Middle-Late Paleozoic conodont ecogeochemistry: an overview
Автор: A.V. Zhuravlev
Журнал: Вестник геонаук @vestnik-geo
Рубрика: Научные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 3 (315), 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The ecogeochemistry is the application of geochemical features to study animal ecology. This approach is promising for using in reconstructions of ancient pelagic ecosystems. Among other Paleozoic fossils of pelagic animals, remains of conodonts are the most suitable for ecogeochemical investigations. The article reviews ecogeochemical applications of Middle to Late Paleozoic conodont elements. The following features are considered as the most informative: calcium isotopic composition and element ratios (e.g. Sr/Ca) of conodont apatite, and isotopic composition of carbon of conodont elements. These parameters allow us supposing ecological specialization of conodont species, and temporal and spatial dynamics of the ecogeochemistry of conodonts can be used to reconstruct transformations of ancient pelagic ecosystems.
Conodonts, pelagic ecosystems, ecogeochemistry, Paleozoic.
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149129477
IDR: 149129477 | УДК: 56.016.3 | DOI: 10.19110/geov.2021.3.5
Текст научной статьи Middle-Late Paleozoic conodont ecogeochemistry: an overview
The ecogeochemistry is the application of stable isotopes and other geochemical features to infer diet and trophic structure in animals [15]. This approach is used for solving fundamental questions in population and community ecology [14]. With some restriction ecogeochemistry is applicable for fossil associations of various ages — from modern to ancient (e. g. [14, 16, 19]). It is used widely in biology and archeology, but in less degree in paleontology (e. g. [1, 8, 18, 20, 23]).
Ecology of ancient pelagic ( s. l. ) ecosystems is hardly known and difficult to study, especially in the Paleozoic. Therefore, a realistic reconstruction of pelagic ecosystems cannot be fully achieved mainly in consequence of a low preservation potential of their primary producers, and significant taphonomic bias of other elements of the ecosystems. Nevertheless, it seems that the application of ecogeochemistry of the organisms composing these ecosystems and preserved in the geological record, could be a valid tool for the ecological reconstructing of pelagic ecosystems.
Conodonts appear as promising Paleozoic fossils for ecogeochemical studies, because their remains (conodont elements) preserve near-primary composition of the mineral and organic components [27]. The preservation of ecogeochemical proxies in conodont elements is better than hard tissues of vertebrates where it can be affected by the rate of closure of intra-crystalline porosity during fos-silization by the occurrence of disordered micro-crystallites [11, 22]. The material of conodont elements seems to be less affected by weathering and diagenetic changes than the host rock and carbonate fossils [27]. However, the impact of diagenetic processes may obscure primary composition of conodont elements, so the trace elements and some isotopic characteristics may reflect the features of pore water, diagenetic fluids, or host rock [7]. For example, strong postmortem uptake was suggested for Fe, Mn, Al, Zn, REE, Pb, Th, Ba, and U [21]. In contrast, concentrations of Ca, Na, Sr, F and oxygen and organic carbon isotopic characteristics are considered as near-primary [4, 13, 27, 28]. Among these chemical signs, Sr/Ca ratio, organic carbon, and calcium isotopic compositions appear to be ecogeochemical proxies of ecological relations of conodonts [3, 16, 17, 26, 27, 28]. Others parameters rather represent “geochemical archive” of the composition of ancient sea water [5, 13, 21, 25].
Methods
The ecogeochemical methods applicable for conodont elements comprise calcium isotopic composition and element ratios (Sr/Ca, Ca/P etc.) of conodont apatite, and isotopic composition of conodont organic matter preserved in conodont elements.
Method of analysis of Ca isotope composition of conodont apatite had been described by Balter with co-authors [3]. Composition of the conodont apatite, including Sr/Ca and Ca/P ratios, is studied with microprobe (e. g. [10, 27, 28]) or inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP MS) equipped with laser-ablation [2]. Methods of analysis of the carbon isotope ratio of the conodont elements had been described in details by Zhuravlev with co-authors [27, 29]. The low content of organic matter in conodont elements (less than 3%) prevents effective and reliable study of nitrogen isotopic composition [16].
