Методы очистки загрязненных тяжелыми металлами почв с использованием (био)сурфактантов (обзор)
Автор: Костина Л.В., Куюкина М.С., Ившина И.Б.
Журнал: Вестник Пермского университета. Серия: Биология @vestnik-psu-bio
Рубрика: Микробиология
Статья в выпуске: 10, 2009 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Рассмотрены варианты классификации тяжелых металлов по физико-химическим свойствам и степени опасности для окружающей среды, взаимодействие их с почвенными компонентами и современные технологии очистки почвы, загрязненной данными ксенобиотиками. Обоснована эффективность применения биосурфактантов для ремедиации почв, загрязненных тяжелыми металлами.
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147204475
IDR: 147204475 | УДК: 579.222.2+579.26
Текст научной статьи Методы очистки загрязненных тяжелыми металлами почв с использованием (био)сурфактантов (обзор)
Тяжелые металлы (ТМ), попадающие в окружающую среду в результате производственной деятельности человека, -опасные загрязнители биосферы (Шулькин, Чернова, 1994; Захаров, Лагунов, 1995; Quintelas et al., 2008). Они способны накапливаться в отдельных звеньях трофической цепи и таким образом попадать в организмы высших животных и человека, подавляя их метаболическую активность и отрицательно воздействуя на жизнедеятельность (Гончарук, Сидоренко, 1986; Дерябина, 1996; Volesky, 1994; Avery et al., 1996). В связи с этим актуален обзор современных технологий очистки почвенных объектов природной среды, загрязненных тяжелыми металлами.
Классификация тяжелых металлов
С конца 1960-х гг. в научной литературе появился термин «тяжелые металлы », который сразу же приобрел негативное значение. С этим термином связано представление о чем-то токсичном и опасном для живых организмов: будь то человек, животные или растения. Несмотря на то, что термин ТМ неудачен, он прочно вошел в экологическую литературу. Однако необходимо иметь в виду, что многие из причисляемых к этой группе элементов жизненно необходимы для живых организмов в качестве микроэлементов (Фрумин, 2002; Gadd, 1992 б).
В понятие ТМ включают все металлы, за исключением щелочных и щелочноземельных элементов. ТМ – группа химических элементов плотностью более 5 г/см3 с относительной атомной массой более 40 а. е. м. (Лозановская и др., 1998; Trevors et al., 1986).
Существует несколько классификаций металлов, основанных на положении химического элемента в периодической таблице Д. И.
Менделеева, удельном весе металла и его валентности. Следует подчеркнуть, что данные классификации, основанные на физикохимических свойствах, не могут предсказать поведение ТМ в экосистеме (Gadd, 1992 а, б). С точки зрения геохимии, классифицируют три группы металлов: 1) сидерофильные элементы (Fe, Ni, Cr, Co, Pt), которые концентрируются в железистых осадках; 2) халькофильные металлы (Sb, As, Cd, Pb, Hg, Ag, Cu, Zn), концентрирующиеся в сульфидных осадках, и 3) литофильные (щелочные металлы, а также Mg, Ca, Cr, V), имеющие сродство к силикатам (Химия окружающей среды, 1982; Орлов, 1992). Номенклатурная классификация ТМ соотносится с химическими свойствами атомов и ионов металлов в растворах (Загрязнение воздуха…, 1988). Согласно этой классификации ТМ делятся на металлы, соединяющиеся с азотом или серой; металлы, соединяющиеся с кислородом; и металлы, выделенные по их предпочтительным связям.
По степени опасности ТМ подразделяют на три класса: 1) высоко опасные: Hg, As, Se, Cd, Pb, Zn; 2) умеренно опасные: Cr, Co, Mo, Ni, Cu, Sb и 3) малоопасные: V, W, Mn, Sr. По свойствам ионов ТМ в воде (Новиков и др., 1990) данные элементы подразделяются на металлы, изменяющие органолептические (Fe, Mn, Zn) и токсикологические (Al, Cd, Cu, Mo, Cr) свойства воды. Существует также классификация ТМ по степени подвижности в почвенных экосистемах (Алексеев, 1987): первые два класса – металлы первичного рассеивания (такого, как вулканическая деятельность), они включают Hg, As, Se, Cd, Pb, Zn (1-й класс) и Cr, Co, Mo, Ni, Cu, Sb (2-й класс); к третьему классу относятся металлы вторичного рассеивания: V, W, Mn, Sr.
Взаимодействие ТМ с компонентами почвы
Связующее звено между атмосферой, гидросферой, литосферой и живыми организмами – почва, в которой протекают жизненно важные процессы и создается уникальное свойство – плодородие. Почва – природный фильтр для техногенных загрязнителей, особенно ТМ (Шинкарев и др., 1998; Ginn et al., 2002), которые влияют на ее биологические свойства (Вальков и др., 1997). При этом наблюдается изменение общей численности почвенных микроорганизмов, сужение биоразнообразия, изменение структуры микробоценозов и снижение ферментативной активности. Присутствие ТМ изменяет консервативные признаки почв: гумусное состояние, структуру, показатель кислотности (Загрязнение почв и растительности…, 1978; Левин и др., 1989; Колесников и др., 2000), что приводит к частичной, а иногда и полной утрате плодородия (Воронина, Орлов, 1987; Janssen et al., 2003). Содержание ТМ в верхних слоях почвы определяется близостью к локальным источникам загрязнения и переносом поллютантов нижними слоями атмосферы, что обусловливается региональными факторами, такими как климат, рельеф, а также растительный покров (Харин и др., 2001; Hernandez et al., 1998). ТМ сравнительно быстро накапливаются в почве и крайне медленно из нее выводятся: период удаления Zn – 500, Cd – 1100, Cu – 1500, Pb – до нескольких тысяч лет (Добровольский, 1983; Тэрыцэ, Валтер, 1988).
В почвах ТМ присутствуют в водорастворимой, ионообменной и непрочно адсорбированной форме (рис. 1). Они обнаруживаются в нескольких пулах почвы: 1) растворенными в почвенном растворе; 2) занимающими сайты обмена на неорганических компонентах почвы; 3) прочно адсорбированными с почвенными частицами; 4) ассоциированными с нерастворимым органическим веществом почвы; 5) выпавшими в осадок в виде твердых частиц; 6) присутствующими в структуре вторичных минералов; 7) присутствующими в структуре первичных минералов. Характер взаимодействия ТМ с почвенными компонентами во многом обусловлен типом минералов (Shuman, 1991; McLean, Bledsoe, 1992). Так, металлы, интродуцированные в окружающую среду в результате производственной деятельности человека, ассоциируются с первыми шестью пулами, тогда как «природные» металлы могут ассоциироваться с любым из пулов почвы в зависимости от геологической истории данного района (Орлов, 1992; Shuman, 1991).
Факторы, определяющие взаимодействие ТМ с почвенными компонентами, включают степень агрегации твердых фаз и характер порового пространства почвы. Следовательно, на перемещение ТМ оказывает влияние не только специфика поверхности твердых фаз (гумусность, гранулометрический состав, емкость поглощения), но и инфильтрационные характеристики почв. Процесс трансформации поступивших в почву ТМ включает следующие стадии: 1) преобразование оксидов металла в гидроксиды (карбонаты, гидрокарбонаты); 2) растворение гидроксидов ТМ (карбонатов, гидрокарбонатов) и адсорбцию соответствующих катионов металла твердыми фазами почв; 3) образование фосфатов ТМ и их соединений с органическим веществом почвы (Лозановская и др., 1998; Фрумин, 2002; Twardowska, Kyziol, 2003).
Процесс миграции ТМ в почве можно подразделить на четыре составляющих, как то: диффузионная, фильтрационная, сорбционная и десорбционная (Фирсова, 2001). В настоящее время хорошо изучено распространение в различных почвах таких металлов, как Cu, Zn, Co и Mo, широко применяемых в сельском хозяйстве. В то же время чрезвычайно мало информации по содержанию в почвах редких и рассеянных элементов, таких как Cr, Hg, Pb, Cd, Sn, являющихся опасными загрязнителями почв (Протасова, 1998; Шинкарев и др., 1998; Pazirandeh et al., 1998). Поведение отдельных металлов в почве описано в работах отечественных и зарубежных исследователей (Орлов, 1992; Лозановская и др., 1998; Volesky, 1990; Shuman, 1991; McLean, Bledsoe, 1992; Markiewicz-Patkowska et al., 2005).
Накопление ТМ в почве обусловлено влиянием ряда взаимосвязанных процессов, включающих круговороты органического и неорганического вещества, окислительно-восстановительные реакции, осаждение / растворение и адсорбцию / десорбцию. Степень адсорбции катионов металлов коррелирует со значениями рН и окислительно-восстановительного потенциала (ОВП), содержанием глины, почвенного органического вещества, окисей железа и марганца, карбоната кальция. Интенсивность адсорбции анионов металлов коррелирует с содержанием окисей железа и марганца, а также значениями рН и ОВП (Volesky, 1990; Shuman, 1991).
