Limitations of social partnership between authorities and business in forming tourist attractiveness of municipalities of the Russian Federation
Автор: Frolova Elena V., Rogach Olga V., Ryabova Tatyana M., Medvedeva Natalia V.
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Social and economic development
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.14, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Social partnership between authorities and business is a strategic factor of a territory’s socio-economic development and increase of the level of competitiveness among local tourist products and services. The purpose of the study is to identify the key limitations in the formation of social partnership between government and business in the context of solving the issues of developing the tourist attractiveness of municipalities of the Russian Federation. The authors used general scientific research methods (generalization, systematization, etc.) and analytical procedures based on comparative and system analysis methods. The key method was a questionnaire survey of experts - heads of municipalities (N = 306). The study was conducted in 2019. As a result of the survey, we identified the key problems of implementing social partnership projects in the tourism sector that do not allow local authorities to form sustainable interaction strategies with business: lack of interest among business, unfavorable investment climate, lack of efficient support for projects in mass media, etc. The authors justified the expediency of using municipal property on the principles of the cooperation economy as a tool for the development of social partnership in the tourism area. By summarizing successful practices of business participation in the development of municipal tourism and analyzing the survey results, we developed the areas for improving activities of local authorities to create conditions for the formation of tourist attractiveness based on social partnership (creation of museum and tourist clusters, branding of the territory, active informational support and popularization of tourist destinations in mass media, organization of project offices for tourism development, etc.). The authors conclude that the institutional environment for the development of social partnership in the tourism area is currently at the formation stage. It requires further study.
Municipality, social partnership, local community, local government, business, tourist attraction
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147234733
IDR: 147234733 | УДК: 352 | DOI: 10.15838/esc.2021.2.74.10
Текст научной статьи Limitations of social partnership between authorities and business in forming tourist attractiveness of municipalities of the Russian Federation
Integration of business and government interests is one of the most significant factors in the economic development of the state and its territories. Social partnership, as a form of cooperation between government and business, is currently considered by experts as an actual trend in transformation of management practices.
Social partnership practice between business and government is particularly relevant in the tourism sector. Today, tourism is positioned as a highly profitable and dynamically developing economic sphere which has a significant impact on quality and pace of socio-economic development of individual regions and municipalities. According to the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC), the tourism industry creates 1 in 10 jobs (313
million) worldwide1. As one of the largest economic sectors, in 2017 tourism industry showed growth of 4.7% which is higher than global average growth rate of 1.7%; in 2019, 10.3% of world GDP was accounted for tourism industry, for Russia this share was 3.9%2. Undoubtedly, the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly transformed the image of outbound tourism (international tourist trips in Russia decreased by 99.0%, the United States – by 95.8%, Spain – by 99.1%, Thailand – by 100%3); however, according to some experts, the closure of international borders has identified new potential growth points for domestic tourism in most countries. This circumstance, together with other advantages of tourism industry development (preservation of ecological balance, low level of environmental pollution, development of social and market infrastructure, growth of local population employment, etc.), becomes a significant factor in the municipalities’ sustainable development [1].
Global economic crisis has put on the agenda such issues as social responsibility of business, support for entrepreneurial activity, and risk sharing for implementation of social partnership projects [2]. The COVID-19 pandemic and the sharp decline in profitability caused by epidemic in tourism industry and related industries (hotel, restaurant, cultural and entertainment sectors) require development of new approaches to the formation of an effective institutional environment and “market optimism” for entrepreneurial initiatives [3; 4]. Due to the restrictions imposed and the closure of world destinations popular for Russian tourists, the effective use of social partnership in terms of maintaining competitiveness of domestic market of tourist services is of particular importance.
We should note that competitiveness of local tourist product and services is determined not only by the territory’s tourist potential and the presence of significant points of attraction, but also by the quality of tourist services, development of tourist infrastructure and innovative practices of tourist services. The readiness and level of involvement of business community in solving issues of developing municipalities’ tourist attraction determine the dynamics of indicators of regional economies, fixity and stability of territories’ socio-economic development [6]. Based on the materials of foreign studies, the paper shows the effect of attracting the private sector to managing tourist infrastructure facilities. The level of competitiveness of services, provided to organize tourist recreation, increases due to the rapid business response to transformation of consumer requests, implementation of models of representatives’ network behavior of commercial sector [7]; payback period of tourist infrastructure objects is decreasing [8], quality of coordination of modernization processes of tourist destinations under the influence of external factors and internal conditions of territorial development is increasing [9; 10].