Material
This overview is based on published data from the Upper Devonian — Middle Permian interval of the East European Platform, Cis-Urals, and Urals [6, 26, 27, 28, 29], Upper Devonian — Lower Carboniferous of North America [17], Upper Devonian of France, Morocco, Vietnam and Australia [3]. Most of the conodont elements analyzed with different methods were of good preservation and demonstrated CAI <3 (low grade of thermal maturation) that promises near-primary nature of the composition of the conodont elements.
Results
Ca isotopic composition of conodont apatite ( δ 44/42Ca) according to data by Balter with co-authors [3] range from —0.38 ‰ to 0.22 ‰, with an average value of –0.10 ± 0.22 ‰. Comparisons between Late Devonian (latest Frasnian — early Famennian) conodonts grouped by genus reveal no taxonomic difference [3].
Sr/Ca atomic percent ratio of conodont apatite varies in different hard tissues from 0.000 to 0.022 [12, 27]. The mean Sr/Ca value is about 0.006. A lamellar tissue demonstrates Sr/Ca ratio in interval from 0.000 to 0.012; a paralamellar tissue — from 0.003 to 0.022; and an albid tissue — from 0.000 to 0.022 (Fig. 1, A). Ca/P ratio of lamellar and albid tissue is close to 1.65 and is characterized by minor variations (Fig. 1, B). It is notable that mineral component of an albid tissue is close to stoichiometric apatite-(CaF) [6].
Carbon isotopic composition of conodont elements ( δ 13Ccon) ranges from –32.6 ‰ to –22.1 ‰, with an average value of —26.1 ± 4.8 ‰ [26] (Fig. 2). The lowest δ 13Ccon value was reported for the latest Famennian (U. praesulcata Zone) specimen of Polygnathus communis communis Branson et Mehl, and the highest δ 13Ccon value was reported for the late Famennian ( expansa Zone s. l. ) specimen of Polygnathus semicostatus Branson et Mehl and early Famennian ( crepida Zone s. l. ) Mitrellataxis sp. Very weak negative correlation between δ 13Ccon values and δ 13Ccarb values of host rock was reported for some stratigraphic intervals [27, 29]. Lack of significant correlation between δ 13Ccon values and δ 13Ccarb values suggests prevalence of the near-primary effects in the variations of δ 13Ccon. Conodont elements of various morphology demonstrate consistency of the carbon isotope composition [26].
