Learner's Satisfactions on ICT Innovations: Omani Learners Viewpoints
Автор: B. Sriram
Журнал: International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science (IJMECS) @ijmecs
Статья в выпуске: 6 vol.7, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has significantly improved the educational environment to higher degrees. The teaching and learning methodologies have been changed to greater extends to motivate the instructors and learners. The learner's satisfaction on these ICT innovations depends on their impact in day to day knowledge gaining processes. This paper discusses some major ICT factors that influence the Omani learners and their corresponding satisfaction levels. This research also identified that these technological innovations motivate the learners in self-learning and in future continuing education. The study identified that the overall significant development educational processes and encouragement in the learning processes by information and communication technology innovations have higher impacts on the learners' satisfaction.
ICT Innovations, Learner's Satisfaction, Omani Learners Viewpoints, Factor's Influences, Learning Processes
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15014765
IDR: 15014765
Текст научной статьи Learner's Satisfactions on ICT Innovations: Omani Learners Viewpoints
Published Online June 2015 in MECS
Technology has become an indispensable part of day – to – day life of every individual. The potentials of technological innovations improved the life style to higher degree. These technological innovations have greater impact in educational processes. These innovations integrated technology and education which is the primary requirement of human development. Various studies were conducted with respect to the impacts and requirements of these ICT innovations on educational processes.
The educational processes are highly influenced with the technology tools and gadgets. The fast growing information technology and its allies have become integral part of the educational processes without which the educational activities cannot be fulfilled. The economic considerations, constraints and requirements may vary with respect to the national level strategies and implementation. But, these Information and communication technology and its corresponding tools need to be incorporated in all levels of educational activities.
Basically the educational activities evolve around the learners’ perspectives and acceptance as the learners are the focal point of the educational systems. Various tools are developed to enable the learners to acquire desired knowledge quite comfortably and easily. The current learner's centered approach needs the learners’ involvement and satisfaction at all levels. As Moyle (2010) said, the technologies offer opportunities to educators and learners for creating meaningful learning environment [2].
Various studies were discussed and studied with respect to this issue. Yien et al (2011) studied about the game based learning approaches to improve students' learning achievement in a nutrition course [1]. Moyle (2010) said the educators should not only provide correct answers to the problems but also reward them for their efforts and the ideas. According to Moyle [2], one of the major challenges for educators is to bridge the divide between formal and informal learning. Varis (2009) studied about the impacts and regional developments in higher education due to new technologies and innovations [3].
Though various studies were found, but very little literatures could be found with respect to Middle East countries, in particular, Sultanate of Oman. The higher education providers in Sultanate of Oman have incorporated maximum facilities of ICT and its innovations in the day – to – day educational processes. But, the user’s (learner’s) satisfaction depends on various factors that supports them in their daily learning activities. Hence to identify the major information technology factors that have major impacts on the Omani learners’, this study was conducted. This paper analyzes some major factors that influence the Omani learners and their corresponding satisfaction levels. The factors were considered based on the previous studies and general requirements of the learners. This research identified that the ICT innovations motivate the learners in self-learning and in future continuing education.
-
A. Research Questions
The following research questions were formulated to identify learner’s satisfactions on IT innovations.
-
1) What are the supports that the ICT innovations provide to the learners in Omani educational perspectives?
-
2) What is the satisfaction level of the users (learners) in using ICT in learning processes?
-
B. Objectives and Hypotheses
Based on the above research questions, the following objectives and hypotheses were set.
Objective 1: To measure the various supports provided by the ICT innovations to the learners
Hypothesis 1: ICT innovations provide tools to measure academic performances, learning atmosphere and quality learning.
Objective 2: To measure the learners’ satisfaction on ICT in learning processes
Hypothesis 2: The learners are highly satisfied with the supports of ICT innovations in learning processes.
-
II. Literature Review
Various studies were conducted by the researchers related to the impacts of information and communication technology in educational processes. Numerous researches were also conducted regarding the learner’s satisfaction, instructor’s satisfaction and user’s satisfaction in using information technology in learning and instructional methodologies. Studies were also conducted with respect to various levels of education, region and demographic.
