Microbial inoculation of plants and its importance for sustainable agriculture
Автор: Yergaryaeva A.
Журнал: Теория и практика современной науки @modern-j
Рубрика: Основной раздел
Статья в выпуске: 6 (108), 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This article highlights the detrimental effects of conventional agricultural practices on human health and the environment, particularly through the use of chemical inputs like fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. It suggests that microbial inoculants could provide a sustainable alternative by promoting plant health and productivity without the negative impacts associated with chemicals. Microbial inoculants consist of beneficial microorganisms like bacteria, fungi, and algae that can enhance soil fertility, control pests and diseases, and promote plant growth. By harnessing the power of these natural agents, farmers can potentially reduce their reliance on chemical inputs, thereby mitigating the adverse effects on human health and the environment. Research into microbial inoculants is crucial for understanding their effectiveness and optimizing their application in agriculture. By exploring advancements in microbial technology and strategies for utilizing these biological resources, we can move towards a more sustainable approach to farming that prioritizes human health and environmental well-being. Overall, the focus on microbial inoculants represents a promising direction for sustainable agriculture, offering a viable solution to the challenges posed by conventional chemical-based farming practices.
Microbial inoculants, human health, biofertilizers, biocontrol agents, plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (pgpr)
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140307145
IDR: 140307145 | УДК: 579.6,
Текст научной статьи Microbial inoculation of plants and its importance for sustainable agriculture
The advent of industrial system of agriculture involving the use of chemicals, preservatives, hormones, and antibiotics resulted in increased food growth and production. This new technique produces crop and livestock in larger quantities than the sustainable agriculture practiced in the past. Industrial agriculture is characterized with mono cropping, in which the same crop is grown season after season. Mono cropping reduces the soil s ability to naturally eliminate pests and replenish nutrients. To combat this menace industrial agriculture uses heavy doses of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Similarly, massive quantities of livestock such as cows, chickens, pigs, and turkeys are raised in confined, overcrowded and unsanitary conditions [1].
Agrochemicals are commonly used in agricultural production to control or prevent diseases, pests and weeds in order to maintain high quality of agricultural products and eliminate or reduce yield losses. With this industrialized system, food is produced at reduced costs and farmers therefore get higher profits from their farm but serious concerns were being raised about health risks resulting from residues in drinking water and food and from occupational exposure. Suyal et al. reiterated that heavy doses of chemical fertilizer, although leading to self reliance in food production, causes harmful impacts on living organisms and also depreciate the environment. The chemical contaminates the food produced and goes further to alter the normal body functions of the consumer [2,3].
Microbial inoculants refer to formulations composed of beneficial microorganisms that play an important role in soil ecosystems for sustainable agriculture. Microbial inoculants are environmentally friendly and are a potential alternative to chemical fertilizers and pesticides. They are composed of active strains of microorganisms which directly or indirectly stimulate microbial activity and hence improve mobility of nutrients from soil. They could be phyto stimulants, bio fertilizers or microbial bio control agents. They provide protection against a range of different pathogens and they are effective bio herbicides.
In view of these, this paper aims to summarize the impact of the conventional agricultural inputs fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides on human health and the ameliorating effect of microbial inoculants on these hazards. Advances in microbial inoculants and technology and strategies to explore this natural, user friendly biological resource for sustainable maintenance of plant health will be discussed.
Direct effects of microbial inoculation
Plants are entirely dependent upon soil microorganisms to utilize soils as a growth medium, and the synergy between both is important for their survival. The rhizosphere, the region of soil surrounding the roots, has the greatest concentration of microorganisms. Root exudates dictate the microbial communities. Manipulating the rhizosphere, changes microbial diversity and could improve plant performance by influencing water dynamics and enzyme activities [4]. A wide range of microscopic organisms inhabits the rhizosphere: bacteria, algae, fungi, protozoa and actinomycetes. Of these, bacteria is the most abundant and important group of microorganisms regarding plant growth and productivity. They either live freely in rhizosphere, or in inter and intracellular spaces of root tissues, forming symbiotic associations with plants. Fungi play an important role in organic matter decomposition, and therefore nutrient cycling. Among soil fungi, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) are the most important and widely studied group as potential biofertilizers and biopesticides. Examples of schematic representation of some importance of microbial inoculants in agriculture and the mechanism of actions have been summarized in Figure 1 [5].
