Municipal-private partnership in education: infrastructural aspect
Автор: Frolova Elena Viktorovna, Rogach Olga Vladimirovna
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Social development
Статья в выпуске: 1 (49) т.10, 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article considers the specifics of implementation of municipal-private partnership projects in the education system of the Russian Federation. The authors use the following research methods: document analysis, expert interviews (heads of local authorities, entrepreneurs from the Moscow Oblast). The goal of this article is to study specific features of public-private partnership in education, to carry out comparative analysis of the estimates that the heads of local authorities and the business community have with regard to these issues, to define the conditions for their effective interaction and its limiting factors. Attracting private investment in the development of the education system is limited by a narrow pragmatic focus of the government on the use of financial resources of business in municipal administration practice. Judging by the results of studies, the heads of local authorities understand the social partnership of business and government as gratuitous help from socially responsible companies who are willing to invest funds in the development of a municipality...
Municipal-private partnership, social infrastructure, local government, education system, municipal entities
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223903
IDR: 147223903 | УДК: 352.07 | DOI: 10.15838/esc.2017.1.49.8
Текст научной статьи Municipal-private partnership in education: infrastructural aspect
Introduction. The trends and challenges of contemporary reality expressed in the change in conceptual ideas about the role, objectives and content of education in the modern world have resulted in a significant transformation of the education basis management in Russia. Nowadays the most important are trends and patterns of education development which carry the potential of social solidarity and consolidation which involves an increase in public participation in education management. The leading mechanism which ensures the necessary transformation of social relations existing in the Russian educational system is the mechanism of social partnership which in new conditions is aimed at ensuring constructive alignment of interests of actors of the educational space.
Modern scientific literature on the establishment of “power-society” partnership relations in education is focused on statepublic education management and as a result, on public-private partnership. Analysis of theoretical and applied aspects of public-private partnership application in various spheres of social development helps interpret this concept as cooperation on a contractual basis of state authorities and representatives of business units in order to improve the quality of services provided to the population. A simple transposition of this term into contemporary education and state management practice does not seem appropriate since the peculiarities of public administration implies the presence of both various community groups as an active subject of partnership relations (parents, teachers, etc.) and business units. This provision is noticeable in piecemeal attempts to promote social demand for education.
However, without considering such an important aspect of public-private partnership in education in terms of scientific research, the scientific community cannot provide a comprehensive idea about the relation of social partnership mechanism and the quality of modern education. This is explained by the fact that the principles of democratization and public opinion monitoring which form the basis of modern education management necessitate the Russian society to introduce social innovations designed to integrate the practices of social process management and self-administration technologies. Moreover, an important role positive sustainable development of education in Russia belongs to the quality of managerial influence of municipal authorities which defines the organizational efficiency of activity of the subjects of educational sphere [11].
That is why municipal-private partnership in education should be the subject of separate applied research. The importance of this issue is confirmed by significant differences in municipal and government practice of building partnership relations, which does not permit consideration of publicprivate and municipal-private partnership as identical in content. This is not only the issue of the differences in the scope and forms of realization, but also about the necessity of establishing partnership by municipal authorities in several ways: with the business community for attracting investment, with government authorities (at the regional and federal level), with the public (target groups and public organizations). The use of the mechanism of municipal-private partnership in municipal education management is hampered by substantial scarcity of financial, material and other resources of municipal authorities, including authority resources.
In addition, in the authors’ opinion, municipal-private partnership is a narrower category compared to social partnership. This is due to the fact that in social partnership the subjects of constructive cooperation based on association of potentials may be all active actors of the educational sphere: except for traditional actors including scientific community, public organizations and movements, and if necessary, the media. However, in modern practice of education management the efforts made by these actors are vague and ambiguous, which primarily concerns the forms of social partnership which the public takes part in (parent communities, supervisory and management boards, various formal and informal social associations which help educational institutions meet their direct obligations). As for public-private partnership, the situation is the opposite, namely, the number of partner actors (they include, as a rule, government and business) is reducing and, as a consequence, the issues of interaction are narrow-targeted. Municipalprivate partnership has a strong economic effect of its application and a financial value for the development of municipal educational complex. Special attention should be given to the fact that these differences are not formalized characteristics of these categories; however, for addressing the objective set in the present study article, the authors suggests to separate the concepts of municipal-private and social partnership.
