Methods for analyzing economic and social development of smart cities
Автор: Popov Evgeny V., Semyachkov Konstantin A.
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Development of science, technology and innovation
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.15, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The purpose of the study is to develop a typology of methods for analyzing economic and social development of smart cities. Having reviewed the works indexed in the global database Web of Science Core Collection we selected one and a half hundred articles on economic problems of smart cities development published in 2015-2021 and available in the public domain. We identify various methods for analyzing economic and social development of smart cities, differentiate them using the method of describing the objects under consideration (static and dynamic) and the method of model description (tables, diagrams, matrices, graphs). Static methods include methods for assessing ecosystem characteristics, input-output analysis, development diagrams, data ecosystems coordination analysis, assessment of the ecosystem for elderly residents. Dynamic methods include the Value Creation - Value Capturing matrices, stimulating management elements, “digital ecosystems - entrepreneurial ecosystems”, graphs showing the life cycle of the smart city ecosystem, evolution of civil ecosystems, stage-by-stage digital transformation, dynamic opportunities for innovation and the quadruple helix. We show the applicability of methods for analyzing the development of smart cities for various territories. We present our own results of assessment of the development of smart cities in Moscow, Yekaterinburg, Oslo, Singapore based on the 7I-model (infrastructure, institutions, intranet, integration, interfaces, innovations, implementation). Theoretical significance of the results obtained consists in the development of a theory of ecosystem analysis related to assessing the formation of smart cities; practical significance of the results lies in the development of applied tools for strategic planning in the field of smart city project development.
Smart cities, analysis methods, static methods, dynamic methods, tables, diagrams, matrices, graphs
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147238034
IDR: 147238034 | УДК: 332.1 | DOI: 10.15838/esc.2022.2.80.7
Текст научной статьи Methods for analyzing economic and social development of smart cities
The development of digital technologies and their applications has led to the formation of a qualitatively new landscape of economic and social changes in the development of human society. Against this background, there was a rapid development of smart cities (Popov, Semyachkov, 2020). Smart cities mean urban settlements in which the use of digital technologies leads to significant economic and social development providing a significant increase in the citizens’ well-being.
The exponential growth of relevant scientific publications, indexed in global databases, demonstrates the researchers’ growing interest in the topic of analyzing the economic and social development of smart cities. At the same time, until now, the analysis methods of the development of such objects of the digital economy have not received a systematic presentation.
In this regard, the purpose of our research is to design a typology of the analysis methods of economic and social development of smart cities. The algorithm of such a study should include an assessment and criticism of previous works, issue formulation, solving the typologization issue of methods for analyzing the economic and social development of smart cities, discussion of the results obtained and demonstration of the applicability of the selected analysis methods.
It is advisable to evaluate previous studies on the economic and social development of smart cities within the framework of ecosystems of urban formations. By the early 2020s, it became clear that the network paradigm of economic relations does not describe the entire landscape of economic interactions. The introduction of digital technologies stimulated the development of economic activity taking into account not only partners, consumers, suppliers and competitors, but also the influence of public organizations, authorities and social media. The paradigm of ecosystem analysis of the economy began developing, the first works on which appeared at the end of the 20th century.
The ancestor of the term “ecosystem” in relation to the economy is considered to be J. Moore. He defined ecosystem as “an economic community supported by a basis of interacting organizations and individuals” (Moore, 1997). The analysis of urban ecosystems involves the assessment of all individuals and organizations interested in relations with these settlements.
Smart city ecosystems
During the formation of smart cities, the development of human-oriented sustainable ecosystem of the urban area takes place. This leads to a better world with improved human well-being, with better cities emphasizing the importance of education and science, promoting wisdom and common sense, rejecting violence. On this side, digital technologies provide successful basis for developing modern society (Bliss et al., 2021). On the other hand, urbanization of the second half of the 20th century contributed to the decline of cities as places of economic value creation. Suburbanization, first of residential buildings and then of industry, led to the devastation and, in some areas, destruction of urban life. In the first half of the 21st century, cities began reviving as innovation engines. This renaissance is an organic response to the digital technology adoption (Engel et al., 2018).