PGPR Microbial Inoculants
Biofertilizer
Biocontrol Agents
Phytohormones Nitrogen Phosphorus Antibiotic Competition Induced Hydrogen
|
Pre |
eduction |
fixat |
on Solubilization production |
Systemic Cyanide |
||
|
Auxin |
l.Sy |
1 mbiotic |
In |
organic Acids |
Resistance (ISR) |
|
|
Nitrogen Fixation 2.The Free Living Nitrogen Fixing System |
Production
|
|||||
Figure 1 – Schematic representation of some importance of microbial inoculants in agriculture and the mechanism of actions
Taking a closer look at the rhizosphere, plants continually secrete synthesized food through their roots, nourishing a diverse community of soil rhizobacteria that in turn can strongly influence plant development by performing vital functions for plant. They are allies of plants, governing several fundamental processes related to plant growth. One of the important functions of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) is phosphorus (P) solubilization in the soil. The dynamics of P in soils are complex. Its availability for plants is often totally dependent on phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB), heterotrophic bacteria that secrete organic acids, which solubilize fixed forms of P and release available forms into the soil solution. Other extensively studied plant growth promoting traits are nitrogen fixation, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC), deaminase activity, nutrient solubilization, chitinase activity, and catalase activity [6].
However, microbes used for these purposes are very specific and need to be screened for specific characteristics before development of biofertilizers. The development of microbial inoculants/biofertilizers is a highly technical and specialized job that goes through a number of steps before its ground level use (Figure 2) [7].
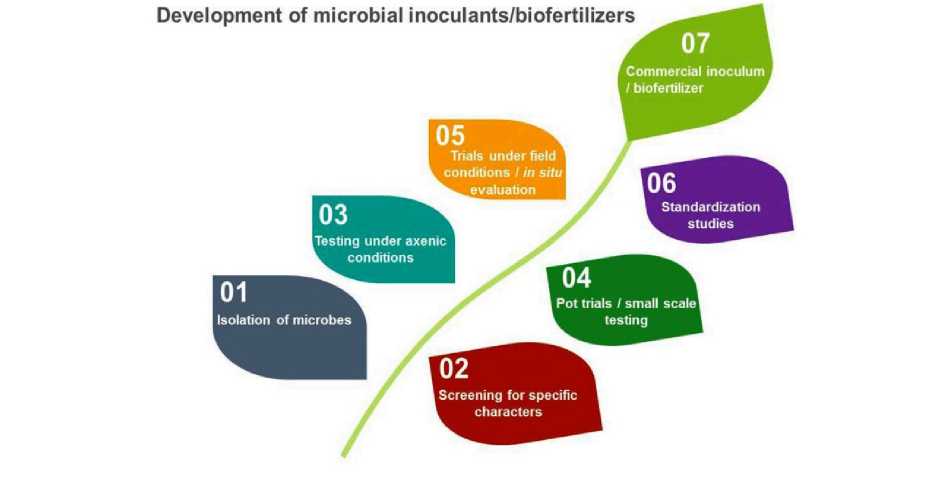
Standardization studies
Screening for specific l characters
Pot trials I small scale t testing
Development of microbial inoculants/biofertilizers
Commercial inoculum I biofertilizer
05 ,
Trials under field ’ conditions I in situ evaluation
Isolation of microbes
Jesting under axenic conditions
Figure 2 - Stages in the development and commercialization of microbial inoculants/biofertilizers
PGPR have direct and indirect plant growth promoting influences through which they help plants to perform better under field conditions. Some of these effects are very common among culturable microbes, while others are specific to certain microbial strains/species. Under diverse environmental conditions, there are large fluctuations in microbial communities in the rhizosphere, influenced by plant species, soil moisture and temperature regimes, environmental conditions and soil physiochemical conditions. For example, Gałazka and Grzadziel reported the fungal genetic diversity and community level through physiological profiling of microbial communities in the soil under long-term maize monoculture [10]. They reported that techniques of maize cultivation and season had a great influence on the fungal genetic structure in the soil. These fluctuations in soil and environmental conditions also induce or suppress different plant growth promoting characteristics of microbial/strains.
The most common direct effects include biological nitrogen fixation, phytohormone production, nutrient solubilization/mobilization, and siderophore production. Indirect effects include biological control of phytopathogens, and production of hydrolytic enzymes. PGPR are also effective in improving plant growth in stress conditions through ACC-deaminase activity, exopolysaccharides, production and scavenging toxic reactive oxygen species. The most important direct effects involved in plant growth promoting include biological nitrogen fixation, phytohormone production, nutrient solubilization, siderophore production, and ACC deaminase activity [8].
