Молекулярно-клеточные механизмы ответа организма на гипоксию
Автор: Бондаренко Н.Н., Хомутов Е.В., Ряполова Т.Л., Кишеня М.С., Игнатенко Т.С., Толстой В.А., Евтушенко И.С., Туманова С.В.
Журнал: Ульяновский медико-биологический журнал @medbio-ulsu
Рубрика: Обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 2, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Гипоксия - это типовой патологический процесс, характеризующийся кислородной недостаточностью в тканях с развитием патологических и защитно-компенсаторных реакций. В статье кратко изложены вопросы истории изучения гипоксии и применения интервальных гипоксических тренировок в клинической и реабилитационной практике при лечении различных заболеваний и патологических процессов. Рассмотрены варианты физиологической и патологической гипоксии, ключевые звенья патогенеза нормо- и гипобарической гипоксии при нормальном и сниженном атмос中ерном давлении, этапы формирования гипоксии. Показано, что физиологические и биохимические реакции интервальных гипоксических тренировок связаны с окислительным стрессом, который развивается вследствие дисбаланса между про- и антиоксидантной системами, и избыточной продукцией активных форм кислорода. Применение интервальных гипоксических тренировок направлено на адекватную активацию защитных систем с формированием устойчивой адаптации к действию повреждающих факторов. Показана ключевая роль биологических эффектов индуцируемого гипоксией 中актора 1-альфа в механизмах клеточной и тканевой адаптации к дефициту кислорода. Проанализирована роль аденозина и аденозиновых рецепторов при острых и хронических воспалительных заболеваниях, сопряженных с тканевой гипоксией.
Гипоксия, интервальные гипоксические тренировки, гипоксией индуцируемый фактор, аденозин
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14128729
IDR: 14128729 | УДК: 616-001.8:577.2+576.5 | DOI: 10.34014/2227-1848-2023-2-6-29
Текст научной статьи Молекулярно-клеточные механизмы ответа организма на гипоксию
В настоящее время внимание медицинского сообщества привлекают альтернативные методы лечения и реабилитации, направленные на активацию адаптационных механизмов при различных патологических процессах [1, 2]. Одним из наиболее распространенных и эффективных методов немедикаментозного лечения сердечно-сосудистых, бронхолегочных, цереброваскулярных и других заболеваний является гипокситерапия, инициирующая увеличение реактивности организма, повышение чувствительности органов-мишеней к действию внешних и внутренних раздражителей [3–7].
Целью данного обзора является анализ регуляторных механизмов поддержания кисло- родного гомеостаза и их роли в физиологии и медицине.
История изучения гипоксии и применения гипоксических тренировок. Одно из первых письменных упоминаний о применении гипоксической терапии в лечебных целях принадлежит Гиппократу (V–IV вв. до н.э.), который рекомендовал больным людям переехать жить на умеренную высоту в горы. Итальянский путешественник Марко Поло (XIII– XIV вв.) отмечал, что жители Азии во время болезни поднимались в горы и выздоравливали. Исследователи ХIХ и начала ХХ в., такие как Поль Бер, Джон Скотт Холдейн, Гарольд Пирс, изучали физиологические эффекты изменений атмосферного давления у воздухопла- вателей, поднимающихся на высоту [8]. Большая заслуга в области изучения реактивности и основных патогенетических механизмов гипобарической гипоксии принадлежит академику Н.Н. Сиротинину [7, 9–11].
В 1980-х гг. отечественными учеными был разработан и предложен для практического применения лечебно-профилактический комплекс режимов как высотных, так и барокамерных гипобарических защитных воздействий с использованием дыхательной газовой смеси с пониженным содержанием кислорода при нормальном атмосферном давлении [12]. Была внедрена методика интервальной гипоксической тренировки (ИГТ) [11, 13]. В настоящее время накоплено большое количество результатов клинических и экспериментальных исследований, характеризующих высокую эффективность ИГТ в медицине, в т.ч. военной, спортивной и реабилитационной [14–17]. Разработано множество гипоксических тренировочных режимов с периодической гипоксией, обладающих доказанной эффективностью при лечении сердечно-сосудистых, дыхательных, цереброваскулярных нарушений, сахарного диабета, заболеваний щитовидной железы и многих других распространенных заболеваний и коморбидных состояний [7, 18–25].
Возрастающий интерес ученых к изучению гипоксии, являющейся одним из основных причинно-следственных факторов большого количества заболеваний, в настоящее время обусловлен открытием фактора, индуцируемого гипоксией, – HIF, благодаря которому клетки способны адаптироваться к присутствию кислорода [26]. Исследование HIF как фактора молекулярных механизмов, который регулирует транскрипционную активность генов в ответ на различное содержание кислорода, особенно при гипоксии, было удостоено Нобелевской премии по физиологии и медицине 2019 г. [27].
Формирование гипоксии как типового патологического процесса. Гипоксию/гипо-ксемию характеризуют как типовой патологический процесс со снижением уровня обеспечения организма молекулярным кислородом или же как состояние, связанное с накоплением недоокисленных продуктов в процессе внутриклеточных окислительно-восстановительных реакций [8, 12, 28].
Развитие кислородной недостаточности также может быть вызвано ишемическими нарушениями органов и тканей, обусловленными патогенетическими механизмами, связанными со снижением напряжения кислорода, доставки энергетических субстратов, в первую очередь глюкозы, энергетического клеточного потенциала за счет угнетения продукции АТФ в митохондриях [29–34].
В организме здорового человека гипоксия может развиваться в результате продолжительного мышечного сокращения при физических нагрузках [35]. Установлено снижение содержания кислорода в нервной ткани коры головного мозга при интенсивной умственной деятельности [36]. Признаки гипоксии иногда могут выявляться в печени, почках, желудочно-кишечном тракте в отсутствие структурно-функциональных нарушений при существенном увеличении их функциональной активности [37, 38].
Формирование гипоксии проходит в 3 взаимосвязанных этапа: 1) первичный ответ на воздействие собственно гипоксического фактора; 2) каскад вторично обусловленных гипоксией нарушений; 3) формирование комплекса компенсаторно-приспособительных реакций, развивающихся на фоне кислородной недостаточности [22, 28].
Гипоксия приводит к нарушению тканевого дыхания и энергетического обмена [39]. Кислородная недостаточность является негативным условием для реакций аэробного гликолиза, окислительного декарбоксилирования пирувата, цикла Кребса и окислительного фосфорилирования. В связи с этим последствиями гипоксии являются развитие энергетического дефицита, сдвиг клеточного метаболизма в сторону катаболических реакций, гликогенолиз и активация реакций протеолиза [40]. Преобладание анаэробного гликолиза приводит к накоплению лактата с развитием ацидоза. Уменьшение продукции пирувата и, как следствие, ацетил-КоА снижает активность ключевых реакций цикла Кребса, процессов посттрансляционной модификации белков, синтеза стероидов, жирных кислот, ацетилхолина, мелатонина и других биологически активных веществ [28, 41]. Снижение синтеза АТФ сопровождается нарушением активности фермента Na+/K+-АТФ-азы при формировании мембранных потенциалов, а также повреждением структурных элементов цитоскелета и транспортных систем клетки. Повышение внутриклеточного pH приводит к увеличению проницаемости мембран лизосом и разрушению клеточных структур под действием лизосомальных гидролитических ферментов. Важнейшими звеньями патогенеза гипоксии являются активация процессов перекисного окисления липидов, увеличение продукции активных форм кислорода (АФК) с развитием оксидативного стресса [40]. В зависимости от патогенетических нарушений выделяют следующие виды гипоксии: гипоксическую, циркуляторную, тканевую и т.д.
Гипоксическая гипоксия возникает в том случае, когда концентрация кислорода в циркулирующей крови снижается в результате уменьшения его содержания во вдыхаемом воздухе при отсутствии нарушений кровоснабжения тканей. Парциальное давление кислорода в артериальной крови становится менее 60 мм рт. ст., сатурация – менее 90 % [42].
Ишемическая гипоксия обусловлена нарушением кровоснабжения ткани, при этом уровень кислорода и углекислого газа в крови может сохраняться в пределах нормы [5].
Тканевая (гистотоксическая) гипоксия связана с нарушением способности клеток связывать кислород при его нормальной доставке к клеткам. Тканевая гипоксия развивается при нарушении активности ферментов биологического окисления, синтеза ферментов, изменениях физико-химических свойств внутренней среды, дезинтеграции клеточной мембраны, разобщении окислительного фосфорилирования [40, 41].
Физиологическая гипоксия может развиваться при физических нагрузках и сопровождаться периодическими метаболическими изменениями в тканях, которые компенсируются в восстановительном периоде [43].