Smart cities are known as systems of material infrastructure, digital technology infrastructure and social infrastructure that exchange information flowing between its numerous subsystems. The built-in infrastructure of digital technologies in smart cities plays a crucial role in the functioning of the entire system. The most important derivative of digital technologies is new communication means, known as social network services, which provide smart cities with additional opportunities (Hajikhani, 2020). Social network services, in turn, contribute to the formation of digital social innovations that use the potential of digital technologies to jointly solve problems in a wide range of social needs (Certoma, 2020).
We should note that digital technologies and solutions, based on the principles of sustainable development, can make cities smarter representing a new technological portfolio for the biodiversity conservation and the provision of a range of ecosystem services, facilitating the necessary adaptation to climate change which cities should give priority to in order to ensure their sustainability
(Colding et al., 2020). The results indicate a spatial interdependence between environmental and socioeconomic processes in urban environments which provides a unique basis for planning strategies and policy intervention in the development of smart city ecosystems (Hazell, 2020). What is the structure of smart city ecosystems?
Since traditional organization models are of little use for smart cities, their structure is based on network, cross-border systems of activity with distributed innovation processes and adaptive policy formation. In this case, five key dimensions can be defined in the configuration fields of smart cities which are displayed in five organizational structures: actors, urban subsystems, activity levels, rules of activity of actors at various activity levels, institutional support for this activity (Pierce et al., 2017). It is necessary to develop active strategies for smart territories including strengthening smart clusters, creating a management ecosystem and providing integrated services that provide hybrid strategies for upstream and downstream design approach to planning for the development of smart cities (Yuan et al., 2020). With regard to smart cities, three key characteristics of growing business and the ability to occupy leading positions can be distinguished: joint creation through the integration of resources and the exchange of services is preferable to meet the market needs; the digital platform is critical for creating the necessary knowledge for the integration of resources and the exchange of services; intelligent services combine the city’s ecosystem and the digital platform and create a result that solves a specific business problem. In other words, all three elements of a smart city – ecosystem, platform and intelligent services – create a single environment in which it is possible to develop business in a new emerging market (Pulkkinen et al., 2019).
Cities are becoming experimental sites for new forms of robotics and automation technologies, used in a wide variety of sectors in all areas of economic and social life. Robotics and automation systems are superimposed on existing urban digital networks expanding the capabilities of infrastructure networks, as well as changing the everyday experience of the city and citizens (Macrorie et al., 2021). The Internet of Things, as a component of smart urbanism, is also used to solve the smart city issues. Internet of Things technologies reconfigure connections between users, suppliers and water and energy infrastructures which ensures reliability in economic activities (Chambers, Evans, 2020).
At the same time, citizens’ trust in a smart city is fundamental for its transparency, residents’ participation in management and entrepreneurial initiatives, and therefore for its economic growth. In this case, blockchain technology provides the most important level of trust in a smart city. The blockchain technology value for smart cities can be represented in three positions: network impact on trust in society, government authorities and manufacturing enterprises; empowering individuals and strengthening the economy; liquid and shared economy (Kundu, 2019).
Big data analytics and artificial intelligence, combined with blockchain technology and the Internet of Things, as well as other new technologies are revolutionizing urban governance. Thanks to the huge amounts of data, collected from citizens, digital devices and traditional information sources, urban areas for the first time in history have the ability to manage urban infrastructure in real time (Engin et al., 2020). How is the smart city ecosystem managed?
Fragmented management of smart city digitalization reduces the scale of economic activity and leads to incompatibility of interdisciplinary data which limits the planning sequence and open data benefits (Kitchin, Moore-Cherry, 2020). In this case, Big Data application strategies transform the activities of city governments so that they become more focused on meeting the citizens’ needs (Lee, 2020).
Smart city ecosystem management relies on regulatory, supportive, and cognitive economic institutions. At the same time, in various smart cities (for example, Amsterdam, Hamburg and Nimbo), combination of strategic management and the dynamics of the use of these institutions differs on a spatial scale to take into account local features (Raven et al., 2019).