The effectiveness of the authorities’ policy to support business initiatives determines the demand level for local tourist products and services, and territory’s attraction for potential tourists [11; 12; 13]. However, according to official data presented in the Concept of the Federal Target Program “Development of Domestic and Inbound Tourism in the Russian Federation (2019–2025)”, domestic market development of tourist services in Russia is hampered by a number of problems among which special attention should be paid to the low pace of modernization and creation of engineering and tourist infrastructure, unsatisfactory condition of tourist attractions and leisure facilities, the lack of long-term credit instruments available to investors allowing recouping investments in objects of the tourist and recreational complex in terms acceptable to investors4. We can assume that institutional restrictions on tourist attraction development of Russian territories limit the practice of using social partnership between government and business. In particular, improving access to finance for small and medium-sized enterprises, according to experts, creates a favorable institutional environment for developing partnership strategies of business and government [14; 15], institutional structures at the regional and local levels, ensuring the order of interaction and taking the necessary measures to resolve conflict situations, creates an organizational basis for respecting mutual interests [16; 17; 18], building formal communication channels [19; 20].
Critical analysis of existing approaches to the study of social partnership and its role in tourism development has shown that scientists’ attention is focused on regional problems and practices. In particular, G.A. Gomilevskaya has identified the most effective model of cluster formation by analyzing practical aspects of budget financing of tourist infrastructure in the Primorsky Krai [21]. The study of tourism development dynamics in the Altai Krai is devoted to the work of N.N. Pestnikova, N.G. Prudnikova, O.S. Strizhevoy which analyzes in detail the growth rate of tourist services, the share and structure of the tourist flow in cities and districts of the region [22]. The works of M.S. Guseva and D.V. Amelkina identify factors limiting development of partner practices in tourism sector, based on the Samara Oblast experience [23]. L. Maksanova, T. Bardakhanova, S. Ausheeva highlight tools for assessing the use of the partnership mechanism in tourism [24]. The work of N.I. Magomedova considers development aspects of public-private partnership in the Russian Federation and formation of a qualitatively new level of tourism potential in the context of sanctions [25].
Despite the fact that in regional studies, the issues of tourism development and special role of social partnership are undoubtedly important, at present, the aspects of partnership between business and government at the municipal level are not yet sufficiently studied. This determined the purpose of our work – to identify the key limitations of social partnership formation between government and business in the context of solving the problems of tourist attraction development of Russia’s municipalities.
The tasks of the research are:
-
1) to analyze financial, organizational, and information resources of municipalities that allow implementing social partnership projects with businesses in tourism sector;
-
2) to consider problems and limitations of building partnerships between government and business in projects for developing tourist attraction of Russia’s municipalities;
-
3) to analyze successful practices of business participation in tourism development at the municipal level;
-
4) to determine the directions for solving the problems of social partnership between government and business in the field of tourism.
Methodology
The sociological study “Social resources for tourist attraction development of Russian territories” was conducted in 2019 as a part of the RFBR research project “Interaction of key actors of local communities in order to increase tourist attraction of Russian territories: constraints, resources and development technologies”. Within the framework of the research, the authors set multi-faceted tasks related to the analysis of the problems of tourist attraction development of Russian territories, identification of key trends and mechanisms for activating social resources. One of the blocks of the questionnaire was devoted to interaction of business and government in the context of tourist attraction development of Russian territories.
The object of the research is interaction practice between municipal authorities and business structures which is framed in social partnership projects. The subject of the work is the possibilities and limitations of social partnership of the use between municipal authorities and business in the context of tourist attraction development of the Russian Federation regions. The emphasis is on the integration of government and business efforts which is due to the importance of solving domestic tourism problems in the Russian Federation, as well as the need to narrow the field of empirical research with specific tasks of territorial development of Russian municipalities.
Research geography covers all Russian federal districts. At the first stage, there were formed groups of municipalities representing various Russia’s federal districts. At the second stage, municipalities are randomly selected taking into account the type of territory (rural or urban), administrative characteristics (urban settlement, rural settlement, urban district, municipal district). The cities of federal significance (Moscow and St. Petersburg) were excluded from the sample due to the truncated scope of powers assigned to municipal authorities. Due to small representation in general population of such types of municipalities as urban districts with inner-city divisions and inner-city districts, they were also not included in the sample. The sample of municipalities by federal district reproduces the structure of general population in proportion to the number of municipalities in the district for 2019. In addition, a number of organizational difficulties did not allow timely obtaining questionnaires from the heads of local authorities in a number of subjects. The final sample consisted of 306 municipalities, while 100 questionnaires were received from the heads of local self-government authorities of rural settlements of 115 municipal districts.
In the course of the work, there were used general scientific methods (generalization, systematization, etc.); the paper uses analytical procedures based on the methods of comparative and system analysis. The key method is a questionnaire survey of experts – heads of municipalities (N = 306). The questionnaires were sent out by e-mail with a cover letter explaining principles of filling out the questionnaire and justifying the research significance. The Committee on Federal Structure and Local Self-Government of the State Duma, the National Association of Territorial Public Self-Government, and the All-Russian Council of Local Self-Government (VSLSG) provided support in collecting information.
