Morphological aspects of orbital defect reconstruction in rats with elastin-based biomaterial
Автор: Anna I. Lebedeva, Rafik T. Nigmatullin, Rinat Z. Kutushev
Журнал: Saratov Medical Journal @sarmj
Статья в выпуске: 1 Vol.2, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The objective of the study was to identify morphological aspects of replacement of xenogeneic decellularized elastin matrix (ХDEM) transplanted into a bone defect of the upper orbital wall in rats. Materials and methods. The experiment was performed on 60 Wistar rats with artificially created 7×4 mm defect in the upper edge of their orbit. In the experimental group (n=30), DХEM was placed in the defect area. Its size matched the size of the defect, and it was attached with a suture material (50 μm silk). Soft tissues were sutured layer by layer in the control group (n=30). Tissue excision was performed after 1, 3 and 12 months. Histological, immunohistochemical and electron microscopic methods were employed. Results. We were gradually replacing DХEM with bone tissue against the background of a pronounced reaction of CD68+/MMP-9+ macrophages, which implied its resorption and lysis. Osteogenesis occurred via intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification, which was preceded by centripetal migration of endothelial kidneys with subsequent differentiation into capillaries and overgrowth of loose fibrous connective tissue containing progenitor cells. The microenvironment, represented by reticulin fibers, TGF-β1, and sulfated glycosaminoglycans, could contribute to the differentiation of progenitor cells in the osteogenic direction and to osteogenesis per se. In the control group, the defect remained open throughout the experiment. Conclusion. Decellularized biomaterial, based on elastin matrix, has osteoconductive and osteoinductive properties and can serve an adequate biomimetic for reconstruction of the bone defects.
Xenogeneic elastin biomaterial, transplantation, regeneration, orbital bones
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149135017
IDR: 149135017 | DOI: 10.15275/sarmj.2021.0101
Текст научной статьи Morphological aspects of orbital defect reconstruction in rats with elastin-based biomaterial
The problem of vibroacoustic stimulation of bone growth remains relevant at present. Traumatic damage to the orbital bones may lead to the formation of extensive defects. The lack of bone tissue and its inadequate regeneration may result in irreversible consequences associated with a high risk of complications in the visual system and the nervous system. Currently, bone tissue autotransplantation is considered the best available standard procedure of the bone volume restoration [1]. However, this method has certain limitations regarding the volume of bone tissue, traumatism and significant defects at the site of bone tissue collection [2]. Xenogeneic biomaterial has a number of advantages: it is harvested in advance, has a long shelf life in the absence of raw materials’ shortage and availability, etc.
One of the methods of directed bone regeneration is the method of bone engineering using such readily available productive bone-replacing biomaterials as xenogeneic decellularized elastin matrix (XDEM) (patent No. 2440148) © 2021, Saratov State Medical University, Saratov, Russia © 2021, LLC Innovative Medical Technologies, Saratov, Russia © 2021, LLC Science and Innovations, Saratov, Russia
-
[3] . However, each specific case of using the graft requires comprehensive investigation.
Objective : to identify morphological aspects of the replacement of xenogeneic decellularized elastin matrix transplanted into a bone defect of the upper orbital wall in rats.
Materials and methods
The experiment was performed on 60 Wistar rats with artificially created 7×4 mm defect in the upper edge of their orbit. For this purpose, a KaVo INTRAsurg 1000 physiological dispenser with a 3 mm tip was used. The study was conducted in compliance with the Good Clinical Practice standards and the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee. In the experimental group (n=30), ХDEM was placed in the defect area. The removed bone fragment included most of the upper rim of the orbit and served a model of extensive orbital trauma. It was covered with a membrane fibrous connective tissue graft from above. Its size matched the size of the defect. The entire complex of transplanted tissues was attached to the edges of the bone defect with a silk ligature 50 µm in diameter. Interrupted sutures were applied to the skin. In the control group (n = 30), a similar defect was created, in which soft tissues were sutured layer by layer. Excision of biopsy tissues was performed after 1, 3 and 12 months. XDEM was made from the nuchal ligament of cattle and was subjected to physicochemical treatment in accordance with the developed protocol (Technical Conditions No. 42-2-537-87).
The tissues under study were fixed in a 10% solution of neutral formalin, dehydrated in a series of alcohols of increasing concentration, and embedded in paraffin according to the conventional technique. Cross-sections were prepared on a LEICA RM 2145 microtome (Germany). They were stained with hematoxylin and eosin sensu Van Gieson, Mallory, Hale, and with Alcian blue at pH 1.0, as well as at pH 2.5 after the methylation. Then they were impregnated with silver salts sensu Foot.