Rezaeean et al (2012) studied the importance of website innovations. According to them, the websites benefit the universities for appropriate academic communication. They identified that innovation is the most important factor influencing the student’s satisfaction. Apart from that, the students trust on these innovations has the positive influence on their satisfaction [4]. Lee (2008) [5] studied the relationship among instructional innovation, learning satisfaction and study achievement. According to him, education that focuses on cultivating creativity helps in creating new innovations. Apart from that the learning environment influences the learner’s satisfaction.
Zhu (2012) [6] studied the student’s satisfaction on online collaborative learning. He said that when the e – learning environment is applied, the effectiveness of elearning should be studied with respect to student’s satisfaction. His study confirmed that there are significant differences between students’ satisfaction and academic achievements in an innovative e – learning environment. Leidner and Jarvenpaa (1995) [7] reviewed the different models of learning and the relationship with the assumptions of electronic teaching technology. According to them, information technology should be used primarily to automate the information delivery functions in the classrooms.
Rouibah and Hamdy (2011) discussed on the technology adoption in the Arab world and the aids in the educational world [8]. They suggested that the companies should understand the technical and social nature of users’ attitude in ICT adoption and satisfaction.
As Negi et al (2011) [9] said, IT aids plenty of resources to enhance the student’s learning abilities in using instructor’s teaching skills. Also, they said that information technology is providing tools, techniques and software to educate poor peoples. Quality in the educational system should ensure the proper integration of information technology in teaching and learning.
Romney and Bruseke (2014) studied the deliveries through new virtualization technology. They identified that the mobile computing devices have become most preferred delivery instruments for the digital contents. According to them, student’s learning by means of cloud has become a collaborative or social process [10]. Eng (2005) studied the impact of ICT on learning. The author suggested that use of ICT in conjunction with other teaching strategies could benefit the learners in different perspectives [11].
Sinkovics et al (2009) investigated the antecedents for successful implementation of information technology based learning environments [12]. They have suggested to consider the quality of virtual interaction for the learner’s satisfaction. Dabbagh and Kitsandas (2011) had described a pedagogical framework to use social media to create personal learning environment that support a learner centered pedagogy and foster self-regulated learning. According to them, in e-learning domain personal learning environments have learner control and personalization [13]. Villanueva (2000) said that information technology have the potential to offer synchronous and asynchronous learning opportunities. He identified that the powerful virtual classrooms provide web based tools and created rich, high quality environment in educational resources [14].
Sriram (2014) conducted a study on impact of internet resources, one of the major information technology development, and identified that in Omani higher education specializations of the learners have significant impact on the usage of technology in learning processes [15]. Robles (2013) identified that the instructors need to identify the various opportunities to integrate appropriate educational tools to suits to their learning preferences, as the internet dependencies are increasing in this modern world [16]. This integrations shall be worth only if the learners have sufficient satisfaction on the suggested web technology.
Though various studies could be found with respect to the information and communication technology impact, very few studies were available with respect to Middle East and Sultanate of Oman. To add to literature and to identify the major factors, this study was conducted in Omani higher education environment at undergraduate level.
-
III. Research Methodology
A questionnaire was prepared in Arabic and English with 5 demographic variables, 20 closed end questions and 1 question related to measure the satisfaction level. 5 point Likert scale was used in closed end questions with 5 – Strongly Agree to 1 – Strongly Disagree. The questionnaire was prepared with the following constructs: development in educational technology, influences on learning skills, available tools, quality in educational activities, learning atmosphere and learning processes.
The above factors were selected based on the literature reviews and the student’s feedbacks. The questionnaire was distributed to the undergraduate students studying at different levels and programs.
