Клеточные и надклеточные уровни взаимодействия ретровирусов с хозяином на примере вируса бычьего лейкоза. Сообщение I. Проникновение в клетку и интеграция в геном хозяина
Автор: Глазко В.И., Косовский Г.Ю., Глазко Т.Т., Донник И.М.
Журнал: Сельскохозяйственная биология @agrobiology
Рубрика: Обзоры, проблемы
Статья в выпуске: 6 т.53, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Диагностика ретровирусных инфекций и предупреждение их распространения у животных сельскохозяйственных видов (в частности, низкая эффективность вакцинации) до сих пор все еще недостаточно разработаны прежде всего в связи с тем, что каскад событий, лежащий в основе взаимодействия ретровируса с объектом заражения имеет сложную иерархию и реализуется на разных уровнях организации - молекулярном (включая клеточные органеллы), собственно клеточном и надклеточном, связанным с функцией клеточных сетей иммунной системы. В настоящей работе представлен обзор собственных и имеющихся в литературе данных о взаимодействии ретровирусного патогена (на примере вируса бычьего лейкоза - bovine leukemia virus, BLV) с внутренними структурами клеток-мишеней. Анализ этих результатов позволил нам предположить, что ключевым фактором, определяющим интеграцию провирусной ДНК в геном хозяина при ретровирусной инфекции, может быть снижение внутриклеточного контроля транспозиций мобильных генетических элементов, тесно связанных по происхождению с ретровирусными инфекциями...
Ретровирус, вирус бычьего лейкоза, инфекционный цикл, в-лимфоциты, рецептор вируса бычьего лейкоза, обратная транскриптаза, интеграза, мобильные генетические элементы
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142220058
IDR: 142220058 | УДК: 636.2:577.212.3 | DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2018.6.1093rus
Текст обзорной статьи Клеточные и надклеточные уровни взаимодействия ретровирусов с хозяином на примере вируса бычьего лейкоза. Сообщение I. Проникновение в клетку и интеграция в геном хозяина
Ретровирусы ( Retroviridae ) — широко распространенные патогены млекопитающих, регулярно наносящие многомиллионные ущербы сельскому хозяйству. Одна из проблем при предупреждении распространения таких инфекций заключается в низкой эффективности вакцинации, причины чего до сих пор недостаточно исследованы. Принцип вакцинации предполагает наличие во взаимодействии между патогеном и хозяином некоего звена, блокирование которого посредством активации соответствующего 1093
антителогенеза у хозяина может прервать инфекционный процесс. Однако, как свидетельствует большое количество экспериментальных данных, развитие ретровирусной инфекции представляет собой каскад событий, при которых взаимодействие между ретровирусом и хозяином происходит на разных уровнях — от внутриклеточных до надклеточных. Следовательно, резистентность к ретровирусу может определяться как множеством внутриклеточных сигнальных, структурных, транспортных и ферментных белков хозяина, так и особенностями популяций лейкоцитов, определяющих состояние его адаптивного и врожденного иммунитета.
Цель представляемого обзора — выявление ключевых этапов во взаимодействии BLV с хозяином. В частности, в первом сообщении будут рассмотрены события, обеспечивающие попадание BLV в клетки-мишени и интеграцию провирусной ДНК в геном хозяина, во втором — влияние интеграции провирусной BLV ДНК на некоторые звенья врожденного и адаптивного иммунитета хозяина.
Cтруктурно-функциональная организация генома вируса бычьего лейкоза (Bovine leukemia virus, BLV), стадии индуцируемого BLV патогенеза, влияние на экспрессию множественных генов хозяина описаны достаточно подробно. Однако механизмы взаимодействия ретровирусов и их хозяев сложны и все еще требуют дальнейшего изучения. Например, у крупного рогатого скота от 7 до 22 % особей имеют антитела к BLV, при том что клоны В-клеток, несущих интегрированную в геном хозяина провирусную ДНК, у этих животных отсутствуют (1, 2). До сих пор не выявлены ключевые этапы метаболических путей, приводящих к лимфолейкозу при инфицировании BLV, и их разнообразие, неясными остаются причины неэффективного формирования иммунитета против BLV при вакцинации. Не разработаны представления о наличии разных механизмов, определяющих резистентность к BLV, что должно существенно влиять на характер профилактических мероприятий. Кроме того, отсутствие такой информации усложняет и снижает точность диагностики и индикации инфекции, прогноза инфекционной опасности животных и индивидуальных особенностей патогенеза.
Настоящее сообщение частично восполняет этот пробел. Выполненный нами системный анализ источников потенциальной резистентности на разных этапах инфекции BLV на клеточном уровне указывает на многообразие взаимоотношений между ретровирусами и клетками-мишенями и множественность клеточных механизмов резистентности к ретровирусной инфекции. При этом принципиальное значение, по-видимому, имеют события, которые связаны с интеграцией провирусной ДНК в геном хозяина. Главную роль в них, по нашему мнению, играет снижение внутриклеточного контроля транспозиций мобильных генетических элементов, тесно связанных по происхождению с ретровирусными инфекциями.
Проникновение вируса бычьего лейкоза в клетку-мишень. BLV, который относится к роду Deltaretrovirus , подсемейству орторетровирусов ( Orthoretrovirinae ) семейства ретровирусов ( Retroviridae ), филогенетически близкородствен вирусу Т-клеточного лейкоза человека I типа (Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1, HTLV-1) (3). HTLV-1 инфицирует CD4+ T-клетки человека, BLV — B-клетки крупного рогатого скота, оба вируса встраивают ДНК-копии своих геномных РНК в геном хозяина как провирусную ДНК (4, 5). У животных, инфицированных BLV, начальные стадии патологии проходят бессимптомно, затем у некоторых усиливается пролиферация В-клеток, и в конечном итоге примерно у 5 % особей формируются В-клеточные лимфомы. Распространение BLV приводит к существенному экономическому ущербу в молочном и мясном скотоводстве 1094
(6), разработать методы эффективной иммунизации животных до сих пор не удается (7). Кроме наиболее распространенных 8 серотипов BLV, которые обусловлены мутациями в гене g51 , кодирующем поверхностный гликопротеин (8), описаны не связанные с этими мутациями варианты нуклеотидных замен. Они позволили подразделить 28 полностью секвенированных геномов BLV на группы А, В и С соответственно с высокой, средней и низкой патогенностью (ее оценивали по размножению вируса в системах in vitro и по вирусной нагрузке у коров in vivo) (9).
