Экспериментальное исследование вязкостных свойств эмульсионных систем с содержанием наночастиц SiO2
Автор: Зейгман Юрий Вениаминович, Мухаметшин Вячеслав Шарифуллович, Сергеев Виталий Вячеславович, Кинзябаев Фанис Сулейманович
Журнал: Нанотехнологии в строительстве: научный интернет-журнал @nanobuild
Рубрика: Результаты исследований ученых и специалистов
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.9, 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
При наращивании объемов добычи нефти в условиях применения интенсивных систем разработки с применением поддержания пластового давления закачкой воды в пласты недропользователи сталкиваются с проблемой прорыва вытесняющего агента по более проницаемым интервалам пластов, что приводит к резкому обводнению продукции добывающего фонда скважин и снижению экономической эффективности эксплуатации скважин. В настоящее время специалистами отрасли предложены более сотни технологий ограничения притоков пластовых вод и вытесняющего агента к забоям добывающих скважин. Технологии ограничения водопритоков различаются по виду применяемых химических составов и способам их доставки в пласт. При этом анализ химических составов, применяемых для ограничения водопритоков, позволил выявить общую особенность. Эта особенность заключается в том, что применяемые химические составы являются неселективными и оказывают изолирующее или блокирующее действие как на водонасыщенные, так и на нефтенасыщенные интервалы пластов. Применение неселективных высокостабильных химических составов приводит к неконтролируемой кольматации всех обрабатываемых интервалов и дополнительным трудностям вовлечения обработанных интервалов в процесс фильтрации. В статье представлена технология интенсификации добычи нефти с применением эмульсионных систем с наночастицами SiO2 и загущенных кислотных составов. Технология разработана для селективного воздействия на призабойную зону пласта (ПЗП), которое обеспечивается блокировкой водонасыщенных интервалов и стимуляцией менее проницаемых нефтенасыщенных интервалов в ПЗП. Представлены результаты комплекса лабораторных экспериментов по исследованию вязкостных свойств эмульсионных систем с содержанием наночастиц SiO2. По результатам лабораторных исследований выявлена способность наночастиц SiO2 увеличивать динамическую вязкость эмульсионных систем прямого и обратного типа. Тесты на термостабильность модифицированных эмульсионных систем показали устойчивость систем при температуре 80°C. При этом модифицированные наночастицами SiO2 эмульсионные системы сохранили способность к значительному снижению вязкости при реакции с углеводородами, т.е. являются селективными составами для ограничения водопритоков.