For immunohistochemical studies, paraffin sections 4 μm thick were stained using Leica Microsystems Bond™ immunohistostaining (Germany). We used c-KIT, CD68, Thy-1, FGF-β, MMP-9, PECAM, TGF-β1, Col1, Col3 at a dilution of 1:300 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA) as initial antibodies. An indirect streptavidin-biotin detection system Leica BOND (Novocastra™, Germany) was used for unmasking. The study and visualization of tissue crosssections were carried out using a light microscope Leica DMD108 (Germany).
For electron microscopic examination, we cut out 1-2 mm3 tissue fragments from biopsy pieces and fixed them in a 2.5% solution of glutaraldehyde prepared in a cacodylate buffer (pH 7.2-7.4), with further fixation in a 1% solution of OsO 4 in the same buffer. The material was then dehydrated in alcohols of increasing concentration and poured into Epon 812 in accordance with the conventional method. Semithin tissue sections were preliminarily prepared on an EM UC7 ultramicrotome (Leica, Germany) and stained with a solution of toluidine blue in a 2.5% solution of anhydrous sodium carbonate. On these sections, areas were selected for electron microscopic examination. Ultrathin sections were contrasted with a 2% aqueous solution of uranyl acetate, lead citrate sensu Reynolds, and studied under the JEM-1011 transmission microscope (Jeol Ltd., Japan).
Results
In the experimental group, 30 days after XDEM transplantation, we observed infiltrative growth of collagen fibers into the interfiber spaces of the biomaterial in addition to the signs of perifocal proliferation of a fibrous connective tissue. The surrounding fibrous connective tissue retained the edges of the graft with orbital bone defects, thus facilitating the reposition and firm attachment of the graft material to the edges of the bone base. In the interfiber spaces of the biomaterial, we identified thin layers of loose fibrous connective tissue, which formed a network in the centripetal direction. Upon impregnation with silver salts and identification of collagen, it was revealed that the fibrous component of the newly formed connective tissue exhibited argentophilic properties and was defined as the type III collagen (Col3). These reticulin fibers are characteristic of immature granulation tissue. Infiltration of the formed fibrous connective tissue, surrounding XDEM, was macrophage-fibroblastic with the involvement of osteogenic and poorly differentiated cells. Lymphocytes were sporadic in the field of view. In addition, there were signs of FGF β+ cell migration. They were present both in the perifocal area and in the central regions of the graft. TGF-β1+ cells were found in small numbers as well. Their number was visually comparable to the number of macrophages and/or FGF-β+ cells.
At this time, the fragments of incipient bone tissue were revealed in the form of small rounded clusters localized along the periphery. The latter are called osteoid and are surrounded by osteoblasts. The cytoplasm of osteoblasts contained numerous reduced channels of the granular endoplasmic reticulum. Centrosomes were identified in the cytosol. Mitochondria were oval, small, with a dense mitochondrial matrix. Cell membrane formed thin, long outgrowths. The nucleus showed signs of activation: it contained uniformly distributed euchromatin. Ultrastructure of the cells indicated their active synthetic function and mitotic readiness ( Fig. 1A ). Macrophages were detected near the biomaterial. They showed signs of active phagocytic activity. Numerous phagosomes and residual bodies were found in their expanded ectoplasm ( Fig. 1B ).
Endothelial PECAM+ cells were penetrating the interfiber spaces and were found near osteoid, which were the early centers of ossification ( Fig. 2A ). We observed c-KIT+ and Thy-1+ cells within the loose fibrous connective tissue, in particular, near the capillaries. Therefore, the cells were either hematogenous of a bone marrow origin, or were mural cells of blood vessels ( Fig. 2B ).
When the total fraction of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) was detected, the reaction was positive. During their differentiation, it was discovered that the bulk of those were sulfated GAGs: dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate, chondroitin 4- sulfate, and chondroitin 6-sulfate. Non-sulfated GAGs were not detected.
Signs of ongoing replacement of xenogeneic elastin biomaterial in the tissue with regenerated connective tissue and bone were detected 90 days after the surgery. MMP-9+ and CD68+ cells were detected in the perifocal zone and, most likely, contributed to the destruction and lysis of elastic fibers. Around the elastin matrix, the bone tissue was formed, which, in the form of a bone capsule, encrusted the matrix on all sides. From the side of the original bone periosteum, the signs of migration of periosteum osteogenic cells towards XDEM were recorded.