Химическое сродство почвенной поверхности со свободными катионами металлов способствует формированию сильных связей. При этом предпочтение отдается менее гидратированным катионам, прочно соединяющимся с глинистой поверхностью почвы. В данном случае важную роль играет конфигурация электронов в атомах ТМ. Следует отметить, что степень адсорбции анионов металлов почвенными частицами менее
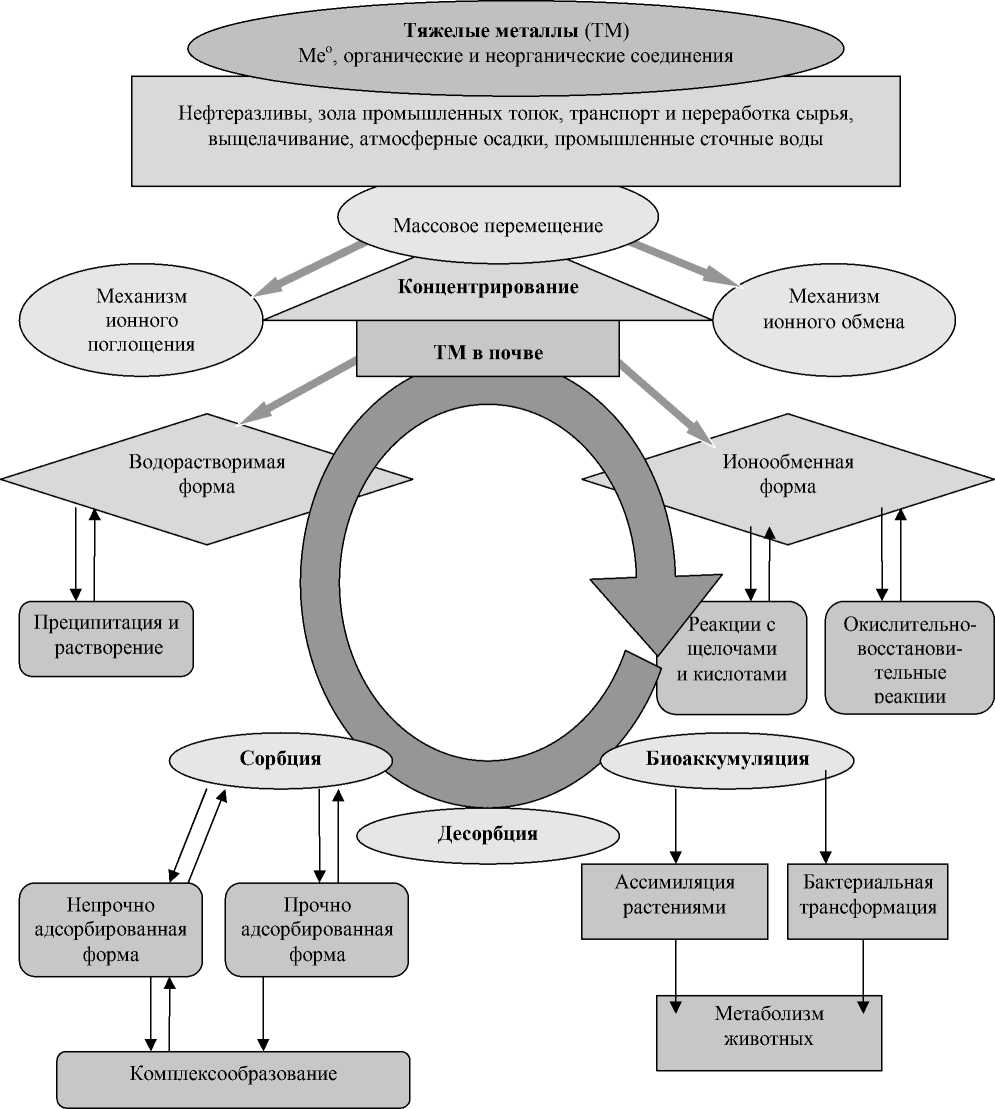
Рис. 1. Влияние абиотических и биотических факторов на распространение и распределение ТМ в
почве.
значительна по сравнению с таковой катионов (Лозановская и др., 1998; Хархордин, Атрощенко, 1998; McLean, Bledsoe, 1992).
Металлы в почве находятся в виде свободных ионов (Cd2+, Zn2+, Cr3+) и разнообразных растворимых комплексов с неорганическими или органическими лигандами (CdSO4, ZnCl+, CdCl2), а также ассоциированы с подвижным коллоидным материалом. Совокупность металлоорганических компонентов в почве охарактеризована хуже, чем неорганических комплексов из-за сложности определения большого числа органических лигандов, присутствующих в почве (Shuman, 1991). Гумусовые субстанции и другие биогенные вещества обеспечивают участки (функциональные группы, такие как карбоксильные, феноловые, спиртовые, гидроксильные и аминогруппы) сорбции ТМ и, в результате хелатирования, образуют растворимые в воде комплексы с металлами, повышая степень их подвижности (Орлов, 1992; Shuman, 1991). Большинство анионов, а также катионы и гидроксиды практически всех ТМ в значительной мере поглощаются почвой по механизму специфической сорбции (Shuman, 1991). Поглощение почвами металлов, поступающих в форме катионов, также может быть обусловлено осаждением труднорастворимых соединений из раствора и, в меньшей степени, специфической сорбцией, физической адсорбцией, а также биологическими процессами. Для анионов большую роль играют процессы специфической сорбции, осаждения труднорастворимых соединений, в меньшей степени – неспецифическая сорбция, физическая адсорбция и биологическое поглощение. Чем прочнее почва удерживает металлы, тем активнее они будут переходить из почвенного раствора в твердую фазу и, следовательно, тем выше буферная способность почвы. На величину буферной способности почв влияют значения рН и ОВП, поскольку с ними связаны заряд поверхности твердой фазы почвы, а также физическое состояние загрязняющих веществ и растворимость солей, в состав которых они входят (Воронина, Орлов, 1987; Хархордин, Атрощенко, 1998; Sekhar et al., 2003).
Соединения ТМ, образующиеся в результате формирования неорганических и органических комплексов, могут быть положительно или отрицательно заряжены либо электрически нейтральны (например, CdCl3, CdCl, CdCl2), при этом свободные ионы металла, как правило, наиболее биодоступны и токсичны. ТМ могут выпадать в осадок, образуя твердую фазу в почвах. Такие осадки представляют собой чистые (CdCO3, Pb(OH)2) и смешанные (Ba(Cr4,SO4)) твердые вещества, образующиеся в результате одновременного выпадения в осадок нескольких элементов. Некоторые металлы (V, As, Se, Cr, Hg) присутствуют в почве более чем в одном состоянии окисления, что влияет на их относительную подвижность, биодоступность и токсичность (Юшков и др., 2004; Kierans et al., 1991; Shuman, 1991). Содержание органического вещества играет значительную роль в накоплении ТМ в почве, их просачивании в грунтовые воды, сорбционной способности, токсичности для растений и почвенных организмов. Знание механизмов закрепления ТМ на органическом веществе почвы и их поведения под воздействием естественных и антропогенных факторов важно для понимания процессов, воздействующих на степень подвижности и биоаккумулирования ТМ в почвах (Twardowska, Kyziol, 2003).
Помимо абиотических процессов на распространение и распределение ТМ в почве существенное влияние оказывают биотические факторы (Тэрыцэ и др., 1990; Christofi, Philp, 1991). Организмы низших трофических уровней: растения (Гиниятуллин и др., 1998; Sawidis, 1988), высшие грибы (Gadd, 1992 а; Kirchner, Daillant, 1998), мхи и лишайники (Нифтонова, 1977; Харин и др., 2001; Eckl et al., 1986), а также микроорганизмы (Евдокимова, Мозгова, 1991; Mulligan, Galvez-Cloutler, 2000) играют важную роль в процессах выведения ТМ из почвы. Живые организмы могут солюбилизовать соли ТМ, повышая их биодоступность, либо иммобилизировать, снижая степень биодоступности (White et al., 1997, 1998).
Таким образом, степень распространения ТМ в почвенной среде зависит от целого ряда взаимообусловленных физико-химических и биологических факторов, поэтому относительное распределение ТМ между абиотическими и биотическими компонентами почвы высоко динамично и вариабельно (Юшков и др., 2004; Gupta et al., 1998; Schneegurt et al., 2001).
Методы очистки почв, загрязненных тяжелыми металлами
В настоящее время наиболее разработаны методы извлечения ТМ из промышленных и бытовых сточных вод, а также их осадков. Основные способы извлечения ТМ из токсичных осадков сточных вод описаны в работах отечественных и зарубежных исследователей (Энхольм, 1980; Яковлев и др., 1987; Хасид, 1989; Farmer et al., 2002; Ayyamperumal et al., 2006). Они включают мембранные технологии, обратный осмос, электрохимические методы, цементирование, адсорбцию активированным углем и твердыми отходами (опилки, кора, пенокерамика и текстильные глины), испарение, разбавление, использование ионообменных смол, а также отмывание ТМ синтетическими сурфактантами (Проскуряков, Шмидт, 1976; Очистка природных …, 1991; Покопова, 1991; Almeida et al., 2009; Lesmana et al., 2009).