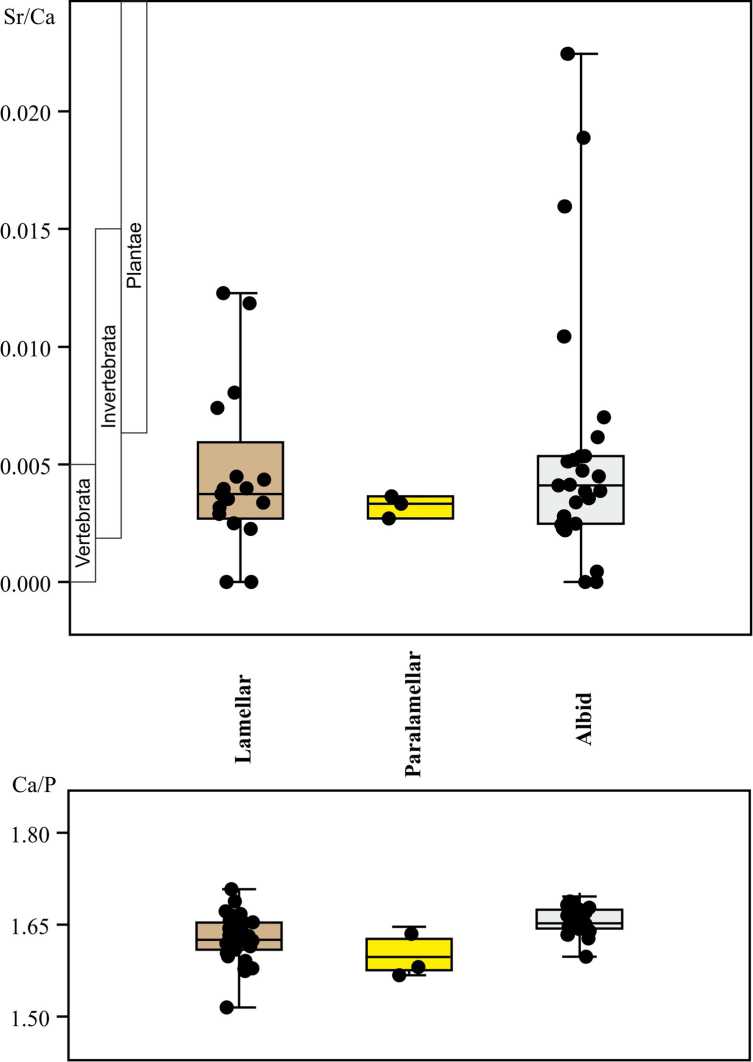
Fig. 1 . Distribution of Sr/Ca and Ca/P atomic ratios in the mineralized tissues of the Late Devonian — Carboniferous conodont elements (box and jitter plots). Sr/Ca is compared with those of Vertebrata, Invertebrata, and plants
Ðèñ. 1. Ðàñïðåäåëåíèå àòîìíûõ îòíîøåíèé Sr/Ca è Ca/P â ìèíåðàëèçîâàííûõ òêàíÿõ êîíîäîíòîâûõ ýëåìåíòîâ ïîçäíåãî äåâîíà — êàðáîíà (ïðÿìîóãîëüíûå è äæèòòåð-ãðàôèêè). Sr/Ca ñðàâíèâàåòñÿ ñ òàêîâûìè ó ïîçâîíî÷íûõ, áåñïîçâîíî÷íûõ è ðàñòåíèé
Discussion
The parameters mentioned above can be used as ecological proxies elucidating position of conodonts in ancient marine ecosystems and, in association with other geochemical features, allow us reconstructing probable perturbations in these ecosystems.
Ca isotopic composition of conodont apatite is considered as a proxy of conodont position in a trophic web. Quite low Ca isotopic composition values suggest that Late Devonian conodonts were first level consumers, probably zooplanktivore [3]. Low values of δ 13Ccon of Late Devonian — Middle Permian conodonts support this assumption as well. It is in accordance with quite high Sr/Ca ratio in conodont elements that is characteristic of herbivore or first level carnivore marine animals [27]. Beyond diet some of these features can be controlled by ambient water composition, temperature, salinity, and metabolic rate of animals (Fig. 3).
Minor variations of Ca/P and Sr/Ca ratios in bioapatite advocate rather weak variability of metabolic rate among conodonts. Lack of correlation of the δ 13Ccon and paleotemperatures suggests weak temperature effect in variations of organic carbon isotopic composition of this group
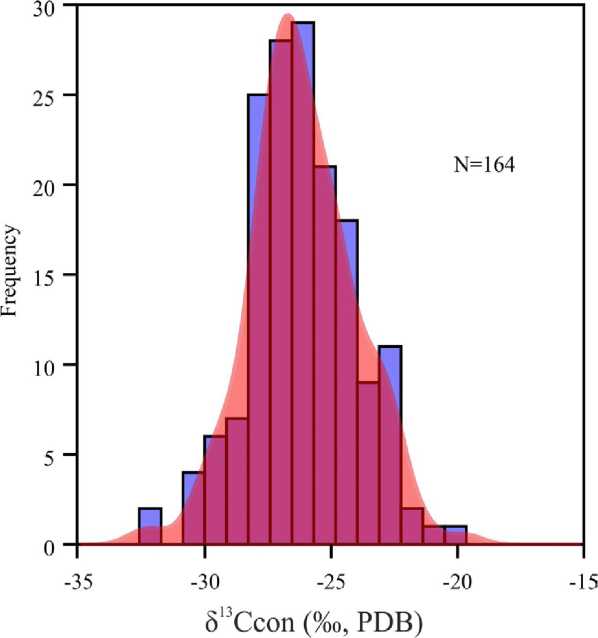
Fig. 2. Distribution of δ 13C of the Late Devonian — Middle Permian conodont elements (histogram with kernel density)
Ðèñ. 2. Ðàñïðåäåëåíèå δ13C êîíîäîíòîâûõ ýëåìåíòîâ ïîçä-íåãî äåâîíà — ñðåäíåé ïåðìè of animals [29]. In contrast, Sr/Ca ratios in some Frasnian-Famennian conodonts of genus Palmatolepis demonstrate significant negative correlation with δ18Oap [12] that suggests probable temperature control (direct or indirect) of this parameter.