To characterize the aforementioned ideas in more detail, the following conclusions have been made:
– the major actors of municipal-private partnership are the government (municipal authorities) and the private sector (business structures);
– municipal-private partnership seems the most cost-effective form of interaction of subjects for implementing perspective municipal education development projects, with no similar alternatives in modern management practices;
– the beneficiaries of municipal-private partnership are municipal authorities with, according to the contract, deferred income and other benefits reflected in the socioeconomic development of a municipal territory, as well as in developing human, intellectual and educational potential of the territory (in the past decade, this figure has been steadily increasing its importance); and business structures which can gain income from municipal property transferred to them by the authorities on a trust property management basis, as well as indirect benefits from reducing the tax burden, etc.
Based on the abovementioned, the authors suggest considering municipal-private partnership in education from the perspective of building constructive interaction with municipal authorities and the business community through consolidation of socio-economic resources on a long-term mutually beneficial basis in order to solve the problems of municipal educational complex development. In the context of this interpretation of municipal-private partnership public or private management is not an adequate alternative as they neutralize the social and economic effect which can be achieved by bringing together efforts and capacity of government and society.
Methodology and methods. Analysis of management of municipal unit social infrastructure development in contemporary
Russia is conducted in the works of A.Yu. Bochkarev [1], O.O. Skryabin [12], J.E. Perevozkina [9], S.P. Fedulov [13].
The role of public-private partnership as a way of establishing interaction between the state and private business, used in the development of social infrastructure is described in works of A.A. Grabar [5], V.G. Varnavskii, A.V. Klimenko [2]. The need for introducing a mechanism of municipalprivate partnership into local governments is justified by A.E. Lapin and I.F. Aliullov [7]. Special attention to issues of consolidated efforts of society and government on solving the issues of education is presented in works of E.V. Piskunova [10] and T.P. Griboedova [4]. The effect of the mechanism of publicprivate partnership in education, its nature and general development trends are described by V.A. Malygin, A.V. Skorobogatov, T.V. Kramin [3], I. Dan’ko [6] etc.
The problematic aspects of using the mechanism of municipal-private partnership when addressing the issues municipal educational complexes functioning and development are revealed in work of N.V. Medvedeva [8]. The practice of publicprivate partnership project implementation in foreign experience is considered in works of M. Simons [17], N. Papanastasiou [18], W.D. Robertson [19]; the role of publicprivate partnership in improving educational programs for teachers is identified in the work of F.W. Tate and E. Malancharuvil-Berkes [20].
However, in scientific literature, the issues revealing the specific character of municipalprivate partnership development factors have not been studied completely. The importance of these processes for socio-economic development of the Russian society in general and education, in particular, requires a more detailed research of constraints, limiting factors in municipal-private partnership development, as well as development of recommendations for improving its efficiency, and optimization of business and government interaction. The purpose for this article is to study the specific characteristics of municipal-private partnership in the social sphere, to conduct comparative analysis of evaluations of local authorities and business community managers concerning the issues of municipal-private partnerships in education, the definition of limiting factors and conditions for their effective cooperation during the implementation of infrastructure projects.
The informational basis includes the results of sociological research conducted by the All-Russian Council of Local SelfGovernment (with our participation) through distributing questionnaires on the Internet. The first study was conducted in 2013, the sampling included experts (leaders of local municipal authorities). The research topic –
“Investment potential of a municipal unit” (N=718). One of the research objectives was analysis of issues of social infrastructure development in various types of municipal entities of the Russian Federation, determination of the limiting factors and the social infrastructure modernization potential. In March–April 2016 the study “Human resources of local self-government” was conducted (N=582) which reviews the state of personnel capacity in municipal units, as well as a number of issues characterizing the socioeconomic factors in local self-government development.
Moreover, in 2015 an expert survey was conducted with participation of entrepreneurs in the Moscow Oblast (N=64) aimed at identifying the specific characteristics of implementation of municipal-private partnership projects and assessing its feasibility and limitations.