Интеграция провирусной ДНК в геном хозяина вызывает существенные изменения в обоих геномах и может рассматриваться как пример инсерционного мутагенеза (10-12). Выделяют две основные стадии инфекционного процесса, индуцируемого BLV, — массовое встраивание прови-русной ДНК в геном В-лимфоцитов и размножение некоторых инфицированных В-клонов (13). У крупного рогатого скота, инфицированного BLV, в периферической крови выявляют менее 1 % клеток с провирусной ДНК в геноме (3). После первых стадий инфицирования провирусная ДНК массово встраивается в активно транскрибируемые участки генома хозяина, но в последующем интегрированные копии сохраняются только в единичных клетках, и лишь некоторые из них в последующем дают начало образованию опухолей (13). Инфекционный процесс сопровождается массовой гибелью клеток с интегрированным провирусным геномом (14). Такая гибель обусловлена и реакцией иммунной системы хозяина на антигены вируса, и тем, что интеграция провирусной ДНК в активно транскрибируемые районы генома хозяина может приводить к снижению жизнеспособности клеток, особенно когда провирусная ДНК встраивается в регуляторные или кодирующие последовательности жизненно важных структурных генов (13).
То есть в общем случае естественный отбор направлен против клеточных популяций, в которых активно экспрессируется провирусная ДНК. Более того, оказалось, что инфицированные BLV В-клетки подразделяются на две субпопуляции — в одной IgM и РНК BLV активно экспрессируются, в другой экспрессия как IgM, так и вирусной РНК отсутствует. Предполагается, что именно вторая клеточная популяция становится предшественником лимфом, поскольку в опухолевых клетках провирусная ДНК (плюс-цепь) не экспрессируется (15). Накапливаются данные о том, что ключевым регуляторным фактором, способствующим инициации неопластической трансформации В-клеток, служит экспрессия микроРНК провирусной ДНК BLV, транскрипция которой обнаруживается в В-лимфоцитах, не экспрессирующих полноразмерный геном BLV (плюс-цепь) (16-18).
Проникновение BLV в клетки-мишени. BLV распространяется вместе к содержащими клеточную компоненту жидкостями (кровь, молоко) и инфицирует в основном В-лимфоциты CD5+ IgM+ (19). Накоплены экспериментальные данные, свидетельствующие о том, что BLV преимущественно проникает в клетки-мишени не непосредственно (при прямом попадании свободных вирусных частиц), а через слияние инфицированных и свободных от инфекции клеток (20). Передача инфекционного агента от одной клетки к другой обеспечивается благодаря тесному взаимодействию двух гликопротеинов, связанных с липидной оболочкой вириона, — поверхностного белка (surface protein, SU) и трансмембранного белка (transmembrane protein, ТМ). Оба гликопротеина образуются при посттрансляционном расщеплении предшественника, кодируемого геном env, и связаны уникальной дисульфидной связью между цистеиновыми мотивами SU (CXXC) и TM (CX6CC). Схематично процесс слияния, индуцируемый взаимодействием рецептор-связывающего домена SU (SU receptor- binding domain, RBD) с рецептором на клетках-мишенях, представлен в работах, посвященных анализу распространения ретровируса (21, 22) (рис. 1).
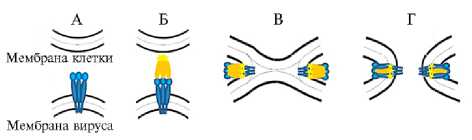
Рис. 1. Мембранное слияние с участием белка оболочки вируса бычьего лейкоза (BLV) на основе модели для вируса лейкоза мышей (22). Исходное состояние, рецептор-связы-вающие белки вируса: поверхностный белок — гликопротеин 51
(gp51) (surface protein, SU, receptor binding domain, RBD; светло-синий цвет), собственно белок слияния — трансмембранный белок 30 (gp30) (transmembrane protein, ТМ; темно-синий цвет) (А). Связывание с рецепторами клеточной мембраны (желтый цвет) вызывает конформационные изменения (Б). В результате конформационных изменений происходит включение клеточного рецептора (желтый цвет) в липидный бислой, что опосредует формирование диафрагмы полуслияния и смешивание вирусных и клеточных липидов (серые точки) (В). Структура слияния после переупаковки, в результате которой SU и ТМ находятся в антипараллельной конформации (Г).
Рецептор-связывающий домен SU (RBD) взаимодействует со специфическим рецептором(ами) на клетках-мишенях. Это взаимодействие индуцирует конформационное изменение, которое инициирует процесс слияния, направляемый TM. После присоединения к рецепторам нарушается дисульфидный мостик, соединяющий SU и TM, что позволяет перевести TM в конформацию, необходимую для слияния мембран. Пептид слияния, расположенный на NH2-терминальной части ТМ, дестабилизирует клеточную мембрану, что делает возможным переход нуклеокапсида вируса в цитоплазму клетки-хозяина (22). Предполагается (и для этого имеется ряд экспериментальных подтверждений), что основным связывающим RBD BLV клеточным рецептором служит адаптерный белковый комплекс (adaptor-related protein complex-3 — AP-3), участвующий в транспорте белков (2325). Этот комплекс вовлечен в формирование транспортных везикул, объединяющих аппарат Гольджи и лизосомы, и высококонсервативен у ряда видов млекопитающих (идентичность его аминокислотных последовательностей у человека и крупного рогатого скота — 88 %, овец и коз — 99 %). В AP3D1 человека выделяют два основных домена — адаптин и рецептор для вируса BLV (рис. 2), причем сравнение аминокислотных последовательностей этих доменов позволило обнаружить 15 различий во втором домене (вирусный рецептор) при полном их отсутствии в домене адаптина (25).
АБ
1 33 „ -™-„w438 460 513 32 583 661 8071207
t^^JMit i ^^^™■■
Рис. 2. Структура белка оболочки вируса бычьего лейкоза (BLV, ген env ) (А) и адаптерного белкового комплекса человека AP3D1 (Б) (25). Позиции 1-33 — сигнальный пептид (SP), 34-438 — поверхностный белок (SU, gp51), 439-460 — трансмембранный белок (TM, gp30), 461-515 — цитоплазматический участок молекулы белка (CR). Сайты связывания ионов Zn2+, содержащие цистеиновые и гистидиновые минокислотные остатки, показаны желтыми кружками, отмечены сайты N-гликозилирования ( ϒ ) (А). Белок AP3D1 (1207 аминокислот) содержит два домена — адаптин (позиции 32-583) и рецептор для BLV (позиции 661-807). AP3D1 несет два сайта связывания ионов Zn2+ (желтые кружки) и 16 консервативных сайтов в домене рецептора BLV (серые кружки) (Б) (25).
Ранее мы показали, что у инфицированных BLV коров экспрессия гена, кодирующего рецептор BLV — AP3D1, выше, но она не коррелирует с увеличением количества лимфоцитов (1). В литературе имеются данные, которые свидетельствуют, что экспрессия этого гена обнаруживается у юных форм В-лимфоцитов и падает по мере их старения (24). Несмотря на отсутствие статистически достоверных корреляций между численностью лимфоцитов и экспрессией гена ap3d1 , у животных с провирусной ДНК BLV мы 1096
отмечали статистически значимое (p < 0,05) усиление экспрессии ap3d1 по сравнению с наблюдаемой у особей, свободных от инфекции. Полученные данные позволяют предполагать, что у инфицированных BLV животных доля юных В-лимфоцитов в популяции клеток относительно повышена.