Наночастицы, эмульсионный состав, интенсификация добычи нефти, призабойная зона пласта, селективная обработка
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14265812
IDR: 14265812 | УДК: 622.276.64 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2017-9-2-16-38
Текст научной статьи Экспериментальное исследование вязкостных свойств эмульсионных систем с содержанием наночастиц SiO2
M achine - readable information on CC- licenses (HTML- code ) in metadata of the paper
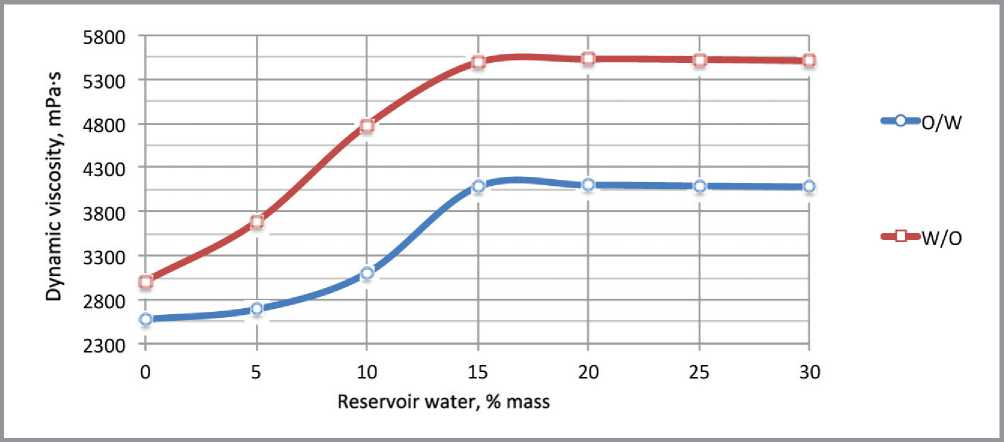
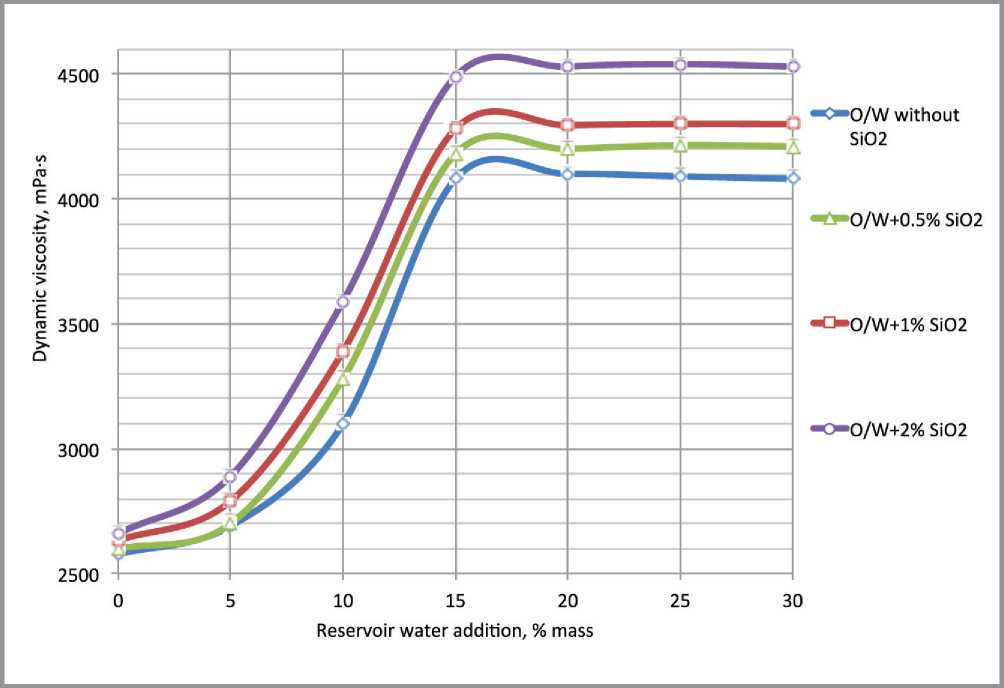
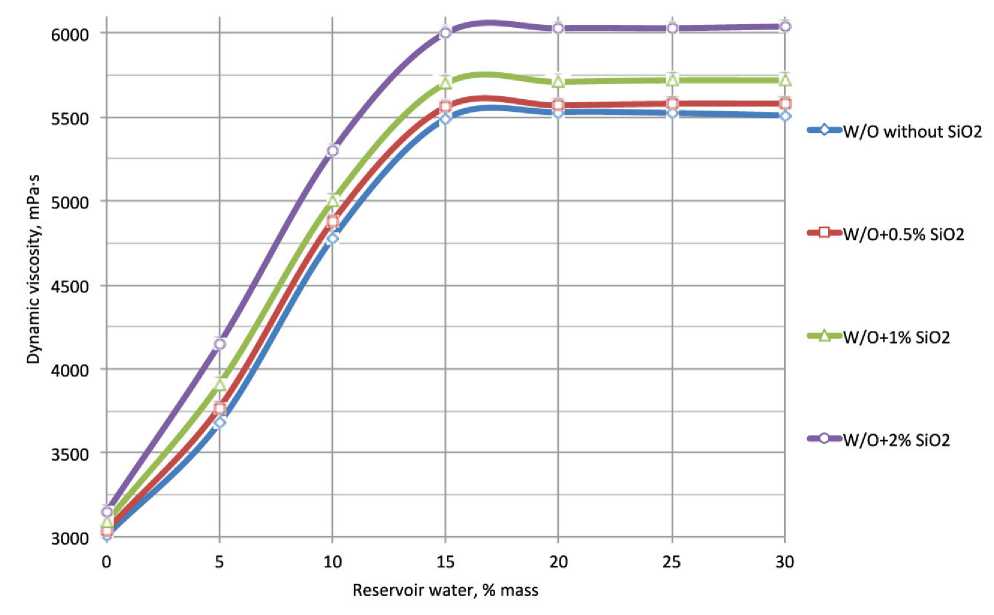
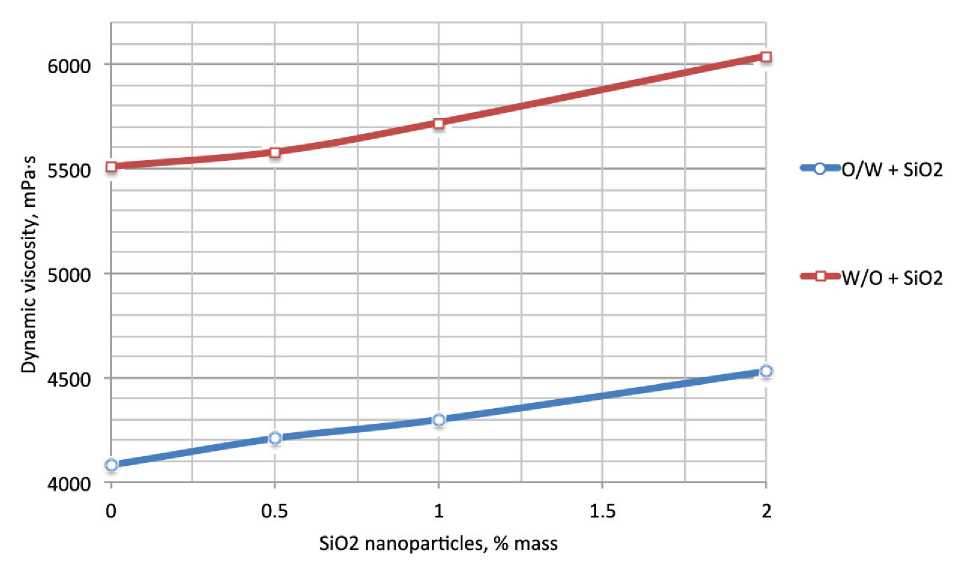
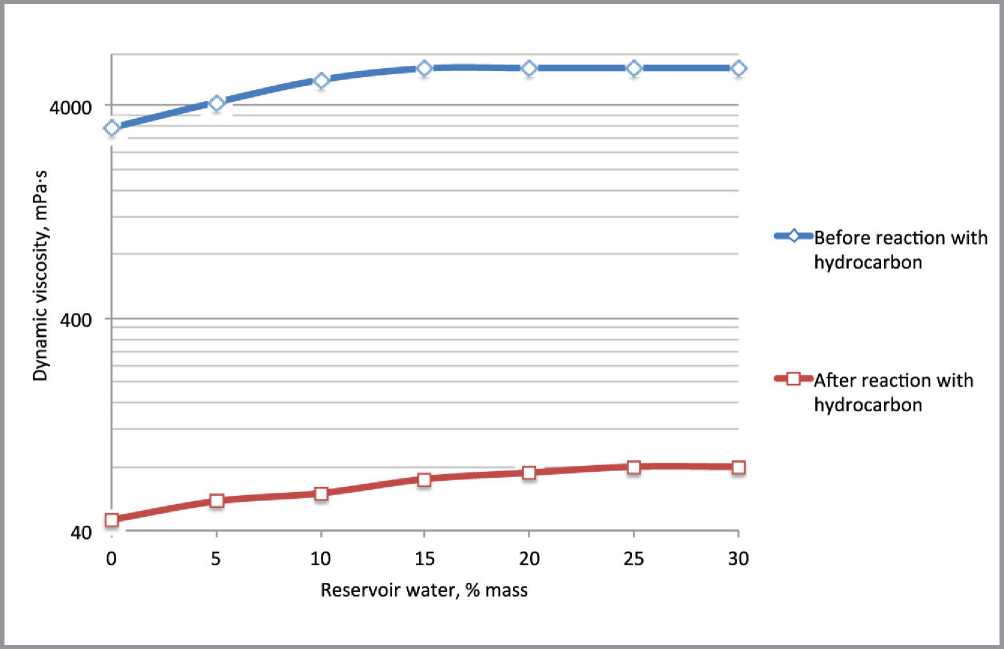
rel="dct:source"> т he most part of the oil-gas fields in Russia are developed by means of artificial waterflooding of reservoirs. During the oil and gas recovery process in the filtration channels moving part of hydrocarbons is gradually substituted for displacement agent. The application of the maintenance of reservoir pressure system allows producers of oil-gas fields to keep the production rate on the high level [1]. Despite the obvious advantages of the maintenance reservoir pressure system in the most cases the decreasing of the nonaqueous production pe- riod takes place. When the break of injection fluid in highly-permeable intervals of reservoir occurs, water-cut of well stock reaches 90 and more percents. Thus further oil extraction in water-cut wells becomes non-profitable [1–3]. The currently applied oil-gas fields development systems make it possible to recover a small part of the reverable resources. Average amount of discovered reserves that remains unextracted is from 55 to 80% [1–4]. In this circumstances, it is necessary to apply the technologies, which allows increase oil resource recovery factor. This type of technologies includes the method for selective reservoir treatment. These technologies treat the oil-saturated zones with active compositions after the water-saturated zones treatment by the selective water-blocking solution [5, 6]. The experience of selective reservoir treatment technology application in the carbonate reservoirs of Pashninsky oilfield The technology is the combination of two different types of treatments with different impact onto bottom-hole zone (BHZ) [7–9]. The combination leads to the synergetic effect. The impact onto formation system is performed in two steps: the first step – highly-permeably water-saturated zones treatment by the emulsion system (ES), the second step – low-permeable zones treatment by acid composition. Application of the emulsion systems to restrict the water-breakthroughs