Патологическая гипоксия развивается при многих заболеваниях и их осложнениях. Острая гипоксия возникает при экстремаль- ных состояниях, является следствием всех видов шока, острой сердечной и дыхательной недостаточности, острых нарушений мозгового кровообращения [44–47]. Хроническая гипоксия развивается при атеросклерозе, цереброваскулярных заболеваниях, ишемической болезни сердца, хронической сердечной и почечной недостаточности и хронической обструктивной болезни легких [48–53]. Гипоксия приводит к активации адаптационных процессов, обеспечивающих поддержание жизнедеятельности в условиях недостаточности кислорода. Адаптация к гипоксии связана с усилением регуляторных механизмов, поддержанием содержания кислорода во внутренней среде организма с образованием энергии и обеспечением энергозависимых реакций. Формирование механизмов адаптации проходит в две стадии: 1) стадия индукции адаптации; 2) стадия долгосрочной адаптации с ге-номзависимыми реакциями [40, 54].
Первая стадия характеризуется срочным ответом на гипоксию, при котором происходит активация сигнальных регуляторных систем с увеличением резистентности к гипоксии, которая в постгипоксический период достаточно быстро восстанавливается до исходного уровня. Срочные адаптационные реакции включают активацию сигнальных путей, медиаторных систем, а также индукцию биосинтеза специфических транскрипционных факторов [55]. Компенсаторные механизмы острой гипоксии связаны с активацией симпатоадреналовой системы, увеличением вентиляционной способности дыхательной системы, тахикардией, увеличением минутного объема кровообращения, вазодилатацией, улучшением микроциркуляции и др. [56].
Долгосрочная адаптация формируется при продолжительном или многократном гипоксическом воздействии и связана с переходом регуляции кислородного гомеостаза на новый уровень со структурно-функциональными и метаболическими изменениями [40]. Активация транскрипционных факторов приводит к увеличению интенсивности синтеза ферментов, мембранных белков, регуляторов клеточного цикла и др. [39, 57, 58]. Повышение эффективности энергетического метаболизма направлено на активность ростовых факторов с их участием в неоваскулогенезе, коллатера-лизации кровообращения и увеличении проницаемости сосудов [59]. В мышечных волокнах усиливается синтез миоглобина [60], развивается гипертрофия гладких миоцитов сосудов, почечных клубочков, что обусловлено активацией биосинтеза белка и процессов пролиферации под влиянием транскрипционных факторов [56, 61]. Нарушение доставки кислорода и снижение синтеза АТФ приводят к подавлению энергозависимых процессов, функциональным и метаболическим нарушениям на различных уровнях организации. Снижение интенсивности наиболее важных энергозависимых функционально-метаболических процессов происходит при снижении уровня АТФ на 10–20 %, а при уменьшении на 30 % наблюдается их полное угнетение. В условиях гипоксии для клеточного функционирования имеют большое значение процессы адаптации аэробного обмена и организма в целом [40]. Процесс адаптации к гипоксии играет значительную роль при канцерогенезе [62]. На начальном этапе опухолевого роста гипоксия тормозит рост опухоли, далее приводит к повышению устойчивости ее клеток, увеличению скорости пролиферации, активации неоангиогенеза [63]. Прогрессирование опухолевого роста, распространенности, инвазии и метастазирования зависит от интенсивности васкуляризации. Происходит индукция ингибиторов апоптоза и подавление синтеза проапоптотических белков, имеют место нарушения процесса метилирования молекул ДНК [64]. Развитие гипоксии в опухолевой ткани является неблагоприятным прогностическим фактором патогенеза онкологических заболеваний [63].
При формировании гипоксических изменений, связанных с переходом от физиологического состояния к патологическому, особое внимание заслуживают защитные механизмы, направленные на повышение резистентности организма [13]. Адаптационный процесс при гипоксии формируется с участием 4 различных по направленности механизмов [40]:
-
1) Первоочередными являются механизмы, мобилизация которых приводит к ста-
- билизации доставки в организм кислорода, что в значительной мере компенсирует его недостаток во внешней среде. К ним относят легочную гипервентиляцию, активацию сердечной деятельности, эритроцитоз, повышение сродства гемоглобина к кислороду [65].
-
2) Важными являются механизмы, ответственные за улучшение транспорта кислорода к головному мозгу, миокарду и другим органам. Их вовлечение в процесс адаптации сопровождается дилатацией артерий, артериол и прекапиллярных сфинктеров (мозг, сердце и т.д.), увеличением капиллярных сетей, повышением проницаемости клеточных мембран.
-
3) На более поздних этапах адаптации к гипоксии подключаются механизмы повышения способности клеток и тканей к утилизации кислорода из крови с одновременным увеличением синтеза молекул АТФ за счет усиления сродства конечного фермента дыхательной цепи цитохромоксидазы к кислороду, улучшения окислительного фосфорилирования, вызванного структурно-функциональными изменениями в митохондриях.
-
4) Важным механизмом адаптации к гипоксии считают и увеличение интенсивности анаэробных процессов в ресинтезе АТФ за счет активации гликолиза. Так, при экзогенных формах гипоксии, несмотря на явное снижение содержания кислорода в окружающей среде, в течение определенного периода в артериальной крови и межклеточной жидкости не происходит существенных сдвигов уровня напряжения кислорода, углекислого газа и уровня рН [28, 39]. Однако при высокой степени напряжения адаптационных механизмов эффективность их снижается, что проявляется симптомами острой или хронической кислородной недостаточности.
Виды экзогенной гипоксической гипоксии. Экзогенная гипобарическая гипоксия формируется в результате снижения во внешней среде парциального давления О2, что сопровождается его уменьшением в альвеолярном воздухе и приводит к снижению уровня напряжения О2 в артериальной крови [66, 67]. Развивающаяся в связи с компенсаторной гипервентиляцией легких гипокапния имеет выраженное патогенное влияние. Гипокапния приводит к нарушению кровоснабжения мозга и сердца из-за сужения сосудов, дыхательному алкалозу. Дыхательный алкалоз компенсируется повышенной экскрецией бикарбонатного аниона почками. Снижение содержания натрия в организме ведет к развитию гиповолемии с водно-электролитными нарушениями.
Экзогенная нормобарическая гипоксия развивается при нормальном атмосферном давлении окружающей среды и снижении парциального давления кислорода во вдыхаемом воздухе, что может повлечь развитие гиперкапнии. Умеренная гиперкапния оказывает благоприятный эффект (увеличение кровоснабжения мозга и сердца) [68, 69].
При содержании в окружающем воздухе 7–9 % СО 2 отмечают умеренную гиперкапнию. При этом напряжение углекислоты в крови достигает 60–75 мм рт. ст. Внешними проявлениями умеренной гиперкапнии являются увеличение частоты и амплитуды экскурсий грудной клетки в связи со стимулирующим действием растворенного в ликворе СО 2 на хемочувствительные нейроны дыхательного центра в бульбарном отделе головного мозга [70]. Прогрессирующая гиперкапния может приводить к ацидозу и электролитному дисбалансу. Развитие метаболического ацидоза происходит в основном за счет увеличения содержания лактата и пирувата [71].
Накопление СО 2 в атмосферном воздухе более 10 % приводит к увеличению напряжения газа в плазме крови и межклеточной жидкости до 90 мм рт. ст. Активирующее влияние СО 2 на инспираторные нейроны дыхательного центра исчезает, вентиляция легких начинает снижаться, констатируют терминальное дыхание на фоне дестабилизации сердечной деятельности, прогрессирующей артериальной гипотензии. Летальный исход чаще всего отмечают при напряжении СО 2 в крови на уровне 130–140 мм рт. ст. [70].
В последнее время в комплекс лечебных мероприятий различных заболеваний сердечно-сосудистой, дыхательной, эндокринной, нервной систем внедряется метод гипокситерапии с применением специализированных устройств – гипоксикаторов. Методика позволяет сохранять внутри гипоксикатора стабильно низкие концентрации О2 при обычных величинах барометрического давления [11]. Важно отметить, что использование ги-поксикаторов, а также газовых смесей с пониженным содержанием О2 позволяет воспроизводить состояние гипоксии, при котором не изменяется барометрическое давление [14].
Кратковременное вдыхание газовой смеси с 11–12 % содержанием O 2 хорошо переносится организмом человека, насыщение крови кислородом (SрO 2 ) снижается не ниже 77–80 %. Данный диапазон гипоксемии является оптимальным для запуска каскада адаптивных механизмов, исключает индукцию негативных, повреждающих изменений [11].