Учитывая широкую представленность в органах и тканях и консерватизм AP3D1 у рассмотренных видов млекопитающих, плейотропые эффекты мутации в гене, который кодирует эту центральную субъединицу комплекса AP-3, обеспечивающего транспорт мембранных белков в лизосомы (26), трудно представить механизмы, обусловливающие избирательное проникновение вируса BLV именно в В-лимфоциты с участием AP-3. Тем не менее ряд экспериментальных работ указывают на наличие таких механизмов (25). Сложность динамических процессов обмена белками между эндосомами, плазматической мембраной, лизосомами дает основание полагать, что определенную специфичность взаимодействия между продуктами гена env и AP3D1 хозяина могут обеспечивать разнообразные лиганды, клеточные элементы цитоскелета и другие факторы, трудно поддающиеся прямому экспериментальному контролю.
Таким образом, BLV попадает в клетки различных тканей у разных видов млекопитающих, но продуцирует полноценное вирусное потомство только у некоторых из них в В-лимфоцитах. Следовательно, существует возможность блокировки воспроизводства BLV на последующих этапах инфекции (обратная транскрипция, интеграция в геном хозяина, размножение инфицированных клеток) (27), что, тем не менее, не исключает проявления резистентности и на этапе проникновения BLV в клетки-мишени.
Формирование провирусной ДНК. После попадания BLV в цитоплазму клетки на матрице геномной РНК вируса синтезируются ее ДНК копии (кДНК). Оказалось, что эффективность построения кДНК цепи существенно зависит от успешности димеризации двух молекул вирусной РНК (28). На этом этапе высока частота рекомбинаций между двумя цепочками вирусной РНК, что может приводить к появлению широкого спектра аберрантных провирусных геномов.
В инициации обратной транскрипции существенную роль играет взаимодействие тРНК хозяина с длинными концевыми повторами (LTR) в вирусном геноме. 5´- и 3´-LTR представляют собой комплексы регуляторных мотивов, необходимых для построения ДНК копии вирусной РНК и последующей транскрипции провирусной ДНК. Мутации в LTR, а также изменения рисунка их метилирования могут существенно влиять на индуцируемый BLV инфекционный процесс (рис. 3) (29). Изначально 5´- и 3´-LTR области вирусного генома сходны, различия в них (в виде нуклеотидных замен, вставок и делеций — инделов) накапливаются уже после встройки в геном хозяина. Типичная последовательность LTR ретровируса включает три основных функциональных единицы: TG…CA бокс с TG на 5´-конце 5´-LTR и CA на 3´-конце 3´-LTR; область TSR (target site repeat) длиной ∼ 4-6 п.н. (короткий прямой повтор, фланкирующий 5´- и 3´-концы; это «роспись» сайтов, которые участвуют в инсерции провирусной ДНК в геном хозяина); PBS (primer binding site) — последовательность длиной примерно 18 п.н., комплементарная 3´-хвосту некоторых тРНК, которая находится около 3´-конца 5´-LTR (этот сайт очень важен, поскольку обратная транскрипция начинается со связывания с тРНК).
Транспорт провирусной ДНК в ядро клетки-хозяина. Во многих исследованиях экспериментально показано, что репликация, формирование преинтеграционного комплекса и дальнейшее взаимодействие с белками ядерных пор на этапе переноса провирусной кДНК через ядер-
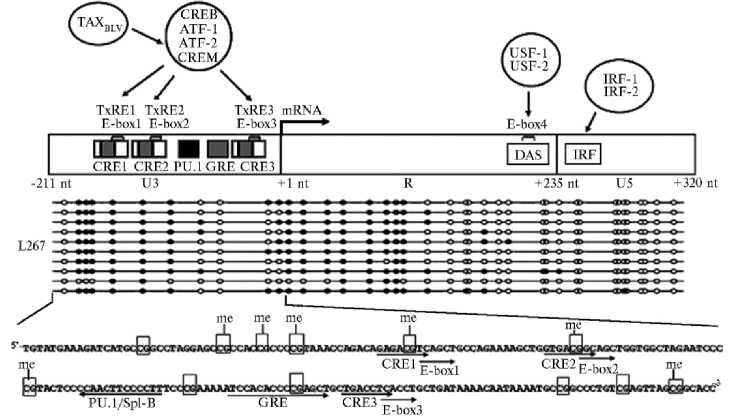
Рис. 3. Схема 5 ′ -LTR генома провируса бычьего лейкоза (BLV) с рисунком метилирования в мотиве CpG (цитозин-фосфат-гуанин) в линии клеток овцы L267 при латентной инфекции BLV (29). Сайт инициации транскрипции мРНК в районе U3—R в 5´-LTR (+1 нуклеотид, nt) отмечен стрелкой. TxRE1, TxRE2 и TxRE3 — три основных последовательности энхансеров транскрипции длиной 21 п.н., взаимодействующие с факторами транскрипции CREB, CREM, ATF-1 и ATF-2 хозяина, что необходимо для активации транскрипции BLV вирусным трансактиватором Tax BLV . Каждый из энхансеров содержит последовательности, которые гомологичны консенсусу последовательностей E-box (E-box1, E-box2 и E-box3) и перекрывают CRE (CRE1, CRE2 и CRE3 — элементы, регулируемые циклической AMP, cyclic-AMP responsive element, CRE). Область U3 включает элемент глюкокортикоидной регуляции GRE (связывание гормон-рецепторного комплекса) и сайт PU.1/Spi-B. USF-1/USF-2 сайт связывания (E-box 4) и сайт связывания интерферон-регуляторного фактора (IRF-1 / IRF-2) локализованы в R участке области U5. Под схемой приведена полная нуклеотидная последовательность области U3 с сайтами связывания факторов транскрипции (отмечены стрелками) и динуклеотидами CpG (прямоугольниками выделены сайты метилирования — me) (29).
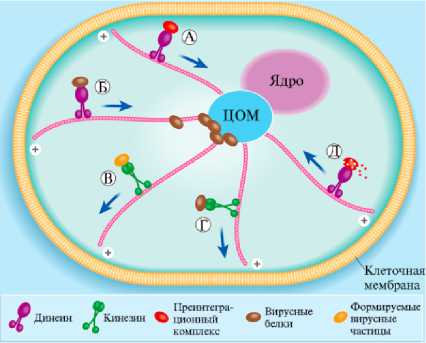
Рис. 4. Моторные белки микротрубочек, участвующие в репликации ретровирусов. Преинтеграционные комплексы ретровирусов используют динеин для транспорта вдоль микротрубочек (А). Вновь синтезированные ретровирусные белки (Gag и Env) при участии динеина перемещаются в перинуклеарную зону для последующего формирования вириона (Б). Образовавшиеся вирусные частицы затем переносятся кинезином на клеточную мембрану для выхода из клетки (В). Те вирусы, которые собираются на плазматической мембране, используют ки-незин для транспорта своих белков и геномных РНК (Г). Для удаления вирусной оболочки также требуется активность динеина (Д). ЦОМ — центр организации микротрубочек. Отмечен плюс-конец микротрубочек (+), стрелки указывают направление движения макромолекул по микротрубочкам (30).
