Modeling of the stress-strain state of rocket-space technology structural elements manufactured by using additive technologies
Автор: Ushakova E.S.
Журнал: Сибирский аэрокосмический журнал @vestnik-sibsau
Рубрика: Авиационная и ракетно-космическая техника
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.20, 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
One of the promising areas for improving the methods of manufacturing structural elements of rocket and space technology is the use of selective laser melting technology which represents a unique opportunity to manufacture metal products by melting powder and producing a one-piece solid phase structure. However, pores and other structural defects can appear in the formed element during laser sintering which causes a decrease in the strength characteristics of the parts produced. An important step in the additive technologies introduction is the development of methodology for the preliminary prediction of the strength characteristics of manufactured structural elements under the influence of mechanical loads with the help of mathematical modeling. The methodology for estimating the material strength reduction of a rocket-space technology element obtained using additive technologies by simulating a porous structure and calculating the characteristics of the stress-strain state is presented. The proposed mathematical model and the methodology for calculating the specimen loading on the basis of the distortion energy theory allow calculating the stress-strain state in the process of numerical simulation for different values of the pore diameter. The reduction in yield strength due to the material porosity of the part is estimated using a coeffi- cient equal to the ratio of equivalent stresses arising when a load is applied to a specimen manufactured using traditional and additive technologies. The value of the introduced coefficient characterizes the structure of the grown product and is considered as a function of the random arrangement of pores in the specimen under study. The appearance of pores is the result of a combination of factors: the composition and dispersion of the original metal powder, feed rate, removal distance and laser power during sintering, part orientation and sintering direction, the height of the level of powder deposited on a special base before sintering, etc. The paper evaluates the reduction in strength for the working part of a series of tensile test specimens grown from metal powder of different dispersity. The non-linear nature of the dependence of the yield strength on the particle diameter of the original metal powder is established. The maximum value of the yield strength corresponds to the specimen with the minimum value of the total surface area of the pores.
Additive technologies, liquid rocket engine, combustion chamber, porosity, stress-strain state, yield strength
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148321917
IDR: 148321917 | УДК: 621.45 | DOI: 10.31772/2587-6066-2019-20-2-243-250
Текст научной статьи Modeling of the stress-strain state of rocket-space technology structural elements manufactured by using additive technologies
Introduction. Currently, improving manufacturability and reducing the cost of manufacturing rocket-space technology (RST) structural elements are important scientific and technical challenges. The disadvantage of traditional methods of manufacturing the most heavily loaded units of a liquid-propellant rocket engine (LRE) – combustion chambers (CCs) – is the problem of ensuring the reliability of structures and controlling their quality due to the use of a large number of soldered joints in manufacturing as well as the need to manufacture expensive tooling. For example, only the process of electroerosive deposition of the “artificial” roughness creating turbulence in the coolant flow on the bottom of the cooling tract channels of the CC inner shell lasts 900 n / h [1].
One of the promising directions of improving the methods of manufacturing the rocket-space technology structural elements is the use of additive technologies (AT) [2]. Their main advantages include: manufacturing objects of complex shape with high accuracy, optimizing time spent on manufacturing, using a combination of metal powders (for example, BrH08 + stainless steel) in order to obtain strength characteristics corresponding to the operating conditions of the grown product [3].
The development of additive technologies, in particular, the technology of selective laser melting (SLM), represents a unique opportunity to manufacture metal products by melting powder and obtaining a one-piece solid phase structure [4]. The use of SLM technology allows increasing the material utilization rate to almost 99 % and, thereby, reducing the cost of production [5]. However, during SLM pores and other structural defects (non-melts, cracks, inclusions, etc.) may appear in the formed element, which causes a decrease in the strength characteristics of the parts produced. One of the objects of RST where the introduction of AT seems to be promising is the LRE chamber.
Since the working process in the LRE is characterized by relatively large values of pressure and temperature in
the CC [6], an important step in the introduction of AT is the development of methods for preliminary prediction of the strength characteristics of manufactured structural elements under the influence of mechanical loads using mathematical modeling.
The purpose of this work is to develop a methodology for evaluating the strength reduction of the material obtained using additive technologies by modeling the porous structure and calculating the characteristics of the stressstrain state (SSS).
Mathematical model. The methodology for assessing the strength reduction of parts manufactured using additive technologies on the basis of the SSS determination in the process of numerical simulation using the distortion energy theory (Mises-Huber-Genki theory) [7] has been developed. According to this methodology it is assumed that the specimen begins to break (or to become unacceptably deformed) under the condition σ eq ≥ σ yield , where σ eq is von Mises equivalent stress arising in the part under the action of a given load, σ yield is the yield strength of the material of the part.