Most of the papers present an analysis of realizing public-private partnership projects at the regional level. We analyze social partnership practices at the municipal level. The special novelty of the research case study is to define barriers to implementation of social partnership between government and business at the municipal level identified on the basis of an expert survey. Theoretical significance is determined by systematization of the key limitations of implementation of social partnership projects of government and business in the field of tourism, justification of the ideas of cooperation economy and their interpretation in the context of the use of municipal property as a tool for developing social partnership in the field of tourism.
The results of the study can be applied in the practice of local self-government authorities to overcome the existing stereotypes of unprofitability of social partnership projects in the field of tourism, the effective use of municipal property as a tool for attracting business to solve the problems of local tourism development, building an effective information policy and information coverage of social partnership projects. The case study and conclusions drawn in the course of the research can be useful in developing strategies and plans for developing the tourist attraction of Russian territories, as well as local business support programs. In addition, the analysis of interaction practices between municipal authorities and business, designed in social partnership projects, as well as the conclusions, made on the basis of it, can be used to optimize techniques and tools for involving people in solving issues of territorial development of local communities.
Research results
In the course of solving the first research task, the experts were asked to assess the available financial resources of the municipality. The results of the experts’ survey indicate the lack of financial support for local budgets (Fig. 1) which does not allow local authorities to solve acute socioeconomic problems of the territory. In addition, the issues of financial support from the regional budget and attracting private investment are now more acute than ever on the municipal agenda.
We can assume that limited resources do not allow municipalities to initiate social partnership projects in the field of tourism. This circumstance is usually associated with both the secondary role of tourism industry development in the field (due to the presence of traditionally acute socioeconomic problems of development of Russian municipalities), and with institutional restrictions in implementing socio-cultural projects of a tourist orientation. In the conditions of low quality of life of the majority of Russia’s population, tourism is perceived by the heads of municipalities as a desirable, but not a priority area for territory’s development.
Experts note the acute lack of socio-economic resources for tourist attraction formation. In foreign practice, special attention is paid to attracting sponsors and developing patronage, but Russian experts’ responses indicate that municipalities are not ready to deal with these issues. It can be assumed that the peculiarities of the Russian mentality and the dominance of paternalistic values limit sponsorship initiatives (Fig. 2) . The lack of entrepreneurial activity of population noted by the respondents is a cause for concern, as the tourism sector is mainly represented by the commercial sector. It is difficult to talk about tourist attraction formation of Russia’s municipalities with weak development of entrepreneurship in them.
The situation is aggravated by the lack of business interest in participating in social partnership projects. The results emphasize the need for a deeper study of the opinion of business structures on this issue which will help to determine
Figure 1. Assessment of municipalities’ provision degree with financial resources for developing territory’s tourist attraction, single choice, % of the number of respondents
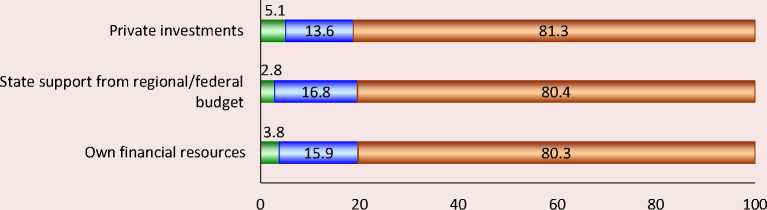
□ Quite enough □ Enough, but not to the full □ Not enough
Source: according to the author’s research results.
Figure 2. Assessment of sufficiency degree of socio-economic resources of the municipality for developing territory’s tourist attraction, % of the number of respondents
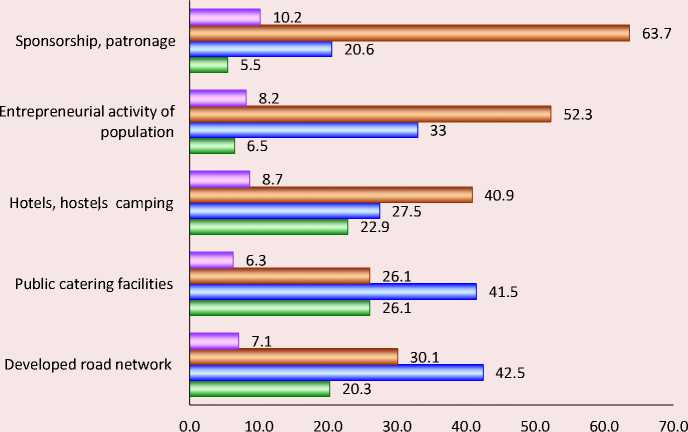
□ Hard to answer в Not enough □ Enough, but not to the full □ Enough
Source: according to the author’s research results.
the reasons for their weak interest, possible areas for integrating the efforts of government and business in the territory’s tourist attraction development, to establish more popular forms of entrepreneurs’ participation in social partnership projects. At the moment, expert assessments allow linking this dysfunction with a weak legal framework and insufficient information support (Fig. 3).