Универсального метода очистки почв от ТМ не существует: эффективность метода зависит от свойств почвы, степени адаптации произрастающих на ней растений и целого ряда других факторов. Выбор конкретной технологии для обработки загрязненного участка зависит от химической структуры загрязняющих примесей и других характеристик (Mulligan et al., 2001 в). Очистку почв, загрязненных ионами ТМ, традиционно осуществляют с применением земляных работ – снятия пластов загрязненной почвы (экскавация) с дальнейшим размещением в местах складирования опасных отходов или на участках для рекультивации (Miller, 1995). Основные способы ремедиации почв, загрязненных ТМ, приведены в табл. 1. Все методы можно разделить на три группы: ограничение, ex situ и in situ обработка. К методам ограничения распространения загрязнителя в почве можно отнести построение геоконтейнеров, механическую изоляцию, герметизацию и витрификацию. Данные методы способствуют удержанию загрязнителя в строго определенном месте и предотвращают интродукцию высокотоксичных ионов ТМ в объекты природной среды. К методам ex situ можно отнести физическую сепарацию, отмывание и пирометаллургическую обработку почвы, загрязненной ТМ. Применение данных методов ограничено, так как для их реализации необходимы специально оборудованные площадки. Третья группа методов – in situ, в частности построение изолирующих водопроницаемых барьеров, электрокинетическая обработка, отмывание почвы, биологическое выщелачивание и фиторемедиация. Правильно подобранное сочетание данных методов позволяет эффективно восстановить почву, загрязненную ТМ. К сожалению, применение биологических методов сегодня ограничивается выращиванием травяных культур (фиторемедиация), которые впоследствии скашивают и увозят в места складирования, решая локальную проблему ремедиации (Christofi, Ivshina, 2002; Jordan et al., 2002; Lebeau et al., 2008). Для снижения степени токсичности загрязненной почвы осуществляют выщелачивание легкоподвижных и перевод остальных ТМ в неподвижную форму, так как трансформация многих ТМ (Hg2+ → CH3-Hg+) зачастую приводит к образованию более токсичных соединений.
Избирательность процесса выщелачивания зависит от ионного радиуса и электронной конфигурации металла (Cu2+>Ni2+>Co2+>Fe2+ >Mn2+), а подвижность ТМ ограничивается естественной гетерогенностью механического состава и содержанием органического вещества в почве (Miller, 1995).
Следует отметить, что применяемые технологии ограничения распространения ТМ в почве (в частности механическая изоляция, герметизация, водопроницаемые барьеры) не могут полностью удалить эти опасные ксенобиотики, лишь стабилизируя их в загрязненной среде. Методы отмывания почвы с помощью органических кислот и синтетических сурфактантов базируются на использовании жестких химико-технологических процессов с применением агрессивных реагентов, что еще больше осложняет экологическую ситуацию
(Кашевский и др., 1996; Martin, Ruby, 2004; Meunier et al ., 2004). К тому же медленная кинетика десорбции ТМ из почвы требует длительного периода отмывания с применением насосного оборудования (Miller, 1995; Hong et al ., 2002). Данные методы очистки не всегда эффективны и менее рентабельны по сравнению с экологически безопасными биологическими методами (применение биогенных сурфактантов микробного происхождения) обработки почвы, загрязненной ТМ (Кашевский и др., 1996; Allen, Brown, 1995; Sanchez et al., 1999). Существует мнение (Maier et al., 2001; Gao et al., 2003; Juwarkar et al., 2007), что биологические способы ремедиации почв должны со временем заменить такие традиционно используемые методы, как вывоз загрязненного материала на свалки или экстракцию с использованием органических кислот и синтетических сурфактантов. Следует отметить, что наиболее эффективные и рентабельные биологические методы обработки загрязненной почвы постоянно совершенствуются и становятся дешевле, поскольку существует значительная потребность в их развитии (Mulligan et al., 2001 а, в, г; Schneegurt et al., 2001).
Биосурфактанты как агенты биоремедиации почв, загрязненных ТМ
Существуют критерии, позволяющие выбрать соединения, обладающие высокими металлохелатирующими способностями, для увеличения мобильности ТМ: 1) высокое сродство с загрязнением; 2) значительная подвижность в почве (устойчивость к агрегированию и низкая степень адсорбции при прохождении через пористые среды); 3) относительно продолжительное время существования; 4) нетоксичность и безопасность для окружающей среды. Всем вышеперечисленным требованиям полностью удовлетворяют биосурфактанты, синтезируемые микроорганизмами (Miller, 1995).
Преимущества биосурфактантов перед синтетическими аналогами – природное происхождение, низкая токсичность, биодеградабельность, высокая активность в экстремальных условиях внешней среды, а также возможность получения на нетрадиционных и относительно дешевых источниках сырья (Christofi, Ivshina, 2002).
Возможность использования биосурфактантов для извлечения ТМ из почвы во многом зависит от нашего понимания механизмов образования комплексов «сурфактант-металл» (Ochoa-Loza et al., 2001). Так, Tan et al . (1994) показали 92 %-ную эффективность комплексообразования ионов кадмия с 5 мМ раствором рамнолипидов. Полученные авторами результаты сопоставимы с данными комплексообразования Cd2+ с экзополимерами представителей Arthrobacter
Таблица 1
|
Технология |
Описание |
Применение |
Стоимость, $ США/тонну |
|
Ограничение |
|||
|
Геоконтейнеры |
Задержание отложений в ограниченной области с помощью геоконтейнеров |
Обработка широкого спектра загрязнений |
20 - 65 |
|
Механическая изоляция |
Построение непроницаемого барьера, предотвращающего перемещение потока жидкости |
Обработка жидких отходов, их концентрирование |
10 - 90 |
|
Герметизация |
Формирование инертных отходов |
Введение реактивов для отвердевания жидких отходов |
60 - 290 |
|
Витрификация |
Превращение загрязнения в стекловидное вещество с помощью электроэнергии |
Поверхностные загрязнения почв нелетучими соединениями ТМ и отходами стекла |
400 - 870 |
|
Ex situ обработка |
|||
|
Физическая сепарация |
Включает вспенивание, флокуляцию, гравитационное разделение, просеивание и т.д. |
При высоких концентрациях загрязнения ТМ |
60 - 245 |
|
Ex situ отмывание почвы |
Добавление сурфактантов и других солюбилизирующих агентов |
Для песка, гравия и почвы, загрязненных водорастворимыми соединениями ТМ |
25 - 300 |
|
Пирометаллургический метод |
Высокотемпературная экстракция |
При высоких концентрациях загрязнителя в почве (5 - 20 %) |
200 - 9000 |
|
In situ обработка |
|||
|
Проникающие барьеры |
Создание водопроницаемого барьера |
Для грунтовых вод, загрязненных ТМ |
60 - 245 |
|
In situ отмывание почвы |
Выщелачивание загрязнителя при промывании почвы |
Подпочвенные горизонты, загрязненные растворимыми соединениями ТМ |
100 - 200 |
|
Электрокинетическая обработка |
Применение электрического тока |
Глубокие слои почвы с низкой подвижностью грунтовых вод |
Нет данных |
|
Биологическое выщелачивание |
Использование бактерий для увеличения степени выщелачивания |
Для песка, гравия и почвы при низких уровнях загрязнения ТМ |
15 - 200 |
|
Фиторемедиация |
Использование растений для извлечения металлов |
Незначительное загрязнение поверхностных слоев почвы и водоемов |
50000 - 200000 за акр |
Примечание. * Цит. по Mulligan et al ., 2001 а, в; Khan et al ., 2004; Martin, Ruby, 2004.
Основные технологии ремедиации почв, загрязненных ТМ*
(Scott, Palmer, 1988) и Klebsiella (Bitton, Freihofer, 1978). Комплексы Cd-рамнолипид устойчивы при pH = 6.0 - 7.0, а небольшие размеры их везикул облегчают движение в почве (Miller, 1995). Следует отметить, что обычно присутствующие в почве катионы (Ca2+, Mg2+, K+) практически не конкурируют с ТМ за комплексообразование с рамнолипидами. В частности, комплексообразование Cd2+ уступает в конкурировании с Ca2+ лишь при стократном превышении концентрации последнего, а для конкурирования с Pb2+ или Cu2+ требуется превышение в 100 тыс. раз концентрации Ca2+ (Schnitzer, Hansen, 1970; Ochoa-Loza et al., 2001). Лиганды биосурфактантов взаимодействуют с ионами ТМ в почве, связывая данные загрязнители, обычно рассеянные в природной среде и устойчивые к микробному разложению. Важно отметить, что биосурфактанты могут связывать ионы ТМ, оставаясь подвижными в почвенных средах и увеличивая тем самым подвижность ТМ (Chen et al., 1995). Помимо практической важности для биоремедиации экосистем, загрязненных ТМ, и биоконцентрирования редких элементов (Mulligan et al., 2001 а; Neilson et al., 2003; Zouboulis et al., 2003; Dahrazma, Mulligan, 2004) изучение механизмов образования металл-сурфактантных комплексов имеет фундаментальное значение для понимания роли биосурфактантов в сложных взаимодействиях микроорганизмов с ионами ТМ и формировании устойчивости микробных клеток к их воздействию.
Связывание ТМ с лигандами катионных биосурфактантов, в частности рамнолипидов, основано на формировании координационных соединений. При этом металлы действуют как кислота Льюиса (акцептор электронов), а органические лиганды - как основание Льюиса (донор электронов). Прочность химической связи между металлом и лигандом определяется количественно через константы условной стабильности (КУС) комплексов - металл-органический лиганд (Manunza et al., 1995; Janssen et al., 2003). KУС = [МЛ]/[М][Л] при постоянных значениях pH и ионной силы, где [M] – концентрация металла, [Л] - концентрация лиганда, а [МЛ] – концентрация комплексного соединения. Образование комплекса происходит, когда лиганд образует координационные связи с металлом посредством более одной пары общедоступных электронов, формируя кольцевую структуру. Хелатный комплекс может быть бидентантным, тридентантным и т. д., в зависимости от числа координационных связей (Chen et al., 1995; Lao et al., 2007).