Роль системного оксидативного стресса в развитии адаптивных реакций при гипоксии. Помимо того, что избыточный уровень активных форм кислорода играет известную роль в развитии патологических состояний, образование АФК и инициация свободнорадикальных процессов являются физиологическими процессами, постоянно протекающими в организме [72]. Главными физиологическими функциями АФК являются: а) окисление различных поврежденных молекул с целью их дальнейшей утилизации; б) синтез молекул мессенджерного типа, например эйкозаноидов, при свободнорадикальном окислении полиненасыщенных жирных кислот и жирных кислот фосфолипидов; в) участие в редокс-сигнализации и внутриклеточной системе передачи внешнего сигнала к клеточному ядру с последующим синтезом белков [55, 72].
Важнейшим следствием инициации редокс-сигнализации является активация факторов транскрипции: транскрипционного фактора NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-B), транскрипционного фактора АР-1 (activator protein 1) и гипоксия-индуцибельных факторов (hypoxiainducible factor – HIF) HIF-1a и HIF-2a, индуцирующих защитные белки, среди которых ферменты антиоксидантной защиты, белки семейства HSP (heat shock proteins – белки теплового шока), Fe-регулирующие белки, ферменты репарации, пероксиредоксины, белки-эффекторы NO-синтазы, К/АТФ-каналов и К/Са-каналов митохондрий и сарколеммы кардиомиоцитов [72].
Кроме того, результатом поступления АФК-сигнала является активация ряда неспецифических молекул: ферментов антиоксидантной защиты, железосвязывающих белков, белков срочного ответа (белки теплового шока) семейства HSP. Белки теплового шока известны своей способностью связываться с денатурированными белками и пептидами, а также с вновь синтезированными белками и придавать им функциональную конформацию. Этот процесс происходит постоянно в клетках живых систем как в нормальных условиях, так и при стрессе и адаптации. Полагается, что такое свойство белков теплового шока способствует формированию адаптационного механизма и повышению резистентности клеток [30].
Рассматривается роль гемоксигеназы (HOx) в осуществлении защитной реакции клетки на воздействие повреждающих агентов. Основной задачей НОх является поддержание физиологического уровня гема в клетке. Существует три изоформы белка: НОх-1, НОх-2, НОх-3. Непосредственно сама гемоксигеназа, а также ее продукты обладают вазодилатирующим антиоксидантным свойством. Кроме того, известна опосредованная роль НОх в ингибировании воспалительного процесса [43].
Одним из важнейших механизмов адаптации является перекрестная адаптация. То есть адаптируя организм к одному виду сигнала, можно индуцировать синтез многих защитных белков, характерных для другого вида сигнала (ишемия, физическая нагрузка, стресс и др.). Это связано с тем, что компенсация прямого или опосредованного АФК-сигнала идет по одним и тем же путям внутриклеточной сигнализации [72]. Описанные экспериментально полученные факты во многом объясняют позитивные клинические эффекты адаптации пациентов к интервальной гипоксии.
Важным вопросом является то, насколько безопасным может быть усиление АФК-сигнала в процессе адаптации к ИГТ. Любой внешний или внутренний повреждающий фактор, вызывающий повышенную продукцию АФК, сопровождается ответом антиоксидантной системы. Основными компонентами антиоксидантной защиты являются:
-
а) ферменты антиоксидантной защиты (супероксиддисмутаза (СОД), глутатионпероксидазы (ГП));
-
б) эндогенные низкомолекулярные антиоксиданты (фенольные антиоксиданты, каротиноиды, липоевая кислота, N-ацетилцистеин, мелатонин, витамины А, С, Е, серосодержащие соединения);
-
в) экзогенные антиоксиданты (витамины С, Е, А, Р и их предшественники, аскорбиновая кислота, α-токоферол, β-каротин, флавоноиды, рутин, а также ионы, входящие в состав антиоксидантных ферментов, например селен).
Ферменты антиоксидантной защиты, эндогенные низкомолекулярные соединения предназначены для нейтрализации избыточного образования свободных радикалов. СОД катализирует дисмутацию супероксидного анион-радикала O 2 в кислород и пероксид водорода, каталаза принимает участие в нейтрализации перекиси водорода, глутатионпероксидазы осуществляют удаление органических перекисей.
Эндогенные низкомолекулярные компоненты антиоксидантной защиты, помимо нейтрализации свободных радикалов, стабилизируют активность СОД, ГП при избыточной продукции АФК, способной нарушить работу СОД и ГП. Каталитическая активность этих компонентов контролирует уровень образования свободных радикалов. В этом случае речь идет о равновесии прооксидантной и антиоксидантной систем [67]. Таким образом, наличие баланса между прооксидантами и антиоксидантами препятствует повреждающему действию АФК.
Ответ клетки на АФК-сигнал реализуется несколькими путями и зависит от исходного состояния организма и интенсивности поступившего сигнала. В любом случае наблюдается синтез защитных белков, но в итоге может быть достигнута компенсация, т.е. возврат к исходному состоянию равновесия, либо декомпенсация, когда уровня синтезируемых защитных белков недостаточно для компенсации АФК-сигнала [12]. Если же синтез защитных систем будет своевременно достаточно увеличен (при помощи повышения интенсив- ности АФК-сигнала), то возможно формирование устойчивости, повышение защиты клетки к повреждающему воздействию. При длительной адаптации может наблюдаться прекращение синтеза защитных белков и возврат их к исходному уровню. На начальной стадии происходит активация синтеза защитных белков с целью компенсации АФК-сигнала, на более поздней стадии адаптации наблюдается изменение направления функционирования клетки – синтез новых изоформ структурных и функциональных белков, устойчивых к воздействию внешнего фактора (стадия устойчивой адаптации) [1].
Считается, что чем более полно происходит нормализация уровня защитных систем, тем выше устойчивость клеточных структур к повреждающим факторам. Важно отметить, что для реализации защитного эффекта необходима дозированность окислительного стресса во избежание истощения резерва защитных систем и срыва адаптации [18].
Таким образом, интервальность, дозиро-ванность и длительность воздействия ИГТ позволяют вызвать адекватную активацию защитных систем и достичь стадии устойчивой адаптации. Умеренное повышение кислорода (30–35 %) в период гипероксии при ИГТ, по сравнению с реоксигенацией (21–24 %) при чередовании гипоксических и нормоксиче-ских тренировок, направлено на увеличение интенсивности АФК-сигнала и формирование резистентности клеток к действию АФК-опо-средованных повреждающих факторов [51].
Роль HIF-1 в формировании механизмов адаптации к гипоксии. Ключевая роль в механизмах клеточной и тканевой адаптации к дефициту кислорода принадлежит фактору транскрипции HIF-1, который является одним из основных медиаторов гомеостаза в тканях человека, подвергающихся воздействию гипоксии. Он участвует практически во всех процессах быстрой экспрессии генов в ответ на низкий уровень кислорода. Наиболее частыми причинами тканевой гипоксии являются воспаление, недостаточное кровообращение или их комбинация [21, 73]. Воспаленные ткани и участки, окружающие злокачественные опухоли, характеризуются гипоксией и низким содержанием глюкозы. Генерализованное воспаление может привести к сепсису и циркуляторному шоку с развитием острой или хронической гипоксии тканей в различных жизненно важных органах, что сопровождается срочным сигналингом во всех ядерных клетках пораженных органов в организме человека. В условиях гипоксии альфа- и бета-субъединицы HIF-1 образуют активный гетеродимер и управляют транскрипцией более 100 генов, важных для выживания клеток, адаптации, анаэробного метаболизма, иммунных реакций, продукции цитокинов, васкуляризации и общего тканевого гомеостаза. Он также является важным медиатором онкогенеза, легочных и сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний. Детальное изучение функций HIF-1 и фармакологической модуляции его активности может сопровождать эффективный терапевтический подход к этим заболеваниям. HIF-1 играет ключевую роль в развитии физиологических систем в эмбриональном и постнатальном периодах.
В последние десятилетия ведется активное изучение биологических эффектов молекулы HIF-1α (фактор, индуцируемый гипоксией 1-альфа), что обусловлено его ключевой ролью в механизмах клеточной и тканевой адаптации к дефициту кислорода и ишемии [26, 40, 74].
Однако, несмотря на традиционные представления о природе сигнального механизма HIF-1α, базирующегося на кислород-дефицит-ной аккумуляции, получены данные и об альтернативных механизмах его активации. Это позволило не только пересмотреть отношение к регуляторным гипоксическим механизмам HIF-1α, но и определить его роль в качестве мишени для потенцирования защитных эффектов от нескольких адаптогенных сигналов. Разработка новых методов и средств увеличения устойчивости органов и тканей к гипо-ксии/ишемии с определением роли HIF-1α является перспективным направлением. Концентрация и стабильность HIF-1α, активность транскрипции прямо зависят от уровня кислорода в клетке [74].