In addition, among the key barriers to the use of social partnership practices in Russian conditions is the complexity of the procedures for approving social partnership projects (64.1%). Shortcomings in development of commercial contracts for partnerships lead to significant dysfunctions and violations of agreements which can trigger negative consequences for both the government and business. Separately, the paper notes that it is difficult to maintain a balance of interests in such areas as commercial success, environmental safety, and compliance with the project implementation deadlines.
Commercial success of government and business partnership projects has been seriously threatened by financial and epidemiological crisis. According to the RBC news agency, the COVID-19 pandemic and the fall in the ruble exchange rate will have a negative impact on more than 340 government and business partnership projects. Representatives of small and medium-sized businesses found themselves in the most vulnerable situation. According to experts, the damage only in the first six months of introduction of quarantine measures will reach 25–30 billion rubles5.
Figure 3. Distribution of answers to the question “Will you indicate the key problems for building partnerships between government and business in projects to develop tourist attraction of Russia’s municipalities?”, multiple elections, % of the number of respondents
Lack of business interest in participating in social partnership projects
Low investment climate of municipalities
Lack of effective support/promotion of social partnership projects in mass media
Gaps in legal framework
Complexity of procedures for approving social partnership projects
Infrastructure projects in tourism sector are mainly focused on large business
Weak population's entrepreneurial activity of municipality
Limited access of investors to information on social partnership projects
Othe r
Difficulty of maintaining a balance between interests of government and business (comercial success, environmental safety, compliance with projects of deadlines, etc.)
Excessive bureucracy of social partnership procedures
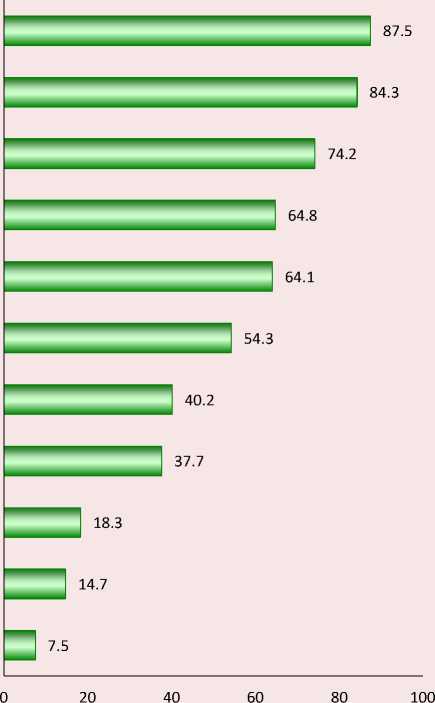
Source: according to the author’s research results.
According to the research results, a special place among limitations of formation and development of social partnership between the authorities and local community is occupied by the weak information promotion of such practices in media (Fig. 4) .
The authors can assume that the problem is related either to the lack of successful projects of social partnership between government and business in the field of tourism, or to the lack of a high level of media interest in covering this topic which correlates with other expert opinions and studies. In particular, a similar position was revealed by the results of monitoring implementation of social projects in Krasnoyarsk conducted by the Agency of Public Initiatives6. According to the Deputy General Director of the Komsomolskaya Pravda Publishing House, R. Karmanov, in order for the interaction based on the principles of social partnership to be
Figure 4. Distribution of answers to the question “Will you indicate whether the following information channels are sufficiently used to promote projects of social partnership between government and business in the field of tourism?”, % of the number of respondents
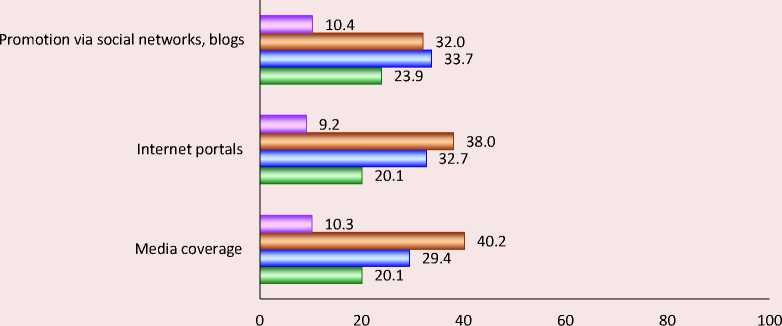
□ Hard to answer □ Not enough □ Enough, but not to the full □ Quite enough
Source: according to the author’s research results.
effective, an intermediary is needed between the media and the participants of social partnership in order to adapt the texts into a structured product that is understandable for media7. Currently, in Russia, the Social Information Agency (SIA) mainly carries out activities to promote social projects. It specializes in covering the topics of NPO, charity, volunteerism, and social responsibility. A special role should belong to the regional and local press which can provide effective information to the public and involve population in the discussion of various issues [26].
According to the results of the analysis of the open question “Will you indicate the key forms/ directions of interaction between government and business in the field of tourism development which, in your opinion, are the most effective/viable in modern conditions” , the following answers received high recognition from experts:
– long-term strategic cooperation with business on the issues of solving specific tasks of developing territory’s tourist potential which, at the same time, do not affect the ownership relations of partners (for example, “service contract”, “agreement on the promotion of a tourist product”);
– business community participation in implementation of programs involving financial support for tourism initiatives, programs with public, private or mixed ownership (for example, “rent of municipal property for tourism purposes”).