ную оболочку обеспечиваются при участии микротрубочек цитоскелета и центра их организации (рис. 4) (30). Вовлеченность цитоскелета и множества белков хозяина в транспорт преинтеграционного комлпекса в ядро характерно для всех ретровирусов. Геном представителей семейства Retro-viridae, включающего два подсемейства — Spumaretrovirinae (род Spumavirus) и Orthoretrovinae (роды Alpharetrovirus, Betaretrovirus, Gammaretrovirus, Delta- retrovirus, Epsilonretrovirus и Lentivirus), состоит из двух копий одноцепочечной РНК. Как уже отмечалось, при проникновении в клетку вирион связывается со специфическим поверхностным белком клетки — рецептором, мембраны вириона и хозяина сливаются (либо на поверхности клетки, либо после интернализации в эндосомы), в результате вирусный капсид, несущий геном и вирусный фермент обратную транскриптазу, транспортируется в цитоплазму. В цитоплазме при взаимодействии обратной транскриптазы с нуклеозидтрифосфатами фермент активируется и ретротранскрибирует геном РНК в двухцепочечную ДНК. Полученная кДНК переносится в ядро клетки в составе преинтеграционного комплекса (ПИК). У разных ретровирусов и в клетках разных типов состав ПИК неодинаков. Компоненты ПИК пока исследованы недостаточно, но известно, что ПИК содержит провирусную ДНК, интегразу и белки капсида.
После интеграции в клеточный геном провирусная ДНК транскрибируется РНК-полимеразой II хозяина, и вирусные мРНК экспортируются в цитоплазму. Далее они транслируются в вирусные белки Gag, Pol и Env (а также во вспомогательные белки, если в геноме вируса присутствуют их генетические детерминанты), которые затем переносятся в плазматическую мембрану при участии везикул, цитоскелета или другими способами. После сборки незрелые вирусные частицы отпочковываются от клеточной мембраны. Созревание вирионов инициируется вирусной протеазой, которая расщепляет белки Gag и Gag ‐ Pol. Каждый этап описанного строго регулируемого процесса требует участия множества белков хозяина, включая элементы цитоскелета клетки. Мутации генов, кодирующих эти белки, могут существенно влиять на инфекционную успешность провирусной ДНК.
руемые геном pol , протеаза (Pro) (Б).
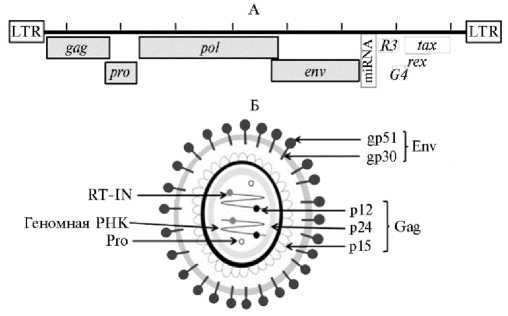
Рис. 5. Геном (А) и структура вириона (Б) вируса бычьего лейкоза (BLV) (31). Структурные гены и гены ферментов env , gag , pro и pol ; регуляторные гены tax и rex ; вспомогательные гены R3 и G4 ; микроРНК (miRNA) (А). Структурные белки и ферменты: внеклеточный и трансмембранный гликопротеины gp51 и gp30 (Env), белки Gag — р12 (нуклеокапсидный), р24 (капсидный) и р15 (матрикс-ный), обратная транскриптаза и интеграза (RТ-IN), коди-
Структура генома BLV подробно описана достаточно давно (рис. 5) (31). Геном BLV состоит из 8714 нуклеотидов, включает основные гены, кодирующие структурные белки и ферменты (основные из них gag , pro , pol и env ), и область pX, окруженную двумя идентичными LTR. Ген gag транслируется с образованием белка-предшественника Pr45, который процессируется в три зрелых белка: матричный белок Р15, который связывает геномные РНК вируса и взаимодействует с липидным бислоем вирусной мембраны, капсидный белок Р24 (в сыворотке крови инфицированных BLV животных выявляются высокие титры антител против этого белка) и белок нуклеокапсида Р12, участвующий в упаковке геномной РНК (см. рис. 5). Ген env кодирует зрелый внеклеточный белок gp51 и трансмембранный белок gp30. Область pX, расположенная между env и 3´-LTR, кодирует регуляторные белки Tax и Rex, а также вспомогательные белки R3
и G4 (см. рис. 5). Регуляторные белки вовлечены в контроль транскрипции и экспорта вирусной РНК в цитоплазму. В частности, G4 существенно увеличивает продукцию вируса (32). Между env и pX локализован участок, кодирующий пять вирусных микроРНК. Их транскрипцию осуществляет РНК-полимераза III. Белки Rex и Gag участвуют в перемещении прови-русной кДНК в ядро клетки. Важно, что Gag также связывается с белками центросом, организующими веретено деления, что может влиять на возникновения многополюсных митозов (33, 34).
В раздевании вириона, его транспортировке, поступлении в клеточное ядро участвуют многие белки хозяина, частично изученные на примере ретровируса ВИЧ-1 (HIV-1) (рис. 6) (35).