Nitrogen fixation
Atmospheric N is reduced to plant available form though natural or artificial means. When done artificially, N2 is reduced to ammonia via the Haber–Bosch process, in which natural gas (CH4) and N2 are converted to reduced forms of N at high temperature and pressure. In nature, N2 reduction is performed by N-fixing microorganisms that use the nitrogenase enzyme to reduce N2 to ammonia. This biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) is responsible for two-thirds of the total fixed N worldwide [9].
The microbes performing BNF can be generally categorized as symbiotic, associative symbiotic, and freeliving. However, a number of free-living N fixing bacteria, such as Azotobacter, Gluconoacetobacter, and Azospirillum spp. are present in nature and fix N for plants . The highest proportion of BNF is performed by symbiotic N2 fixers, i.e., rhizobia, which make symbiotic associations with the roots of leguminous plants [9]. The establishment of symbiotic association involves a complex mechanism and exchange of chemical signals between host plant and symbionts i.e., rhizobia, leading to the formation of root knots, also called nodules. These develop from the swelling of cortical cells that host rhizobia as intracellular symbionts.
PGPR other than rhizobia also have the nitrogenase enzyme and can fix N in non-leguminous plants, such as diazotrophs, which are capable of forming non-obligate interactions with host plants other than legumes. Nitrogenase is a two-component metallo-enzyme that consists of an iron (Fe) protein (dinitrogenase reductase) and molybdenum (Mo)-Fe protein (dinitrogenase). For nitrogenase complex to function, both components should be present. During N fixation, the Fe protein receives electrons with high reducing power from a low redox donor, such as reduced ferredoxin (Fd) or flavodoxin, and is reduced itself [9].
Phytohormone production
Plants produce plant growth regulators/phytohormones, complex organic compounds that control plant growth and productivity. Due to their complexity, plants need a considerable amount of energy and nutrients to synthesize them. Bacteria synthesize significant quantities of phytohormones, and release them into the plant, resulting in pronounced positive effects on plant growth and development. It is reported that bacteria can produce up to 60 times more plant growth regulators than plants themselves.
Phytohormones, such as indole acetic acid (IAA), ethylene, abscisic acid, cytokinins, and gibberellins production by PGPR help to improve crop growth and performance. Phytohormones are involved in plant growth at different scales, such as cell division, cell enlargement, seed germination, root formation, and stem elongation [9]. Microbially-produced phytohormones have direct influence on plants’ internal physiological processes and are involved in plant growth. The effectiveness of these microbially produced phytohormones to improve crop productivity has been well-documented. Microbes can meet the plant’s hormonal requirements, saving the plant’s metabolic energy for growth and reproduction. Microbially produced phytohormones play an effective role both under normal and stress conditions.
Auxins can alleviate the adverse effects of stress on plant growth. Some plants produce enough auxins to cope with adverse conditions, while others produce insufficient amounts, resulting in an inability to alleviate stress conditions. To meet the plant’s auxin requirements, exogenous application of auxins or inoculation with microbes capable of producing auxins can be helpful and allow for resumption of normal metabolic functions. Ahmad et al. evaluated the potential of auxin-producing Pseudomonas and Rhizobium strains to improve osmotic stress tolerance in Vigna radiata reporting an increase in total dry matter and salt tolerance index [10]. In another study, Jamil et al. exogenously applied L-tryptophan in combination with Pseudomonas fluorescens under drought conditions, and reported a significant increase in growth, physiology, and yield. Abscisic acid (ABA) also improves plant development under stress conditions and plays an important role in photoperiodic induction of flowering. Patten and Glick inoculated canola plants with IAAproducing bacterial strains and reported increase in root length in comparison to IAA-deficient mutant and control plants [10].
Soil microorganisms are solely responsible for nutrient cycling. Around 50% of soil organic matter is composed of carbon, while the rest consists of N, P, S, and other nutrients. In addition to the decomposition of soil organic matter, microbes also make chemically fixed nutrients, such as phosphorus (P), zinc (Zn), potassium (K), and iron (Fe) available. The main mechanism in the solubilization of P, K, Fe, and Zn is the lowering of pH from the production of organic acids. The P solubilizing soil bacteria include free living rhizobacteria, such as Pseudomonas, the symbiotic nitrogen fixers (rhizobia), and asymbiotic nitrogen fixers (Azotobacter) [11].