HIF представляет собой гетеродимерный фактор транскрипции, состоящий из консти- тутивно экспрессируемой β-субъединицы (HIF-1β) и α-субъединицы (представленной в виде изоформ HIF-1α и HIF-2α).
Когда уровень кислорода не снижен, HIF-α и HIF-2α подвергаются срочной протеа-сомной деградации, включающей два этапа гидроксилирования (рис. 1).
На первом этапе реакции фактор, ингибирующий HIF (FIH), гидроксилирует остаток аспарагина в С-концевом домене активации (CAD) HIF [75]. Этот этап предотвращает связывание коактиватора и тем самым функционально ингибирует активность HIF.
Вторая стадия гидроксилирования обеспечивается группой ферментов, которые функционируют как пролилгидроксилазы PHD1, PHD2 или PHD3, маркирующие остатки пролина для убиквитинирования [57, 76]. PHD гидроксилируют консервативные остатки пролина в N-концевом домене активации белка HIF-1α или HIF-2α. Эта стадия гидроксилирова-ния облегчает связывание продукта гена фон Гиппеля-Линдау (VHL), тем самым способствуя распознаванию убиквитином и последующей протеасомной деградации HIF-1α или HIF-2α [75].

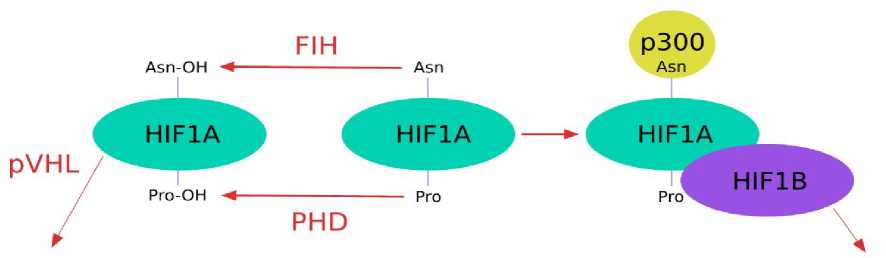
Протеасомная деградация Proteasomal degradation
Транскрипция гена Gene transcription
Рис. 1. Кислородзависимый путь регуляции факторов HIF.
В условиях нормоксии (левая часть схемы) гидроксилазы инактивируют HIF-1α-субъединицы. FIH гидроксилирует остаток аспарагина в карбоксиконцевом домене активации (CAD), предотвращая рекрутирование коактиватора (p300). PHD гидроксилируют остатки пролина в N-концевом домене активации (в домене кислородзависимой деградации), способствуя зависимому от pVHL убиквитинированию и протеасомной деградации. При гипоксии PHDs и FIH ингибируются, а коактиватор p300 рекрутируется на HIF-1α-субъединицу, которая образует гетеродимер с HIF-1β, комплекс является транскрипционно активным
Fig. 1. Oxygen-dependent pathway for HIF regulation.
Under normoxia (left), hydroxylases inactivate HIF-1α subunits. FIH hydroxylates asparagine residue in the carboxy-terminal activation domain, preventing coactivator recruitment (p300). PHDs hydroxylate proline residues in N-terminal activation domain (oxygen-dependent degradation domain), contributing to pVHL-dependent ubiquitination and proteasome degradation. Under hypoxia, PHDs and FIH are inhibited, and p300 coactivator is recruited to HIF-1α subunit, which forms a heterodimer with HIF-1β. The complex is transcriptionally active
Избыток АФК при гипоксии ингибирует PDH, тем самым препятствуя расщеплению HIF-1α [77]. Стабилизация и накопление HIF-1 приводят к активации транскрипции некоторых белков, направленной на сохранение клеточной функциональной активности в условиях гипоксии. К ним относятся гликолитические ферменты (альдолаза, пируваткиназа, лактатдегидрогеназа и др.) [78], мембранные переносчики глюкозы и лактата, регуляторы клеточной дифференцировки, метаболизма жиров и углеводов (PPARGC1A), клеточного апоптоза и аутофагии (BNIP3) [57], эритропоэтин [79], фактор роста эндотелия сосудов VEGF и др. [80].
HIF-1α индуцирует биосинтез киназы пируватдегидрогеназы-1, которая путем фосфорилирования ингибирует пируватдегидрогеназу и тем самым препятствует поступлению коэнзима A в цикл трикарбоновых кислот. Это приводит к уменьшению потребления кислорода митохондриями и поддержанию его внутриклеточного уровня [81]. Когда острая гипоксия сменяется хронической, экспрессия HIF-1α постепенно уменьшается и активность пируватдегидрогеназы восстанавливается. С этим связана эффективность регулярных физических тренировок для уменьшения продукции лактата в скелетных мышцах и увеличения их устойчивости к повышению нагрузки [82]. HIF-1α на уровне транскрипции запускает перестройку цитохром С-оксидазы, в результате чего расход кислорода и образование АФК уменьшаются, а синтез АТФ возрастает [41].
В адаптивных механизмах клеток при гипоксии для поддержания их функциональной активности необходим баланс факторов HIF-1α и HIF-2α [83]. Снижение уровня HIF-1α ведет к накоплению HIF-2α и СОД, уменьшению клеточного редокс-потенциала, чувствительности рецепторов каротидных телец и нарушению дыхательной функции при кислородном голодании. Снижение синтеза HIF-2α сопровождается увеличением уровня NADPH и функциональной активности каротидных телец [46].
Поскольку факторам PHD и FIH необходим кислород в качестве кофактора для реак- ций гидроксилирования, то развитие гипоксии будет связано с функциональным ингибированием FIH и PHD [77]. Таким образом, гипоксические состояния связаны с посттрансляционной стабилизацией HIF-1α и HIF-2α. Уровни косубстратов и продуктов, таких как 2-оксиглутарат, сукцинат, также могут модулировать активность FIH и PHD [77]. HIF-1α экспрессируется повсеместно, а экспрессия HIF-2α ограничена некоторыми тканями (например, эндотелием сосудов). В настоящее время проводятся исследования дифференциальных эффектов HIF-1α и HIF-2α, указывающие на то, что специфический ответ, вызванный гипоксией, преимущественно опосредуется либо HIF-1α, либо HIF-2α [84]. Например, исследование пациентов с семейным эритроцитозом выявило мутацию в гене HIF-2α как причину заболевания [85].
После стабилизации HIF-1α/HIF-2α и связывания коактиватора α-субъединица образует гетеродимер с HIF-1β, транслоцируется в ядро и связывается с промоторными областями генов-мишеней HIF. Консенсусной основной последовательностью для HRE является 58-RCGTG-38 (где R представляет собой A или G) [74]. Сайт связывания с HIF-1, присутствующий в HRE, является цис-зоной транскрипционной регуляторной последовательности, которая может быть расположена в 58-фланкирующих, 38-фланкирующих или промежуточных последовательностях генов-мишеней. Наличие интактного сайта связывания HIF-1 необходимо, но недостаточно, чтобы эти элементы опосредовали активацию транскрипции [50].
Зависимое от HIF изменение экспрессии генов участвует во многих адаптивных реакциях на гипоксию, таких как индукция эритропоэтина при анемии или индукция VEGF в гипоксических тканях. Помимо зависимой от гипоксии стабилизации HIF, имеются также примеры независимой от гипоксии стабилизации HIF при воспалительных или инфекционных заболеваниях [86].
Особого внимания заслуживает ключевая роль белка VHL в протеасомной деградации с участием HIF-1α и HIF-2α, а также связи онкогенеза с экспрессией HIF. Болезнь фон Гип- пеля-Линдау (аутосомно-доминантный наследственный раковый синдром) сопровождается наличием у членов семьи мутации, нарушающей либо связывание VHL с HIF-1α, либо функцию комплекса VHL-убиквитин-Е3-ли-газа. Носители гетерозиготного варианта имеют очень высокую предрасположенность к развитию сосудистых опухолей в почках, сетчатке, мозжечке, мозговом веществе надпочечников и поджелудочной железе. В этих опухолях отмечена приобретенная потеря второй VHL-аллели. Также известно, что у половины пациентов со светлоклеточным раком почки обнаруживают биаллельную потерю генов VHL. Из-за снижения/отсутствия синтеза белка VHL конституитивно экспрессируется HIF-1α, что играет важную роль в патогенезе опухоли [62, 64]. Вовлеченные в адаптацию к гипоксии HIF-зависимые продукты, такие как VEGF, эритропоэтин и TGF, индуцируют выраженную васкуляризацию, изменение внеклеточного матрикса и регуляцию клеточного цикла VHL-ассоциированных опухолей [87].