In smart cities, a transition to sustainable development is possible for the circular economy, based on the rational management concept, i.e. combination of cooperation and competition. In this case, it is necessary to support intelligent technologies that develop digital society (Hirvensalo et al., 2021). Smart city management can take place at the following levels (for example, Dublin): local authorities – steering committee – advisory network – smart city management group – local working groups (Coletta et al., 2019). But the most interesting topic of any research is the analysis of the development of smart cities. What are the prospects for such development?
The sustainable development issue is also important in the context of the problems faced by modern cities. Three fundamental pillars of sustainable development: economic growth, environmental management and social integration are manifested in all economic sectors. They mainly affect cities, rapid urbanization process, and the development of infrastructure, energy and transport. City authorities are planning and acting toward a more sustainable future characterized by investments in innovative, integrated technologies and services such as smart buildings, population mobility, controlled lighting and broadband (Derlukiewicz, Mempel-Sniezyk, 2018).
In 2016, the Government of Japan unveiled an initiative and a call to action to introduce a “super smart society”, announced as Society 5.0. The stated goal of such a society is to meet the various needs of its members by providing goods and services to those who need them, when they are required and in the required quantity, which will allow citizens to lead active and comfortable life. In this case, the intellectual community should be defined as a human-oriented organization where technologies are used to provide citizens with information and services that they can use to justify their decisions. Such a perspective may be one of the directions for the development of smart cities (Iqbal, Olariu, 2021).
The determinants of the development of smart cities are internal factors, related to the citizens’ involvement in digitalization projects, authorities’ leadership and formation of the necessary infrastructure, as well as external factors, based on the political will of decision makers, the interest of various parties and the influence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In addition, it is necessary to have communication channels and public hearings (Myeong et al., 2018).
Urban “living laboratories” are used to develop new products, based on distributed knowledge as a driving force for sustainable innovation. In laboratories, innovative ideas converge in developing an experimental framework of various stakeholders that structures mechanisms and practices within dynamic collaborative ecosystems and defines boundary conditions for such open ecosystems (Robaeyst et al., 2021).
Evaluation of the previous studies demonstrates various analysis methods of smart city ecosystems.
However, there is currently no systematization of these methods, whereas a systematic analysis of the development of smart cities requires a targeted approach to such assessments. Hence, there is a problem associated with the need to develop a typology of the methods for analyzing economic and social development of smart cities.
Research procedure
The research object is the smart city ecosystems. The subject of the study is economic and social relations in their development. The information base is the world database Web of Science Core Collection, in which one and a half hundred articles, published in 2015–2021 and in open access, were selected according to the keywords “Smart City Ecosystem” in the titles and annotations. The research method is logical hierarchical analysis.
After a critical analysis of the previous studies and formulation of the problem, we have identified various analysis methods of the economic and social development of smart cities for study. The differentiation of the selected methods was carried out by the method of describing the objects under consideration (static and dynamic) and by the method of model description (tables, diagrams, matrices, graphs). In this case, tabular and diagrammatic methods of description were attributed to static methods of analysis, and matrix and graphical modeling – to dynamic ones (Popov, 2020). As a result, we have obtained a typology of methods for analyzing the development of smart cities.
Typology of methods for analyzing the development of smart cities
The data obtained as a result of the study are summarized in a Table .
Application of methods for analyzing the development of smart cities
The results of the data analysis in the table demonstrate a wide range of possible methods for analyzing the development of smart cities and the geography of application of these methods.
