Многокритериальный подход к проектированию ансамбля нейросетевых классификаторов с отбором информативных признаков для решения задачи распознавания эмоций
Автор: Иванов И.А., Сопов Е.А., Панфилов И.А.
Журнал: Сибирский аэрокосмический журнал @vestnik-sibsau
Рубрика: Математика, механика, информатика
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.16, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Снижение размерности признакового пространства и настройка алгоритмов обучения для решения практических задач являются важными проблемами машинного обучения. Предложен подход, основанный на многокритериальной оптимизации, для отбора информативных признаков и настройки параметров алгоритмов обучения. Эффективность предлагаемого многокритериального подхода сравнивается с однокритериальным подходом. В качестве тестовой практической задачи машинного обучения для сравнения двух упомянутых подходов выбрана задача распознавания эмоций по аудиовизуальной информации. В качестве базового алгоритма обучения выбрана нейронная сеть, параметры которой настраиваются автоматически с помощью генетического алгоритма. В результате применения многокритериального подхода к настройке параметров нейросети пользователь получает множество нейросетей с парето-оптимальными значениями параметров. Для того чтобы получить единственное выходное значение, полученные парето-оптимальные нейросети объединяются в коллектив. В работе протестировано несколько способов слияния выходов алгоритмов коллектива, таких как метод голосования, усреднение апостериорных вероятностей классов и метаклассификация. Согласно полученным результатам, подход к отбору признаков, основанный на многокритериальной оптимизации, обеспечил точность классификации эмоций в среднем на 2,8 % больше, чем однокритериальный подход. Многокритериальный подход на 5,4 % эффективнее, чем использование метода главных компонент, и на 13,9 % эффективнее, чем использование первоначального набора признаков для классификации без проведения предварительного снижения размерности. Многокритериальный подход применительно к оптимизации параметров нейросети обеспечил точность классификации в среднем на 7,1 % больше, чем однокритериальный подход. Полученные результаты доказывают, что многокритериальный подход, предложенный в данной статье, более эффективен при решении задачи распознавания эмоций, чем однокритериальный подход и стандартные методы отбора признаков и настройки параметров нейросетей.
Многокритериальная оптимизация, распознавание эмоций, слияние данных, слияние моделей, человеко-машинное взаимодействие, нейронная сеть
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148177499
IDR: 148177499 | УДК: 004.5
Текст научной статьи Многокритериальный подход к проектированию ансамбля нейросетевых классификаторов с отбором информативных признаков для решения задачи распознавания эмоций
Введение. На сегодняшний день такие области, как машинное обучение и обнаружение знаний в данных, составляют важнейшую часть разработки интеллектуальных систем. Выбор нужного алгоритма машинного обучения для конкретной задачи важен для построения эффективных моделей. Другой ключевой момент - это настройка параметров выбранного алгоритма для достижения наибольшей эффективности.
Существует много способов настройки параметров алгоритма обучения. Самым простым является ручная настройка, но она эффективна только при небольшом числе параметров и когда имеется достаточная информация о влиянии параметров алгоритма на эффективность решения задачи. Для большинства алгоритмов данные условия не выполняются, поэтому ручная настройка становится непригодной и целесообразнее использовать другие методы.
Традиционные методы оптимизации параметров алгоритмов - поиск по сетке, байесовская оптимизация, случайный поиск и градиентная оптимизация. Также используются более сложные алгоритмы оптимизации для выбора оптимального набора значений параметров алгоритма.
В данной работе предложен метод многокритериальной оптимизации параметров алгоритма обучения. Используются многокритериальные генетические алгоритмы для оптимизации параметров нейронной сети. Предложенный многокритериальный метод сравнивается с классическим однокритериальным методом оптимизации параметров на тестовой задаче распознавания эмоций человека по аудио- и видеозаписи.
В однокритериальной постановке параметры нейронной сети, такие как число нейронов и число итераций обучения сети, были использованы в качестве входных переменных задачи, а точность классификации эмоций соответствующей нейронной сетью -в качестве максимизируемого критерия. Результат оптимизации - нейронная сеть с оптимальными значениями параметров. В многокритериальной постановке был добавлен второй (минимизируемый) критерий - число нейронов сети. Результат оптимизации -множество нейронных сетей с парето-оптимальными настройками. Мы объединили данные нейросети в коллектив, чтобы получить единственный, обобщенный выход системы классификации. Было опробовано несколько методов слияния классификаторов коллектива: метод голосования, усреднение апостериорных вероятностей классов, метаклассификация методом опорных векторов.
Другой ключевой аспект при решении задач машинного обучения связан с отбором информативных признаков и снижением размерности данных. Модели, построенные на данных с меньшим числом признаков, более простые и робастные, а следовательно, обеспечивают лучшие обобщающие свойства и требуют меньших вычислительных затрат. Выделяют 2 способа снижения размерности - трансформация признаков и отбор признаков.
В методах, использующих способ трансформации признаков, как и следует из названия, множество признаков по некоторым правилам отображается в другое, меньшее множество признаков. Самый известный метод этого класса - метод главных компонент (principal components analysis, PCA).