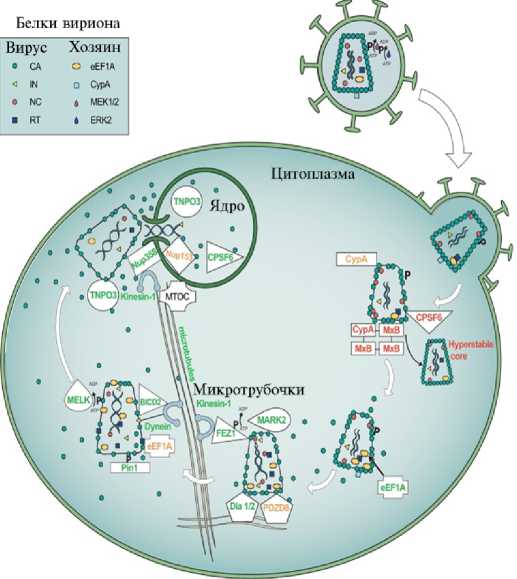
Рис. 6. Факторы клетки-хозяина, участвующие в удалении белковой оболочки HIV-1 (35). CA — капсид; CPSF6 — специфический фактор 6 разрезания и полиаденилирования; CypA — циклофилин A; BICD2 — бикаудальная D2; Dia1/2 — формин 1 и формин 2, связанные с диафаном; eEF1A — эукариотический фактор 1А элонгации трансляции; ERK2 — киназа 2 (регулируемая внеклеточными сигналами); FEZ1 — фасцилизирующий и элон-гирующий фактор зета 1; IN — интеграза; KIF5B — кинезин 1 (тяжелая цепь); NC — нуклеокапсид; NPC — ядерный поровый комплекс; Nup — нуклеопорин; MARK2 — киназа 2, регулирующая аффинность микротрубочек; MEK1/2 — ми-тоген-активируемые белок 1 и белок 2; MELK — материнская эмбриональная лей-цин-связывающая киназа; MTOC — центры организации микротрубочек; MxB — белок В резистентности к миксовирусу; PDZD8 — PDZ домен-содержащий белок 8, участвующий во взаимодействии между эндоплазматическим ретикулюмом и митохондриями; PIC — комплекс преинтеграции; RT — обратная транскриптаза; RTC — комплекс обратной транскрипции; TNPO3 — транспортин 3; Hyрerstable core — гиперстабильное ядро.
Факторы клетки-хозяина регулируют инфекционную активность ВИЧ-1. Вирион ВИЧ-1 содержит белки хозяина CypA, ERK2, eEF1A, регулирующие слияние с мембраной клетки-хозяина и выход вириона в ее цитоплазму. PDZD8 и CypA связывают CA, чтобы стабилизировать вирион, что необходимо для развития инфекции, однако инфекционный процесс блокируется, если CypA связывается с MxB, образуя комплекс, в котором олигомеры MxB вызывают гиперстабилизацию вириона. Клеточная eEF1A взаимодействует с вирусной RT и активирует ее. Dia1 и Dia2 связывают комплексы CA—NC, что облегчает их удаление (вероятно, благодаря локальной стабилизации микротрубочек). Деинин взаимодействует с вирионом через адаптерный белок BICD2 или при прямом взаимодействии с IN, кинезин 1 взаимодействует с вирионом через адаптер FEZ1 (фосфорилированный МАРК2). Это важно для перехода комплексов репликации через цитоплазму к MTOC на периферии ядра. Pin1 связывает CA. Фосфорилированный MEK1/2, который активируется ERK2 при созревании вириона, облегчает его раздевание. MELK также фосфорилирует CA, что ускоряет этот процесс. Вирусная RT связывает eEF1A для стабилизации RTC. Белки ядерных пор Nup358 и Nup153 способствуют импорту PIC, Nup358 перемещается в цитоплазму с помощью KIF5B, а Nup153 продлевает ассоциацию вириона с PIC в ядре. TNPO3 удерживает CPSF6 в ядре, чтобы предотвратить CPSF6-зависимую гиперстабилизацию вириона, TNPO3 также облегчает отделение CA от репликационных комплексов в ядре. Белки, отмеченные зеленым цветом, обеспечивают оптимальную кинетику раздевания вириона, оранжевым — задерживают раздевание, красным — вызывают гиперстабилизацию вириона, что подавляет инфекцию. На рисунке показаны только вирусные белки и белки хозяина, существенные для раздевания и транспорта вириона (35).
Следующий критический этап инфекционного процесса связан со взаимодействием преинтеграционного комплекса с хроматином. В случае ретротранспозона вируса мышиного лейкоза (murine leukemia virus, MLV) оно опосредовано продуктом разрезания белка Gag белком p12 (36). Предполагается, что определенный вклад в интеграцию провирусной ДНК в геном хозяина вносят взаимодействие интегразы вируса с клеточной серин-треониновой фосфатазой 2А (PP2A) (37).
Провирусная ДНК BLV встраивается предпочтительно в районы генома хозяина, богатые CpG, что типично для промоторных участков и кодирующих белок генов, близко к генам тРНК и псевдогенам тРНК. Гены тРНК (в отличие от генов, кодирующих белки и транскрибируемых РНК полимеразой II с образованием мРНК) конститутивно транскрибируются РНК-полимеразой III (Pol III). Псевдогены тРНК утрачивают способность производить функциональную тРНК, но их считывание все еще ассоциировано с активностью Pol III. Не обнаружено преимущественной интеграции провирусной ДНК BLV в участки с диспергированными повторами LINE BovB, SINE BOV-A2, SINE ART2A и LTR ERV (13). Отмечается предпочтительная локализация сайтов интеграции ретровирусов в геном клетки-хозяина в участках с повышенной частотой формирования палин-дромных структур (38, 39), в сайтах инициации транскрипции (41) или в областях, обладающих некоторыми другими структурно-функциональными особенностями, в частности предрасположенностью к взаимодействию с вирусной интегразой (42-44). На основании сопоставления сайтов интеграции ретровирусов BLV и HTLV-1 утверждается их сходство по ряду параметров, например оба провируса локализуются в активно транскрибируемых районах близко к генам тРНК и псевдогенам тРНК (13). В другой работе на основании анализа 264 сайтов интеграции BLV в геномы коров сделан вывод о том, что чаще всего такие сайты обогащены AT-нуклеотидами и длинными диспергированными ядерными элементами (LINE) (45). Ранее наши собственные исследования показали, что у крупного рогатого скота, который инфицирован BLV, в последовательностях, фланкированных инвертированным повтором микросателлита AGC, а также в идентификационной последовательности ДНК транспозона Helitron повышена плотность мобильных генетических элементов и продуктов их рекомбинации (46, 47).
Накопленные нами экспериментальные данные позволяют предполагать, что один из факторов предрасположенности к интеграции прови-русной ДНК в ядерный геном — общее снижение активности защитных механизмов, препятствующих транспозициям мобильных генетических элементов. Следует отметить, что предпочтительная локализация провирусной ДНК BLV в районах генов и псевдогенов тРНК свидетельствует в пользу нашего предположения, поскольку копирование и распространение псевдогенов осуществляется посредством транспозиций мобильных генетических элементов, а сами псевдогены тРНК — это предшественники большой группы неавтономных мобильных генетических элементов SINE (Short Interspersed Nuclear Element). Интересно, что выявленные нами фрагменты геномной ДНК, фланкированные инвертированными повторами микроса-телита AGC, а также идентификационная последовательность Helitron по длине варьируют от 300 до 1500 п.н. и за счет комплементарности флангов предрасположены к формированию коротких петель.