Комплексообразование ТМ с фульвовыми и гуминовыми кислотами почвы, а также илом сточных вод подробно описано (Gould, Genetelli, 1978; Sposito et al., 1979; Sааr, Weber, 1979, 1980; Breault et al., 1996; Wang, Mulligan, 2009). Однако следует отметить, что бактериальные биосурфактанты, в частности рамнолипиды, успешно конкурируют с природными лигандами за комплексообразование с большинством ТМ (Ochoa-Loza et al., 2001). Так, значения КУС комплексов рамнолипидов с ТМ аналогичны либо превышают таковые для фульвовой, щавелевой, уксусной и лимонной кислот. Величины КУС комплексов рамнолипид-металл располагаются в следующем порядке: Al3+>Cu2+>Pb2+>Cd2+>Zn2+> Fe3+>Hg2+>Ca2+>Co2+>Ni2+>Mn2+>Мg2+>K+, что соответствует порядку Ирвинга-Уильямса (Irving, Williams, 1948; Gu et al., 1994). Некоторые исследователи (Khanna, Stevenson, 1962; Khan, 1969; 2004) считают, что этот порядок максимально приближен к степени комплексообразования ТМ с органическим веществом в почве. В табл. 2 приведены сравнительные значения КУС синтетических и природных лигандов, предлагаемых для извлечения ТМ из почвы. Следует отметить, что при выборе оптимального способа очистки загрязненной ТМ почвы необходимо учитывать экологическую безопасность используемых реагентов. Так, применение синтетических лигандов нежелательно вследствие их токсичности и низкой деградабельности, несмотря на высокие показатели КУС данных соединений (Ochoa-Loza et al., 2001).
Таблица 2
Константы стабильности органических лигандов с ТМ
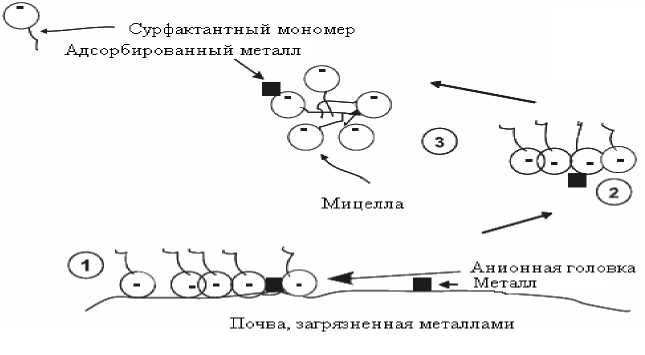
Рис. 2. Потенциальный механизм удаления ионов металлов из почвы под действием анионного биосурфактанта (цит. по Mulligan et al ., 1999 в; Mulligan, 2005):
1. аккумуляция биосурфактанта и ТМ на поверхности почвы;
2. десорбция ТМ посредством снижения межфазного натяжения и электростатического взаимодействия;
3. образование комплекса ТМ с сурфактантной мицеллой
Вставка изображает поверхность мицеллы биосурфактанта с гидрофобными частями (“хвостами”), выдающимися на внешнюю поверхность
Существует два предполагаемых механизма извлечения ТМ из почвы с помощью биосурфактантов (рис. 2). Первый – образование комплексов биосурфактантных молекул со свободными ионами металла, находящимися в растворе, что снижает его химическую активность в почвенной среде. Второй механизм основан на увеличении степени солюбилизации ТМ, сорбированных почвой, в результате их прямого контакта с биосурфактантом, что приводит к снижению межфазного натяжения на поверхности раздела фаз твердое вещество – раствор (Miller, 1995; Singh, Cameotra, 2004). Наиболее вероятно, что ионы металлов присоединяются к внешней отрицательно заряженной поверхности сурфактантных мицелл. Однако возможно также некоторое химическое сродство ТМ с неполярной частью сурфактантных мицелл, имеющих отличную от сферической форму поверхности (рис. 2).
Металлы имеют более высокое сродство с мицеллами при низких концентрациях сурфактанта, что обусловливает возможность более эффективного отмывания почвы при использовании пониженной (до 0.25 %) концентрации рамнолипида. Кроме того, при высоких концентрациях сурфактанта увеличивается размер мицелл, что снижает степень упаковывания активных анионных головок и сокращает время удержания металлов на мицеллах (Mulligan et al ., 1999 б).
Биосурфактанты выводят ТМ из почвенного раствора эффективнее, чем глины (Christofi, Ivshina, 2002). При этом эффективность извлечения металлов растворами биосурфактантов зависит от типа почвы, характера и уровня загрязнения, показателя кислотности среды (табл. 3). Так, эксперименты по очистке почвы, загрязненной кадмием и свинцом, посредством обработки аэсцином (биосурфактантом, синтезируемым Aesculus hippocastanum L.) показали, что металлы интенсивно мигрируют в водную фазу почвы в зависимости от значения pH среды (Hong et al., 1998).
Использование серии последовательных процедур отмывания и грамотный подбор комбинации биосурфактантов позволяют достигать практически полного извлечения ионов ТМ из почвы ( см . табл. 3).
Сложную экологическую проблему представляет комплексное загрязнение почвы органическими веществами и ТМ. Так, более 40 % нефтезагрязненных почв содержат высокие концентрации ТМ, таких как As, Hg, V, Pb, Zn, Ni и Mo (Kovalick, 1991). Участки, загрязненные смесью металлов и нефтяных углеводородов, ставят уникальные задачи перед ремедиацией. Можно предположить, что добавление биосурфактанта в почву, загрязненную ТМ и органическими поллютантами, будет способствовать одновременной десорбции органических загрязнителей (Christofi, Ivshina, 2002) и ТМ (Mulligan et al., 1999 в; 2001 б; Singh, Cameotra, 2004). В экспериментах Zhang и Miller (1992) рамнолипидный биосурфактант снижал токсичность ТМ и ускорял процесс деградации нефтепродуктов. Возможный механизм данного процесса заключается в связывании металла с мицеллами сурфактанта, которые содержат солюбилизированные молекулы углерода (рис. 3).
Таблица 3.
Десорбция ионов ТМ из почвы под действием сурфактантов
|
Загрязнение почвы |
Используемый сурфактант |
Продуцент |
Эффективность отмывания ТМ |
Литературный источник |
|
Однократное отмывание |
||||
|
420 мг/кг Cu, 890 мг/кг Zn, 12.6 % нефти |
0.25% сурфактин, 1% NaOH |
Bacillus subtilis |
25% Cu, 6% Zn |
Mulligan et al., 1999 а, б |
|
110 мг/кг Cu, 3300 мг/кг Zn |
15% Cu, 6% Zn |
Mulligan et al., 1999 б; 2001 б |
||
|
420 мг/кг Cu, 890 мг/кг Zn, 12.6 % нефти |
4% софоролипид, 0.7% HCl |
Torulopsis bombicola |
37% Cu, 6% Zn |
Mulligan et al., 1999 а, в |
|
12 % рамнолипид |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
20% Cu, 35% Zn |
||
|
110 мг/кг Cu, 3300 мг/кг Zn |
0.5% рамнолипид |
P . aeruginosa |
65% Cu, 18% Zn |
Mulligan, 2000; Mulligan et al., 2001 б |
|
4% софоролипид, 0.7% HCl |
T . bombicola |
25% Cu, 15.8% Zn |
||
|
83.9 % Cd |
80 мМ рамнолипид |
P . aeruginosa |
52.9 % Cd |
Aşςi et al., 2008 а |
|
Серия последовательных отмываний (от 5 до 10) |
||||
|
420 мг/кг Cu, 890 мг/кг Zn, 12.6 % нефти |
0.1% сурфактин, 1% NaOH |
B . subtilis |
70% Cu, 25% Zn |
Mulligan et al., 1999 а, б, в, 2001 а; Mulligan, 2000 |
|
4% софоролипид, 0.7% HCl |
T . bombicola |
50% Cu, 100% Zn |
||
|
0.1% рамнолипид, 1% NaOH |
P . aeruginosa |
38% Cu, 17% Zn |
Mulligan, Yong, 1997; Mulligan et al., 1999 а, в; Mulligan et al., 2001 а |
|
|
Вода |
- |
1% Cu, 1% Zn |
||
|
Cd и Pb (н. д.) |
30 мМ аэсцин |
Aesculus hippocastanum |
41% Cd (pH = 7.8), 25% Pb (pH = 2.8) |
Hong et al ., 1998 |
|
435.4 мг/кг Cd, 905.4 мг/кг Pb |
0.1% рамнолипид |
P . aeruginosa |
0.5 мг/кг Cd, 120.5 мг/кг Pb |
Juwarkar et al., 2007 |
|
1484 мг/кг Cd, 2155 мг/кг Cu, 7288 мг/кг Pb, 692 мг/кг Zn |
3% сапонин |
Clematis manchurica |
85% Cd, 42% Cu, 20% Pb, 68% Zn |
Hong et al., 2002 |
|
1026 мг/кг Cd, 2181 мг/кг Cu, 7161 мг/кг Pb, 551 мг/кг Zn |
3% сапонин |
0% Cd, 36% Cu, 25% b, 55% Zn |
||
|
701 мг/кг Cd, 1521 мг/кг Cu, 5253 мг/кг Pb, 472 мг/кг Zn |
3% сапонин |
90% Cd, 62% Cu, 58% Pb, 80% Zn |
Hong et al., 2002 |
|
|
500 и 2000 мг/л Cu |
12.5 мМ рамнолипид |
P . aeruginosa |
21.1 и 39.8 % Cu |
Maier et al ., 2001 |
|
50 мМ рамнолипид |
34.5 и 59.4 % Cu |
|||
|
Контроль (вода) |
- |
5.2 и 2.8 % Cu |
||
|
140 мг/кг Cu, 76 мг/кг Ni, 4854 мг/кг Zn |
5% рамнолипид |
P . aeruginosa |
37% Cu, 33.2% Ni, 7.5% Zn |
Dahrazma, Mulligan, 2004; 2007 |
|
1.73 мМ Zn |
25 мМ рамнолипид |
83.9 % Zn |
Aşςi et al., 2008 б |
|
Окончание табл. 3.