The questionnaire had 3 separate sections. 1st section had 5 questions related to demographic profile of the respondents, 2nd section had 20 questions related to research ideas and the last section had one question related to the respondents overall satisfaction. The respondents were clearly explained about the research perspectives. Some sample questionnaires were distributed to the students in the classrooms and their feedbacks were studied initially. The questionnaire was distributed to 250 students. The questionnaire which were partially filled or multiple answers were selected were considered for the study. Finally, 240 responses were considered for this study.
Cronbach's Alpha Reliability Analysis was conducted to check the validity of the collection instrument which showed a reliability value 0.842 for the selected collection tool. The KMO measure of sampling adequacy was 0.880 and the Bartlett's test of sphericity significance was 0.000.
-
A. Demographic Analysis
-
45.8% of the respondents were studying in Information and Technology department, 35.8% were studying in Business Administration department, 6.7% were studying in Engineering Department and 11.7% were studying in General Foundation Program.
-
46.7% of the respondents were less than 20 years of age. 51.7% of the respondents were between 21 up to 40 years. 1.6% of the respondents were above 40 years of age. In this, 52 respondents were male and 188 respondents were female.
-
46.7% of the respondents were at diploma level and 41.7% of the respondents were at bachelor level. 48.2% of the diploma level learners were at first year level and 51.3% of the learners were at 2nd year level. 52% of the bachelor level learners were at 3rd of study and 48% of the learners were at final (4th) year level.
The demographic profile showed that 28 students were studying foundation level, 112 students were studying diploma and 100 students were studying bachelor level.
Table 1 shows the level of study of the respondents in specialization wise.
Table 1. Specialization Wise Respondents Level
|
Level / Speciali Zation |
IT |
IS |
MM |
Acc |
FB |
Eng |
Tot |
|
Foundation |
8 |
6 |
6 |
4 |
4 |
0 |
28 |
|
Diploma |
36 |
28 |
22 |
16 |
10 |
0 |
112 |
|
Bachelor |
28 |
18 |
20 |
12 |
6 |
16 |
100 |
|
Total |
72 |
52 |
48 |
32 |
20 |
16 |
240 |
B. Analysis and Findings
-
C. Analysis on Demographic Variables
Fig 1 shows the gender analysis of the respondents with respect to the specialization wise.
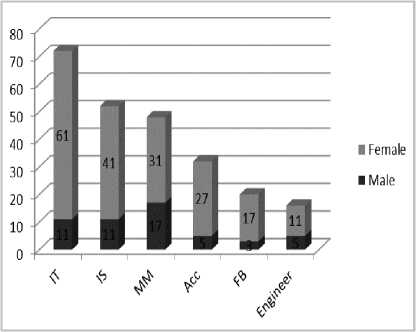
Fig 1. Gender / Specialization Wise
Fig 2 shows the age groups of the respondents in department wise.
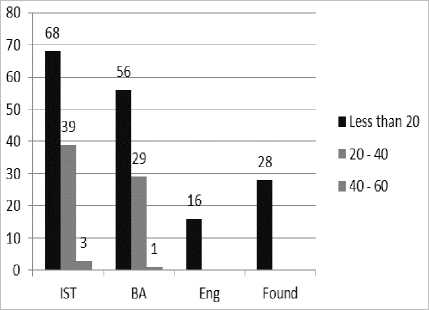
Fig 2. Age / Department Wise
-
D. Analysis on Research Questions
-
31.25 % and 47.08% of the respondents either strongly agreed or agreed that the ICT innovations have made
-
17.9 % of the respondents strongly agreed that the ICT innovations have significant positive influences on learning skills. 37.9% of the respondents have agreed on this fact. 9.2% and 7.5% of the respondents either disagreed or strongly disagreed with this statement. 27.5% of the respondents do not give any opinion on this fact. Very few (14%) foundation level students either disagreed or strongly disagreed on this statement. None of the Engineering students strongly disagreed with this statement. Only 2 out of 16 engineering students disagreed on this fact. None of the respondents above 40 years either strongly disagreed or disagreed on this statement.