Транскрипция провирусной ДНК. В транскрипции прови- русной ДНК участвуют многие факторы клеточного происхождения, контролируемые генами, которые локализуются вблизи области встраивания провирусной ДНК, взаимодействующей при интеграции с хроматином клетки-хозяина, а также регуляторные факторы, кодируемыми геномом ретровируса. Tax — ключевой из этих факторов (48). Область U3 в 5´-LTR (см. рис. 3) содержит канонический промотор CAT-бокс (CCAACT в координатах от -97 до -92) и TATA-боксы (GATAAAT между позициями -44 и -38). TxRE — якорные последовательности, содержащие элементы, функции которых регулирует циклическая AMP (cyclic-AMP responsive element, CRE). Последовательность длиной 21 нуклеотид также служит мишенью связывания с белком Tax — ключевым активатором транскрипции прови-русной ДНК, усиливающим ассоциацию CREB с ДНК. Фактически внутренние CRE-подобные последовательности (GACGTCA, TGACG, TGAC, TCA) близки к консенсусу TGACGTCA. Мотив E-бокса (5´-CACGTG-3´), локализованный перед сайтом инициации транскрипции, присоединяет базовые факторы регуляции транскрипции USF1 и USF2. Многие гены таких факторов локализованы в последовательности R. В U5 находятся участки связывания с интерферон-регулирующими факторами IRF-1 и IRF-2, которые стимулируют базовую экспрессию в отсутствие Tax.
На посттранскрипционном уровне экспрессию у BLV регулирует вирусный белок Rex, который взаимодействует с последовательностью РНК в 3´-LTR, расположенной между AATAAA сигналом и сайтом полиаденилирования. Этот участок с повышенной частотой формирования стабильной шпильки связывается с двумя сигналами терминации транскрипции. Для экспорта вирусных транскриптов из ядра в цитоплазму необходимо присоединение Rex.
Как уже отмечалось, в опухолевых клетках отсутствует транскрипция провирусной ДНК, контролируемая Pol II, но транскрибируется участок геномной ДНК, в который встроены ДНК пяти микроРНК BLV, считываемых с участием Pol III. Показано, что микроРНК вовлечены в регуляцию многих ключевых процессов в клетках как в норме, так и при различных заболеваниях, в том числе онкологических (49). Транскрипция микроРНК в опухолевых клетках, инфицированных BLV, приводит к изменениям экспрессии набора генов, связанных с сигнальными функциями, иммунной системой, онкогенезом (16, 17, 50). Оказалось также, что в инфицированных В-лимфоцитах и опухолевых клетках активно транскрибируется и вторая цепь провирусной ДНК BLV, причем микроРНК участвует в разрушении антисмыслового транскрипта (51). Предполагается, что у BLV и HTLV-1 баланс между транскрипцией плюс- и минус-цепей ДНК провируса определяет его латентную или реактивированную форму (52).
Итак, имеющиеся данные свидетельствуют о многообразии взаимоотношений между геномом ретровируса BLV и клетками хозяина. Ключевые события при этом происходят на этапах проникновения вириона в клетку, когда осуществляется взаимодействие с транспортными системами хозяина, обеспечивающими обмены между плазматической мембраной клетки и внутриклеточными органеллами, с последующей обратной транскрипцией вирусной РНК, транспортом кДНК в ядро, множественной интеграцией провирусной кДНК в геном хозяина (инфекционный цикл), ее внутриклеточной транскрипцией и репродукцией вируса и преимущественным размножением некоторых инфицированных клеточных клонов. При таком многообразии инфекционный процесс может быть остановлен на любом из перечисленных этапов вследствие полиморфизма генов (либо патогена, либо хозяина), продукты которых вовлечены в каскад этих со-1102
бытий. Само инфицирование приводит к повышению частоты мутагенных событий (как при подготовке к обратной транскрипции двух цепочек геномной РНК вируса, так и на этапе интеграции провирусной ДНК в геном). В итоге примерно 1 % инфицированных клеток-мишеней дает начало активно пролиферирующим клонам. Поскольку детекция антител, индуцируемых покровными белками вируса, не позволяет достаточно надежно выявлять инфицированных животных и не служит основой для высокоэффективной вакцинации, для инфекционного цикла, по-видимому, принципиально важны события, связанные с интеграцией провирусной ДНК в геном хозяина. Накапливаются экспериментальные данные, которые позволяют предположить, что на этом этапе ключевым фактором служит снижение активности внутриклеточных систем контроля транспозиций мобильных генетических элементов хозяина, по происхождению тесно связанных с ретровирусными инфекциями. В пользу такого предположения свидетельствуют данные о предпочтительной интеграции провирусной ДНК BLV в участки с повышенной плотностью псевдогенов тРНК, LINE, а также о большей представленности мобильных генетических элементов в участках генома, фланкированных инвертированными повторами некоторых микросателлитов и идентификационной последовательностью Helitron, у коров, инфицированных BLV, чем у животных, свободных от инфекции. В следующем сообщении будут рассматриваться особенности взаимоотношений клеток, инфицированных вирусом BLV, и клеточными сетями иммунной системы хозяина, которые тоже могут оказывать определяющее влияние на развитие инфекционного процесса, индуцируемого ретровирусами.
Список литературы Клеточные и надклеточные уровни взаимодействия ретровирусов с хозяином на примере вируса бычьего лейкоза. Сообщение I. Проникновение в клетку и интеграция в геном хозяина
- Nishiike M., Haoka M., T., Kohda T., Mukamoto M. Development of a preliminary diagnostic measure for bovine leukosis in dairy cows using peripheral white blood cell and lymphocyte counts. J. Vet. Med. Sci., 2016, 78(7): 1145-1151 ( ) DOI: 10.1292/jvms.16-0022
- Kosovskii G.Yu., Glazko V.I., Koval’chuk S.N., Arkhipova A.L., Glazko T.T. Expression of NK-lysin, blvr, ifn-a and blood cell populations in cows infected by bovine leukemia virus. Sel’skokhozyaistvennaya Biologiya , 2017, 52(4): 785-794 ( ) DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2017.4.785eng
- Sagata N., Yasunaga T., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Ohishi K., Ogawa Y., Ikawa Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of bovine leukemia virus: its evolutionary relationship to other retroviruses. PNAS USA, 1985, 82: 677-681
- Mirsky M.L., Olmstead C.A., Da Y., Lewin H.A. The prevalence of proviral bovine leukemia virus in peripheral blood mononuclear cells at two subclinical stages of infection. J. Virol., 1996, 70: 2178-2183.
- Schwartz I., Bensaid A., Polack B., Perrin B., Berthelemy M., Levy D. In vivo leukocyte tropism of bovine leukemia virus in sheep and cattle. J. Virol., 1994, 68: 4589-4596.