В методах, использующих способ отбора признаков, из начального множества признаков выбирается подмножество наиболее информативных признаков. В методах данного класса зачастую используются однокритериальные оптимизационные процедуры для нахождения оптимального подмножества признаков. В данной работе мы предлагаем использовать методы многокритериальной оптимизации для отбора признаков. К традиционному максимизируемому критерию - точности классификации, мы добавляем второй (минимизируемый) критерий - число выбранных признаков. Добавляя данный критерий, мы усиливаем эффект снижения размерности. На тестовой задаче сравнивается эффективность однокритериального и многокритериального метода к отбору признаков, метода главных компонент, а также случая без снижения размерности.
Задача распознавания эмоций используется в качестве тестовой для сравнения эффективности рассматриваемых методов. Распознавание эмоций - важная часть систем человеко-машинного взаимодействия (ЧМВ). Для построения интеллектуального интерфейса между машиной и пользователем машина должна обладать как можно более полной информацией о пользователе, такой как пол пользователя, его возраст, эмоциональное состояние и др. Сегодня существует множество работ различных исследователей в области создания диалоговых систем, важнейшей частью которых является сбор информации о пользователе.
Распознавание человеческих эмоций - наиболее сложная часть глобальной задачи построения эффективной диалоговой системы. Сложности возникают вследствие того, что человеческие эмоции зачастую внешне слабо выражены и быстро меняются. Тем не менее, в данной работе мы делаем попытку построить систему, распознающую эмоции человека по голосу и видеозаписи лица.
Обзор значимых публикаций. Метод, описанный в данной статье, основан на использовании процедуры многокритериальной оптимизации. Ниже мы приведем обзор наиболее значимых современных эволюционных методов многокритериальной оптимизации.
Алгоритм многокритериальной оптимизации Strength Pareto Evolutionary algorithm (SPEA) был предложен Цицлером и Тилем [1]. В нем напрямую используется идея доминирования по Парето для ведения поиска в направлении фронта Парето. Разнообразие популяции решений поддерживается благодаря встроенной процедуре кластеризации. Non-dominated Sorting Genetic algorithm (NSGA) - еще один известный алгоритм многокритериальной оптимизации, разработанный Дебом и др. [2]. Идея алгоритма заключается в недоминируемой сортировке решений популяции. Пусть имеется некоторая популяция решений. Сначала находят среди них недоминируемые, присваивают им ранг 1 и исключают из популяции. Затем среди оставшихся решений также ищут недоминируемые, присваивают им ранг 2, исключают из популяции. Данная процедура продолжается до тех пор, пока каждому решению популяции не будет присвоен ранг. После недоминируемой сортировки выполняются стандартные генетические операторы -селекция (вероятность выбора решений с меньшим рангом больше), скрещивание, мутация, элитизм. Vector Evaluated Genetic algorithm (VEGA), предложенный Шафером [3], является классическим алгоритмом многокритериальной оптимизации, относящимся к классу эволюционных алгоритмов. В нем используется идея селекции по каждому критерию в отдельности, в следующее поколение переходит часть решений, оптимальных по первому критерию, часть - по второму и т. д.
Идея использования алгоритмов оптимизации для настройки алгоритмов машинного обучения не нова. Классические методы используют градиентные алгоритмы оптимизации. Но в случае, когда не имеется явно заданной функциональной зависимости между параметрами алгоритма и его эффективностью, вычисление градиента невозможно, следовательно, надо использовать поисковые алгоритмы нулевого порядка, в которых требуется только вычисление оптимизируемой функции, без вычисления ее производных.
Наибольшее число исследований в области оптимизации параметров алгоритмов машинного обучения было проведено применительно к нейросетям. Берг-стра и Бенджио в своей работе [4] показали, что случайный поиск статистически более эффективен для настройки нейронных сетей и сетей глубокого обучения, чем поиск по сетке и поиск вручную. Они заявили, что в проведенных экспериментах при использовании разных выборок данных на эффективность работы нейросети оказывали влияние разные параметры, причем число параметров, влияющих на эффективность, невелико. Данное наблюдение делает поиск по сетке непригодным для настройки нейросетей на новых данных.
Ларошель и др. [5] использовали жадную послойную процедуру для обучения многослойной сети глубокого обучения. Они разделили процесс настройки параметров сети на два этапа. На первом этапе настраиваются параметры сети, соответствующие отдельным слоям. На втором этапе все параметры сети настраиваются, используя алгоритм обратного распространения ошибки и градиентный спуск по глобальной функции издержек. Параметры сети, найденные на первом этапе, используются в качестве начального приближения на втором этапе.
В работе Opitz, Shavlik [6] авторы использовали генетический алгоритм для поиска популяции эффективных нейросетей, которые при этом были несходны друг с другом. Несхожесть определяется как дисперсия между выходом, производимым сетью, и выходом, производимым ансамблем нейросетей популяции. Пригодность каждой сети вычисляется как взвешенная сумма ее точности и несхожести относительно других сетей. Конечная популяция сетей объединяется в ансамбль, из выходов сетей формируется взвешенная сумма, где вес каждой сети пропорционален ее точности.
