Микробиом и мозг: кишечная микробиота и нейроэндокринная система
Автор: Булгакова Светлана Викторовна, Романчук Наталья Петровна, Тренева Екатерина Вячеславовна
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Медицинские науки
Статья в выпуске: 6 т.8, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Микробная экосистема, населяющая желудочно-кишечный тракт всех млекопитающих, - кишечная микробиота - на протяжении многих тысячелетий находится в симбиотических отношениях со своими хозяевами. Благодаря современным технологиям выясняется множество функций организма, которые контролируются или модулируются кишечной микробиотой. Одной из систем, тесно взаимосвязанных с кишечной микробиотой, является нейроэндокринная система, контролирующая различные процессы в организме в ответ на стресс, а именно гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковая ось (HPA). В настоящей статье описывается двунаправленная связь между кишечной микробиотой и осью HPA, обсуждаются лежащие в ее основе механизмы и связи с другими системами организма, такими как иммунная, вегетативная, центральная нервная системы, органы чувств, кишечный и гематоэнцефалический барьеры. Проведен анализ полезной роли пробиотиков и пребиотиков, вклад приема антибактериальных препаратов.
Микробиом, мозг, кишечная микробиота, гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковая ось, пробиотик, пребиотик, нейроэндокринная система
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14124469
IDR: 14124469 | УДК: 616.83/.85:616.43/57 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/79/32
Текст обзорной статьи Микробиом и мозг: кишечная микробиота и нейроэндокринная система
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
УДК 616.83/.85:616.43/57
Нейроэндокринная система классически определяется как организованный набор эндокринных клеток с детерминацией нервной системы, которые продуцируют гормоны или нейропептиды [1, 2] . Гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковая ось (ГГН) считается важнейшей нейроэндокринной осью, регулирующей различные процессы организма в ответ на психологические и физические стрессоры, включая инфекции, обеспечивая адекватный на них ответ [3] . Кортикотропин-рилизинг-фактор (CRF), основной регулятор оси HPA, высвобождается из паравентрикулярного ядра (PVN) гипоталамуса в ответ на стресс и индуцирует высвобождение в системный кровоток адренокортикотропного гормона (АКТГ). Впоследствии АКТГ индуцирует секрецию глюкокортикоидов (кортизола у человека и кортикостерона у грызунов) корой надпочечников [3] . Высвобождение глюкокортикоидов, в свою очередь, приводит к ингибированию АКТГ по принципу обратной связи за счет связывания глюкокортикоидов с глюкокортикоидными рецепторами (GR), локализованными в чувствительных к стрессу областях мозга посредством модуляции транскрипции [4] .
Современные данные указывают на двустороннюю связь между нейроэндокринной системой и кишечной микробиотой, сложным сообществом микроорганизмов, обитающих в кишечном тракте млекопитающих. Все чаще признается, что формирование микробиоты кишечника в раннем возрасте влияет на несколько аспектов функции и поведения мозга, включая нейроэндокринные реакции на стресс [5, 6]. Потенциальная связь между микробиотой кишечника и нейроэндокринной системой также подтверждается расстройствами, которые связаны с нарушениями в обеих системах, такими как депрессия и синдром раздраженного кишечника (СРК). У пациентов с депрессией, особенно меланхолического подтипа, неоднократно наблюдалась повышенная активация HPA [7]. Хотя оценка активности оси HPA при СРК дала противоречивые результаты, большинство исследований подтверждают повышенную активность оси HPA при СРК [8]. Кроме того, стресс в раннем возрасте, а также хронические стрессоры являются факторами риска развития депрессии и СРК [9, 10, 11]. В то время как хронически повышенный уровень кортизола негативно влияет на функцию мозга [11, 12], активация оси HPA также способна влиять на состав кишечной микробиоты и повышать проницаемость желудочно-кишечного тракта [13, 14].]. Было высказано предположение, что дисбактериоз микробиоты кишечника и бактериальная транслокация способствуют хроническому слабовыраженному воспалению, которое наблюдается у пациентов с СРК или депрессией [15, 16]. В ряде исследований сообщалось о повышенном количестве Firmicutes, тогда как количество Bacteroidetes было снижено, по крайней мере, у части пациентов с СРК [17, 18]. Изменения в составе микробиоты также отмечаются у пациентов с депрессией, тогда как микробная сигнатура для этого состояния еще не определена [19, 20, 21]. Причинная роль микробиоты в развитии как депрессии, так и СРК была дополнительно продемонстрирована в исследованиях трансплантации кала. Трансплантация микробиоты пациентов с депрессией грызунам способна вызывать депрессивноподобное поведение [22]. Kelly J.R. (2016) [19] наблюдали ангедонию и тревогу у крыс в ответ на трансплантацию фекальной микробиоты от пациентов с депрессией. В то время как трансплантация микробиоты индуцировала показатели иммунной активации, тем не менее, не влияла на стресс-индуцированные уровни кортикостерона [19]. Хотя этот результат довольно удивителен, однократное измерение параметров оси HPA требует подтверждения [19]. Трансплантация фекальной микробиоты от пациентов с СРК с диареей (СРК-Д) безмикробным (GF) мышам с тревогой или без нее вызывала более быстрый желудочно-кишечный транзит, дисфункцию кишечного барьера, активацию врожденного иммунитета и поведение, подобное тревоге [23]. Иммунная активация в толстой кишке мыши-реципиента была особенно выражена при введении фекальной микробиоты от пациентов с СРК-Д с тревожным поведением. Эти мыши также демонстрировали повышенную экспрессию генов толстой кишки, которые участвуют в передаче сигналов пути GR [23]. Хотя функциональное значение микробиоты в нейроэндокринных нарушениях еще предстоит подробно определить, вполне вероятно, что изменения кишечной проницаемости и иммунных параметров также могут способствовать наблюдаемым нейроэндокринным нарушениям [24]. В этом обзоре в основном рассматриваются доклинические исследования, которые предполагают связь между микробиотой кишечника, нейроэндокринной системой и мозгом, которая осуществляется через несколько прямых и косвенных путей, включая: 1) гуморальные пути (через микробные метаболиты, гормоны кишечника) [25, 26] ; 2) иммунные пути (включая провоспалительные цитокины) [27] и 3) нервные пути (через кишечную нервную систему, блуждающий нерв и спинномозговые афференты) [28].
Ранний период жизни и ось HPA
События раннего периода жизни способны программировать ось HPA. В то время как положительный опыт, такой как уход матерью за новорожденным, может привести к ослаблению реакции HPA в более позднем возрасте [29, 30] , воздействие стрессовых событий может вызвать дезадаптацию оси, обеспечивая механистическую основу для изменений восприимчивости к стрессу в более позднем возрасте. [31] . Таким образом, стресс в раннем возрасте обычно приводит к повышенной реакции HPA на стресс, что связано с усилением передачи сигналов CRF и нарушением отрицательной обратной связи, опосредованной через GR [31] . Кроме того, стресс в раннем возрасте вызывает воздействие кортикостероидов на развивающийся мозг, что приводит к изменениям экспрессии GR [31 ,32] , влияет на функцию различных областей мозга, которые способны модулировать ось HPA, такие как миндалевидное тело, гиппокамп и префронтальная кора [31] . Хотя в целом стресс в раннем возрасте приводит к гиперактивности миндалевидного тела [33] , он ингибирует синаптическую пластичность и снижает экспрессию субъединиц NR 1 и NR 2B рецептора N -метил-D-аспартата (NMDA) в гиппокампе [34] , область, которая оказывает ингибирующее действие на ось HPA. Известно,что префронтальная кора способна подавлять активность оси HPA, при этом стресс в раннем возрасте нарушает функцию префронтальной коры [31, 35] . Кроме того, норадренергические нейроны, происходящие главным образом из ядра солитарного тракта в стволе мозга, играют ключевую роль в активации оси HPA [36] . Ядро солитарного тракта имеет особое значение в отношении оси кишечник-мозг, так как оно получает висцеральные афференты от блуждающего нерва и активируется воспалительными процессами [37, 38] .
Еще одним признаком стресса в раннем возрасте является повышение активности врожденной иммунной системы, которая сохраняется во взрослом возрасте, тогда как приобретенная иммунная система менее активна [39, 40] . Ось HPA механически вовлечена в этот ответ, поскольку хроническая активация оси HPA приводит к компенсаторному снижению передачи сигналов GR посредством эпигенетических изменений [41] , что приводит к устойчивости иммунных клеток к противовоспалительным свойствам кортизола [39, 42] .]. Новые данные также указывают на роль микробиоты и проницаемости кишечника в этом процессе, поскольку стресс влияет на состав микробиоты [43] и ослабляет барьер слизистой оболочки кишечника [43, 14] . Вызванные стрессом изменения состава микробиоты кишечника могут быть связаны с нейроэндокринными гормонами, такими как норадреналин (NE) и дофамин (DA), которые, как известно, увеличивают рост грамотрицательных бактерий [44] . В свою очередь, предполагается, что повышенная проницаемость кишечника вызывает воспалительную реакцию за счет транслокации бактериальных компонентов через просвет кишечника [13] . Наконец, воспалительные медиаторы, в том числе провоспалительные цитокины и простагландины, являются мощными активаторами оси HPA [45] , усложняя микробиотно-иммуно-нейроэндокринные взаимодействия.
Микробиота кишечника как источник микробных компонентов, активирующих ось HPA
Хотя ясно, что воспалительные процессы приводят к активации оси HPA за счет высвобождения провоспалительных цитокинов и простагландинов, механизмы, лежащие в основе вклада кишечной микробиоты в качестве стимулятора иммунной системы, исследуются. Существуют данные того, что активация оси HPA микробиотой кишечника может происходить в результате повышенной проницаемости кишечного барьера и провоспалительного состояния, вызванного этим процессом [13] . Было высказано предположение, что пептидогликан кишечной микробиоты, составляющий клеточную стенку большинства бактерий, может транслоцироваться в мозг и активировать специфические рецепторы распознавания образов врожденной иммунной системы и тем самым влиять на развитие мозга [46].] . Кроме того, было продемонстрировано, что пептидогликан, полученный из микробиоты кишечника, активирует врожденный иммунитет путем активации одного из его рецепторов, нуклеотидсвязывающего белка-1, содержащего домен олигомеризации (Nod1) [47].] . Помимо пептидогликана, липополисахарид (LPS), компонент внешней мембраны грамотрицательных бактерий и активатор Toll-подобного рецептора (TLR) 4, как предполагается, проникает через кишечный эпителиальный барьер в ответ на стресс или питание с высоким содержанием жиров (HFD) и, таким образом, приводит к активации иммунной и гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковой оси. Транслокация и взаимодействие различных бактериальных компонентов и их влияние на иммунную систему и ось HPA могут иметь большое патофизиологическое значение. В связи с этим сообщалось о синергических взаимодействиях для LPS и агонистов Nod, а также для LPS и агониста TLR2 липотейхоевой кислоты [48, 49] .
В то время как бактериальные компоненты способны резко активировать иммунную систему и ось HPA, воздействие этих факторов на новорожденных грызунов может вызывать пролонгированные эффекты. Таким образом, как и при стрессе, воздействие LPS на новорожденных приводит к усилению реакции АКТГ и кортикостерона на стресс, связанный с ограничениями, и снижению ингибирования глюкокортикоидной обратной связи во взрослом возрасте, примером чего является ослабленное индуцированное дексаметазоном подавление ответов АКТГ на стресс [50]. Соответственно, воздействие LPS на новорожденных снижает плотность церебрального GR, тогда как экспрессия CRF увеличивается [50]. Кроме того, воздействие LPS на новорожденных индуцирует усиленную простагландин-опосредованную реактивность системы HPA на LPS во взрослом возрасте [51].]. В дополнение к влиянию на ось HPA неонатальное воздействие LPS способно перепрограммировать катехоламинергические нейроны [52]. Таким образом, у новорожденных, зараженных LPS, наблюдается заметное увеличение активности тирозингидроксилазы и экспрессии белка во взрослом возрасте, в частности, в голубом пятне [52].
Микробные короткоцепочечные жирные кислоты: центральные эффекты и индукторы высвобождения гормонов кишечника
Способность микробов ферментировать неперевариваемые углеводные волокна и превращать их в короткоцепочечные жирные кислоты (SCFAs) приобретает особое значение в различных физиологических и патофизиологических процессах. Уксусная кислота, масляная кислота и пропионовая кислота являются наиболее широко изученными SCFAs и выполняют различные функции внутри и вне желудочно-кишечного тракта. На местном уровне SCFAs являются важными источниками энергии для самой кишечной микробиоты и эпителиальных клеток кишечника. Они повышают целостность кишечного эпителия, увеличивают выработку слизи, модулируют перистальтику кишечника и оказывают противовоспалительное действие, такое как инактивация ядерного фактора каппа-В и стимулирование регуляторных Т-клеток [53, 54, 55].] . Кроме того, они индуцируют высвобождение гормонов и нейропептидов, таких как глюкагоноподобный пептид 1 (GLP-1) и пептид YY (PYY) из кишечных энтероэндокринных клеток [56] . С одной стороны, эти эффекты опосредованы активацией рецепторов, связанных с G-белком (GPR), GPR43, GPR41 и GPR109A, тогда как, с другой стороны, SCFA также являются эпигенетическими регуляторами, влияющими на экспрессию генов, действуя как ингибиторы гистонов деацетилазы. Интересно, что SCFAs являются решающим фактором для созревания и функционирования микроглии, резидентных макрофагов центральной нервной системы (ЦНС) [57] . Таким образом, микроглия мышей GF имеет незрелый фенотип и проявляет нарушенный врожденный иммунный ответ [58]. Важно отметить, что дефицит SCFAs у мышей GF и их действия на GPR43 (кодируемый Ffar2 лежат в основе этих дефицитов. Таким образом, 4-недельное лечение SCFAs восстанавливает пороки развития и незрелость микроглии у мышей GF, тогда как у мышей Ffar2 -/- обнаруживается порок развития микроглии, напоминающий микроглию у мышей GF [57] . Особо следует отметить, что экспрессия мРНК Ffar2 не была обнаружена ни на одном типе клеток ЦНС (включая микроглию), тогда как высокая экспрессия была обнаружена в селезенке. Следовательно, прямое действие SCFAs на микроглию вряд ли опосредует наблюдаемые эффекты, хотя SCFAs способны проникать в мозг через транспортеры, через гематоэнцефалический барьер [26]. Полное определение эффектов SCFAs у мышей Ffar2 -/- могло бы дать дальнейшее понимание механизмов, способствующих созреванию микроглии, индуцированному SCFAs.