- Gillet N., Florins A., Boxus M., Burteau C., Nigro A., Vandermeers F., Balon H., Bouzar A.B., Defoiche J. Mechanisms of leukemogenesis induced by bovine leukemia virus: prospects for novel anti-retroviral therapies in human. Retrovirology, 2007, 4: 18 ( )
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-4-18
- Gutiérrez G., Rodríguez S.M., de Brogniez A., Gillet N., Golime R., Burny A., Jaworski J.P., Alvarez I., Vagnoni L., Trono K., Willems L. Vaccination against d-retroViruses: the bovine leukemia virus paradigm. Viruses, 2014, 6(6): 2416-2427 ( )
- DOI: 10.3390/v6062416
- Forti K., Rizzo G., Cagiola M., Ferrante G., Marini C., Feliziani F., Pezzotti G., De Giuseppe A. Identification of a novel overlapping sequential E epitope (E') on the bovine leukaemia virus SU glycoprotein and analysis of immunological data. Vet. Microbiol., 2014, 172(1-2): 157-167 ( )
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.05.016
- Murakami H., Uchiyama J., Suzuki C., Nikaido S., Shibuya K., Sato R., Maeda Y., Tomioka M., Takeshima S.N., Kato H., Sakaguchi M., Sentsui H., Aida Y., Tsukamoto K. Variations in the viral genome and biological properties of bovine leukemia virus wild-type strains. Virus Res., 2018, 253: 103-111 ( )
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2018.06.005
- Melamed A., Yaguchi H., Miura M., Witkover A., Fitzgerald T.W., Birney E. Bangham C.R. The human leukemia virus HTLV-1 alters the structure and transcription of host chromatin in cis. eLife, 2018, 7: e36245 ( )
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.36245
- Satou Y., Miyazato P., Ishihara K., Yaguchi H., Melamed A., Miura M., Fukuda A., Nosaka K., Watanabe T., Rowan A.G., Nakao M., Bangham C.R. The retrovirus HTLV-1 inserts an ectopic CTCF-binding site into the human genome. PNAS USA, 2016, 113(11): 3054-3059 ( )
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1423199113
- Artesi M., Marçais A., Durkin K., Rosewick N., Hahaut V., Suarez F., Trinquand A., Lhermitte L., Asnafi V., Avettand-Fenoel V., Burny A., Georges M., Hermine O., Van den Broeke A. Monitoring molecular response in adult T-cell Leukemia by high-throughput sequencing analysis of HTLV-1 clonality. Leukemia, 2017, 31(11): 2532-2535 ( )
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2017.260
- Gillet N.A., Gutiérrez G., Rodriguez S.M., de Brogniez A., Renotte N., Alvarez I., Trono K., Willems L. Massive depletion of bovine leukemia virus proviral clones located in genomic transcriptionally active sites during primary infection. PLoS Pathog., 2013, 9(10): e1003687 ( )
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003687
- Barez P.Y., de Brogniez A., Carpentier A., Gazon H., Gillet N., Gutiérrez G., Hamaidia M., Jacques J.R., Perike S., Neelature Sriramareddy S., Renotte N., Staumont B., Reichert M., Trono K., Willems L. Recent advances in BLV research. Viruses, 2015, 7(11): 6080-6088 ( )
- DOI: 10.3390/v7112929
- Ikebuchi R., Konnai S., Okagawa T., Nishimori A., Nakahara A., Murata S., Ohashi K. Differences in cellular function and viral protein expression between IgMhigh and IgMlow B-cells in bovine leukemia virus-infected cattle. J. Gen. Virol., 2014, 95: 1832-1842 (doi 10.1099/vir.0.065011-0)
- DOI: :10.1099/vir.0.065011-0
- Gillet N.A., Hamaidia M., de Brogniez A., Gutiérrez G., Renotte N., Reichert M., Trono K., Willems L. The bovine leukemia virus microRNAs permit escape from innate immune response and contribute to viral replication in the natural host. Retrovirology, 2015, 12(Suppl. 1): O9 ( )
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-12-S1-O9
- Gillet N.A., Hamaidia M., de Brogniez A., Gutiérrez G., Renotte N., Reichert M., Trono K., Willems L. Bovine leukemia virus small noncoding RNAs are functional elements that regulate replication and contribute to oncogenesis in vivo. PLoS Pathog., 2016, 12(4): e1005588 ( )
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005588
- Rosewick N., Momont M., Durkin K., Takeda H., Caiment F., Cleuter Y., Vernin C., Mortreux F., Wattel E., Burny A., Georges M., Van den Broeke A. Deep sequencing reveals abundant noncanonical retroviral microRNAs in B-cell leukemia/lymphoma. PNAS USA, 2013, 110(6): 2306-2311 ( )
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1213842110
- Panei C.J., Takeshima S., Omori T., Nunoya T., Davis W.C., Ishizaki H., Matoba K., Aida Y. Estimation of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) proviral load harbored by lymphocyte subpopulations in BLV-infected cattle at the subclinical stage of enzootic bovine leucosis using BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR. BMC Vet. Res., 2013, 9: 95 ( )
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-6148-9-95
- Aida Y., Murakami H., Takahashi M., Takeshima S. Mechanisms of pathogenesis induced by bovine leukemia virus as a model for human T-cell leukemia virus. Front. Microbiol., 2013, 4: 328 ( )
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00328
- Wallin M., Ekström M., Garoff H. Receptor-triggered but alkylation-arrested env of murine leukemia virus reveals the transmembrane subunit in a prehairpin conformation. J. Virol., 2006, 80(19): 9921-9925 ( )
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00380-06
- de Brogniez A., Mast J., Willems L. Determinants of the bovine leukemia virus envelope glycoproteins involved in infectivity, replication and pathogenesis. Viruses, 2016, 8(4): 88 ( )
- DOI: 10.3390/v8040088
- Suzuki T., Matsubara Y., Kitani H., Ikeda H. Evaluation of the d subunit of bovine adaptor protein complex 3 as a receptor for bovine leukaemia virus. J. Gen. Virol., 2003, 84: 1309-1316 ( )
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.18763-0
- Lavanya M., Kinet S., Montel-Hagen A., Mongellaz C., Battini J.L., Sitbon M., Taylor N. Cell surface expression of the bovine leukemia virus-binding receptor on B and T lymphocytes is induced by receptor engagement. J. Immunol., 2008, 181(2): 891-898 ( )
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.2.891
- Corredor A.P., Conzalez J., Baquero L.A., Curtidor H., Olaya-Galan N.N., Patarroyo M.A., Gutierrez M.F. In silico and in vitro analysis of boAP3d1 protein interaction with bovine leukaemia virus gp51. PLoS ONE, 2018, 13(6): e0199397 ( )
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199397
- Ammann S., Schulz A., Krägeloh-Mann I., Dieckmann N.M., Niethammer K., Fuchs S., Eckl K.M., Plank R., Werner R., Altmüller J., Thiele H., Nürnberg P., Bank J., Strauss A., von Bernuth H., Zur Stadt U., Grieve S., Griffiths G.M., Lehmberg K., Hennies H.C., Ehl S. Mutations in AP3D1 associated with immunodeficiency and seizures define a new type of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Blood, 2016, 127(8): 997-1006 ( )
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-09-671636