Смит и Джин в своей работе [7] предложили гибридный многокритериальный эволюционный алгоритм для оптимизации структуры рекуррентных нейросетей, используемых для анализа временных рядов. Они используют несколько методов выбора решений из найденного множества Парето. В первом методе выбираются все решения ниже определенного порогового значения, во втором - по ошибке обучения. Также выбираются решения вблизи точки перегиба фронта Парето и решения, отличающиеся от других решений популяции. Авторы заявляют, что такой гибридный подход к селекции решений превосходит по эффективности отдельно взятые первый и второй метод.
Отбор признаков - это этап предобработки данных в задачах машинного обучения. Отбор признаков наиболее актуален в задачах с большим числом признаков. Данная предобработка данных производится с целью упрощения будущей модели, что приводит к уменьшению вычислительных затрат и к лучшим обобщающим свойствам модели. В сложных задачах машинного обучения число признаков в используемой выборке может быть велико, поэтому исследователи используют алгоритмы глобальной оптимизации для поиска оптимального подмножества признаков. Методы отбора признаков, в которых используются процедуры оптимизации, называются метаэвристиче-скими методами. Данные методы разделяют на три группы по тому, как в них объединяется алгоритм отбора признаков и построение модели: фильтровые методы (filter), оберточные методы (wrapper) и встроенные методы (embedded). Фильтровые методы отбирают признаки отдельно от построения модели. Оберточные методы оценивают подмножества признаков [8]. Это позволяет выявлять взаимное влияние признаков, но увеличивает время вычислений. Во встроенных методах в алгоритм обучения уже встроен алгоритм отбора признаков [9]. Это уменьшает время вычислений, но налагает некоторые ограничения на решаемую задачу: алгоритм обучения должен заранее обладать информацией о том, какой набор признаков является «хорошим выбором» для решаемой задачи.
Задача распознавания эмоций также освещалась в статьях некоторых исследователей. В статье Рашида и др. [10] предлагается объединять аудио- и видеопризнаки при распознавании эмоций. Из аудиопотока он извлекает просодические признаки и мел-частотные кепстральные коэффициенты. Для видео применяются алгоритмы обнаружения лицевых признаков (нос, рот, глаза и т. п.), их координаты образуют видеопризнаки. Для снижения размерности видеопризнаков используется метод PCA. После этого на аудио- и видеовыборках используется мультиклас-совый метод опорных векторов и производится слияние выходов построенных классификаторов. Построив классификатор на аудиоданных, автор достиг точности классификации 67,39 %, на видеоданных -74,15 %. Объединение аудио- и видеоданных увеличило точность до 80,27 %.
Каху и др. в своей работе [11] описали метод, который они с коллегами использовали в 2013 году для участия в соревновании по распознаванию эмоций (Emotion Recognition in the Wild Challenge). Метод объединял несколько сетей глубокого обучения, включая глубокие конволюционные нейронные сети (CNN) для анализа выражения лица по видео, deep belief network (DBN) для анализа аудиоинформации, deep autoencoder для моделирования пространственно-временной информации о человеческих действиях и неглубокие сети (shallow network architecture) для анализа области рта основного субъекта анализируемой сцены. Авторы использовали выборку лиц Торонто (Toronto Face Dataset), содержащую 4178 изображений, вручную помеченных изображенными на них эмоциями, а также выборку изображений, извлеченную из поиска изображений Google (35887 изображений, 7 классов эмоций). Все изображения были уменьшены до размера 48 х 48 и переведены в чернобелый формат. Были опробованы несколько методов интеграции перечисленных выше систем: усреднение предсказанных вероятностей классов, метаклассификация методом опорных векторов (SVM) и многослойным персептроном (MLP). Наилучшая достигнутая ими точность классификации на тестовой выборке конкурса - 41,03 %.
В статье Круза и др. [12] использована идея моделирования изменений признаков. Сначала производится извлечение лица из первоначального изображения и извлекаются гистограммы LocalPhaseQuantization (LPQ) из каждой области n >. Гистограммы объединяются и формируют вектор признаков, вычисляется производная признаков. Данные подаются на вход линейного SVM, изменения признаков моделируются скрытыми марковскими моделями. Предложенный метод был протестирован на выборке конкурса Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge 2011 года, которая содержит 63 видео 13 человек, проходящих интервью. Авторы заявляют, что им удалось улучшить точность классификации на исследуемых данных на 13 %.
В статье Soleymani и др. [13] авторы используют энцефалограмму, реакцию зрачков и дальность взгляда для классификации возбужденности субъекта на три класса - спокойный, средневозбужденный, активный, а также настроения субъекта на три класса - плохое, нейтральное, хорошее. Используемые данные включают в себя 20 видео эмоционального содержания, взятых из кинофильмов. Достигнутая точность классификации настроения - 68,5 %, возбужденности - 76,4 %.