from high-permeable zones leads to the block of the water-saturated zones. Capability of the emulsion systems to decrease viscosity under reaction with hydrocarbons prevents from the colmatation of the middle- and low-permeable oil saturated zones. These actions provide further selective impact by acid composition onto oil-saturated zones. Basing on the results of 6 months monitoring of the wells, which were treated by the selective technology, it was determined that the average positive effect equals to 4 months [9]. After this period the watercut index rises to the initial treatment level. In this regard, to improve the water-blocking solution properties a series of the laboratory experiments for the enhancement of the stability and viscosity properties was performed. Laboratory studies of viscosity properties of emulsion systemswith SiO2 nanoparticles The application of nanoparticles in the area of development of oil and gas fields became popular in early 2000s. Today we know a large number of nanoparticle types and the methods tor apply them to create the modified systems with new physicochemical properties [10–17]. The main idea of the laboratory research was to develop emulsion systems with high stability physicochemical properties. The experiments were carried out with two types of emulsions: oil in water (O/W) and water in oil (W/O). Laboratory experiments that studied the emulsion systems viscosity properties were carried out by using rotational viscosimeter DV-E VISCOMETER «BROOKFIELD». Before emulsion systems viscosity parameters were measured, the components of the basic emulsion (diesel fuel, emulsifier and model of reservoir water with density 1020 kg/m3) had been mixed in the device «CAT R50 D» for 15 min. To determine the emulsion viscosity dynamics and viscosity dependence from the water content NaCl and CaCl2 taken in volume: 5…30% mas under temperature 20оС were added into the samples of emulsion (Fig. 1). Fig. 1. Dynamic viscosity curves for the basic samples of the O/W and W/O emulsions on the reservoir water content (spindle speed 30 rpm.) When the measurement of base samples was fulfilled, the experiments to identify O/W and W/O emulsions dynamic viscosity dependence on mass fraction of SiO2 nanoparticles content, determination of the optimal concentration of the additives and thermostability of the modified emulsion systems were performed. At the first step of the experiments experimental samples with 0.5, 1 and 2% mass fraction of SiO2 nanoparticles were prepared. After that, the reservoir water was added (5…30% mass) in each sample of emulsions and mixed on stirrer «CAT R50 D» due 20 min. Then