Methods for analyzing the development of smart cities
|
Description method (modeling) |
Name of the method |
Method content |
|
Static (tables) |
Assessment of ecosystem characteristics |
Assessment of the content of three ecosystem characteristics: marketing (user perspective is emphasized), strategic management (the reasonableness concept is used to attract stakeholders for decision-making purposes), technology (the use of artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, machine learning with data analysis to provide smart services) (Ruohomaa et al., 2019) |
|
Input-output analysis |
Analysis of the mutual correlation of costs and output in nine industries: agriculture, mining, traditional production, IT production, construction, energy, IT services, information services, traditional services, etc. (Jo et al., 2021) |
|
|
Static (diagrams) |
Development diagram |
Expert assessment in four areas: development strategy, digital technologies (capacities, data, technological experiments), management (security, vertical and horizontal scales), stakeholders (funding, stakeholder values) (Hamalainen, 2020) |
|
Data ecosystem coordination analysis |
Three coordination elements in smart city data ecosystems: openness (technological, organizational), dissemination (knowledge mobility, trust building), common vision (management tools, central coordination structures) (Gupta et al., 2020) |
|
|
Ecosystem assessment for age-related residents |
Expert evaluation of eight city indicators: housing conditions, urban environment, transport, social engagement, social participation, information communications, health, employment (work) (Marston et al., 2020) |
|
|
Dynamic (matrices) |
“Value Creation – Value Capturing ” |
Four business models: “glass balls” (all is individually); “tetris” (values are created individually, but profitable models occupy part of the ecosystem); “janga” (ecosystem actors study each other with limited income potential for each); “puzzles” (synergy within the ecosystem for the greatest value for consumers) (Brock et al., 2019) |
|
Stimulating controls |
Evaluation of stimulating controls (transformational leadership, cooperative strategies, goal setting) and hindering controls (lack of expectation management) at the initial stage of smart city formation; during the growth phase, stimulating elements (transactionalleadership, creative strategies, performance measurement, promotion organization) and hindering elements (lack of leadership, lack of goal setting, lack of focus on communications) (Ooms et al., 2020) |
|
|
“Digital – entrepreneurial ecosystems” |
Four digital entrepreneurial ecosystems: digital infrastructure management (infrastructure institutions); citizens› digital technologies (user institutions); digital entrepreneurship (digital infrastructure agents); digital market (user agents) (Gorelova et al., 2021) |
|
|
Dynamic (graphics) |
Ecosystem life cycle |
Assessment of various phases of city development: integration of innovations, integration of functions, financial management, project management – City 1.0 – understanding of ecosystem evolution, development and adjustment, sustainable city, integration of innovations – City 2.0 – continuous improvement (Rochet, Correa, 2016) |
|
Evolution of civil ecosystems |
The analysis of the evolution of innovative ecosystems (living laboratories and knowledge integrators) is carried out in the space of an “organizational field” that includes the private sector, scientific and educational sector, public sector and citizens (Claudel, 2018) |
|
|
Digital transformation stages |
Assessment stages: vision and concepts – digital ecosystem of smart city area – dissemination (through hackathons) and events (Elberzhager et al., 2021) |
|
|
Dynamic innovation opportunities |
Expert assessment of dynamic opportunities for ecosystem innovation: ecosystem sensing (screening capabilities, partner exploration), ecosystem utilization (value development proposals, ecosystem formation), ecosystem reconfiguration (creation of adaptive values, ecosystem resilience) (Linde et al., 2021) |
|
|
Quadruple helix |
Development assessment of the four sides of a smart city: civil society, private business sector, public sector management, scientific and educational sector (Paskaleva et al., 2021) |
The method of assessing ecosystem characteristics (Ruohomaa et al., 2019) was implemented in the study of small towns in Finland (Hamenlina, Riihimaki, Forsa). The research shows that a relatively small city can take significant steps in the development of smart city technologies by choosing a specific topic for organizing events on its territory. Examples of the implementation of smart city technologies highlighted the importance of public sector entities which play a key role in creating the foundations for fruitful work on the development of smart territory ecosystems.
The input-output analysis (Jo et. al., 2021) was applied to assess smart city ecosystems in Korea. For comparative analysis, data from the Bank of Korea from 1960 to 2015 were used. The study has found that smart industries such as smart buildings and smart transportation systems are anchor industries in Korean smart cities and positively correlate with three other industries: IT manufacturing, IT services and information services. The results of the analysis show that the traditional industrial structure of labor-intensive production has been transformed into developing high-tech industries. Smart industries such as IT manufacturing, IT services and information services have led to sustained national economic growth with greater added value than other industries. Consequently, intellectual industries become anchor industries that create value chains of new industries, acting as accelerators or incubators for their development.