Буссо и др. [14] также исследовали идею интеграции акустической информации и выражения лица. Они использовали базу данных видеозаписей актрисы, читающей 258 предложений с выражением эмоций. Были построены классификаторы, использующие только аудиоданные (точность 70,9 %) и только видеоданные (85 %). Авторы опробовали интеграцию аудио- и видеоинформации на уровне данных, т. е. соединив выборки в единую выборку и построив на ее основе классификатор (90 %), и на уровне классификаторов, т. е. построив отдельные классификаторы по аудио- и видеоданным и объединив их выходы (84-89 %).
Методология. В данной работе мы предлагаем применить многокритериальной подход к оптимизации параметров алгоритмов машинного обучения и к отбору признаков.
Предложенный метод отбора признаков, использующий многокритериальную оптимизацию, относится к классу оберточных методов. Мы сравнили его с методом PCA и однокритериальным отбором признаков. Методы отбора признаков, основанные на оптимизации, были спроектированы следующим образом. Входящие переменные представляют собой бинарный вектор длины m , где m - это исходное число признаков выборки. Каждый бит такого вектора принимает значение 1 либо 0, где 1 означает, что соответствующий признак выбран для дальнейшего включения в модель, 0 - не выбран. В однокритериальной постановке точность классификации является максимизируемым критерием и задается следующим образом:
R = ( Nc / N ) - 100 %, (1) где Nc - число верно классифицированных объектов выборки; N - общее число объектов выборки; R -точность классификации.
В многокритериальной постановке добавляется второй (минимизируемый) критерий - число выбранных признаков. Идея данного критерия в том, что модели, построенные на выборках с меньшим количеством признаков, проще, а следовательно, обладают лучшей обобщающей способностью.
Мы выбрали класс эволюционных алгоритмов оптимизации для решения задачи отбора признаков в вышеприведенной постановке, потому что алгоритмы данного класса позволяют эффективно находить глобальный оптимум и для их использования не требуется информация о поверхности оптимизируемой функции.
В однокритериальной постановке мы использовали коэволюционный генетический алгоритм (ГА). Данный алгоритм объединяет несколько стандартных ГА, у которых различаются значения параметров. Стандартные ГА параллельно работают некоторое количество итераций, после чего обмениваются индивидами между собой (миграция индивидов) и сохраняют лучшие найденные решения (элитизм). Такой алгоритм освобождает исследователя от настройки параметров стандартного ГА, неправильная настройка которых может зачастую привести к неудовлетвори тельным результатам оптимизации.
В многокритериальной постановке мы использовали алгоритм SPEA. Значения параметров алгоритмов оптимизации представлены в табл. 1. Вероятность скрещивания и мутации указана как низкая. Количественно данные вероятности вычислялись по следующей формуле:
1 p =-------, k X | P |,
где k = 3 в наших экспериментах, но может принимать и другие действительные неотрицательные значения; | P | - размер популяции; p - значение вероятности.
Многокритериальный подход был также применен для оптимизации параметров нейронной сети. Нейронная сеть прямого распространения была выбрана в качестве алгоритма обучения по нескольким причинам. Во-первых, нейронные сети ранее успешно применялись для решения практических задач анализа изображений. Во-вторых, эффективность нейронных сетей в значительной мере зависит от настройки их параметров. Была использована однослойная нейронная сеть с переменным числом нейронов и сигмоидной активационной функцией.
В однокритериальной постановке входящие переменные включают общее число нейронов сети Nn
(границы изменения Nn = 2,50) и число итераций обучения сети Nt (границы изменения Nt = 2,200). Оптимизируемый критерий - точность классификации, как и в задаче отбора признаков.
В многокритериальной постановке отличие заключается в том, что добавляется второй (минимизируемый) критерий - число нейронов сети. Данный критерий одновременно является первой входящей переменной.
Таблица 1
Значения параметров генетических алгоритмов
|
Параметр генетических алгоритмов |
Значение |
|
Размер популяции |
50 |
|
Число итераций |
50 |
|
Вероятность скрещивания |
Низкая |
|
Тип скрещивания |
Равномерный |
|
Вероятность мутации |
Низкая |
|
Максимальный размер внешнего множества (SPEA) |
50 |
|
Интервал адаптации |
5 |
|
Размер штрафа (% от размера популяции) |
10 |
|
Минимальный гарантированный размер популяции (% от начального размера популяции) |
10 |
Для решения сформулированных задач оптимизации также были использованы эволюционные алгоритмы оптимизации: в однокритериальной постановке - коэволюционный ГА, в многокритериальной постановке - SPEA, NSGA-2, VEGA и SelfCOMOGA [15]. В алгоритме SelfCOMOGA алгоритмы SPEA, NSGA-2 и VEGA работают параллельно и через фиксированное число итераций производят процедуру миграции индивидов и элитизма подобно тому, как это делается в коэволюционном ГА. Для ранжирования индивидов производится их недоминируемая сортировка, которая является обобщением обычной сортировки на случай многих критериев.