Discussion
Social partnership between business and government allows integrating the advantages of the commercial sector (innovation, technical knowledge and skills, organizational efficiency, entrepreneurship) into the territory’s tourist attraction development [27]. The basis for implementing productive cooperation strategies is the ability and willingness of local authorities to form strong working relationships with partners [28], and the resource support of project activities [29].
As the practice of a number of Russian municipalities shows, active policy of local authorities to involve business structures in the local tourism development processes contributes to the growth of representatives’ trust and involvement of local communities in social partnership projects. Active position of local authorities, supported by measures of information promotion, consulting support and informal interaction practices, leads to mobilization of resources of local community in order to develop tourist attraction of municipalities. In conditions of limited municipal budgets, such an approach to social partnership projects is extremely important, as it contributes to the development of private museums and workshops, micro-entrepreneurship, and growth of investment attraction of the territory for larger players in tourist market. A striking example of the effective work of the municipal authorities in this area is the history of Myshkin. Initially, tourist traffic volume in it was small which was due to the lack of necessary tourist infrastructure (accommodation, food, etc.), as well as low brand awareness among potential consumers. Its increase was due to the active involvement of the local community in tourism development: the proportion of local residents in relation to tourists was established at 1:34 which provided a multiplier effect for the territory’s development8.
The presented practice of the tourism industry development within the borders of a small town indicates that a municipality that does not have a rich cultural heritage can become an object of tourist display due to the concentration of efforts on the part of local authorities to create a brand of the territory and actively promote it. Having your own brand for municipalities can make them attractive to tourists, will help to activate the initiatives of the local community and integrate them into the territory’s development. At the same time, tourism should be one of the priorities in the municipality’s development strategy which will not only ensure a steady tourist flow, but also increase the municipality’s investment attraction.
At the same time, positive practices of business participation in the development of tourism at the municipal level are usually limited, implemented in the form of projects of municipal-private partnership between 2–3 participants on the basis of concession agreements with an average implementation period of 30 years. Examples are such projects as “Reconstruction and Further Use of the Property Complex for Recreation Facilities” (Belgorod, Lipki tract), “Reconstruction of the Object for Realizing Activities in the Field of Tourism” (Cherepovets, Vologda Oblast), “Reconstruction and Operation of the Object “Health and Recreation Center “Nizhnekamsk Baths” (Nizhnekamsk, Republic of Tatarstan), etc.
The results of the research have proved that the municipalities’ financial capabilities determine the boundaries and potential for implementing interaction projects between business and government. On the one hand, the low level of financial security of local budgets does not allow local governments to have a sufficient economic base to act as a potentially attractive partner for business. On the other hand, due to the existence of financial problems in municipalities, the formation of organizational mechanisms for supporting joint projects with business is not fully ensured. Sufficiency of human resources in local administrations determines the effectiveness of information and consulting assistance to business, the timely prevention and regulation of conflict risks of joint activities. This conclusion is supported by international studies. I. Marques argues that the differences in the administrative capabilities of regional and local governments explain the uneven development of public-private partnership projects. Strong administrative capacity, political responsibility, and provision of resources (human and financial) for management practices are important [16]. Russian municipalities are characterized by the following problems of staffing: restrictions on the number of employees of local administrations, the lack of a significant number of municipal employees of specialized education, insufficient legal and economic training [30]. These dysfunctions do not allow municipal employees to initiate and support joint projects with businesses in a timely manner, and to provide adequate consulting assistance, especially in conditions of fairly high legal uncertainty.
In Russia, there is a noticeable level of municipalities’ differentiation according to the level of profitability of local budgets. Large urban settlements have a strong position and proximity to the administrative centers also ensures the territory’s investment attraction.
The results of the study have showed that the majority of municipalities have difficulties in providing financial support for even basic powers related to the life support of population. As a result, in many municipalities of the Russian Federation, there is practically no system for monitoring business problems, and no diagnostics of the effectiveness of implemented measures and programs to support business sector is carried out [15]. The lack of human and financial resources puts rural settlements and small towns of the Russian Federation in a vulnerable position, and limits their initiatives to develop partnerships with business.
At the same time, small and medium-sized towns have municipal property that is not always used effectively. This resource, as a rule, remains not involved in social partnership projects. At the same time, “empty” objects of municipal infrastructure can be provided to investors on preferential terms in order to create new tourist points of attraction (museums, art spaces, etc.). One of the examples of such successful cooperation between government and business is the project of social entrepreneurship museum “Kolomenskaya Pastila” which is a part of the museum and creative cluster “Kolomenskii Posad”. This project’s implementation allowed not only preserving the town’s cultural heritage, but also strengthening the territory’s brand, to develop such new areas as gastronomic tourism and creative industries. The creation of a technical library and a museum of the machine tool with the history of the Tula industry made possible only through the use of empty areas of the Oktava plant. As a result, this project contributed to preservation and popularization of the town’s industrial heritage and became a new object of tourist display.