So a reasonable hypothesis could be that δ 13Ccon and, partly, Sr/Ca values were controlled mainly by diet of conodonts. In this case decreased δ 13Ccon and increased Sr/Ca could be signs of prevalence of the 13C-depleted and Sr enriched phytoplankton in forage of conodonts, but increased δ 13Ccon associated with low Sr/Ca could be caused by predominance of the 13C-enriched and Sr depleted zooplankton as conodont food.
Temporal variations of the ecogeochemical characteristics of a single species of conodonts could reflect changes in the structure of pelagic ecosystem and hydrological conditions. For example, changes in trophic position or diet structure of a species could be caused by eutrophication and consequent shortening in the food chains, or oligotrophication and increasing of seston and zooplankton portion in forage [9, 24].
Conclusions
The ecogeochemical parameters, such as Sr/Ca ratios, δ 44/42Ca and δ 13Ccon values, allow us supposing ecological (mainly trophical) specialization of conodont species. Temporal and spatial dynamics of the ecogeochemistry of conodonts can be used for reconstructing of the perturbation of ancient pelagic ecosystems. However it is difficult to discriminate environmental effects (caused by changes in sea water composition, salinity, and temperature) and biotic effects (structure of forage and its composition) in conodont ecogeochemical characteristics. Synthesis of the data on various environmental and ecogeochemical proxies could be useful for solving this problem. Another problem is discrimination of primary, or near-primary, ecogeochemical signs and results of secondary (post-mortem) and near-secondary (e. g. inorganic carbon incorporation from ambient water into the conodont apatite) changes in composition of conodont elements. Also, some obstacles may be caused by variation in composition of different tissues of conodont elements, which is known in Sr/Ca ratio [28], and differences in preservation of the tissues. Solving of these problems is subject of the forthcoming investigations.
Acknowledgements
The author thanks anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions that greatly helped to improve the manuscript.
Proxies
Structure of
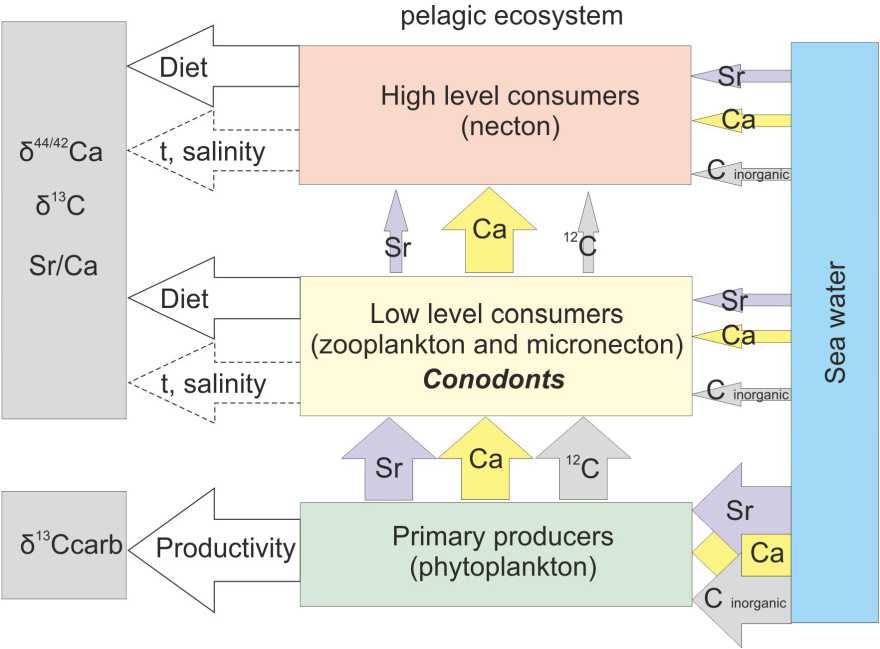
Fig. 3. Supposed controlling factors of ecogeochemical parameters of pelagic ecosystem
Ðèñ. 3. Ïðåäïîëàãàåìûå êîíòðîëèðóþùèå ôàêòîðû ýêîãåîõèìè÷åñêèõ ïàðàìåòðîâ ïåëàãè÷åñêèõ ýêîñèñòåì
Список литературы Middle-Late Paleozoic conodont ecogeochemistry: an overview
- Anas M. U. M., Simpson G. L., Leavitt P. R., Cumming B. F., Laird K. R., Scott K. A., Das B., Wolfe J. D., Hesjedal B., Mushet G. R., Walker A., Meegahage B. J., Wissel B. Taxon- specific variation in 13C and 15N of subfossil invertebrate re- mains: Insights into historical trophodynamics in lake food-webs. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 102, pp. 834—847. DOI: 10.1016/j. ecolind.2019.03.026
