Нативный полиморфизм двойных спиралей ДНК
Автор: Чесноков Юрий Валентинович
Журнал: Овощи России @vegetables
Рубрика: Селекция и семеноводство сельскохозяйственных растений
Статья в выпуске: 6 (56), 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Дезоксирибонуклеиновая кислота (ДНК) является одним из основных носителей наследственной информации. Структурная физико-химическая информация ДНК определяет в конечном счете строение и функционирование всех живых организмов. В ДНК же накапливаются разнообразные мутационные и происходят рекомбинационные события, которые приводят к изменчивости организмов и подлежат как естественному, так и искусственному отбору. Взаимодействие «генотип-среда» присущее всем живым организмам свойственно и ДНК, которая находится во внутриклеточном и внутриядерном физико-химическом окружении молекул воды, сахаров, ионов металлов, рН, нуклеотидов и других компонентов. Установление и изучение физико-химических свойств нативной ДНК способствует не только пониманию механизмов строения основной наследственной биомолекулы, но и выяснить их функционирование, а также взаимодействие с другими молекулами на молекулярном уровне. Обнаружение разнообразных форм двойных спиралей: A, A', B, α-B', β-B', C, C′, C′′, D, E и Z наталкивает на мысль о молекулярно-генетическом разнообразии существующем на уровне ДНК и установление их структурно-функциональных особенностей способно привести к пониманию реализации генетической информации на общебиологическом уровне. Структура природных ДНК в целом, по-видимому, не зависит от последовательности и нуклеотидного состава. Для природных молекул - сателлитных ДНК с повторами или ДНК без повторов, подтверждено наличие только А-, В- и С-форм. Структура ДНК зависит не только от температуры, но и от природы присутствующих катионов. Наличие в среде определенного количества ионов металлов может приводить к переходу В-формы ДНК в Z-форму. В ↔ Z-переход модифицирует общую структуру ДНК, а, следовательно, может оказаться важным для регуляции генной экспрессии. Изучение биологической роли Z-ДНК возможно в ближайшем будущем поможет понять механизм экспрессии генов, прежде всего эпигенетического характера, который до конца пока еще не выяснен.
Днк, физико-химическое строение, структурные переходы, регуляция генной экспрессии
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140250352
IDR: 140250352 | УДК: 577.323.3:577.113.5:575.113.15 | DOI: 10.18619/2072-9146-2020-6-51-57
Текст обзорной статьи Нативный полиморфизм двойных спиралей ДНК
О ткрытие Джеймсом Уотсоном и Френсисом Криком в 1953 году структуры ДНК явилось началом бурного развития молекулярной биологии в ее современном понимании ( [1]. Другим краеугольным камнем этой науки стали быстро последовавшие за ним рентгеновские расшифровки структуры глобулярных белков. Представляется чрезвычайно важным не только узнать, как построены биомолекулы, но и выяснить механизм их функционирования и взаимодействия на молекулярном уровне, т.е. проникнуть в самую основу жизненных процессов и накопления генетической изменчивости на уровне основного наследственного материала, а также механизмов реализации сохраняемого в генетических ресурсах генетического разнообразия. Фактически речь может идти об установлении взаимодействии «генотип-среда», где генотип представляет ДНК, а ее непосредственное физико-химическое окружение, представленное молекулами воды, сахаров, ионов металлов, рН, нуклеотидов и другими внутриклеточными и внутриядерными компонентами, окружающую среду. Вместе с тем рентгеноструктурный анализ, наряду с другими методами, как экспериментальными, так и теоретическими, продемонстрировал конформационный полиморфизм нуклеиновых кислот. Это закономерное молекулярное многообразие прослеживается на всех уровнях организации, включая низкомолекулярные компоненты ДНК и РНК (основания, нуклеозиды и нуклеотиды), одно- и многоцепочечные полимерные системы и, наконец, комплексы нуклеиновых кислот со специфическими белками, тем самым демонстрируя универсальность закона гомологических рядов в наследственной изменчивости Н.И. Вавилова, в том числе и на молекулярном уровне нуклеиновых кислот [2].
Установление нативного полиморфизма нуклеиновых кислот и их функциональности играет важнейшую роль в определении генетического полиморфизма не только на молекулярном, но и на эволюционном уровнях, особенно с учетом того, что в ДНК накапливается разнообразные мутационные изменения, которые приводят к изменчивости организмов и подлежат естественному и/или искусственному отбору. Следовательно, выявление и понимание нативного полиморфизма ДНК есть путь к пониманию общебиологических процессов формирования и реализации генетического разнообразия, существующего в природе, в том числе и на молекулярном уровне [3, 4].
Так, например, при различных экспериментальных условиях были обнаружены разнообразные формы двойных спиралей: A, Aʹ, B, α -Bʹ, β -Bʹ, C, Cʹ, Cʹʹ, D, E и Z [5]. Буквами от А до Z обозначены различные структурные полиморфные модификации, приставки α и β относятся к чисто упаковочным отличиям, обусловленным симметрией кристаллической решетки, а штрихи указывают на незначительные вариации структуры внутри одного семейства. Так, если природная ДНК со случайной последовательностью при определенных условиях находится в С-форме, у которой число нуклеотидов на виток равно 9,33, то для синтетического полинуклеотида poly(dA-dG-dC) • poly (dG-dC-dT) с повторяющимся тринуклеотидным мотивом в тех же условиях наблюдается Сʹʹ-форма с девятью нуклеотидами на виток, а структура poly(dA-dG) • poly (dC-dT) повторяется лишь через 2 витка (9 • 2 нуклеотидов) и представляет собой Сʹ-ДНК (рис.1).