|
Загрязнение почвы |
Используемый сурфактант |
Продуцент |
Эффективность отмывания ТМ |
Литературный источник |
|
1710 мг/кг Cd, 2010 мг/кг Ni |
0.5% пена рамнолипида |
P . aeruginosa |
73.2% Cd, 68.1% Ni |
Wang, Mulligan, 2004; Mulligan, Wang, 2006 |
|
0.5% рамнолипид |
61.7% Cd, 51.0% Ni |
|||
|
0.5% пена тритона X100 |
Синтетический сурфактант |
65.5% Cd, 57.3% Ni |
Wang, Mulligan, 2004 |
|
|
0.5% тритон X100 |
52.8% Cd, 45.2% Ni |
|||
|
Контроль (вода) |
- |
17.8% Cd, 18.7% Ni |
||
|
2180 мг/кг As, 12860 мг/кг Cu, 11009 мг/кг Pb, 5075 мг/кг Zn |
0.1 % рамнолипид |
P . aeruginosa |
148 мг/кг As, 74 мг/кг Cu, 2379 мг/кг Pb, 259 мг/кг Zn |
Wang, Mulligan, 2009 |
|
630 мг/кг Cd, 1019 мг/кг Cu, 1205 мг/кг Ni, 2567 мг/кг Pb, 1877 мг/кг Zn |
2 % рамнолипид |
35 %Cd, 48 % Cu, 64 % Ni, 52 % Pb, 87 % Zn |
Franzetti et al., 2009 |
|
|
2 % биоэмульсан |
Gordonia sp. |
19 % Cd, 17 % Cu, 25 % Ni, 47 % Pb, 31 % Zn |
||
|
Природное (не антропогенное) загрязнение почвы |
||||
|
Pb (н. д.) |
10 мМ рамнолипид |
P . aeruginosa |
до 15% Pb |
Maier et al., 2001; Neilson et al., 2003 |
|
16.5 мг/кг Cd, 118.6 мг/кг Pb |
0.1% рамнолипид |
P . aeruginosa |
13.4 мг/кг Cd, 108.6 мг/кг Pb |
Juwarkar et al., 2007 |
Примечание: н. д. – недостаточно данных.
Многими исследователями (Mulligan et al., 1999 а, б, в; Maslin, Maier 2000; Maier, Soberon-Chavez, 2000; Czaplicka et al., 2008) показано, что биосурфактанты увеличивают скорость деградации гидрофобных органических загрязнителей почвы и способствуют удалению из нее солей Cd2+, Cu2+, Zn2+ и Pb2+. Кроме того, ингибирование процесса минерализации фенантрена ионами Cd2+ снижается в результате добавления рамнолипида, который достоверно уменьшает степень токсичности данного ТМ в отношении почвенной микрофлоры (Mulligan et al., 1999 а; Maslin, Maier, 2000). Механизм снижения токсичности, по-видимому, включает формирование комплексов Cd – рамнолипид и взаимодействие рамнолипида с поверхностью микробных клеток (Sandrin et al., 2000; Sandrin, Maier, 2002).
Необходимо отметить, что основная часть исследований касается рамнолипидов, синтезируемых P. aeruginosa. Однако патогенность бактерии-продуцента существенно ограничивает возможность промышленного применения рамнолипидов. В связи с этим актуально изучение металл-хелатирующих свойств других биосурфактантов, продуцируемых непатогенными микроорганизмами.
Например, сурфактин, продуцируемый B . subtilis , эффективен в удалении ТМ из почвы, загрязненной смесью Cu, Zn и углеводородов (Mulligan et al., 1999 в). Трегалозолипидный биосурфактант, синтезируемый Rhodococcus ruber , успешно используется для десорбции нефти от почвы и биоремедиации нефтезагрязненных почв и грунтов (Ившина и др., 2003; Kuyukina et al., 2003). В настоящее время исследуется возможность применения бактериальных сурфактантов для биоремедиации почв, загрязненных наряду с нефтяными углеводородами такими токсичными металлами, как U, Cd, Pb и Zn (Zosim et al., 1983; Marques et al., 1990; Ron, Rosenberg, 2001; Gautam, Tyagi, 2006).
Подводя итог вышесказанному, необходимо отметить, что технология извлечения ТМ из почвы, основанная на применении биосурфактантов, является экологически безопасной и перспективной альтернативой традиционным физико-химическим методам. С учетом потенциальной эффективности использования биосурфактантов для биоремедиации загрязненных ТМ почв развитие данной технологии требует более детального исследования, как-то: степени избирательности биосурфактантов в отношении ТМ в растворах и почвенных системах, а углеводород
Ультрафильтрационная мембрана
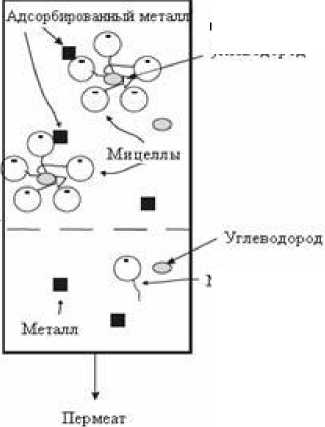
Рис. 3. Схематичная диаграмма процесса ультрафильтрации комплекса сурфактант-поллютант (углеводород и металл) (по Mulligan, 2005)
Гончарук Е. И. Гигиеническое нормирование химических веществ в почве / Е. И. Гончарук, Солюбипизовалный Г. И. Сидоренко. М.: Мысль, 1986. 320 с.
Дерябина Т . Г . Дикий кабан ( Sus биоиндикатор загрязнения мест
тяжелыми металлами /
Т. Г.
scrofa L.)
–
его обитания
Дерябина //
Экология. 1996. № 6. С. 474-475.
Добровольский В . В . География микроэлементов: глобальное рассеяние / В. В. Добровольский. М.: Мысль, 1983. 272 с.
Евдокимова Г . А . Аккумуляция меди и никеля почвенными грибами / Г. А. Евдокимова, Р. П.
Мономер биосурфакта! Мозгова // Микробио логия. 1991. Т. 60, № 5. С. 801 – 805.
Загрязнение воздуха и жизнь растений / под ред.
М. Трешоу. Л.: Гидрометиздат, 1988. 534 с.
Загрязнение почв и растительности тяжелыми металлами. М.: ВАСХНИЛ. 1978. 52 с.
Захаро в В . Д . Основные направления прикладных
также механизмов взаимодействия ионов ТМ с сурфактантными мицеллами в комплексе металл – биосурфактант (Miller, 1995). При проведении биоремедиации необходимо также учитывать тот факт, что на извлечение ТМ из
экологических исследований сообществ животных и растений в Челябинской области / В. Д. Захаров, А. В. Лагунов // Проблемы экологии Южного Урала. 1995. № 1. С. 59-62.
Ившина И . Б . Применение экологически безопасной экспресс-технологии очистки нефтезагрязненных почв и грунтов (на примере районов нефтедобычи Пермской области) / И. Б. Ившина, М. С. Куюкина, С. М. Костарев // Нефтяное хозяйство. 2003. № 9. С. 116-119.
почвы оказывают влияние: химическая структура, размер мицеллы биосурфактанта, тип и значение рН почвы, состав и степень загрязнения и другие факторы (Frazer, 2000; Markiewicz-Patkowska et al., 2005; Shawabkeh, 2005).
Работа выполнена при поддержке грантов Президента РФ "Ведущие научные школы" № НШ-4112.2008.4 и Президиума РАН «Молекулярная и клеточная биология»
Список литературы Методы очистки загрязненных тяжелыми металлами почв с использованием (био)сурфактантов (обзор)
- Алексеев Ю. В. Тяжелые металлы в почвах и растениях/Ю. В. Алексеев. Л.: Агропромиздат, 1987. 141 с.
- Вальков В. Ф. Влияние загрязнения тяжелыми металлами на микроскопические грибы и Azotobacter чернозема обыкновенного/В. Ф. Вальков, С. И. Колесников, К. Ш. Казеев и др.//Экология. 1997. № 5. С. 388-390.
- Воронина А. Д. Современные физические и химические методы исследования почв/А. Д. Воронина, Д. С. Орлов. М.: Изд-во МГУ, 1987. 204 с.