the dynamic viscosity parameters were measured on the rotational viscometer. Experiments were carried out at 20 . Same measurements were carried out for the modified emulsion systems with SiO2 nanoparticles content (O/W and W/O types). The characteristic curves are presented in figures 2 and 3. Fig. 2. Dynamic viscosity curves for the O/W emulsions + SiO2 nanoparticles on the reservoir water content (spindle speed 30 rpm.) Fig. 3. Dynamic viscosity curves for the W/O emulsions + SiO2 nanoparticles on the reservoir water content (spindle speed 30 rpm.) The type of the emulsion system is chosen in dependence on the wetability of rock. In case of the hydrophilic rocks O/W emulsion system with SiO2 nanoparticles was applied. In case of the hydrophobic rocks W/O emulsion system with SiO2 nanoparticles was applied. The revealed dependences make it possible to conclude that the presence of the SiO2 nanoparticles (2% mass) in emulsion systems leads to increasing dynamic viscosity up to 6000 mPa·s by mixing with 30% mass fraction of reservoir water (Fig. 4). The thermostability experiments were carried out by using water bath «LOIP LB-161». Analysis of experimental results made it possible to determine that the sample of W/O + SiO2 nanoparticles (15% mass reservoir water content) were stable at 80оС for 48 hours (the period of the experiment). Fig. 4. Dependence of the dynamic viscosity of emulsion systems with 30% mass reservoir water on SiO2 nanoparticles content (spindle speed 30 rpm.) Studying the emulsion systems with SiO2 nanoparticles content ability to decrease viscosity properties in reaction with hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are hydrophobic compounds which are incompatible with water. However, the ability of hydrocarbons to diffuse to the center of the micelles has an influence on their shape, size, and consequently on the rheological properties [18, 19]. For the experiments the samples with 2% mass fraction of nanoparticles were chosen. In these samples different amount of the reservoir water were added: 5…30% mass respectively. Alternately the samples were mixed with crude oil (viscosity 22 mPa•s, density 866 kg/m3) in the test glass at a ratio of 50 ml emulsion and 20 ml of oil. The samples were shaken for 20 seconds. After that, the samples were held in water bath at 40оC for 1 hour. After thermostability tests the gravitational segregation of the emulsion system were observed in two phase: hydrocarbon and water phases. After that the viscosity parameters were measured on a rotational viscometer at a spindle speed of 30 rpm/min. The results for the W/O system are presented at figure 5. The