Methods for improving the energy characteristics of OFDM modems in frequency selective fading communication channels
Автор: Luferchik P.V., Konev A.N., Bogatyrev E.V., Galeev R.G.
Журнал: Siberian Aerospace Journal @vestnik-sibsau-en
Рубрика: Informatics, computer technology and management
Статья в выпуске: 2 vol.23, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
It is a fact that during data transmission, inter-symbol interference can occur, caused by the presence of multipath propagation and frequency-selective fading in the radio channel, which can significantly reduce the energy efficiency of communication systems. One of the methods to combat such effects, relevant today, is the use of OFDM modulation (OFDM – Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing), which allows to flexibly change the data rate, reduce the frequency resource by improving the spectral efficiency, and also deal with frequency – selective fading and selective interference. However, there are channels that are particularly susceptible to inter-symbol interference, such as, for example, the tropospheric channel. Also, the problem of selective interference is particularly acute in near-field magnetic induction communication systems. For such channels, the use of OFDM modulation itself is not a panacea; the task of increasing the energy efficiency of an OFDM signal is an urgent one. This paper presents the key features of the OFDM mode of operation, which make it possible to increase the energy potential of the radio link in channels subject to intersymbol distortion. The results of modeling methods for PAPR reduction and digital predistortion for the linearization of the transmission path are presented. The practical significance of the work lies in the fact that the use of transmission path linearization methods will increase the maximum bandwidth of communication systems, primarily those using tropo-spheric, radio relay and near-field magnetic induction communication channels. At present, this issue is particularly acute, since there are no high-speed tropospheric stations with a data transfer rate of 50 Mbps in Russia. Increasing the throughput in tropospheric communication will provide communication to hard-to-reach settlements with difficult terrain. Also, the use of high-speed tropospheric communication is a cost-effective alternative to satellite communication, since its use does not require the lease of a satellite channel.
Digital signal processing, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing, tropospheric radio channel, frequency-selective fading channel, intersymbol interference, frequency-selective fading, multi-path
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148329620
IDR: 148329620 | УДК: 621.391.01 | DOI: 10.31772/2712-8970-2022-23-2-189-196
Текст научной статьи Methods for improving the energy characteristics of OFDM modems in frequency selective fading communication channels
In channels where the occurrence of reflected, time-delayed signals is possible, the fight against the consequences of intersymbol interference caused by frequency-selective fading and selective interference is especially acute [1]. The phenomenon of multipath propagation leads to fluctuations in amplitude, phase, angle of arrival, which, in turn, causes a distortion of the shape of the correlation peak of the signal and a shift in the estimate of the true delay [2]. The purpose of this work is to develop algorithms that increase the energy efficiency of communication in such channels, increase resistance to frequency-selective fading and thereby increase throughput. The main features that allow increasing the energy potential in a radio channel with private selective fading will be considered below.
OFDM
At present, the use of OFDM modulation is relevant for a number of tasks, such as digital television and digital broadcasting [3]. This type of digital modulation is used in WLAN (IEEE 802.11 Wi-Fi), MAN (LTE, IEEE 802.16 WiMax), and many other applications [4; 5]. The key factors that contributed to such a wide distribution are stability in a multipath radio channel and relatively low computational complexity, which, in particular, manifests itself with a significant duration of the time scattering profile (large delay of secondary beams) [6].
OFDM is a multi-carrier system. Its most commonly used structure is simplistically described as
F follows. An input modulated symbol stream with symbol rate Fs is converted from serial stream to N parallel symbol rate streams at Fs / N rate. For example, the first symbol stream will contain the 1st, N+1, 2N+1, 3N+1, etc. symbols. Thus, the duration of each symbol increases by N times and becomes T • N equal to s . Each of the N symbol streams is transmitted on its own carrier frequency. The distance between frequencies is chosen in such a way that oscillations at these frequencies are orthogonal, as a result of which each of the symbol streams is transmitted independently; the streams do not affect each other. The spectrum of the system practically does not expand, since each of the streams has a spectrum width which is N times smaller than the spectrum width of the original stream. One of the most important disadvantages of an OFDM signal is its high peak factor [7].
