Komi Republic's agro-industrial potential
Автор: Ivanov Valentin Aleksandrovich, Terentyev Vitaly Vasilevich, Maltseva Irina Stanislavovna
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Continuing the previous issue theme
Статья в выпуске: 1 (9) т.3, 2010 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In this article the condition of the land and the agro-climatic resources, the agricultural sector, the zones of agricultural production’s specialization and accommodation are considered; the conceptual directions of the regional agricultural development are offered.
Land resources, agricultural sector, agricultural development
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223167
IDR: 147223167 | УДК: 338.436.33(470.13),
Текст научной статьи Komi Republic's agro-industrial potential
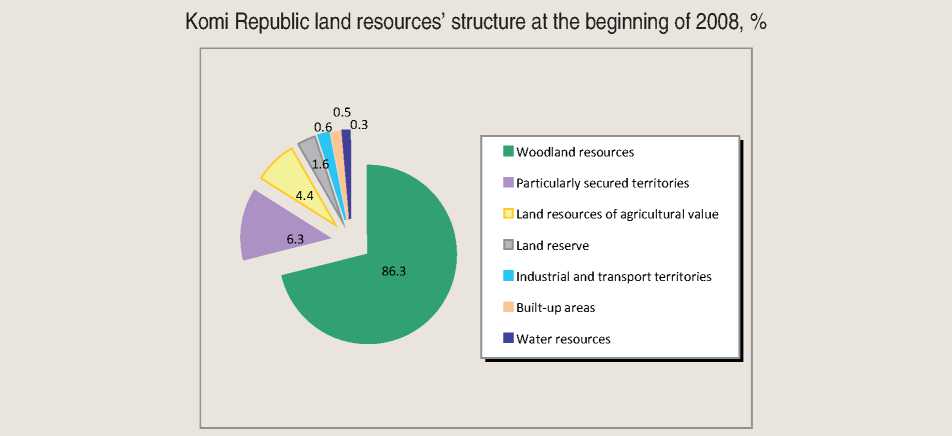
Land resources. At the beginning of the year 2008 the available land of Komi Republic made 41 677.4 thousand hectares. Among all the land categories woods prevail (they make 35 950.7 thousand hectares, or 86.3%), and the significant territory is occupied by the particularly secured territories (they make 2 613.1 thousand hectares, or 6.3%); the agricultural lands make 1 856.0
thousand hectares (4.4%; figure ). Reindeer pastures are located on the agricultural lands (1 110.9 thousand hectares), on the particularly secured territories (413.8 thousand hectares) and on the woodlands (7 972.3 thousand hectares). The land reallocation fund, making 206.5 thousand hectares, annually increases, as private owners, farmers and farming enterprises refuse the lands.
Komi Republic occupies 2.4% of Russia’s territory. The share of the most productive holdings (plough-lands) only makes 0.3% of the area while in the country in general this parameter is 7.9%. The share of the tilled lands reaches 25% to the average 60% in Russia in general. The low rate of the Republic lands’ development is caused by the unfavorable environment for agriculture, by huge areas of wood, and by its low population density.
Not only the low agricultural land development, but also the irregularity of accommodation on zones and administrative areas are characteristic for the republic. The basic areas of agricultural lands are concentrated in the southern and the central parts, and also in Udorskoye, Izhemskoye and Ust-Tsilemskoye municipal formations. In the structure of agricultural holdings natural hay-makings and pastures prevail (3 hectares of meadows to 1 hectare of arable lands). The share of the tilled lands decreases from 42% in MF (municipal formation – here and further ) “Priluzsky region” to 3% in MF “Ust-Tsilemsky region”.
As a whole in Komi Republic a bit more than half of farmlands (51.5%) are used by agricultural organizations, and 59.1% of holdings are used by farmers and individual businessmen. Most of all the holdings are deserted in the northern areas (Vorkuta, Izhemsky region, Ust-Tsilemsky region), and also in Sysolsky and
Troitsko-Pechorsky regions that is connected with hard financial situation, bankruptcy and agricultural productions’ liquidation in these areas.
The situation of the usage of the lands by farming enterprises is similar. Most of all agricultural holdings are deserted in Usinsky, Izhemsky, Ust-Kulomsky and Syktyvdinsky regions. The owners of personal subsidiary farms use agricultural holdings practically completely. The main part of Komi Republic is located in the taiga-wood zone where the dominance of the podsolic soils is typical (22% of the territory). Low natural fertility and heat deficiency (in connection with long seasonal frost penetration) determine low productivity of these soils. However by virtue of the normal water mode they can be used as arable lands rather actively.