Поскольку микроглия, помимо своей иммунной функции, важна для формирования нейронных цепей в развивающемся мозге, их функция, зависящая от микробиоты, может иметь отношение к цепям, регулирующим ось HPA [59] . Интересно, что помимо влияния на микроглию системное введение бутирата оказывает антидепрессивное действие и модулирует нейротрансмиссию [28, 60, 61] .
Помимо других функций, нейропептиды GLP-1 и PYY, которые высвобождаются энтероэндокринными клетками в ответ на SCFAs, способствуют насыщению через эндокринные и вагус-зависимые пути [62, 63] . В дополнение к SCFAs исследование Breton J. et al. (2016) предполагает, что бактериальные белки могут контролировать аппетит через локальные механизмы в кишечнике или через систему кровообращения [64] . Полученные данные демонстрируют, что доступность питательных веществ стабилизирует экспоненциальный рост Escherichia coli и что белки E. coli способны повышать уровень PYY в плазме и подавлять потребление пищи при системном введении [64] . Интересно, что E. coli белковая казеинолитическая протеаза В является антигеном-миметиком α-меланоцитстимулирующего гормона, ключевого сатиогенного нейропептида [65] . Кроме того, применение казеинолитической протеазы В к срезам гипоталамуса увеличивает частоту потенциала действия проопиомеланокортиновых нейронов, которые продуцируют α-меланоцитостимулирующий гормон [64] .
Экспрессия GPR41 и GPR43, а также PYY, GLP-1 и холецистокинина, другого пептида насыщения кишечника, снижена у мышей GF (Рисунок 1) [66] .
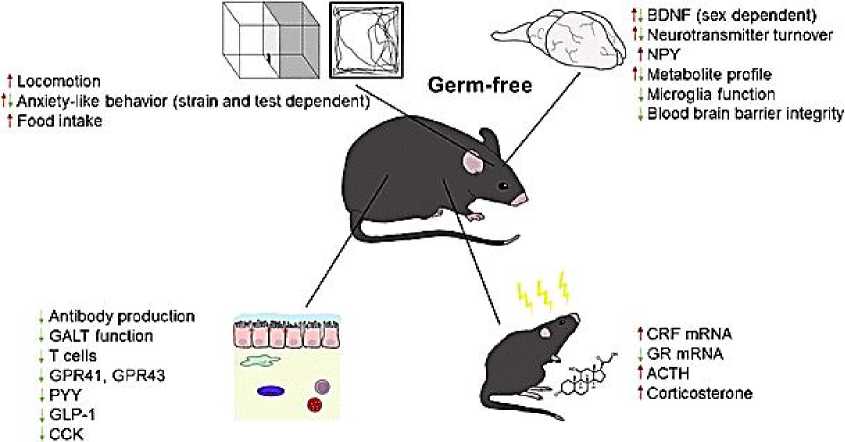
Locomotion
Germ-free f. BDNF (sex dependent)
1, Neurotransmitter turnover tNPY t. Metabolite profile
, Microglia function
, Blood brain barrier integrity
. Antibody production
. GALT function
, T cells
, GPR41, GPR43
. PYY
, GLP-1
. CCK tCRF mRNA
, GR mRNA
1ACTH t Corticosterone t. Anxiety-like behavior (strain and lest dependent)
* Food intake
Рисунок 1. Нейроразвивающие изменения у безмикробных мышей
Кроме того, мыши GF имеют более низкие уровни циркулирующего лептина, сниженную циркулирующую глюкозу и повышенный метаболизм жиров, метаболический профиль, напоминающий состояние натощак [66] . В гипоталамусе мышей GF повышен уровень орексигенного нейропептида Y (NPY), тогда как уровень анорексигенных нейропептидов снижен [67]. Таким образом, возникает вопрос, в какой степени эти различия способствуют повышенной реактивности HPA -оси мышей GF, учитывая, что, помимо влияния на аппетит, эти нейропептиды способны влиять на поведение, работу мозга и нейроэндокринную систему (Рисунок 2) [25, 68] .
У стерильных мышей обнаруживаются изменения в развитии, которые влияют на различные системы организма и могут влиять на активность гипоталамуса, гипофиза и надпочечников. BDNF = мозговой нейротрофический фактор; NPY = нейропептид Y; GALT = лимфоидная ткань, связанная с кишечником; GPR = рецептор, связанный с G-белком; PYY = пептид YY; GLP-1 = глюкагоноподобный пептид 1; CCK = холецистокинин; CRF = фактор, высвобождающий кортикотропин; GR = глюкокортикоидный рецептор; АCTG = адренокортикотропный гормон
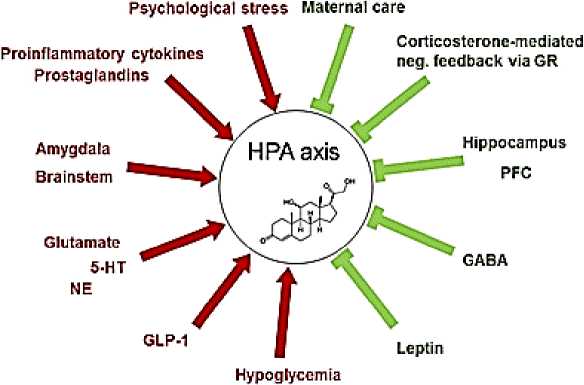
Рисунок 2. Модуляторы оси гипоталамус-гипофиз-надпочечники (HPA). Существует несколько активаторов (→) и ингибиторов (˧) оси HPA. GR = глюкокортикоидный рецептор; ПФК = префронтальная кора; ГАМК = γ-аминомасляная кислота; GLP-1 = глюкагоноподобный пептид 1; НЭ = норадреналин; 5-HT = 5-гидрокситриптамин
Кроме того, микробиота не только контролирует высвобождение различных кишечных пептидов, но и сама производит различные нейротрансмиттеры. Например, Lactobacillus brevis и Bifidobacterium dentium способны продуцировать γ-аминомасляную кислоту (ГАМК) [69] , тогда как другие виды бактерий продуцируют катехоламины [70] . Хотя эти нейротрансмиттеры, вероятно, оказывают местное воздействие, все еще необходимо установить, будут ли эти бактериальные нейротрансмиттеры иметь какое-либо отношение к оси кишечник-мозг [71] .
Про- и пребиотики как преимущественно полезные модуляторы нейроэндокринной системы
В то время как дисбаланс микробного сообщества кишечника (вызванный стрессом или питанием) может привести к воспалительным процессам и активации оси HPA, экспериментальные работы указывают на потенциальную полезную роль пробиотиков, включая лактобациллы и бифидобактерии в этом процессе.
Исследование Moya-Perez A. et al. (2017) показало, что пробиотик Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum CECT 7765, вводимый со второго (P2) по двадцать первый (P21) постнатальный день, модифицировал нейроэндокринные изменения, вызванные разлучением с матерью (MS) [72] . При тестировании на P21 B. pseudocatenulatum не ослаблял вызванное стрессом повышение уровня кортикостерона при рассеянном склерозе, в то время как вызванное стрессом повышение уровня катехоламинов в гипоталамусе и тонком кишечнике ослаблялось пробиотиком. Однако на Р41 B. pseudocatenulatum полностью убирал вызванное стрессом повышение кортикостерона в кале и катехоламинов в гипоталамусе, а также тревожноподобное поведение [72] . На иммуномодулирующие эффекты B. pseudocatenulatum указывает заметное снижение базального и стресс-индуцированного уровня интерферона (IFN)-γ в тонком кишечнике, а также стресс-индуцированного уровня интерлейкина (IL)-18 в сыворотке мышей, получавших пробиотики [76] .
Дальнейшие исследования, проведенные Agusti A. et al. (2017), показали, что B. pseudocatenulatum CECT 7765 способен ослаблять различные нейроэндокринные изменения в ответ на HFD пищу у взрослых самцов мышей [73] . Опять же, пробиотик нормализовал индуцированный HFD пищей фекальный уровень кортикостерона (базальный и в ответ на острый стрессовый фактор) и, кроме того, обращал вспять тенденцию к снижению уровней GR в гиппокампе. Более того, B. pseudocatenulatum оказывала противовоспалительное действие и снижала вызванные HFD поведенческие и метаболические нарушения [73]. Наконец, пробиотик влиял на уровни DA, NE, адреналина и 5-гидрокситриптамина (5-HT) в тонком кишечнике и головном мозге. Хотя точные пути этих пробиотических эффектов не определены, данные ясно показывают, что B. pseudocatenulatum способен ослаблять последствия ожирения, вызванного HFD питанием, вероятно, за счет противовоспалительного действия и модуляции нейроэндокринной системы.
В то время как упомянутые выше исследования указывают на способность определенных штаммов бифидобактерий воздействовать на нейроэндокринную систему, в группах, использующих другие экспериментальные протоколы и разные штаммы бифидобактерий, не наблюдалось изменений кортикостерона, хотя иные параметры были изменены. Таким образом, Bifidobacterium infantis 35624, вводимый крысам, разлученным с матерью, в течение 6 недель с P50 до дня умерщвления (P95), не изменял исходные уровни кортикостерона, тогда как стресс-индуцированные уровни гормона не оценивались [74] . Однако B. Infantis нормализовал депрессивно-подобное поведение, вызванное рассеянным склерозом, проявлял определенные противовоспалительные эффекты и влиял на центральные уровни NE и 5-гидроксииндолуксусной кислоты, основного метаболита 5-HT [74] . Исследование проведенное Savignac H.M. et al. (2014), сравнило эффекты Bifidobacterium longum 1714 и Bifidobacterium breve 1205 у взрослых самцов мышей BALB/c [75] . Опять же, хотя оба пробиотика демонстрировали различные анксиолитические и антидепрессантоподобные эффекты, они не влияли на исходные или вызванные стрессом уровни кортикостерона [75] . Таким образом, из этих исследований можно сделать вывод, что некоторые штаммы Bifidobacterium способны оказывать особые поведенческие эффекты, не зависящие от нейроэндокринной системы. В отличие от этих результатов, комбинация Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 и Propionibacterium jensenii 702 (пробиотик, выделенный из молочных продуктов), вводимые крысам Wistar за 10 дней до отъема от матери, повышали уровень кортикостерона у потомства женского пола [76] .
Ряд исследований оценивали центральные и нейроэндокринные эффекты различных штаммов Lactobacillus. В частности, обнаружено, что лечение взрослых самцов мышей BALB/c, не подвергавшихся стрессу, пробиотиком Lactobacillus rhamnosus (JB-1) в течение 28 дней способно снижать уровень кортикостерона, депрессивно-подобное поведение и уменьшать тревожность [77] . Однако эти эффекты L. rhamnosus(JB-1), по-видимому, зависят от штамма и вида, учитывая, что пробиотик не влияет на исходное социальное и тревожное поведение у самцов мышей C57BL/6, тогда как он ослабляет поведенческие нарушения, вызванные стрессом [78] . Аналогичным образом, 8-недельный прием L. rhamnosus (JB-1) 29 здоровыми мужчинами не изменил уровень кортизола в слюне, настроение, тревогу, качество сна, субъективный стресс, работу зрительно-пространственной памяти, переключение внимания, быструю обработку зрительной информации, эмоции. распознавание и связанные параметры электроэнцефалографии [79] .
Поскольку поведенческие эффекты в ответ на L. rhamnosus отсутствуют у ваготимизированных мышей, предполагается, что блуждающий нерв является критическим путем связи между пробиотическими сигналами и ЦНС [77]. Аналогично, ваготомия предотвращала некоторые изменения в экспрессии центрального рецептора ГАМК, индуцированные L. rhamnosus, тогда как об уровнях кортикостерона у мышей с ваготомией не сообщалось [77].
В дополнение к этим эмоционально-аффективным и нейрохимическим изменениям известно, что лактобациллы оказывают благоприятное влияние при различных протоколах стресса. Так, двухнедельное лечение самок крыс Wistar Lactobacillus farciminis с последующим стрессовым воздействием способно блокировать вызванное стрессом повышение уровня АКТГ и кортикостерона, а также CRF в PVN [80] . Кроме того, показано, что пробиотик способен ингибировать вызванную стрессом гиперпроницаемость кишечного барьера, а также повышать уровень LPS в портальной крови. L. farciminis предотвращал вызванное стрессом увеличение экспрессии мРНК IL-1β, IL-6 и фактора некроза опухоли (TNF)-α в гипоталамусе [80].] . 2-недельный профилактический прием Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 и B. longum R0175, снижает повышенный уровень кортикостерона, NE и адреналина, активность нейронов (экспрессия c-Fos) в чувствительных к стрессу областях мозга, включая PVN и миндалевидное тело у взрослых самцов мышей в ответ на стресс [81] , предотвращает нарушение кишечного барьера, увеличивает нейрогенез гиппокампа. Кроме того, пробиотическая композиция влияла на гены гипоталамуса, участвующие в синаптической пластичности у мышей, подвергшихся стрессу, увеличивая экспрессию мозгового нейротрофического фактора (BDNF) и снижая экспрессию маркеров активации микроглии [81] . Пробиотическая комбинация L. rhamnosus R0011 и L. helveticusR0052, введенная крысятам, разлученным с матерью, снижала повышенный уровень кортикостерона, а также повышала проницаемость толстокишечного барьера [82] . Кроме того, введение Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 новорожденным крысам снижает проницаемость кишечника in vivo в том числе и на стресс [83] . Более того, пробиотик увеличивал секрецию IFN-γ [маркер ответа T-хелперов (Th)1] активированными спленоцитами, тогда как секреция IL-4 (маркер ответа Th2) ингибировалась. Наконец, L. fermentum увеличил двигательную активность и исследовательское поведение [83] .
Поскольку было высказано предположение, что комбинация нескольких видов пробиотиков может оказывать аддитивное действие, Abildgaard A. et al. (2017) изучили комбинацию HFD (начиная с 4-недельного возраста) с многовидовым пробиотиком (начиная с 9-недельного возраста), содержащем 8 бактериальных штаммов ( Bifidobacterium bifidum W23, Bifidobacterium lactis W52, Lactobacillus acidophilus W37, L. brevis W63, Lactobacillus casei W56, Lactobacillus salivarius W24, Lactococcus lactis W19, Lactococcus lactis W58) у самцов крыс Sprague-Dawley [84]. Установлено, пробиотическая композиция не влияла на вызванное HFD повышение уровня LPS в плазме и метаболические изменения.