In relation to the smart city of Helsinki, the capital of Finland, the method of the development diagram (Hamalainen, 2020) was applied; the main directions for the implementation of initiatives for the formation of smart territories were identified. Using the example of London, the capital of the United Kingdom, the study was carried out by the method of data coordination ecosystem analysis (Gupta et al., 2020). The problems faced in complex urban data environments by the authorities, involved in such ecosystems and coordinating data collection initiatives from the point of view of their organization, are identified. The need to apply flexible approaches in order to develop initiatives for the formation of smart territories is also shown on the example of London. For this purpose, the ecosystem assessment method for age-related residents was used (Marston et al., 2020).
The introduction of Philips Lighting digital technologies in the cities of the Netherlands served as a testing ground for the Value Creation – Value Capturing matrices (Brock et al., 2019). The research highlights various business models that allow existing organizations to enter the structure of smart cities. Stimulating and hindering control elements for the development of smart cities are also analyzed using the example of the Netherlands (Ooms et al., 2020). The authors have found that the use of specific control elements varies depending on the evolution stages of the smart city ecosystem. At the initial stage, the key ones management structures, aimed at strengthening internal relations. At this stage, elements such as trust and commitment to common goals are important. During the growth phase, the ecosystem focuses on establishing external relationships with other parties, such as competitors and suppliers. At this stage, the control elements, such as a collaborative creative strategy and a special organization for promotion, become important because they facilitate communication with the outside world.
The analysis of European cities on the six main components of smart cities: smart people, smart management, smart economy, smart housing environment, smart environment, smart transport – was carried out on the basis of the matrix “digital ecosystems – entrepreneurial ecosystems” (Gorelova et al., 2021). The research shows that digital entrepreneurial ecosystems are an integral part of any smart city.
Using the example of Washington, the US capital, Singapore and a number of French cities, the applicability of the smart city ecosystem life cycle method for analyzing to assess its development is demonstrated (Rochet, Correa, 2016). Based on the life cycle, it is possible to determine the tasks that the integrator of the functions that make up the smart city should perform. The conducted research determined that the role of the integrator of functions should be played by public administration.
Amsterdam, Barcelona, Copenhagen acted as platforms for the application of the analysis of the evolution of civil innovation ecosystems (Claudel, 2018). The paper proves that the development of living laboratories and innovation integrators leads to the formation of information hubs, which act as a “niche” that promotes radical innovations and new processes. As these prototypes are increasingly deployed and adopted, there is a change in the innovation regime, creating a new culture of experimenters. For example, urban living laboratories can evolve into urban experimental platforms (Rehm et al., 2021).
The assessment of the digital transformation stages (Elberzhager et al., 2021) was carried out on the example of smart cities in Germany. In this case, we have to look for new ways to identify the needs and requirements for digital solutions, not yet knowing the citizens who will live in the new areas. Consequently, the assessment of the stages of digitalization is a possible strategy for the formation of a digital society. Note that such strategies can be formed on the basis of digital urban-scale counterparts (Nochta et al., 2021).
The analysis of dynamic opportunities for the innovation ecosystem (Elberzhager et al., 2021) was carried out in the study of smart cities in Sweden. Based on numerous interviews, three coordination mechanisms have been identified for organizing innovation in ecosystems: setting up partnerships in ecosystems, deploying value propositions, and managing ecosystem coordination.
To analyze the development of Manchester (UK), Eindhoven (the Netherlands) and Stavanger
(Norway), the method of estimating the quadruple helix was used (Paskaleva et al., 2021). The study shows that the involvement of the quadruple helix stakeholders in the joint assessment of activities increases the ability of projects to ensure and measure the impact of digital technologies and applications which is important for cities and citizens.
We have previously proposed a method of phasing digital transformation of smart cities, developed a scheme of seven successive levels in the development of smart cities: engineering infrastructure (Infrastructure), institutes (Institutions), communication and communications systems (Intranet), data integration (Integration), interaction of users and technical systems (Interfaces), innovations (Innovations), application innovations in smart city components (Implementation) (Popov, Semyachkov, 2020). The superimposition of the 7I-model on the six main components of the smart city development made it possible to obtain a matrix of the smart city development indicators which makes it possible to compare different territories with each other (Popov, Semyachkov, 2021).