Fig. 1. Infiltration of xenogeneic decellularized elastin matrix. TEM images:
А – osteoblasts; В – macrophages
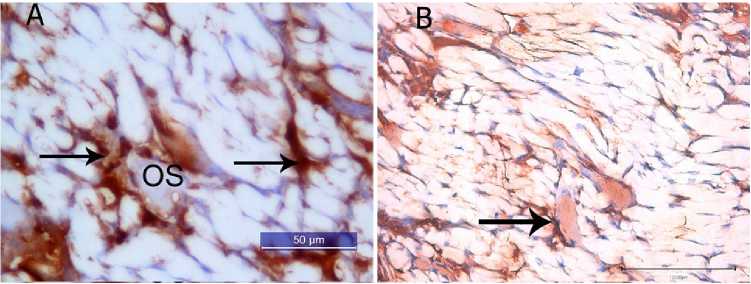
Fig. 2. Proliferation of blood vessels in the interfiber spaces of the biomaterial with mural cells:
А – osteoid (OS) surrounded by PECAM+ cells ( ↑ ) in the interfiber spaces of xenogeneic decellularized elastin matrix. Indirect immunoperoxidase method for PECAM detection with additional hematoxylin staining; В – identification of с-KIT+ cells ( ↑ ). Indirect immunoperoxidase method for detecting c-KIT with additional hematoxylin staining
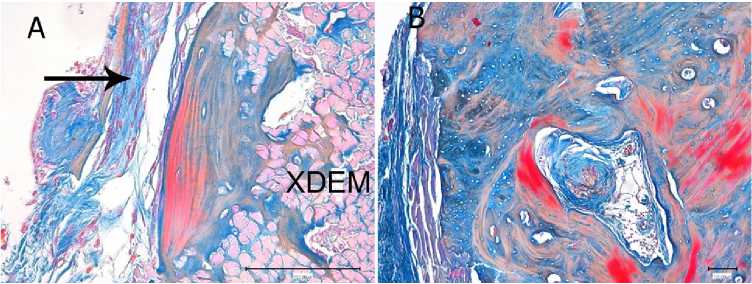
Fig. 3. Replacement of xenogeneic decellularized elastin matrix (XDEM) with bone tissue:
А – osteogenesis after 90 days. Fragments of biomaterial are detectable. Newly formed fibrous connective tissue is periosteum ( ↑ ); В – newly formed cancellous bone after 365 days, Haversian canals, blood vessels. Mallory’s stain
The newly formed bone gradually grew and differentiated. The osteon structure of the bone was determined by the presence of lamellae. The plates formed Haversian canals containing loose fibrous connective tissue and osteogenic cells ( Fig. 3A ). The connective tissue membrane serving as a graft limiter was gradually lysed and resorbed by macrophages. Fibroblasts migrated to replace phagocytes, and the connective tissue graft was replaced with autologous fibrous connective tissue in accordance with a specified vector. Thus, the newly formed bone was covered outside with a dense fibrous connective tissue.
After 365 days, all animals in the experimental group (100%) exhibited a regenerate consisting of differentiated bone tissue with all its structural elements present: Haversian canals and Volkmann’s canals with a developed network of capillaries. Immured osteocytes were found in the bone lacunae. The newly formed bone matrix retained the features of the chronological heterogeneity of the matrix. In part of the bone, the fibrous matrix still predominated, while the bone consisted mainly of dense lamellae. The newly formed bone was covered by the periosteum ( Figure 3B ).
In the control group, the defect remained open in all animals throughout the experiment. Bone tissue was not formed over the entire orbital wound area. At the site of the defect, fibrous connective tissue proliferated. Progenitor fibroblastic cells Thy-1+, as well as profibrogenic growth factors FGF-β and TGF-β1 were virtually absent. The immunohistochemical study revealed that macrophages CD68+ were contained in the stroma in small numbers and only during the initial stage of the experiment, as well as MMP-9+ cells.
Discussion
In the experimental group, in the area of elastin biomaterial transplantation, cancellous bone was formed, which replaced the defect throughout the entire wound surface. A number of key factors preceded a more productive and efficient course of healing in the experimental group. XDEM served a substrate replacing a bone defect and meeting the requirements for biocompatibility of biomaterials [4].
Analyzing the cellular response to transplantation of elastin biomaterial, it can be concluded that XDEM was rather inert and did not induce immune inflammation in the tissue. The cellular reaction 30 days after the transplantation was aimed at fibrosis of the biomaterial. The lymphocytic reaction was weak. It was observed mainly at the initial stage of replacement, since it was probably associated with surgical trauma. Consequently, the elastin biomaterial had a low immunogenicity.