Следует подчеркнуть, что в строгом смысле точное повторение структурного мотива возможно только для синтетических полинуклеотидов с определенной последовательностью. В случае природных ДНК и РНК со случайной нуклеотидной последовательностью термин – точное повторение – относится к сахарофосфат-ному остову, а каждая отдельная пара оснований в данном случае рассматривается как некий усредненный элемент Уотсон-Криковских AT(U)- и GC-пар. В то же время двухцепочечная РНК независимо от того, природная она или синтетическая, при различных экспериментальных условиях имеет структуру, относящуюся к одной из двух близких друг другу форм двойных спиралей: A или Aʹ. Структурные возможности ДНК гораздо богаче. ДНК со случайными последовательностями могут находиться в А-, В- и С-формах. К этому списку следует добавить D-, E- и Z-формы – полинуклеотиды, у которых повторяется определенный олиго-нуклеотидный мотив, при этом Z-форма представляет собой левую двойную спираль [11, 12].
Структура природных ДНК в целом, по-видимому, не
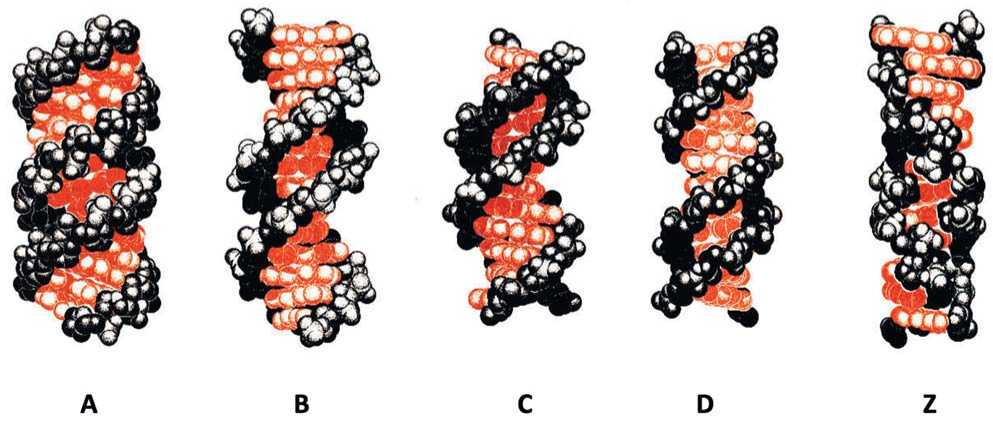
Рис. 1. Структуры пространственных форм ДНК. Буквами от A до Z обозначены соответствующие структурные формы двойных спиралей ДНК (по [6-10])
Fig.1. Structures of spatial forms of DNA. Letters from A to Z denote the corresponding structural forms of DNA double helices (according to [6-10])
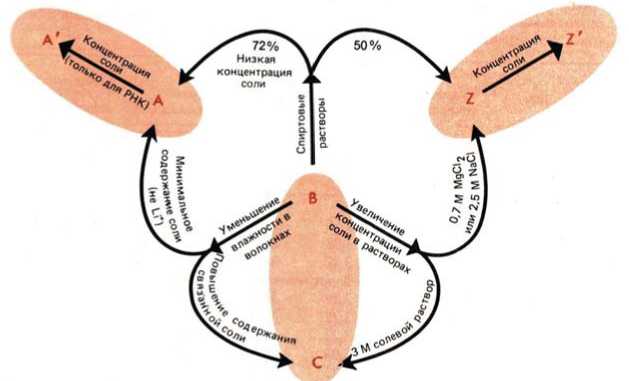
Рис. 2. Обобщенная схема, иллюстрирующая связь между различными семействами природных ДНК и РНК. Внутрисемейственные переходы (овалы) происходят при изменении концентрации соли. Межсемейственные переходы индуцируются изменением относительной влажности и концентрации соли в волокнах или пленках и изменением ионной силы или полярности растворителя в растворе. Критические значения концентраций соли и этанола дают среднюю точку, а не границу перехода. Заметим, что РНК-область на схеме ограничивается А-семейством, а Z-семейство, включающее левые спирали, возможно, состоит только из чередующихся последовательностей пурин-пиримидин (по [23])
Fig. 2. Generalized diagram illustrating the relationship between various families of natural DNA and RNA.
двухцепочечной ДНК (или РНК), то при определенной температуре будет наблюдаться резкое увеличение поглощения, обусловленного разрушением спиральной структуры. Среднюю точку такого перехода называют температурой плавления ( T m ). Переход спираль-клубок в двухцепочечных структурах осуществляется по принципу «все или ничего». Tm двухцепочечных нуклеиновых кислот растет не только с увеличением их дины, но и с повышением ионной силы раствора и GC-содержания полинуклеотида. Обычно GC-пара примерно в 100 раз более стабильна, чем пара АТ. При этом важную роль играют и фланкирующие пары оснований. В молекуле ДНК со случайной последовательностью длиной в 106 нуклеотидов при 25°C примерно 10 GC-пар и 500 АТ-пар не будут связаны водородными связями и не будут участвовать в стэкинг-взаимодействии с соседними парами. Из всего этого следует, что двухцепочечные нуклеиновые кислоты представляют собой не статичные цилиндрические структуры, а конформационно подвижные, «дышащие» объекты, реагирующие на любые химические модификации [24, 25].