-
22.1 % and 40.4% of the respondents had either strongly agreed or agreed that ICT innovations provide necessary and sufficient tools to measure academic achievement in various perspectives. 11.3% and 6.3% either disagreed or strongly disagreed on this statement. 20% of the respondents do not have any opinion on this issue. All the respondents above 40 years agreed on this fact.
-
72.5 % of the respondents had the opinion that the ICT innovations have significantly increased the quality in all educational activities. The recent developments in ICT innovations had significant improvement in the all perspectives of the educational activities. Around 15% of the respondents felt that the ICT innovations shall make more significant improvements in quality of educational activities.
-
25.8 % of the respondents strongly felt that the ICT innovations have made the learning atmosphere very meaning full. 42.9% of the respondents agreed on this fact. 11.7% and 6.3% of the respondents either disagreed or disagreed on this fact. 13% of the respondents had no opinion of this statement. None of the foundation level students strongly disagreed on this statement.
The responses were analyzed with respect to the research objectives using various statistical measures such as descriptive analysis, percentage and regression analysis.
significant development in educational technology in order to attain desired learning outcomes. Nearly 12% of respondents found to have no opinion in this regard. Around 10% of the respondents either disagreed or strongly disagreed with this fact. None of the foundation level students either strongly disagreed or disagreed with the fact that the ICT innovations had made significant development in the education field. This showed that the recent developments in ICT innovations were implemented and utilized in beginning of the studies itself. Very few bachelor level students (5%) have disagreed or strongly disagreed with this statement.
Nearly 75% of the respondents either strongly agreed or agreed that the ICT innovations have encouraged the knowledge sharing at all levels of learning processes. 15% of the respondents only disagreed or strongly disagreed on this statement. None of the engineering students have disagreed on this fact.
The users were asked to provide their level of satisfaction on ICT innovations that they use in their day – to – day educational activities. 18.3% of the respondents said that they were highly satisfied, 53.6% suggested that they were satisfied, 10% said that they do not want to comment, 11.3% were dissatisfied and 6.8% were highly dissatisfied with the level of impact of information technology on their satisfaction.
From the above analysis, it is evident that more that 50% of the respondents were satisfied in using ICT innovations in their learning processes. 71% of the foundation level students, 70% of the diploma level students and 75% of the bachelor level students were either highly satisfied or satisfied with this statement.
71% of the male respondents and 72% of the female respondents were highly satisfied or satisfied in using ICT innovations in their educational processes. 16% of the bachelor level students, 22% of the diploma level students and 7% of the foundation level students were either dissatisfied or highly dissatisfied with this fact.
-
E. Descriptive Analysis on the Research Questions
The results collected were analyzed with respect to various statistical measures to identify the impact levels and significance. The mean, sample standard deviation, standard error in mean, skewness, kurtosis and coefficient of variation were calculated to identify the impact level. Table 2 shows the descriptive analysis on research questions.
Table2. Descriptive Analysis
|
Variable |
Mean |
Sample SD |
CV |
SE Mean |
Skewness |
Kurtosis |
Rank |
|
X 1 |
3.97 |
0.98 |
24.75% |
0.06 |
-1.12 |
1.09 |
1 |
|
X 2 |
3.50 |
1.04 |
31.94% |
0.07 |
-0.62 |
-0.17 |
6 |
|
X 3 |
3.61 |
1.13 |
31.42% |
0.07 |
-0.70 |
-0.23 |
5 |
|
X 4 |
3.78 |
1.17 |
31.06% |
0.08 |
-1.03 |
0.30 |
3 |
|
X 5 |
3.70 |
1.16 |
31.24% |
0.07 |
-0.84 |
-0.11 |
4 |
|
X 6 |
3.86 |
1.19 |
30.78% |
0.08 |
-1.08 |
0.35 |
2 |
|
Y |
3.66 |
1.11 |
30.21% |
0.07 |
-1.00 |
0.27 |
In the above analysis, the following variable assumptions were made.