- Гиниятуллин Р. Х. Содержание некоторых металлов в листьях и ветвях Populus balsamifera L. в условиях промышленного загрязнения/Р. Х. Гиниятуллин, А. Ю. Кулагин, И. Р. Кагарманов//Экология. 1998. № 2. С. 94-97.
- Гончарук Е. И. Гигиеническое нормирование химических веществ в почве/Е. И. Гончарук, Г. И. Сидоренко. М.: Мысль, 1986. 320 с.
- Дерябина Т. Г. Дикий кабан (Sus scrofa L.) -биоиндикатор загрязнения мест его обитания тяжелыми металлами/Т. Г. Дерябина//Экология. 1996. № 6. С. 474-475.
- Добровольский В. В. География микроэлементов: глобальное рассеяние/В. В. Добровольский. М.: Мысль, 1983. 272 с.
- Евдокимова Г. А. Аккумуляция меди и никеля почвенными грибами/Г. А. Евдокимова, Р. П. Мозгова//Микробио логия. 1991. Т. 60, № 5. С. 801 -805.
- Загрязнение воздуха и жизнь растений/под ред. М. Трешоу. Л.: Гидрометиздат, 1988. 534 с.
- Загрязнение почв и растительности тяжелыми металлами. М.: ВАСХНИЛ. 1978. 52 с.
- Захаров В. Д. Основные направления прикладных экологических исследований сообществ животных и растений в Челябинской области/В. Д. Захаров, А. В. Лагунов//Проблемы экологии Южного Урала. 1995. № 1. С. 59-62.
- Ившина И. Б. Применение экологически безопасной экспресс-технологии очистки нефтезагрязненных почв и грунтов (на примере районов нефтедобычи Пермской области)/И. Б. Ившина, М. С. Куюкина, С. М. Костарев//Нефтяное хозяйство. 2003. № 9. С. 116-119.
- Кашевский С. С. Поиск экологически чистой биотехнологии извлечения родия/С. С. Кашевский, С. Р. Андреев, М. Н. Иванов//Экологически чистые технологические процессы в решении проблем окружающей среды. Пермь, 1996. Т. 1. С. 36 -37.
- Колесников С. И. Влияние загрязнения тяжелыми металлами на эколого-биологические свойства чернозема обыкновенного/С. И. Колесников, К. Ш. Казеев, В. Ф. Вальков//Экология. 2000. № 3. С. 193-201.
- Левин С. В. Тяжелые металлы как фактор антропогенного воздействия на почвенную микробиоту/С. В. Левин, В. С. Гузев, И. В. Асеева и др.//Микроорганизмы и охрана почв/Под ред. Д. Г. Звягинцева. М.: Изд-во МГУ, 1989. С. 5-47.
- Лозановская И. Н. Экология и охрана биосферы при химическом загрязнении/И. Н. Лозановская, Д. С. Орлов, Л. К. Садовникова. М.: Высш. школа, 1998. 287 с.
- Нифтонова М. Г. Влияние изотопных и неизотопных носителей на накопление 90Sr и 137Cs лишайниками из водных растворов/М. Г. Нифтонова//Экология. 1977. № 6. С. 78-80.
- Новиков Ю. Ю. Методы исследования качества воды водоемов/Ю. Ю. Новиков, К. О. Ласточкина, З. Н. Болдина. М.: Медицина, 1990. 400 с.
- Орлов Д. С. Химия почв: учебник/Д. С. Орлов. М.: Изд-во МГУ, 1992. 400 с.
- Очистка природных и сточных вод. Аналитический обзор. ВНТИЦ. М., 1991. 145 с.
- Покопова Ю. В. Эффективные адсоpбенты для очистки и выделения тяжелых металлов из водных растворов/Ю. В. Покопова. ЛДHТП. Л., 1991. 67 с.
- Проскуряков В. А. Очистка сточных вод в химической промышленности/В. А. Проскуряков, Л. И. Шмидт. Л.: Химия, 1976. 169 с.
- Протасова Н. А. Микроэлементы: биологическая роль, распределение в почвах, влияние на распределение заболеваний человека и животных/Н. А. Протасова//Соросовский образовательный журнал. 1998. № 12. С. 32-37.
- Тэрыце К. Математическое моделирование влияния свинца (Pb2+) и цинка (Zn2+) на биологическую активность почв/К. Тэрыце, Э. Менчер, Х. Тэрыце//Экология. 1990. № 2. С. 39-43.
- Тэрыцэ К. В. Некоторые вопросы количественной оценки влияния тяжелых металлов на биологическую активность почв/К. В. Тэрыцэ, П. Валтер//Экология. 1988. № 2. С. 12-18.
- Фирсова Л. П. Процессы адсорбции, десорбции и фильтрации растворов радиоцерия в почвах/Л. П. Фирсова//Вестник Московского университета. Сер. Химия. 2001. Т. 42, № 1. С. 66-70.
- Фрумин Г. Т. Экологическая химия и экологическая токсикология. -СПб.: Изд-во РГГМУ, 2000. 204 с.
- Харин В. Н. Географические закономерности аккумуляции тяжелых металлов во мхах и лесных подстилках на территории Карелии/В. Н. Харин, Н. Г. Федорец, Г. В. Шильцова и др.//Экология. 2001. № 2. С. 155-158.
- Хархордин И. Л. Моделирование миграции металлов в торфяных отложениях/И. Л. Хархордин, Ф. Г. Атрощенко//Экологическая химия. 1998. Т. 8, № 1. С. 37-43.
- Хасид Е. В. Опыт внедрения новых мембранных методов водообработки стоков/Е. В. Хасид. Л.: Стройиздат, 1989. 189 с. Химия окружающей среды/под ред. О. М. Бокриса. М.: Химия, 1982. С. 672.
- Шинкарев А. А. Миграция меди из верхних горизонтов обрабатываемых почв при загрязнении тяжелыми металлами/А. А. Шинкарев, И. П. Бреус, Г. Р. Садриева, Г. Ф. Копосов//Экология. 1998. № 3. С. 234-236.
- Шулькин В. М. Концентрации тяжелых металлов в митилидах амурского залива (Японское море)/В. М. Шулькин, Е. Н. Чернова//Экология. 1994. № 4. С. 80-88.
- Энхольм Э. Окружающая среда и здоровье человека/Э. Энхольм. М.: Пpогpесс, 1980. 95 с.
- Юшков В. В. Химия и экология 3d-элементов/В. В. Юшков, Т. А. Юшкова, В. В. Стрелков. Екатеринбург: Изд-во УрО РАН, 2004. 171 с.
- Яковлев С. В. Технология электрохимической обработки воды/С. В. Яковлев, И. Г. Краснобородько, Н. М. Рогов Л.: Стройиздат, 1987. 246 с.
- Allen S. J. Isotherm analyses for single component and multi-component metal sorption onto lignite/S. J. Allen, P. A. Brown//J. Chem. Tech. Biotechnol. 1995. Vol. 62. P. 17-24.
- Almeida C. M. R. Influence of surfactants on the Cu phytoremediation potential of a salt marsh plant // C. M. R. Almeida, A. C. Dias, A. P. Mucha et al. // Chemosphere. 2009. doi:10.1016/j.chemisphere. 2008.12.037.
- Aşςi Y. A comparative study for the sorption of Cd(II) by soils with different clay contents and mineralogy and the recovery of Cd(II) using rhamnolipid biosurfactant/Y. Aşςi, M. Nurbaş, Y. S. Aςikel//J. Hazard. Mater. 2008 а. Vol. 154. P. 663-673.
- Aşςi Y. Removal of zinc ions from a soil component Nafeldspar by a rhamnolipid biosurfactant/Y. Aşςi, M. Nurbaş, Y. S. Aςikel//Desalination. 2008 б. Vol. 223. P. 361-365.
- Avery S. V. Copper toxicity towards Saccharomyces cerevisiae: dependence on plasma membrane fatty acid composition/S. V. Avery, N. G. Howlett, S. Radice//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996. Vol. 62, № 11. P. 3960-3966.
- Ayyamperumal T. Assessment of acid leachable trace metals in sediment cores from river Uppanar, Cuddalore, Southeast coast of India/T. Ayyamperumal, M. P. Jonathan, S. Srinivasalu et al.//Environ. Poll. 2006. Vol. 143. P. 34-45.
- Bitton G. Influence of extracellular polysaccharides on the toxicity of copper and cadmium toward Klebsiella aerogenes/G. Bitton, V. Freihofer//Microbiol. Ecol. -1978. Vol. 4. P. 119-125.
- Breault R. F. Copper speciation and binding by organic matter in copper-contaminated streamwater/R. F. Breault, J. A. Colman, G. R. Aiken, D. McKnight//Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996. Vol. 30. P. 3477-3486.
- Chen J. H. Trace Metal Mobilization in Soil by Bacterial Polymers/J. H. Chen, D. R. Czajka, L. W. Lion et al.//Environ. Health Perspectives. 1995. Vol. 1. P. 53-58.
- Christofi N. Microbial surfactants and their use in field studies of soil remediation/N. Christofi, I. B. Ivshina//J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002. Vol. 93. P. 915-929.
- Christofi N. Microbiology of subterranean waste sites/N. Christofi, J. C. Philp//Experientia. 1991. Vol. 47. P. 524-527.