After assessing the current state of municipal management of education, the authors suggest that a significant disadvantage of managerial influence of municipal authorities is disagreement in the positions of the authorities and the public (especially businesses) about the nature and specific character of municipal-private partnership in education. In their research, the authors proceeded from the fact that the most promising area of implementing the practice of municipal-private partnership in education is the infrastructure of municipal educational complex. Moreover, it is undeniable that the degree and quality of providing the territories with the appropriate infrastructure creates favorable conditions for socioeconomic development of municipal units. Before proceeding to the presentation of the research results, the authors define the research position concerning the correlation of the concepts “education” and “social infrastructure”: in particular, in the context of this article infrastructure of an educational network and social infrastructure can be considered as two equivalent concepts as they imply the study of social profile of the territory’s infrastructure development with a focus on the educational potential of municipal territories.
Research results. According to expert evaluations, the current level of infrastructure support of the vast majority of municipal units is not high enough, which is usually associated with their weak financial and economic basis. Financial resources of local authorities only help maintain the current level of social infrastructure without supporting the process of its development. In this situation, municipal units are not able to fully finance the implementation of all social obligations of the state, which results in the violation of constitutional rights for the residents’ equal access to social benefits and services.
Analysis of the budgetary system of the Russian Federation does not help identify clear principles of tax revenue division between budgets of different levels. The structure of federal taxes is mainly determined by the profitability factor since they include tax payments which provide the largest amounts of revenues. Analysis of statutory regulations of budget legislation and helps make a conclusion about the artificial subsidization of both Russian constituent entities and municipal units. Exemption from the major share of tax revenues in favor of superior budgets and their return in the form of inter-budgetary transfers maintains high level of power centralization, dependence of local authorities on regional and federal ones [14, p. 163].
According to the research results, 74.9% of heads of local authorities, when assessing the budget capacity of their authorities in 2015 said that the need of a municipal unit for finance exceeded budgeted allocations. The research results illustrate the deterioration of the economic and financial situation in local self-government. More than half of the experts (58.4%) believe that the revenues of a municipal unit in 2015 declined compared to 2014.
This fact raises a new issue concerning the need to search for additional municipal education resources, in particular by involving actors of the educational sphere for expanding and developing educational infrastructure. In this context of municipal authority functioning the use of the mechanism of municipal-private partnership in education is not only an effective tool for infrastructure development of municipal educational systems, but also a means of overcoming crisis phenomena in the economy of municipal units, thus ensuring positive and sustainable development of the whole territory.
Analysis of issues of implementation of the mechanism of municipal-private partnership in education indicates that the level of actual
Evaluations of educational infrastructure in the Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation
|
Mark |
Municipal district |
Urban district |
Urban settlement |
Rural settlement |
|
“1” |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1.8 |
|
“2” |
0.7 |
0 |
0 |
1.8 |
|
“3” |
7.4 |
4.4 |
21.4 |
17.1 |
|
“4” |
69.1 |
64.8 |
52.4 |
62.7 |
|
“5” |
22.8 |
30.8 |
26.2 |
16.6 |
|
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
|
Compiled from results of survey of local heads of local authorities. |
||||
supply of municipal and urban districts of the Moscow Oblast of social infrastructure amenities by a number of indicators significantly below standard requirements ( Table ). Particular difficulties occur in providing municipal units with pre-school educational establishments (70% of municipal units). According to research results, the most severe situation is typical of rural settlements.
The results of population surveys indicate that the most significant issues of secondary education are high prices, unavailability of paid services, and low logistical support of educational institutions. As for preschool education, the evaluations of experts and the public are lower. The most acute problem is shortage of places in kindergartens. According to the Federal State Statistics Service, the number of children registered with preschool educational establishments is 2,849.9. Statistical data also indicate the negative dynamics of the level of support for child preschool educational establishments, which has a disincentive effect on the population’s quality of life forming a negative perception and low estimates of the level of social infrastructure development. Thus, in 2014, there were 51 thousand organizations engaged in preschool educational programs, in 2015 – 50.1 thousand [16].
