Legal measures of protection of water bioresources of the Arctic region
Автор: Kulikova O.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Ecology of the Arctic and the North, nature resources
Статья в выпуске: 4, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In article the questions connected with a general characteristic of the operating faunistic legislation regarding protection of water biological resources are considered. In connection with a wide circulation of environmental problems including in the Arctic region questions of protection of the given kind of natural resources are very actual. The author analyses existing system of sources in the field of rational use and protection of water bioresources, concrete norms of the right are resulted and characterized.
Environment, natural resources, water biological resources, rational use, protection of water bioresources, liability of infringement of the faunistic legislation
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148320494
IDR: 148320494 | УДК: 349.41:502.171(98)(045)
Текст научной статьи Legal measures of protection of water bioresources of the Arctic region
Located within the Arctic territory, continental shelf and exclusive economic zone of the eight Arctic states - Russia, Canada, the United States (Alaska), Norway, Denmark (Greenland and the Faroe Islands), Finland, Sweden and Iceland. The maximum length of the borders in the Arctic is Russian. The Arctic is extremely rich in almost all types of natural resources. In 2009, the magazine «Science» published a study of natural resources in the Arctic (Donald L. Gautier, Kenneth J. Bird, Ronald R. Charpentier, Arthur Grantz, David W. Houseknecht, Timothy R. Klett, Thomas E. Moore, Janet K. Pitman , Christopher J. Schenk, John H. Schuenemeyer, Kai Sørensen, Marilyn E. Tennyson, Zenon C. Valin, Craig J. Wandrey). According to the research group under the ice of the Arctic contains around 83 billion barrels of oil (about 10 billion), accounting for 13% of the world's undiscovered. Natural gas in the Arctic, according to scientists around 1550000000000000. cubic meters. A large portion of undiscovered oil lies off the coast of Alaska, and nearly all Arctic natural gas reserves - off the coast of Russia. Scientists note that most of the resources are at depths less than 500 m1.
Most of the natural gas is concentrated in the Kara and Barents seas - the territory that Russia is committed.
Picture 3. Assessment of Undiscovered Oil and Gas in the Arctic URL: http://www.sciencemag.
org/content/324/5931/1175/suppl/DC1;
Possessing significant hydrocarbon resources in the Arctic, Russia set up a policy of respect for the natural environment. September 17, 2008 under the leadership of the President of the Russian Federation Dmitry A. Medvedev held a meeting of the Security Council of the Russian Federation. As part of his training has been a lot of study and analysis of the most important issue for Russia - the protection of national interests in the Arctic. The priorities of the Russian Federation in the Arctic are:являются:
active exploration of the natural resources of the region; development of transport and border infrastructure; development of information and telecommunications environment.
At the meeting, the Security Council approved the "Principles of State Policy of the Russian Federation in the Arctic up to 2020 and beyond", and adopted a plan of action to implement them. It should be noted that according to the Russian Prime Minister Vladimir Putin, "not a single industrial project in the Russian Arctic will not be realized without the most stringent environmental requirements. This is a position of principle. We shall be guided and development of the Yamal Peninsula and the Shtokman field in the Barents Sea, and in the development of the Krasnoyarsk
Territory and Yakutia. A hundred other industrial facilities and infrastructure projects that are created by the state and the business2». Thus, in particular in the field of environmental safety should:
-
1) to ensure the conservation of biological diversity of the Arctic flora and fauna, including through the expansion of the network of protected areas and water bodies, taking into account the national interests of the Russian Federation, the need to preserve the natural environment in the expansion of economic activity and global climate change;
-
2) to implement the planned disposal of ships with nuclear power plants, end-of-schedule operation.
It is clear that the wealth of the Arctic is not only huge reserves of oil and gas. The Arctic seas are rich in fish stocks, but in the Barents Sea is concentrated five percent of the world production of marine and ocean fish3. The system of the Russian legislation on aquatic resources includes many links, from federal laws and ending acts of local self-government. Of key importance here is the Federal Law "On fishing and conservation of living aquatic resources"4, creating a uniform framework for regulating relations in the sphere under consideration. The conceptual apparatus of the Act contains many definitions, which facilitates understanding of the consolidation and implementation of the law. In particular, given the notion of the living aquatic resources and their conservation.