We discovered that XDEM was a chemoattractant of a moderate amount of CD68+ macrophages, which indicated its gradual lysis and resorption. The congestion of the cytoplasm with secondary vacuoles is a clear indicator of the elastin matrix biodegradation. MMP-9 is an enzyme of the metalloproteinase family and is involved in extracellular matrix remodeling. Sources of MMP-9 are keratinocytes, monocytes, leukocytes, macrophages, and fibroblasts [5]. Matrix metallopeptidases cause degradation of extracellular matrix components, such as basement membrane components (type IV collagen, laminin, entactin, proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans); type I, II, and III collagens, fibronectin, non-fibrillar collagens, and elastin. The latter, when it is excessively concentrated, contributes to both tissue degradation and fibrosis. The number and localization of CD68+ and MMP-9+ cells were comparable; therefore, it could be assumed that macrophage cells were the main source of collagenases. We are aware of the heterogeneity and polarity of macrophage cells. They can secrete either profibrogenic or proinflammatory factors [6]. Based on the presented data, the phenotype of macrophages corresponded to M2 differentiation, which confirmed the low immunogenicity of the graft.
Fibrogenic factors FGF-β and TGF-β1 can activate various cell populations: macrophages, fibroblasts, and myofibroblasts. The identified cytokines stimulate the development of poorly differentiated cells in the fibroblastic direction and their synthesis of both collagen fibers and newly formed stroma. It is also known that FGF-β and TGF-β1 are potent angiogenic factors [7]. In our experiment, these facts were confirmed by the active growth of the extracellular matrix, represented by type III collagen – reticulin fibers and sulfated glycosaminoglycans.
Along with collagen genesis, intensive angiogenesis was occurring, which preceded resorption and fibrous replacement of the biomaterial. There was a centripetal migration of endothelial kidneys (PECAM+) followed by differentiation into capillaries in the interfiber spaces. Recent studies have shown that exosomes secreted by endothelial cells were directly related to osteogenesis. Bone lesions mobilize endothelial progenitor cells from the bone marrow into peripheral blood, directing them to damaged bone areas, which could promote angiogenesis and bone regeneration. Along with angiogenesis, the action of stromal cell-derived factor-1, present in pericytes, also contributes to accelerated healing and effective mineralization. With a deficiency of endothelial-derived exosomes, effective bone regeneration does not occur; hence, the healing time substantially extends [8].
In our study, mesenchymal stem cells c-KIT and Thy-1 were detected among the mural cells. If Thy-1 cells are regarded as progenitor fibroblastic cells, then c-KIT+ cells can be represented by pericytes. Pericytes are present in any organ as part of microvessels. They are able to differentiate in osteogenic, adipogenic, chondrogenic and mural directions. It is known that c-KIT+ – poorly differentiated primitive mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) – have pluripotency and, hence, can develop into various cell clones: osteogenic, adipogenic chondrogenic, and angiogenic (endotheliocytes and pericytes) [9].
The microenvironment, represented by reticulin fibers (Col3) and containing TGF-β1 with sulfated glycosaminoglycans, could contribute to the differentiation of progenitor cells in the osteogenic direction and the formation of mineralized clusters and bone calluses. TGF-β1 is one of the members of the TGF-β family, and its role in bone remodeling is well understood. It stimulates the differentiation of MSC into osteoblasts [10]. The mechanical properties of a biomaterial may have both direct and indirect effects on the cell response, in particular on MSC. It is also known that mechanical properties of the matrix play an important role in the fate of cells, and a number of stem cells are particularly sensitive to mechanical rigidity. Latent TGF-β binding proteins are key components of the large latent complex. They bind to elastin scaffold proteins and elastin cross-linking proteins, such as fibrillin-1 and fibulin-5. Given these data, proteolytic degradation of elastin and release of TGF-β may be one of the mechanisms contributing to the development of vascular calcification [11].
It is recognized that mechanical, structural and biochemical signals affect the biological activity of cells. This set of substrate properties can act synergistically or destructively, or else, it can differentially initiate cell responses to other signals, making strategies for orthogonal control of these signals an important project design goal. The results presented in this publication provide important evidence for the principle of coordinated approach to studying the intersection of mechanical and biomolecular signals. We have discovered that the matrix rigidity promoted osteogenic proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal cells.