В однокритериальной постановке решением задачи является нейронная сеть с найденными оптимальными значениями параметров. В многокритериальной же постановке мы получаем множество Парето оптимальных нейронных сетей. Для того чтобы можно было сравнивать два эти подхода, получаемое парето-оптимальное множество нейросетей объединяется в коллектив. Мы опробовали три метода объединения классификаторов в коллектив:
-
1. Метод голосования.
-
2. Усреднение вероятностей классов - получаемые на выходе классификатора вероятности классов усредняются по всем классификаторам коллектива.
-
3. Метаклассификация - обучающую выборку разделяют на 2 части, первая часть используется для обучения классификаторов коллектива. Получаемые на выходе классификаторов вероятности классов используют в качестве входящих переменных дополнительного метаклассификатора, который обучают на второй части выборки. Метаклассификатор на выходе выдает класс, предсказанный для данного объекта выборки.
Все использованные в нашей работе алгоритмы оптимизации были программно реализованы на языке C#. Также была использована готовая реализация на языке R- алгоритмов нейронная сеть, метод опорных векторов и метод PCA.
В качестве исходных данных использовалась аудиовизуальная база данных эмоций SAVEE [16]. Распределение классов эмоций в базе данных представлено на рис. 1. Для того чтобы можно было строить количественные модели, из «сырых» данных были извлечены количественные аудио- и видеопризнаки. Для извлечения аудиопризнаков мы использовали программу openSMILE - свободно распространяемое ПО для извлечения признаков из аудио и видео (Eyben и др., [17]). Видеопризнаки были извлечены 3 алгоритмами (см. рисунок):
-
1) Quantized Local Zernike Moments (QLZM) (Sariyanidi и др., [18]);
-
2) Local Binary Patterns (LBP) (Ojala и др., [19]);
-
3) Local Binary Patterns on Three Orthogonal Planes (LBP-TOP) (Zhao, Pietikainen, [20]).
Мы выбрали алгоритмы QLZM и LBP-TOP, потому что они современны и успешно использовались другими исследователями при анализе изображений и видео. Алгоритм LBP выбран, потому что это классический алгоритм для анализа изображений, который может служить как нижняя оценка эффективности построенной системы распознавания, с которой удобно сравнивать другие методы.
Алгоритмы QLZM и LBP извлекают признаки из каждого последовательного кадра видеозаписи, тогда как LBP-TOP учитывает изменение пикселей кадров во времени и извлекает вектор признаков из нескольких последовательно идущих кадров. Векторы признаков, извлеченные алгоритмами QLZM и LBP, усреднялись по всей длине видеозаписи. Мы также объединили извлеченные аудио- и видеопризнаки в единую выборку, чтобы проверить, поможет ли объединение аудио- и видеопризнаков в улучшении эффективности распознавания эмоций. Количество извлеченных аудио- и видеопризнаков представлено в табл. 2. Объединенная выборка аудио- и видеопризнаков обозначена как «аудио + видео». Количество извлеченных признаков велико, поэтому этап предобработки данных с целью отбора информативных признаков имеет смысл.
Результаты экспериментов. Результаты экспериментов по снижению размерности и отбору инфор мативных признаков показаны в табл. 2. Мы провели сравнение трех методов снижения размерности: PCA, отбор признаков методом однокритериальной и многокритериальной оптимизации. По результатам видно, что многокритериальный метод отбора признаков превзошел другие методы по эффективности на выборках QLZM, LBP-TOP, аудио и аудио + видео (4 из 5 рассмотренных выборок), проиграв однокритериальному методу незначительные 0,3 % на выборке LBP.
Эксперименты по оптимизации параметров нейронных сетей проводились для каждой имеющейся выборки данных, различных алгоритмов оптимизации и различных методов объединения коллектива классификаторов. Пример полученного множества парето-оптимальных нейронных сетей с помощью алгоритма многокритериальной оптимизации NSGA-2 представлен в табл. 3.