Evaluation of the modern condition of the agricultural sector. The share of agriculture is about 2.5% of the gross regional output, approximately 0.6% of investments into the fixed capital, 3.9% of the mid-annual number of employed people. In view of subventions the branch has been profitable since 2005. The branch structure is mainly focused on dairy and meat cattle-breeding, poultry-breeding, pigbreeding and reindeer-breeding. Crop production is specialized on potatoes and vegetables raising, and also provides cattle-breeding with succulent and rough forages.
For January, 1, 2008 133 agricultural organizations, including 73 large-scale and middlescale ones, 92.4 thousand personal subsidiary farms, 274 country farming facilities, 75.6 thousand families of gardeners and 30.3 thousand families of truck farmers were engaged in agricultural production. In 2007 the share of agricultural organizations made 50.1%, the share of the population’s facilities made 46.9%, and the share of the country farming facilities made 3% in the total amount of agricultural products (table) .
In 2007 the agricultural enterprises of the republic made 49% of the whole volume of milk, 73.6% of the whole volume of meat, 99.2% of the whole volume of eggs, 13.4% of the whole volume of vegetables and 3% of the whole volume of potatoes). The population’s facilities produced 96.1% of the whole volume of potatoes, 85.3% of the whole volume of vegetables, 45.7% of the whole volume of milk and 23.1% of the whole volume of meat. In 2007 the share of the country farming facilities in the total production amount of potatoes made 0.9%, of vegetables – 1.1%, of milk – 5.3%, and of meat – 3.3%).
The transition to the market with the use of the monetarism’s approaches extremely negatively affected the agrarian sector of Komi Republic. The mid-annual rates of the production decrease of agriculture made 5.7% at the period of 1991 – 1995, 0.6% in 1996 – 2006, 1.8% in 2001 – 2005, and 7.7% in 2006 – 2007. At the period of 1990 – 2007 along with the significant population’s reduction in the republic (from 1,245 to 968 thousand people) meat production decreased with 31 up to 15.7 kg per head, milk production was reduced from 166 to 69 kg
Dynamics of share ratio of various social facilities’ types in Komi Republic agricultural production, %
|
Types of products and facilities’ categories |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
|
Potatoes, total |
100 . 0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
Agricultural collective enterprises |
42.1 |
14.4 |
9.8 |
5.9 |
5.6 |
3.0 |
|
Population’s facilities |
57.9 |
84.7 |
89.6 |
93.5 |
93.6 |
96.1 |
|
Farms |
- |
0.9 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
0.8 |
0.9 |
|
Vegetables, total |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
Agricultural collective enterprises |
89.6 |
50.7 |
31.3 |
14.3 |
14.3 |
13.4 |
|
Population’s facilities |
10.4 |
49.2 |
67.9 |
84.4 |
84.9 |
85.3 |
|
Farms |
- |
0.1 |
0.8 |
1.3 |
0.8 |
1.3 |
|
Meat, total |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
Agricultural collective enterprises |
80.1 |
58.2 |
53.4 |
64.0 |
70.3 |
73.6 |
|
Population’s facilities |
19.9 |
40.6 |
45.6 |
33.3 |
26.8 |
23.1 |
|
Farms |
- |
1.2 |
1.0 |
2.7 |
2.9 |
3.3 |
|
Dairy, total |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
Agricultural collective enterprises |
84.6 |
63.6 |
50.0 |
45.6 |
48.8 |
49.0 |
|
Population’s facilities |
15.4 |
35.3 |
48.8 |
52.0 |
48.1 |
45.7 |
|
Farms |
- |
1.1 |
1.2 |
2.4 |
3.1 |
5.3 |
|
Eggs, total |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
Agricultural collective enterprises |
97.7 |
95.4 |
98.7 |
99.2 |
98.9 |
99.2 |
|
Population’s facilities |
2.3 |
4.5 |
1.3 |
0.8 |
1.1 |
0.7 |
|
Farms |
- |
0.1 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.1 |
|
Gross output, total |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
Agricultural collective enterprises |
80.1 |
53.0 |
47.8 |
45.6 |
48.4 |
50.1 |
|
Population’s facilities |
19.9 |
46.1 |
51.4 |
52.7 |
49.6 |
46.9 |
|
Farms |
- |
0.9 |
0.8 |
1.7 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
|
The source: Agriculture in Komi Republic: Statistical collection. – Syktyvkar, 2007; Agriculture in Komi Republic: Statistical collection. – Syktyvkar, 2008. |
||||||
per head, egg production decreased from 294 to 175 eggs. The inhabitants’ consumption of the basic food stuffs makes now 230 kg, 65 kg and 261 pieces accordingly.