Структура ДНК зависит не только от температуры, но и от природы присутствующих катионов. В литературе можно найти множество примеров того, что структура спирали натриевой и литиевой солей природных или синтетических ДНК в волокнах различается [5, 26-28]. Сходная ситуация наблюдается в рас зависит от последовательности и нуклеотидного состава [13]. На основании целого ряда исследований, проведенных методами рассеяния рентгеновских лучей [14], рентгеновской дифракции на волокнах [15], методами линейного дихроизма в ИК-свете [16] и кругового дихроизма в УФ-свете [17] на образцах ДНК с различным содержанием АТ-пар, в том числе на микро- и мини-сателлитных ДНК, содержащих большое число повторов, был сделан вывод о том, что, помимо традиционных А-, В- и С-форм, существуют и иные структурные модификации ДНК. Другие исследователи, также использующие методы кругового дихроизма в УФ-свете [18] и дифракции рентгеновских лучей на волокнах [5, 19, 20], подвергают этот вывод серьезным сомнениям. По существу, для природных молекул – сателлитных ДНК с повторами или ДНК без повторов – подтверждено наличие только А-, В- и С-форм. Но так как результаты перечисленных методов ограничиваются описанием лишь общей структуры молекулы, и ни один из них не выявляет тонких структурных деталей, мы не можем исключить, что имеют место незначительные локальные структурные вариации, как, например, в случае В-ДНК с чередованием конформации [21]. Конечно, не следует думать, что ДНК с разным АТ-содержанием будут обладать одинаковыми термодинамическими свойствами. На самом деле было показано [22], что при GC-содержании ниже 30% В → А-переход затруднен, но облегчается по мере доли GC-пар в молекуле (рис. 2).
Одним из параметров, характеризующих двойную спираль, является ее температура плавления Tm. Образование стэкинга сопровождается уменьшением поглощения УФ-света (гипохромизм), поэтому, наблюдая за спектром поглощения в этой области, удобно следить за образованием и разрушением двойной спирали. Если медленно повышать температуру раствора творе, где на поведение ДНК влияют тип и концентрация катионов и температура. При этом наличие разных анионов почти никак не сказываются на поведении ДНК [29, 30]. Вообще говоря, появление структурных перестроек, связанных с изменением окружения, характерно только для В-ДНК; А-ДНК, очевидно, имеет более «жесткую» молекулярную конформацию, точно так же как и РНК, которая существует только в виде А- и А’-форм независимо от последовательности, нуклеотидного состава и окружения (рис. 2).
Главное различие между спиралями А- и В-типа состоит в неодинаковой конформации сахара. Для А-семейства характерна С 3' -эндо -конформация, а для В-семейства – С 2' - эндо (или, что почти то же самое, С 3' -экзо ). Различием в конформации сахара обусловлены вариации в расстоянии между соседними фосфатами в одной полинуклеотидной цепи: оно колеблется от 0,59 нм при конформации сахара С 3' -эндо до 0,7 нм при С 2' -эндо -конформации. Вследствие этого спирали выглядят совершенно по-разному.
Расстояние h между остатками вдоль оси спирали сильнее варьирует у А-ДНК, а угол спирального вращения – у В-ДНК. Расстояние между нуклеотидными остатками h в Уотсон-Криковских двойных спиралях А-типа колеблется от 0,256 до 0,329 нм и сопровождается относительно малыми вариациями в значении угла спирального вращения: 30,0-32,7°. В двойных спиралях В-типа h , напротив, меняется незначительно, от 0,303 нм у D-ДНК до 0,337 нм у В-ДНК, а диапазон значений угла спирального вращения шире, чем в А-семействе, и составляет 36-45°. В результате двойные спирали А-типа больше походят друг на друга, чем спирали В-типа. Обусловлено это тем, что при изменении угла спирального вращения от 36 до 45° число остатков на виток уменьшается от 10 до 8, что существенно меняет вид спирали.
Для полинуклеотидов А-семейства характерен структурный консерватизм. Двойные спирали А-семей-ства, у которых сахарные остатки имеют конформацию С 3' -эндо . Представлены только структурно близкими формами А- и Аʹ-РНК, а также А-ДНК. Из-за С 3' -эндо -конформации сахара расстояние между фосфатами уменьшается до 0,59 нм, поэтому полинуклеотидная цепь закручена в меньшей степени, чем в двойных спиралях В-типа: на виток приходится 11-12 нуклеотидов (или пар оснований), что соответствует углу спирального вращения 30,0-32,7°. Пары наклонены к оси спирали на 8-20°; это приводит к расстоянию между нуклеотидами вдоль оси спирали 0,329-0,256 нм.
Для полинуклеотидов В-семейства, состоящего из В-, С- и D-форм, характерно структурное многообразие. Спиральные структуры, принадлежащие В-семей-ству, образуют только молекулы ДНК. У РНК ни одна из этих структур не обнаружена. В случае С 2' -эндо- или эквивалентной ей С3'-экзо-конформации сахарных остатков в В-семействе соседние фосфаты в полинук-леотидной цепи расходятся на расстояние ~ 0,7 нм, и это приводит к более сильному закручиванию спирали по сравнению со спиралями А-семейства. Вследствие этого угол спирального вращения увеличивается до 3645°, а расстояние между нуклеотидами вдоль оси спирали – до 0,303-0,337 нм, т.е. в целом становиться больше, чем в спиралях А-типа. С этими характеристиками связан угол наклона пары. В данном случае он меньше, а кроме того, отрицателен: -1,66 – -0,59 нм.