Aquatic biological resources – are fish, aquatic invertebrates, aquatic mammals, algae and other aquatic animals and plants that are in a state of natural liberty. Preservation of the marine biological resources - maintaining marine biological resources or restored to levels that can produce the maximum sustainable yield (catch) aquatic biological resources and biodiversity, through the implementation of science-based measures for the study, preservation, reproduction, management of living aquatic resources and the protection of their environment
Aquatic resources are the foundation of human life and activity, including its ho-agricultural activities. This provision stems from the provisions of the Constitution of the Russian Federation. According to Art. 9, land and other natural resources are used and protected as the basis of life and of living on its territory peoples. In terms of other natural resources, decided to include the atmosphere, mineral resources, forests, wildlife, and water. However, the Constitution of the Russian Federation can be considered the basis of life and activities of the people of Russia not only aquatic resources, but also their habitat.
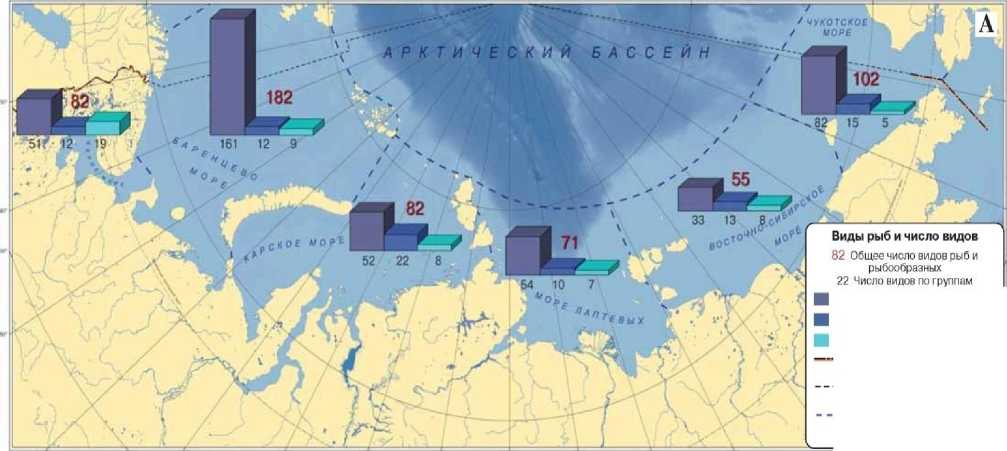
Picture 5. The species diversity of fish, fish-like / / Atlas of the biodiversity of the seas and coasts of the Russian Arctic / edited by VA Spiridonov, Gavrilo MV, Krasnova ED and Nikolaeva NG - WWF, Geography
Department of Moscow State University. M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, 2011.
The status of stocks of living aquatic resources, effective management is becoming increasingly important both for the Russian population with high-quality food, and for the supply of raw materials in many industries (poultry, livestock, etc.), as well as recreational fishing. From 1991 to 2002 the total harvest (catch) of aquatic biological resources decreased from 6.93 to 3.29 million tons (52.5 percent). The volume of catch (production) fell within the exclusive economic zones of foreign countries by 58.5 percent and in the open ocean by 67 percent. Significantly reduced stocks of marine biological resources that are in high demand in the world market (pollock, cod, some species of crustaceans, sturgeon fish, etc.). This was caused by economic factors in the country, and the tightening of regulation of fishing in the exclusive economic zones of foreign countries and regions affected by international conventions on fisheries5. In the 80-ies of XX century it was predicted that by 2025, global fisheries production will reach 230-250 million tons, including from aquaculture - 60-70 million tons in 90 years the forecast for 2025 - 125 -130 million tonnes and aquaculture - 80-90 million tons is considered obvious that the growth rate of the Earth's population will exceed the growth rate of fish. It should be noted importance of fishing for income, wealth and food security of all nations and its particular importance for low-income food-deficit countries. Considering this and the special importance of the conservation of biological resources for future generations, in 1995, 95 states, including Russia, have adopted the Kyoto Declaration and Plan of Action on the Sustainable Contribution of Fisheries to Food Security. It was found necessary to establish the policy, strategy and management of resources for the sustainable development of fisheries based on the following guidelines:
-
> conservation of ecological systems;
-
> use of objective scientific data;
-
> improving the socio-economic well-being;
-
> equitable distribution of resources within and between generations.
-
> use of objective scientific data;
-
> improving the socio-economic well-being;
-
> equitable distribution of resources within and between generations.