Таким образом, лечение пробиотиками уменьшает депрессивное поведение и экспрессию мРНК рецепторов CRF (CRFR)1 и CRFR2 в гиппокампе, что указывает на снижение активности оси HPA. В соответствии с другими данными, пробиотическая композиция модулирует продукцию цитокинов, происходящих из Т-лимфоцитов (IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4), стимулированными мононуклеарными клетками крови, тогда как уровни цитокинов, связанных с макрофагами (TNF-α, IL-4) сокращаются. Кроме того, пробиотическая композиция повышала уровень индол-3-пропионовой кислоты, микробного метаболита триптофана, который, как было показано, обладает нейропротекторным действием и уменьшает воспаление ЦНС [85] .
Выводы о преимущественных положительных эффектах пробиотиков у грызунов совпадают с рядом позитивных эффектов у людей. Например, в рандомизированном, двойном слепом, плацебо-контролируемом исследовании Lactobacillus plantarum 299v вводили 41 студенту перед предстоящим экзаменом, что ассоциировалось со снижением уровня кортикостерона через 10 дней [86] . Точно так же пробиотическая композиция, состоящая из L. helveticus R0052 и B. longum R0175 (которая была эффективна на мышах), снижала средний уровень свободного кортизола в моче и психологическое расстройство при введении 26 здоровым добровольцам в течение 30 дней в двойном слепом, рандомизированное, плацебо контролируемом исследовании [87] . Сходным образом, B. longum 1714, принимаемый 22 здоровыми мужчинами-добровольцами в плацебо контролируемом исследовании, снижал уровень кортизола и субъективную тревогу в ответ на острый стресс [88] . Эти эффекты сопровождались улучшением производительности зрительно-пространственной памяти, зависящей от гиппокампа, и изменениями активности мозга, что оценивалось с помощью электроэнцефалографии [88] .
Сообщалось, что в дополнение к пробиотикам пребиотики — неперевариваемые соединения клетчатки, которые стимулируют рост полезных бактерий, — также оказывают положительное влияние на ось микробиота-кишечник-мозг. Исследование Burokas A. et al. (2017) сравнило эффекты 3-недельного введения фруктоолигосахаридов (FOS), галактоолигосахаридов (GOS) и их комбинации у взрослых самцов мышей [89] . Введение пребиотиков снижало вызванные стрессом уровни кортикостерона в плазме, при этом GOS и комбинация FOS и GOS оказывали наиболее сильное воздействие и ослабляли экспрессию мРНК CRFR1 в гиппокампе. Кроме того, введение GOS и FOS + GOS уменьшало тревожное и депрессивное поведение. В частности, комбинация FOS + GOS увеличивала экспрессию BDNF и GABA B рецептора в гиппокампе и уровни 5-НТ в префронтальной коре. Пребиотики также вызывали изменения в составе кишечной микробиоты с неожиданным снижением относительной численности лактобацилл и бифидобактерий. Напротив, содержание ацетата и пропионата SCFAs в слепой кишке увеличивалось, тогда как содержание изобутирата уменьшалось под действием пребиотиков. Примечательно, что изменения уровней SCFA коррелировали с поведенческими изменениями. В дополнение к этим эффектам, 3-недельное введение ФОС + ГОС, как было показано, притупляет эффекты хронического социального стресса в виде повышения уровня кортикостерона и продукции цитокинов селезенки в ответ на стимуляцию конканавалином А, а также снижает вызванные стрессом поведенческие нарушения [89] . В соответствии с этими положительными эффектами на мышах, клиническое исследование показало, что GOS, но не FOS, способны снижать уровень кортизола слюны у здоровых добровольцев [90] .
Однако не следует упускать из виду, что пре- и пробиотики также могут оказывать неблагоприятное воздействие на гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковой систему и поведение. Так, исследование Barrera-Bugueno C. et al. (2017), в ходе которого самцам крыс Sprague-Dawley вводили L. casei 54-2-33, пребиотик инулин или смесь пробиотика и пребиотика (синбиотик), начиная с P21 в течение 14 дней, выявило стресс-индуцированное увеличение кортикостерона при приеме пробиотика или пребиотика в отдельности, тогда как синбиотик ослаблял [91] .
Микробиота кишечника и ось HPA: данные моделей мышей GF
Исследования, проведенные на мышах, которые были выращены в изоляторах GF и, следовательно, лишены каких-либо микроорганизмов, имели существенное значение для дальнейшего определения роли кишечной микробиоты в формировании нейроэндокринной системы. Так, было продемонстрировано, что у мышей GF повышена экспрессия CRF, снижена экспрессия GR в коре головного мозга и повышены уровни АКТГ и кортикостерона в плазме в ответ на иммобилизационный стресс [93, 95]. Колонизация новорожденных мышей GF с помощью B. infantis способна ослабить повышенную реактивность оси HPA у мышей GF, тогда как колонизация энтеропатогенными E. coli увеличивает ответ HPA на стресс [93]. Хотя точные пути не выяснены, предполагается, что изменения в иммунноопосредованных эффектах на ось HPA играют значительную роль. Кроме того, только E. coli приводит к увеличению IL-1β в плазме с максимальным уровнем через 12 часов после инокуляции [93]. Колонизация мышей GF фекалиями мышей, свободных от специфических патогенов (SPF) в возрасте 6 недель способна предотвратить усиление ответа HPA, тогда как колонизация в возрасте 14 недель не влияет на ось HPA, что свидетельствует о зависимости эффектов от возраста [93].
Для мышей GF характерно множество нейроэндокринных и нейрохимических изменений, которые указывают на возможное участие микробиоты. Например, есть данные о снижении экспрессии центрального гена субъединиц рецептора NMDA и BDNF у мышей GF [93] . Субъединицы рецептора BDNF и NMDA играют роль медиаторов синаптической пластичности, и изменения в их экспрессии связаны с психическими расстройствами [92, 94, 95] . Интересно, что снижение уровня BDNF в гиппокампе, а также субъединиц рецептора глутамата NMDA индуцируется материнской депривацией и, как предполагается, способствует долговременному нарушению функции головного мозга [96]. Снижение уровня BDNF в гиппокампе и миндалевидном теле мышей GF связано со снижением экспрессии клона А, индуцируемого фактором роста нервов, тогда как белок постсинаптической плотности 95 и синаптофизин, маркеры, связанные с синаптогенезом и созреванием, повышены у мышей GF. Кроме того, увеличивается метаболизм NE, DA и 5-HT, как и мРНК рецептора DA D1 [97] .
Neufeld K.M. et al. (2011) [98] сообщили о повышении уровня кортикостерона у самок мышей GF. В отличие от сниженных уровней BDNF в гиппокампе самцов мышей, они наблюдали увеличение мРНК BDNF в гиппокампе самок мышей. Clarke G. et al. (2013) [99] также сравнивали самцов и самок мышей GF и отметили заметные половые различия в нейрохимических параметрах, тогда как нейроэндокринные и иммунологические показатели не различались между полами. В соответствии с вышеупомянутыми исследованиями, они продемонстрировали, что у самцов мышей GF снижены уровни BDNF в гиппокампе, тогда как уровни BDNF у самок мышей имеют тенденцию к небольшому повышению. Половые различия также наблюдались для гиппокампального 5-HT и его основного метаболита 5-гидроксииндолуксусной кислоты, поскольку повышенные уровни наблюдались только у самцов мышей GF. Напротив, уровни кортикостерона в ответ на новый стресс были увеличены как у самцов, так и у самок мышей [99]. При попытке установить потенциальную связь между иммунной и нейроэндокринной системами было обнаружено, что высвобождение цитокинов из спленоцитов после стимуляции LPS у мышей GF уменьшатся. Поскольку снижение образования цитокинов не было связано с полом, можно предположить, что повышение уровня кортикостерона в плазме скорее связано с иммунологическими, а не нейрохимическими изменениями у мышей GF.
Исследование, изучающее стресс в раннем возрасте, пришло к выводу, что изменения оси HPA в ответ на стресс не зависят от микробиоты кишечника, тогда как поведенческие нарушения связаны с дисбактериозом микробиоты кишечника [100]. Этот вывод был основан на обнаружении того, что вызванное стрессом повышение уровня кортикостерона было сопоставимо у мышей GF и SPF, тогда как тревожное поведение индуцировались стрессом только в присутствии кишечной микробиоты [100].
Таким образом, можно сделать вывод, что повышенная реактивность оси HPA часто обнаруживается у мышей GF. В отличие от других параметров, таких как нейрохимические изменения и поведение, которые варьируют в зависимости от пола, штамма мыши и других факторов, повышенная реактивность оси HPA часто обнаруживается у мышей и крыс GF. Ось HPA находится во взаимоотношениях с нейронными системами лимбического, среднего и стволового мозга, а также с симпатической и парасимпатической нервной системой [3] . Таким образом, в то время как модуляция гормонов стресса из-за отсутствия микробиоты кишечника потенциально может вызывать изменения в системах нейромедиаторов, другие факторы могут оказывать влияние на нейроцепи, которые впоследствии влияют на ось HPA. В связи с этим дефекты развития иммунной системы и изменения метаболизма мышей GF, вероятно, вносят вклад в нейроэндокринный фенотип в отсутствие кишечной микробиоты.
Нейроэндокринно -ассоциированный поведенческий фенотип мышей GF
В связи с повышенной реактивностью оси HPA у мышей GF, у мышей GF BALB/c для них характерно повышенные тревожное поведение и спонтанная двигательная активность [101] . Однако ряд авторов обнаружили снижение тревожного поведения мышей GF при тестировании в светлом/темном ящике, несмотря на повышенную чувствительность оси HPA [97, 98] . Противоречивость результатов дополнительно иллюстрируется сообщением об увеличении и уменьшении тревожного поведения у мышей GF в зависимости от поведенческого теста (понижающий тест и предпочтение света соответственно) [100] . Наконец, исследование Crumeyrolle-Arias M. et al. (2014), проведенное на самцах крыс F344, выявило повышенное тревожное поведение в OFT тесте [102].] . Таким образом, можно сделать вывод, что использованный поведенческий тест, тестируемые виды животных и генетический фон оказывают влияние на поведенческий фенотип грызунов GF. Похоже, что чувствительные к стрессу линии, такие как мыши BALB/c и крысы F344, проявляют повышенную тревожность в условиях GF [101, 102] , тогда как умеренно эмоциональные линии, такие как мыши Swiss и NMRI, этого не делают [97, 98] . Кроме того, на поведенческие различия разных линий мышей также влияет микробиота кишечника [103] . Таким образом, перенос микробиоты от мышей BALB/c к мышам GF NIH Swiss снижает исследовательское поведение по сравнению с колонизация микробиотой NIH Swiss, тогда как колонизация мышей BALB/c микробиотой мышей NIH Swiss увеличивает их исследовательское поведение [103] . Другим потенциальным искажающим фактором при оценке тревожноподобного поведения у мышей GF может быть гиперлокомоция, которая постоянно наблюдается у мышей GF [98, 101] и рыбок данио GF [104] . Таким образом, повышенная двигательная активность может мешать оценке тревожного и депрессивно-подобного поведения, которое может быть неправильно истолковано как парадоксальные «анксиолитикоподобные» поведенческие паттерны [105, 106] .
Влияние дефектов развития мышей GF на нейроэндокринную систему
Помимо изменений в нейроэндокринной системе, у мышей GF обнаруживаются дефекты развития желудочно-кишечного тракта (рис. 1 [107] . Интересно, что тяжесть животных моделей Th17-клеточно-зависимого артрита и экспериментального аутоиммунного энцефаломиелита заметно снижается при тестировании на мышах GF
[108, 109] . Напротив, мыши GF имеют большее количество инвариантных Т-клеток естественных киллеров в собственной пластинке толстой кишки и более восприимчивы к воспалительным состояниям, таких как индуцированный оксазолоном колит, которые зависят от инвариантных Т-клеток естественных киллеров [110].] . На роль микробиоты в созревании иммунной системы указывают данные о том, что колонизация новорожденных мышей GF обычной микробиотой способна предотвратить индуцированный оксазолоном колит, тогда как колонизация взрослых мышей GF его не предотвращает [110] .
Неясно, в какой степени дефицит дифференцировки лимфоцитов может способствовать нейроэндокринным нарушениям у мышей GF. Интересно, однако, что мыши с дефицитом гена активатора рекомбиназы 1, у которых отсутствуют зрелые В- и Т-лимфоциты, демонстрируют нарушение непространственной памяти и повышенное тревожное поведение, а также высокий уровень кортикостерона [111] . Кроме того, введение пробиотической смеси, содержащей L. rhamnosus и L. helveticus, начиная с отъема от грудного вскармливания, способно улучшить поведенческие нарушения и частично восстановить дисбиоз кишечной микробиоты, в то время как уровни кортикостерона остаются повышенными [111] . Кроме того, у мышей GF обнаруживаются различные функциональные и биохимические изменения головного мозга [57, 112, 113, 114] , которые также могут быть факторами развития нейроэндокринных и поведенческих нарушений. Так, полногеномный транскрипционный профиль миндалевидного тела мышей GF выявил признаки повышенной активности нейронов, тогда как гены, связанные с иммунной системой, были подавлены [115] . Кроме того, у мышей GF увеличены миндалина и гиппокамп, ассоциированные с дендритной гипертрофией субнаборов миндалевидных нейронов, тогда как нейроны гиппокампа обнаруживают дендритную атрофию [116] . Также было продемонстрировано, что посттранскрипционная экспрессия генов контролируется микробиотой кишечника, поскольку мыши GF демонстрируют измененный профиль экспрессии микроРНК (миРНК) в миндалевидном теле и префронтальной коре [117]. Интересно, что роль miRNA miR-21-5p также была продемонстрирована в индуцированном микробиотой увеличении проницаемости кишечного эпителия за счет усиления фактора рибозилирования 4 аденозиндифосфата малой гуанозинтрифосфатазы [118] .