- Czaplicka M. Application of biosurfactants and non-ionic surfactants for removal of organic matter from metallurgical lead-bearing slime/M. Czaplicka, A. Chmielarz//J. Hazard. Mat. 2008 DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.010
- Dahrazma B. Extraction of copper from mining residues by rhamnolipids/B. Dahrazma, C. N. Mulligan//Prac. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2004. Vol. 8, № 3. P. 166-172.
- Dahrazma B. Investigation of the removal of heavy metals from sediments using rhamnolipid in a continuous flow configuration/B. Dahrazma, C. N. Mulligan//Chemosphere. 2007. Vol. 69. P. 705-711.
- Eckl P. Uptake of natural and man-made radionuclides by lichens and mushrooms/P. Eckl, W. Hofmann, R. Turk//Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 1986. Vol. 25. P. 43-54.
- Farmer J. G. Chromium speciation and fractionation in ground and surface waters in the vicinity of chromite ore processing residue disposal sites/J. G. Farmer, R. P. Thomas, M. C. Graham et al.//J. Environ. Monit. 2002. Vol. 4. P. 235-243.
- Franzetti A. Potential applications of surface active compounds by Gordonia sp. strain BS29 in soil remediation technologies/A. Franzetti, P. Caredda, C. Ruggeri et al.//Chemosphere. 2009. 052 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.12
- Frazer L. Innovations. Lipid lather removes metals/L. Frazer//Environ. Health Perspectives. 2000. Vol. 108. P. 320-323.
- Gadd G. M. Interactions of fungi with toxic metals/G. M. Gadd//New Phytot. 1992 а. Vol. 121, № 47. P. 25-60.
- Gadd G. M. Metals and microorganisms: a problem of definition/G. M. Gadd//FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1992 б. Vol. 100. P. 197-204.
- Gao Y. Effects of organic acids on cooper and cadmium desorption from contaminated soils/Y. Gao, J. He, W. Ling et al.//Environ. Int. 2003. Vol. 29. P. 613-618.
- Gautam K. K. Microbial surfactants: a review/K. K. Gautam, V. K. Tyagi//J. Oleo Sci. 2006. Vol. 55, № 4. P. 155-166.
- Ginn T. R. Processes in microbial transport in the natural subsurface/T. R. Ginn, B. D. Wood, K. E. Nelson et al.//Advances Wat. Res. 2002. Vol. 25. P. 1017-1042.
- Gould M. S. Heavy metal complexation behavior in anaerobicalli digested sludges/M. S. Gould, E. J. Genetelli//Wat. Res. 1978. Vol. 12. P. 505-512.
- Gu B. Adsorption and desorption of natural organic matter on iron oxide: mechanisms and model/B. Gu, J. Schmitt, Z. Chen et al.//Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994. Vol. 28. P. 38-46.
- Gupta A. Effects of halides on plasmid-mediated silver resistance in Escherichia coli/A. Gupta, M. Maynes, S. Silver//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998. Vol. 64, № 12. P. 5042-5045.
- Hernandez A. Metal accumulation and vanadiuminduced multidrug resistance by environmental isolates of Escherichia hermanii and Enterobacter cloacae/A. Hernandez, R. P. Mellado, J. L. Martinez//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998. Vol. 64, № 11 P. 4317-4320.
- Hong K.-J. Removal of cadmium and lead from soil using aescin as a biosurfactant/K.-J. Hong, Y.-K. Choi, S. Tokunaga et al.//J. Surfactant Deterg. 1998. Vol. 1, № 2. P. 247-250.
- Hong K-J. Evaluation of remediation process with plantderived biosurfactant for recovery of heavy metals from contaminated soils/K-J. Hong, S. Tokunaga, T. Kajiuchi//Chemosphere. 2002. Vol. 49, № 3. P. 379-387.
- Irving M. Order of stability of metal complexes/M. Irving, R. J. Williams//Nature. 1948. Vol. 162. P. 746-747.
- Janssen C. R. Environmental risk assessment of metals: tools for incorporating bioavailability/C. R. Janssen, D. G. Heijerick, K. A. C. De Schamphelaere, H. E. Allen//Environ. Int. 2003. Vol. 28. P. 793-800.
- Jordan F. L. A comparison of chelator-facilitated metal uptake by a halophyte and a glycophyte/F. L. Jordan, M. Robin-Abbott, R. M. Maier, E. P. Glenn//Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002. Vol. 21, № 12. P. 2698-2704.
- Juwarkar A. A. Biosurfactant technology for remediation of cadmium and lead contaminated soils/A. A. Juwarkar, A. Nair, K. V. Dubey et al.//Chemosphere. 2007. Vol. 68. P. 1996-2002.
- Khan F. I. An overview and analysis of site remediation technologies // F. I. Khan, T. Husain, R. Hejazi // J. Environ. Microbiol. 2004. Vol. 71. P. 95-122.
- Khan S. U. Interaction between the humic acid fraction of soils and certain metallic cations/S. U. Khan//Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1969. Vol. 33. P. 851-854.
- Khanna S. S. Metallo-organic complexes in soil: I. Potentiometric titration of some soil organic matter isolates in the presence of transition metals/S. S. Khanna, F. J. Stevenson//Soil Sci. 1962. Vol. 93. P. 298-305.
- Kierans M. Silver tolerance and accumulation in yeasts/M. Kierans, A. M. Staines, H. Bennett, G. M. Gadd//Biol. Met. 1991. Vol. 4, № 2. P. 100-106.
- Kirchner G. Accumulation 210Pb, 226Ra and radioactive cesium by fungi/G. Kirchner, O. Daillant//Sci. Total Environ. 1998. Vol. 222. P. 63-70.
- Kovalick W. Perspectives on resks of soil pollution and experience with innovative remediation technologies strategies 2000/W. Kovalick//Proc. W. Congr. Chem. Eng. 4th. 1991. P. 282-295.
- Kuyukina M. S. Bioremediation of crude oil contaminated soil using slurry-phase biological treatment and landfarming techniques/M. S. Kuyukina, I. B. Ivshina, M. I. Ritchkova et al.//Soil Sediment Contam. 2003. Vol. 12. P. 85-99.
- Lao U. L. Cadmium removal from contaminated soil by thermally responsive elastin (ELPEC20) biopolymers/U. L. Lao, A. Chen, M. R. Matsumoto et al.//Biotechnol. Bioengineering. 2007. Vol. 98, № 2. P. 349-355.
- Lebeau T. Performance of bioaugmentation-assisted phytoextraction applied to metal contaminated soils: a review/T. Lebeau, A. Braud, K. Jezequel//Environ. Poll. 2008. Vol. 153. P. 497-522.
- Lesmana S. O. Studies on potential applications of biomass for the separation of heavy metals from water and wastewater/S. O. Lesmana, N. Febriana, F. E. Soetaredjo et al.//Biochem. Engineering J. 2009. 12.009 DOI: 10.1016/j.bej.2008
- Maier R. M. Remediation of metal-contaminated soil and sluge using biosurfactant technology/R. M. Maier, J. W. Neilson, J. F. Artiola et al.//Int. J. Occupational Medicine and Environ. Health. 2001. Vol. 14, № 3. P. 241-248.
- Maier R. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids: biosynthesis and potential applications/R. M. Maier, G. Soberon-Chavez//Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000. Vol. 54. P. 625-633.
- Manunza B. Stability constants of metal-humate complexes: titration data analyzed by bimodal Gaussian distribution/B. Manunza, S. Deiana, V. Maddau et al.//Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995. Vol. 59. P. 1570-1574.
- Markiewicz-Patkowska J. The interaction of heavy metals with urban soils: sorption behavior of Cd, Cu, Cr, Pb and Zn with a typical mixed brownfield deposit/J. Markiewicz-Patkowska, A. Hursthouse, H. Przybyla-Kij//Environ. Int. 2005. Vol. 31. P. 513-521.
- Marques A. M. Removal of uranium by an exopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas sp./A. M. Marques, R. Bonet, M. D. Simon-Pujol et al.//Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1990. Vol. 34. P. 429-431.
- Martin T. A. Review of in situ remediation technologies for lead, zinc, and cadmium in soil/T. A. Martin, M. V. Ruby//Wiley Periodicals, Inc. 2004 DOI: 10.1002/rem.20011
- Maslin P. Rhamnolipid-enchanced mineralization of phenanthrene in organic-metal cocontaminated soils/P. Maslin, R. M. Maier//Biorem. J. 2000. Vol. 4. P. 295-308.
- McLean J. E. Behavior of metals in soils/J. E. McLean, B.E. Bledsoe//Ground Wat. Issue. 1992. № 5. P. 1-22.
- Meunier N. Removal of heavy metals from acid soil leachate using cocoa shells in a batch countercurrent sorption process/N. Meunier, J.-F. Blais, R. D. Tyagi//Hydrometallurgy. 2004. Vol. 73. P. 225-235.
- Miller R. M. Biosurfactant-facilitated remediation of metal-contaminated soils/R. M. Miller//Environ. Health Perspectives. 1995. Vol. 103. P. 59-62.
- Mulligan C. N. Environmental applications for biosurfactants/C. N. Mulligan//Environ. Poll. 2005. Vol. 133. P. 183-198.
- Mulligan C. N. On the capability of biosurfactants for the removal of heavy metals from soil and sediments/C. N. Mulligan//Dissertation Abstracts Int. 2000. Vol. 60, № 12. P. 6255.