- Balter V., Lécuyer C. Determination of Sr and Ba parti- tion coefficients between apatite and water from 5 °C to 60 °C: a potential new thermometer for aquatic paleoenvironments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68, pp. 423—432. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00453-8
- Balter V., Martin J. E., Tacail T., Suan G., Renaud S., Girard C. Calcium stable isotopes place Devonian conodonts as first level consumers. Geochemical Perspectives. Letters, 2019, 10, pp. 36—39. DOI: 10.7185/geochemlet.1912
- Barham M., Joachimski M. M., Murray J., Williams D. M. Diagenetic alteration of the structure and 18O signature of Palaeozoic fish and conodont apatite: Potential use for corrected isotope signatures in palaeoenvironmental interpretation. Chemical Geology, 2012, 298—299, pp. 11—19.
- Ebneth S., Diener A, Buhl D., and Veizer J. Strontium isotope systematics of conodonts: Middle Devonian, Eifel Mountains, Germany. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 1997, 132, pp. 79—96.
- Frank-Kamenetskaya O. V., Rozhdestvenskaya I. V., Rosseeva E. V., Zhuravlev A. V. Refinement of apatite atomic structure of albid tissue of Late Devon conodont. Crystallogr Rep., 2014, 59(1), pp. 41—47.
- Golding M. L. & McMillan R. The impacts of diagene- sis on the geochemical characteristics and Color Alteration Index of conodonts. Palaeobiodiversity and Palaeoenvironments, 2020. DOI: 10.1007/s12549-020-00447-y
- Grupe G., Hölzl S., Mayr C., Söllner F. () The Concept of Isotopic Landscapes: Modern Ecogeochemistry versus Bioarchaeology. In: Grupe G., Grigat A., McGlynn G. (eds) Across the Alps in Prehistory. Springer, 2017. https://doi. org/10.1007/978-3-319-41550-5_2
- Hempson T. N., Graham N. A. J., MacNeil M. A., Williamson D. H., Jones G. P., Almany G. R. Coral reef meso- predators switch prey, shortening food chains, in response to hab- itat degradation, Ecology and Evolution, 2017, 7, pp. 2626—2635. DOI: 10.1002/ece3.2805
- Katvala E. C. & Henderson C. M. Chemical element distributions within conodont elements and their functional im- plications. Paleobiology, 2012, 38, pp. 447—458. DOI:10.1666/11038.1
- Kolodny Y., Luz B., Sander M., and Clemens W. A. Dinosaur bones: Fossils or pseudomorph? The pitfalls of physiol- ogy reconstruction from apatite fossils. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1996, 126, pp. 161—171.
- Le Houedec S., Girard C., Balter V. Conodont Sr/Ca and 18O record seawater changes at the Frasnian–Famennian boundary. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 376, pp. 114—121.