Наличие глубокого и мелкого желобков и смещение пар от оси – макроскопические особенности, отличающие спирали А-типа от спиралей В-типа. С различными размеров желобков связана специфическая способность к комплексообразованию. Геометрия главного желобка в двойных спиралях А-типа зависит от угла наклона пар, а, следовательно, и от расстояния h между остатками вдоль оси. Если это расстояние мало и составляет величину порядка 0,26 нм, спирали (А-ДНК и А-РНК) имеют глубокий и узкий главный желобок, доступный только молекулам воды и ионов металлов. При увеличении h до 0,329 нм главный желобок, оставаясь таким же глубоким, может раскрываться до такой степени, что в нем уменьшается еще одна поли-нуклеотидная цепь. В полимерных двухцепочечных нуклеиновых кислотах специфическое координационное связывание ионов натрия в минорном желобке с атомами О2 урацилов могли бы привести к зависимости структуры молекулы от вида катиона. По-видимому, именно по этой причине некоторые структурные модификации ДНК наблюдаются только в присутствии определенных катионов. С другой стороны, катионы взаимодействуют с фосфатными группами, имеются данные, указывающие на определенную степень специфичности этого взаимодействия [31]. Например, в ряду щелочных металлов радиус катиона от Li+ к Cs+ увеличивается. Однако радиус гидратированных ионов уменьшается от 0,74 нм для Li+ до 0,36 нм для Cs+. Это означает, что Li+ по своим размерам должен хорошо встраиваться в широкий минорный желобок В-ДНК, а Cs+, расположенный на другом конце ряда, – в узкий минорный желобок D-ДНК. Этот вывод согласуется с экспериментальными данными о «закручивающейся» способности упомянутых ионов. Кроме того, во взаимодействии ДНК и РНК с другими молекулами важную роль играет не только стерическая комплементарность, но и компле-ментарность зарядов. Когда было рассчитано распределение электростатического потенциала для ряда олигомеров и полимеров ДНК в предположении, что противоионы Na+ располагаются на биссектрисах РО2-- групп, оказалось, что оно сильно зависит от нуклеотидной последовательности [32]. Следует отметить, что электростатический потенциал G-C и C-G пар различается, а для А-Т и Т-А он одинаков. Это означает, что распределение электростатического потенциала у поверхности молекул нуклеиновых кислот обеспечивает специфичность связывания.
Нативная ДНК находится в В-форме [33]. Порядок спирали В-ДНК равен в точности 10 только для кристаллического состояния и в растворе не сохраняется. Это означает, что как только кристаллическая решетка разрушается, и прямой контакт между спиралями исчезает, структурные ограничения, обусловленные кристаллической упаковкой, устраняются, и молекула ДНК немного раскручивается, что приводит к увеличению числа пар оснований на виток до 10,3-10,6. Поскольку в волокнах при высокой влажности и в водных растворах ДНК находится в В-форме, принято считать, что именно эта форма отвечает состоянию нативной ДНК в клетке. ДНК имеет такую же молекулярную структуру и тогда, когда она намотана на гистоновый кор нуклеосом.
Гибриды ДНК-РНК образуют только двойные спирали типа А- и Aʹ-РНК. Такие гибриды имеют большое биологическое значение. Они образуются при транскрипции последовательностей оснований ДНК в комплементарную ей последовательность информационной РНК. Процесс транскрипции катализирует РНК-полимераза – фермент, который, связываясь с двойной спиралью ДНК, разделяет две ее цепи и синтезирует по одной из них цепь РНК. Следовательно, по крайней мере, в области активного центра полимеразы, размер которого эквивалентен длине участка примерно в 40 нуклеотидов, действительно образуется гибрид ДНК-РНК [34]. Гибриды формируются и тогда, когда под действием обратной транскриптазы осуществляется синтез ДНК с использованием РНК (фаговой) как матрицы, а также в ходе репликации ДНК, при образовании коротких молекул РНК-праймеров (затравок). Гибриды ДНК-РНК, вообще говоря, не способны переходить в спиральные формы В-семейства. Это означает, что структурный консерватизм РНК затрагивает не только дуплексы РНК, но сохраняется даже тогда, когда хотя бы одна из цепей двойной спирали является цепью РНК.
РНК может находиться только в двух близких конформациях: А и Аʹ, причем обе они принадлежат А-семейству двойных спиралей. Напротив, ДНК в зависимости от окружающих условий (природы противоиона и относительной влажности), а также в зависимости от нуклеотидной последовательности и нуклеотидного состава в случае синтетических полинуклеотидов, праймеров, например, из повторяющихся блоков может принимать и другие конформации. Двойные спирали ДНК относятся либо к А-типу, где единственной представительницей является А-ДНК, либо к В-типу, который включает В-, Вʹ-, C-, Cʹ-, Cʹʹ-, D-, E- и Т-ДНК. Все перечисленные спирали являются правыми. Кроме того, было открыто семейство левых спиралей (Z-ДНК), и это еще раз подчеркивает «хамелеоновскую» природу ДНК, ее способность к адаптации [35].
Интересно поведение ДНК, выделенной из фага Т2, в которой цитозин замещен на 5-гидроксиметилцитозин, на 70% гликозилированный и еще на 5% дигликозили-рованный. При высокой относительной влажности эта ДНК находится в В-форме. При понижении влажности она, минуя стадию образования А-формы, непосредственно переходит в Т-форму [36] – D-подобную двойную спираль. Это напоминает поведение синтетических ДНК, у которых гуанин замещен на инозин [5].
Если удалить гликозидные остатки, ДНК фага Т2 становится похожей на обычную ДНК и в зависимости от окружающих условий находится в А-, В- или С-форме.