A safety factor – the ratio of yield strength to equivalent stress σ yield determined, for example, according to Mises [7] – can be used as a characteristic of the strength reliability of a RST product:
Ks=
σ yield σ eq
Then the safety factor for parts made using additive technology will be determined by the formula:
n ⋅σ yield σ eq
In this formulation, the value of the coefficient n characterizes the structure of the grown product and is considered as a function of the random arrangement of pores in the specimen under study. The appearance of pores is the result of the influence of a combination of factors: the composition and dispersion of the original metal powder, feed rate, removal distance and laser power during sintering, part orientation and sintering direction, the height of the level of the powder deposited on a special base before sintering, etc. [8–12].
Pores (as well as cracks, non-melts, etc.) in the structure of any material are local sharp changes in the uniformity of shape and rigidity of the product structure and lead to local increase in the value of internal stresses. Consequently, the value of the equivalent stress σ eq.pore caused by a given load for a part with pores will be higher than the value for a monolithic part σ eq made of material with the same physical and mechanical properties. The safety factors for the cases considered are determined by the formulas:
σ yield
σ eq
σ yield
Ks . pore = ; (2)
σ eq . pore
By presenting a part grown from metal powder as a monolithic one with the presence of local inhomogeneities in the material structure it is possible to consider the values of safety factors from formulas (1) and (2): Ks.add = Ks.pore to be equal. Then, in accordance with the idea of the physical meaning of the coefficient n , its value will be equal to the ratio of equivalent voltages:
n ⋅ σ yield σ yield
= ;
σeq σeq. pore n=
σ eq
.
σ eq . pore
Consequently, the decrease in the tensile strength of a metal part made by the method of SLM is due to increase in the value of equivalent stresses as compared to a metal part made using traditional methods.
The porosity of the part material is determined by the formula:
ε pore lay ,
Vpore where: klay =1- V is the packing factor, V is part volume, Vpore is the pore volume in the part material.
Calculation model of the specimen loading . Structural cryogenic steel AISI 316L the mechanical properties [13] of which are listed in Table 1 is considered as a material of the structural RST element.
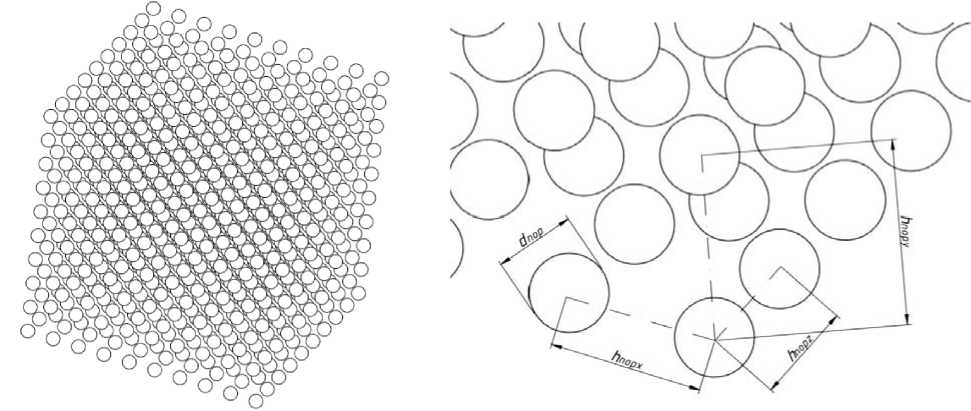
The porous structure of the specimen created by the method of selective laser sintering from ASIS 316L steel was studied in [14]. The relationship between the structure of the grown material and the sintering and the dispersion modes of the original metal powder was experimentally established in this work. A complex configuration of pores can be approximated by a set of spherical surfaces on the basis of a number of images obtained on the surface of thin sections of material specimens. In the first approximation we will consider the diameter and distance between pores commensurate with the diameter of a metal particle d p (fig. 1):
d «2-d , h «2-d . pore p , pore pore .
In this paper it is expedient to evaluate the reduction in strength for a specimen of a material and not for the design of a LRE chamber as a whole. For this purpose a series of specimens for tensile test were modeled according to GOST 1497–84 [15]. The dimensions the specimens correspond to type 3, number 9 (fig. 2).