Municipal-private partnership in the estimates of heads of local authorities. In order to mitigate the problems of providing municipal units with educational infrastructure amenities it seems appropriate to attract private partners as the most effective mechanism for addressing this issue as they are focused on constructive cooperation with municipal authorities. The need for private investment is particularly acute at the municipal level. Most of the experts noted that budget efficiency the main effort should be aimed at establishing mutually beneficial cooperation with the business community for developing the territory’s social infrastructure and increasing the level and quality of life. However, as shown by the research results, heads of local authorities consider social partnership of business and government as pro bono support from socially responsible companies ready to invest in the development of a municipal unit [15, p. 56]. Answering the question “Is business actively involved in the development of the social infrastructure of your municipal unit?”, only 4.2% of respondents chose the answer “Yes, in the framework of public-private partnership” (Figure). The rest of the answers illustrated the implementation of traditional forms of interaction with the business community.
It is interesting that the majority of experts (80.6%) believe that the most effective tool for addressing the issues of social infrastructure is municipal-private partnership; however, they rarely use this practice (4.2%). The propagated idea of corporate social
Distribution of answers to the question:
“Is business actively involved in the development of the social infrastructure of your municipal unit?”, %
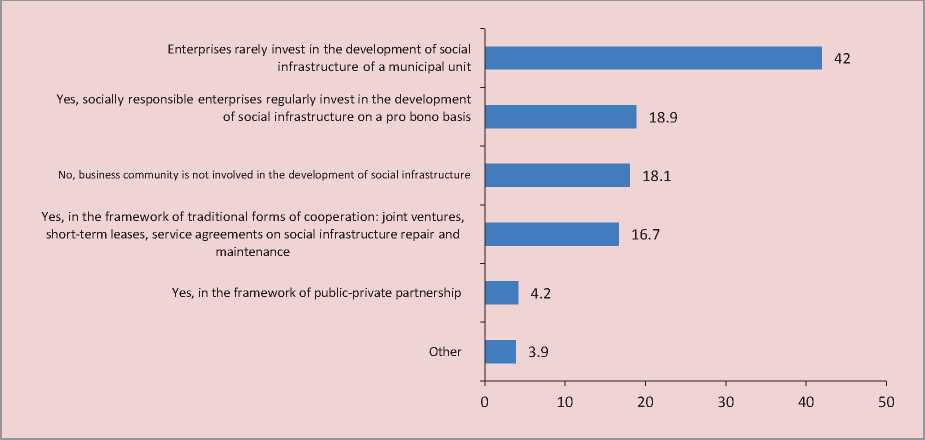
responsibility determines the formation of a sustainable system of partners in cooperation of government and the business community who mainly invest in the development of social infrastructure of the municipal on a pro bono basis.
The authors also review expert evaluation of factors limiting effective collaboration between business and government implemented for the development of social infrastructure of Russian territories. Leaders of local authorities consider that the most significant limitation is municipal budget deficit (76.2 % indicated the importance of this factor) which prevents the government from acting as an effective partner in implementing joint infrastructure projects. Among financial, economic and regulatory constraints is also lack of motivation from municipal authorities for private investment (70.1% of experts rated this factor as very important). According to experts, tax burden reduction and income tax exemption could be sufficiently effective incentives for attracting businesses to solving social problems of the territory. The most important factors (64.8% and 64.1%, respectively) are inadequate legal framework, lengthy and complex approval procedures.
Judging by the research results, the second level constraints are organizational and informational factors. Thus, 54.3% of experts believe that the target focus of the projects on large businesses significantly limits the effectiveness of their implementation. According to 37.7% of heads of local authorities, investors’ limited access to information affects the implementation of municipal-private partnership. The average significance of this factor is noted by 45.1% of respondents, while 43.9% of heads of local authorities believe that the stereotypes of public-private partnership project unprofitability significantly limit their implementation.
Municipal-private partnership in the evaluations of entrepreneurs. To identify possible issues of implementing municipalprivate partnership in education (infrastructural aspect) in 2015 the authors conducted a monitoring of opinions of entrepreneurs in the Moscow Oblast (N=64) regarding the feasibility and complexity of municipal project implementation.