- Suzuki T., Ikeda H., Masse M. Restricted viral cDNA synthesis in cell lines that fail to support productive infection by bovine leukemia virus. Arch. Virol., 2018, 163(9): 2415-2422 ( )
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-018-3887-6
- Dubois N., Marquet R., Paillart J.-C., Bernacchi S. Retroviral RNA dimerization: from structure to functions. Front. Microbiol., 2018, 9: 527 ( )
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00527
- Pierard V., Guiguen A., Colin L. et. al. DNA cytosine methylation in the bovine leukemia virus promoter is associated with latency in a lymphoma-derived B-cell line: potential involvement of direct inhibition of cAMP-responsive element (CRE)-binding protein/CRE modulator/activation transcription factor binding. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010, 285(25): 19434-19449 ( )
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.107607
- Arriagada G. Retroviruses and microtubule-associated motor proteins. Cellular Microbiology, 2017, 19(9): e12759 ( )
- DOI: 10.1111/cmi.12759
- Polat M., Takeshima S.N., Aida Y. Epidemiology and genetic diversity of bovine leukemia virus. Virol. J., 2017, 14(1): 209 ( )
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-017-0876-4
- Murakami H., Asano S., Uchiyama J., Sato R., Sakaguchi M., Tsukamoto K. Bovine leukemia virus G4 enhances virus production. Virus Res., 2017, 238: 213-217 ( )
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2017.07.005
- Choi E.-A., Hope T.J. Mutational analysis of bovine leukemia virus rex: identification of a dominant-negative inhibitor. J. Virol., 2005, 79(11): 7172-7181 ( )
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.11.7172-7181.2005
- Stake M.S., Bann D.V., Kaddis R.J., Parent L.J. Nuclear trafficking of retroviral RNAs and Gag proteins during late steps of replication. Viruses, 2013, 5(11): 2767-2795 ( )
- DOI: 10.3390/v5112767
- Rawle D.J., Harrich D. Toward the "unravelling" of HIV: host cell factors involved in HIV-1 core uncoating. PLoS Pathog., 2018, 14(10): e1007270 ( )
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007270
- Wanaguru M., Barry D.J., Benton D.J., O’Reilly N.J., Bishop K.N. Murine leukemia virus p12 tethers the capsid-containing pre-integration complex to chromatin by binding directly to host nucleosomes in mitosis. PLoS Pathog., 2018, 14(6): e1007117 ( )
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007117
- Maertens G.N. B´-protein phosphatase 2A is a functional binding partner of delta-retroviral integrase. Nucleic Acids Res., 2016, 44(1): 364-376 ( )
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1347
- Wu X., Li Y., Crise B., Burgess S.M., Munroe D.J. Weak palindromic consensus sequences are a common feature found at the integration target sites of many retroviruses. J. Virol., 2005, 79(8): 5211-5214 ( )
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.8.5211-5214.2005
- Holman A.G., Coffin J.M. Symmetrical base preferences surrounding HIV-1, avian sarcoma/leukosis virus, and murine leukemia virus integration sites. PNAS USA, 2005, 102(17): 6103-6107 ( )
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0501646102
- Wu X., Li Y., Crise B., Burgess S.M. Transcription start regions in the human genome are favored targets for MLV integration. Science, 2003, 300(5626): 1749-1751 ( )
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1083413
- Mitchell R.S., Beitzel B.F., Schroder A.R., Shinn P., Chinn H., Chen H., Berry C.C., Ecker J.R., Bushman F.D. Retroviral DNA integration: ASLV, HIV, and MLV show distinct target site preferences. PLoS Biol., 2004, 2(8): e234 ( )
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020234
- Wang G.P., Ciuffi A., Leipzig J., Berry C.C., Bushman F.D. HIV integration site selection: analysis by massively parallel pyrosequencing reveals association with epigenetic modifications. Genome Res., 2007, 17(8): 1186-1194 ( )
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.6286907
- Lewinski M.K., Yamashita M., Emerman M., Ciuffi A., Marshall H., Crawford G., Collins F., Shinn P., Leipzig J., Hannenhalli S., Berry C.C., Ecker J.R., Bushman F.D. Retroviral DNA integration: viral and cellular determinants of target-site selection. PLoS Pathog., 2006, 2(6): e60 ( )
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020060
- Derse D., Crise B., Li Y., Princler G., Lum N., Stewart C., McGrath C.F., Hughes S.H., Munroe D.J., Wu X. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 integration target sites in the human genome: comparison with those of other retroviruses. J. Virol., 2007, 81(12): 6731-6741 ( )
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02752-06
- Miyasaka T., Oguma K., Sentsui H. Distribution and characteristics of bovine leukemia virus integration sites in the host genome at three different clinical stages of infection. Arch. Virol., 2015, 160(1): 39-46 ( )
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-014-2224-y
- Babii A., Kovalchuk S., Glazko T., Kosovsky G., Glazko V. Helitrons and retrotransposons are co-localized in Bos taurus genomes. Current Genomics, 2017, 18(3): 278-286 ( )
- DOI: 10.2174/1389202918666161108143909
- Glazko V.I., Kosovsky G.Yu., Glazko T.T. High density of transposable elements in sequenced sequences in cattle genomes, associated with AGC microsatellites. Global Advanced Research Journal of Agricultural Science, 2018, 7(2): 034-045.
- Perès E., Blin J., Ricci E.P., Artesi M., Hahaut V., Van den Broeke A., Corbin A., Gazzolo L., Ratner L., Jalinot P., Dodon M.D. PDZ domain-binding motif of Tax sustains T-cell proliferation in HTLV-1-infected humanized mice. PLoS Pathog., 2018, 14(3): e1006933 ( )
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006933
- Jiang Q., Wang Y., Hao Y., Juan L., Teng M., Zhang X., Li M., Wang G., Liu Y. miR2 disease: a manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res., 2009, 37(Database issue): D98-104 ( )
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn714
- Frie M.C., Droscha C.J., Greenlick A.E., Coussens P.M. MicroRNAs encoded by bovine leukemia virus (BLV) are associated with reduced expression of B cell transcriptional regulators in dairy cattle naturally infected with BLV. Front. Vet. Sci., 2018, 4: 245 ( )
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2017.00245
- Durkin K., Rosewick N., Artesi M., Hahaut V., Griebel P., Arsic N., Burny A., Georges M., Van den Broeke A. Characterization of novel Bovine Leukemia Virus (BLV) antisense transcripts by deep sequencing reveals constitutive expression in tumors and transcriptional interaction with viral microRNAs. Retrovirology, 2016, 13(1): 33 ( )
- DOI: 10.1186/s12977-016-0267-8
- Kulkarni A., Bangham C.R.M. HTLV-1: regulating the balance between proviral latency and reactivation. Front. Microbiol., 2018, 9: 449 ( )
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00449