Recent published sources indicated that, when an elastinlike protein was used, osteogenic differentiation was manifested in stem cells of human adipose tissue, and a closer resemblance to the natural mechanism of bone tissue formation was demonstrated, compared with collagen hydrogels. Elastin matrix has stronger and more rigid mechanical properties versus collagen matrices. The threedimensional structure of the extracellular matrix influences cell orientation and differentiation. It has been shown that more rigid collagen-glycosaminoglycan substrates direct the osteogenic bond of adipose tissue stem cells regardless of the presence or absence of growth factors, which significantly affects the microstructural signals, presented to stem cells, and increases the extent of their osteogenic response [12].
Hence, the results of our study are consistent with the results of other scientists, confirming the hypothesis that a more rigid scaffold would mimic similar extracellular microenvironment of native bone cells and signal the cells about proliferation, differentiation and mineralization to a greater extent. The connective tissue graft, which served as a case for the elastin complex, did not have mechanical rigidity and was replaced by fibrous connective tissue.
In the control group, we observed the absence of cells with earlier described spectrum of growth factors, which implied a weakening of reactive fibrosing processes in the tissue and stabilization of relationships between cells and the stroma. As a result, incomplete osteogenesis was observed due to bone tissue deficiency.
Thus, analyzing our results, we can conclude that, in the experimental group, osteogenesis occurred via intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification. XDEM possesses the osteoconductive properties – i.e., it serves a matrix for the formation of a new bone during reparative osteogenesis and is able to direct its growth. Also, it possesses osteoprotective properties, which means that it replaces the bone in terms of its mechanical properties.
Conclusion
Decellularized biomaterial, based on the elastin matrix, has osteoconductive and osteoinductive properties and can serve an adequate biomimetic for the restoration of bone defects. The study presented in this article serves the basis for the ongoing research in our laboratory on increasing the regenerative potential of spatially-graded elastin scaffolds for the reconstruction of bone defects.
Acknowledgеments
The study was completed within the framework of the Government Procurement No. 056-00110-18-00, 26 December, 2017.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Список литературы Morphological aspects of orbital defect reconstruction in rats with elastin-based biomaterial
- Sjostrom M, Sennerby L, Nilson H, et al. Reconstruction of the atrophic edentulous maxilla with free iliac crest grafts and implants: a 3-year report of a prospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2007; 9 (1): 46-59. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2007.00034.x
- Joshi A. An investigation of post-operative morbidity following chin graft surgery. Brit Dent J 2004; 196 (4): 215-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.4810987
- Muldashev ER, Nigmatullin RT, Galimova VU, et al. Xenogeneic biomaterial for regenerative surgery. Patent No. 2440148.; priority of 21 December, 2009; publ. 20 January, 2012, Bull. 2. (In Russian).
- Sevastyanov VI. Biocompatibility. Moscow: Information Center of VNII Geosystem, 1999; 367 p. (In Russian).
- Benyon RC, Iredate JP. Is liver fibrosis reversible? Gut 2000; 46: 443-6. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.46.4.443
- Van Ginderachter JA, Movahedi K, Hassanzadeh Ghassabeh G, et al. Classical and alternative activation of mononuclear phagocytes: Picking the best of both worlds for tumor promotion. Immunobiology 2006; 211 (6-8): 487-501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2006.06.002.
- Rachmiel A, Leiser Y. The molecular and cellular events that take place during craniofacial distraction osteogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2014; 2: e98. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000000043
- Jia Y, Zhu Y, Qiu Sh, Xu J, et al. Exosomes secreted by endothelial progenitor cells accelerate bone regeneration during distraction osteogenesis by stimulating angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019; 10: 12.https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-1115-7
- Pavlova SV, Rozanova IA, Chepeleva EV, et al. Angiogenic potential of cardiac stem and mesenchymal stromal cells of bone marrow in rats. Circulatory Pathology and Cardiac Surgery 2015; 19 (4-2): 77-84. (In Russian).
- Hu BT, Chen WZ. MOTS-c improves osteoporosis by promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via TGF-β/Smad pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2018; 22 (21): 7156-63. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201811_16247
- Ngai D, Lino M, Bendeck MP. Cell-matrix interactions and matricrine signaling in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification. Front Cardiovasc Med 2018; 5: 174. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2018.00174
- Gurumurthy B, Bierdeman PC, Janorkar AV. Composition of elastin like polypeptide–collagen composite scaffold influences in vitro osteogenic activity of human adipose derived stem cells. Dental Materials 2016; 32 (10): 1270-80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2016.07.009