Влияние нарушения обмена веществ у мышей GF на нейроэндокринную систему
Микробиота кишечника вносит важный вклад в пищеварение и метаболизм хозяина и является важным поставщиком витаминов [119] . Таким образом, мыши GF нуждаются в экзогенном витамине K и витамине B в своем рационе [119] . Таким образом, возникает вопрос о том, достаточно ли удовлетворяются высокие метаболические потребности мозга в условиях отсутствия или дисбиотической микробиоты, особенно в критические периоды развития, например в раннем возрасте, и как эти потенциальные дефициты могут способствовать развитию долгосрочных нейроэндокринных нарушений, учитывая известное влияние пищевых дефицитов на ось HPA [120 -122] . Интересно, что полиненасыщенная жирная кислота (эйкозапентаеновая кислота) не обнаруживается у мышей GF [114] , а длительное добавление смеси полиненасыщенных жирных кислот, включающей эйкозапентаеновую кислоту, обращает вспять индуцированный рассеянным склерозом дисбактериоз и ослабляет реакцию кортикостерона на острый стресс [123] . Напротив, имеются данные о том, что свободные жирные кислоты активируют и ингибируют ось HPA у крыс и людей соответственно [124, 125] .
Существуют и другие метаболические изменения в крови мышей GF. Например, нарушено опосредованное бактериями производство биоактивных индолсодержащих метаболитов, происходящих из триптофана, тогда как доступность триптофана, который является предшественником 5-HT, увеличена [114]. В то время как Clarke G. et al. [99] обнаружили повышенные уровни 5-НТ в гиппокампе самцов, но не самок, мышей GF, метаболомная оценка префронтальной коры мышей-самцов GF не выявила каких-либо различий в уровнях 5-HT. Напротив, метаболиты, участвующие в путях гликолиза, изменены у мышей GF, что предполагает, что эти животные потребляют меньше энергии за счет гликолиза, чем обычные мыши. В отличие от церебральной ГАМК, которая не изменена, концентрация DA была в два раза выше у мышей GF, и было высказано предположение, что она лежит в основе повышенной двигательной активности, наблюдаемой у этих животных [113].
Влияние антибиотиков на кишечную микробиоту и нейроэндокринную систему
В отличии от мышей GF, дисбиоз кишечника, вызванный антибиотиками, представляет собой альтернативный способ манипулирования микробиотой у взрослых животных, не вызывая изменений в их развитии и с преимуществом выбора момента времени и тяжести заболевания. Поскольку состав микробиоты кишечника может быть изменен самим стрессом [126] , мы сначала обсудим влияние дисбиоза кишечника, вызванного антибиотиками, на нейроэндокринные, нейрохимические и поведенческие параметры, а затем обсудим эффекты дисбактериоза в сочетании с различными протоколами острого и хронического стресса.
Дисбиоз кишечника, вызванный антибиотиками:
влияние на нейроэндокринные, нейрохимические и поведенческие параметры
Дисбактериоз, нарушающий формирование зрелой микробиоты, возникший в детском возрасте может оказывать долгосрочное воздействие на микробиоту, развитие оси HPA и общее состояние здоровья хозяина. В соответствии с данными, полученными на животных GF, несколько исследований демонстрируют повышение уровня кортикостерона в ответ на вызванный антибиотиками дисбиоз кишечника. Чтобы изучить роль лечения антибиотиками в раннем возрасте, Scheer et al. [127] подвергали мышей воздействию коктейля антибиотиков, содержащего ампициллин, стрептомицин, ванкомицин и метронидазол, а также искусственного подсластителя сукралозы с момента беременности до отъема от груди (P21). В то время как уровни кортикостерона в сыворотке были одинаковыми у контрольных и получавших антибиотики детенышей на P7, уровни кортикостерона в сыворотке имели тенденцию к увеличению у мышей, получавших антибиотики, на P21 и P42. Интересно, что совместное содержание мышей, получавших антибиотики, с контрольными животными через 1 неделю после отнятия от груди (P28) было способно обратить вспять повышение уровня кортикостерона в сыворотке крови, которое оценивалось на P56. Хотя состав кишечной микробиоты в этом исследовании не изучался, этот вывод может свидетельствовать о том, что вызванные антибиотиками изменения в составе кишечной микробиоты и последующее воздействие на ось HPA можно обратить вспять за счет совместного проживания мышей и связанной с этим нормализацией состава кишечной микробиоты [128] .
Кроме того, было показано, что лечение взрослых самцов мышей смесью антибиотиков (ампициллин, бацитрацин, меропенем, неомицин, ванкомицин) в течение 10 дней серьезно нарушает микробный состав (16S рДНК) в толстой кишке и влияет на различные уровни оси кишечник-мозг [129]. Отмечено повышение базального уровня кортикостерона, липидов и бактериальных метаболитов в плазме, снижение концентрации SCFAs в содержимом толстой кишки и нарушение непространственной памяти у животных, получавших антибиотики. Экспрессия генов в головном мозге животных, получавших антибиотики, была изменена. Так, в миндалевидном теле и гипоталамусе экспрессия мРНК NPY — орексигенного нейропептида, способствующего стрессоустойчивости [130] — увеличивалась у мышей, получавших антибиотики, тогда как экспрессия рецептора NPY снижалась в миндалевидном теле и гиппокампе. Экспрессия транспортера 5-НТ и субъединицы рецептора NMDA повышалась в миндалине животных, получавших антибиотики, а экспрессия мРНК BDNF снижалась в медиальной префронтальной коре, гиппокампе и гипоталамусе. В то время как уровни цитокинов в крови не повышались при лечении антибиотиками, экспрессия мРНК IL-1β снижалась в гиппокампе и гипоталамусе. Кроме того, на паттерны экспрессии мРНК 3 белков плотных контактов в миндалевидном теле и гиппокампе влияло лечение антибиотиками [129]. Эти данные свидетельствуют о том, что увеличение активности оси HPA, связанное с дисбиозом кишечника, вызванным антибиотиками, может быть связано со сложными изменениями взаимодействия кишечник – головной мозг.
Wang T. et al. показали, что лечение только ампициллином заметно изменяет состав фекальной микробиоты (по оценке с помощью количественной полимеразной цепной реакции) у крыс и повышает уровень кортикостерона в сыворотке [131] . При лечении крыс пробиотиком L. fermentumNS9 (NS9) повышение уровня кортикостерона в сыворотке, вызванное ампициллином, было нейтрализовано NS9. В то время как уровни GR и BDNF в гиппокампе оставались неизменными, уровни минералокортикоидных и NMDA-рецепторов у крыс, получавших антибиотики, снижались. Лечение NS9 также нормализовывало уровни NMDA и минералокортикоидных рецепторов в гиппокампе. На поведенческом уровне лечение антибиотиками само по себе вызывало легкое тревожное поведение и дефицит сохранения пространственной памяти; эти нарушения были предотвращены совместным лечением пробиотиком NS9 [131] . В отличие от упомянутых исследований, прием крысятами-самцами ванкомицина в различных концентрациях от Р4 до Р13 не влияла на базальные уровни кортикостерона в плазме во взрослом возрасте [132], тогда как висцеральная чувствительность и поведение, связанное с болью, увеличивались при лечении этим антибиотиком дозозависимым образом. Кроме того, у крыс, получавших самую высокую дозу ванкомицина 100 мг/кг, базальные уровни ИЛ-6 и нейтрофилов в спленоцитах были повышены, тогда как различий в уровнях цитокинов в цельной крови обнаружено не было [132] .
Антибиотикоиндуцированный дисбиоз в сочетании с острыми или хроническими стрессорами
Исследования влияние острого стресса на ось HPA в условиях антибиотикоиндуцированного дисбиоза дают возможность измерить базальный и стресс-индуцированный уровни кортикостерона. Ait-Belgnaoui A. et al. [80] показали, что лечение антибиотиками (ампициллин, неомицин) в течение 12 дней предотвращало увеличение уровня кортикостерона в плазме самок крыс, подвергшихся острому стрессу частичной иммобилизации (2 часа). Кроме того, лечение антибиотиками было способно обратить вспять вызванное стрессом увеличение экспрессии мРНК CRF, IL-1β, IL-6 и TNF-α в гипоталамусе. В то же время, концентрация LPS в портальной крови была значительно снижена у животных, получавших антибиотики [80] . Desbonnet L. et al. [133] исследовали модель дисбиоза, вызванного антибиотиками у животных, которых лечили с момента отлучения от груди, а затем подвергали острому иммобилизационному стрессу (30 минут)
непосредственно перед умерщвлением. Антибиотики снизили вызванное стрессом увеличение количества и разнообразия бактерий. В то время как лечение антибиотиками не влияло на экспрессию мРНК CRF в гипоталамусе и не изменяло уровни кортикостерона в плазме до и после острого иммобилизационного стресса, наблюдались изменения в поведении и HPA оси. Таким образом, экспрессия мРНК BDNF гиппокампа и мРНК гипоталамического вазопрессина снижалась при лечении антибиотиками. Лечение антибиотиками дополнительно повышало уровни NE в гиппокампе, а также L-3,4-дигидроксифенилаланина и метаболита DA гомованилиновой кислоты в миндалевидном теле [133] . Garate I. et al. (2011) взрослым самцам крыс давали в течение 13 недель смесь антибиотиков (ампициллин, ванкомицин, ципрофлоксацин, имипенем, метронидазол), в это время животные один раз подвергались тесту принудительного плавания в качестве острого стрессора. В то время как длительное воздействие антибиотиков не влияло на базальный и вызванный стрессом уровень кортикостерона, у животных, получавших антибиотики, вызываемый стрессом выход фекалий увеличивался. Уровни мРНК GR и мРНК CRFR1 были снижены в миндалевидном теле и гиппокампе крыс, получавших антибиотики, тогда как экспрессия мРНК BDNF увеличивалась в миндалевидном теле. На поведенческом уровне лечение антибиотиками усиливало депрессию, вызывало дефицит пространственной памяти и влияло на уровень моноаминов в ряде областей головного мозга [134] .
Исследование, изучающее эффекты приема антибиотиков (пенициллин G, сульфат стрептомицина) во время воздействия хронического легкого стресса (21 день), показало, что антибиотики способны предотвращать вызванное стрессом повышение уровня кортикостерона в плазме взрослых самцов крыс [135] . Кроме того, у животных, подвергшихся стрессу, лечение антибиотиками оказывало противовоспалительное действие на головной мозг, поскольку вызываемое стрессом повышение уровней кортикальных воспалительных медиаторов (включая циклооксигеназу-2, IL-1β и простагландин E 2 предотвращалось. Кроме того, лечение антибиотиками также блокировало вызванное стрессом снижение противовоспалительного медиатора 15-дезокси-дельта- 12,14-простагландина J 2 .в префронтальной коре, а так же изменения уровней кортикального ядерного фактора каппа В. Интересно, что лечение антибиотиками не влияло на депрессивное поведение, но количество фекальных масс, выделяемых во время модифицированного теста принудительного плавания, увеличивалось у мышей, получавших антибиотики, независимо от протокола стресса. У животных, получавших антибиотики, предотвращалось вызванное стрессом повышение концентрации LPS и LPS-связывающего белка в плазме, уровня TLR4 в префронтальной коре [135] .
Aguilera M. et al. (2013), используя повторяющийся психологический стресс в течении 7 дней, показали, что дисбиоз, вызванный антибиотиками, не изменяет эндокринные реакции на хронический стресс, но предотвращает усиленную реакцию, связанную с висцеральной болью, наблюдаемую у стрессированных самок мышей. В то время как несколько воспалительных маркеров (IL-6, TNF-α) оставались неизменными, уровень секреторного иммуноглобулина А в просвете слепой кишки повышался у животных, получавших антибиотики, независимо от стресса [136] .
Рассмотренные исследования показывают непоследовательное влияние вызванного антибиотиками дисбиоза на активность оси HPA, что оставляет дискутабельным предположение всестороннего взаимодействия между кишечной микробиотой и нейроэндокринной системой (Рисунок 3). Противоречивые результаты могут быть связаны с рядом факторов, включая различия в видах животных, штаммах, выборе антибиотиков и/или схемах лечения. Влияние антибиотиков на конкретные изменения в составе кишечной микробиоты часто оценить невозможно, поскольку состав микробиоты не был определен или определен лишь частично в ряде исследований, кроме того, микробиота исходно различалась в работах, нельзя исключить влияние самих антибиотиков на наблюдаемые параметры, что также обсуждается в следующем разделе.
Активировация (+) или ингибирование (-) оси HPA в исходных условиях или в ответ на различные стрессоры ( ) GF по сравнению с моделями дисбиоза, вызванного антибиотиками.
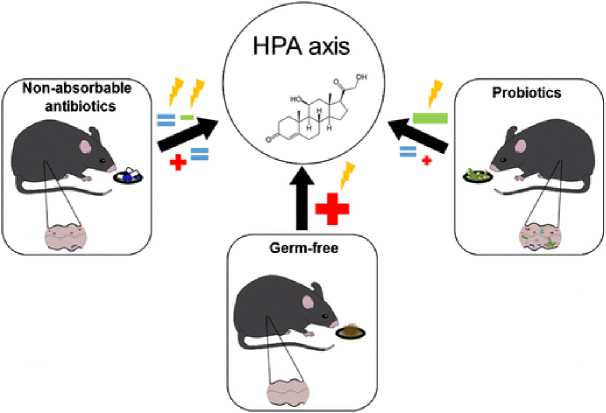
Рисунок 3. Влияние кишечной микробиоты и воздействий на нее на ось гипоталамус-гипофиз-надпочечники (HPA)
Одной из основных задач текущих исследований микробиоты является получение доказательств причинного ее участия в конкретных физиологических и патофизиологических процессах. Основные экспериментальные подходы к этому вопросу в настоящее время основаны на использовании грызунов GF, с одной стороны, и животных с дисбиозом вследствие лечения антибиотиками, с другой. Оба подхода имеют свои преимущества и недостатки и различаются своей научной ценностью, учитывая, что условия GF не могут быть изучены у людей. Модель дисбиоза, вызванного антибиотиками, дает возможность изучить микробные изменения и их патофизиологические последствия у животных, рожденных и выращенных с обычной/нормальной микробиотой. При проведении обоснованных исследований с применением антибиотиков особое внимание необходимо уделять выбору антибиотиков и их фармакокинетике, поскольку сами антибиотики могут непосредственно влиять на изучаемые процессы (например, нейроэндокринные реакции). Следовательно, важно выбрать антибиотики, которые не всасываются или всасываются в минимальной степени из желудочно-кишечного тракта, и проверить это условие на используемых экспериментальных видах животных [137]. В этом отношении подход, используемый Bercik et al. (2011) [103] представляет собой эталонную модель для изучения последствий дисбиоза, вызванного антибиотиками, в поведении мышей и биохимии мозга. Было обнаружено, что пероральное введение смеси антибиотиков мышам SPF вызывает дисбиоз кишечника, усиливает исследовательское поведение и изменяет уровни BDNF в мозге. Участие микробиоты кишечника в поведенческих нарушениях, вызванных антибиотиками, было подтверждено тем фактом, что дисбиоз кишечника и изменения поведения наблюдались только после перорального, но не внутрибрюшинного введения антибиотиков. Кроме того, никаких поведенческих изменений не наблюдалось у мышей GF, получавших смесь антибиотиков перорально [103]. Измерение присутствия антибиотиков в крови и исследуемых органах является еще одним подходом к выявлению точек действия антибиотиков и исключению прямого воздействия на такие органы, как головной мозг [129]. Таким образом, исследования с применением антибиотиков, которые легко всасываются из желудочно-кишечного тракта и даже способны проникать через гематоэнцефалический барьер, неубедительны в отношении взаимосвязи между кишечной микробиотой, функцией головного мозга и поведением. Этот факт, относится к метронидазолу [137, 138], который не только всасывается из кишечника и попадает в головной мозг, но и может оказывать нейротоксическое действие [139, 140].
