Lichens as bioindicators of air pollutants
Автор: Trk R.
Журнал: Вестник Международной академии наук (Русская секция) @vestnik-rsias
Рубрика: Проблемы экологии, образования, экологической культуры, науки о земле
Статья в выпуске: 1, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The specific sensitivity of lichens to air pollutants enables us to use them for monitoring the effects of airborne toxic gases, such as sulphur dioxide and nitrous oxides. The monitoring can be carried out by mapping the epiphytic lichen biodiver sity and the exposure of sensitive lichen species to the environment. Because of their anatomical structure and the rela tively high absorption layer of lichens they are able to accumulate heavy metals and radionuclides. Thus the spatial distri bution of manmade radionuclides and of heavy metals originating from traffic and industrial processes can be demonstrated by using lichens as monitoring organisms.
Lichens, air pollution, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen compounds, radionuclides
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143162077
IDR: 143162077
Текст научной статьи Lichens as bioindicators of air pollutants
Lichens are symbiotic organisms comprising fungi and algae or cyanobacteria as photosynthetic active partners (photobionts). Lichens rank as the most resistant living organisms against natural stress factors such as temperature, drought and radiation. In scientific experiments they are able to survive in the moist (hydrated) state at temperatures from — 196 °C and in the dry state up to +80°C. They can also survive more than two years of absolute dehydration and 15 days of long-term exposure under space conditions (Sancho et al. 2007). In the hydrated state they are very sensitive to temperatures over 35°C. Lichens from Antarctica and from cold sites in the high altitudes of the mountains maintain photosynthetic CO2-uptake down to — 18°C [9—11, 16].
However, the anatomical, morphological features and the physiological conditions between the symbiotic partners in lichens result in a very high sensitivity to chemical stressors such as air pollutants and diverse biocides used in agriculture. Lichens do not develop any dermal tissue like the epidermis of higher plants with wax layers. The symbiotic coexistence of the partners requires complicated physiological adaption processes, which can be severely disturbed by external chemical compounds. In the presence of gaseous or dusty air pollutants or aerosols they absorb these foreign substances through their open surface. In the moist and physiological active state the poisonous substances can disturb — depending on the concentration — the physiological processes in the photobiont and the interactive processes between the mycobiont, photobiont and the involved bacteria.
Besides air pollutants, the occurrence and frequency of epiphytic lichens in conurbation (metropolitan) areas is a function of urban heat island effects and common climate changes [18]. Thus lichens also indicate changes in urban climate, climatic change and levels of air pollution.
Since the nineteenth century it is known that the gas sulphur dioxide is poisonous for epiphytic lichens. Many investigations on the epiphytic lichen vegetation in cities, industrial conurbations and around factories with high emission of smoke and gaseous compounds showed a decline in the diversity and abundance of macro-lichens. Only some very resistant crustose lichens were able to survive in areas with high emission rates. Observations on the differential growth of various lichen species in regions with high deposition rates led to the choice of lichens as bio-indicators for air pollution (e. g. [6, 7]). The observations of the differing SO2 resistance of various lichen species in the field were confirmed by physiological studies on the SO2-resistance of lichens under laboratory conditions [15, 22, 26].
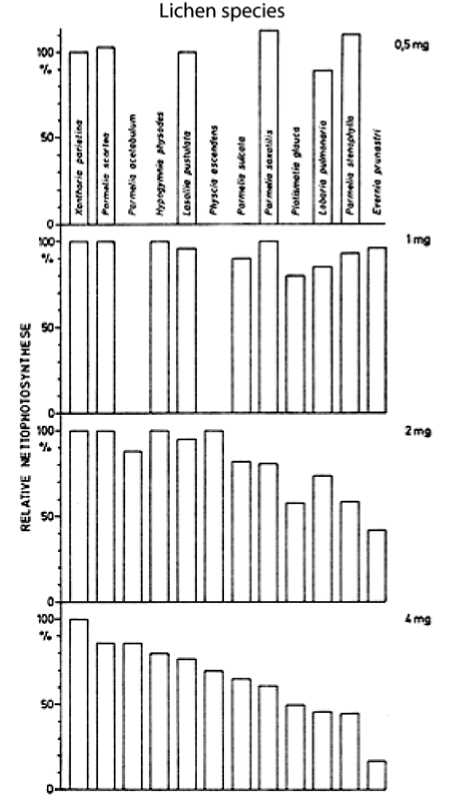
Fig. 1. Means of the net photosynthesis (in % of the normal value) after 14 hours gassing with SO 2 concentrations 0,5, 1, 2 and 4 mg SO 2 m -3 air (from: Turk et al. [19]).