ACC deaminase activity
Ethylene is an endogenously produced phytohormone with a specific role in determining plant maturity. Lower levels of ethylene are essential for plant metabolism during normal growth and development. It is a stress hormone that helps plants to cope with biotic and abiotic stress. Ethylene negatively affects normal metabolic processes in plants leading to decrease in root and shoot growth. For example, Ahmad et al. reported a decrease in root and shoot length and increased stem diameter due to salinity stress and linked it to increased concentrations of ethylene [11]. It has been well-documented that PGPR strains belonging to genera Bacillus, Enterobacter, and Pseudomonas isolated from stress conditions contain ACC deaminase enzyme and improve plant growth under biotic and abiotic stresses. ACC is the immediate precursor of ethylene and cleaves it into α-ketobutyrate and NH3. Therefore, these bacterial strains can increase stress tolerance in plants by decreasing ethylene levels, allowing increased plant growth even under stress. Consequently, the use of these bacteria as biofertilizers and biopesticides can be helpful in reducing the dependence on chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
Microbial Inoculants as Biocontrol Agents (Biopesticides, Bioherbicides, Biofungicides)
Many microorganisms have antifungal and antibacterial activities, so they can be used as biopesticides. Microbial inoculants play an essential role in biological control technologies used in agricultural ecosystems. The biological control mechanisms exerted by most microbial inoculants can be attributed to the release of extracellular hydrolytic enzymes, competition for nutrients and secondary metabolites that are toxic to plant pathogens. at very low concentrations, while some induce defense responses such as systemic acquired resistance in the host plant. These organisms help reduce damage to plants from pathogens and can also regulate levels of certain plant hormones such as ethylene and auxin. Beneficial effects of microbial inoculants on plants include control of fungal . Biological control activity demonstrated by a number of microbial preparations includes herbicidal activity; including Colletotrichum cocodes velvet leaf fungicide, biological fungicide Fusarium spp. and the fungicide Striga. Trichoderma harzianum, by producing volatile antibiotics, inhibits wood rot and other fungal pathogens by up to 60% [12].
Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus niger, Penicillium funiculosum Penicillium aurantiogriseum, Penicillium citrinum and Trichoderma koningii have been shown to be effective against the phytopathogenic fungus Phytophthora infestans. Even more, Cavaglieri et al., Pereira et al., Etcheverry et al. and Nesci et al. also reported that Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Amphibacillus xylanus, Microbacteria oleovorans and Sporolactobacillus inulinus exhibited growth inhibition against pathogenic fungi. Bacillus subtilis has been reported to control Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin production both in the field and in store. Mitsuaria sp. provides effective biological control on bacterial stains. Pseudomonads are also reported to exert biocontrol effects against Fusarium wilt. Bacillus spp. has the ability to produce inhibitory volatiles and is therefore effective in biological control of bacterial diseases in many crops. The Rhizobia group has shown positive effects as biological control agents against Pythium disease [13].
Conclusion
This paper overviewed methods to restore and sustain the environment with the use of microorganisms for site decontamination. It demonstrated that microbes are effective in the degradation of agrochemicals, industrial effluents, and petroleum products. Microorganisms have great potential to decontaminate polluted sites though their direct role in the degradation of organic pollutants and detoxification of inorganic compounds, and their indirect role of decreasing the need for agrochemicals through plant growth promoting mechanisms.
The reviewed literature shows that microbial inoculants can be successfully used as biofertilizers and biopesticides by using diverse plant growth promoting traits. Microorganisms either improve plant growth by direct effects, such as BNF, hormone production, nutrients solubilization, or are indirectly involved in the protection of plants from biotic and abiotic stresses.
Knowledge of the mechanism of action of microbial inoculants will play an essential role in their use in sustainable agriculture. The use of chemicals in agriculture can be avoided and thus eliminated from human food. Pest and weed control can be achieved by using microbial inoculants as biological control agents and bioherbicides. Harnessing natural resources, including beneficial microorganisms, is one of the most effective methods to sustainably improve agricultural productivity and food quality. Microbial product technology will ensure healthy food security for people in the future.