-
X 1 = Significant Development
-
X 2 = Positive influences on learning skills
-
X 3 = Tools to measure academic performances
-
X4 = Improvement in quality in learning processes
-
X5 = Meaningful Learning Atmosphere
-
X6 = Encouragement in Learning Processes
Y = Overall Satisfaction on Using ICT innovations in Learning Processes
The above descriptive analysis showed that the significant development made by the ICT innovations have the highest impact on the learners. The highest negative skewness showed that the most of the respondents have agreed or strongly agreed on this fact. The respondents felt that the ICT innovations encourage them in various perspectives in their learning processes. Thus it had got the 2nd highest rank. The ICT innovations have significantly increased the quality in learning processes various ways and hence it had the 3rd rank. The respondents felt that the ICT innovations have created a meaningful learning atmosphere and hence this fact had scored the 4th rank. The tools provided by the ICT innovations and the positive influences by the ICT innovations on learners in different perceptions had scored the least ranks. The mean values of factors X 1 , X 6 , X 4 , X 5 were higher than that of the overall satisfaction. The mean values of X2 and X3 were lower than that of the overall satisfaction.
-
F. One Sample t – Test
One sample t – test (2 – tailed, 99% confidence interval at 239 df) has been conducted to identify the impact of the factors on overall satisfaction of the users. The result showed that the factors such as significant development t = 61.477, p < 0.01; positive influences on learning skills t = 48.781, p < 0.01; tools to measure academic performance t = 49.620, p < 0.01; improvement in quality in learning processes t = 49.878, p < 0.01; meaningful learning atmosphere t = 49.593, p < 0.01; encouragement in learning environment t = 50.324, p < 0.01 had significant impact on the student’s satisfaction of using technology innovation in learning processes. The result showed that the hypotheses set were significantly satisfied same as suggested in descriptive analysis.
-
G. Regression Analysis
To measure the strength of relationship between the assumed variables and the overall satisfaction, regression analysis was conducted. The coefficient of determination and p values were analyzed between the overall satisfaction of the students and the considered factors. Table 3 shows the simple linear regression analysis. The R2 values were compared for level of impact and ranking. The level of impact was measured as the following scale: 0 – 10% - No Relationship; 10% - 30% Low Relationship; 30% - 60% - Medium Relationship; 60% - 90% - High Relationship and 90% and above very high Relationship.
The highest R2 value was ranked 1 and lowest R2 value was ranked 6.
Table 3. Regression Analysis
|
Factor |
R2 - Value |
p - Value |
Level |
Rank |
|
X 1 |
0.592 |
0.000 |
Medium |
3 |
|
X 2 |
0.391 |
0.000 |
Medium |
6 |
|
X 3 |
0.573 |
0.000 |
Medium |
5 |
|
X 4 |
0.659 |
0.000 |
High |
2 |
|
X 5 |
0.586 |
0.000 |
Medium |
4 |
|
X 6 |
0.668 |
0.000 |
High |
1 |
From the above analysis, it is evident that all factors considered for the study had significant impact on the user’s satisfaction. The factors ‘Encouragement in Learning Process” and “Improvement in quality in Learning Process” had high level relationship whereas the all the other factors had medium level relationship.
-
IV. Discussion And Conclusion
The above results show that the ICT innovations have been significantly improved the learning processes in various degrees. The educational services uses various ICT tools in measuring the academic performances of the learners. The higher educational providers use different learning management systems. They maintain e – learning portals and deliver sufficient learning materials to provide the meaningful learning atmosphere. These learning management systems are also used to measure the learners academic performance using online examinations, multiple choices etc.
The higher education providers in Sultanate of Oman have benchmarked their programs with various international systems. The programs are quality assured by international universities. All the courses are developed with significant intended learning outcomes to achieve the desired mission and vision of the programs. Information and communication technology has developed various tools to achieve these required intended learning outcomes. Thus the learners are satisfied with the ICT innovations. Furthermore, the ICT has provided various systems like interactive tutor systems, online search systems and resources management systems which are useful in day – to – day learning processes. Apart from that the electronic devices such as smart boards, projectors and other gadgets help the learners to acquire required knowledge and develop their cognitive skills. Thus the information technology has tremendously improved the quality of educational environment.