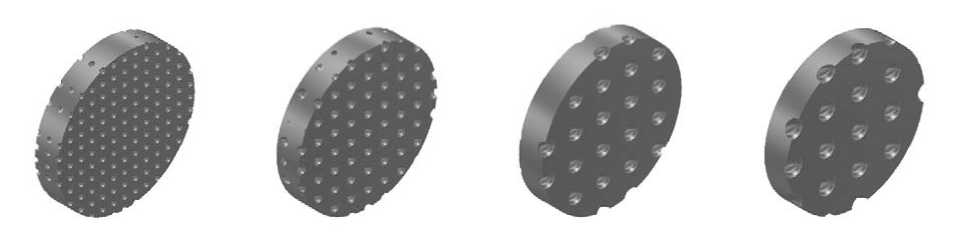
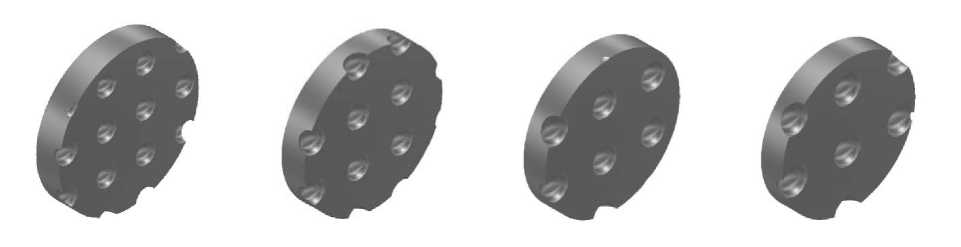
The results of the stress-strain state calculations. Assuming that the applied load is evenly distributed over the cross section the strength calculation was carried out directly for a cylindrical fragment of the specimen working part ( h = 0.5 mm, V = 3.534 mm3, fig. 2) grown from AISI 316L powder of the following series of diameters: d pi = 60; 90; 120; 150; 180; 210; 240; 270; 300 microns (fig. 3). The calculated values of the packing factors k layi for each element are presented in tab. 2 A fragment of the working part was fixed on the surface of the rear end; a tensile load was applied along the normal to the surface of the front end. An example of a finite-element model of a calculation object with dp = 60 μm in the form of a computational grid using tetrahedral elements with a total number of ~ 6 · 104 is shown in fig. 4. Verification of the calculated diagram of porous specimens tension (fig. 5) was carried out using an experimental diagram for steel [15]. Comparison of dependences shows satisfactory coincidence of the qualitative nature of the calculated and experimental diagrams for elastic and the beginning of plastic deformations.
Table 1
Steel AISI 316L mechanical properties at T = 20 oC
|
Density |
Yield strength |
Tensile strength |
Young’s modulus |
Poisson’s ratio |
|
kg ρ, 3 m |
σ yield , MPa |
[ σ tens ] , MPa |
E ,GPa |
μ |
|
7860 |
300 |
570 |
200 |
0,26 |
а б
Fig. 1. Scheme of distribution ( a ) and geometrical characteristics ( b ) of pores in the object under study
Рис. 1. Схема распределения ( а ) и геометрические характеристики пор ( b ) в объекте исследования
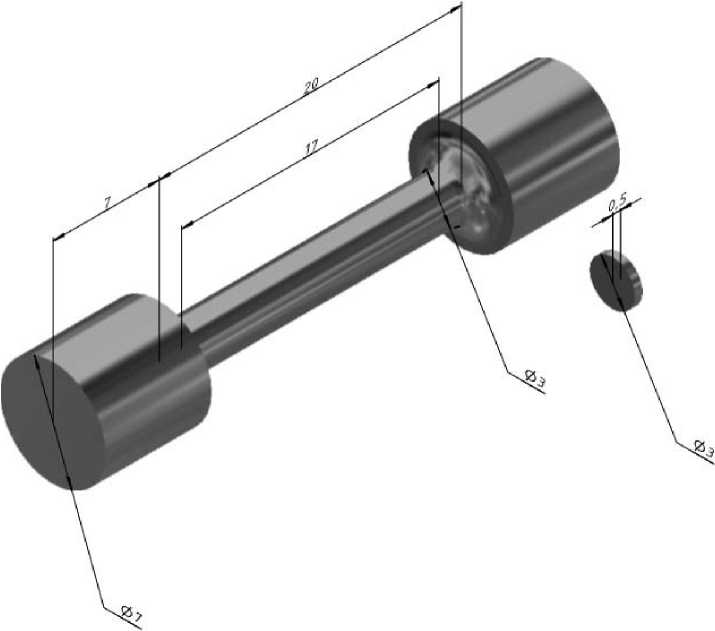
Fig. 2. 3D-model of the object under study
Рис. 2. 3D-модель объекта исследования
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
Fig. 3. 3-D models of porous specimens grown from metal powder with dpi :
60 μm ( 1 ), 90 μm ( 2 ), 150 μm ( 3 ), 180 μm ( 4 ), 210 μm ( 5 ), 240 μm ( 6 ), 270 μm ( 7 ), 300 μm ( 8 )
Рис. 3. 3-D модели пористых образцов выращенных из металлического порошка с dpi : 60 мкм ( 1 ), 90 мкм ( 2 ), 150 мкм ( 3 ), 180 мкм ( 4 ), 210 мкм ( 5 ), 240 мкм ( 6 ), 270 мкм ( 7 ), 300 мкм ( 8 )
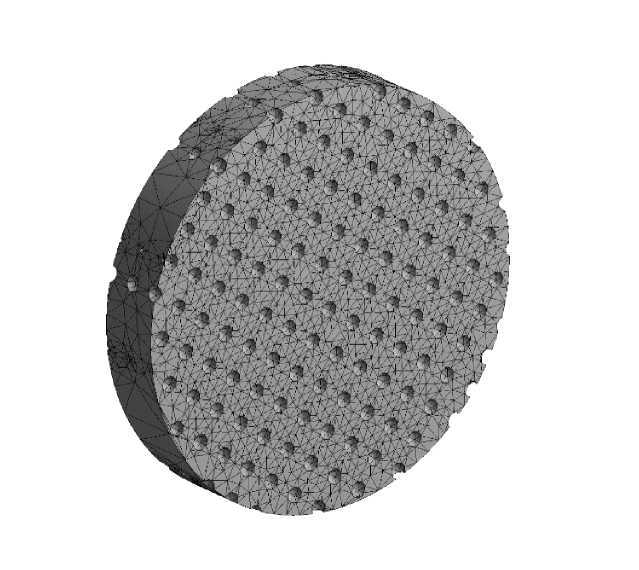