The active use of municipal property in tourism industry development will allow creating museum and tourist clusters. As a result, it will be possible to develop cultural and educational tourism by attracting all interested parties: local governments, investors and local community which will contribute to the formation of social partnership. In specific tourist destinations, management of such clusters will ensure a stable tourist flow and formation of a comfortable tourist environment.
The research results have proved that the lack of additional financial opportunities for local authorities does not allow for an effective municipal policy aimed at interacting with business in tourism sector. The problems are related to the narrow range of variability of management actions in determining priority areas of budget spending, and high dependence of local self-government on regional and federal authorities. The findings are supported by other studies. The formation of a polycentric management system and growth of the municipalities’ authority ensure sustainable socioeconomic development of the territories improving population’s quality and living standards of, and entrepreneurial activity [31; 32]. The provision of local autonomy is considered as a guarantor of implementation of strategic goals for the territory’s development, implementation of local tasks [33].
The limitations of implementing social partnership projects in the field of tourism are the information vacuum on the issues under consideration in the mass media, the established stereotypes of the unprofitability of these projects. In modern conditions, the involvement of business in solving issues of socio-economic development of the territory does not provide sustainable reputational benefits. A possible way out of this situation is to focus the efforts of municipalities on ensuring information openness of business and government interaction strategies, providing wide access to information for potential investors, and large-scale coverage of upcoming projects in the regional and municipal press. No less important is the targeted development of participation models with potential investors. Consulting support should include an analysis of investment risks, working out mechanisms for reducing them, lending models, and attracting additional participants. Public support for entrepreneurial activity in the tourism sector is considered as a driver for the implementation of successful strategies of social partnership between government and business. The increase in the reputational benefits of entrepreneurs involved in the development of local tourist products and services, construction and operation of tourist infrastructure facilities can be achieved through the coverage of their activities in local press, recognition, and moral incentives.
Conclusion
The severity of Russia’s traditional socioeconomic problems and relatively low living standards in most municipalities do not allow the municipal authorities to focus on developing tourism industry as a whole. In view of this circumstance, we conclude that institutional environment for developing social partnership practice in the field of tourism is at the stage of formation.
The heads of municipalities note the following barriers to the formation of partnerships with business to develop tourist attraction of Russia’s territories:
– financial: insufficient own financial resources of municipalities, low level of state support from the regional/federal budget, lack of private investment;
– legal: gaps in legal framework, confusing procedures for approving social partnership projects, shortcomings in development of commercial contracts for partnerships, violation of agreements;
– organizational: difficulty of maintaining a balance of interests in such areas as commercial success, environmental safety, compliance with the project implementation deadlines, the lack of qualified municipal personnel, excessive bureaucracy inherent in the authorities, information closeness of the authorities and the lack of effective support for the practices of social partnership between government and business in the media. There is a low level of trust between the government and business, and the lack of interest among entrepreneurs in participating in social partnership projects.
To boost tourism activity at the municipal level, tourism should be one of the priority areas in the municipalities’ development strategy. Local authorities should participate in the formation of tourist products and creation and promotion of the territory’s brand which will help both attract private investors and increase the activity of the local community. In addition, the creation of project offices for tourism development at the municipal level can serve as a catalyst for promoting the territory’s tourist potential and attracting business to the projects’ implementation in this area.
In a crisis, the formation of museum and tourist clusters on the municipalities’ territory can help strengthen partnership of local governments, business and public. The cluster approach in tourism industry development will provide a multiplier effect. The joint use of tourism resources, the presence of common priorities, cooperation and collaboration between all the cluster subjects will contribute to the formation of trust between them.
The table systematizes measures to overcome barriers of social partnership between government and business in tourism sector. The financial insufficiency of local budgets actualizes organizational measures that do not incur serious costs. Overcoming legal barriers requires in-depth study of the regulatory framework and development of legislative initiatives which can be the subject of separate scientific research.