Микробиом взаимодействует с иммунной системой хозяина, регулируя обмен веществ различными механизмами: непосредственным физическим контактом, выработкой метаболитов и сбросом структурных компонентов (Рисунок 4). Они влияют на метаболический гомеостаз путем иммунной модуляции слизистой оболочки и путем отдаленных изменений метаболических органов, таких как жировая ткань, мышцы и печень [141].
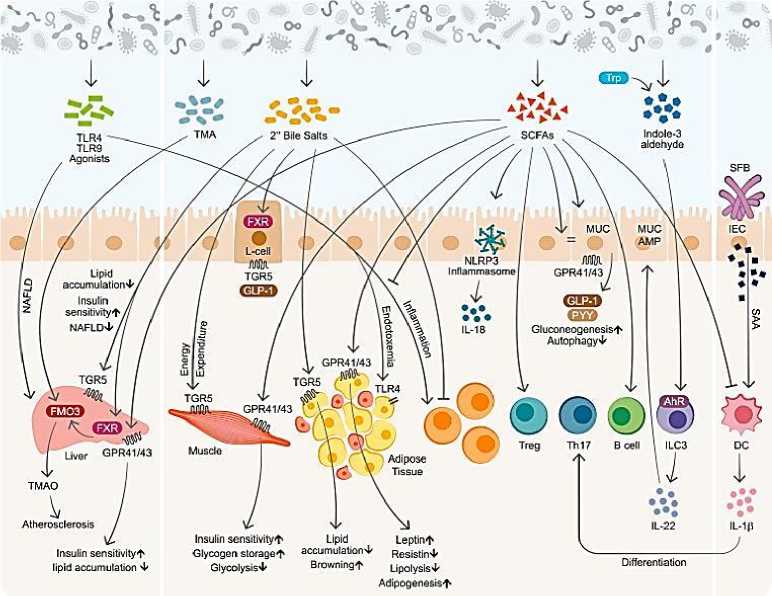
Рисунок 4. Микробиом и иммунно - метаболические взаимодействия [141]
Особенностью лимбической системы является то, что между ее структурами имеются простые двусторонние связи и сложные пути, образующие множество замкнутых кругов. Такая организация создает условия для длительного циркулирования одного и того же возбуждения в системе и тем самым для сохранения в ней единого состояния и доминирование этого состояния над другими системами мозга. Лимбическая система организует и обеспечивает протекание вегетативных, соматических и психических процессов при эмоционально-мотивационной деятельности. А также осуществляет восприятие и хранение эмоционально значимой информации, выбор и реализацию адаптивных форм эмоционального поведения. В связи с этим лимбическая система носит название «висцерального мозга».
Главной медицинской и социальной значимостью висцерального мозга является формирование эмоций. Висцеральный мозг участвует в регуляции функций внутренних органов, обоняния, автоматической регуляции, эмоций, памяти, сна, бодрствования и др. Висцеральный мозг определяет выбор и реализацию адаптационных форм поведения, динамику врожденных форм поведения, поддержание гомеостаза, генеративных процессов. Он обеспечивает гормональную стимуляцию организма, создание эмоционального фона, формирование и реализацию процессов высшей нервной деятельности.
Повреждение гиппокампа у человека нарушает память на события, близкие к моменту повреждения. Нарушаются продуктивность запоминания, обработка новой информации, различение пространственных сигналов. Повреждение гиппокампа ведет к снижению эмоциональности, инициативности, замедлению скорости протекания основных нервных процессов, повышаются пороги вызова эмоциональных реакций.
Миндалина - подкорковая структура лимбической системы, расположенная в глубине височной доли мозга. Нейроны миндалины разнообразны по форме, функциям и нейрохимической природе. Функции миндалины связаны с обеспечением оборонительного поведения, вегетативными, двигательными, эмоциональными реакциями, мотивацией условно-рефлекторного поведения. Лимбическая система организует и обеспечивает протекание вегетативных, соматических и психических процессов при эмоциональномотивационной деятельности. А также осуществляет восприятие и хранение эмоционально значимой информации, выбор и реализацию адаптивных форм эмоционального поведения. В связи с этим лимбическая система носит название «висцерального мозга» (Рисунок 5, 6).
Наиболее многофункциональными образованиями лимбической системы являются гиппокамп и миндалевидные тела. Лимбическая система (синоним: лимбический комплекс, висцеральный мозг, ринэнцефалон, тимэнцефалон) – комплекс структур среднего, промежуточного и конечного мозга, участвующих в организации висцеральных, мотивационных и эмоциональных реакций организма. Основную часть структур лимбической системы составляют образования головного мозга, относящиеся к древней, старой и новой коре, расположенные преимущественно на медиальной поверхности полушарий большого мозга, а также многочисленные подкорковые структуры, тесно с ними связанные. Нужно отметить, что древняя и старая кора лимбической системы имеет прямое отношение к обонятельной функции. В свою очередь обонятельный анализатор, как самый древний из анализаторов, является неспецифическим активатором всех видов деятельности коры большого мозга. Роль висцерального мозга в гормональной стимуляции организма. Лимбическая система обладает уникальным набором эффекторных структур. В них входят управление моторикой внутренних органов, двигательной активностью для выражения эмоций и гормональной стимуляцией организма (Рисунок 7).
Чем ниже уровень развития неокортекса (коры больших полушарий), тем больше поведение животного зависит от лимбической системы. Некоторые авторы называют лимбическую систему висцеральным мозгом, т.е. структурой ЦНС, участвующей в регуляции деятельности внутренних органов. И действительно, миндалевидные тела, прозрачная перегородка, обонятельный мозг при их возбуждении изменяют активность вегетативных систем организма в соответствии с условиями окружающей среды. Это стало возможно благодаря установлению морфологических и функциональных связей с более молодыми образованиями мозга, обеспечивающими взаимодействие
экстероцептивных, интероцептивных систем и коры височной доли.
мозолистое тело
Прозрачная перегородка
Серый покров мозолистого тела . / Свод
Поясная извилина
Ядра прозрачной перегородки
Ядра поводков
Передняя спайка
Перешеек поясной извилины
Зубчатая извилина
Обонятельная луковица
Обонятельный тракт / ,----
/ Миндалевидное / тело
Обонятельные полоски „
XV^—Гиппокамп Х^Х. Концевая полоска
К х. Парагиппокампальная \ извилина
Сосцевидноталамический пучок
Рисунок 5. Лимбический комплекс
Сосцевидное тело
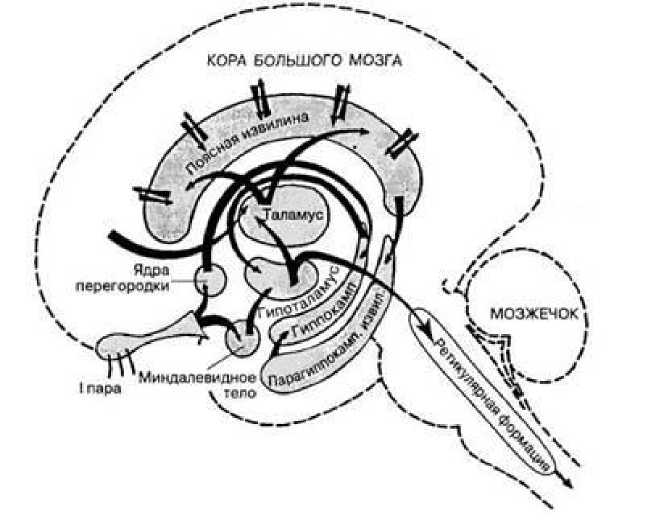
Рисунок 6. Многофункциональные связи лимбического комплекса
Нейрофизиология и нейробиология – мультидисциплинарно синхронизированы с медициной, генетикой, молекулярной биологией, различными физическими, оптическими, математическими методами и инструментами, с нейроинтерфейсами и искусственным интеллектом [142]. Нейропластичность - это внутреннее свойство и перепрограммирование мозга на протяжении всей его жизнедеятельности [142].
(сс) ®
«Нейроинтерфейсный камень» самооценки Homo sapiens для самоактуализации и самореализации личности — это, самооткрытие, саморазвитие, самообладание, самореализация.

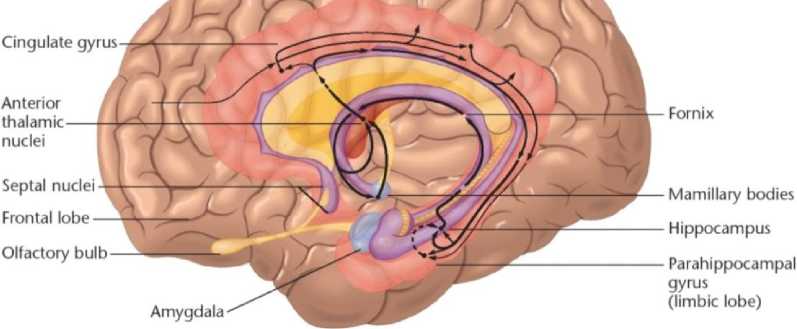
Рисунок 7. Висцеральный мозг
Депрессия вызывает патологические изменения в секреции и моторике пищеварительной системы, а сбой в работе двунаправленных кишечно-мозговых связей модифицируют микробиоту кишечника. Хроническая депрессия дестабилизирует работу «когнитивного и висцерального мозга» [142].
Хронический дистресс и ассоциированная с ним депрессия служат первопричиной нарушений нейропластичности/нейрогенеза и развития нейродегенеративных изменений в структурах лимбической системы [142].
В свою очередь, стрессовые переживания приводят к изменению секреции и моторики желудочно-кишечного тракта. В настоящее время продолжаются исследования о клинической значимости двунаправленной связи наряду с модификацией состава микробиоты кишечника. Двунаправленная кишечно-мозговая связь может начинаться как сенсорная информация из желудочно-кишечного тракта, и, следовательно, трансформируется в нейронные, гормональные и иммунологические сигналы [143].
В исследованиях Романчук Н.П. показано, что для нового нейрогенеза и нейропластичности, для управления нейропластичностью и биологическим возрастом человека, для современной нейрофизиологии и нейрореабилитации когнитивных нарушений и когнитивных расстройств необходимо достаточное функциональное и энергетическое питание мозга с использованием современных нейротехнологий ядерной медицины [143].
Современные знания о нейрогенезе мозга и нейрональной дифференциации — будущая концепция глубокой биологии как эффективный подход к разгадке ключевых процессов нейронной регенерации [144].
Биоэлементология и нутрициология мозга Homo sapiens XXI века – это комбинированное лечение с применением функциональных продуктов питания (персонифицированных по содержанию макро- и микроэлементов, витаминов и клетчатки) и лекарственных препаратов (с положительным влиянием на биомикробиоту) способных к нормализации патологически измененных биологических ритмов — перспективное направление Нейронутрициологии ХХI века [145].
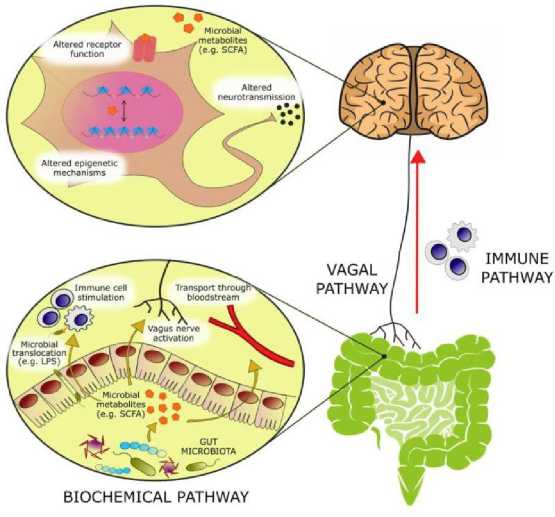
Рисунок 8. Биологически активные молекулы, происходящие из микробного метаболизма, модулируют эмоциональное поведение через несколько механизмов [146]: активация афферентных нервных волокон блуждающего нерва, стимулирование иммунной системы или циркуляторных иммунных клеток после транслокации от кишки в циркуляцию, абсорбция в кровоток, и биохимическое взаимодействие с несколькими дистальных органов
Кишечный микробиом играет решающую роль в нормальном развитии головного мозга, а также модуляции физиологических систем хозяина, важных при стрессовых расстройствах. Среди разнообразных путей, по которым кишечник может сигнализировать мозгу, эндокринная система, по-видимому, играет важную роль, поскольку она способна модулировать не только другие эндокринные функции, но и нервную и иммунную системы. Пептиды управляют молекулярными, функциональными, поведенческими и автономными реакциями, которые происходят в ответ на изменения микробного сообщества кишечника. Структурно-функциональные нейрокоммуникации пептидов влияют на психическое здоровье человека [146].
Желудочно-кишечный тракт и его центральная функция неразрывно связаны с кишечной микробиотой - экосистемой, которая развивалась совместно с хозяином для расширения своих биотрансформационных возможностей и взаимодействия с физиологическими процессами хозяина посредством продуктов его метаболизма. Аномалии в микробиоте-кишечно-мозговой оси появились в качестве ключевого компонента патофизиологии депрессии, что привело к более глубоким исследованиям, направленным на изучение нейроактивного потенциала продуктов микробного метаболизма кишечника. С приблизительно тремя-четырьмя миллионами различных генов в коллективных геномах микробиоты кишечника в микробиоме человека содержится примерно в 100-150 раз больше генетической информации, чем в человеческом геноме [146]. В головном мозге такие метаболиты могут активировать рецепторы на нейронах или глиях, модулировать нейрональную возбудимость и изменять паттерны экспрессии с помощью эпигенетических механизмов.