HIF-α существует в виде множества изоформ: HIF-1α, HIF-2α, HIF-3α. HIF-1α и HIF-2α вызывают синтез одних и тех же белков. На сегодня известно более 100 белков, индуцируемых HIF-1α и участвующих в регуляции энергетического обмена, обмена железа и гем-содержащих белков, поддержании антиоксидантной системы (КАТ, СОД, ГП, белки теплового шока), ангиогенеза (VЕGF), ингибировании апоптоза (ингибиторы Bcl-2, активатор Bax) [72, 84, 88, 89].
Фактор HIF-1 играет важную роль в клеточном ответе на изменение кислородного гомеостаза [26, 37, 45, 74, 84]. По разным оценкам, HIF-1 регулирует транскрипцию 1–2 % всех генов. Количество установленных генов-мишеней, активируемых HIF-1, продолжает увеличиваться и включает в себя гены, участвующие в ангиогенезе [49], энергетическом метаболизме [22, 81], эритропоэзе [78, 79], клеточной пролиферации [90], ремоделировании сосудов и вазомоторных реакциях [5, 55].
Наряду с классическим путем активации HIF-1, обусловленным воздействием гипоксии и процессом накопления HIF-1α, существует целый ряд альтернативных (неканони- ческих) механизмов. Эти сигнальные механизмы затрагивают практически все этапы регуляции активности фактора HIF-1 и его альфа-субъединицы: экспрессию, синтез, трансактивацию, накопление и деградацию. Так, синтез HIF-1α может реализовываться через О2-независимые механизмы посредством реакций, контролируемых системами MAPK (mitogen activated proteinkinase) и PI3K (рhosphoinositide 3-kinases), имеющих большое значение в процессах роста, пролиферации и дифференцировки [57, 84]. HIF-1α может активироваться некоторыми переходными металлами (Co2+, Ni2+, Mn2+) и хелатированием железа. Также известно, что повышение транскрипционной активности HIF-1 наблюдается под действием оксида азота (II), цитокинов ФНОα, ИЛ-1 и ангиотензина [75].
При этом известно, что хелаторы железа, индуцирующие экспрессию HIF-1α подобно гипоксии, предотвращают и его убиквитини-рование [12, 78]. Доказано, что эти препараты нарушают ассоциацию VHL и HIF-1α, тогда как эти белки остаются связанными в клетках, подверженных гипоксии [4].
В последнее время появились доказательства существования неканонического пути деградации HIF-1, который зависит от шаперон-опосредованной лизосомальной аутофагии [89, 90]. Показано, что применение ингибиторов лизосомальной деградации в модели in vitro приводит к повышению уровня HIF-1α и активности HIF-1, а использование активаторов шаперон-опосредованной аутофагии производит противоположный эффект. При этом HSP70 (белок теплового шока 70) и LAMP2 (лизосомально-ассоциированный мембранный белок 2) аналогичным образом влияют на активность HIF-1, выступая основными компонентами механизма лизосомальной аутофагии. Транскрипционный фактор EB (TFEB) – главный регулятор лизосомального биогенеза – также ингибирует HIF-1. Таким образом, модуляция активности лизосомальной аутофагии играет существенную роль в активации HIF-1 по независимому от кислорода пути.
Кроме того, активированный HIF-1 оказывает провоспалительное и антимикробное действие посредством модуляции клеточного иммунного ответа, проявляет проапоптотиче-ские эффекты, регулирует эмбриональное развитие через повышение экспрессии VEGF [63, 75, 88]. При нормоксии Fe2+-содержащие про-лилгидроксилазы подвергают субъединицу HIF-1α процессу гидроксилирования. Доказано, что изоформа HIF-1α наиболее активна при острой, кратковременной (2–24 ч) выраженной (менее 0,1 % О2) гипоксии или аноксии, в то время как HIF-2α опосредует адаптацию к умеренной (менее 5 % О2) хронической гипоксии [83].
Фактор транскрипции АР-1 (белки Fos- и Jun-семейств) играет основную роль в регуляции активности значительного числа генов, которые участвуют в воспалении и иммунном ответе.
Таким образом, в результате запуска редокс-сигнализации и происходит АФК-ин-дуцированная активация ядерных факторов транскрипции, которые, как правило, находятся в неактивном состоянии.
Наиболее значимыми в защите клеток от патологических факторов различной природы считаются NFkB, AP-1, HIF. Активируясь, они запускают экспрессию большого числа генов, обеспечивающих устойчивость клеток к стрессорным воздействиям и контроль процессов неспецифического и адаптивного иммунитета [66, 72, 91].
Роль сигнальных эффектов аденозина в адаптации к гипоксии. Важным механизмом действия HIF является увеличение внеклеточных сигнальных эффектов аденозина и защита тканей от гипоксии, ишемии и воспаления. Исследования с использованием фармакологических подходов, изучающие внеклеточную передачу сигналов аденозина, указывают на участие этого пути в ослаблении воспаления, связанного с гипоксией [39, 92]. Гипоксия и воспаление являются взаимосвязанными патологическими процессами. Активный воспалительный процесс потребляет большое количество кислорода. Например, полиморфноядерные нейтрофилы при активации, потребляя большое количество кислорода, могут вызывать гипоксию в окружающих соединительнотканных или эпителиальных клетках. Другие воспалительные клетки, такие как естественные клетки-киллеры, эозинофилы, макрофаги или Т-клетки, способствуют формированию метаболической среды в воспалительных или инфекционных очагах [23, 68]. Кроме того, изменения специфических метаболитов (например, накопление сукцината) могут дополнительно формировать гипоксическую микросреду и способствовать перепрограммированию транскрипции [93]. Во многих исследованиях установлено, что при индуцированном гипоксией воспалении (воспалительной гипоксии) повышены внеклеточные уровни аденозина [94]. В свою очередь вовлечение внеклеточной передачи сигналов аденозина приводит к ослаблению воспаления, вызванного гипоксией [95]. Аденозин является частью группы пуринов, которые определяются как гетероциклические ароматические молекулы, состоящие из аденина и гуанина, и представляют собой важный строительный материал для генов и часть биологической энергии. Аденозин играет роль сигнальной молекулы благодаря активации четырех рецепторов: Adora1, Adora2a, Adora2b, Adora3. Эти рецепторы, связанные с G-белком, выполняют множество биологических функций. Например, активация Adora1 замедляет частоту сердечных сокращений, что позволяет использовать инъекции аденозина для лечения суправентрикулярной тахикардии. Adora2a экспрессируется на иммунных клетках, таких как полиморфноядерные нейтрофилы и T-клетки, и ослабляет реакцию воспаления. Adora3 участвует в активации тучных клеток и патогенезе астматических заболеваний дыхательных путей. В отличие от трех других аденозиновых рецепторов, Adora2b является уникальным по своей роли в адаптации к гипоксии и считается сигналом безопасности во время гипоксии, связанной с воспалением [91, 95]. Две особенности делают Adora2b подходящим для адаптации к гипоксии. Во-первых, Adora2b транскрипционно индуцируется фактором HIF-1α, поэтому уровни Adora2b являются самыми высокими во время гипоксии или воспалительных состояний [94]. Во-вторых, этому рецептору для активации необходимы высокие концентрации аденозина. Высокие концентрации внеклеточ- ного аденозина присутствуют при гипоксии и воспалении, что создает условия для активации рецептора Adora2b [95]. Вызванное гипоксией увеличение внеклеточного аденозина считается эндогенным механизмом обратной связи, способствующим адаптации к гипоксии [91].
Кратковременная активация рецепторов Adora2b уменьшает воспаление. Благодаря широкому распространению в организме Adora2b активирует защиту тканей и клеток от гипоксии и ишемии. Однако чрезмерное количество Adora2b при хронических заболеваниях оказывает патогенное действие, регулируя дифференцировку миофибробластов и поляризацию макрофагов, что приводит к прогрессированию фиброза.
Пуриновые нуклеотиды и нуклеозиды участвуют в различных физиологических и патологических механизмах. Нарушение пу-ринергической регуляции способствует развитию различных хронических заболеваний дыхательной системы, сердца, почек и др. [95].
В последние годы исследования, посвященные роли аденозина и его рецепторов в патогенезе хронических заболеваний, сделали их ценной мишенью для лекарственных средств. Рецепторы Adora2b являются парадоксальными модуляторами воспаления, которые демонстрируют как противовоспалительные, так и провоспалительные эффекты, что зависит от срока действия и концентрации.