The study has showed that 42% of respondents assess the condition of educational institutions as “satisfactory”, while 39% of respondents characterize it as “bad”. 66% of entrepreneurs believe that the number of educational institutions which serve as city infrastructure assets of the Moscow Oblast is clearly insufficient to adequately ensure the quality of life. It is noteworthy that the respondents’ opinions regarding the change in the number of infrastructure assets (capacity, area, total number, etc.) are different: “rather increased” – 31% of respondents; “rather decreased” – 28%; 9% of respondents were undecided. The situation is similar with respondents rating the overall condition of educational institutions and their material and technical support: according to 44% of respondents, it has improved, while 47% of entrepreneurs note its impairment; 9% of respondents were also undecided.
It is interesting that in the ranking of factors which, in the entrepreneurs’ opinion, would contribute to the quantitative growth and optimization of the quality of infrastructure facilities in the Moscow Oblast, the first position is “use of the mechanism of social partnership” – 23%, and “enthusiasm of local authorities” – 19%. In the ranking of factors contributing to the deterioration of social infrastructure, “low efficiency of local authorities” holds the last position (15%), while the first position is taken by “corruption” (32%).
Specifying the personal attitude of entrepreneurs to the use of partnership relations for infrastructure development, the authors established that entrepreneurs are not fully familiar with the peculiarities of municipal-private partnership projects in education. This position is clearly seen in the respondents’ answer to the survey question about the possible mechanisms for joint participation of local authorities and businesses (78% were undecided). The respondents’ answers are mostly negative: according to 60% of respondents, private business is not involved in the development of infrastructure in the Moscow Oblast; projects proposed by local authorities are unprofitable and futile (39%); local authorities see the role of business only in financial investment (40%). Although in the current situation 26% of respondents are still undecided about the feasibility of municipal-private partnership development in education, 43% of entrepreneurships note that it is necessary to join efforts of local authorities and businesses for developing the social infrastructure. Moreover, 58% of respondents are willing, even in the current socio-economic conditions, to be actively involved in municipal-private partnership projects on social infrastructure development as they consider it the most effective tool in addressing educational problems of a municipal unit (31%).
Thus, answering the question about the forms of stimulating the participation of private businesses in creating and maintaining good condition of infrastructure facilities in education, the most desirable means (27%) is “local tax benefits”.
Discussion. Cooperation of authorities and the business community is characterized by a wide range of interaction practices: from attracting finance from organizations on a pro bono basis to implementing publicprivate partnership projects. Between these poles there are forms of interaction such as short-term contracts on the implementation of a certain kind of works, provision of public services, service agreements on social infrastructure repair and maintenance, joint ventures (share of private capital as a shareholder in a public enterprise). However, as evidenced by global practice, large-scale public-private partnership projects is the most effective form of cooperation ensuring the implementation of strategic goals of social infrastructure modernization.
The authors analyzed the current practices of public-private partnership in education and identified three most common models.
First, investment contracts between municipal authorities and businesses which regulate partners’ investment risks and responsibilities, determine the form and ratio of their participation in investment activities. In this case, municipal authorities make an agreement in the form of a municipal contract implying certain obligations on the part of a municipal unit regarding the entrepreneurs, and on the part of business units – cofinancing of projects aimed at meeting the needs of municipal educational complex.
Second, leasing municipal property to entrepreneurs for solving socially significant objectives of municipal socio-economic development. This form of municipalprivate partnership in education most often causes public discontent, which is explained by public unawareness of specific features of implementing this model and, as a rule, negative media coverage of examples of “exclusion” of educational establishments to “the property” of individuals.
The third model generated on the basis of concession agreements, projects of municipalprivate partnership is the most effective in addressing social development objectives of a municipal unit. The example is a joint project of the Perm city Administration with the non-operated building reconstruction investor for accommodating private preschool establishments. Following the implementation of the 25-year concession agreement, it is planned to create additional pre-school education establishments with the provision of a certain number of places under the municipal contract. Return on investment is ensured through provision of the population by an educational establishment with a set of educational services [8].
The following practices are of special importance:
-
1. Construction of infrastructure facilities with support of a municipal unit in terms of legitimating their educational activities, which partly reflects the specific character of the second model, however, does not cause “social discontent”.