These ICT innovations considerably motivate the learners in self-learning processes. The current education system requires various search tactics which motivate the learners to acquire required self-learning techniques. The learners have made to use various gadgets like mobile and other electronic mediums in their learning processes. Thus the ICT innovations have improved the overall dimensions on the educational processes which made the learners to utilize during their learning processes. The educators need to motivate the learners to utilize the full potentials of the information technology and its products in their daily learning processes in order to achieve the required knowledge.
Limitations And Scopes
This study is conducted in bachelor level of education. The results may vary if other levels of education are included. Various other factors based on the regional usages may be identified and studied.
Acknowledgement
I would like to thank the Dean of Sur University College for his motivations and supports in conducting researches and studies. I would like to thank the management of Sur University College for its financial and moral supports.
Список литературы Learner's Satisfactions on ICT Innovations: Omani Learners Viewpoints
- Yien, J.M., Hung, C.M., Hwang, G.J., and Lin, Y.C. (2011). A Game Based Learning Approach to Improving Students Learning Achievements in a Nutrition Course. The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology. 10(2).
- Moyle. K., (2010). Building Innovation: Learning with Technologies. Australian Education Review: 56. ISBN: 9780864318619.
- Varis, T., (2007). New Technologies and Innovation in Higher Education and Regional Development. RUSC. 4(2). 16 – 24.
- Rezaeean, A., Bairamzadeh, S., and Bolhari, A., (2012). The importance of Website Innovation on Students' Satisfaction of University Websites.World Applied Sciences Journal. 18(8): 1023 – 1029.
- Lee, Y.J., (2008). A Study of the Influence of Instructional Innovation on Learning Satisfaction and Study Achievement. The Journal of Human Resource and Adult Learning. 4(2): 43 – 54.
- Zhu, C., (2012). Student's Satisfaction, Performance and Knowledge Construction in Online Collaborative Learning. Educational Technology & Society, 15(1): 127 – 136.
- Leidner, D. E., and Jarvenpaa, S.L., (1995). The Use of Information Technology to Enhance Management School Education: A Theoretical View. MIS Quarterly, 19(3): 265 – 291.
- Rouibah, K., and Hamdy, H., (2011). Factors Affecting Information Communication Technologies Usage and Satisfaction: Perspectives from Instant Messaging in Kuwait. IGI Global. 133 – 161. DOI: 10.4018/978-1-60960-605-3.ch007.
- Negi, P.S., Negi, V., and Pandey, A.C., (2011). Impact of Information Technology on Learning, Teaching and Human Resource Management in Educational Sector. International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications. 2(4): 66 – 72.
- Romney, G.W., and Brueseke, (2014). Merging the Tower and the Cloud through Virtual Instruction: The New Academy of Distance Education. Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching. 7(1): 93 – 110.
- Eng, T.S., (2005). The Impact of ICT on Learning: A Review of Research. International Education Journal. 6(5): 635 – 650.
- Sinkovics, R.R., Haghirian, P., and Yu, S., (2009). Information Technology Based Innovation in International Marketing Education: An Exploration of Two Learning Environments. Journal of Teaching in International Business. 20: 123 – 148.
- Dabbagh, N., and Kitsantas, A., (2011). Personal Learning Environments, Social Media, and Self Regulated Learning: A natural Formula for Connecting Formal and Informal Learning. Internet and Higher Education. DOI: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2011.06.002.
- Villanueva, C.L. (2000). Newer Technologies for a Learning Society: Information Technologies in Educational Innovation for Development. 38 – 44. Report of Sixth UNESCO – ACEID International Conference on Education.
- Sriram. B. (2014). Specialization Impact on Internet Resource Usage: Omani Undergraduate Learner's Perspectives. International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Sciences. 6(8): 10 – 17.
- Robles. A.C.M.O (2013). The Use of Educational Web Tools: An Innovative Technique in Teacher Education Courses. International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Sciences. 5(2): 34 – 40.