Peak factor OFDM
The peak factor (PAPR - peak to average power ratio) depends on the number of subcarriers of the signal under consideration, as well as on the modulation. Thus, an OFDM symbol with N = 2048 subcarriers used by us will have the maximum possible PAPR [8] for QPSK (quadrature phase-shift keying) equal to 10log(N) = 33.3 dB.
There is a definition of PAPR OFDM. Let P be a vector containing the powers of all samples of some OFDM symbol, [W], Pav is the average power of a given OFDM symbol, [W]. Then the peak factor of the considered OFDM symbol is
PAPR = 10 log [ ma^ ] [дБ], (1)
к F av )
where max( P ) is a function that determines the largest value among the vector of values.
By the efficiency or performance of PAPR reduction algorithms, we will further mean how much the algorithm reduces the PAPR of an OFDM symbol after processing. For example, an algorithm that reduces PAPR by 3 dB (ceteris paribus) is more efficient (performance) than one that reduces it by 1 dB.
A number of peak factor reduction algorithms were screened out at the stage of analysis and modeling of review articles [7–10]. The peak factor reduction methods that are applicable to our task of reducing PAPR at large IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform) sizes are listed below:
– Peak Cancelation Crest-Factor Reduction (PC-CFR);
– Partial Transmit Sequence (PTS);
– Selected Mapping (SLM);
– Discrete Fourier Transform spread OFDM (DFT-s-OFDM);
– Active Constellation Extension (ACE);
– Tone Reservation (TR).
The best results were achieved by connecting ACE and TR in series. Active Constellation Extension (ACE) uses the ability to expand the signal constellation on the sides without distorting the transmitted symbols. Obviously, with an increase in the modulation order, the number of symbols that can be extended sideways will decrease relative to the total number of symbols, which will affect the performance of the algorithm. So, for QPSK, 100% of the symbols can be expanded sideways. In our work, the classical algorithm is used [11]. Tone Reservation (TR) is a very flexible method. Its performance is highly dependent on the chosen number of iterations [12]. The process and approaches to designing the TR algorithm are described in detail in this work [13]. The simulation results of TR and ACE peak factor reduction methods are shown in Fig. 1.
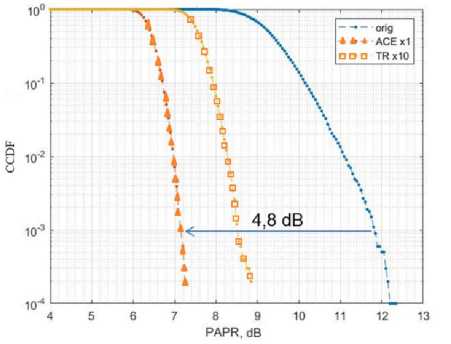
Рис. 1. Результат снижения PAPR в зависимости от CCFD (кумулятивная функция распределения) алгоритмами ACE и TR для OFDM с модуляцией QPSK
-
Fig. 1. The result of PAPR reduction depending on CFD (cumulative distribution function) by ACE and TR algorithms for OFDM with QPSK modulation
OFDM simulation in size 2048-point FFT with QPSK modulation, reduces peak factor to 7.2 dB relative to the original signal with a peak factor of 12 dB with a probability of 10–3 at sharing of TR (Tone Reservation) and ACE (Active Constellation Extension) algorithms. Thus, the gain from applying the peak factor reduction algorithm amounted to 4.8 dB.
Implementation of digital pre-detections for linearization of the radio transmission path
The use of a digital pre-detection input system assumes the presence of a functional block in the signal generation path that allows you to distort the useful signal in accordance with the inverse transfer characteristic of the radio frequency path [14]. The block diagram of the learning predetection input system is shown in Fig. 2.