Increasing the level of business interest in participating in social partnership projects involves implementation of a number of proposals. Based on the analysis, the authors consider it appropriate to conduct a targeted information policy which would include the creation of a single information portal that consolidates information about potential and ongoing social partnership projects, a database of successful practices and feedback from direct participants in project work. It is also possible to prepare information events and their coverage in the media; formation of information content about social partnership projects and its broadcasting in the form of social advertising, outdoor advertising, etc. The elimination of the information vacuum will allow business structures to determine the limits of possible participation in social partnership projects. The next proposal is to improve the procedure for legal advice to representatives of business structures including legal support for business in social partnership projects. This approach will help to increase the confidence level of the commercial sector in social partnership projects, as well as openness and transparency of the legal framework for organizing partner projects. On the basis of the
Measures to overcome barriers of social partnership between government and business in the field of tourism
|
Barriers |
Measures |
|
Organizational |
Concentration of the municipalities’ efforts is on ensuring the information openness of the strategies of interaction between business and government, providing wide access to information for potential investors, and large-scale coverage of upcoming projects in the regional and municipal press; consulting support by municipalities for representatives of business community to participate in social partnership projects including through creation of project offices and involvement of qualified specialists in this field; implementation of a system for monitoring business problems, diagnostics of the effectiveness of business sector support programs; media coverage of the activities of entrepreneurs involved in development of local tourist products and services, construction and operation of tourist infrastructure facilities. |
|
Financing |
Activation of using municipal property, provision of infrastructure facilities to investors on preferential terms in order to create new tourist points of attraction; creating museum and tourism clusters |
|
Legal |
Improving legal framework and procedures for approving social partnership projects; inclusion of directions/projects of social partnership in tourism in local regulations/legislative initiatives of local authorities. |
|
Source: own calculations. |
|
above proposals, it is expected to increase business interest level in participating in social partnership projects.
In the conditions of limited financial resources of most municipalities, the effective use of municipal property can become a resource for increasing business interest in social partnership projects. Its application on the principles of the economy of cooperation will attract additional investors who can not only create new objects of tourist display, but also preserve the cultural heritage of the territory. At the same time, information support is of particular importance. On the part of the authorities, it is necessary to more actively carry out activities to create Internet portals and communication platforms that can bring together all interested parties to develop tourist attraction of Russian territories. Popularization of tourist destinations of municipalities in social networks, as well as through the Internet technologies, will provide an opportunity to ensure the competitive advantages of the territory for developing its tourist attraction.
Thus, the presented directions for improving the activities of local self-government authorities will create the necessary conditions for the formation of the municipalities’ tourist attraction on the basis of social partnership.
Список литературы Limitations of social partnership between authorities and business in forming tourist attractiveness of municipalities of the Russian Federation
- Kvashnina E.B. Method of estimation the multiplier effect of investments in the tourism industry in the region. Izvestiya Sankt-Peterburgskogo gosudarstvennogo ekonomicheskogo universiteta=Izvestiâ Sankt-Peterburgskogo Gosudarstvennogo Èkonomičeskogo Universiteta, 2012, no. 2 (74), pp. 70–73 (in Russian).
- Kryukova E.M., Khetagurova V.SH. Cluster approach in the development of social tourism in Russia. Contemporary Problems of Social Work, 2019, vol. 5, no. 4 (20), pp. 4–14.
- Higgins-Desbiolles F. Socialising tourism for social and ecological justice after COVID-19. Tourism Geographies, 2020. DOI: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1757748
- Jang Y., Lee W.J., Hadley B. Interactive effects of business environment assessment and institutional programs on opportunity entrepreneurship. Sustainability, 2020, no. 12 (13). DOI: 10.3390/su12135280
- Remington T.F., Yang P. Public-private partnerships for skill development in the United States, Russia, and China. Post-Soviet Affairs, 2020, no. 36 (5-6), pp. 495–514. DOI: 10.1080/1060586X.2020.1780727
- Yang A.M., Liu W.L., Wang R. Cross-sector alliances in the global refugee crisis: An institutional theory approach. Business Ethics-A European Review, 2020, vol. 29 (3), pp. 646–660. DOI: 10.1111/beer.12288
- Broegaard R.B. Rural destination development contributions by outdoor tourism actors: A Bornholm case study. Tourism Geographies, 2020. DOI: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1795708
- Ly T.P., Zhang C.Z. Why public-private cooperation is not prevalent in national parks within centralized countries. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 2019, no. 24 (12), pp. 1109–1125. DOI: 10.1080/10941665.2019.1666154
- Beynon M.J., Jones P., Pickernell D., Huang S.F. Growth and innovation of SMEs in local enterprise partnerships regions: A configurational analysis using fsQCA. International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation, 2020, no. 21, vol. 2, pp. 83–100. DOI: 10.1177/1465750319846827
- Gonzalez-Morales O., Talavera A.S. CSR as a strategy for public-private relationships in protected island territories: Fuerteventura, Canary Islands. Island Studies Journal, 2019, no. 14 (1), pp. 147–162. DOI: 10.24043/isj.83
- Androsova I.V., Melnichuk A.V., Bondaletov V.V., Vinichenko M.V., Duplij E.V. On the issue of state support of agriculture: Regional aspect. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 2016, no. 6 (S1),pp. 114–119.
- Rogach O.V., Frolova E.V., Ryabova T.M., Morozova L.S., Litvinova E.V. Management of potential tourist development of municipalities in Russia. International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences, 2020, vol. 7, no. 8, pp. 43–52. DOI: 10.21833/ijaas.2020.08.006
- Medvedeva N.V., Frolova E.V., Rogach O.V., Ryabova T.M. Public participation in shaping the tourist attractiveness of Russian territories at the turn of the XIX-XX centuries. Bylye Gody, 2019, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 838–847. DOI: 10.13187/bg.2019.2.838
- Qi S., Nguyen D. Government connections and credit access around the world: Evidence from discouraged borrowers. Journal of International Business Studies. DOI: 10.1057/s41267-020-00341-x
- Kusakina O.N., Trukhachev V.V. Organizational and functional architectonic coordination mechanism of power and business structures interaction at the regional and municipal levels. Terra Economicus, 2012, no. 10 (3-3), pp. 135–139 (in Russian).