- Mulligan C. N. Bioleaching of copper mining residues by Aspergillus niger/C. N. Mulligan, R. Galvez-Cloutler//Water Sci. Technol. 2000. Vol. 41, № 12. P. 255-262.
- Mulligan C. N. The use of biosurfactants in the removal of metals from oil-contaminated soil/C. N. Mulligan, R. N. Yong//Contaminated Ground: Fate of Pollutants and Remediation. Ed. R. N. Yong. London: Thomas Telford Publishers, 1997. P. 461-466.
- Mulligan C. N. Remediation of a heavy metalcontaminated soil by a rhamnolipid foam/C. N. Mulligan, S. Wang//Engineering Geology. 2006. Vol. 85. P. 75-81.
- Mulligan C. N. An evaluation of technologies for the heavy metal remediation of dredged sediments/C. N. Mulligan, R. N. Yong, B. F. Gibbs//J. Hazard. Mat. 2001 а. Vol. 85. P. 145-163.
- Mulligan C. N. Heavy metal removal from sediments by biosurfactants/C. N. Mulligan, R. N. Yong, B. F. Gibbs//J. Hazard. Mat. 2001 б. Vol. 85. P. 111-125.
- Mulligan C. N. On the use of biosurfactants for the removal of heavy metals from oil-contaminated soil/C. N. Mulligan, R. N. Yong, B. F. Gibbs//Process Safety Progress. 1999 а. Vol. 18, № 1. P. 50-54.
- Mulligan C. N. Remediation technologies for metalcontaminated soils and groundwater: an evaluation/C. N. Mulligan, R. N. Yong, B. F. Gibbs//Engineering Geology. 2001 в. Vol. 60. P. 193-207.
- Mulligan C. N. Removal of heavy metals from contaminated soil and sediments using the biosurfactant surfactin/C. N. Mulligan, R. N. Yong, B. F. Gibbs//J. Soil Contamination. 1999 б. Vol. 8, № 2. P. 231-254.
- Mulligan C. N. Surfactant-enchanced remediation of contaminated soil: a review/C. N. Mulligan, R. N. Yong, B. F. Gibbs//Engineering Geology. 2001 г. Vol. 60. P. 371-380.
- Mulligan C. N. Metal removal from contaminated soil and sediments by the biosurfactant surfactin/C. N. Mulligan, R. N. Yong, B. F. Gibbs et al.//Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999 в. Vol. 33. P. 3812-3820.
- Neilson J. W. Characterization of lead removal from contaminated soils by non-toxic soil-washing agents/J. W. Neilson, J. F. Artiola, R. M. Maier//J. Environ. Qual. 2003. Vol. 32. P. 899-908.
- Ochoa-Loza F. J. Stability constants for the complexation of various metals with a rhamnolipid biosurfactant/F. J. Ochoa-Loza, J. F. Artiola, R. M. Maier//J. Environ. Qual. 2001. Vol. 30. P. 479-485.
- Pazirandeh M. Development of bacterium-based heavy metal biosorbents: enhanced uptake of cadmium and mercury by Escherichia coli expressing a metal binding motif/M. Pazirandeh, B. M. Wells, R. L. Ryan//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998. Vol. 64, № 10. P. 4068-4072.
- Quintelas C. Removal of Cd(II), Cr(VI), Fe(III) and Ni(II) from aqueous solutions by an E. coli biofilm supported on kaolin // C. Quintelas, Z. Rocha, B. Silva et al. // Chem. Engineering J. 2008. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2008.11.025.
- Ron E. Z. Natural roles of biosurfactants/E. Z. Ron, E. Rosenberg//Environ. Microbiol. 2001. Vol. 3, № 4. P. 229-236.
- Sааr R. A. Complexation of cadmium (II) with water-and soil-derived fulvic acids: effect of pH and fulvic acid concentration/R. A. Sааr, J. H. Weber//Can. J. Chem. 1979. Vol. 57. P. 1263-1268.
- Sanchez A. Biosorption of copper and zinc by Cymodocea nodosa/A. Sanchez, A. Ballester, M. L. Blazquez et al.//Microbiol. Rew. 1999. Vol. 23. P. 527-536.
- Sandrin T. R. A rhamnolipid biosurfactant reduces cadmium toxicity during naphthalene biodegradation/T. R. Sandrin, A. M. Chech, R. M. Maier//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000. Vol. 66, № 10. P. 4585-4588.
- Sandrin T. R. Effect of pH on cadmium toxicity, speciation, and accumulation during naphthalene biodegradation/T. R. Sandrin, R. M. Maier//Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002. Vol. 21, № 10. P. 2075-2079.
- Sawidis T. Uptake of radionuclides by plants after Chernobyl accident/T. Sawidis//Environ. Poll. 1988. Vol. 50. P. 317-324.
- Schneegurt M. A. Biomass byproducts for the remediation of wastewaters contaminated with toxic metals/M. A. Schneegurt, J. C. Jain, J. A. Menicucci et al.//Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001. Vol. 35. P. 3786-3791.
- Schnitzer M. Organo-metallic interactions in soils: 8. An evaluation of methods for the determination of stability constants of metalfulvic acid complexes/M. Schnitzer, E. H. Hansen//Soil Sci. 1970. Vol. 109. P. 333-340.
- Scott J. A. Cadmium biosorption by bacterial exopolysaccharide/J. A. Scott, S. J. Palmer//Biotechnol. Lett. 1988. Vol. 10. P. 21-24.
- Sekhar K. C. Fractionation studies and bioaccumulation of sediment-bound heavy metals in Kolleru lake by edible fish/K. C. Sekhar, N. S. Chary, C. T. Kamala et al.//Environ. Int. 2003. Vol. 29. P. 1001-1008.
- Shawabkeh R. A. Solidification and stabilization of cadmium ions in sand-cement-clay mixture/R. A. Shawabkeh//J. Hazard. Mat. 2005. Vol. 125. P. 237-243.
- Shuman L. M. Chemical forms of micronutrients in soils / L. M. Shuman // In: Micronutrients in agriculture / Ed. J. J. Mortvedt, F. R. Cox, L. M. Shuman, R. M. Welch // Soil Sci. Soc. Amer.. 1991. P. 113- 144.
- Singh P. Enhancement of metal bioremediation by use of microbial surfactants/P. Singh, S. S. Cameotra//Biochem. Biophysical Res. Communications. 2004. Vol. 319. P. 291-297.
- Sposito G. Cupric ion complexation by fulvic acid extracted from sewage sludge-soil mixtures/G. Sposito, K. M. Holtzclaw, C. S. LeVesque-Madore//Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1979. Vol. 43. P. 1148-1155.
- Tan H. Complexation of cadmium by a rhamnolipid biosurfactant/H. Tan, J. T. Champion, J. F. Artiola et al.//Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994. Vol. 28. P. 2402-2406.
- Trevors J. T. Cadmium transport, resistance, and toxicity in bacteria, algae, and fungi/J. T. Trevors, G. W. Stratton, G. M. Gadd//Can. J. Microbiol. 1986. Vol. 32, № 6. P. 447-464.
- Twardowska I. Sorption of metals onto natural organic matter as a function of complexation and adsorbentadsorbate contact mode/I. Twardowska, J. Kyziol//Environ. Int. 2003. Vol. 28. P. 783-791.
- Volesky B. Advances in biosorption of metals: selection of biomass types/B. Volesky//FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1994. Vol. 14. P. 291-302.
- Volesky B. Biosorption of heavy metals/B. Volesky//ed. B. Volesky. CRC Press, Boca Ration, 1990. P. 7-43.
- Wang S. Enhanced mobilization of arsenic and heavy metals from mine tailings by humic acid/S. Wang, C. N. Mulligan//Chemosphere. 2009. Vol. 74. P. 274-279.
- Wang S. Rhamnolipid biosurfactant-enhanced soil flushing for the removal of arsenic and heavy metals from mine tailings/S. Wang, C. N. Mulligan//Process Biochem. 2009. Vol. 44. P. 296-301.
- Wang S. Rhamnolipid foam enhanced remediation of cadmium and nikel contaminated soil/S. Wang, C. N. Mulligan//Water, Air, and Soil Poll. 2004. Vol. 157. P. 315-330.
- White C. Microbial solubilization and immobilization of toxic metals: key biogeochemical processes for treatment of contamination/C. White, J. A. Sayer, G. M. Gadd//FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1997. Vol. 20. P. 503-516.
- White C. An integrated microbial process for the bioremediation of soil contaminated with toxic metals/C. White, A. K. Sharman, G. M. Gadd//Nat. Biotechnol. 1998. Vol. 16, № 6. P. 572-575.
- Zhang Y. Enhanced octadecane dispersion and biodegradation by a Pseudomonas rhamnolipid surfactant (biosurfactant)/Y. Zhang, R. M. Miller//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992. Vol. 58, № 10. P. 3276-3282.
- Zosim Z. Uranium binding by emulsan and emulsanosols/Z. Zosim, D. Guthnick, E. Rosenberg//Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1983. Vol. 25. P. 1725-1735.
- Zouboulis A. I. The use of biosurfactants in flotation: application for the removal of metal ions/A. I. Zouboulis, K. A. Matis, N. K. Lazaridis, P. N. Golyshin//Mining Engineering. 2003. Vol. 16. P. 1231-1236.