The consumer market of the republic is substantially formed due to foodstuffs’ import from other regions of the country and from abroad. In 2006 the share of the republic’s production made: meat and meat foods – 25.9%, milk and dairy produce – 31.3%, eggs – 68.4%, potatoes – 97.6%, vegetables – 42.4%. In 1990 these parameters made 38.6, 39.7, 94.4, 68.0, and 15.7% accordingly.
The republic provides itself with 98% of potatoes, and with 42% of vegetables. The insufficient provision with native products indicates the crisis condition of agriculture, and also the low competitiveness of the local manufacturers’ products.
During the years of the agrarian reforms the degradation of the branch industrial potential occurred. The number of workers at the agricultural organizations reduced in 3 times. At the period of 1990 – 2007 the farmland reduced from 353 to 211 thousand hectares, arable lands reduced from 100.5 to 52.8 thousand hectares, cattle stock decreased from 173.5 to 43.7 thousand heads, including cows – from 71 to 21 thousand heads, pigs – from 136.3 to 27.1 thousand heads, deer – from 123.6 to 83.5 thousand heads.
Cattle stock’s, arable lands’, and the workers number’s reduction took place in all areas, but it is especially appreciable in the agricultural zone of the Far North and in the northern territories. For example, at the period of 1990 – 2006 in MF “Vorkuta” cattle stock reduced from 9,590 to 171 heads, in MF “Inta” – from 5,445 to 1,165 heads, in MF “Pechora” – from 7,521 to 1,160 heads, in MF “Ust-Tsilemsky region” – from 16,114 to 4,141 heads, in MF “Izhemsky region” – from 13,634 to 3,640 heads.
Also agro-chemical and water-physical land properties’ deterioration, water-logged and overgrown with shrubs grounds (in connection with the ameliorative grounds’ destruction and the ameliorative works’ reduction) occur. Nutrients’ carrying out from the ground exceeds their carrying in. Nowadays 11 kg of mineral and 3.5 t of organic fertilizers are carried into the fields; that makes accordingly 18 and 17% of the required nutrients for the land fertility’s maintenance.
The main part of agricultural production is made in suburbs (Syktyvdinsky, Kortkerossky regions), in the municipal districts of the cities of Syktyvkar, Ukhta, Inta and in the southern part of the Priluzskaya area.
More than half of the republics’ agricultural organizations are insolvent, the third part is unprofitable. The organizations’ debts to their creditors in the form of activity “Agriculture and granting services in this branch” at the end of 2007 made 464 million rubles, including the failed payments on time (they made 98 million rubles). Also in 2007 the accounts receivable made 238 million rubles, including the failed payments on time (they made 25 million rubles).
The agricultural sector’ processing enterprises, except for the enterprises on processing milk and meat, almost completely work on the imported raw stuff. Through the unsupported condition with agricultural raw material the most part of the processing enterprises works with incomplete capacity.
The zones of specialization and accommodation of farming industry. Under the influence of natural and economic conditions of agricultural production and public needs four agricultural zones in the Far North, and in the northern, central and southern parts were formed in Komi Republic.
In 2007 16.4% of the republic’s population lived in the agricultural zone of the Far North (MF “Vorkuta” and MF “Inta”), the agricultural gross output made 5.7%. The most perspective branch for this zone is the production of milk, eggs, and the development of reindeer-breeding and poultry-breeding.
The northern agricultural zone includes the MFs “Izhemsky region”, “Ust-Tsilemsky region”, “Udorsky region”, “Troitsko-Pechorsky region”, “the town of Vuktyl”, the town of Pechora”, “the town of Sosnogorsk”, “the town of Usinsk” and “the town of Ukhta”. 39.4% of the republic’s population lived here and the agricultural gross output made 23.6%. This zone’s specialization is directed to milk and meat production, and to the development of reindeer-breeding; the additional branches are raising of potatoes and vegetables.