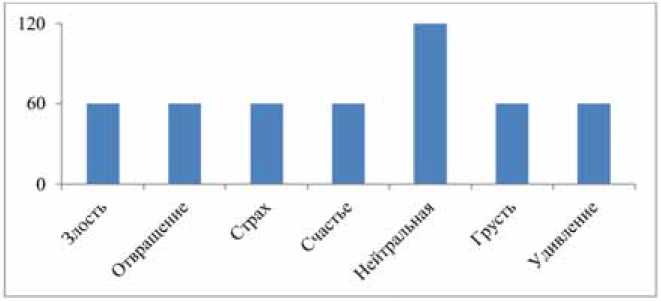
Распределение классов в базе данных эмоций
Таблица 2
Точность классификации эмоций (%) для различных выборок и подходов к снижению размерности
|
Выборка |
Аудио |
QLZM |
LBP |
LBP-TOP |
Аудио + видео |
||
|
Число признаков |
991 |
656 |
59 |
177 |
1883 |
||
|
Точность классификации после снижения размерности |
Все признаки |
28,542 |
10,506 |
20,486 |
22,847 |
19,732 |
|
|
Метод главных компонент |
35,923 / 131 |
21,458 / 36 |
23,75 / 4 |
32,017 / 10 |
31,718 / 180 |
||
|
Отбор признаков |
Однокритериальная оптимизация |
38,095 / 476 |
20,208 / 301 |
25,3972 / 33 |
40,278 / 77 |
33,661 / 902 |
|
|
Многокритериальная оптимизация |
39,702 / 484 |
24,911 / 319 |
25,694 / 31 |
45,694 / 90 |
35,893 / 885 |
||
Таблица 3
Парето-оптимальное множество нейронных сетей, многокритериальная постановка, аудиоданные, алгоритм оптимизации NSGA-2
|
№ |
Число нейронов |
Число итераций обучения |
Точность классификации |
|
1 |
10 |
119 |
10,88 |
|
2 |
12 |
20 |
29,49 |
|
3 |
13 |
113 |
30,34 |
|
4 |
24 |
150 |
33,38 |
|
5 |
14 |
73 |
33,69 |
|
6 |
11 |
119 |
15,88 |
|
7 |
29 |
100 |
35,38 |
|
8 |
39 |
144 |
32,02 |
|
9 |
15 |
51 |
15,44 |
|
10 |
23 |
74 |
27,89 |
В табл. 4 представлены обобщенные результаты экспериментов по оптимизации параметров нейросетей. Заметим, что объединение парето-оптимальных нейронных сетей, представленных в табл. 3, в коллектив увеличило точность классификации эмоций до 39,76 %. Согласно полученным результатам, многокритериальный метод оптимизации параметров нейронных сетей применительно к задаче распознавания эмоций превосходит однокритериальный метод на всех 5 рассмотренных выборках данных.
Мы не можем дать определенных рекомендаций по поводу того, какой многокритериальный алгоритм оптимизации лучше использовать, так как каждый из них обеспечил наилучшую точность на разных выборках данных. Метаклассификация по результатам экспериментов оказалась наиболее эффективным методом объединения коллектива классификаторов, обеспечив лучшую точность классификации на 4 из 5 выборках. Тот факт, что на разных выборках лучшие результаты были получены разными алгоритмами многокритериальной оптимизации, но одинаковым методом объединения парето-оптимальных классификаторов в коллектив, означает, что метод метаклассификации инвариантен к выбору алгоритма оптимизации.
Мы объединили все полученные нами результаты по решению задачи распознавания эмоций в табл. 5, выделив наиболее эффективные использованные методы. Самый эффективный из опробованных нами методов - использование многокритериального подхода к оптимизации параметров нейросетей на выборке данных LBP-TOP, полученная точность классификации эмоций - 45,7 %. Базовая модель, которая для всех объектов тестовой выборки предсказывает класс, наиболее часто встречающийся в обучающей выборке, для данной задачи обеспечивает точность 25 %. Учитывая сложность решаемой задачи распознавания эмоций, полученное улучшение точности распознавания является значительным.
Заключение. В данной работе использован метод многокритериальной оптимизации для отбора при знаков и оптимизации параметров нейронных сетей, предложенный метод апробирован на задаче распознавания эмоций.
Согласно полученным результатам, многокритериальный метод отбора признаков обеспечил в среднем по выборкам на 2,8 % лучшую точность классификации, чем однокритериальный метод. Также мы установили, что многокритериальный метод отбора признаков на 5,4 % эффективнее, чем алгоритм PCA, и на 13,9 % эффективнее, чем использование исходного набора признаков для построения системы классификации. Таким образом, предложенный многокритериальный метод отбора признаков оказался самым эффективным из рассмотренных для решения задачи распознавания эмоций. Мы рекомендуем использовать его в дальнейших работах по распознаванию эмоций, а также в смежных задачах машинного обучения.
Также в работе применен многокритериальный метод для оптимизации параметров нейросетей. Полученные результаты доказывают, что объединение нейросетей с парето-оптимальными настройками в коллектив позволяет получить лучшую точность классификации эмоций, чем использование одной нейросети с оптимальными настройками, найденными с помощью однокритериальной оптимизации. Разница в эффективности составляет 7,1 %. Мы советуем использовать метаклассификацию в качестве метода объединения парето-оптимальных классификаторов в коллектив, так как данный метод в ходе проведения экспериментов обеспечил лучшую точность классификации эмоций на 4 из 5 выборок. Однако необходимо провести дальнейшее исследование на других задачах машинного обучения, чтобы доказать справедливость полученных в данной работе результатов.
Acknowledgments. The research was supported by President of the Russian Federation grant (MK-3285.2015.9).