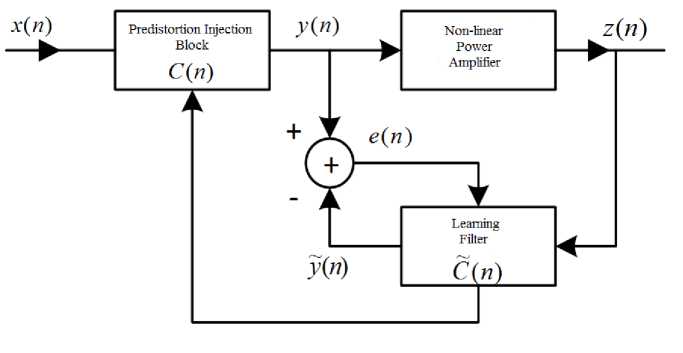
Рис. 2. Структурная схема системы ввода предыскажений с обучением
-
Fig. 2. Block diagram of the system for entering pre-detection with training
Adaptation of the parameters of the pre-detection system occurs according to the error signal, which is the difference between the signal at the output of the pre-detection input block in the forward channel and the signal at the output of the learning filter in the reverse channel [15]. The coefficients of the pre-detection system are constantly adjusted (recursive algorithm) when comparing two signals from the output of the pre-detection block and the output of the learning filter [16]. The main adaptation algorithms for learning systems are:
– least squares method (LMS);
– normalized least squares method (NLMS);
– recursive least squares method (RLS);
– recursive error prediction method (RPEM).
To evaluate digital predistortion algorithms in the matlab/simulink environment, a model for the LMS, NLMS, RLS, RPEM methods and a power amplifier model with real characteristics were developed. Power amplifier model parameters are
– frequency range – 4.4–5 GHz;
– maximum radiated power – 100 W;
-
– intermodulation distortion of the third order – minus 27 dB.
Based on the results of modeling algorithms, RLS was chosen. In addition, within the framework of this work, a modified version of the adaptation algorithm based on the recursive least squares method (RLSm) was developed. The main result of the modification was
-
– reduction in the number of arithmetic operations required to perform one iteration (more than 5 times);
-
– increasing the stability of adaptation algorithms by introducing regularization methods;
-
– reduction of the convergence time due to the introduction of an exponential dependence of the forgetting factor.
The developed model made it possible to estimate the spectral characteristics of signals (ACPR), the rate of convergence of algorithms, and the error vector modulus (EVM) relative to the input signal.
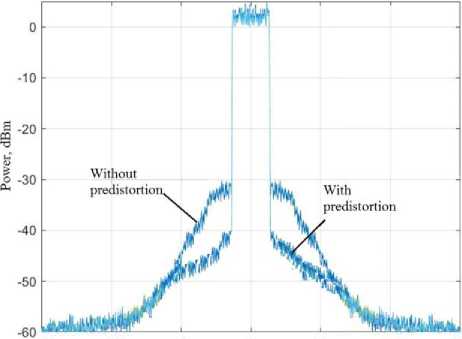
This model in matlab/simulink made it possible to obtain results in automatic mode for all developed algorithms, power amplifier radiation frequencies and radiated power. The signal spectrum at the output of the model for the 28 MHz band and the carrier signal frequency of 5 GHz are shown in Fig. 3.
150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150
Frequency. MHz
Рис. 3. Спектр сигнала на выходе модели до и после алгоритмов предыскажений
Fig. 3. The signal spectrum at the model output before and after the pre-detection algorithms
As can be seen from Fig. 3, the use of pre-detections can significantly reduce the level of nonlinear distortion (the noise level in the adjacent channel has decreased by 10 dB). The use of pre- emphasis reduces the magnitude of the error vector magnitude (EVM) by 13.5 dB, and also significantly increases the modulation/error ratio (MER) by 13.6 dB.