При исследовании волокон ДНК методом рентгеновской дифракции было показано, что если литиевую соль природной ДНК поместить в условия с достаточно низкой относительной влажностью (44-66%), то образуется новая форма, С-ДНК. Такую же форму ДНК можно получить при высокой концентрации соли и значениях влажности, промежуточных между теми, при которых образуются А- и В-ДНК [37], используя в качестве противоиона натрий. Аналогичные данные были получены методом инфракрасного линейного дихроизма, на ориентированных пленках ДНК, выделенной из различных вирусов и сильно различающейся по нуклеотидному составу. В этих исследованиях, кроме того, было выявлено наличие еще одного фактора, способствующего В → С-переходу, - низкое содержание GC-пар в образце [38].
Пока не были получены данные, показавшие, что С-ДНК так же важна, как А- и В-ДНК [39], С-ДНК рассматривали как промежуточную форму между А- и В-ДНК. Оказалось, что, если уменьшать концентрацию Na+ и влажность, можно перевести в С-форму природные ДНК с GC-содержанием от 31 до 72% и даже гликозилированную ДНК фага Т2. Если затем опять медленно добавлять воду, происходит обратимый С → А → В-переход.
Природные ДНК не образуют двойных спиралей D-типа. Исключение составляют АТ-богатые участки в ДНК с чередующимися последовательностями и ДНК фага Т2, которую отличает высокая степень модификации. В этой ДНК вместо цитозина содержится 5-гидроксиметилцитозин, а кроме того, она гликозилирована более чем на 70%. Конформационные параметры ДНК фага Т2 близки к таковым для D-ДНК. В D-ДНК, как и в других двойных спиралях В-семейства, фуранозные кольца находятся в конформации С 3'- экзо . По сравнению с В-ДНК эта спираль закручена сильнее: на виток приходится всего восемь пар оснований, высота витка равна 2,43 нм. Отсюда следует, что угол спирального вращения в D-ДНК равен 45°, а расстояние между нуклеотидами вдоль оси спирали составляет 0,303 нм. Ось проходит через минорный желобок двойной спирали и поэтому вандерваальсов диаметр D-спирали равен 2,1 нм. Поскольку ось спирали проходит через минорный желобок, главный желобок становится более мелким, чем у В- и С-ДНК, а минорный – очень глубоким и узким и представляет собой удобную полость для размещения молекул воды и катионов. ДНК фага Т2 – единственная из известных природных ДНК, находящаяся в D-форме.
Если полинуклеотид poly(dG-dC) поместить в водный раствор с высокой концентрацией MgCl2, NaCl или спирта, то образуется левая двойная спираль – Z-ДНК. У этой спирали сохраняется Уотсон-Криковское спаривание оснований, но поскольку «фосфатный» радиус спирали меняется, принимая попеременно два разных значения, а соседние сахара «смотрят» в противоположные стороны, линия, последовательно соединяющая атомы фосфора в цепи, перестает быть гладкой, как в двойных спиралях с эквивалентными нуклеотидами, и приобретает зигзагообразный вид. Отсюда и название – Z-ДНК. В зависимости от условий среды (например, в зависимости от количества связанных молекул воды и соли) образуются Z-, ZI-, ZII- и Zʹ-ДНК, которые составляют Z-семейство [40].
Для осуществления В → Z-перехода не требуется расхождения цепей. Процесс превращения правой В-ДНК в левую спираль Z-ДНК инициируется разрывом нескольких пар оснований, после чего гуанин «закрепляется» в син-конформации, а дезоксицитидин поворачивается как одно целое (при таком повороте анти-конформация сохраняется). Затем водородные связи восстанавливаются, и осно- вания вновь образуют Уотсон-Криковские пары. Это означает, что полного расхождения цепей те требуется, и область В → Z-перехода перемещается вдоль спирали в идее небольшой петли. Процесс превращения правой спирали в левую характеризуется большой величиной энергии активации, 21 ккал х моль-1 [41]. Термодинамические исследования показали, что переход В ↔ Z кооперативен [41]. Это означает, что, если в двойной спирали В-ДНК образуется зародыш Z-формы, он индуцирует В ↔ Z-переход в соседних парах и, таким образом, разрастается по полинуклеотидной цепи. В ↔ Z-переход, как и переход В ↔ А, практически не зависит от температуры (ΔН ~ 0 ккал х моль-1) и этим отличается от В ↔ С-перехода (ΔН = -10 ккал х моль-1), у которого равновесие сдвигается в сторону образования С-формы при понижении температуры.
Существует ли Z-ДНК только при высоких концентрациях соли и спирта или В ↔ Z-переход может происходить и в условиях, близких к физиологическим? Этот вопрос особенно важен при планировании биологических экспериментов с Z-ДНК. В ↔ Z-переход можно индуцировать при существенно более низкой концентрации соли, если добавить в систему спирт, двухвалентные ионы или спермин в концентрации до 2 мкМ (табл. 1).
В ДНК эукариот последовательность (dm5C-dG) встречается довольно часто (главным образом из-за метилирования ДНК), что сопряжено с работой аппарата регуляции транскрипции генов [42]. Как видно из таблицы 2 полинуклеотид poly(dG-dm5C) • poly(dG-dm5C) при физиологических условиях образует Z-форму. Следовательно, вполне возможно, что наиболее длинные участки последовательности (dG-dm5C) в молекуле ДНК находятся в Z-форме. К какому же результату может привести появление Z-ДНК в геноме?