- Luz, B., Kolodny Y. & Kovach J. Oxygen isotope varia- tions in phosphate of biogenic apatites, III. Conodonts. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 69, pp. 255—262.
- McMahon, K. W., Hamady, L. L., & Thorrold, S. R. A review of ecogeochemistry approaches to estimating movements of marine animals. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58(2), pp. 697—714. DOI:10.4319/lo.2013.58.2.0697
- Mizutani, H., Kabaya Y., & Wada E. Nitrogen and car- bon isotope compositions relate linearly in cormorant tissues and its diet. Isotopenpraxis, 1991, 27, pp. 166—168. DOI:10.1080/10256019108622500
- Nicholas C., Murray J., Goodhue R. & Ditchfield P. Nitrogen and carbon isotopes in conodonts: Evidence of trophic levels and nutrient flux in Palaeozoic oceans. The Palaeontological Association 48th Annual Meeting, 17th—20th December 2004, University of Lille, ABSTRACTS, pp. 126—127.
- Over D. J. & Grossman E. L. Carbon isotope analysis of conodont organic material — procedure and preliminary results. Geological Society of America, Abstracts with Programs, 1992, 24, A214.
- Schoeninger M. J. & DeNiro M. J. Carbon isotopes ra- tios of apatite from fossil bone cannot be used to reconstruct diets of animals. Nature, 1982, 297, pp. 577—578.
- Schoeninger, M. J. & DeNiro, M. J. Nitrogen and car- bon isotopic composition of bone collagen from marine and ter- restrial animals. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48, pp. 625—639.
- Schoeninger M. J., DeNiro M., Tauber H. Stable nitro- gen isotope ratios of bone collagen reflects marine and terrestrial components of prehistoric human diet. Science, 1983, 220, pp. 1380–1383.
- Trotter J. A. & Eggins S. M. Chemical systematics of conodont apatite determined by laser ablation ICPMS. Chemical Geology, 2006, 233, pp. 196—216.
- Trueman C. N. Chemical taphonomy of biomineralized tissues. Palaeontology, 2013, 56(3), pp. 475—486. DOI: 10.1111/ pala.12041
- Wada E., Mizutani H. & Minagawa M. The use of stable isotopes for food web analysis. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1991, 30(4), pp. 361—371 DOI: 10.1080/10408399109527547
- Ward C. L., McCann K.S. A mechanistic theory for aquatic food chain length. Nature Communications, 2017, 8, 2028. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02157-0
- Wright J., Seymour R. S., and Shaw R. F. REE and Nd isotopes in conodont apatite: variations with geological age and depositional environment. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap., 196, 1984, pp. 325—340.
- Zhuravlev A. V. Trophic position of some Late Devonian-Carboniferous (Mississippian) conodonts revealed on carbon organic matter isotope signatures: a case study of the East European basin. Geodiversitas, 2020, 42 (24), pp. 443—453. DOI: 10.5252/geodiversitas2020v42a24
- Zhuravlev A. V., Plotitsyn A. N., Gruzdev D. A. Carbon Isotope Ratios in the Apatite-Protein Composites of Conodont Elements—Palaeobiological Proxy. Lecture Notes in Earth System Sciences. Frank-Kamenetskaya, O. V., Vlasov, D. Y., Panova, E. G., Lessovaia, S.N. (Eds.). Processes and Phenomena on the Boundary between Biogenic and Abiogenic Nature, 2020, Chapter 40, pp. 749—764 DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-21614-6_40
- Zhuravlev, A. V. & Shevchuk, S.S. Strontium distribu- tion in Upper Devonian conodont elements: a palaeobiological proxy. Riv. It. Paleontol. Strat. 2017, 123(2), pp. 203—210.
- Zhuravlev A. V. & Smoleva I. V. Carbon isotope values in conodont elements from the latest Devonian — Early Carboniferous carbonate platform facies (Timan-Pechora Basin). Estonian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2018, 67(4), pp. 238—246. DOI: 10.3176/earth.2018.17