These studies showed that the SO2 resistance of lichens is species specific, dependent upon the growth form, the moisture status during the emission level of sulphur dioxide and the intensity of the physiological activity. Also the pH of the substrate and the thalli is an essential factor of the SO2 resistance. At a low pH the damaging effect is more pronounced than at a high pH. The species specificity of SO2 sensitivity is shown in Fig 1. The nitro-and neutrophytic species Xanthoria parietina and Parmelina scortea (syn. Parmelina tiliacea ) are the most resistant, whereas the acidophytic species Platismatia glau-ca, Parmelia stenophylla (syn.: Xanthoparmelia stenophylla ) and the foliose macrolichen Lobaria pulmonaria and the fruticose Evernia prunastri are the most sensitive lichens.
Thus the difference in the sensitivity of lichens to SO2 in concentrations which occur due to specific emissions in the environment is an important precondition for the interpretation of the distribution of lichens found by mapping studies in areas with different concentrations of this air pollutant. In Central Europe many lichen species of the fruticose genera (Usnea, Bryoria and Evernia) as well as the foliose species (Lobaria, Nephroma, Hypogymnia and Parmelina) became extinct in wide areas. «Lichen deserts» in which absolutely no macrolichens occured were registered in the course of mapping studies in the city of Salzburg [19] and industrial conurbation areas of Linz, [1]. Both are located in Austria, where the climatic conditions are commonly well suitable for the growth of epiphytic lichens. Mapping studies on the diversity of epiphytic lichens as an indicator of air quality play an important role for determining the effects of air pollutants in the environment. In the Federal Republic of Germany applicable guidelines have been established (VDI-Richtlinie 3957 [25]).
Furthermore transplant experiments were initiated to evaluate the effects of SO 2 pollution on lichens [2, 12, 17]. Fast results could be obtained after the exposure of the lichens at varying locations by measuring the CO 2 -gas exchange. In the city of Salzburg transplanted samples of Hypogymnia physodes and Parmelia sulcata ceased net photosynthesis after an exposition time of six weeks between November 1977 and March 1978 («heating sea-son») [20]. The lower concentration of SO2 during spring and summer caused no physiological effect on the exposed specimens (Fig. 2).
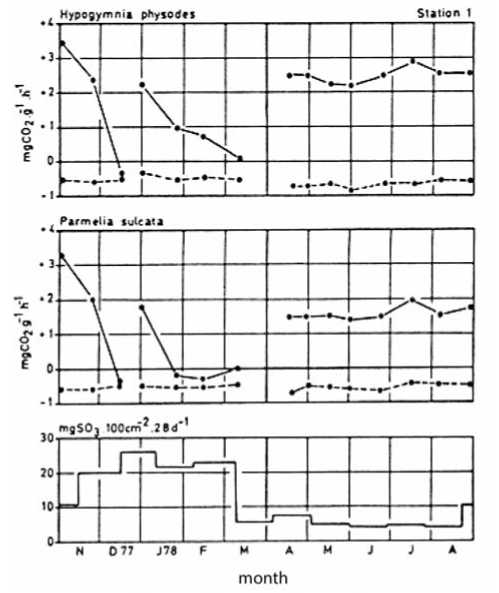
Fig. 2. Net photosynthesis and dark respiration of transplanted Hypogymnia physodes and Parmelia sulcata at station 1 (in the city of Salzburg) and the average SO 2 -concentration during the exposure time (Turk & Christ [20]).
In the summer, the photosynthetic rate was determined depending upon the local climatic changes, especially moisture availability from precipitation. On days with moist, rainy weather the net photosynthesis was higher than during dryer weather periods.