Включение в плазмиду участка, находящегося в Z-форме, меняет топологию этой молекулы. Плазмиды – замкнутые кольцевые молекулы двухцепочечных ДНК – разрезали, встраивали в них участки с последовательностью poly(dG-dC) и вновь замыкали в кольцо [45, 46]. Как известно, кольцевые замкнутые ДНК могут образовывать сверхспирали (т.е. спирали из замкнутой двухцепочечной спира-лизованной ДНК). При высокой плотности сверхвитков в (dG-dC) n -блоках таких плазмид даже при физиологических условиях (200 мМ NaCl) происходит В ↔ Z-переход. Более того, в соответствии со сказанным выше, замена dC на dm5C во фрагментах (dG-dC) способствует переходу и, что самое удивительное, если уменьшить концентрацию NaCl, можно получить Z-форму даже при меньшей плотности сверхвитков. Как отмечается в работе [45], в данном случае В ↔ Z-переход является неполным: в месте перехода от В-к Z-форме имеется участок длиной в 11 пар оснований, который находится в состоянии, промежуточном между левой и правой спиральными формами. Примечательно, что даже если длина фрагментов (dG-dC) составляет всего лишь 1,3% от полной длины плазмидной ДНК, параметры сверхспирализации плазмиды уже радикально изменяются. Чередование В- и Z-форм в плазмиде меняет райзинг и кручение, т.е. параметры, описывающие общую топологию кольцевой замкнутой ДНК, Таким образом, В ↔ Z-переход модифицирует общую структуру ДНК, а следовательно, может оказаться важным для регуляции генной экспрессии. Но существует ли Z-ДНК in vivo ?
При инъекции кроликам модифицированных poly(dG-dC), которые при физиологических условиях находятся в Z-форме, удается вызвать образование у них антител к Z-ДНК. Такие антитела были выделены, в них ввели флуоресцентную метку, а затем инкубировали с поли-тенными хромосомами Drosophila melanogaster [47].
Таблица 1. Концентрация катионов или этанола в средней точке В ↔Z-перехода для полинуклеотида poly(dG-dC) • poly(dG-dC) и его аналога, содержащего метилированный цитозин (по [43, 44]) Table 1. Concentration of cations or ethanol at the midpoint of the B ↔Z transition for poly (dG-dC) • poly (dG-dC) polynucleotide and its analog containing methylated cytosine (according to [43, 44])
Это особая форма хромосом, которая состоит из тысячи и более хроматид, уложенных бок о бок без какого-либо сдвига, что позволяет усилить любой сигнал, который с помощью обычных хромосом обнаружить невозможно. В результате эксперимента были зафиксированы яркие флуоресцирующие полосы, которые однозначно указывали на наличие Z-ДНК в междисковых областях политенных хромосом. Этот эксперимент доказывает, что Z-ДНК в хромосомах действительно существует. Хотя описанные исследования проведены in vitro, тем не менее есть основания полагать, что in vivo в хромосомах также содержатся участки Z-ДНК [48-50]. В этой связи интересен следующий факт. Полинуклеотид poly(dG-dm5C) при низкой концентрации соли, т.е. в условиях, когда он находится в В-форме, связывается с гистоновыми октамерами и образует нуклеосомы [51]. Однако при высокой концентрации соли, когда полинуклеотид имеет конформацию левоспиральной Z-ДНК, он хотя и связывается с гистонами, но характерных нуклео-сомных частиц уже не образует. Следовательно, нуклео-сомные частицы может образовывать только В-ДНК. Переход в Z-форму разрушает структуру нуклеосомы, а значит, и структуру состоящего из нуклеосом хроматина. К сожалению, биологическая роль Z-ДНК еще не до конца выяснена. По-видимому, она выполняет какую-то регуляторную функцию [48-50], тем более что В ↔ Z-переход обратим. Регуляция экспрессии может включать и сверхспирализацию [47], и связывание с белка- ми, специфичными к Z-ДНК [48], и связывание с определенными катионами типа спермидина (табл. 1), и метилирование d(С) [42].
Левая спираль Z-ДНК транскрибируется и взаимодействует с лекарственными препаратами. Было показано, что MgCl 2 и этанол действуют синергично и переводят poly(dG-dC) в Z-форму даже тогда, когда их концентрация очень мала [52]. Z-ДНК, которая при этом продуцируется, седиментирует быстрее, чем такая же Z-ДНК, образующаяся при высокой концентрации соли, поэтому ее назвали Z*-ДНК. Z*-ДНК служит матрицей для РНК-полимеразы E.coli, причем скорость транскрипции примерно вдвое меньше, чем в случае правой спирали poly(dG-dC). Неясно, однако, действительно ли РНК-полимераза транскрибирует Z*-ДНК или левая спираль в ходе транскрипции преобразуется в правую. Z*-ДНК, кроме того, связывается с интеркалирующими соединениями – этидием и актиномицетом D, а также образует комплекс с неинтеркалирующим антибиотиком – митрамицином.
Таким образом, обнаружение Z-ДНК – это еще одна веха в истории структурных исследований ДНК. На сегодня изучение биологической роли Z-ДНК проводится довольно интенсивно, и есть основания надеяться, что в ближайшем будущем эти исследования помогут понять механизм экспрессии генов, прежде всего эпигенетического характера, пока до конца не выясненный [53, 54].
Об авторе:
Yuriy V. Chesnokov – Doc. Sci. (Biology), Director of Agrophysical Research Institute,
(79)90507-2
Список литературы Нативный полиморфизм двойных спиралей ДНК
- Сивожелезова Н.А., Мишакова В.Н. Значение открытия структуры ДНК для молекулярной генетики и сельского хозяйства. Известия Оренбургского государственного аграрного университета. 2014;(4):164-167.
- Чесноков Ю.В. Закон гомологических рядов в наследственной изменчивости и молекулярная гомология генов. Сельскохозяйственная биология. 2007;(5):9-14.
