C.E., Gibbs C.J., Iadarola M.J., London W.T., Rice J. A modified polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid complex that induces interferon in primates. J Infect Dis. 1975; 132(4): 434-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/132.4.434.
- Salazar A.M., Levy H.B., Ondra S., Kende M., Scherokman B., Brown D., Mena H., Martin N., Schwab K., Donovan D., Dougherty D., Pulliam M., Ippolito M., Graves M., Brown H., Ommaya A. Long-term treatment of malignant gliomas with intramuscularly administered polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid stabilized with polylysine and carboxymethylcellulose: an open pilot study. Neurosurgery. 1996; 38(6): 1096-103; discussion 1103-4.
- De Waele J., Verhezen T., van der Heijden S., Berneman Z.N., Peeters M., Lardon F., Wouters A., Smits E.L.J.M. A systematic review on poly(I:C) and poly-ICLC in glioblastoma: adjuvants coordinating the unlocking of immunotherapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021; 40(1): 213. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-02017-2.
- Ott P.A., Hu Z., Keskin D.B., Shukla S.A., Sun J., Bozym D.J., Zhang W., Luoma A., Giobbie-Hurder A., Peter L., Chen C., Olive O., Carter T.A., Li Sh., Lieb D.J., Eisenhaure T., Gjini E., Stevens J., Lane W.J., Javeri I., Nellaiappan K., Salazar A., Daley H., Seaman M., Buchbinder E.I., Yoon C.H., Harden M., Lennon N., Gabriel S., Rodig S.J., Barouch D.H., Aster J.C., Getz G., Wucherpfennig K., Neuberg D., Ritz J., Lander E.S, Fritsch E.F., Hacohen N., Wu C.J. An Immunogenic Personal Neoantigen Vaccine for Melanoma Patients. Nature. 2017; 547(7662): 217-21. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22991.
- Ott P.A., Hu-Lieskovan S., Chmielowski B., Govindan R., Naing A., Bhardwaj N., Margolin K., Awad M.M., Hellmann M.D., Lin J.J., Friedlander T., Bushway M.E., Balogh K.N., Sciuto T.E., Kohler V., Turnbull S.J., Besada R., Curran R.R., Trapp B., Scherer J., Poran A., Harjanto D., Barthelme D., Ting Y.S., Dong J.Z., Ware Y., Huang Y., Huang Z., Wanamaker A., Cleary L.D., Moles M.A., Manson K., Greshock J., Khondker Z.S., Fritsch E., Rooney M.S., DeMario M., Gaynor R.B., Srinivasan L. A Phase Ib Trial of Personalized Neoantigen Therapy Plus Anti-PD-1 in Patients with Advanced Melanoma, Non-small Cell Lung Cancer, or Bladder Cancer. Cell. 2020; 183(2): 347-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.053.
- Baryshnikova M.A., Ponomarev A.V., Rudakova A.A., Sokolova Z.A., Golubtsova N.V., Tsarapaev P.V., Levagina G.M., Danilenko E.D., Kosorukov V.S. Sravnenie Ridostina Pro i Poly(I:C) v kachestve ad"yuvanta dlya protivoopukholevoi neoantigennoi vaktsiny. Rossiiskii bioterapevticheskii zhurnal. 2022; 21(3): 82-9. https://doi.org/10.17650/1726-9784-2022-21-3-82-89.
- Kaplina O.N., Gamalei S.G., Ivanova O.S., Danilenko E.D. Dvuspiral'nye RNK - perspektivnye ad"yuvanty dlya povysheniya immunogennosti vaktsin. Zhurnal mikrobiologii, epidemiologii i immunobiologii. 2022; 99(6): 661-8. https://doi.org/10.36233/0372-9311-342.
- Bloom M.B., Perry-Lalley D., Robbins P.F., Li Y., el-Gamil M., Rosenberg S.A., Yang J.C. Identification of tyrosinase-related protein 2 as a tumor rejection antigen for the B16 melanoma. J Exp Med. 1997; 185(3): 453-9. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.185.3.453.
- Ponomarev A.V., Rudakova A.A., Sokolova Z.A., Baryshnikova M.A., Kosorukov V.S. Vliyanie Poly(I:C) i melanomy V16-F10 na immunofenotip kletok selezenki myshei. Rossiiskii bioterapevticheskii zhurnal 2021; 20(4): 51-8. https://doi.org/10.17650/1726-9784-2021-20-4-51-58.