Изучение роли сигнальных путей аденозиновой регуляции предоставит новую и важную информацию о потенциальной роли аденозина и его рецепторов.
Анализ данных современной литературы свидетельствует о существовании многоуровневых физиологических механизмов поддержания газового состава крови. Трактовка установленных фактов о молекулярно-клеточной регуляции кислородного гомеостаза не позволяет однозначно судить о протективных и повреждающих эффектах различных типов гипоксии, что требует проведения дальнейших исследований.
Список литературы Молекулярно-клеточные механизмы ответа организма на гипоксию
- Глasa4ee О.С., Крыжaновскaя С.Ю. Адаптационная медицина: стратегия психофизиологического приспособления человека к критически измененной окружающей среде. Вестник Международной академии наук. Русская секция. 20l9; l: 48-55.
- Aшaгре С.М., Борукaевa И.Х. Патофизиологическое обоснование применения интервальной гипо-кситерапии и энтеральной оксигенотерапии в лечении гипертонической болезни. ^временные проблемы науки и образования. 2022; l. URL: https://science-education.ru/ru/article/view?id=31506 (дата обращения: 06.04.202З). DOI: 10.17513/spno.31506.
- Игнaтенко r.A., Дубовaя A.B., HayMeHKo Ю.В. Возможности применения нормобарической гипо-кситерапии в терапевтической и педиатрической практиках. Российский вестник перинатологии и педиатрии. 2022; 67 (6): 46-53. DOI: doi.org/10.21508/1027-4065-2022-67-6-46-53.
- Brocherie F., Millet G.P. Hypoxic exercise as an efective nonpharmacological therapeutic intervention. Exp Mol Med. 2020; 52 (3): 529-530.
- Игнaтенко r.A., Мухин И.В., naHueea Н.Ю. Качество жизни у гипертензивных больных гипотиреозом на фоне разных режимов терапии. Вестник гигиены и эпидемиологии. 2020; 24 (2): 185-188.
- Millet G.P., Debevec T., Brocherie F., Malatesta D., Girard O. Therapeutic use of exercising in hypoxia: promises and limitations. Front. Physiol. 2016; 7: 224. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00224.
- Paul S., Gangwar A., Bhargava K., Khurana P., Ahmad Y. Diagnosis and prophylaxis for high-altitude acclimatization: adherence to molecular rationale to evade high-altitude illnesses. Life Sci. 2018; 203: 171-176.
- Rybnikova E.A., Zenko M.Y., Barysheva V.S., Vetrovoy O. Acclimatization to middle attitude hypoxia masks the symptoms of experimental posttraumatic stress disorder, but does not affect its pathogenetic mechanisms. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020; 168: 614-617. DOI: 10.1007/s10517-020-04763-3.
- Яцкевич С.Н., Завьялов А.И., Моррисон В.В., Захарова Н.Б. Академик Н.Н. Сиротинин и его научный вклад в развитие отечественной медицины (к 120-летию со дня рождения). Саратовский научно-медицинский журнал. 2016; 12 (4): 627-632.
- Chavala A. A journey between high altitude hypoxia and critical patient hypoxia: what can it teach us about compression and the management of critical disease? Med. Intensiva. 2018; 42 (6): 380-390.
- Serebrovska Z.O., Xi L., Tumanovska L.V., Shysh A.M., Goncharov S.V., Khetsuriani M., Kozak T.O., Pashevin D.A., Dosenko V.E., Virko S.V., Kholin V-А., Grib О.И., Utko Ы.А., Egorov Е., PolischukА.О., Serebrovska Т. V. Response of circulating inflammatory markers to intermittent hypoxia-hyperoxia training in healthy elderly people and patients with mild cognitive impairment. Life. 2022; 12: 432. DOI: doi.org/10.3390.
- ChenP.S., Chiu W.T., HsuP.L., LinS.C., PengI.C., WangC.Y., TsaiS.J. Pathophysiological implications of hypoxia in human diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020; 27 (63): 1-19.
- Li Y., Li J., Atakan M.M., Wang Z., Hu Y., Nazif M., Zarekookandeh N., Ye H.Z., Kuang J., Ferri A., Petersen A., Garnham A., Bishop D.J., Girard O., Huang Y., Yan X. Methods to match high intensity interval exercise intensity in hypoxia and normoxia - a pilot study. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2022; 20 (1): 7076. DOI: 10.1016/j.jesf.2021.12.003.
- Allsopp G.L., Hoffmann S.M., Feros S.A., Pasco J.A., Russell A.P., Wright C.R. The effect of normobaric hypoxia on resistance training adaptations in older adults. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2022; 36 (8): 2306-2312.
- Burtscher M., Gatterer H., Szubski C., Pierantozzi E., Faulhaber M. Effects of interval hypoxia on exercise tolerance: special focus on patients with CAD or COPD. Sleep Breath. 2010; 14: 209-220. DOI: 10.1007/s11325-009-0289-8.
- Glazachev O.S., Kryzhanovskaya S.Y., Zapara M.A., DudnikE.N., Samartseva V.G., Susta D. Safety and efficacy of intermittent hypoxia conditioning as a new rehabilitation/ secondary prevention strategy for patients with cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2021; 17 (6): e051121193317. DOI: 10.2174/1573403X17666210514005235.
- Hein M., Chobanyan-Jurgens K., Tegtbur U., Engeli S., Jordan J., Haufe S. Effect of normobaric hypoxic exercise on blood pressure in old individuals. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021; 121 (3): 817-825.
- Игнатенко Г.А. Современные возможности адаптационной медицины. Клиническая медицина. 2008; 11. URL: http://www.health-ua.com/articles/2798.html (дата обращения: 06.04.2023).
- Игнатенко Г.А., Денисова Е.М., Сергиенко Н.В. Гипокситерапия как перспективный метод повышения эффективности комплексного лечения коморбидной патологии. Вестник неотложной и восстановительной хирургии. 2021; 6 (4): 73-80.
- Игнатенко Г.А., Майлян Э.А., Игнатенко Т.С., Капанадзе Г.Д. Влияние гипокситерапии на содержание аутоантител к антигенам щитовидной железы у женщин с аутоиммунным тиреоидитом. Медико-социальные проблемы семьи. 2022; 27 (3): 46-51.
- Игнатенко Г.А., Мухин И.В., Сочилин А.В., Гончаров А.Н., Субботина Е.А. Влияние гипокситерапии на респираторные расстройства у гипертензивных больных пылевой хронической обструктивной болезнью легких в период их реабилитации. Университетская клиника. 2023; 4 (45): 12-18.
- Gangwar A., Paul S., Ahmad Y., Bhargava K. Intermittent hypoxia modulates redox homeostasis, lipid metabolism associated infammatory processes and redox post-translational modifcations: benefts at high altitude. Sci Rep. 2020; 10 (1): 7899. DOI: doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64848-x.
- Lee К., Staples K.J., Spalluto C.M., Watson A., Wilkinson T.M. Influence of hypoxia on the epithelial-pathogen interactions in the lung: implications for respiratory disease. Front. Immunol. 2021; 12: 653969. DOI: org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.653969.
- Wang H., Shi X., Schenck H., Hall J.R., Ross S.E., Kline G.P., Chen S., MalletR. T., Chen P. Intermittent hypoxia training for treating mild cognitive impairment: a pilot study. Am. J. Alzheimers. Dis. Other. Demen. 2020; 35: 1533317519896725. DOI: 10.1177/1533317519896725.
- Zhang Y., Geng X., Tan Y., Li Q., Xu C., Xu J., Hao L., Zeng Z., Luo X., Liu F., Wang H. New understanding of the damage of SARS-CoV-2 infection outside the respiratory system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020; 127: 110195. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110195.
- Alexander-Shani R., Mreisat A., Smeir E., Gerstenblith G., Stern M.D., Horowitz M. Long-term HIF-1a transcriptional activation is essential for heat-acclimation-mediated cross tolerance: mitochondrial target genes. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017; 312 (5): R753-R762. DOI: 10.1152/ ajpregu.00461.2016.
- Richalet J.-P. The invention of hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021; 130: 1573-1582. DOI: 10.1152/ japplphysiol.00936.2020.
- Литвицкий П.Ф. Патофизиология. 4-е изд. М.: ГЭОТАР-Медиа; 2009. 496.
- Smith K.A., Waypa G.B., Schumacker P.T. Redox signaling during hypoxia in mammalian cells. Redox Biol. 2017; 13: 228-234. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.05.020.
- Adam-Vizi V., Chinopoulos C. Bioenergetics and the formation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006; 27 (12): 639-645. DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2006.10.005.
- Balaban R.S. Modeling mitochondrial function. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006; 291 (6): 1107-1113. DOI: org/10.1152/ajpcell.00223.2006.