The central agricultural zone includes MFs “Ust-Kulomsky region”, “Ust-Vymsky region”, “Knyazhpogostsky region”, “Ko-rtkerossky region”, “Syktyvdinsky region”, “Sysolsky region” and “the city of Syktyvkar”. 40.9% of the republic’s population live here and the agricultural gross output makes 61.8%, potatoes – 56.3%, vegetables – 65.7, milk – 48.4%, meat – 74.7%, eggs – 75.8%.
The agricultural producers of this zone specialize on producing milk, meat, and eggs; they also produce potatoes and vegetables. The part of these agricultural products is delivered to the north of the republic.
The southern agricultural zone includes MFs “Kojgorodsky region” and “Priluzsky region”. 3.3% of the republic’s population live here. The total agricultural production of this zone makes 8.9%, potatoes – 10.6%, vegetables – 21.5%, milk – 10.4%, meat – 4.4%, eggs – 0.1%, 98.3% – grain.
The prospects of agricultural development. In view of difficult natural and economic conditions for agricultural development the principle of bootstrapping with foodstuffs is unacceptable for the republic; however the production of the basic food stuffs has favorable conditions, and it is the barest necessity. The priority in the development of the southern and the central zones’ specialization should be given to agricultural production integrated with forestry and trades. Here arable lands and natural forage holdings should be used most intensively.
The basic aim of the agricultural sector’s development in Komi Republic is that by 2020 it will have to start producing the minimal set of the basic kinds of the foodstuffs necessary for the population health’s maintenance and for the stable life-support. In the long term the republic has the opportunity to completely provide its population with potatoes and vegetables, to expand vegetables’ raising in greenhouses; to provide the population with milk and dairy produce for 40 – 45%, with meat and meat products for 30 – 35%, with dietary eggs for 70 – 75%; to increase the region’s role in fishery, reindeer-breeding, hunting-trade economy, wood resources (mushrooms and berries).
In the field of specialization and production accommodation in the southern agricultural zone the expansion of milk, meat, potatoes and vegetables production is anticipated. In the central agricultural zone specialization will be directed to producing milk, meat, and eggs; it will also produce potatoes and vegetables. In the northern agricultural zone specialization will be directed to milk and meat production, and to the development of reindeer-breeding; to the raising of potatoes and vegetables. In the zone of the Far North agriculture should provide the population with full cream milk, with dietary egg, and with reindeer-breeding products.
In the suburban agriculture first of all it is necessary to direct the fodder resources to the production of full cream milk and sour-milk production. Here it is economically expedient to build highly-mechanized farms for 400 cows with milk yield of 5 – 6 thousand kg, with the closed cycle of the herd reproduction.
By 2020 it is also expedient to construct in the suburbs and regional centers 17 – 20 dairy complexes for 400 cows with the unleashed keeping and with the automated systems of feeding, watering and dung removal.
In small rural settlements there can be farms for 100 – 200 cows. It is also possible to apply modern highly effective means of mechanization and automation for carrying-out technological processes in them. There it’s possible to process some part of milk to butter and cheese.
In peripheral rural areas (MFs “Izhemsky region”, “Ust-Tsilemsky region”, “Udorsky region”, “Ust-Kulomsky region”) where dairy cattle-breeding will not receive intensive development, for the rational use of the forage holdings, of manpower, and for filling the market with fresh beef it is expedient to be engaged in meat cattle-breeding under the condition of the state support’s strengthening of these branches.
The system of provender milling should be directed to the all-the-year-round full and guaranteed providing of the cattle-breeding branch with the basic kinds of forages of the native production, under the obligatory creation of the insurance fund; and to providing full dietary intake for each kind of cattle at every stage of its keeping. Production of all kinds of forages is planned to be finished up to 200 – 220 thousand tons of forage units by 2020. For this purpose it is required to bring 1,670 – 1,800 thousand tons of organic fertilizers and 14.6 thousand tons of mineral fertilizers, including nitrogen – 3.8 thousand tons, phosphorus – 2.8 thousand tons, potassium – 8 thousand tons annually. Actually in 2006 it was brought 142 thousand tons of organic and 0.58 thousand tons of mineral fertilizers that accordingly makes 9% and 4% from need. Nowadays the natural fertility of soils in the republic is low and still continues to reduce from year to year. 92.2% of the arable soils of the republic are poorly cultivated and have poor stocks of organic substance; they contain about 2.32% of humus on the average. A lot of means of chemicalization are not effective at such low level of organic substance.