For example, Figure 1 shows a comparison of the use of digital technologies in various cities studied.
The data in Figure 1 demonstrate close development of various cities in the direction of the household’s digitalization.
On the other hand, the data, presented in Figure 2, demonstrate a sharp difference in digital technologies for accounting for utility needs in cities that have the characteristics of a smart city.
Thus, the use of various methods for analyzing the economic and social development of smart cities allows creating a basis for making management decisions on the strategic formation of such territories.
The scientific novelty of the conducted research lies in the typologization of methods for analyzing
Figure 1. Use of digital technologies in the household in Moscow, Yekaterinburg, Singapore, Oslo, %
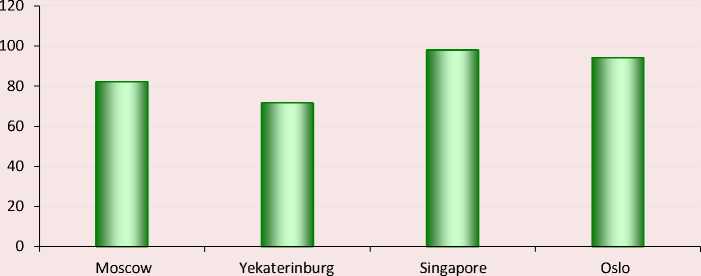
Source: own compilation.
Figure 2. Number of smart metering devices per 1,000 households in Moscow, Yekaterinburg, Singapore, Oslo
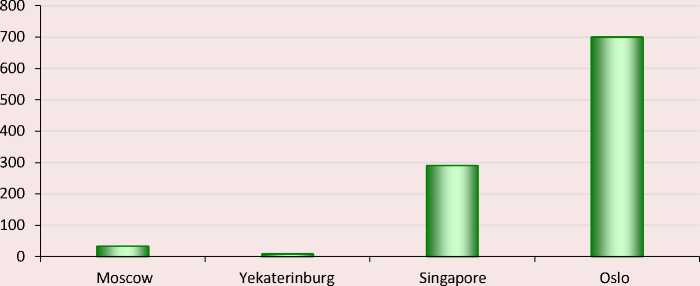
Source: own compilation.
the economic and social development of smart cities which develops the theory of ecosystem analysis of territories’ digitalization.
Conclusion
In the course of the research, conducted to develop a typology of the analysis methods of economic and social development of smart cities, we have obtained the following theoretical and practical results.
First, we have analyzed the results of the previous studies of the smart cities ecosystem, and formulated the problem associated with the need to develop a typology of methods for analyzing their economic and social development.
Second, based on the analysis of the works indexed in the world database Web of Science Core Collection we have selected one and a half hundred articles on the economic problems of the development of smart cities published in 2015–2021 and in the public domain.
Third, we have highlighted various methods for analyzing the economic and social development of smart cities. The research carries out differentiation of the selected methods by the method of describing the objects under study (static and dynamic) and by the model description method (tables, diagrams, matrices, graphs). Static methods include methods for assessing ecosystem characteristics, input-output analysis, development diagrams, data ecosystem coordination analysis, ecosystem assessment for age-related residents; dynamic ones include the Value Creation – Value Capturing matrices, stimulating controls, “digital ecosystems – entrepreneurial ecosystems”, as well as graphs of the life cycle of the smart city ecosystem, the evolution of civil ecosystems, digital transformation stages, dynamic innovation opportunities and the quadruple helix.
Fourth, we show the applicability of methods for analyzing the development of smart cities for various territories.
Fifth, for clarity, we have presented the author’s results of the assessment of the development of smart cities in Moscow, Yekaterinburg, Oslo, Singapore based on the 7I-model (infrastructure, institutions, intranet, integration, interfaces, innovations, implementation).