- Hansen J.M., Go Y.M., Jones D.P. Nuclear and mitochondrial compartmentation of oxidative stress and redox signaling. An. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006; 46: 215-234. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.pharm-tox.46.120604.141122.
- Soares R.O.S., Losada D.M., Jordani M.C., Evora P., Castro-E-Silva' O. Ischemia/reperfusion injury revisited: an overview of the latest pharmacological strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019; 20 (20): 5034. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20205034.
- Timon R., Martinez-Guardado I., Brocherie F. Effects of Intermittent Normobaric Hypoxia on Health-Related Outcomes in Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Sports Medicine-Open. 2023; 9: 19. DOI: org/10.1186/s40798-023-00560-0.
- Verges S., Bachasson D., Wuyam B. Effect of acute hypoxia on respiratory muscle fatigue in healthy humans. Resp. Res. 2010; 11: 109. DOI: doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-11-109.
- Бурых Э.А., Паршукова О.И. Физиологические и биохимические индикаторы стресс-реакции организма человека в динамике нормобарической гипоксии. Ульяновский медико-биологический журнал. 2023; 1: 104-113. DOI: 10.34014/2227-1848-2023-1-104-113.
- Nakayama K., Kataoka N. Regulation of Gene Expression under Hypoxic Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019; 20 (13): 3278. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20133278.
- Игнатенко Г.А., Мухин И.В., Игнатенко Т.С., Паниева Н.Ю. Динамика клинико-лабораторных проявлений тироидного синдрома у гипертензивных больных первичным гипотиреозом на фоне лечения. Университетская клиника. 2020; 2 (35): 25-32. DOI: doi.org/10.26435/uc.v0i2(35).533.
- Приходько В.А., Селизарова Н.О., Оковитый С.В. Молекулярные механизмы развития гипоксии и адаптации к ней. Ч. I. Архив патологии. 2021; 83 (2): 52-61. DOI: doi.org/10.17116/patol20218302152.
- ЛукьяноваЛ.Д. Сигнальные механизмы гипоксии. М.: РАН; 2019. 215.
- Guo R., Gu J., Zong S., Wu M., Yang M. Structure and mechanism of mitochondrial electron transport chain. Biomed. J. 2018; 41 (1): 9-20. DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.bj.2017.12.001.
- Berger M.M., GrocottM.P. W. Facing acute hypoxia: from the mountains to critical care medicine. Br J. Anaesth. 2017; 118 (3): 283-286. DOI: doi.org/10.1093/bja/aew407.
- Zheng L., Kelly C.J., Colgan S.P. Physiologic hypoxia and oxygen homeostasis in the healthy intestine. A review in the theme: cellular responses to hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2015; 309 (6): 350-360. DOI: doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00191.2015.
- Bonanno F.G. Management of hemorrhagic shock: physiology approach, timing and strategies. J. Clin. Med. 2022; 12 (1): 260. DOI: 10.3390/jcm12010260.
- SepehrvandN., Ezekowitz J.A. Oxygen therapy in patients with acute heart failure: friend or foe? JACC Heart Fail. 2016; 4 (10): 783-790. DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.jchf.2016.03.026.
- DuanE.H., Adhikari N.K.J., D'AragonF., CookD.J., Mehta S., Alhazzani W., Goligher E., CharbonneyE., Arabi Y.M., Karachi T., Turgeon A.F., Hand L., Zhou Q., Austin P., Friedrich J. Management of acute respiratory distress syndrome and refractory hypoxemia. A Multicenter Observational Study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017; 14 (12): 1818-1826. DOI: doi.org/10.1513/AnnalsATS.201612-1042OC.
- Hoiland R.L., Bain A.R., Rieger M.G., Bailey D.M., Ainslie P.N. Hypoxemia, oxygen content, and the regulation of cerebral blood flow. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016; 310 (5): 398-413. DOI: doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00270.2015.
- Barnes L.A., Mesarwi O.A., Sanchez-Azofra A. The cardiovascular and metabolic effects of chronic hypoxia in animal models: a mini-review. Front. Physiol. 2022; 13: 873522. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.20 22.873522.
- Ferns G.A., HeikalL. Hypoxia in atherogenesis. Angiology. 2017; 68 (6): 472-493. DOI: 10.1177/00033 19716662423.
- Wong B.W., Marsch E., Treps L., Baes M., Carmeliet P. Endothelial cell metabolism in health and disease: impact of hypoxia. EMBO J. 2017; 36 (15): 2187-1203. DOI: doi.org/10.15252/embj.201696150.
- Abe H., Semba H., Takeda N. The roles of hypoxia signaling in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular D+dis-eases. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017; 24 (9): 884-894. DOI: doi.org/10.5551/jat.RV17009.
- AllwoodM.A., Edgett B.A., Eadie A.L., Huber J.S., Romanova N., Millar P.J., Brunt K.R., Simpson J.A. Moderate and severe hypoxia elicit divergent effects on cardiovascular function and physiological rhythms. J. Physiol. 2018; 596 (15): 3391-3410. DOI: doi.org/10.1113/JP275945.
- Fu Q., Colgan S.P., Shelley C.S. Hypoxia: the force that drives chronic kidney disease. Clin Med Res. 2016; 14 (1): 15-39. DOI: doi.org/10.3121/cmr.2015.1282.
- Зенько М.Ю., Рыбникова E.A. Перекрестная адаптация: от Ф.З. Меерсона до наших дней. Ч. 1. Адаптация, перекрестная адаптация и перекрестная сенсибилизация. Успехи физиологических наук. 2019; 50: 3-13.
- Jurcau A., Ardelean A.I. Oxidative stress in ischemia/reperfusion injuries following acute ischemic stroke. Biomedicines. 2022; 10 (3): 574. DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030574.
- Bourdier G., D'etrait M., Bouyon S., Lemari'e E., Brasseur S., Doutreleau S., P'epin J.L., Godin-Ribuot D., Belaidi E., Arnaud C. Intermittent hypoxia triggers early cardiac remodeling and contractile dysfunction in the time-course of ischemic cardiomyopathy in rats. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020; 9 (16): e016369. DOI: 10.1161.
- Nagao A., Kobayashi M., Koyasu S., Chow C.C.T., Harada H. HIF-1-dependent reprogramming of glucose metabolic pathway of cancer cells and its therapeutic significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019; 20 (2): 238. DOI: doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020238.
- Zembron-Lacny A., Tylutka A., Wacka E., Wawrzyniak-Gramacka E., Hiczkiewicz D., Kasperska A. Intermittent hypoxic exposure reduces endothelial dysfunction. Biomed Res. Int. 2020; 2020: 6479630. DOI: 10.1155/2020/6479630.
- Podkalicka P., Stfpniewski J., Mucha O., Kachamakova-Trojanowska N., Dulak J., Loboda A. Hypoxia as a Driving Force of Pluripotent Stem Cell Reprogramming and Differentiation to Endothelial Cells. Biomolecules. 2020; 10 (12): 1614. DOI: 10.3390/biom10121614.
- Kanatous S.B., Mammen P.P., Rosenberg P.B., Martin C.M., White M.D., Dimaio J.M., Huang G., Mual-lem S., Garry D.J. Hypoxia reprograms calcium signaling and regulates myoglobin expression. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2009; 296 (3): 393-402. DOI: doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00428.2008.
- Cowburn A.S., Macias D., Summers C., ChilversE.R., Johnson R.S. Cardiovascular adaptation to hypoxia and the role of peripheral resistance. Elife. 2017; 6: e28755. DOI: doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28755.
- Belisario D.C., Kopecka J., Pasino M., Akman M., Smaele E.D., Donadelli M., Riganti C. Hypoxia dictates metabolic rewiring of tumors: implications for chemoresistance. Cells. 2020; 9: 2598. DOI: 10.3390/cells9122598.
- Jun J.C., Rathore A., Younas H., Gilkes D., Polotsky V.Y. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and Cancer. Curr. Sleep. Med. Rep. 2017; 3 (1): 1-10. DOI: doi.org/10.1007/s40675-017-0062-7.
- Camuzi D., de Amorim I.S.S., Ribeiro Pinto L.F., Oliveira Trivilin L., Mencalha A.L., Soares Lima S.C. Regulation is in the air: the relationship between hypoxia and epigenetics in cancer. Cells. 2019; 8 (4): 300. DOI: doi.org/10.3390/cells8040300.
- Glazachev O.S., Kryzhanovskaya S.Y., Zapara M.A., DudnikE.N., Samartseva V.G., Susta D. Safety and efficacy of intermittent hypoxia conditioning as a new rehabilitation / secondary prevention strategy for patients with cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2021; 17 (6): e051121193317. DOI: 10.2174/1573403X17666210514005235.