Список литературы Microbial inoculation of plants and its importance for sustainable agriculture
- Compant, S., Clément, C., & Sessitsch, A. Plant growth-promoting bacteria in the rhizo- and endosphere of plants: Their role, colonization, mechanisms involved and prospects for utilization / S. Compant, C. Clément, A. Sessitsch // Soil Biology and Biochemistry. - 2010. - V. 42(5). - P. 669- 678.
- Brader, G., Compant, S., Mitter, B., Trognitz, F., & Sessitsch, A. Metabolic potential of endophytic bacteria / G. Brader, S. Compant, B. Mitter, F. Trognitz,
- A. Sessitsch // Current Opinion in Biotechnology. - 2014. - V. 27. - P. 30-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2013.09.012.
- Gunatilaka, A. A. L. Natural products from plant-associated microorganisms: distribution, structural diversity, bioactivity, and implications of their occurrence / A. A. L. Gunatilaka // Journal of Natural Products. - 2006. - V. 69. - P. 509526.
- Gou, B., Dai, J., Ng, S., Huang, Y., Ong, L. W., & Carte, B. K. Cytonic acids A and B: novel tripeptide inhibitors of HCMV protease from the endophytic fungus Cytonaema species / B. Gou, J. Dai, S. Ng, Y. Huang, L.W. Ong, B. K. Carte // Journal of Natural Products. - 2000. - V. 63. - P. 602-604.
- Strobel, G., & Daisy, B. Bioprospecting for microbial endophytes and their natural products / G. Strobel, B. Daisy // Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. - 2003. - V. 67(4). - P. 491-502.
- Glick, B. R. Plant growth-promoting bacteria: Mechanisms and applications / B. R. Glick // Scientifica. - 2012.
- Pieterse, C. M. J., Zamioudis, C., Berendsen, R. L., Weller, D. M., Van Wees, S. C. M., & Bakker, P. A. H. M. Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes / C. M. J. Pieterse, C. Zamioudis, R. L. Berendsen, D. M. Weller, S. C. M. Van Wees, P. A. H. M. Bakker // Annual Review of Phytopathology. - 2014. - V. 52. - P. 347-375.
- Siegel, M. R., & Bush, L. P. Phytochemical diversity and redundancy in ecological interaction / M. R. Siegel, L. P. Bush // In J. T. Romeo, J. A. Saunders, & P. Barbosa (Eds.), Recent Advances in Phytochemistry. - 1996. - V. 30. - P. 81-119. New York: Plenum Press.
- Clay, K., & Schardl, C. L. Evolutionary origins and ecological consequences of endophyte symbiosis with grasses / K. Clay, C. L. Schardl // The American Naturalist. - 2002. - V. 160(Suppl 4). - P. S99-S127.
- Zhao, K., Penttinen, P., Zhang, X., Ao, X., Liu, M., Yu, X., & Chen, Q. Maize rhizosphere in Sichuan, China, hosts plant growth-promoting Burkholderia cepacia with phosphate solubilizing and antifungal abilities /K. Zhao, P. Penttinen, X. Zhang, X. Ao, M. Liu, X. Yu, Q. Chen // Microbiological Research. - 2011. - V. 166(6). - P. 448-461.
- Rojas-Solís, D., Zetter-Salmón, E., Contreras-Pérez, M., Rocha-Granados, M. del C., Macías-Rodríguez, L., & Santoyo, G. Pseudomonas stutzeri E25 and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia CR71 endophytes produce antifungal volatile organic compounds and exhibit additive plant growth-promoting effects / D. Rojas-Solís, E. Zetter-Salmón, M. Contreras-Pérez, M. del C. Rocha-Granados, L. Macías-Rodríguez, G. Santoyo // Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology.- 2018. - V. 13. - P. 46-52. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcab.2017.11.007.
- Chen, P., Yu, K., & He, Y. The dynamics and transmission of antibiotic resistance associated with plant microbiomes / P. Chen, K. Yu, Y. He // Environment International. - 2023. - V. 176. - P. 107986.
- Orozco-Mosqueda, Ma. del Carmen, & Santoyo, G. Plant-microbial endophytes interactions: Scrutinizing their beneficial mechanisms from genomic explorations / Ma. del Carmen Orozco-Mosqueda, G. Santoyo // Current Plant Biology. - 2021. - V. 25. - P. 100189. https://doi.org/10.1016Zj.cpb.2020.100189.