The theoretical significance of the results obtained lies in the development of the theory of ecosystem analysis in relation to the assessment of the formation of smart cities; the practical significance consists in the development of applied tools for strategic planning in the field of smart city project development.
Список литературы Methods for analyzing economic and social development of smart cities
- Bliss D., Garbos R., Kane P., Kharchenko V., Kochanski T. Rucinski A. (2021). Homo digitus: Its dependable and resilient smart ecosystem. Smart Cities, 4, 514–531.
- Brock K., Ouden E., Klauw K., Podoynitsyna K., Langerak F. (2019). Light the way for smart cities: Lessons from Philips Lighting. Technological Forecasting & Social Change, 142, 194–209.
- Certoma C. (2020). Digital social innovation and urban space: A critical geography agenda. Urban Planning, 5(4), 8–19.
- Chambers J., Evans J. (2020). Informal urbanism, and the Internet of Things: Reliability, trust, and the reconfiguration of infrastructure. Urban Studies, 57(14), 2918–2935.
- Claudel M. (2018). From organizations to organizational fields: The evolution of civic innovation ecosystems. Technology Innovation Management Review, 8(6), 34–47.
- Colding J., Wallhagen M., Sorqvist P., Marcus L., Hillman K., Samuelsson K., Barthel S. (2020). Applying a system perspective on the notion of the smart city. Smart Cities, 3(22), 1–10.
- Coletta C., Heaphy L., Kitchin R. (2019). From the accidental to articulated smart city: The creation and work of “smart Dublin”. European Urban and Regional Studies, 26(4), 349–364.
- Derlukiewicz N., Mempel-Sniezyk A. (2018). European cities in the face of sustainability development. Ekonomia I Pravo. Economics and Law, 17(2), 125–135.
- Elberzhager F., Mennig P., Polst S., Scherr S., Stupfert P. (2021). Towards a digital ecosystem for a smart city district: Procedure, results, and lessons learned. Smart Cities, 4, 686–716.
- Engel J.S., Berbegal-Mirabent J., Pique J.M. (2018). The renaissance of the city as a cluster of innovation. Cogent Business and Management, 5, 1532777, 1–20.
- Engin Z. Dijk J., Lan T., Longley P.A., Treleaven P., Batty M., Penn A. (2020). Data-driven urban management: Mapping the landscape. Journal of Urban Management, 9, 1140–1150.
- Gorelova I., Dmitrieva D., Dedova M., Savastano M. (2021). Antecedents and consequences of digital entrepreneurial ecosystems in the interaction process with smart city development. Administrative Sciences, 11(94), 1–14.
- Gupta A., Panagiotopoulos P., Bowen F. (2020). An orchestration approach to smart city data ecosystems. Technological Forecasting & Social Change, 153, 119929, 1–12.
- Hajikhani A. (2020). Impact of entrepreneurial ecosystem discussions in smart cities: Comprehensive assessment of social media data. Smart Cities, 3, 112–137.
- Hamalainen M. (2020). Digital transformation in the Helsinki smart city. In: Ratten V. (Ed.). Entrepreneurship and the Community: A Multidisciplinary Perspective on Creativity, Social Challenges, and Business. Springer.
- Hazell E.C. (2020). Disaggregating ecosystem benefits: An integrated environmental-deprivation index. Sustainability, 12, 7589, 1–20.
- Hirvensalo A., Teerikangas S., Reynolds N.-S., Kalliomaki H., Mantysalo R., Mattila H., Granqvist K. (2021). Agency in circular city ecosystem – a rationalities perspective. Sustainability, 13, 2544, 1–15.
- Iqbal A., Olariu S. (2021). A survey of enabling technologies for smart communities. Smart Cities, 4, 54–77.
- Jo S.-S., Han H., Leem Y., Lee S.-H. (2021). Sustainable smart city, and industrial ecosystem; structural and relational changes of the smart city industries in Korea. Sustainability, 13, 9917, 1–17.
- Kitchin R., Moore-Cherry N. (2020). Fragmented governance, the urban data ecosystem and smart city-regions: The case of metropolitan Boston. Regional Studies, 1735627, 1–11. DOI: 10.1080/00343404.2020.1735627
- Kundu D. (2019). Blockchain and trust in a smart city. Environment and Urbanization ASIA, 10(1), 31–43.