The analysis proves economic practicability of poultry farming production in MFs “Syktyvkar”, “Inta” and “Syktyvdinsky region”. The cost price of egg and poultry production at the integrated poultry farms of the republic (despite of the price raising factors) is a little bit higher than the similar parameters at the poultry-farming enterprises of Russia.
Reindeer-breeding prospects are connected with the intensive development of this branch both in tundra (forest-and-tundra), and taiga zones. The development of bogs, which are not practically used nowadays, and of low-productive for forestry boggy woods on the territory of Izhemsky, Ust-Tsilemsky, Uhtinsky, Sosnogorsky, Pechorsky and Udorsky regions is one of the measures directed to the dynamical development’s maintenance of reindeerbreeding.
Deer livestock in agricultural organizations and country farming facilities is planned to keep at the level 62.5 – 63.0 thousand heads by 2012, and to increase up to 72 – 75 thousand heads by 2020. Deep processing of venison with the use of modern high-efficiency equipment will be carried out in MFs “Vorkuta” and “Izhemsky region”.
According to the Federal Law “About agricultural development” and to the Federal Program “The State program of agricultural development and of regulation of the agricultural production’s markets (raw material and foodstuffs) for 2008 – 2012” Komi Republic Government authorizes “Actions on agricultural development and on regulation of agricultural production’s markets of raw material and foodstuffs in Komi Republic for 2008 – 2012”. The main task of actions for the medium-dated term are: the increase of competitiveness of agricultural production made on the territory of Komi Republic; preservation and reproduction of lands and other natural resources used in agricultural production; the increase of the incomes’ level for manufacturers of agricultural production, raw material and foodstuffs.
The steps are taken in five directions:
-
1) creation of general conditions on agricultural functioning;
-
2) priority agricultural sub industries’ development;
-
3) agricultural financial stability’s achievement;
-
4) agricultural production, raw material and foodstuffs market’s development;
-
5) steady development of rural territories.
The development of reindeer-breeding, the traditional branch for the North, will be promoted by realization of the actions directed to reindeer’s livestock stabilization, and also by carrying out planning works and by the complex resource estimation of deer pastures.
The state support is anticipated; it will concern the development of trading stations (intermediate bases) on the nomadic ways of reindeer breeders, and also the departure of reindeer breeders’ children to tundra and back for the period of summer vacations.
Actions on fishery development, directed to the volumes’ increase in manufacturing high-quality fish products, will be realized within the framework of the departmental purposeful program “Development of fishery, and aqua-culture; reproduction of fish resources in Komi Republic (2008 – 2010)”. As a result the volume of the raised fish will increase up to 1200 tons a year (i. e. in 9.5 times to the level of the year of 2007), and the realization of the caught fish will increase almost in 2 times and will make 200 tons.
Among the actions on crop production’s development there are the following ones: support of agricultural producers in purchase of high-quality seed material and stimulation of forage crops’ cultivation; support of elite seed farming and agricultural products’ makers in the Far North regions and in the districts equal to them for the creation of own forage reserve for cattle-breeding and for the crop production’s increase of low-productive arable lands.
The actions on elite seed farming support includes: the state support of elite seeds crops’ purchase; the increase of areas under potatoes’ planting with the use of elite planting material. For the solution of the mentioned problems the realization of the following actions is necessary: the state support on delivery of forage crops’ seeds and the expansion of areas under forage crops’ planting. As a result by 2012 elite seeds’ crop area will make 6.5 thousand hectares, and planting densities of potatoes with elite seeds’ use will grow more than twice in the general planting area (without taking into account personal subsidiary farms).
With a view of agricultural financial stability’s achievement the following actions will be realized:
-
1. Increase of credit resources’ availability for agricultural producers. The state support
will be carried out by means of giving grants to agricultural organizations for compensation of some part of expenses for payment of interests on credits received from the Russian credit organizations, and loans received from agricultural credit consumer cooperative societies. In 2012 the volume of subsidized credit resources will make 814 million rubles, including 447 million rubles of investment. In 2007 the volume of debt credits in agricultural organizations was equal to 57 million rubles.
-
2. Increase of the financial stability of smallscale country forms of managing due to the state support of personal subsidiary farms of citizens; the state support of the country farming facilities; assistance to the development of agricultural and consumer cooperative societies; the increase of credit resources’ availability for the small-scale forms of managing received from the Russian credit organizations. Owing to these actions’ realization it is planned to provide an annual 2 – 3% gain of the production’s realization made by the small-scale forms of managing.