-
2. Support for a municipal unit in building relations between educational establishments and businesses based on the “patronage” principles.
The research results illustrate certain contradictions in the modern practices of interaction between business and government. On the one hand, the representatives of the business community express their willingness to participate in the implementation of municipal-private partnership projects, and, on the other hand, heads of local authorities note lack of private investment, rare cases of implementation of these projects. At the same time, both representatives of business and authorities believe that only joint efforts can contribute to the development of regional social infrastructure, defining municipalprivate partnership as the most effective tool for addressing educational issues of a municipal unit.
The research results show that the main reasons for this contradiction is the implementation of traditional practices of using financial resources of business entities, non-repayable transfers of funds of socially responsible enterprises for the needs of municipal education. The government’s consumer attitude to business, limitedpragmatic focus on the use of its resources in the development of social infrastructure become unviable amid market economy. It is necessary to not only make business socially responsible, but also expand the forms and boundaries of mutually beneficial cooperation of government and private capital. Only in this case active participation of the latter will give a positive result.
The authors subject the following points to public debate:
-
• municipal-private partnerships in education should be considered from the standpoint of organization of constructive interaction with municipal authorities and the public by consolidating on a long-term and mutually beneficial basis the resources of the society and the government in order to solve the issues of municipal educational complex development;
-
• in the framework of the mechanism of municipal-private partnership in education, the forms of public participation and ways of its attraction to solving the issues of development of municipal educational complexes have not yet been developed, which greatly limits the potential of social capital of municipal units;
-
• the main spheres of support for the mechanisms of public-private partnership in education include: provision of a wide access of potential investors to information; overcoming the stereotypes of unprofitable municipal-private partnership projects; consulting support for private investors; training of specific category of municipal employees (development of skills in preparing
and managing municipal-private partnership projects).
Conclusions. The results of the expert survey show contradictions between the focus of heads of local authorities on the implementation of municipal-private partnership projects and rare practice of their implementation. The vast majority of leaders believe that such projects are the most effective form of cooperation between businesses and government aimed at social infrastructure modernization, while only 4.2% indicate that such projects are being implemented in their municipal unit. The most convenient form of interaction is exploitation of the concept of social corporate responsibility; in almost every fifth municipal unit educational establishments regularly receive funds on a pro bono basis for social infrastructure development.
The research results help make the following conclusions concerning specific features of implementation of municipalprivate partnership projects in modern Russian conditions:
-
1. The current practice of using the mechanism of municipal-private partnership in education does not meet the needs of infrastructure development of municipal educational complexes of the majority of municipal units in the Russian Federation.
-
2. The barriers to the use of this mechanism in practice of municipal
-
3. Despite the current situation, the entrepreneurs express their willingness to participate in municipal-private partnership in case of changes in the existing forms of stimulation.
management are local budget deficit, inadequate legal framework, unawareness of target public groups of the features of municipal-private partnership projects in education; business representatives’ distrust of the actions of the authorities; disagreement of potential partners with the role, which, according to them, is attributed to them by municipal authorities.
Список литературы Municipal-private partnership in education: infrastructural aspect
- Bochkarev A.Yu. Perspektivnye napravleniya razvitiya sotsial'noi infrastruktury munitsipal'nykh obrazovanii v rynochnykh usloviyakh: monografiya . Moscow: PIAR-agentstvo "M-OST", 2012..
- Varnavskii V.G., Klimenko A.B., Korolev V.A. Gosudarstvenno-chastnoe partnerstvo: teoriya i praktika . Moscow: Gos. un-t Vysshei shkoly ekonomiki, 2010. 287 p..
- Malgin V.A., Skorobogatov A.V., Kramin T.V. et al. Gosudarstvenno-chastnoe partnerstvo v obrazovanii: sushchnost', tendentsii, sotsial'naya otvetstvennost' . Ed. by T.G. Timiryasov. Kazan': Poznanie, 2013. 232 p..
- Griboedova T.P. Soderzhanie ponyatiya i osobennosti realizatsii sotsial'nogo partnerstva v sovremennom obrazovanii . Izvestiya Rossiiskogo gosudarstvennogo pedagogicheskogo universiteta im. A.I. Gertsena , 2008, no. 68, pp. 51-60..