- Broadhurst L., Breed M., Lowe A., Bragg J., Catullo R., Coates D.J., Ensinas-Viso F., Gellie N., James E., Krauss S., Potts B., Rossetto M., Shepherd M., Byrne M. Genetic diversity and structure of the Australian flora. Divers. Distrib. 2017;(23):41-52. DOI: 10.1111/ddi.12505
- Coates D.J., Byrne M., Moritz C. Genetic Diversity and Conservation Units: Dealing With the Species-Population Continuum in the Age of Genomics. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018;(6):165. DOI: 10.3389/fevo.2018.00165
- Leslie A.G.W., Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Ratliff R.L. Polymorphism of DNA double helices. J. Mol. Biol. 1980;(143):49-72. DOI: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90124-2
- Arnott S., Hukins D.W.L. Opimised parameters for a-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1972;(47):1504-1509.
- DOI: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90243-4
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R. Fibrous polynucleotide duplexes have very polymorphic secondary structures. In Biomolecular stereodynamics (ed. R.H. Sarma). Adenine Press, New York. 1981;(I): 99-122.
- Marvin D.A., Spencer M., Wilkins M.H.F., Hamilton L.D. The molecular configuration of DNA. III. X-ray diffraction study of the C form of the lithium salt. J. Mol. Biol. 1961;(3):547-565.
- DOI: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80021-1
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hukins D.W.L., Smith P.L.C., Watts L. Structural details of a double-helix observed for DNAs containing alternating purine-pyrimidine sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1974;(88):523-533. https://doi.org/10.1016.0022-2836(74)90499-9
- Wang A.H.-J., Quigley G.J., Kolpak F.J., Crawford J.L., Boom J.H. van, Marel G van der, Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979;(282):680-686.
- DOI: 10.1038/282680a0
- Ghosh A., Bansal M. A glossary of DNA structures from A to Z. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003;(59):620-626.
- DOI: 10.1107/s0907444903003251
- Du Y., Zhou X. Targeting non-B-form DNA in living cells. Chem. Rec 2013;(13):371-384.
- DOI: 10.1002/tcr.201300005
- Waters J.T., Lu X.-J., Galindo-Murillo R., Gumbart J.C., Kim H.D., Cheatham T.E. III, Harvey S.C. Transitions of Double-Stranded DNA Between the A- and B-Forms. J. Phys. Chem B. 2016;(120):8449-8456.
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b02155
- Bram S. Secondary structure of DNA depends on base composition. Nature New Biol. 1971;(232):174-176.
- DOI: 10.1038/newbio232174a0
- Bram S., Tougard P. Polymorphism of natural DNA. Nature New Biol. 1972;(239):128-131.
- DOI: 10.1038/newbio239128a0
- Pilet J., Blicharski J., Brahms J. Conformations and structural transitions in polydeoxynucleotides. Biochemistry. 1975;(14):1869-1876.
- DOI: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90124-2
- Gray D.M., Gall J.G., The circular dichroism spectra of three Drosophila virilis satellite DNA's. J. Mol. Biol. 1974;(85):665-679.
- DOI: 10.1016/S0022-2836(75)80112-4
- Arnott S. The sequence dependence of circular dichroism spectra of DNA duplexes. Nucl. Acids Res. 1975;(2):1493-1502.
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1493
- Selsing E., Arnott S. Conformations of A-T rich DNA's. Nucl. Acids Res. 1976;(3):2443-2450.
- DOI: 10.1093/narZ3.10.2443
- Premilat S., Albiser G. X-ray diffraction study of three DNA fibers with different base composition. J. Mol. Biol. 1975;(99):27-36.
- DOI: 10.1006/viro.2002.1602
- Klug A., Jack A., Viswamitra M.A., Kennard O., Shakked Z., Steitz T.A. A hypothesis on a specific sequence-dependent conformation of DNA and its relation to the binding of the lacrepressor protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1979;(131):669-680.
- DOI: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1
- Pilet J., Brahms J. Dependence of B-A conformational change in DNA on base composition. Nature New Biol. 1972;(236):99-100.
- DOI: 10.1038/new-bio236099a0
- Drew H., Takano T., Tapaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R.E. High-salt d(CpGpCpG): A left-handed Z DNA double helix. Nature. 1980;(286):567-573.
- DOI: 10.1038/286567a0
- Svozil D., Kalina J., Omelka M., Schneider B. DNA conformations and their sequence preferences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;(36):3690-3706.
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn260
- Dans P.D., Balaceanu A., Pasi M., Patelli A.S., Petkevičiuté D., Walther J., Hospital A., Bayarri G., Lavery R., Maddocks J.H., Orozco M. The static and dynamic structural heterogeneities of B-DNA: extending Calladine-Dickerson rules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;(47):11090-11102.
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz905
- Langridge R., Marvin D.A., Seeds W.E., Wilson H.R., Hooper C.W., Wilkins M.H.F., Hamilton L.D. The molecular configuration of deoxyribonucleic acid. II. Molecular models and their Fourier transforms. J. Mol. Biol. 1960;(2):38-64.
- DOI: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90507-2
- Marvin D.A., Spencer M., Wilkins M.H.F., Hamilton L.D. The molecular configuration of DNA. III. X-ray diffraction study of the C form of the lithium salt. J. Mol. Biol. 1961;(3):547-565.
- DOI: 10.1016/S0022-2836(61)80021-1
- Fuller W., Wilkins M.H.F., Wilson H.R., Hamilton L.D. The molecular configuration of deoxyribonucleic acid. IV. X-ray diffraction study of the A-form. J. Mol. Biol. 1965;(12):60-80.
- DOI: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80282-0
- Anderson P., Bauer W. Supercoiling in closed circular DNA: dependence upon ion type and concentration. Biochemistry. 1978;(17):594-601.