-
3. Modernization of the basic means of agricultural production’s, raw materials’ and foodstuffs’ makers. Modernization will be carried out by realization of the following actions: construction and reconstruction of cattle-breeding premises, industries on cattlebreeding production’s processing; technological and technical renovation of the basic means of agricultural products’, raw materials’ and foodstuffs’ makers; creation of the conditions for highly technological complexes’, machines’ and equipment’s introduction into agricultural production. In 2012 in the comparison with 2007 it is planned to increase tractors’ purchase in 2.5 times. Nowadays the spade-work on innovational projects’ development in the sphere of construction and reconstruction of cattle-breeding premises is carried out. After cattle-breeding premises’ construction and reconstruction it is planned to introduce into practice from 600 to 1,000 cattle-stalls annually.
The following steps will be taken for the development of the agricultural products’, raw materials’ and foodstuffs’ market on the basis of the production competitiveness’ increase: perfection of the mechanism of granting the state support to agricultural products’, raw materials’ and foodstuffs’ manufacturers for indemnification of some part of the expenses connected with producing, processing and realization of agricultural production; purchases of agricultural production from personal subsidiary farms of citizens; certification of agricultural production, raw material and foodstuffs; organizing fairs of agricultural production, raw material and foodstuffs on the territory of Komi Republic; providing participation of agricultural products’, raw materials’ and foodstuffs’ makers of Komi Republic in taking orders for food stuffs’ delivery both for the state and municipal needs.
The actions on rural territories’ steady development will be carried out within the framework of subprogram “Individual housebuilding’s development” and “Assistance in construction and reconstruction of the municipal infrastructure’s objects”, of the purposeful republican program “Habitation” for 2008 – 2012 and of the departmental purposeful program of the Komi Republic’s Department of industry and power engineering “Gasification of Komi Republic’s settlements for 2007 – 2009 (the 1st stage)”. In 2008 – 2012 from Komi Republic’s budget 344.5 million rubles will be spent on financing the actions on the improvement of living conditions of citizens, young families and beginners living in the country.
More than 3.5 billion rubles from Komi Republic’s budget, including 3.2 billion rubles on agricultural production’s support and 345 million rubles on grants for construction and purchase of habitation in the rural areas are required for the planned actions’ realization. For 2008 – 2012 the federal budget’s charges will grow twice.
As a whole the mentioned actions’ realization will allow increasing agricultural production volume for 10% to the level of the year of 2006. The milk sale will increase from 37.5 thousand tons in 2008 to 39.6 thousand tons in 2012; meat sale will grow from 20.7 to 24.5
thousand tons, eggs’ sale will grow from 140 to 148 million pieces accordingly.
For this period the share of production made in Komi Republic in the total amount of food resources will increase from 26.4% to 28.3% (milk and dairy produce), from 26.2% to 27.7% (meat and meat products).
Perspective legal forms of agricultural production’s organization. The multi-mode and multivariant approach of the organizational-legal forms of agricultural production (agricultural production co-operatives, societies with limited liability, joint-stock companies, state unitary enterprises, population’s facilities, farms) generated in the region during the years of reforms will be kept further. Basis of agrarian economy will make large-scale commodity production. Large-scale collective production can be carried out at enterprises with various organizational-legal forms of managing. In addition to the large-scale commodity sector it is necessary to develop small-scale forms such as farms, personal subsidiary farms and citizens’ gardening societies. On the basis of cooperative and integration relations’ development both ways can cooperate, using benefits of production specialization and socialization.
Список литературы Komi Republic's agro-industrial potential
- Rukina, S.N. Municipalities’ budget revenues management in terms of reform /S.N. Rukina//The journal “Finansovye issledovaniya”. -2008. -№ 3. -P. 47.
- Hodzhabiyan, O.M. Financial aspects of the local government reform in Russia /O.M. Hodzhabiyan//Finansovye issledovaniya. -2004. -№ 9. -P. 58.
- Batov, G. Problems of local government organization /G. Batov//Ekonomist. -2008. -№ 3. -P. 81.
- Kiselev, I. The transfer of additional and differentiated tax regulations to municipalities and strengthening their financial independence /I. Kiselev//Federalizm. -2009. -№ 1. -P. 217.
- Likhachev, D.A. Problems of financial support of municipalities in terms of the municipal reform /D.A. Likhachev//Federalizm. -2009. -№ 3. -P. 209.