- Grabar A.A. Rol' chastno-gosudarstvennogo partnerstva v razvitii sotsial'noi infrastruktury regiona . Rossiiskoe predprinimatel'stvo , 2009, no. 12-2 (149), pp. 20-24..
- Dan'ko K., Gromyko I. Gosudarstvenno-chastnoe partnerstvo v sfere zdravookhraneniya i obrazovaniya v usloviyakh finansovogo krizisa . Gosudarstvenno-chastnoe partnerstvo: prilozhenie k zhurnalu "Korporativnyi yurist" , 2009, no. 5, pp. 29-31..
- Lapin A.E., Aliullov I.F. K voprosu o formirovanii munitsipal'no-chastnogo partnerstva v RF . Problemnyi analiz i gosudarstvenno-upravlencheskoe proektirovanie , 2011, no. 4, pp. 38-44..
- Medvedeva N.V. Munitsipal'no-chastnoe partnerstvo: voprosy teorii i praktiki . Materialy Ivanovskikh chtenii , 2015, no. 5, pp. 85-89..
- Perevozkina Yu.E. Innovatsionnoe razvitie sotsial'noi infrastruktury sovremennogo goroda . Sovremennye nauchnye issledovaniya i innovatsii Modern scientific researches and innovations], 2013, no. 10. Available at: http://web.snauka.ru/issues/2013/10/26733 (accessed 18.08.2016)..
- Piskunova E.V. Sotsial'noe partnerstvo: grazhdanskaya otvetstvennost' i vozmozhnost' razvitiya . Universum: Vestnik Gertsenovskogo universiteta , 2011, no. 2, pp. 30-34..
- Rogach O.V. Upravlenie razvitiem innovatsionnogo potentsiala obshchego obrazovaniya na munitsipal'nom urovne v usloviyakh sotsial'no-ekonomicheskoi modernizatsii . Materialy ivanovskikh chtenii , 2011, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 216-220..
- Skryabin O.O. Osobennosti razvitiya infrastruktury munitsipal'nogo obrazovaniya . Molodoi uchenyi , 2014, no. 19, pp. 360-363..
- Fedulov S.P. Sotsial'naya infrastruktura sovremennogo rossiiskogo goroda . Sotsiologicheskie issledovaniya , 2000, no. 4, pp. 122-125..
- Frolova E.V., Kabanova E.E. Razvitie turisticheskoi privlekatel'nosti rossiiskikh territorii: sovremennye tendentsii i upravlencheskie praktiki . Ekonomicheskie i sotsial'nye peremeny: fakty, tendentsii, prognoz , 2016, no. 1 (43), pp. 153-169..
- Frolova E.V. Sotsial'naya infrastruktura sovremennykh rossiiskikh munitsipal'nykh obrazovanii: sostoyanie i resursy modernizatsii . Sotsiologicheskie issledovaniya , 2014, no. 12 (368), pp. 51-58..
- Rossiya v tsifrakh -2016 g. . Federal'naya sluzhba gosudarstvennoi statistiki . Available at: http://www.gks.ru/bgd/regl/b16_11/Main.htm..
- Robertson H.-J. Toward a theory of negativity: teacher education and information and communications technology. Journal of Teacher Education, 2003, September, no. 54, pp. 280-296 DOI: 10.1177/0022487103255499
- Simons M., Lundahl L., Serpieri R. The governing of education in Europe: commercial actors, partnerships and strategies. European Educational Research Journal, 2013, December, no. 12, pp. 416-424 DOI: 10.2304/eerj.2013.12.4.416
- Papanastasiou N. Commercial actors and the governing of education: the case of academy school sponsors in England. European Educational Research Journal, 2013, December, no. 12, pp. 447-462 DOI: 10.2304/eerj.2013.12.4.447
- Tate W.F., Malancharuvil-Berkes E. A contract for excellence in scientific education: may I have your signature please? Journal of Teacher Education, 2006, May/June, no. 57, pp. 278-285 DOI: 10.1177/0022487105285965