results of the experiments identified that the emulsion systems with SiO2 nanoparticles content possess high sensitivity to hydrocarbons. Reaction with oil leads to significant reduction of viscosity: maximum – 6040 to 80 mPa•s and minimum – 3150 up to 40 mPa•s. At the last stage of the experiments the each sample after reaction with oil was filtered through a sieve (cell size 500 micron). Precipitation and high viscosity individual clumps were not observed. We can make an assumption that these changes in viscosity parameters were result of hydrocarbon micelles solubilizing. The results of the carried out complex of the rheological experiments confirmed the abilities of the emulsion systems with SiO2 nanoparticles content increase stability, dynamic viscosity with the reaction with water and significantly decrease viscosity properties and decompose due the re- Fig. 5. Dynamic viscosity of the W/O system + 2% SiO2 nanoparticles before and after reaction with the hydrocarbons action with hydrocarbons. These are important properties if we are talking about the application of the emulsion systems to improve oil recovery methods. The new limits of the emulsions physicochemical properties provides opportunity for selective treatment of the water-saturated intervals in petroleum reservoir. The selectivity is one of the main advantage of the emulsion systems compared to other currently used water-blocking solutions.
org/dc/terms/" href="" property="dct:title" rel="dct:type">Experimental study of viscosity properties of emulsion system with SiO2 nanoparticles is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at 
Список литературы Экспериментальное исследование вязкостных свойств эмульсионных систем с содержанием наночастиц SiO2
- Diachyk IA. Razrabotka zavodnennyh neftjanyh plastov na zavershajushhih stadijah . Diachyk I.A., Zeigman Y.V. Kazan. 2015. 274 p..
- Yakupov R.F., Mukhametshin V.Sh. Voprosy jeffektivnosti razrabotki nizko-produktivnyh karbonatnyh kollektorov na primere Turnejskogo jarusa Tujmazin-skogo mestorozhdenija . Oil industry. 2013. № 12. p. 106-110..
- Zeigman Y.V., Sergeev V.V., Ayupov R.R. Klassifikacija fiziko-himicheskih metodov intensifikacii dobychi nefti po mehanizmu vozdeistvija na plastovuju sistemu . Geology, geophysics and development of oil and gas fields. 2017. № 1. p. 50-54..
- Gazizov A.Sh, Gazizov AA, Kabirov M.M. et al. Intensification of oil production in abnormal operating conditions. Kazan: Center of Innovative technologies. 2008. 304 p.
- Ibragimov I.G., Musabirov M.Kh., Yartiev A.F. Jeffektivnost' kompleksa tehnologij stimuljacii skvazhin v OAO «Tatneft'» . Oil Industry. 2014. № 7. p. 43-52..