- Marques I., Remington T., Bazavliuk V. Encouraging skill development: Evidence from public-private partnerships in education in Russia’s regions. European Journal of Political Economy, 2020, vol. 63. UNSP 101888. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpoleco.2020.101888
- Volokhova N. Government and business interaction in Eastern Europe: Specific features of the pubicprivate partnership. Economic Annals-XXI, 2020, vol. 180, no. 11-12, pp. 31–39. DOI: 10.21003/ea.V180-04
- Kiselev V.I. Cooperation of business and power: conflict resolution aspect. Teoriya i praktika obshchestvennogo razvitiya=Theory and Practice of Social Development, 2013, no. 7, pp. 174–178 (in Russian).
- Roy O.M. Business and government: Interaction strategies. Vestnik Omskogo universiteta. Seriya «Ekonomika»=Herald of Omsk University. Series «Economics», 2019, no. 3, pp. 150–160 (in Russian).
- Huang C., Yi H.T., Chen T., Xu X.L., Chen S.Y. Networked environmental governance: Formal and informal collaborative networks in local China. Policy Studies, 2020. DOI: 10.1080/01442872.2020.1758306
- Gomilevskaya G.A. Practical aspects of budget funding tourist infrastructure (on example of Primorye territory). Azimut nauchnykh issledovanii: ekonomika i upravlenie=ASR: Economics and Management, 2016, vol. 5, no. 4 (17), pp. 118–122 (in Russian).
- Prazdnikova N.N., Prudnikova N.G., Strizheva O.S. Analysis of tourism development in the Altai region. Vestnik Altaiskogo gosudarstvennogo agrarnogo universiteta=Bulletin of Altai State Agricultural University, 2017, no. 9 (155), pp. 53–60 (in Russian).
- Guseva M.S., Amel’kina D.V. Interaction of the state and business in the development of domestic and inbound tourism. Ars Administrandi (Iskusstvo upravleniya), 2017, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 217–236. DOI: 10.17072/2218-9173-2017-2-217-236 (in Russian).
- Maksanova L., Bardakhanova T., Ayusheeva S. A Toolkit for Assessing the Use of Public-Private Partnerships in Tourism. 2019. DOI: 10.2991/icsdcbr-19.2019.196
- Magomedova N.I. Aspects of public-private partnership in tourism of the Russian Federation in the sanctions. UEPS: upravlenie, ekonomika, politika, sotsiologiya=UEPS: Management, Economics, Politics and Sociology, 2016, no. 3, pp. 42–49 (in Russian).
- Dzyaloshinskii I. Civil communications and civil society. Biznes. Obshchestvo. Vlast’=Business. Society. Power, 2010, no. 4, pp. 143–197 (in Russian).
- Wong E. L.Y., Yeoh E., Chau P. Y.K., Yam C. H.K., Cheung A. W.L., Fung H. How shall we examine and learn about public-private partnerships (PPPs) in the health sector? Realist evaluation of PPPs in Hong Kong. Social Science & Medicine, 2015, p. 147.
- Ollerenshaw А., Murphy А., McDonald К. Leading the way: The integral role of local government within a multisector partnership delivering a large infrastructure project in an Australian growth region. Local Government Studies, 2017, vol. 43, is. 2, pp. 291–314. DOI: doi.org/10.1080/03003930.2016.1274259
- Frolova E.V., Rogach O.V., Ryabova T.M. Tourism attraction in Russian regions in cyberspace: New tendencies of tourism media marketing. Humanities and Social Sciences Reviews, 2019, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 1313–1318.
- Frolova E.V., Rogach O.V. Staffing of local authorities in modern Russian conditions. Monitoring of Public Opinion: Economic and Social Changes Journal (Public Opinion Monitoring), 2018, no. 4, pp. 369–385. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14515/monitoring.2018.4.19
- Jones G., Stewart J. Local government: The past, the present and the future. Public Policy and Administration, 2012, vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 346–367.
- Nared J. Local Self-government reforms in Slovenia: Discourse on centrality and peripherality. In: Pelc S., Koderman M. (eds) Nature, Tourism and Ethnicity as Drivers of (De)Marginalization. Perspectives on Geographical Marginality, 2018, vol. 3, pp. 243–256. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59002-8_17
- Fábián A. Local self-government in Hungary: The impact of crisis. In: Nunes Silva C., Buček J. (eds) Local Government and Urban Governance in Europe. Springer, Cham, 2017. Pp. 71–87. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-43979-2_4