Fig. 4. A finite-element model in the form of a structured grid of the calculation object at dp = 60 μm
Рис. 4. Конечно-элементная модель в виде структурированной сетки объекта расчета при dp = 60 мкм
The value of the equivalent stress σeq.porei (tab. 2) arising from the application of tensile load equal to F = 2000 N is obtained as a result of a series of calculations for each specimen. The values of the coefficient ni and the yield strength σyield.porei are presented in tab. 2. The dependence of the value of the yield strength on the particle diameter (hence, on the pore diameter) is nonlinear (fig. 6). The existence of an extremum can be explained by the opposite influence of geometrical parameters on the value of the surface area of the pores in the entire volume of the specimen. The total area of spherical surfaces is proportional to the number of pores in the specimen and at the same time to the diameter of each pore dporei. The smaller the specified diameter of the initial metal powder particle is, the smaller the diameter and surface area of the pore formed in the SLM are, but the smaller the distance between the pores (hpore ≈ 2·dpore) is, the greater their number is, and, therefore, the larger the total surface area of pores is.
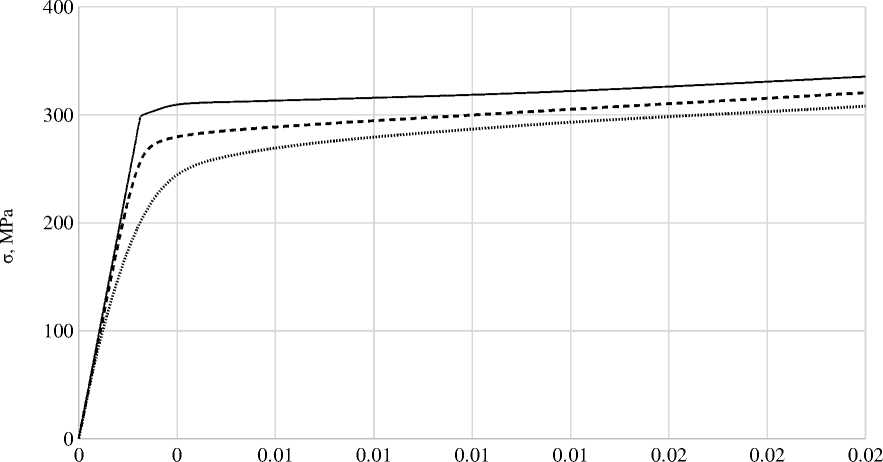
ε, mm
Fig. 5. The calculated diagram of the specimen stress-strain state with:
1 – dp = 0 µm; 2 – dp = 180 µm; 3 – dp = 300 µm
Рис. 5. Расчетная диаграмма напряженно-деформированного состояния образца при: 1 – dp = 0 мкм; 2 – dp = 180 мкм; 3 – dp = 300 мкм
Table 2
The results of the yield strength calculation for porous specimens
|
№ |
dpi |
eq . porei |
ni |
σ yield . porei |
klayi |
|
mkm |
MPa |
– |
MPa |
– |
|
|
1 |
60 |
254.4 |
0.917 |
275.0 |
0.929 |
|
2 |
90 |
251.3 |
0.928 |
278.4 |
0.929 |
|
3 |
150 |
240.8 |
0.968 |
290.4 |
0.955 |
|
4 |
180 |
239.6 |
0.973 |
291.9 |
0.956 |
|
5 |
210 |
240.7 |
0.969 |
290.7 |
0.944 |
|
6 |
240 |
244.5 |
0.954 |
286.2 |
0.939 |
|
7 |
270 |
249.1 |
0.936 |
280.9 |
0.929 |
|
8 |
300 |
255.1 |
0.914 |
274.2 |
0.914 |
|
0 (monolithic) |
233.2 |
1 |
300.0 |
1 |
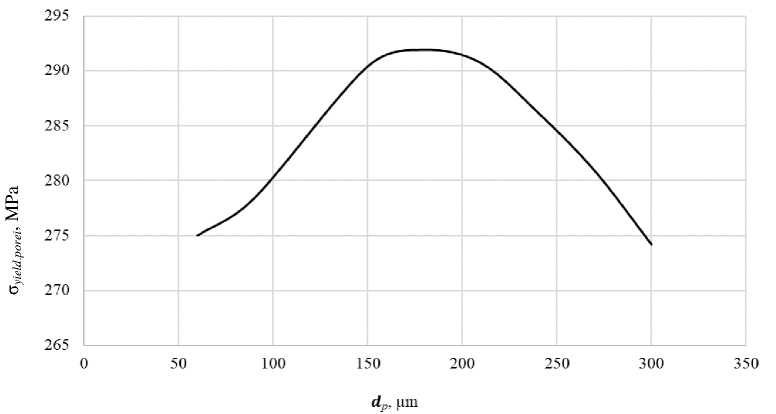
Fig. 6. The dependence of the specimen yield strength value on the metal powder particle diameter