Помимо патологии ЦНС, у пациентов с депрессией также наблюдаются изменения в метаболической, иммунной и эндокринной системах. Существует все больше доказательств того, что микробиота кишечника ассоциируется с патофизиологией депрессии. В ряде таксономических ассоциативных исследований у людей наблюдались различия в составе фекальной микробиоты больных с психиатрическими заболеваниями по сравнению со здоровыми субъектами [147] и др.
Исследования, посвященные пероральному введению пробиотиков или невсасывающихся антибактериальных препаратов, а также анализу животных GF, выявляют разнонаправленное взаимодействие между кишечной микробиотой и нейроэндокринной системой. Демонстрация гомеостатических эффектов пробиотиков на нейроэндокринную систему имеет большое трансляционное значение, поскольку указывает на новые возможности терапевтического вмешательства.
Большинство доклинических данных подтверждают способность определенных пробиотических штаммов оказывать благоприятное влияние на ось кишечник-мозг, особенно в условиях стресса. Положительные эффекты, вероятно, опосредованы иммуномодулирующими эффектами пробиотиков и их способностью уменьшать кишечную транслокацию микробных компонентов через кишечный барьер. Однако, несмотря на эти обнадеживающие данные, лежащие в основе механизмы, а также клиническая эффективность этих пробиотических штаммов еще предстоит продемонстрировать. В отличие от в основном ингибирующих эффектов пробиотиков на активность оси HPA, повышенную активность оси HPA у мышей GF можно обратить вспять колонизацией кишечника в раннем детском возрасте. Хотя это наблюдение указывает на центральную роль микробиоты кишечника в развитии и регуляции оси HPA, лежащие в основе процессы остаются неясными, учитывая имеющиеся полиорганные нарушения у мышей GF, включая изменения в иммунной системе, желудочно-кишечном тракте, метаболизме и головном мозге. Наконец, было продемонстрировано, что пероральное введение антибактериальных препаратов влияет на кишечную микробиоту и нейроэндокринную систему следующим образом: с одной стороны, вызванное антибиотиками нарушение микробиоты повышает уровень кортикостерона, тогда как, с другой стороны, аналогично действию пробиотиков, были показаны защитные эффекты вызванного антибиотиками снижения микробиоты кишечника в условиях стресса. Последний эффект можно объяснить снижением связанной с микробиотой активации иммунной системы в ответ на стресс. Таким образом, пероральные антибиотики могут оказывать благоприятное или негативное воздействие на кишечную микробиоту и нейроэндокринную систему в зависимости от ранее существовавшего состава кишечной микробиоты, ее взаимодействия с антибиотиками, побочных эффектов препарата (например, действия на иммунную и эндокринную системы, а также ЦНС) и воздействия окружающей среды. Раскрытие точных механизмов, лежащих в основе многогранной связи между кишечной микробиотой и нейроэндокринной системой, может привести к новым терапевтическим возможностям влияния на нарушения нейроэндокринной системы путем контролируемого воздействия на кишечную микробиоту.
Brain Homo sapiens работая в режиме гениальности (таланта, креативности) требует создания и поддержание современных нейрокоммуникаций между новой корой и гиппокампом (библиотекой памяти, винчестером памяти), формированием новых структурно-функциональных нейрокоммуникаций в Brain Homo sapiens которые происходят непрерывно на протяжении всей жизнедеятельности от рождения до сверхдолголетия, и имеют творческие преимущества в эпоху современного нейробыта и нейромаркетинга [148].
Системное нейрокогнитивное и нейроэкономическое принятие решений становится одной из величайших проблем качественной жизни Homo sapiens в XXI веке. Исследован процесс принятия решений человеком на нейрокогнитивном, нейросоциальном и нейроэкономическом уровнях [148].
Все этапы, связанные с медико-биологическим направлением нейронаук и технологий — диагностика, терапия, реабилитация и профилактика неврологических и психических расстройств — имеют свои сложности, что ведет к недостаточно эффективной помощи больным. Поэтому критически важной задачей является дальнейшее развитие технологий и методик в этих областях, наряду с прорывами в накоплении фундаментальных знаний о возникновении и развитии данных заболеваний [149].
Глобальный доступ к медицинской визуализации и ядерной медицине, позволил разработке и внедрению радиопротекторной фармацевтики и диетологии [149]. Одной из областей интереса является то, что радиопротекторные агенты часто являются фитонутриентами, которые содержатся в хорошо сбалансированной диете, особенно в растительной диете. Это наблюдение предполагает, что только модификация диеты может обеспечить радиопротекторные эффекты [149].
Комбинированная медикаментозная платформа и обогащенная биоэлементология и нутрициология (мозга/микробиоты и генома/эпигенома), гибридная нейровизуализация и нейротехнологии ядерной медицины работают как превентивно, так и в долгосрочных программах медицинской реабилитации [150].
Культурная парадигма здоровья мозга Homo sapiens в десятилетнем исследовании «Активное долголетие: биофизика генома, нутригеномика, нутригенетика, ревитализация» активизирует проникновение эволюционных и социально-когнитивных нейрокоммуникаций мозга человека в современные нейротехнологии ядерной медицины, новую 5P Medicine and 5G technology [150].
Список литературы Микробиом и мозг: кишечная микробиота и нейроэндокринная система
- Toni R. The neuroendocrine system: organization and homeostatic role // Journal of endocrinological investigation. 2004. V. 27. №6 Suppl. P. 35-47. PMID: 15481802.
- Prevot V. Plasticity of neuroendocrine systems // European Journal of Neuroscience. 2010. V. 32. №12. P. 1987-1988. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07533.x
- Farzi A., Fröhlich E. E., Holzer P. Gut microbiota and the neuroendocrine system // Neurotherapeutics. 2018. V. 15. №1. P. 5-22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-017-0600-5
- Keller-Wood M. E., Dallman M. F. Corticosteroid inhibition of ACTH secretion // Endocrine reviews. 1984. V. 5. №1. P. 1-24. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv-5-1-1
- Булгакова С. В., Романчук Н. П., Волобуев А. Н. Новая личность и нейрокоммуникации: нейрогенетика и нейросети, психонейроиммуноэндокринология, 5P медицина и 5G технологии // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2021. Т. 7. №8. С. 202-240. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414-2948/69/26
- O’Mahony S. M., Clarke G., Dinan T. G., Cryan J. F. Early-life adversity and brain development: Is the microbiome a missing piece of the puzzle? // Neuroscience. 2017. V. 342. P. 37-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.09.068
- Juruena M. F., Bocharova M., Agustini B., Young A. H. Atypical depression and nonatypical depression: Is HPA axis function a biomarker? A systematic review // Journal of affective disorders. 2018. V. 233. P. 45-67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.09.052
- Videlock E. J., Shih W., Adeyemo M., Mahurkar-Joshi S., Presson A. P., Polytarchou C., Chang L. The effect of sex and irritable bowel syndrome on HPA axis response and peripheral glucocorticoid receptor expression // Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016. V. 69. P. 67-76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.03.016
- Прохуровская, Е. В., Булгакова, С. В., Меликова, А. В., & Захарова, Н. О. Роль микробиоты кишечника в развитии болезни Паркинсона у лицпожилого и старческого возраста // Клиническая геронтология. 2021. V. 27. №7-8. P. 63-68. https://doi.org/10.26347/1607-2499202107-08063-068
- Bradford K., Shih W., Videlock E. J., Presson A. P., Naliboff B. D., Mayer E. A., Chang L. Association between early adverse life events and irritable bowel syndrome // Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology. 2012. V. 10. №4. P. 385-390. e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2011.12.018
- Liu B., Liu J., Wang M., Zhang Y., Li L. From serotonin to neuroplasticity: evolvement of theories for major depressive disorder // Frontiers in cellular neuroscience. 2017. V. 11. P. 305. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00305
- Heim C., Newport D. J., Heit S., Graham Y. P., Wilcox M., Bonsall R., Nemeroff C. B. Pituitary-adrenal and autonomic responses to stress in women after sexual and physical abuse in childhood // Jama. 2000. V. 284. №5. P. 592-597. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.284.5.592
- De Punder K., Pruimboom L. Stress induces endotoxemia and low-grade inflammation by increasing barrier permeability // Frontiers in immunology. 2015. V. 6. P. 223. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00223
- Kelly J. R., Kennedy P. J., Cryan J. F., Dinan T. G., Clarke G., Hyland N. P. Breaking down the barriers: the gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders // Frontiers in cellular neuroscience. 2015. P. 392. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00392
- Булгакова С. В., Захарова Н. О., Романчук П. И. Микробиота кишечника: новый регулятор сердечно-сосудистой функции // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2021. Т. 7. No1. С. 200-222. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414-2948/62/20
- Slyepchenko A., Maes M., Jacka F. N., Köhler C. A., Barichello T., McIntyre R. S., Carvalho A. F. Gut microbiota, bacterial translocation, and interactions with diet: pathophysiological links between major depressive disorder and non-communicable medical comorbidities // Psychotherapy and psychosomatics. 2017. V. 86. №1. P. 31-46. https://doi.org/10.1159/000448957
- Rajilić-Stojanović M., Jonkers D. M., Salonen A., Hanevik K., Raes J., Jalanka J., Penders J. Intestinal microbiota and diet in IBS: causes, consequences, or epiphenomena? // The American journal of gastroenterology. 2015. V. 110. №2. P. 278. https://doi.org/10.1038%2Fajg.2014.427
- Collins S. M. The intestinal microbiota in the irritable bowel syndrome // International review of neurobiology. 2016. V. 131. P. 247-261. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.irn.2016.08.003
- Kelly J. R., Borre Y., O'Brien C., Patterson E., El Aidy S., Deane J., Dinan T. G. Transferring the blues: depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat // Journal of psychiatric research. 2016. V. 82. P. 109-118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.07.019
- Naseribafrouei A., Hestad K., Avershina E., Sekelja M., Linløkken A., Wilson R., Rudi K. Correlation between the human fecal microbiota and depression // Neurogastroenterology & Motility. 2014. V. 26. №8. P. 1155-1162. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12378
- Jiang H., Ling Z., Zhang Y., Mao H., Ma Z., Yin Y., Ruan B. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2015. V. 48. P. 186-194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.03.016
- Zheng P., Zeng B., Zhou C., Liu M., Fang Z., Xu X., Xie P. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism // Molecular psychiatry. 2016. V. 21. №6. P. 786-796. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.44
- De Palma G., Lynch M. D., Lu J., Dang V. T., Deng Y., Jury J., Bercik P. Transplantation of fecal microbiota from patients with irritable bowel syndrome alters gut function and behavior in recipient mice // Science translational medicine. 2017. V. 9. №379. P. eaaf6397. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf6397
- Doolin K., Farrell C., Tozzi L., Harkin A., Frodl T., O’Keane V. Diurnal hypothalamicpituitary- adrenal axis measures and inflammatory marker correlates in major depressive disorder // International journal of molecular sciences. 2017. V. 18. №10. P. 2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102226
- Holzer P., Reichmann F., Farzi A. Neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide in the gut–brain axis // Neuropeptides. 2012. V. 46. №6. P. 261-274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2012.08.005
- Clarke, G., Stilling, R. M., Kennedy, P. J., Stanton, C., Cryan, J. F., & Dinan, T. G. Minireview: gut microbiota: the neglected endocrine organ // Molecular endocrinology. 2014. V. 28. №8. P. 1221-1238. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2014-1108
- El Aidy S., Dinan T. G., Cryan J. F. Gut microbiota: the conductor in the orchestra of immune–neuroendocrine communication // Clinical therapeutics. 2015. V. 37. №5. P. 954-967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.03.002
- Sherwin E., Sandhu K. V., Dinan T. G., Cryan J. F. May the force be with you: the light and dark sides of the microbiota–gut–brain axis in neuropsychiatry // CNS drugs. 2016. V. 30. №11. P. 1019-1041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-016-0370-3
- Meaney M. J., Aitken D. H., Bhatnagar S., Sapolsky R. M. Postnatal handling attenuates certain neuroendocrine, anatomical, and cognitive dysfunctions associated with aging in female rats // Neurobiology of aging. 1991. V. 12. №1. P. 31-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-4580(91)90036-J
- Singh-Taylor A., Molet J., Jiang S., Korosi A., Bolton J. L., Noam Y., Baram T. Z. NRSF-dependent epigenetic mechanisms contribute to programming of stress-sensitive neurons by neonatal experience, promoting resilience // Molecular psychiatry. 2018. V. 23. №3. P. 648-657. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.240
- Van Bodegom M., Homberg J. R., Henckens M. J. A. G. Modulation of the hypothalamicpituitary- adrenal axis by early life stress exposure // Frontiers in cellular neuroscience. 2017. V. 11. P. 87. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00087
- Levitt N. S., Lindsay R. S., Holmes M. C., Seckl J. R. Dexamethasone in the last week of pregnancy attenuates hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor gene expression and elevates blood pressure in the adult offspring in the rat // Neuroendocrinology. 1996. V. 64. №6. P. 412-418. https://doi.org/10.1159/000127146
- Sadler T. R., Nguyen P. T., Yang J., Givrad T. K., Mayer E. A., Maarek J. M. I., Holschneider D. P. Antenatal maternal stress alters functional brain responses in adult offspring during conditioned fear // Brain research. 2011. V. 1385. P. 163-174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2011.01.104
- Son G. H., Geum D., Chung S., Kim E. J., Jo J. H., Kim C. M., Kim K. Maternal stress produces learning deficits associated with impairment of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic plasticity // Journal of Neuroscience. 2006. V. 26. №12. P. 3309-3318. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3850-05.2006
- Sowa J., Bobula B., Glombik K., Slusarczyk J., Basta-Kaim A., Hess G. Prenatal stress enhances excitatory synaptic transmission and impairs long-term potentiation in the frontal cortex of adult offspring rats // PLoS One. 2015. V. 10. №3. P. e0119407. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119407
- Herman J. P., McKlveen J. M., Ghosal S., Kopp B., Wulsin A., Makinson R., Myers B. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical stress response // Comprehensive physiology. 2016. V. 6. №2. P. 603. https://doi.org/10.1002%2Fcphy.c150015
- Holzer P., Wultsch T., Edelsbrunner M., Mitrovic M., Shahbazian A., Painsipp E., Pabst M. A. Increase in gastric acid–induced afferent input to the brainstem in mice with gastritis // Neuroscience. 2007. V. 145. №3. P. 1108-1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.12.025
- Dantzer R. O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW // From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008. V. 9. P. 46-56.