Conclusion
As a result of the analysis and modeling, the methods that made it possible to increase the energy efficiency of the OFDM mode were developed. Modeling of various algorithms for lowering the peak factor has been carried out. Two best PAPR reduction algorithms, most suitable for use in a channel with fading due to the use of a large number of OFDM subcarriers, namely Active Constellation Extension (ACE) and Tone Reservation (TR), which are used in cascade and allow to reduce the peak factor by 4, 8 dB, have been implemented. To increase the linearity of the transmission path, the RLSm digital pre-detection algorithm was selected and upgraded; it allowed reducing the magnitude of the error vector modulus (EVM) by 13.5 dB, and also increasing the modulation/error ratio (MER) by 13.6 dB. The obtained results will significantly increase the energy efficiency of the OFDM mode, lead to stable communication in a non-stationary channel subject to inter-symbol interference, and increase the throughput.
Список литературы Methods for improving the energy characteristics of OFDM modems in frequency selective fading communication channels
- Gustafsson R. Combating Intersymbol Interference and Cochannel Interference in Wireless Communication Systems. Blekinge Institute of Technology, 2003.
- ITU-R P.1407-8. Multipath propagation and parameterization of its characteristics. International Telecommunication Union, 2021.
- Umesha G. B., Shanmukha Swamy M. N. “Performance of OFDM System for Wireless Com-munication through Channel Estimation” // International Journal of Electronics, Electrical and Compu-tational System. 2017. Vol. 6, No. 1. P. 21–26.
- Rahman M., Das S., Fitzek F. Ofdm based wlan systems,Center for TeleInFrastruktur (CTiF), Technical report R-04- 1002, 2005.
- Songchar Jiang, White Lin and Shao-kuang Tsou. Performance evaluation and improvement of the OFDM-based Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks. 2007 Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications. 2007, P. 137–140. Doi: 10.1109/APCC.2007.4433522.
- Wang F. The application of MIMO-OFDM system in troposcatter communication. 2008 Inter-national Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology. 2008, P. 1957–1959. Doi: 10.1109/ICMMT.2008.4540872.
- Mehdi Hosseinzadeh Aghdam, Abbas Ali Sharif. PAPR reduction in OFDM systems: An eff-cient PTS approach based on particle swarm optimization. Department of Computer Engineering, University of Bonab, Bonab, Iran.
- Krongold B. S., Jones, D. L. Par reduction in ofdm via active constellation extension. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting. 2003, No. 49(3), P. 258–268. Doi:10.1109/TBC.2003.817088 (https://doi.org/10.1109/TBC.2003.817088).
- Singh M., Patra S. K. Partial transmit sequence optimization using improved harmony search algorithm for PAPR reduction. OFDM, ETRI J. 2017, No. 39 (6), P. 782–793.
- Lee B. M., Kim Y., R. P. F, Performance analysis of the clipping scheme with SLM technique for PAPR reduction of OFDM signals in fading channels. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2012, No. 63 (2), P. 331–344.
- Tellado J. Multicarrier Modulation with Low PAR. The International Series in Engineering and Computer Science. 2002. Doi:10.1007/b117134 (https://doi.org/10.1007/b117134).
- Seung Hee Han, Jae Hong Lee. Modulation, coding and signal processing for wireless commu-nications – An overview of peak-to-average power ratio reduction techniques for multicarrier trans-mission. IEEE Wireless Communications. 2005, No. 12(2), P. 56–65. Doi: 10.1109/MWC.2005.1421929 (https://doi.org/10.1109/MWC.2005.1421929).
- Morgan D. Ma, Kim, Zierdt, Pastalan. A generalized memory polynomical model for digital predistortion of RF power amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Sig. Proc. 2006, Vol. 54, P. 3852–3860.
- Kashchenko I. E. [Linearization method for a decameter radio transmission path based on non-linear distortion compensation tables]. Tekhnika radiosvyazi. 2015, No. 1 (24), P. 78–85 (In Russ.).
- Gan L. Adaptive digital predistortion of nonlinear systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Electrical and Information Engineering, Graz University of Technology, Graz, Austria. 2009.
- Ding L., Ma Z., Morgan D. R., Zierdt M., Pastalan J. A least square/Newton method for digital predistortion of wideband signals. IEEE Trans. on Communications. 2006, Vol. 54, No. 5, P. 833–840.