- Xie X., W. W., Tong Z.J., & Morrow N.R. (2005, September 1). Improved Oil Recovery from Carbonate Reservoirs by Chemical Stimulation. Society of Petroleum Engineers DOI: 10.2118/89424-PA
- Zeigman Y.V., Sergeev V.V., Kinzyabaev F.S. Analiz jeffektivnosti primenenija tehnologii intensifikacii dobychi nefti na zavershajushhei stadii razrabotki neftegazovyh mestorozhdeni . Oilfield Engineering. 2017. № 1. p. 32-36..
- Sergeev V.V. Sposob obrabotki prizaboinoi zony plasta . Patent for invention № 2583104. Issued 17/12/2014.
- Zeigman Y.V., Sergeev V.V. Opytno-promyshlennoe vnedrenie kompleksnoj tehnolo-gii intensifikacii dobychi nefti iz karbonatnyh kollektorov . Oilfield Engineering. 2015. № 8. 2015. p. 32-37..
- XueZ, Foster E, Wang Y. et al. 2014. Effect of Grafted Copolymer Composition on Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Stability and Transport in Porous Media at High Salinity. Energy Fuels 28 (6): 3655-3665. http://dx.doi.o DOI: rg/10.1021/ef500340h
- Yoon K.Y., Kotsmar C., Ingram D.R. et al. 2011. Stabilization of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoclusters in Concentrated Brine With Cross-Linked Polymer Shells. Langmuir 27 (17): 10962-10969. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/la2006327.
- Yoon K.Y., Li Z., Neilson B.M. et al. 2012. Effect of Adsorbed Amphiphilic Copolymers on the Interfacial Activity of Superparamagnetic Nanoclusters and the Emulsification of Oil in Water. Macromolecules 45 (12): 5157-5166. http://dx.doi.o DOI: rg/10.1021/ma202511b
- Worthen A., TaghavyA., AroonsriA. et al. 2015. Multi-Scale Evaluation of Nanoparticle-Stabilized CO2-in-Water Foams: From the Benchtop to the Field. Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, 28-30 September. SPE-175065-MS. http://dx.doi.o DOI: rg/10.2118/175065-MS
- Ko S, Prigiobbe V., Huh C. et al. 2014. Accelerated Oil Droplet Separation From Produced Water Using Magnetic Nanoparticles. Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Amsterdam, 27-29 October. SPE-170828-MS. http://dx.doi.o DOI: rg/10.2118/170828-MS
- Denney D. (2011, January 1). Nanosized Particles for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Society of Petroleum Engineers DOI: 10.2118/0111-0054-JPT
- Torsater O., Engeset B, Hendraningrat L., & Suwarno S. (2012, January 1). Improved Oil Recovery by Nanofluids Flooding: An Experimental Study. Society of Petroleum Engineers DOI: 10.2118/163335-MS
- Alomair OA, Matar K.M., & Alsaeed Y.H. (2014, October 14). Nanofluids Application for Heavy Oil Recovery. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi:10.2118/171539-MS.
- Shokrlu Y.H., & Babadagli T. (2011, January 1). Transportation and Interaction of Nano and Micro Size Metal Particles Injected to Improve Thermal Recovery of Heavy-Oil. Society of Petroleum Engineers DOI: 10.2118/146661-MS
- Mcelfresh P.M., Holcomb D.L., & Ector D. (2012, January 1). Application of Nanofluid Technology to Improve Recovery in Oil and Gas Wells. Society of Petroleum Engineers DOI: 10.2118/154827-MS
- Shibaev A.V. How a viscoelastic solution of wormlike micelles transforms into a microemulsion upon absorption of hydrocarbon: New insight . A.V. Shibaev, M.V. Tamm, V.S. Molchanov, A.V. Rogachev, A.I. Kuklin, E.E. Dormidontova, O.E. Philippova. Langmuir. 2014. V. 30. No 13. P. 3705-3714.
- Pletneva VA. Viscoelasticity of Smart Fluids Based on Wormlike Surfactant Micelles and Oppositely Charged Magnetic Particles. V.A. Pletneva, V.S. Molchanov, O.E. Philippova . Langmuir. 2015. V. 31 (1). Р. 110-119.