- Miller M. A., Kandala N. B., Kivimaki M., Kumari M., Brunner E. J., Lowe G. D., Cappuccio F. P. Gender differences in the cross-sectional relationships between sleep duration and markers of inflammation: Whitehall II study // Sleep. 2009. V. 32. №7. P. 857-864. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/32.7.857
- Shirtcliff E. A., Coe C. L., Pollak S. D. Early childhood stress is associated with elevated antibody levels to herpes simplex virus type 1 // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2009. V. 106. №8. P. 2963-2967. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0806660106
- Weaver I. C., Cervoni N., Champagne F. A., D'Alessio A. C., Sharma S., Seckl J. R., Meaney M. J. Epigenetic programming by maternal behavior // Nature neuroscience. 2004. V. 7. №8. P. 847-854. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1276
- Klengel T., Mehta D., Anacker C., Rex-Haffner M., Pruessner J. C., Pariante C. M., Binder E. B. Allele-specific FKBP5 DNA demethylation: A molecular mediator of gene-childhood trauma interactions // Nature Neuroscience. 2012.
- Bailey M. T., Coe C. L. Maternal separation disrupts the integrity of the intestinal microflora in infant rhesus monkeys // Developmental Psychobiology: The Journal of the International Society for Developmental Psychobiology. 1999. V. 35. №2. P. 146-155. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-2302(199909)35:2-146::AID-DEV7-3.0.CO;2-G
- Lyte M., Ernst S. Catecholamine induced growth of gram-negative bacteria // Life sciences. 1992. V. 50. №3. P. 203-212. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(92)90273-R
- Serrats J., Schiltz J. C., García-Bueno B., van Rooijen N., Reyes T. M., Sawchenko P. E. Dual roles for perivascular macrophages in immune-to-brain signaling // Neuron. 2010. V. 65. №1. P. 94-106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.11.032
- Arentsen T., Qian Y., Gkotzis S., Femenia T., Wang T., Udekwu K., Diaz Heijtz R. The bacterial peptidoglycan-sensing molecule Pglyrp2 modulates brain development and behavior // Molecular psychiatry. 2017. V. 22. №2. P. 257-266. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.182
- Clarke T. B., Davis K. M., Lysenko E. S., Zhou A. Y., Yu Y., Weiser J. N. Recognition of peptidoglycan from the microbiota by Nod1 enhances systemic innate immunity // Nature medicine. 2010. V. 16. №2. С. 228-231. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2087
- Farzi A., Reichmann F., Meinitzer, A., Mayerhofer, R., Jain, P., Hassan, A. M., Holzer P. Synergistic effects of NOD1 or NOD2 and TLR4 activation on mouse sickness behavior in relation to immune and brain activity markers // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2015. V. 44. P. 106-120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2014.08.011
- Mayerhofer R., Fröhlich E. E., Reichmann F., Farzi A., Kogelnik N., Fröhlich E., Holzer P. Diverse action of lipoteichoic acid and lipopolysaccharide on neuroinflammation, blood-brain barrier disruption, and anxiety in mice // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2017. V. 60. P. 174-187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.10.011
- Shanks N., Larocque S., Meaney M. J. Neonatal endotoxin exposure alters the development of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: early illness and later responsivity to stress // Journal of Neuroscience. 1995. V. 15. №1. P. 376-384. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-01-00376.1995
- Mouihate, A., Galic, M. A., Ellis, S. L., Spencer, S. J., Tsutsui, S., & Pittman, Q. J. Early life activation of toll-like receptor 4 reprograms neural anti-inflammatory pathways // Journal of Neuroscience. 2010. V. 30. №23. P. 7975-7983. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6078-09.2010
- Ong L. K., Fuller E. A., Sominsky L., Hodgson D. M., Dunkley P. R., Dickson P. W. Early life peripheral lipopolysaccharide challenge reprograms catecholaminergic neurons // Scientific reports. 2017. V. 7. №1. P. 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40475
- Chang P. V., Hao L., Offermanns S., Medzhitov R. The microbial metabolite butyrate regulates intestinal macrophage function via histone deacetylase inhibition // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2014. V. 111. №6. P. 2247-2252. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1322269111
- Usami, M., Kishimoto, K., Ohata, A., Miyoshi, M., Aoyama, M., Fueda, Y., & Kotani, J. Butyrate and trichostatin A attenuate nuclear factor κB activation and tumor necrosis factor α secretion and increase prostaglandin E2 secretion in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells // Nutrition research. 2008. V. 28. №5. P. 321-328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2008.02.012
- Furusawa Y., Obata Y., Fukuda S., Endo T. A., Nakato G., Takahashi D., Ohno H. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells // Nature. 2013. V. 504. №7480. P. 446-450. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12721
- Rooks M. G., Garrett W. S. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity // Nature reviews immunology. 2016. V. 16. №6. P. 341-352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.42
- Erny D., de Angelis A. L. H., Jaitin D., Wieghofer P., Staszewski O., David E., Prinz M. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS // Nature neuroscience. 2015. V. 18. №7. P. 965-977. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4030
- Castillo-Ruiz A., Mosley M., George A. J., Mussaji L. F., Fullerton E. F., Ruszkowski E. M., Forger N. G. The microbiota influences cell death and microglial colonization in the perinatal mouse brain // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2018. V. 67. P. 218-229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.08.027
- Bilimoria P. M., Stevens B. Microglia function during brain development: new insights from animal models // Brain research. 2015. V. 1617. P. 7-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.11.032
- Schroeder, F. A., Lin, C. L., Crusio, W. E., & Akbarian, S. Antidepressant-like effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor, sodium butyrate, in the mouse // Biological psychiatry. 2007. V. 62. №1. P. 55-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.06.036
- Han A., Sung Y. B., Chung S. Y., Kwon M. S. Possible additional antidepressant-like mechanism of sodium butyrate: targeting the hippocampus // Neuropharmacology. 2014. V. 81. P. 292-302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.02.017
- De Silva A., Bloom S. R. Gut hormones and appetite control: a focus on PYY and GLP-1 as therapeutic targets in obesity // Gut and liver. 2012. V. 6. №1. P. 10. https://doi.org/10.5009%2Fgnl.2012.6.1.10
- Brooks L., Viardot A., Tsakmaki A., Stolarczyk E., Howard J. K., Cani P. D., Bewick G. A. Fermentable carbohydrate stimulates FFAR2-dependent colonic PYY cell expansion to increase satiety // Molecular metabolism. 2017. V. 6. №1. P. 48-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2016.10.011
- Breton J., Tennoune N., Lucas N., Francois M., Legrand R., Jacquemot J., Fetissov S. O. Gut commensal E. coli proteins activate host satiety pathways following nutrient-induced bacterial growth // Cell metabolism. 2016. V. 23. №2. P. 324-334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.10.017
- Tennoune N., Chan P., Breton J., Legrand R., Chabane Y. N., Akkermann K., Fetissov S. O. Bacterial ClpB heat-shock protein, an antigen-mimetic of the anorexigenic peptide α-MSH, at the origin of eating disorders // Translational psychiatry. 2014. V. 4. №10. P. e458-e458. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2014.98
- Duca F. A., Swartz T. D., Sakar Y., Covasa M. Increased oral detection, but decreased intestinal signaling for fats in mice lacking gut microbiota // PLoS one. 2012. V. 7. №6. P. e39748. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039748
- Schéle E., Grahnemo L., Anesten F., Hallén A., Bäckhed F., Jansson J. O. The gut microbiota reduces leptin sensitivity and the expression of the obesity-suppressing neuropeptides proglucagon (Gcg) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Bdnf) in the central nervous system // Endocrinology. 2013. V. 154. №10. P. 3643-3651. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2012-2151
- Holzer P., Farzi A. Neuropeptides and the microbiota-gut-brain axis // Microbial endocrinology: the microbiota-gut-brain axis in health and disease. 2014. P. 195-219. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0897-4_9
- Dhakal R., Bajpai V. K., Baek K. H. Production of GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) by microorganisms: a review // Brazilian Journal of Microbiology. 2012. V. 43. №4. P. 1230-1241.
- Asano, Y., Hiramoto, T., Nishino, R., Aiba, Y., Kimura, T., Yoshihara, K., ... & Sudo, N. Critical role of gut microbiota in the production of biologically active, free catecholamines in the gut lumen of mice // American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 2012. V. 303. №11. P. G1288-G1295. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00341.2012
- Mazzoli R., Pessione E. The neuro-endocrinological role of microbial glutamate and GABA signaling // Frontiers in microbiology. 2016. V. 7. P. 1934. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01934
- Moya-Perez A., Perez-Villalba A., Benitez-Paez A., Campillo I., Sanz Y. Bifidobacterium CECT 7765 modulates early stress-induced immune, neuroendocrine and behavioral alterations in mice // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2017. V. 65. P. 43-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.05.011
- Agusti A., Moya-Perez A., Campillo I., Montserrat-De La Paz S., Cerrudo V., Perez-Villalba A., Sanz Y.Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum CECT 7765 ameliorates neuroendocrine alterations associated with an exaggerated stress response and anhedonia in obese mice // Molecular neurobiology. 2018. V. 55. №6. P. 5337-5352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0768-z
- Desbonnet L., Garrett L., Clarke G., Kiely B., Cryan J. F., Dinan T. Effects of the probiotic Bifidobacterium infantis in the maternal separation model of depression // Neuroscience. 2010. V. 170. №4. P. 1179-1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.08.005
- Savignac H. M., Kiely B., Dinan T. G., Cryan J. F. B ifidobacteria exert strain‐specific effects on stress‐related behavior and physiology in BALB/c mice // Neurogastroenterology & Motility. 2014. V. 26. №11. P. 1615-1627. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12427
- Barouei J., Moussavi M., Hodgson D. M. Effect of maternal probiotic intervention on HPA axis, immunity and gut microbiota in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046051
- Bravo J. A., Forsythe P., Chew M. V., Escaravage E., Savignac H. M., Dinan T. G., Cryan J. F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2011. V. 108. №38. P. 16050-16055. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1102999108
- Bharwani A., Mian M. F., Surette M. G., Bienenstock J., Forsythe P. Oral treatment with Lactobacillus rhamnosus attenuates behavioural deficits and immune changes in chronic social stress // BMC medicine. 2017. V. 15. №1. P. 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-016-0771-7
- Kelly J. R., Allen A. P., Temko A., Hutch W., Kennedy P. J., Farid N., Dinan T. G. Lost in translation? The potential psychobiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus (JB-1) fails to modulate stress or cognitive performance in healthy male subjects // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2017. V. 61. P. 50-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.11.018
- Ait-Belgnaoui A., Durand H., Cartier C., Chaumaz G., Eutamene H., Ferrier L., Theodorou V. Prevention of gut leakiness by a probiotic treatment leads to attenuated HPA response to an acute psychological stress in rats // Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2012. V. 37. №11. P. 1885-1895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.03.024
- Ait‐Belgnaoui A., Colom A., Braniste V., Ramalho L., Marrot A., Cartier C., Tompkins T. Probiotic gut effect prevents the chronic psychological stress‐induced brain activity abnormality in mice // Neurogastroenterology & Motility. 2014. V. 26. №4. P. 510-520. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12295
- Gareau M. G., Jury J., MacQueen G., Sherman P. M., Perdue M. H. Probiotic treatment of rat pups normalises corticosterone release and ameliorates colonic dysfunction induced by maternal separation // Gut. 2007. V. 56. №11. P. 1522-1528. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.2006.117176
- Vanhaecke T., Aubert P., Grohard P. A., Durand T., Hulin P., Paul‐Gilloteaux P., Neunlist M. L. fermentum CECT 5716 prevents stress‐induced intestinal barrier dysfunction in newborn rats // Neurogastroenterology & Motility. 2017. V. 29. №8. P. e13069. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13069
- Abildgaard A., Elfving B., Hokland M., Wegener G., Lund S. Probiotic treatment reduces depressive-like behaviour in rats independently of diet // Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017. V. 79. P. 40-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.02.014
- Rothhammer V., Mascanfroni I. D., Bunse L., Takenaka M. C., Kenison J. E., Mayo L., Quintana F. J. Type I interferons and microbial metabolites of tryptophan modulate astrocyte activity and central nervous system inflammation via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor // Nature medicine. 2016. V. 22. №6. P. 586-597. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4106
- Andersson H., Tullberg C., Ahrné S., Hamberg K., Lazou Ahrén I., Molin G., Håkansson Å. Oral administration of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v reduces cortisol levels in human saliva during examination induced stress: a randomized, double-blind controlled trial // International Journal of Microbiology. 2016. V. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8469018
- Messaoudi M., Lalonde R., Violle N., Javelot H., Desor D., Nejdi A., Cazaubiel J. M. Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects // British Journal of Nutrition. 2011. V. 105. №5. P. 755-764.