Russia, like other countries, has committed itself to guide the implementation of the national strategy for fisheries by the following principles:
-
1) Recognition of the important role of marine fisheries, inland fisheries and aquaculture for food security of the world and its economic well-being;
-
2) the effective and full application of the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea, the UN Agreement on Straddling Fish Stocks and Highly Migratory Fish Stocks Agreement to Promote the implementation of international management measures by fishing vessels on the high seas and the Code for Responsible Fisheries, and changes in their national legislation accordingly these instruments;
-
3) the development of scientific research as the fundamental basis for sustainable development of fisheries and aquaculture for food security, as well as scientific and technical assistance to countries with low R & D capabilities;
-
4) evaluation of productivity of the stocks in the waters under national jurisdiction, both domestic and offshore, bringing fishing capacity in these waters to a level comparable with the long-term productivity of the stock, and the timely adoption of appropriate measures to restore overfished stocks to a steady state, as well as the necessary cooperation for the adoption of similar measures for stocks of the high seas;
-
5) conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity in aquatic organisms in particular, the prevention of actions leading to irreversible changes, such as the destruction of species, genetic damage, destruction of habitat;
-
6) to promote mariculture and aquaculture in coastal and inland waters through: the establishment of appropriate legal mechanisms, coordination of land and water use with other activities, the use of the best and most suitable genetic material in accordance with the requirements of the conservation and sustainable use of the environment and conservation biological diversity, use of impact assessment of the social plan and the impact on the environment.
Criteria for making economic decisions and indicators of sustainable development must ensure the harmonious functioning of the triad: the nature - fish farming - the population of Russia. The specific type of economic mechanisms for the implementation of this requirement should include a full assessment of the costs, benefits and risks of fishing with the following criteria:
-
> no commercial fishing activity can not be justified if the benefits would not exceed the damage caused by nature;
-
> environmental damage should be minimal with a maximum consideration of economic and social factors6.
The fishing capacity and fishing in the Arctic it - this is a new reserve for the growth of fish and seafood in Russia. So, in terms of the intensification of foreign economic cooperation of Russia with other countries is possible to implement large-scale "Arctic projects" to create specialized joint ventures (JVs).
The sustainable development of the fisheries in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation can not be viewed in isolation from the general provisions applicable to both domestic and international law. Sustainable development (English sustainable development) - the process of change in which the exploitation of resources, the direction of the investments, the orientation of technological development, personal development and institutional changes are consistent with each other and strengthen the current and future potential to meet human needs and aspirations7.

Director of the National Park "Russian Arctic" Roman Ershov at the map of Franz Josef Land. Photo: Anastasia Sazhenova.
Of the great importance for the conservation of the marine biological resources in the Arctic is the creation and the expansion of the network of protected areas and objects. For example, the National Park "Russian Arctic", which includes the archipelago of Franz Josef Land, is of great international interest, and the development of tourism in the national park - one of the priorities. Government Decree on the establishment of the national park "Russian Arctic" was signed on 15 June 2009. Its territory includes the northern part of Novaya Zemlya archipelago; here are the largest in the Northern Hemisphere bird rookeries, walrus rookeries, as well as one of the most important breeding areas polar bear Barents-Kara sea population. The total area of the park, including areas of marine water - 1.426 million hectares. In accordance with the articles of association, the National Park "Russian Arctic" is responsible for protection of the territory of the park and the state natural reserve of federal significance, "Franz Josef" formed in 1994. The Government of the Russian Federation in December 2010 ordered to allocate 23.4 million rubles to finance the activities of the state budget organization "National Park" Russian Arctic "in 20118.
Humanity is becoming more and more closely to the current boundaries of its habitat, where bioenergy and is rapidly being depleted. Not only to underdeveloped countries, but also quite safe for today states face in the near future shortage of fuel and electricity, drinking water, living space, and even food. Moreover, the global climate is changing significantly in the direction of warming, making everything more accessible those parts of the planet where previously it was not possible to lead an active economic and business activities. In these circumstances, the eyes of experts and politicians in many countries regularly rush to the "kingdom of white silence" - the Arctic. The Arctic - a new object of management, in which development is actively entering the United States, Canada, European Union, China, Norway and others is lawful with the onset of Russian oil and gas industry into new and promising areas of our Arctic intensify the development of marine fisheries, aquaculture and fishing industry9.