- Lee J.W. (2020). Big data strategies for government, society and policy-making. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(7), 475–487.
- Linde L., Sjodin D., Parida V., Wincent J. (2021). Dynamic capabilities for ecosystem orchestration. Technological Forecasting & Social Change, 166, 120614, 1–12.
- Macrorie R., Marvin S., While A. (2021). Robotics and automation in the city: A research agenda. Urban Geography, 42, 2, 197–217.
- Marston H.R., Shore L., White P.J. (2020). How does a (smart) age-friendly ecosystem look in a post-pandemic society? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17, 8276, 1–43.
- Moore J.F. (1997). The Death of Competition: Leadership and Strategy in the Age of Business Ecosystems. New York: Harper Collins.
- Myeong S., Jung Y., Lee E. (2018). A study on determinant factors in smart city development: An analytical hierarchy process analysis. Sustainability, 10, 2606, 1–17.
- Nochta T., Wan L., Schooling J.M., Parlikad A.K. (2021). A socio-technical perspective on urban analytics: The case of city-scale digital twins. Journal of Urban Technology, 28, 1-2, 263–287.
- Ooms W., Caniels M.C.J., Roijakkers N., Cobben D. (2020). Ecosystems for smart cities: Tracing the evolution of governance structures in a Dutch Smart City Initiative. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 16, 1225–1258.
- Paskaleva K., Evans J., Watson K. (2021). Co-producing smart cities: A quadruple helix approach to assessment. European Urban and Regional Studies, 28, 4, 395–412.
- Pierce P., Ricciardi F., Zardini A. (2017). Smart cities as organizational fields: A framework for mapping sustainability-enabling configurations. Sustainability, 9, 1506, 1–21.
- Popov E., Semyachkov K. (2020). 7I-model for smart city development. Archives of Business Research, 8(7), 143–157.
- Popov E., Semyachkov K. (2021). Smart city assessment matrix. SHS Web of Conferences, Socio-Economic Sciences, 94, 01019, 1–5.
- Popov E.V. (2020). Ekonotronika [Econotronics]. Tyumen: Izdatel’stvo Tyumenskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta.
- Popov E.V., Semyachkov K.A. (2020). Umnye goroda: monografiya [Smart Cities: Monograph]. Moscow: Yurait.
- Pulkkinen J., Jussila J., Trotskii A., Laiho A. (2019). Smart mobility: Services, platforms and ecosystems. Technology Innovation Management Review, 9(9), 15–24.
- Raven R., Sengers F., Spaeth P., Xie L., Cheshmehzangi A., Jong M. (2019). Urban experimentation and institutional arrangements. European Planning Studies, 27(2), 258–281.
- Rehm S.-V., McLoughlin S., Maccani G. (2021). Experimental platforms as bridges to urban sustainability. Smart Cities, 4, 569–587.
- Robaeyst B., Baccarne B., Duthoo W., Schuurman D. (2021). The city as an experimental environment: The identification, selection and activation of distributed knowledge in regional open innovation ecosystems. Sustainability, 13, 6954, 1–18.
- Rochet C., Correa J.D.P. (2016). Urban lifecycle management: A research program for smart government of smart cities. Revista de Gestão e Secretariado -GeSec, São Paulo, 7(2), 1–20.
- Ruohomaa H., Salminen V., Kunttu I. (2019). Towards a smart city concept in small cities. Technology Innovation Management Review, 9(9), 5–14.
- Storolli W.G., Makiya I.K., Cesar F.I.G. (2019). Comparative analyses of technological tools between Industry 4.0 and smart cities approaches: The new society ecosystem. Independent Journal if Management & Production, 10(3), 1134–1158.
- Yuan J., Xie H., Yang D., Xiahou X., Skibniewski M.J., Huang W. (2020). Strategy formulation for the sustainability development of smart cities: A case study of Nanjing, China. International Journal of Strategic Property Management, 24(6), 379–399.