- Castle J.C., Kreiter S., Diekmann J., Lower M., van de Roemer N., de Graaf J., Selmi A., Diken M., Boegel S., Paret C., Koslowski M., Kuhn A.N., Britten C.M., Huber C., Tureci O., Sahin U. Exploiting the mutanome for tumor vaccination. Cancer Res. 2012; 72(5): 1081-91. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3722.
- Lam H., McNeil L.K., Starobinets H., Cohen R.B., Twardowski P., Johnson M.L., Gillison M.L., Stein M.N., Vaishampayan U.N., DeCillis A.P., Foti J.J., Vemulapalli V., Tjon E., Ferber K., DeOliveira D.B., Broom W., Agnihotri P., Jaffee E.M., Wong K.K., Drake C.G., Carroll P.M., Davis T.A., Flechtner J.B. An Empirical Antigen Selection Method Identifies Neoantigens That Either Elicit Broad Antitumor T-cell Responses or Drive Tumor Growth. Cancer Discov. 2021; 11(3): 696-713. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0377.
- Heil F., Hemmi H., Hochrein H., Kirschning C., Akira S., Lipford G., Wagner H., Bauer S. Species-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA via toll-like receptor 7 and 8. Science. 2004; 303(5663): 1526-9. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1093620.
- Levine A.S., Levy H.B. Phase I-II trials of poly IC stabilized with poly-L-lysine. Cancer Treat Rep. 1978; 62(11): 1907-12.
- Takeda Y., Kataoka K., Yamagishi J., Ogawa S., Seya T., Matsumoto M. A TLR3-Specific Adjuvant Relieves Innate Resistance to PD-L1 Blockade without Cytokine Toxicity in Tumor Vaccine Immunotherapy. Cell Rep. 2017; 19(9): 1874-87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.015.
- Cossarizza A., Chang H.-D., Radbruch A. et al. Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies (second edition). Eur J Immunol. 2019; 49(10): 1457-973. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201970107.
- Bahl K., Hüebner A., Davis R.J., Welsh R.M. Analysis of apoptosis of memory T cells and dendritic cells during the early stages of viral infection or exposure to toll-like receptor agonists. J Virol. 2010; 84(10): 4866-77. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02571-09.
- Tough D.F., Borrow P., Sprent J. Induction of bystander T cell proliferation by viruses and type I interferon in vivo. Science. 1996; 272(5270): 1947-50. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5270.1947.
- Bardhan K., Anagnostou T., Boussiotis V.A. The PD1:PD-L1/2 Pathway from Discovery to Clinical Implementation Front Immunol. 2016; 7: 550. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00550.
- Kythreotou A., Siddique A., Mauri F.A. Bower M., Pinato D.J. PD-L1. J Clin Pathol. 2018; 71(3): 189-94. https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2017-204853.
- Kinter A.L., Godbout E.J., McNally J.P. Sereti I., Roby G.A., O’Shea M.A., Fauci A.S. The common gamma-chain cytokines IL-2, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21 induce the expression of programmed death-1 and its ligands. J Immunol. 2008; 181(10): 6738-46. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.6738.
- Cibrián D., Sánchez-Madrid F. CD69: from activation marker to metabolic gatekeeper. Eur J Immunol. 2017; 47(6): 946-53. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201646837.
- Testi R., Phillips J.H., Lanier L.L. T cell activation via Leu-23 (CD69). J Immunol. 1989; 143(4): 1123-8.
- Esplugues E., Sancho D., Vega-Ramos J., Martínez C., Syrbe U., Hamann A., Engel P., Sánchez-Madrid F., Lauzurica P. Enhanced antitumor immunity in mice deficient in CD69. J Exp Med. 2003; 197(9): 1093-106. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20021337.
- Radulovic K., Manta C., Rossini V., Holzmann K., Kestler H.A., Wegenka U.M., Nakayama T., Niess J.H. CD69 regulates type I IFNinduced tolerogenic signals to mucosal CD4 T cells that attenuate their colitogenic potential. J Immunol. 2012; 188(4): 2001-13. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1100765.
- Shiow L.R., Rosen D.B., Brdicková N., Xu Y., An J., Lanier L.L., Cyster J.G., Matloubian M. CD69 acts downstream of interferon-alpha/beta to inhibit S1P1 and lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs. Nature. 2006; 440(7083): 540-4. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04606.
- Walzer T., Bléry M., Chaix J., Fuseri N., Chasson L., Robbins S.H., Jaeger S., André P., Gauthier L., Daniel L., Chemin K., Morel Y., Dalod M., Imbert J., Pierres M., Moretta A., Romagné F., Vivier E. Identification, activation, and selective in vivo ablation of mouse NK cells via NKp46. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007; 104(9): 3384-9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0609692104.