- DOI: 10.1021/bi00597a006
- Chan A., Kilkuskie R., Hanlon S. Correlation between the duplex winding angle and the circular dichroism spectrum of calf thymus DNA. Biochemistry. 1979;(18):84-91.
- DOI: 10.1021/bi00568a013
- Ivanov V.I., Minchenkova L.E., Schyolkina A.K., Poletayev A.I. Different con formations of double stranded nucleic acids in solution as revealed by circular dichroism. Biopolymers. 1973;(12):89-100
- DOI: 10.1002/bip.1973.360120109
- Weiner P.K., Langridge R., Blaney J.M., Schaefer R., Kollman P. Electrostatic potential molecular surfaces. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1982;(79):3754-3758.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3754
- Barone G., Guerra C.F., Bickelhaupt F.M. B-DNA structure and stability as function of nucleic acid composition: Dispersion-corrected DFT study of dinucleoside monophosphate single and double strands. Chemistry Open. 2013;(2):186-193.
- DOI: 10.1002/open.201300019
- Wang J.C., Jacobsen J.H., Saucier J.-M. Physicochemical studies on interaction between DNA and RNA polymerase. Unwinding of the DNA helix by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Nucl. Acids Res. 1977;(4):1225-1241.
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1225
- Dickerson R.E., Drew H.R., Conner B.N., Wing R.M., Fratini A.V., Kopka M.L. The anatomy of A-, B-, and Z-DNA. Science. 1982;(216):475-485.
- DOI: 10.1126/science.7071593
- Мокульский М.А., Капитонова К.А., Мокульская Т.Д. Вторичная структура ДНК фага Т2. Мол. Биол. 1972;(6):34-38. [Mokulsky M.A., Kapitonova K.A., Mokulskaya T.D. Secondary structure of T2 phage DNA. Mol. Biol. 1972;(6:)34-38. (in Russian)]
- Arnot S., Selsing E. The conformation of C-DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1975;(98):265-269.
- DOI: 10.1016/S0022-2836(75)80115-X
- Brahms J., Pilet J., Lan T.-T.P., Hill L.R. Direct evidence of the C-like form of sodium deoxyribonucleate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1973;(70):3352-3355.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3352
- Rhodes N.J., Mahendrasingam A., Pigram W.J., Fuller W., Brahms J., Vergne J.,Warren R.A.J. The C conformation in low salt form of sodium DNA. Nature. 1982;(296):267-269.
- DOI: 10.1038/296267a0
- Ussery D.W. DNA Structure: A-, B- and Z-DNA helix families. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. Macmillan Publishers Ltd, Nature Publishing Group. 2002. P.1-7.
- DOI: 10.1038/npg.els.0003122
- Pohl F.M., Jovin T.M. Salt-induced cooperative conformational change of a synthetic DNA: equilibrium and kinetic studies with poly d(G-C). J. Mol. Biol. 1972;(67):375-396.
- DOI: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90457-3
- Razin A., Riggs A.D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980;(210):604-610. https://doi.orgV
- DOI: 10.1126/science.6254144
- Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effects on methylation on a synthetic polynucleotide: The B-Z transition in poly(dG-m5C) • poly(dG-m5C). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1981;(78):1619-1623.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1619
- Sande J.H. van de, Jovin T.M. Z*DANN, the left-handed helical from of poly[d(G-C)] in MgCl2-ethanol, is biologically active. EMBO J. 1982;(1):115-120.
- DOI: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01133.x
- Klysik J., Stirdivant S.M., Larson J.E., Hart P.A., Wells R.D. Left-handed DNA in restriction fragments and a recombinant plasmid. Nature. 1981;(290):672-677.
- DOI: 10.1038/290672a0
- Singleton C.K., Klysik J., Stirdivant S.M., Wells R.D. Left-handed Z-DNA is induced by supercoiling in physiological ionic conditions. Nature. 1982;(299):312-316.
- DOI: 10.1038/299312a0
- Santella R.M., Grunberger D., Weinstein I.B., Rich A. Induction of the Z conformation of poly(dG-dC) • poly(dG-dC) by binding of N-2-acetiylaminofluorene to guanine residues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1981;(78):1451-1455.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1451
- Job D., Marmillot P., Job C., Jovin T.M. Transcription of left-handed Z-DNA templates: increased rate of single-step addition reactions catalyzed by wheat germ RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1988;(27):6371-6378.
- DOI: 10.1021/bi00417a027
- Ferl R.J., Paul A.L. Chemical detection of Z-DNA within the maize Adh1 promoter. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992;(18):1181-1184.
- DOI: 10.1007/BF00047722
- Cerna A., Cuadrado A., Jouve N., Diaz dela Espina S.M., De la Torre C. Z-DNA, a new in situ marker for transcription. Eur. J. Histochem. 2004;(48):49-56.
- DOI: 10.4081/856
- Nicol J., Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effect of the B-Z transition in poly(dG-dm5C) • poly(dG-dm5C) on nucleosome formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1982;(79):1771-1775.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1771
- Sande J.H. van de, Jovin T.M. Z*-DNA, the left-handed helical form of poly[d(G-C)] in MgCl2-ethanol, is biologically active. EMBO J. 1982;(1 ):115-120.
- DOI: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01133.x
- Zhou C., Zhou F., Xu Y. Comparative analyses of distributions and functions of Z-DNA in Arabidopsis and rice. Genomics. 2009;(93):383-391.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.11.012
- Vongsutilers V., Shinohara Y., Kawai G. Epigenetic TET-catalyzed oxidative products of 5-methylcytosine impede Z-DNA formation of CG decamers. ACS Omega. 2020;(5):8056-8064.
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00120