The improvement in the air quality as a result of the reduction of the SO 2 concentration by stricter environmental laws between 1980 and 1990 led to a reinvasion of lichens into former highly polluted areas within five to eight years. However, since the beginning of the 1990s until present the emission of gaseous nitrogen compounds has increased dramatically in Central Europe. In the northern parts of the Austrian Alps the deposition of these airborne nitrogen compounds have reached such high levels that they have detrimental effects on the forest ecosystems and their biodiversity [3, 14]. Long term (1993— 2010) monitoring results of lichens from a remote site in Austria, showed that the lichen cover on tree trunks has decreased significantly. N-sensitive species vanished significantly, whereas the amount and the coverage of nitrophytic species increased. Epiphytic lichens with cyanobacteria as photobiontes (e. g. species of the genera Collema, Leptogium, Lobarina, Nephroma, Peltigera, Pannaria, Sticta ) disappeared almost entirely along the slopes of the northern Alps up to the ascent of the calcareous mountains in Austria. Acidophytic and sensitive macrolichens (e.g. Lobaria pulmonaria, Ramalina spec., Parmelia saxatilis etc.) also vanished [21, 28]. In the pre-Alpi foothills nitrophilous and nitrotolerant species ( Xanthoria spec., Physcia spec., Phaeophyscia spec.) dominate the epiphytic eutrophic associations not only on broadleaf trees with neutral bark, but also surprisingly on trees with acidic
Список литературы Lichens as bioindicators of air pollutants
- Bortenschlager S., Schmidt H. Luftverunreinigung und Flechtenverbreitung in Linz, Ber. Naturwiss. -Med. Ver. Innsbruck. 1963, 53: 23-27.
- Brodo I. Transplant experiments with corticolous lichens using a new tech nique, Ecology. 1961, 42: 838-841.
- Eckl P., Türk R., Hofmann W. Anreicherung natürlich und künstlich radioak tiver Spurenelemente in Flechten und Pilzen, Jahrb. Univ. Salzburg (1981-1983). Salzburg, 1984 (Hrsg. A. Buschmann): 227-235.
- Fenton A.F. Lichens as indicators of atmospheric pollution, Irish Nat. J. 1960; 13: 153158.
- Gilbert O.L. The effects of SO2 on lichens and bryophytes around Newcastle upon Tyne. In: Air Pollution. Proc. Of the First European Congress on the Influence of Air pollution on plants and animals, Wageningen 1968.Wageningen: Pudoc. 1969: 223-235.
- Stapper N.J. Baumflechten in Düsseldorf unter dem Einfluss von Luftverunreinigungen, Stadtklima und Klimawandel, Bibliotheca Lichenologica. 2012; 108: 221-240.
- Türk R. Die Veränderungen der Flechtenzonen und der Luftqualität im Stadtgebiet von Salzburg von den Jahren 1948/49 bis 1974/75. -In: Studie über die umwelthygienischökologische Situation der Stadt Salzburg (Hrsg.: Bundesministerium für Gesundheit und Umweltschutz). 1975: 131-135.
- Türk R., Christ R. Untersuchungen des CO2Gaswechsels von Flechtenexplantaten zur Indikation von SO2Belastung im Stadtgebiet von Salzburg. -In: Bioindikation auf subzellularer und zellularer Ebene (Hrsg.: R. Schubert & J. Schuh), MartinLutherUniversität HalleWittenberg. Wissenschaftliche Beiträge 1980/25 (P 9) Halle (Saale) 1980: 39-45.
- Türk R., Pfleger H.S. Das stumme Siechtum der Flechten. NATUR&Land. 2007; 93 (Heft 6): 22-26.
- Türk R., Wirth V. The pH dependence of SO2damage to lichens. Oecologia (Berl.) 1975; 19: 285-291.
- Türk R., Wirth V., Lange O.L. CO2GaswechselUntersuchungen zur SO2 Resistenz von Flechten, Oecologia (Berl.). 1974; 15: 33-64.
- Wunder B., Türk R. Effects of air pollutants on the growth rates of lichens in Linz, Upper Austria, Berichte f. Ökologie u. Naturschutz der Stadt Linz. 2012; 3: 55-112.