- Allen, A. P., Hutch, W., Borre, Y. E., Kennedy, P. J., Temko, A., Boylan, G., ... & Clarke, G. Bifidobacterium longum 1714 as a translational psychobiotic: modulation of stress, electrophysiology and neurocognition in healthy volunteers // Translational psychiatry. 2016. V. 6. №11. P. e939-e939. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.191
- Burokas A., Arboleya S., Moloney R. D., Peterson V. L., Murphy K., Clarke G., Cryan J. F. Targeting the microbiota-gut-brain axis: prebiotics have anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects and reverse the impact of chronic stress in mice // Biological psychiatry. 2017. V. 82. №7. P. 472-487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.12.031
- Schmidt K., Cowen P. J., Harmer C. J., Tzortzis G., Errington S., Burnet P. W. Prebiotic intake reduces the waking cortisol response and alters emotional bias in healthy volunteers // Psychopharmacology. 2015. V. 232. №10. P. 1793-1801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3810-0
- Barrera-Bugueño C., Realini O., Escobar-Luna J., Sotomayor-Zárate R., Gotteland M., Julio-Pieper M., Bravo J. A. Anxiogenic effects of a Lactobacillus, inulin and the synbiotic on healthy juvenile rats // Neuroscience. 2017. V. 359. P. 18-29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.06.064
- Lu B., Nagappan G., Lu Y. BDNF and synaptic plasticity, cognitive function, and dysfunction // Neurotrophic factors. 2014. P. 223-250. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-45106-5_9
- Sudo N., Chida Y., Aiba Y., Sonoda J., Oyama N., Yu X. N., Koga Y. Postnatal microbial colonization programs the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal system for stress response in mice // The Journal of physiology. 2004. V. 558. №1. P. 263-275. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2004.063388
- Duman R. S. Pathophysiology of depression and innovative treatments: remodeling glutamatergic synaptic connections // Dialogues in clinical neuroscience. 2022. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2014.16.1/rduman
- Cohen S. M., Tsien R. W., Goff D. C., Halassa M. M. The impact of NMDA receptor hypofunction on GABAergic neurons in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia // Schizophrenia research. 2015. V. 167. №1-3. С. 98-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2014.12.026
- Roceri M., Hendriks W. J. A. J., Racagni, G., Ellenbroek, B. A., & Riva, M. A. Early maternal deprivation reduces the expression of BDNF and NMDA receptor subunits in rat hippocampus // Molecular psychiatry. 2002. V. 7. №6. P. 609-616. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001036
- Heijtz R. D., Wang S., Anuar F., Qian Y., Björkholm B., Samuelsson A., Pettersson S. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2011. V. 108. №7. P. 3047-3052. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1010529108
- Neufeld K. M., Kang N., Bienenstock J., Foster J. A. Reduced anxiety‐like behavior and central neurochemical change in germ‐free mice // Neurogastroenterology & Motility. 2011. V. 23. №3. P. 255-e119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2010.01620.x
- Clarke G., Grenham S., Scully P., Fitzgerald P., Moloney R. D., Shanahan F., Cryan J. The microbiome-gut-brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner // Molecular psychiatry. 2013. V. 18. №6. P. 666-673. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.77
- De Palma G., Blennerhassett P., Lu J., Deng Y., Park, A. J., Green W., Bercik P. Microbiota and host determinants of behavioural phenotype in maternally separated mice // Nature communications. 2015. V. 6. №1. P. 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8735
- Nishino R., Mikami K., Takahashi H., Tomonaga S., Furuse M., Hiramoto T., Sudo N. Commensal microbiota modulate murine behaviors in a strictly contamination‐free environment confirmed by culture‐based methods // Neurogastroenterology & Motility. 2013. V. 25. №6. P. 521-e371. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12110
- Crumeyrolle-Arias M., Jaglin M., Bruneau A., Vancassel S., Cardona A., Daugé V., Rabot S. Absence of the gut microbiota enhances anxiety-like behavior and neuroendocrine response to acute stress in rats // Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014. V. 42. P. 207-217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.01.014
- Bercik P., Denou E., Collins J., Jackson W., Lu J., Jury J., Collins S. M. The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice // Gastroenterology. 2011. V. 141. №2. P. 599-609. e3. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.04.052
- Phelps D., Brinkman N. E., Keely S. P., Anneken E. M., Catron T. R., Betancourt D., Tal T. Microbial colonization is required for normal neurobehavioral development in zebrafish // Scientific reports. 2017. V. 7. №1. P. 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10517-5
- Weiss S. M., Wadsworth G., Fletcher A., Dourish C. T. Utility of ethological analysis to overcome locomotor confounds in elevated maze models of anxiety // Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 1998. V. 23. №2. P. 265-271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0149-7634(98)00027-X
- Strekalova T., Spanagel R., Dolgov O., Bartsch D. Stress-induced hyperlocomotion as a confounding factor in anxiety and depression models in mice // Behavioural pharmacology. 2005. V. 16. №3. P. 171-180.
- Round J. L., Mazmanian S. K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease // Nature reviews immunology. 2009. V. 9. №5. P. 313-323. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2515
- Lee Y. K., Menezes J. S., Umesaki Y., Mazmanian S. K. Proinflammatory T-cell responses to gut microbiota promote experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2011. V. 108. №Supplement 1. P. 4615-4622. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1000082107
- Wu H. J., Ivanov I. I., Darce J., Hattori K., Shima T., Umesaki Y., Mathis D. Gutresiding segmented filamentous bacteria drive autoimmune arthritis via T helper 17 cells // Immunity. 2010. V. 32. №6. P. 815-827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2010.06.001
- Olszak T., An D., Zeissig S., Vera M. P., Richter J., Franke A., Blumberg R. S. Microbial exposure during early life has persistent effects on natural killer T cell function // Science. 2012. V. 336. №6080. P. 489-493. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1219328
- Smith C. J., Emge J. R., Berzins K., Lung L., Khamishon R., Shah P., Gareau M. G. Probiotics normalize the gut-brain-microbiota axis in immunodeficient mice // American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 2014. V. 307. №8. P. G793-G802. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00238.2014
- Braniste V., Al-Asmakh M., Kowal C., Anuar F., Abbaspour A., Tóth M., Pettersson S. The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice // Science translational medicine. 2014. V. 6. №263. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3009759
- Matsumoto M., Kibe R., Ooga T., Aiba Y., Sawaki E., Koga Y., Benno Y. Cerebral lowmolecular metabolites influenced by intestinal microbiota: a pilot study // Frontiers in systems neuroscience. 2013. V. 7. P. 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2013.00009
- Wikoff W. R., Anfora A. T., Liu J., Schultz P. G., Lesley S. A., Peters E. C., Siuzdak G. Metabolomics analysis reveals large effects of gut microflora on mammalian blood metabolites // Proceedings of the national academy of sciences. 2009. V. 106. №10. P. 3698-3703. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0812874106
- Stilling R. M., Ryan F. J., Hoban A. E., Shanahan F., Clarke G., Claesson M. J., Cryan J. F. Microbes & neurodevelopment–Absence of microbiota during early life increases activity-related transcriptional pathways in the amygdala // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2015. V. 50. P. 209-220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.07.009
- Luczynski P., Whelan S. O., O'Sullivan C., Clarke G., Shanahan F., Dinan T. G., Cryan J. F. Adult microbiota‐deficient mice have distinct dendritic morphological changes: Differential effects in the amygdala and hippocampus // European Journal of Neuroscience. 2016. V. 44. №9. P. 2654-2666. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13291
- Hoban A. E., Stilling R. M., Moloney G. M., Moloney R. D., Shanahan F., Dinan T. G., Clarke G. Microbial regulation of microRNA expression in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex // Microbiome. 2017. V. 5. №1. P. 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-017-0321-3
- Nakata K., Sugi Y., Narabayashi H., Kobayakawa T., Nakanishi Y., Tsuda M., Takahashi K. Commensal microbiota-induced microRNA modulates intestinal epithelial permeability through the small GTPase ARF4 // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2017. V. 292. №37. P. 15426-15433. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.788596
- Smith K., McCoy K. D., Macpherson A. J. Use of axenic animals in studying the adaptation of mammals to their commensal intestinal microbiota // Seminars in immunology. Academic Press, 2007. V. 19. №2. P. 59-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2006.10.002
- Chen H. F., Su H. M. Exposure to a maternal n-3 fatty acid-deficient diet during brain development provokes excessive hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis responses to stress and behavioral indices of depression and anxiety in male rat offspring later in life // The Journal of nutritional biochemistry. 2013. V. 24. №1. P. 70-80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.02.006
- Sartori S. B., Whittle N., Hetzenauer A., Singewald N. Magnesium deficiency induces anxiety and HPA axis dysregulation: modulation by therapeutic drug treatment // Neuropharmacology. 2012. V. 62. №1. P. 304-312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.07.027
- Marissal-Arvy N., Hamiani R., Richard E., Moisan M. P., Pallet V. Vitamin A regulates hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis status in LOU/C rats // J Endocrinol. 2013. V. 219. №1. P. 21-27. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-13-0062
- Pusceddu M. M., El Aidy S., Crispie F., O’Sullivan O., Cotter, P., Stanton C., ... & Dinan, T. G. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) reverse the impact of early-life stress on the gut microbiota // PloS one. 2015. V. 10. №10. P. e0139721. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139721
- Widmaier E. P., Rosen K., Abbott B. Free fatty acids activate the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenocortical axis in rats // Endocrinology. 1992. V. 131. №5. P. 2313-2318. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.131.5.2313
- Lanfranco F., Giordano R., Pellegrino M., Gianotti L., Ramunni J., Picu A., Arvat E. Free fatty acids exert an inhibitory effect on adrenocorticotropin and cortisol secretion in humans // The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2004. V. 89. №3. P. 1385-1390. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-031132
- Bailey, M. T., Dowd, S. E., Parry, N. M., Galley, J. D., Schauer, D. B., & Lyte, M. Stressor exposure disrupts commensal microbial populations in the intestines and leads to increased colonization by Citrobacter rodentium // Infection and immunity. 2010. V. 78. №4. P. 1509-1519. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00862-09
- Scheer S., Medina T. S., Murison A., Taves M. D., Antignano F., Chenery A., Zaph C. Early‐life antibiotic treatment enhances the pathogenicity of CD4+ T cells during intestinal inflammation // Journal of leukocyte biology. 2017. V. 101. №4. P. 893-900. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.3MA0716-334RR
- Trobonjaca Z., Leithäuser F., Möller P., Bluethmann H., Koezuka Y., MacDonald H. R., Reimann J. MHC-II-independent CD4+ T cells induce colitis in immunodeficient RAG−/− hosts // The Journal of Immunology. 2001. V. 166. №6. P. 3804-3812. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.166.6.3804
- Fröhlich E. E., Farzi, A., Mayerhofer R., Reichmann F., Jačan A., Wagner B., Holzer P. Cognitive impairment by antibiotic-induced gut dysbiosis: analysis of gut microbiota-brain communication // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2016. V. 56. P. 140-155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.02.020
- Farzi A., Reichmann F., Holzer P. The homeostatic role of neuropeptide Y in immune function and its impact on mood and behaviour // Acta Physiologica. 2015. V. 213. №3. P. 603-627. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12445
- Wang T., Hu X., Liang S., Li W., Wu X., Wang L., Jin F. Lactobacillus fermentum NS9 restores the antibiotic induced physiological and psychological abnormalities in rats // Beneficial microbes. 2015. V. 6. №5. P. 707-717. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2014.0177
- O’mahony S. M., Felice V. D., Nally K., Savignac H. M., Claesson M. J., Scully P., Cryan J. F. Disturbance of the gut microbiota in early-life selectively affects visceral pain in adulthood without impacting cognitive or anxiety-related behaviors in male rats // Neuroscience. 2014. V. 277. P. 885-901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.054
- Desbonnet L., Clarke G., Traplin A., O’Sullivan O., Crispie F., Moloney R. D., Cryan J. F. Gut microbiota depletion from early adolescence in mice: Implications for brain and behaviour // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2015. V. 48. P. 165-173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.04.004
- Hoban A. E., Moloney R. D., Golubeva A. V., Neufeld K. M., O’Sullivan O., Patterson E., Cryan J. F. Behavioural and neurochemical consequences of chronic gut microbiota depletion during adulthood in the rat // Neuroscience. 2016. V. 339. P. 463-477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.10.003
- Gárate I., García-Bueno B., Madrigal J. L., Bravo L., Berrocoso E., Caso J. R., Leza J. C. Origin and consequences of brain Toll-like receptor 4 pathway stimulation in an experimental model of depression // Journal of neuroinflammation. 2011. V. 8. №1. P. 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-8-151
- Aguilera M., Vergara P., Martinez V. Stress and antibiotics alter luminal and walladhered microbiota and enhance the local expression of visceral sensory‐related systems in mice // Neurogastroenterology & Motility. 2013. V. 25. №8. P. e515-e529. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12154
- Kim S., Covington A., Pamer E. G. The intestinal microbiota: antibiotics, colonization resistance, and enteric pathogens // Immunological reviews. 2017. V. 279. №1. P. 90-105. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12563
- Nau R., Sorgel F., Eiffert H. Penetration of drugs through the blood-cerebrospinal fluid/blood-brain barrier for treatment of central nervous system infections // Clinical microbiology reviews. 2010. V. 23. №4. P. 858-883. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00007-10
- Roy U., Panwar A., Pandit A., Das S. K., Joshi B. Clinical and neuroradiological spectrum of metronidazole induced encephalopathy: our experience and the review of literature // Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR. 2016. V. 10. №6. P. OE01. https://doi.org/10.7860%2FJCDR%2F2016%2F19032.8054
- Goolsby T. A., Jakeman B., Gaynes R. P. Clinical relevance of metronidazole and peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review of the literature // International journal of antimicrobial agents. 2018. V. 51. №3. P. 319-325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.08.033
- Zmora N., Bashiardes S., Levy M., Elinav E. The role of the immune system in metabolic health and disease // Cell Metabolism. 2017. V. 25. №3. P. 506-521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.02.006
- Романчук Н. П., Пятин В. Ф., Волобуев А. Н., Булгакова С. В., Тренева Е. В., Романов Д. В. Мозг, депрессия, эпигенетика: новые данные // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №5. С. 163-183. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414-2948/54/21
- Романчук Н. П. Здоровая микробиота и натуральное функциональное питание: гуморальный и клеточный иммунитет // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №9. С. 127-166. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414-2948/58/14
- Романчук Н. П. Мозг человека и природа: современные регуляторы когнитивного здоровья и долголетия // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2021. Т. 7. №6. С. 146-190. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414-2948/67/21
- Романчук Н. П. Биоэлементология и нутрициология мозга // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2021. Т. 7. №9. С. 189-227. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414-2948/70/22
- Caspani G., Kennedy S., Foster J. A., Swann J. Gut microbial metabolites in depression: understanding the biochemical mechanisms // Microbial Cell. 2019. V. 6. №10. P. 454. https://doi.org/10.15698%2Fmic2019.10.693
- Chung Y. C. E., Chen H. C., Chou H. C. L., Chen I. M., Lee M. S., Chuang L. C., Kuo P. H. Exploration of microbiota targets for major depressive disorder and mood related traits // Journal of psychiatric research. 2019. V. 111. P. 74-82.
- Романчук Н. П. Мозг Homo sapiens XXI века: нейрофизиологические, нейроэкономические и нейросоциальные механизмы принятия решений // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2021. Т. 7. №9. С. 228-270. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414-2948/70/23
- Романчук Н. П., Булгакова С. В., Тренева Е. В., Волобуев А. Н., Кузнецов П. К. Нейрофизиология, нейроэндокринология и ядерная медицина: маршрутизация долголетия Homo sapiens // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2022. Т. 8. №4. С. 251-299. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414-2948/77/31
- Романов Д. В., Романчук Н. П. Болезнь Альцгеймера и ядерная медицина: циркадианный стресс и нейровоспаление, нейрокоммуникации и нейрореабилитация // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2022. Т. 8. №5. С. 256-312. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414-2948/78/35