Таблица 4
Точность классификации (%) для задачи распознавания эмоций в различных постановках
|
Алгоритм оптимизации (число критериев) |
Схема слияния выходов ансамбля |
Данные |
||||
|
Аудио |
QLZM |
LBP |
LBP-TOP |
Аудио+ видео |
||
|
Коэволюцион-ный ГА (1) |
— |
35,923 |
21,458 |
23,75 |
32,917 |
31,718 |
|
SPEA (2) |
Голосование |
31,012 |
16,319 |
16,667 |
34,167 |
27,292 |
|
Усреднение вероятностей классов |
16,994 |
10,903 |
16,458 |
39,583 |
14,256 |
|
|
Метаклассификация |
28,631 |
16,042 |
18,264 |
34,583 |
25,06 |
|
|
NSGA-2 (2) |
Голосование |
29,226 |
21,181 |
19,236 |
33,403 |
24,554 |
|
Усреднение вероятностей классов |
29,435 |
14,722 |
16,667 |
17,639 |
23,571 |
|
|
Метаклассификация |
39,762 |
11,528 |
17,5 |
38,125 |
34,94 |
|
|
VEGA (2) |
Голосование |
33,839 |
17,5 |
24,514 |
32,639 |
22,5 |
|
Усреднение вероятностей классов |
27,262 |
24,306 |
20,069 |
21,042 |
15,119 |
|
|
Метаклассификация |
38,899 |
13,958 |
29,167 |
36,736 |
37,292 |
|
Окончание табл. 4
|
Алгоритм оптимизации (число критериев) |
Схема слияния выходов ансамбля |
Данные |
||||
|
Аудио |
QLZM |
LBP |
LBP-TOP |
Аудио+ видео |
||
|
SelfCOMOG A (2) |
Голосование |
26,577 |
20,347 |
33,125 |
36,25 |
19,94 |
|
Усреднение вероятностей классов |
23,244 |
15,935 |
25,417 |
22,708 |
17,768 |
|
|
Метаклассификация |
36,518 |
26,756 |
38,333 |
36,319 |
29,405 |
|
Таблица 5
Обобщенное ранжирование методологий и данных, с помощью которых была получена наибольшая точность распознавания эмоций
|
Ранг |
Методология |
Данные |
Точность классификации, % |
|
1 |
Отбор признаков, многокритериальная оптимизация |
LBP-TOP |
45,694 |
|
2 |
Оптимизация нейросети, NSGA-2, схема слияния выходов: метаклассификация методом опорных векторов |
Аудио |
39,762 |
|
3 |
Отбор признаков, многокритериальная оптимизация |
Аудио |
39,702 |
|
4 |
Оптимизация нейросети, SPEA, схема слияния выходов: усреднение вероятностей классов |
LBP-TOP |
39,583 |
|
5 |
Оптимизация нейросети, SelfCOMOGA, схема слияния выходов: метаклассификация методом опорных векторов |
LBP |
38,333 |
|
6 |
Оптимизация нейросети, VEGA, схема слияния выходов: метаклассификация методом опорных векторов |
Аудио + видео |
37,292 |
|
7 |
Отбор признаков, многокритериальная оптимизация |
Аудио + видео |
35,893 |
Список литературы Многокритериальный подход к проектированию ансамбля нейросетевых классификаторов с отбором информативных признаков для решения задачи распознавания эмоций
- Zitzler E., Thiele L. Multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: a comparative case study and the strength Pareto approach//IEEE transactions on evolutionary computation. 1999. Р. 257-271.
- A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II/K. Deb //IEEE Trans. on Evolutionary Computation. 2002. Vol. 6, No. 2. P. 182-197.
- Schaffer J. D. Multiple objective optimization with vector evaluated genetic algorithms//Proc. of the 1st Intern. Conf. on Genetic Algorithms. 1985. P. 93-100.
- Bergstra J., Bengio Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization//Journal of Machine Learning Research. 2012. 13. P. 281-305.
- Exploring strategies for training deep neural networks/H. Larochelle //Journal of Machine Learning Research. 2009. 1. P. 1-40.
- Opitz D. W., Shavlik J. W. Generating accurate and diverse members of a neural-network ensemble//Advances in neural information processing systems. 1996. P. 535-541.
- Smith C., Jin Y. Evolutionary multi-objective generation of recurrent neural network ensembles for time series prediction//Neurocomputing. 2014. Vol. 143. P. 302-311.
- Phuong T. M., Lin Z., Altman R. B. Choosing SNPs using feature selection//Proceedings IEEE Computational Systems Bioinformatics Conference. 2005. P. 301-309.
- Duval B., Hao J.-K., Hernandez Hernandez J. C. A memetic algorithm for gene selection and molecular classification of an cancer//In Proceedings of the 11th Annual conf. on Genetic and evolutionary computation, GECCO ’09. New York, 2009. P. 201-208.
- Rashid M., Abu-Bakar S. A. R., Mokji M. Human emotion recognition from videos using spatio-temporal and audio features//Vis Comput. 2013. 29. P. 1269-1275.
- Combining modality specific deep neural networks for emotion recognition in video/S. E. Kahou //Proceedings of the 15th ACM on Intern. Conf. on Multimodal Interaction. Sydney, 2013. P. 543-550.
- Cruz A., Bhanu B., Thakoor N. Facial emotion recognition in continuous video//Proceedings of the 21st Intern. Conf. on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2012) (November 11-15, 2012, Tsukuba, Japan). P. 1880-1883.
- Soleymani M., Pantic M., Pun T. Multimodal emotion recognition in response to videos//IEEE Transactions on affective computing. 2012. Vol. 3, no. 2. P. 211-223.