- Pham K., Parikh K., Heinrich E.C. Hypoxia and inflammation: insights from high-altitude physiology. Front. Physiol. 2021; 12: 676782. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.676782.
- Santocildes G., Viscor G., Pag'es T., Ramos-Romero S., Torres J.L., Torrella J.R. Physiological effects of intermittent passive exposure to hypobaric hypoxia and cold in rats. Front. Physiol. 2021; 12: 673095. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.673095.
- Gumbert S.D., Kork F., Jackson M.L., Vanga N., Ghebremichael S.J., Wang C.Y. Perioperative acute kidney injury. Anesthesiology. 2020; 132: 180-204. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002968.
- Pramsohler S., Burtscher M., Faulhaber M., Gatterer H., Rausch L., Eliasson A. Endurance training in normobaric hypoxia imposes less physical stress for geriatric rehabilitation. Front. Physiol. 2017; 8: 514. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00514.
- Колядич Ж.В., Семеник Т.А., Андрианова Т.Д. Взаимодействие центральных и периферических хеморецепторов в условиях гипоксии и гиперкапнии. Оториноларингология. Восточн. Европа. 20l3; 12 (3): 63-75.
- Мурач Е.И., Баранов И.А., Ерлыкина Е.И. Адаптогенные эффекты композиции дигидрокверцетин-хитозан в условиях моделирования острой гипоксии. Бюл. эксперим. биол. и медицины. 2013; 156б (9): 280-283.
- Sazontova T.G., Bolotova A.V., Kostin N.V. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1a), HSPs, antioxidant enzymes and membrane resistance to ROS in endurance exercise performance after adaptive hypoxic preconditioning. Adaptation biology and medicine. 2011; 6: 161-179.
- LobodaA., JozkowiczA., Dulak J. HIF-1 and HIF-2 transcription factors - similar but not identical. Mol. Cells. 2010; 5: 435-442. DOI: 10.1007/s10059-010-0067-2.
- Semenza G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine. Cell. 2012; 148 (3): 399-408. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.021.
- Della Rocca Y., Fonticoli L., Rajan T.S., Trubiani O., Caputi S., Diomede F., Pizzicannella J., Marconi G.D. Hypoxia: molecular pathophysiological mechanisms in human diseases. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2022; 78 (4): 739-752. DOI: 10.1007/s13105-022-00912-6.
- Appelhoff R.J., Tian Y.M., Raval R.R., Turley H., Harris A.L., Pugh C.W., Ratcliffe P.J., Gleadle J.M. Differential function of the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004; 279 (37): 38458-38465. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M406026200.
- Masson N., Singleton R.S., Sekirnik R., Trudgian D.C., Ambrose L.J., Miranda M.X., Tian Y.M., Kessler B.M., Schofield C.J., Ratcliffe P.J. The FIH hydroxylase is a cellular peroxide sensor that modulates HIF transcriptional activity. EMBO Rep. 2012; 13 (3): 251-257. DOI: doi.org/10.1038/embor.2012.9.
- Haase V.H. Hypoxic regulation of erythropoiesis and iron metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2010; 299 (1): 1-13. DOI: doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00174.2010.
- Lobigs L.M., Sharpe K., Garvican-Lewis L.A., Gore C.J., Peeling P., Dawson B., Schumacher Y.O. The athlete's hematological response to hypoxia: a meta-analysis on the influence of altitude exposure on key biomarkers of erythropoiesis. Am. J. Hematol. 2018; 93 (1): 74-83. DOI: 10.1002/ajh.24941.
- Papandreou I., CairnsR.A., Fontana L., Lim A.L., Denko N.C. HIF-1 mediates adaptation to hypoxia by actively downregulating mitochondrial. oxygen consumption. Cell. Metab. 2006; 3 (3): 187-197. DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2006.01.012.
- LeMoine C.M., MorashA.J., McClelland G.B. Changes in HIF-1a protein, pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphorylation, and activity with exercise in acute and chronic hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011; 301 (4): 1098-1104. DOI: doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00070.2011.
- Fukuda R., Zhang H., Kim J.W., Shimoda L., Dang C.V., Semenza G.L. HIF-1 regulates cytochrome oxidase subunits to optimize efficiency of respiration in hypoxic cells. Cell. 2007; 129 (1): 111-122. DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.047.
- Drevytska T., Gavenauskas B., Drozdovska S., Nosar V., Dosenko V., Mankovska I. HIF-3a mRNA expression changes in different tissues and their role in adaptation to intermittent hypoxia and physical exercise. Pathophysiology. 2012; 19 (3): 205-214. DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.pathophys.2012.06.002.
- Adams J.M., Difazio L.T., Rolandelli R.H., Lujan J.J., Hasko G., Csoka B., Selmeczy Z., Nemeth Z.H. HIF-1: a key mediator in hypoxia. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2009; 96 (1): 19-28.
- Percy M.J., Furlow P.W., Lucas G.S., Li X., Lappin T.R., McMullin M.F., Lee F.S. A gain-of-function mutation in the HIF2A gene in familial erythrocytosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008; 358 (2): 162-168. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa073123.
- Gao R.Y., Wang M., Liu Q., Feng D., Wen Y., Xia Y., Colgan S.P., Eltzschig H.K., Ju C. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2a reprograms liver macrophages to protect against acute liver injury through the production of interleukin-6. Hepatology. 2020; 71 (6): 2105-2117. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30954.
- Shenoy N., Pagliaro L. Sequential pathogenesis of metastatic VHL mutant clear cell renal cell carcinoma: putting it together with a translational perspective. Ann. Oncol. 2016; 27 (9): 1685-1695. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdw241.
- Flora R., Zulkarnain M., Sorena E., Deva I.D.S., Widowati W. Correlation between hypoxia inducible factor-1a and vesicular endothelial growth factor in male wistar rat brain tissue after anaerobic exercise. Trends Med. Res. 2016; 11: 35-41. DOI: 10.3923/tmr.2016.35.41.
- Qureshi-Baig K., Kuhn D., Viry E., Pozdeev V.I., Schmitz M., Rodriguez F., Ullmann P., Koncina E., Nurmik M., Frasquilho S., Nazarov P.V., Zuegel N., Boulmont M., Karapetyan Y., Antunes L., Val D., Mittelbronn M., Janji B., Haan S., Letellier E. Hypoxia-induced autophagy drives colorectal cancer initiation and progression by activating the PRKC/PKC-EZR (ezrin) pathway. Autophagy. 2020; 16: 14361452. DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1687213.
- Hubbi M.E., Hu H., Kshitiz Ahmed I., Levchenko A., Semenza G.L. Chaperone-mediated autophagy targets hypoxia-inducible factor-1a (HIF-1a) for lysosomal degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013; 288 (15): 10703-10714. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.414771.
- Kiers D., Wielockx B., Peters E., van Eijk L.T., Gerretsen J., John A., Janssen E., Groeneveld R., Peters M., Damen L., Meneses A.M., Krüger A., Langereis J.D., Zomer A.L., Blackburn M.R., Joosten LA., Netea M.G., Riksen N.P., van der Hoeven J. G., Scheffer G.J., Eltzschig H.K., Pickkers P., KoxM. Short-term hypoxia dampens inflammation in vivo via enhanced adenosine release and adenosine 2B receptor stimulation. EBioMedicine. 2018; 33: 144-156. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.06.021.
- LiX., Berg N.K., Mills T., Zhang K., Eltzschig H.K., Yuan X. Adenosine at the interphase of hypoxia and inflammation in lung injury. Front. Immunol. 2021; 11: 604944. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.604944.
- Vohwinkel C.U., Coit E.J., Burns N., Elajaili H., Hernandez-Saavedra D., Yuan X., Eckle T., Nozik E., Tuder R.M., Eltzschig H.K. Targeting alveolar-specific succinate dehydrogenase A attenuates pulmonary inflammation during acute lung injury. FASEB J. 2021; 35 (4): e21468. DOI: 10.1096/fj.202002778R.
- Wang W., Chen N.Y., Ren D., Davies J., Philip K., Eltzschig H.K., Blackburn M.R., Akkanti B., Karmouty-Quintana H., Weng T. Enhancing extracellular adenosine levels restores barrier function in acute lung injury through expression of focal adhesion proteins. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021; 8: 636678. DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.636678.
- Effendi W.I., Nagano T. A2B Adenosine receptor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: pursuing proper pit stop to interfere with disease progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023; 24 (5): 4428. DOI: 10.3390/ ijms24054428.