Рис. 6. Зависимость значения предела текучести образца от диаметра частиц металлического порошка
Conclusion. The paper considers the methodology of evaluating the reduction of the strength of the RST structural element material obtained by the SLM method by modeling the porous structure and calculating the characteristics of the stress-strain state. During the calculation it was found that the value of the total surface area of the pores in the material due to the size of the original metal powder particles is directly proportional to the value of the equivalent stress σ eq . porei arising in the object under study when tensile load is applied.
The dispersion value of the metal powder d p is determined using tensile testing of a series of metal specimens. The value determined provides the minimum total surface area of pores in the material structure resulting from laser beam sintering, thereby causing greater value of the yield strength σ yield.pore of the part. The optimum value of the powder dispersion for steel AISI 316L in the preparation of specimens for tensile is d p opt = 150...200 microns.
Список литературы Modeling of the stress-strain state of rocket-space technology structural elements manufactured by using additive technologies
- Отработка конструктивных и технологических решений для изготовления опытных образцов внутренней оболочки камеры сгорания многофункционального жидкостного ракетного двигателя с использованием аддитивных технологий / Артемов А. Л. [и др.] // Космическая техника и технологии. 2017. № 1. С. 50-62.
- Абдуллин М. И., Басыров А. А., Николаев А. В. Металлополимерные композиции для 3D печати // Universum: химия и биология. 2015. № 11(18). URL: http//7universum.com/ru/nature/archive/item/2701 (дата обращения 20 декабря 2018).
- Григорьянц А. Г., Казарян М. А., Лябин Н. А. Лазерная прецизионная микрообработка материалов: монография. М.: Физматлит, 2017. 413 с.
- Елистратова А. А., Коршакевич И. С., Тихоненко Д. В. Технологии 3D-печати: преимущества и недостатки // Решетневские чтения: сб. матер. XVIII Междунар. науч.-практ. конф. (Красноярск, 11-14 ноября 2014 г.) / СибГАУ. Красноярск, 2014. С. 557-559.
- Зленко М. А., Попович А. А., Мутылина И. Н. Аддитивные технологии в машиностроении. СПб.: Изд-во Политехн. ун-та, 2013. 223 с.