- Analysis of emotion recognition using facial expressions/C. Busso //Proceedings of the 6th Intern. Conf. on Multimodal interfaces. 2004. P. 205-211.
- Иванов И. А., Сопов Е. А. Самоконфигурируемый генетический алгоритм решения задач поддержки многокритериального выбора//Вестник СибГАУ. 2013. № 1 (47). С. 30-35.
- Haq S., Jackson P. J. B. Speaker-dependent audio-visual emotion recognition//Proc. Int. Conf. on Auditory-Visual Speech Processing (AVSP'09), Norwich, UK, 2009, p.53-58.
- Eyben F., Wullmer M., Schuller B. OpenSMILE -the Munich versatile and fast open-source audio feature extractor//In Proceedings ACM Multimedia (MM), ACM. Florence, 2010. P. 1459-1462.
- Local Zernike moment representation for facial affect recognition/E. Sariyanidi //Proc. of British Machine Vision Conference. 2013. P. 1-13.
- Ojala T., Pietikäinen M., Harwood D. A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on feature distributions//Pattern Recognition. 1996. 29. P. 51-59.
- Zhao G., Pietikäinen M. Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions//IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2007. 29(6). P. 915-928.
- Zitzler E., Thiele L. Multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: a comparative case study and the strength Pareto approach. IEEE transactions on evolutionary computation, 1999, P. 257-271.
- Deb K., Pratap A., Agarwal S., Meyarivan T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. on Evolutionary Computation, Vol. 6, No. 2, April 2002, P. 182-197.
- Schaffer J. D. Multiple objective optimization with vector evaluated genetic algorithms. Proc. of the 1st International Conference on Genetic Algorithms, 1985,
- P. 93-100.
- Bergstra J., Bengio Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. Journal of Machine Learning Research 13, 2012, P. 281-305.
- Larochelle H., Bengio Y., Louradour J, Lamblin P. Exploring strategies for training deep neural networks. Journal of Machine Learning Research 1, 2009, P. 1-40.
- Opitz D. W., Shavlik J. W. Generating accurate and diverse members of a neural-network ensemble. Advances in neural information processing systems, 1996, P. 535-541.
- Smith C., Jin Y. Evolutionary multi-objective generation of recurrent neural network ensembles for time series prediction. Neurocomputing, 2014, Vol. 143,
- P. 302-311.
- Phuong T. M., Lin Z., Altman R. B. Choosing SNPs using feature selection. Proceedings IEEE Computational Systems Bioinformatics Conference, 2005,
- P. 301-309.
- Duval B., Hao J.-K., Hernandez Hernandez J. C. A memetic algorithm for gene selection and molecular classification of an cancer. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual conference on Genetic and evolutionary computation, GECCO ’09, New York, NY, USA, 2009, P. 201-208.
- Rashid M., Abu-Bakar S. A. R., Mokji M. Human emotion recognition from videos using spatio-temporal and audio features. Vis Comput, 2013, Vol. 29, P. 1269-1275.
- Kahou S. E., Pal C., Bouthillier X., Froumenty P., Gulcehre C., Memisevic R., Vincent P., Courville A., Bengio Y. Combining modality specific deep neural
- networks for emotion recognition in video. Proceedings of the 15th ACM on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, 2013, Sydney, Australia, P. 543-550.
- Cruz A., Bhanu B., Thakoor N. Facial emotion recognition in continuous video. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2012), November 11-15, 2012, Tsukuba, Japan,
- P. 1880-1883.
- Soleymani M., Pantic M., Pun T. Multimodal emotion recognition in response to videos. IEEE Transactions on affective computing, Vol. 3, No. 2, April-June, 2012, P. 211-223.
- Busso C., Deng Z., Yildirim S., Bulut M., Lee C. M., Kazemzadeh A., Lee S., Neumann U., Narayanan S. Analysis of emotion recognition using facial expressions. Proceedings of the 6th international conference on Multimodal interfaces, 2004, P. 205-211.
- Ivanov I. A., Sopov E. A. . Vestnik SibGAU, 2013, No. 1 (47),
- P. 30-35 (In Russ.).
- Haq, S., Jackson, P. J. B. Speaker-dependent audio-visual emotion recognition. Proc. Int. Conf. on Auditory-Visual Speech Processing (AVSP'09), Norwich, UK, 2009, P.53-58.
- Eyben F., Wullmer M, Schuller B. OpenSMILE -the Munich versatile and fast open-source audio feature extractor. In Proceedings ACM Multimedia (MM), ACM, Florence, Italy, ISBN 978-1-60558-933-6, 25.-29.10. 2010, P. 1459-1462.
- Sariyanidi E., Gunes H., Gokmen M., Cavallaro A. Local Zernike moment representation for facial affect recognition. Proc. of British Machine Vision Conference, 2013, P. 1-13.
- Ojala T., Pietikäinen M., Harwood D. A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on feature distributions. Pattern Recognition 29, 1996,
- P. 51-59.
- Zhao G., Pietikäinen M. Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 29(6), 2007, P. 915-928.


